Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
-
Giuseppe Gullo
, Eleonora Conti
Abstract
Background
Infertility is a multifactorial condition that affects both men and women and is influenced by various factors, including overweight and obesity. These conditions, especially in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), are strongly associated with hormonal and metabolic imbalances that can impair fertility. Targeted nutritional interventions, such as nutraceutical supplementation, may offer support in improving reproductive outcomes.
Methods
A narrative review was conducted using PubMed, focusing on publications from the past 12 years with the keywords “nutraceutical,” “overweight,” and “infertility.” The review aimed to identify the main nutraceuticals used in managing infertility and to highlight the importance of a personalized approach tailored to individual patient characteristics.
Results
Nutraceuticals may represent a safe and cost-effective adjunctive strategy to support fertility in overweight patients, particularly in those with PCOS. Evidence suggests that their effectiveness increases when integrated into a personalized treatment plan based on individual needs and clinical profiles.
Conclusions
This review offers an updated overview of nutraceutical use in overweight individuals with infertility, outlining both benefits and limitations. It also addresses the often-overlooked medico-legal aspects of prescribing nutraceuticals, emphasizing the need for ethical and legal awareness when incorporating these interventions into clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Infertility is a condition characterized by the inability of a couple to conceive after at least 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse [1]. It is a growing global concern, affecting approximately one in seven couples. The causes of infertility are multifactorial and can be classified into male-only factors (30% of cases), combined male and female factors (20%) [2], female-only factors (35%) [3], and unexplained causes (15%) [4,5]. This classification highlights the complexity of infertility and underscores the need for personalized treatment approaches. Among the many causes of female infertility, ovulatory disorders, tubal pathologies, and chronic conditions are the most common [6]. One of the leading causes of infertility in women is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition affecting a significant number of women during their reproductive years. PCOS is recognized as one of the most prevalent endocrine disorders in women of reproductive age, characterized primarily by a combination of hyperandrogenism (elevated male hormone levels), oligo-/anovulation (infrequent or absent ovulation), and the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries, as observed on ultrasound [7]. A major challenge for women with PCOS is the creation of a vicious cycle between obesity and infertility, in which obesity exacerbates hormonal imbalances, such as insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism, which in turn impair ovulation and fertility. Moreover, the hyperandrogenism characteristic of PCOS often promotes the accumulation of visceral fat, further disrupting the hormonal environment and perpetuating the cycle of worsening symptoms [8,9]. This interplay highlights the need for effective interventions that address both metabolic and reproductive issues in managing PCOS-related infertility.
The relationship between obesity and infertility is well-established, with numerous studies demonstrating that excess body weight can significantly impact fertility. Obesity alters the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis, a crucial hormonal pathway that regulates reproductive function. Increased adipose tissue results in higher aromatization of androgens (male hormones) into estrogens (female hormones), disrupting the hormonal balance within the reproductive system [10]. This hormonal imbalance triggers a negative feedback loop on the HPG axis, leading to reduced gonadotropin production and impairing ovulation and menstrual cycles [11,12]. As a result, women with obesity often experience menstrual irregularities and reduced fertility.
In addition to hormonal disruptions, obesity has been shown to negatively affect oocyte quality and endometrial receptivity – two critical factors for successful conception. The impact of obesity on oocyte quality presents challenges for both natural conception and assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) [7]. Several studies have demonstrated that a body mass index (BMI) greater than 25 kg/m² significantly reduces the success of ART. Women with higher BMI levels tend to have lower-quality eggs and embryos, requiring higher doses of gonadotropins to stimulate ovulation and longer durations of ovulation induction. Additionally, obesity is associated with a higher risk of complications during ART procedures, such as oocyte retrieval and embryo transfer, as well as an increased likelihood of miscarriage following conception. The growing body of evidence linking obesity to infertility has raised questions about how nutrition can be utilized to improve fertility outcomes, particularly in overweight or obese individuals. Research has shown that dietary patterns play a crucial role in reproductive health. Diets high in fatty acids, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars have been found to negatively impact fertility by exacerbating insulin resistance, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances. Conversely, a balanced diet that includes fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals has been associated with improved fertility outcomes.
These nutrients are essential for maintaining hormonal balance, reducing inflammation, and promoting healthy ovarian function [4]. Given the positive effects of nutrition on fertility, nutraceutical supplementation has emerged as a potential strategy for enhancing reproductive outcomes, particularly in overweight or obese patients. Nutraceuticals, which include vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and plant-based compounds, are thought to support fertility by addressing dietary deficiencies or imbalances. By filling specific nutritional gaps, nutraceuticals may help improve metabolic and hormonal balance, thereby enhancing fertility in overweight and obese individuals.
This review aims to analyze the benefits and limitations of nutraceutical supplementation in the management of infertility, with a particular focus on patients who are overweight or obese. Given the well-established correlation between obesity and PCOS, numerous authors, following a review of the literature, frequently include PCOS patients in their analyses of nutraceutical use in overweight women with infertility; accordingly, the present review also includes patients with PCOS within its scope of investigation. It will explore how specific dietary supplements may influence reproductive function, hormonal balance, and metabolic health, while also addressing the current scientific evidence, safety concerns, and gaps in knowledge related to their use in this specific population. Therefore, we examine the mechanisms through which various nutraceuticals, such as antioxidants, micronutrients, amino acids, and plant-derived extracts, may improve reproductive outcomes by targeting oxidative stress, insulin resistance, inflammation, and endocrine dysfunction. Furthermore, this review discusses the current clinical evidence supporting their efficacy and safety and identifies potential interactions or contraindications. We try to provide a perspective that can support clinical decision-making and guide future research in this evolving field.
2 Materials and methods
Literature research was conducted to investigate nutraceutical supplementation in overweight infertile patients. A comprehensive search was performed in PubMed and Scopus, covering the period from 2014 to 2025. The keywords used were “nutraceutical,” “overweight,” and “infertility.” A total of 63 papers were identified, and only those written in English were included. Initially, the titles and abstracts of all identified papers were reviewed. Papers were first analyzed based on their titles and abstracts to assess their potential relevance to the research topic. If a study appeared to be potentially useful, it was then considered for full-text reading and detailed analysis. Inclusion criteria were articles that were pertinent to the research topic, involved only human data, and consisted of either reviews or studies with empirical data. Only articles related to the most commonly used nutraceuticals were included in the research, while acknowledging the infinite variety of nutraceutical products that may be potentially used.
Ultimately, 38 articles were selected that addressed the role of nutraceutical supplementation in overweight infertile patients (Figure 1). Additionally, the relevant forensic literature was reviewed to assess the medico-legal implications of such supplementation.
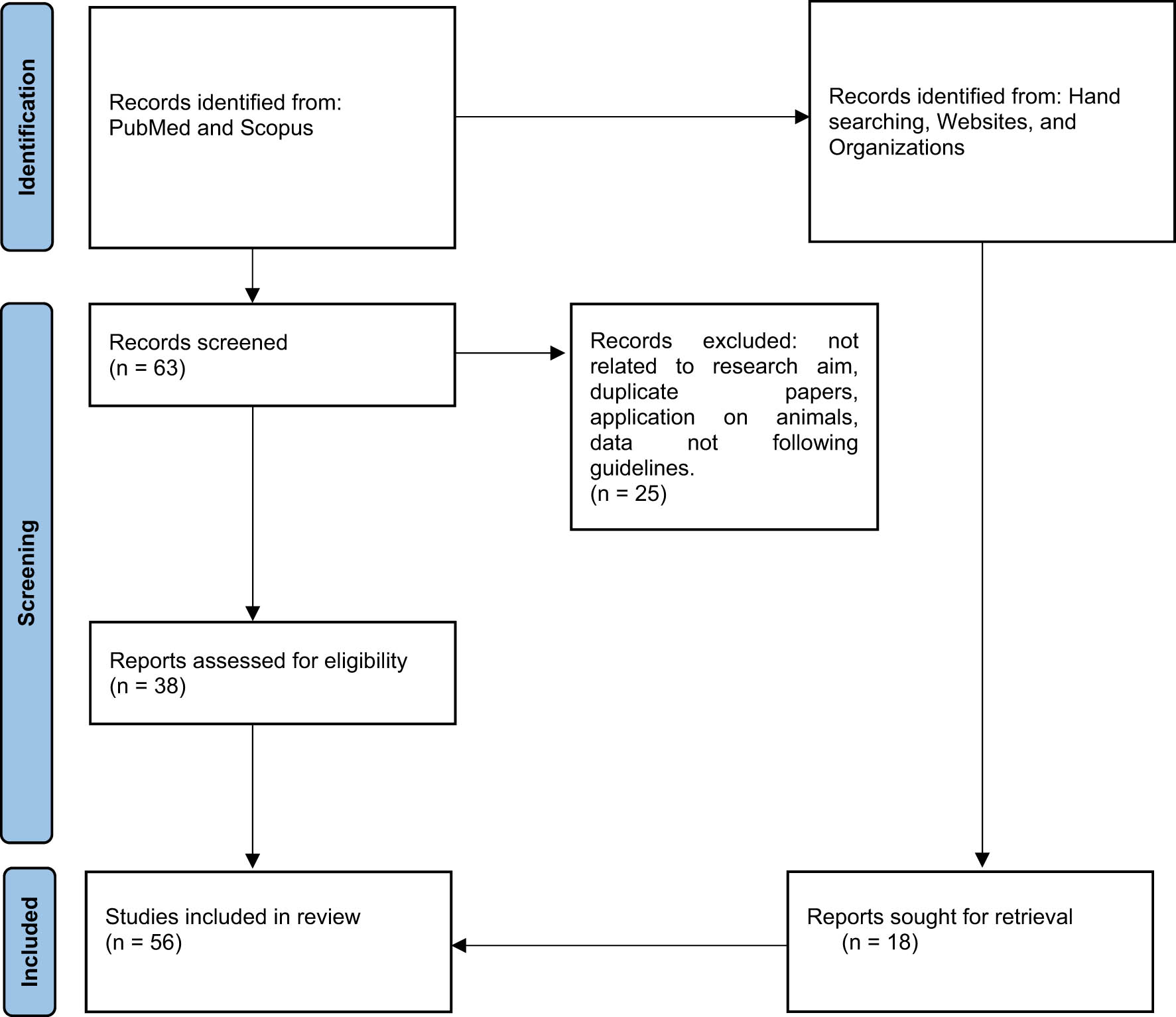
PRISMA flow chart.
This review aims to analyze the benefits of nutraceutical supplementation in improving the fertility of overweight patients, such as those with PCOS, while also identifying potential gaps in the existing research.
3 Results
3.1 Role of vitamin D
Many authors have focused on evaluating the role of vitamin D supplementation in cases of infertility, as there appears to be a correlation between vitamin D deficiency and infertility. In 2015, a review by Dabrowski et al. [13] examined the role of vitamin D in the treatment of infertility in patients with PCOS, uterine fibroids, or male-factor infertility, including 235 articles. This review concluded that vitamin D supplementation is recommended in infertility therapy for both partners, noting that couples with a serum vitamin D concentration around 50 nmol/L have a higher chance of conception. Supplementation was particularly recommended for obese, insulin-resistant women with low anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Additionally, no adverse effects were reported with an intake of up to 10,000 IU/day.
In 2019, Bosdou et al. [14] conducted a review on the impact of vitamin D deficiency and obesity on male and female infertility. They examined both observational and interventional studies and demonstrated that vitamin D deficiency and obesity negatively affect fertility in both genders. However, the evidence from interventional studies on vitamin D supplementation was limited, as these studies had small sample sizes and significant variability in dosage and duration.
Some authors have investigated the impact of vitamin D supplementation on serum levels of AMH, a key ovarian biomarker for folliculogenesis and ovarian reserve. Moridi et al. [15] conducted a systematic review in 2019 analyzing 18 observational and 6 interventional studies on the association between vitamin D and AMH. They concluded that the relationship between vitamin D and AMH is complex and non-linear.
Specifically, the effects of vitamin D on AMH appear to depend on the ovulatory status of the patient. In patients with PCOS, vitamin D seems to decrease AMH levels, while in those without PCOS, it appears to increase AMH levels. Since AMH is abnormally elevated in patients with PCOS, vitamin D supplementation seems to improve folliculogenesis in these individuals.
Another study conducted by Lerchbaum et al. [16] was a single-center, double-blind trial performed from 2011 to 2017 at the Medical University of Graz, Austria. The study included 180 women with PCOS and 150 without PCOS, all with serum vitamin D concentrations <75 nmol/L. The markers evaluated included AMH, LH, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and androstenedione. The study showed that, in women with PCOS, vitamin D supplementation had a significant effect on FSH values and the FSH/LH ratio but no effect on AMH levels. Furthermore, no significant effects were observed in women without PCOS.
The effects of vitamin D supplementation on AMH levels, metabolic profiles, and gene expression related to lipid and insulin metabolism in PCOS patients undergoing IVF have also been studied. Dastorani et al. [17] conducted a randomized, double-blind study on 40 infertile women aged 18 to 40 with a diagnosis of PCOS undergoing IVF. One group received 50,000 IU of vitamin D weekly for 8 weeks, while the other group received a placebo. Vitamin D supplementation demonstrated beneficial effects on lipid and insulin metabolism in these patients. Vitamin D appears to play a protective role by modulating blood pressure in hypertensive disorders, improving insulin sensitivity in gestational diabetes, and contributing to the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation in carcinogenesis [18,19]. These findings reveal conflicting results regarding the correlation between vitamin D levels and AMH. However, such discrepancies may be attributed to factors such as variations in vitamin D dosage, differences in study design, baseline vitamin D status of the participants, the presence of underlying metabolic disorders, or even the sample size of the studies.
Nonetheless, most of the studies included in our analysis reported a positive correlation between vitamin D and AMH levels.
3.2 Role of antioxidants: Omega-3 and vitamin E
Various studies have demonstrated that oxidative stress plays a significant role in infertility in patients with PCOS. Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them with antioxidants [20]. This imbalance has been shown to increase the production of androgens and insulin, while also contributing to poorer ovarian follicle quality [21]. It has been observed that patients with PCOS exhibit elevated levels of oxidative stress indices, such as malondialdehyde [22]. In this context, omega-3 fatty acids are considered one of the primary nutritional supplements for counteracting oxidative stress in PCOS patients. Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fatty acids found predominantly in vegetable and marine oils [23], and they have beneficial effects on various health conditions. For example, omega-3s have been shown to significantly impact obesity, with higher levels of omega-3s resulting in a reduction in fat mass [24]. Since obese patients with PCOS tend to have more severe hyperandrogenism, a higher incidence of anovulatory cycles, and oligomenorrhea, they are at an increased risk of infertility. As a result, several studies have explored the potential benefits of omega-3 supplementation in these patients.
Nadjarzadeh et al. [25] conducted a randomized, double-blind study in 2015 on 84 obese infertile patients with PCOS, investigating the effects of omega-3 intake on adiponectin, LH, FSH, and visfatin levels. The study found that these patients exhibited elevated visfatin levels, an adipokine produced by visceral fat and associated with insulin resistance, which plays a role in the pathogenesis of PCOS. Additionally, adiponectin levels were reduced, while adiponectin is an adipokine that improves insulin sensitivity and exerts anti-inflammatory effects. The study demonstrated that omega-3 supplementation led to an increase in adiponectin, beneficial effects on LH concentrations, and an improved LH/FSH ratio. However, no effects were observed on visfatin, FSH, prolactin, or BMI.
The potential impact of omega-3 supplementation on spontaneous conception has also been studied. In 2022, Stanhiser et al. [26] analyzed data from a study conducted between 2008 and 2015 involving 1,036 women aged 30–44, all attempting conception for less than three months without a history of infertility. The study concluded that women who took omega-3 supplements had a 1.51 times greater chance of spontaneous conception compared to those who did not.
In addition to omega-3, vitamin E is another potent antioxidant known to have significant effects on women’s reproductive processes. A 2022 review by Amin et al. [27] assessed the role of vitamin E supplementation in female reproduction, focusing on its effects on fertility, reproductive hormone levels, and assisted reproductive technologies. Although the exact mechanism by which vitamin E acts is not fully understood, the review suggests that it has promising potential to improve fertility rates and overall reproductive health in women.
Given that both omega-3 and vitamin E are strong antioxidants, a study also explored the potential combined effects of these supplements in infertile patients with PCOS and a BMI greater than 25. In a randomized, double-blind study [28], 62 patients were assigned to either the intervention group (group A) or the control group (group B). Group A received co-supplementation of 2 g of omega-3 and 400 IU of vitamin E for 8 weeks, while group B received a placebo for the same duration. The study evaluated total antioxidant capacity, glutathione levels, catalase activity, and malondialdehyde concentrations before and after the supplementation period. The results showed that co-supplementation with omega-3 and vitamin E led to a significant increase in total antioxidant capacity (1.15 ± 0.93 vs 0.6 ± 0.72; P < 0.001), catalase activity (1.19 ± 1.06 vs 0.12 ± 0.36; P < 0.001), and glutathione levels (1.5 ± 1.06 vs 0.23 ± 1.43; P = 0.028), along with a significant reduction in malondialdehyde levels (0.34 ± 0.32 vs 0.57 ± 2.20; P = 0.008) compared to the placebo group.
3.3 Role of supplementation with probiotics and synbiotics
In patients with PCOS and BMI > 25, a strategy to address obesity and improve reproductive outcomes involves dietary supplementation with probiotics and synbiotics. Probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits to the host, while synbiotics are dietary supplements that combine probiotics with prebiotics (non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of probiotics). Their beneficial effects are attributed to their ability to modulate the intestinal microbiota [29,30,31,32].
Chudzicka-Strugała et al. [33] conducted a randomized, double-blind study in 2021 involving 65 patients diagnosed with PCOS and a BMI of >25, recruited from the Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Clinical Services at Poznan University of Medical Sciences. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either synbiotic supplementation or a placebo. The synbiotic supplement included several probiotics: two strains of Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus salivarius, and Lactobacillus lactis. The study evaluated changes in BMI and testosterone levels.
The synbiotic group exhibited an 8% reduction in BMI, significantly greater than the 5% reduction observed in the placebo group (P = 0.03). Additionally, a reduction in total testosterone levels was observed in 90% of the women in the synbiotic group compared to 53% in the placebo group, with a significant difference between the groups (P = 0.008). Testosterone levels decreased by 32% in the synbiotic group, compared to only a 6% decrease in the placebo group.
This study supports the hypothesis that synbiotic supplementation can enhance the effects of diet and exercise in promoting weight loss and reducing hyperandrogenism in obese patients with PCOS.
3.4 Role of inositols
Inositols are a group of cyclic polyols with a six-carbon ring, which have been shown to play an important role in insulin-activated signaling pathways [34,35,36]. The most important isoforms are myo-inositol and d-chiro-inositol. These compounds are considered insulin-sensitizing, and therefore, their deficiency leads to insulin resistance. For this reason, their role has been studied in patients with PCOS [37,38,39].
A review conducted by Coldebella et al. in 2022 [38] analyzed the role of inositol treatment in patients with PCOS, demonstrating a reduction in hyperinsulinemia and an improvement in the metabolic and ovulatory characteristics of these patients. Beneficial effects on oocytes and ovarian quality were also shown in patients undergoing ART. However, this review did not determine which of the two isoforms is the most effective or what the optimal dosage is.
Some animal studies have also evaluated the effect of myo-inositol and d-chiro-inositol in the treatment of PCOS and have shown that a 40:1 ratio of the two positively modulates the steroidogenic pathway of the ovarian theca cells and increases the concentration of FSH receptors in granulosa cells [35].
Inositols have often been combined in PCOS treatment [40,41] with alpha-lactalbumin [42], a milk whey globular protein produced by the epithelial cells of the mammary gland, which has prebiotic, mucoprotective, and anti-inflammatory actions. Due to its prebiotic effect, alpha-lactalbumin appears to promote the intestinal absorption of certain substances, including inositols, thereby enhancing their effects on PCOS [43].
3.5 Other nutraceuticals
Another promising nutraceutical is melatonin, a low molecular weight hormone that modulates multiple metabolic pathways in humans, including the regulation of circadian rhythms, reproductive mechanisms, and immune responses [44]. In the context of female fertility, supplementation with melatonin has been shown to improve oocyte and embryo quality, as well as luteal function [45,46]. These findings support the growing interest in melatonin as a promising adjunct in the treatment of female infertility [47]. It has also been demonstrated that melatonin supplementation, particularly when combined with magnesium, has beneficial effects in patients with PCOS, improving parameters such as hirsutism, BMI, waist circumference, and serum levels of TNF-alpha [48]. Moreover, the combined administration of myo-inositol and melatonin has been compared with myo-inositol alone in PCOS patients undergoing IVF, and it was observed that the addition of 3 mg of melatonin to 400 mg of myo-inositol enhances both oocyte and embryo quality [49].
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a powerful antioxidant and free radical scavenger that acts primarily within mitochondria – organelles essential for energy metabolism and highly susceptible to oxidative damage [50]. CoQ10 plays a protective role in female gametes against oxidative stress, with studies showing that its concentration in follicular fluid declines significantly with age [51,52]. Furthermore, CoQ10 supplementation has been associated with improvements in ovarian response, oocyte quality, and embryo development, particularly in women with diminished ovarian reserve [53].
Selenium is another compound – specifically a micronutrient – with significant effects in women with PCOS, particularly as an adjuvant to pharmacological treatment with metformin. It has been shown to improve fasting blood glucose levels, reduce insulin resistance, and lower free testosterone levels [54,55]. Although selenium supplementation in infertile PCOS patients undergoing IVF has shown beneficial effects on glycemic control, it does not appear to influence pregnancy rates, lipid profile, total antioxidant capacity, or total glutathione levels [56].
From our research, we have created Table 1 that summarizes the most significant data of the most used nutraceuticals in clinical practice.
Most prescribed nutraceuticals
| Nutraceutical | Main function | Fertility benefits | Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Regulation of the immune system and hormonal balance | Improves oocyte quality, insulin sensitivity, endometrial receptivity, and embryo quality | 20,000–50,000 UI/week |
| Omega-3 (EPA and DHA) | Essential fatty acids for the body | Improves oocyte quality and sperm motility and has a significant impact on obesity | 500–1,500 mg daily |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant that protects from radiation and oxidative stress | Improves semen quality and ovarian function. Enhances the endometrial environment and improves endometrial thickness | 400UI twice daily |
| Myo-Inositol | Helps insulin function and regulates ovulation | Supports oocyte quality, useful in women with PCOS | 2 g twice a day |
| Alpha-Lipoic Acid | Powerful antioxidant that supports metabolism and reduces inflammation | Improves oocyte and sperm quality, useful in patients with PCOS and insulin resistance | 600 mg twice daily or 800 mg daily |
| Melatonin | A low molecular weight hormone that modulates the regulation of circadian rhythms, reproductive mechanisms, and immune responses | Improves oocyte, embryo quality, and luteal function | 3 mg daily |
| Coenzyme Q10 | A powerful antioxidant and free radical scavenger that acts primarily within mitochondria | Improves ovarian response, oocyte quality, and embryo development | 100–200 mg daily |
| Selenium | Improves fasting blood glucose levels and reduces insulin resistance | Increases AMH index and antral follicle count | 200 ng/day |
3.6 Legal framework
From a medico-legal perspective, the use of nutraceutical therapies in overweight or obese individuals, particularly those affected by single or multiple systemic or solely gynecological conditions, involves numerous and complex issues that go beyond the simple prescription of a supplement. Many nutraceuticals are prescribed or purchased independently by patients as potentially effective solutions for weight management and the improvement of metabolic and aesthetic conditions; however, the scientific evidence supporting their efficacy is often limited or even conflicting.
Therefore, the use of these products should only occur in the presence of sufficiently robust clinical data or with regulatory approval comparable to that of traditional pharmaceuticals, thus avoiding medical problems resulting from their unverified safety [57]. The possibility of side effects, drug interactions, or the lack of adequate monitoring for some of these products could lead to significant direct or indirect harm to the patient. The risks associated with unverified and unsafe products cannot be ignored. In extreme cases, some nutraceuticals or substances contained within them can be used as additives in the production of synthetic drugs, such as in the case of “bath salts” [58,59]. Preventing the expansion of this market begins with proper education and appropriate prescriptions, not only of medications but also of nutraceutical supplements, to avoid their potential conversion into dangerous and illegal substances that end up in the black market for illicit purposes [60]. It is crucial that nutraceuticals be prescribed carefully, also for public safety reasons, and that healthcare professionals educate patients on the correct use of these products and the dangers of their abuse or the use of unregulated or unauthorized substances [61,62]. Proper regulation and transparency in prescriptions can also prevent the overproduction of unnecessary or misused substances [63].
From a medico-legal standpoint, healthcare professionals are required to ensure the scientific validity of any nutraceutical treatment. This choice should be based on a careful evaluation of the risk-benefit ratio, in line with available scientific evidence and sector guidelines, while always adhering to the principle of primum non nocere (first, do not harm) [64] and the legality of the medical treatment. The professional responsibility of prescribing healthcare providers also extends to ensuring the proper information is given to the patient [65]. Just as with other prescribed medications or vitamins, healthcare providers must inform patients adequately about the potential side effects and limitations of the treatment to avoid any form of negligence. Informed consent, as in many other areas of medicine, cannot be overlooked and must always be based on clarity of information, transparency of data, simplicity in conveying scientific information, and up-to-date medical knowledge.
Moreover, the prescription of nutraceuticals should be contextualized within a global therapeutic plan that considers the patient’s specific health conditions. As previously mentioned, the prescription of these substances should follow the principle of personalized medicine, especially in the presence of significant systemic comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia, which could also affect the efficacy and safety of nutraceutical intake. Close attention must be given to the consequences or benefits for fertility [7,66,67,68]. This aspect must be clearly communicated to patients, particularly to avoid misunderstandings and potential disputes. The lack of stringent regulation for nutraceuticals, compared to pharmaceuticals, should lead to greater caution on the part of the prescribing physician, particularly in the continuous monitoring of effects and management of potential complications. In the case of harm arising from the use of such therapies, the physician could face legal disputes related to professional responsibility based on negligence. This could especially occur in cases where the treatment is not adequately and scientifically justified, if risks were not properly considered, or if sufficient information was not provided. It is also important to note that even when adequate information is provided, it must always be well documented and verifiable, as there are cases in professional healthcare liability where legal disputes are based on the lack of documentation proving that information was given [69]. Proper documentation of the decision-making process and transparency in communications with the patient are, therefore, crucial to preventing potential legal disputes and protecting the healthcare professional’s legal responsibility, as well as safeguarding the patient’s right to health and self-determination.
Therefore, to enhance clarity, we conducted a concise comparison between the regulatory frameworks of the European Union (EU) and the United States regarding the use of nutraceuticals in gynecology, particularly with reference to the medico-legal context, highlighting substantial differences.
In the EU, nutraceuticals are generally classified as food supplements and are subject to the regulatory framework governing functional foods. Conversely, in the United States, the term falls under dietary supplements, regulated by the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 [70].
The main European regulations include Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 (nutritional and health claims) [71], Regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011 (labeling requirements) [72], and Directive 2002/46/EC (food supplements) [73].
Any health claim (e.g., “supports female health”) must be evaluated and approved by EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). These supplements cannot replace conventional medical treatments and must not suggest curative effects, but rather be positioned as adjunctive aids to health [74].
In the United States, the federal DSHEA permits manufacturers to market dietary supplements without being required to demonstrate their safety or effectiveness beforehand [75]; nutraceuticals are regulated by the FDA as dietary supplements but are not subject to the same premarket approval processes as pharmaceuticals [76]. The manufacturer is entirely responsible for product safety and the truthfulness of any benefit-related statements. The FDA may only intervene in post-marketing, once the product is already available to consumers [77].
Moreover, if a health claim is made, it’s legally required to include the disclaimer “This statement has not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.”
In Europe, the use of nutraceuticals for medical purposes is not typically covered by public health insurance. Physicians may face professional liability if they recommend a product with unproven pharmacological efficacy for therapeutic purposes.
In the United States, physicians have greater prescriptive freedom, yet they can still be held legally accountable for adverse outcomes resulting from inappropriate use of nutraceuticals or failure to recommend recognized conventional treatments [74].
The fundamental differences between the EU and the United States are therefore summarized in Table 2.
Summary of key differences
| Aspect | EU | The United States |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-market evaluation | Rigorous (EFSA approval required) | Minimal (FDA acts post-market) |
| Manufacturer liability | High, moderated by EFSA authorization | Full responsibility, no pre-approval control |
| Physician liability | High, especially in cases of unproven claims | High, particularly if informed consent is lacking |
| Patient protection | Strongly oriented toward the precautionary principle | More focused on individual freedom |
Therefore, the EU adopts a more restrictive and precautionary approach, requiring scientific evidence for all health claims and holding physicians accountable for nutraceutical prescriptions. In contrast, the United States follows a more liberal model, characterized by limited initial oversight and regulation, but with significant legal consequences in cases of adverse effects or misleading claims.
4 Discussion
Our research suggests that overweight infertile patients may benefit from nutraceutical supplementation, particularly when addressing underlying conditions such as PCOS, which is commonly diagnosed in these patients. The prevalence of PCOS among women with infertility underscores the need for targeted nutritional interventions to improve fertility outcomes. One key component in this approach is vitamin D, a secosteroid hormone with crucial roles in both metabolic and reproductive processes [78].
In women with PCOS, vitamin D supplementation has shown significant potential in improving various aspects of reproductive health. Vitamin D is involved in several physiological mechanisms essential for fertility. It helps enhance insulin sensitivity, which is a critical concern for many women with PCOS who experience insulin resistance. Additionally, vitamin D has been shown to positively affect endometrial receptivity – an essential factor for embryo implantation – along with promoting proper oocyte (egg) development and embryo quality. These beneficial effects of vitamin D are primarily mediated through its receptors in ovarian granulosa cells, which are essential for ovarian function and overall reproductive health [79].
Another important aspect of vitamin D in fertility is its influence on ovarian reserve, commonly assessed by AMH levels [80,81]. AMH is produced by granulosa cells during the follicular phase of ovarian development and serves as a crucial marker of ovarian reserve. Research suggests that vitamin D plays a role in regulating AMH expression and serum levels. A deficiency in vitamin D may lead to disturbances in AMH production [82]. AMH binds to two types of receptors (type I and type II), and its interaction with type II receptors can inhibit follicular maturation and decrease ovarian sensitivity to FSH, which is vital for follicle development [83]. Vitamin D supplementation appears to counteract this effect by inhibiting the expression of the AMHR-II receptor, thus promoting follicular maturation and improving ovarian function [84,85]. Therefore, the assessment of vitamin D status may represent a valuable component in fertility protocols, particularly in patients with PCOS or borderline ovarian reserve. Appropriate vitamin D supplementation has the potential to enhance reproductive outcomes; yet, it requires individualized dosing strategies and regular monitoring of serum levels to ensure efficacy and safety. This interaction further supports the potential role of vitamin D as an adjuvant in hormonal treatment protocols, especially within clinically supervised and personalized reproductive care settings.
Despite the growing evidence supporting the benefits of vitamin D for PCOS patients, no universally accepted standard exists for the optimal serum levels of vitamin D in fertility treatment. The Endocrine Society’s guidelines suggest that vitamin D levels above 30 ng/mL are sufficient, levels between 20 and 29 ng/mL indicate insufficiency, and levels below 20 ng/mL signal deficiency. For PCOS patients with insulin resistance and low AMH levels, particularly those undergoing fertility treatments, the recommended dosage of vitamin D3 is 1,500–2,000 IU per day. This supplementation is thought to improve fertility outcomes by addressing both metabolic and reproductive dysfunctions in these patients [86].
In addition to vitamin D, vitamin E has demonstrated potential benefits in enhancing female fertility, particularly due to its antioxidant properties [87]. A deficiency in vitamin E has often been linked to recurrent pregnancy loss, highlighting its importance in maintaining a healthy pregnancy [88]. Some studies investigating the effects of vitamin E supplementation in women with unexplained infertility have produced mixed results. While some studies failed to show significant improvements in pregnancy rates, others suggest that vitamin E may help improve the endometrial environment and increase endometrial thickness, particularly in women experiencing implantation failure [84].
Vitamin E levels in both follicular fluid and serum have been associated with oocyte maturation, particularly in women undergoing IVF [89]. Studies suggest that optimal vitamin E levels in follicular fluid (ranging from 0.35 to 2 mg/dL) are crucial for proper oocyte maturation, and higher concentrations (10–15 mg/dL) are linked to improved embryo quality. Based on these findings, vitamin E supplementation (400 IU twice daily) may enhance outcomes in ART by improving oocyte quality and supporting embryo development [90].
Beyond vitamins D and E, other dietary components have shown promising effects in improving fertility, particularly in women with PCOS. One such component is green cardamom, a spice from the Zingiberaceae family. Green cardamom is rich in polyphenols and flavonoids, which possess potent antioxidant, antiinflammatory, and antibacterial properties [91,92]. Research suggests that administering 3 g/day of green cardamom to obese women with PCOS can improve key metabolic and endocrine markers, including hormonal balance and inflammatory cytokine levels. These benefits may, in turn, lead to improved reproductive outcomes for women with PCOS [93]. It is important to note that these findings have certain limitations. The study relies on self-reported data regarding diet and physical activity, involved slow patient recruitment due to strict eligibility criteria, was conducted in a single center, and faced challenges with patient non-compliance toward the end of the trial. This research investigates the effects of green cardamom on blood glucose levels, lipid profile, inflammatory markers, and blood pressure in obese individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, suggesting that improvements in these factors could positively influence fertility. However, these results should be interpreted with caution, and further studies are necessary to confirm or challenge these findings.
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a naturally occurring antioxidant found in foods such as potatoes, broccoli, spinach, and red meat, also shows promise in the treatment of PCOS. ALA has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and insulin-sensitizing effects, which could be particularly beneficial for women with PCOS who experience insulin resistance. ALA is also an enzymatic cofactor in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, with the ability to enhance insulin sensitivity. It can eliminate reactive oxygen and nitrogen species both in vivo and in vitro, regenerating essential antioxidant molecules, such as coenzyme Q10, vitamin C, and vitamin E, and repairing proteins, lipids, and DNA damaged by oxidative stress. Some studies suggest that ALA supplementation, particularly when combined with inositol, may reduce symptoms of PCOS and improve biochemical markers. However, the effects on reproductive hormones remain unclear, and further research is needed to establish its full potential [40]. Suggested dosages for ALA vary, with some studies recommending 600 mg twice daily and others suggesting 800 mg per day [94].
It has long been evident that inositol is involved in the transduction of various endocrine signals, including insulin, thyroid hormones, gonadotropins, and prostaglandins. The modulatory role of inositol in glucose and insulin metabolism alone does not fully account for its clinical efficacy. Emerging evidence indicates that d-chiro-inositol directly regulates the expression of steroidogenic enzyme genes in human granulosa cells; moreover, d-chiro-inositol has been shown to increase testosterone levels in theca cells of women with PCOS [82]. Myo-inositol is believed to enhance ovarian function and fertility. However, the impact of myo-inositol on pregnancy rates remains uncertain, especially in women undergoing IVF. Randomized trials comparing myo-inositol with other antioxidants, insulin-sensitizing agents, and ovulation-inducing medications are necessary to determine its role in infertility treatment [95].
Looking forward, the use of nutraceutical supplements in treating infertility, particularly in overweight women with PCOS, holds significant promise. These supplements are accessible, affordable, and generally considered safe, making them an attractive option for many patients. However, future research must focus on identifying the most effective nutraceuticals and determining their optimal dosages to improve fertility outcomes. More randomized controlled trials are needed to establish definitive guidelines for their use in clinical practice, ensuring that these supplements are used effectively and safely in infertility treatments.
While nutraceutical supplementation holds promise for improving fertility outcomes in overweight infertile patients, particularly those with PCOS [96,97], further studies are essential to fully understand the underlying mechanisms and to establish clear treatment protocols. The combination of vitamins, antioxidants, and other dietary components could potentially provide a comprehensive approach to enhancing fertility, but continued research is necessary to refine these strategies.
The analysis of the scientific studies presented here outlines a promising framework for the use of nutraceutical supplementation as an adjunctive strategy in managing infertility, especially in patients with PCOS and overweight. However, it is crucial to interpret these results with caution.
There are potential benefits: Vitamin D emerges as a key modulator of reproductive and metabolic mechanisms, with positive effects on insulin sensitivity, endometrial receptivity, and ovarian function. Antioxidants such as vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids can counteract oxidative stress, a significant factor in infertility, and improve reproductive outcomes. Probiotics and synbiotics show potential in modulating the composition of the intestinal microbiota, with beneficial effects on body weight and testosterone levels in overweight patients with PCOS. Other nutraceuticals, such as green cardamom, ALA, and myoinositol, may offer additional advantages, although further studies are needed to confirm their efficacy and establish optimal dosages.
However, there are some limitations. Despite the promising results, defining optimal vitamin D levels and the dosages of other nutraceuticals for fertility requires further research. Additionally, the individual variability in response to nutraceutical supplementation highlights the need for a personalized approach. The potential interactions between nutraceuticals and pharmacological treatments also necessitate careful clinical evaluation. Future research should focus on the synergistic effects of these nutraceuticals, determining how they might complement or enhance the efficacy of other fertility treatments.
Interactions between nutraceuticals can be synergistic, such as the combination of soy isoflavones and vitamin D [98], which has demonstrated benefits for postmenopausal bone health, or antagonistic, as in the case of iron and calcium, which compete for intestinal absorption [99].
Other relevant interactions include St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) and oral contraceptives, which can result in serious clinical consequences, such as an increased risk of unintended pregnancy, since St. John’s Wort induces the CYP3A4 enzyme, thereby reducing the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives [100]. Likewise, melatonin may act synergistically with anxiolytic medications (e.g., benzodiazepines) [101], leading to enhanced sedative effects, which are clinically significant in the treatment of insomnia during pregnancy or in the postpartum period [102].
Additionally, nutraceuticals containing grapefruit or grapefruit-derived compounds may interfere with the metabolism of a wide range of pharmaceutical drugs, due to the inhibition of cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) in the intestinal wall [103]. This can result in elevated plasma concentrations of co-administered drugs, enhancing their pharmacological or toxic effects. In gynecology and obstetrics, this interaction is particularly relevant for medications such as oral contraceptives [104], antihypertensives [105], or immunomodulators, commonly used in various treatment protocols. Therefore, grapefruit-containing supplements should be used with caution or completely avoided when potential drug-nutraceutical interactions are a concern.
In gynecological and obstetric practice, these interaction dynamics take on particular importance due to the delicate physiological phases involved – pregnancy, postpartum, hormonal imbalance, and fertility treatments [106]. For example, phytoestrogens can interfere with hormonal therapies or contraceptive methods [107]; probiotics taken concurrently with antibiotics may alter treatment efficacy for bacterial vaginosis; and sedative agents such as valerian must be used cautiously during pregnancy, given the lack of robust safety data.
From a medico-legal standpoint, it is essential that the use of nutraceuticals is carefully evaluated by healthcare providers, always framed as adjunctive rather than substitutive therapy, and appropriately documented in the medical record. This is especially important in complex scenarios such as ART or the management of chronic conditions in women of reproductive and post-reproductive age [108,109]. Inadequate prescription or failure to assess potential interactions may expose clinicians to legal liability, particularly in the absence of strong scientific evidence or in the case of predictable adverse outcomes [110].
Nutraceutical supplementation can represent a safe, cost-effective adjunctive option for improving fertility outcomes in patients with PCOS and overweight. The integration of nutraceuticals into clinical practice should be based on an evidence-driven, personalized approach to ensure the most effective results.
Moreover, open communication between doctors and patients is essential to evaluate individual needs, monitor potential side effects, and make necessary adjustments in treatment plans.
In summary, while nutraceutical supplementation shows great promise in improving fertility in patients with PCOS and overweight, further studies are needed to optimize its clinical use and refine clinical practices and treatment protocols. This includes a deeper understanding of the optimal dosages, potential interactions, and long-term effects. Additionally, a more comprehensive understanding of the metabolic aspects of PCOS, such as insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, is crucial for tailoring nutraceutical interventions more effectively. Future advancements in the field may also benefit from the integration of emerging scientific methodologies and artificial intelligence [111], which could enable more personalized and evidence-based approaches to nutraceutical use in reproductive medicine.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, infertility is a complex issue affecting many couples globally, with obesity, particularly in women with PCOS, being a significant contributing factor. Nutritional interventions, including nutraceutical supplementation, offer potential benefits in improving fertility in overweight and obese patients by addressing underlying metabolic and hormonal imbalances.
The clinical management of obesity-related infertility goes beyond simple caloric restriction. It involves a personalized nutritional plan tailored to each patient’s hormonal and metabolic profile. Nutraceuticals are employed in a targeted manner, often alongside pharmacological treatments or ART, to enhance fertility outcomes.
Among the most commonly used nutraceuticals is vitamin D, widely prescribed for patients with deficiencies, especially women with PCOS, as it improves insulin sensitivity, endometrial receptivity, and embryo quality, all crucial for implantation and pregnancy success. However, serum vitamin D levels in women undergoing IVF do not appear to influence clinical outcomes, and the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on female fertility are still under investigation. Vitamin E, known for its antioxidant properties, is used to improve semen quality in men and support ovarian function in women. Omega-3 fatty acids are commonly recommended due to their anti-inflammatory effects and their role in enhancing sperm motility and oocyte quality, thus contributing to a more favorable reproductive environment. Myoinositol is arguably one of the most prescribed supplements for women with PCOS, due to its proven ability to restore ovulatory function and improve insulin sensitivity, thereby reducing hyperinsulinemia and promoting hormonal balance. ALA, another powerful antioxidant with insulin-sensitizing properties, is also frequently used in PCOS patients to reduce oxidative stress and improve metabolic parameters.
As reported in this narrative review, the most promising approaches involve nutraceuticals aimed at optimizing weight reduction or mitigating oxidative stress, with direct effects on the regulation of the menstrual cycle, particularly in overweight patients. Moreover, in the context of PCOS, it is essential to identify the specific phenotype and to select the most appropriate support through a tailored approach.
Drawing on our clinical experience, nutraceuticals may serve as adjuncts to pharmacological therapies, with their use grounded in the need to address nutritional deficiencies and to ensure the optimal intake of specific compounds. Such an approach may positively influence key fertility parameters, including hormonal balance, ovulation, oocyte quality, embryo development, and the likelihood of achieving a full-term pregnancy.
Moreover, we have observed in our clinical practice what may be described as a placebo effect in patients taking nutraceuticals. Their mood often appears positively influenced by the belief that a simple product, such as a nutraceutical, can have a significant beneficial effect on their condition. It remains unclear whether this response is primarily driven by the patients’ own convictions or possibly influenced by our approach as healthcare providers prescribing these supplements. We aim to further explore this phenomenon through future research, potentially by correlating clinical data with patient surveys.
While promising evidence supports the benefits of specific nutrients and supplements, further research is needed to establish clear, evidence-based guidelines for their use. Nevertheless, a diet rich in essential nutrients, combined with the appropriate use of nutraceuticals, could represent a valuable tool in managing infertility, providing a more holistic approach to improving reproductive health.
6 Limitations
This article aims to provide an overview of the current situation regarding the topic at hand, without delving too deeply into the specifics of each individual issue. The intention is to avoid an overly complex analysis that could make the reading and understanding too burdensome for the reader. However, while the article does not explore the various issues in depth, it strives to remain comprehensive and accessible, making it easily digestible for the scientific community. A more detailed examination of each issue raised could be the subject of future research. Furthermore, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to take some limitations into account. The sample sizes reported in the different studies are often variable, which may limit statistical power and the generalization of the conclusions. In addition, the included articles show considerable heterogeneity in terms of the types of nutraceuticals used, dosages, duration of treatment, and characteristics of the studied populations; such variability makes direct comparison of the results challenging. Another critical issue concerns potential sources of bias: in several studies, the methods of randomization and blinding were not clearly described, leading to a possible risk of selection or performance bias; moreover, the presence of publication bias cannot be excluded, with a higher likelihood of publication for studies showing positive rather than negative results. Taken together, these elements suggest that the data should be interpreted with caution, while acknowledging that the available evidence supports a growing interest in and a potential role for nutraceuticals in the management of obesity.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Conceptualization, G.G., E.C., and L.D.; methodology, E.C., V.B., and S.M.; validation, G.C., L.D., and S.M.; formal analysis, E.Ch., K.K., and R.S.; investigation, R.K., A.V., and R.S.; writing – original draft preparation, E.C., V.B., S.P., Y.K., and A.P.; and writing – review and editing, G.G., G.C., S.M., and L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Giuseppe Gullo serves as Editor for Open Medicine Journal, but it does not affect the peer-review process. Other authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Infertility Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/infertility (accessed on 17 March 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Brannigan RE, Hermanson L, Kaczmarek J, Kim SK, Kirkby E, Tanrikut C. Updates to male infertility: AUA/ASRM guideline (2024). J Urol. 2024;212:789–99. 10.1097/JU.0000000000004180.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Gu R, Wu T, Fu J, Sun Y-J, Sun X-X. Advances in the genetic etiology of female infertility. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024;41:3261–86. 10.1007/s10815-024-03248-w.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Skoracka K, Ratajczak AE, Rychter AM, Dobrowolska A, Krela-Kaźmierczak I. Female fertility and the nutritional approach: the most essential aspects. Adv Nutr. 2021;12:2372–86. 10.1093/advances/nmab068.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Awonuga AO, Camp OG, Biernat MM, Abu-Soud HM. Overview of infertility. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2025;71:116–42. 10.1080/19396368.2025.2469582.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Carson SA, Kallen AN. Diagnosis and management of infertility: a review. JAMA. 2021;326:65–76. 10.1001/jama.2021.4788.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Cena H, Chiovato L, Nappi RE. Obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, and infertility: a new avenue for GLP-1 receptor agonists. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e2695–709. 10.1210/clinem/dgaa285.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Moran LJ, Norman RJ, Teede HJ. Metabolic risk in PCOS: phenotype and adiposity impact. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26:136–43. 10.1016/j.tem.2014.12.003.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Broughton DE, Moley KH. Obesity and Female infertility: potential mediators of obesity’s impact. Fertil Steril. 2017;107:840–7. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.01.017.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Jungheim ES, Moley KH. Current knowledge of obesity’s effects in the preand periconceptional periods and avenues for future research. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:525–30. 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.06.043.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Ramlau-Hansen CH, Thulstrup AM, Nohr EA, Bonde JP, Sørensen TIA, Olsen J. Subfecundity in overweight and obese couples. Hum Reprod. 2007;22:1634–7. 10.1093/humrep/dem035.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] van der Steeg JW, Steures P, Eijkemans MJC, Habbema JDF, Hompes PGA, Burggraaff JM, et al. Obesity affects spontaneous pregnancy chances in subfertile, ovulatory women. Hum Reprod. 2008;23:324–8. 10.1093/humrep/dem371.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Dabrowski FA, Grzechocinska B, Wielgos M. The role of vitamin D in reproductive health--a trojan horse or the golden fleece? Nutrients. 2015;7:4139–53. 10.3390/nu7064139.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Bosdou JK, Konstantinidou E, Anagnostis P, Kolibianakis EM, Goulis DG. Vitamin D and obesity: two interacting players in the field of infertility. Nutrients. 2019;11:1455. 10.3390/nu11071455.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Moridi I, Chen A, Tal O, Tal R. The association between vitamin D and anti-müllerian hormone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:1567. 10.3390/nu12061567.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Lerchbaum E, Theiler-Schwetz V, Kollmann M, Wölfler M, Pilz S, Obermayer-Pietsch B, et al. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on surrogate markers of fertility in PCOS women: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021;13:547. 10.3390/nu13020547.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Dastorani M, Aghadavod E, Mirhosseini N, Foroozanfard F, Zadeh Modarres S, Amiri Siavashani M, et al. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic profiles and gene expression of insulin and lipid metabolism in infertile polycystic ovary syndrome candidates for in vitro fertilization. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16:94. 10.1186/s12958-018-0413-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Domaracki P, Sadlecki P, Odrowaz-Sypniewska G, Dzikowska E, Walentowicz P, Siodmiak J, et al. Serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels in polish women during pregnancies complicated by hypertensive disorders and gestational diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1574.10.3390/ijms17101574Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Walentowicz-Sadłecka M, Sadłecki P, Walentowicz P, Grabiec M. [The role of vitamin D in the carcinogenesis of breast and ovarian cancer. Ginekol Pol aprile. 2013;84(4):305–8.10.17772/gp/1581Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Oxidative Stress in the Development of Insulin Resistance and Hyperandrogenism in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PubMed Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16249279/(accessed on 26 March 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Mohammadi E, Rafraf M, Farzadi L, Asghari-Jafarabadi M, Sabour S. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on serum adiponectin levels and some metabolic risk factors in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2012;21:511–8.Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Sabuncu T, Vural H, Harma M, Harma M. Oxidative stress in polycystic ovary syndrome and its contribution to the risk of cardiovascular disease. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:407–13. 10.1016/s0009- 9120(01)00245-4.Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Kwintkiewicz J, Spaczynski RZ, Foyouzi N, Pehlivan T, Duleba AJ. Insulin and oxidative stress modulate proliferation of rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells through diverse signal transduction pathways. Biol Reprod. 2006;74:1034–40. 10.1095/biolreprod.105.049908.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Skoracka K, Eder P, Łykowska-Szuber L, Dobrowolska A, Krela-Kaźmierczak I. Diet and nutritional factors in male (In)fertility-underestimated factors. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1400. 10.3390/jcm9051400.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Nadjarzadeh A, Dehghani-Firouzabadi R, Daneshbodi H, Lotfi MH, Vaziri N, Mozaffari-Khosravi H. Effect of Omega-3 supplementation on visfatin, adiponectin, and anthropometric indices in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J Reprod Infertil. 2015;16:212–20.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Stanhiser J, Jukic AMZ, McConnaughey DR, Steiner AZ. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and fecundability. Hum Reprod. 2022;37:1037–46. 10.1093/humrep/deac027.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Md Amin NA, Sheikh Abdul Kadir SH, Arshad AH, Abdul Aziz N, Abdul Nasir NA, Ab Latip N. Are Vitamin E supplementation beneficial for female gynaecology health and diseases? Molecules. 2022;27:1896. 10.3390/molecules27061896.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Sadeghi F, Alavi-Naeini A, Mardanian F, Ghazvini MR, Mahaki B. Omega-3 and vitamin E co- supplementation can improve antioxidant markers in obese/overweight women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2020;90:477–83. 10.1024/0300-9831/a000588.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Cerdó T, García-Santos JA, Bermúdez MG, Campoy C. The role of probiotics and prebiotics in the prevention and treatment of obesity. Nutrients. 2019;11:635. 10.3390/nu11030635.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Fijan S Microorganisms with claimed probiotic properties: an overview of recent literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11:4745–67. 10.3390/ijerph110504745.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Pandey KR, Naik SR, Vakil BV. Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics- a review. J Food Sci Technol. 2015;52:7577–87. 10.1007/s13197-015-1921-1.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Abenavoli L, Scarpellini E, Colica C, Boccuto L, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, et al. Gut microbiota and obesity: a role for probiotics. Nutrients. 2019;11:2690. 10.3390/nu11112690.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Chudzicka-Strugała I, Kubiak A, Banaszewska B, Zwozdziak B, Siakowska M, Pawelczyk L, et al. Effects of synbiotic supplementation and lifestyle modifications on women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106:2566–73. 10.1210/clinem/dgab369.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Fedeli V, Unfer V, Dinicola S, Laganà AS, Canipari R, Monti N, et al. Inositol restores appropriate steroidogenesis in PCOS ovaries both in vitro and in vivo experimental mouse models. Cells. 2024;13:1171. 10.3390/cells13141171.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Laganà AS, Myers SH, Forte G, Naem A, Krentel H, Allahqoli L, et al. Inositols in treating polycystic ovary syndrome and non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: now and the future. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024;20:61–72. 10.1080/17425255.2024.2306851.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[36] Laganà AS, Forte G, Bizzarri M, Kamenov ZA, Bianco B, Kaya C, et al. Inositols in the ovaries: activities and potential therapeutic applications. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2022;18:123–33. 10.1080/17425255.2022.2071259.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Genazzani AD. Inositol as putative integrative treatment for PCOS. Reprod Biomed Online. 2016;33:770–80. 10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.08.024.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[38] Coldebella D, Buzzaccarini G, Ferrari J, Sleiman Z, Dʼnalterio MN, Della Corte L, et al. Inositols administration: Further insights on their biological role. Ital J Gynaecol Obstet. 2023;35(1):30–6. 10.36129/jog.2022.40.Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Bloomgarden ZT. Second world congress on the insulin resistance syndrome: mediators, pediatric insulin resistance, the polycystic ovary syndrome, and malignancy. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1821–30. 10.2337/diacare.28.7.1821.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Laganà AS, Monti N, Fedeli V, Gullo G, Bizzarri M. Does alpha-lipoic acid improve effects on polycystic ovary syndrome? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022;26:1241–7. 10.26355/eurrev_202202_28116.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Fitz V, Graca S, Mahalingaiah S, Liu J, Lai L, Butt A, et al. Inositol for polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis to inform the 2023 update of the international evidence-based PCOS guidelines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024;109:1630–55. 10.1210/clinem/dgad762.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Basciani S, Nordio M, Dinicola S, Unfer V, Gnessi L. Diet plus inositols, α-lactalbumin and gymnema sylvestre: the successful combo to restore body weight and metabolic profile in obese and dysmetabolic patients. Nutrients. 2023;15:3142. 10.3390/nu15143142.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Kamenov Z, Gateva A, Dinicola S, Unfer V. Comparing the efficacy of myo-inositol plus α- lactalbumin vs myo-inositol alone on reproductive and metabolic disturbances of polycystic ovary syndrome. Metabolites. 2023;13:717. 10.3390/metabo13060717.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Fernando S, Rombauts L. Melatonin: shedding light on infertility? --a review of the recent literature. J Ovarian Res. 2014;7:98. 10.1186/s13048-014-0098-y.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Batıoğlu AS, Sahin U, Gürlek B, Oztürk N, Unsal E. The efficacy of melatonin administration on oocyte quality. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28:91–3. 10.3109/09513590.2011.589925.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[46] Luddi A, Capaldo A, Focarelli R, Gori M, Morgante G, Piomboni P, et al. Antioxidants reduce oxidative stress in follicular fluid of aged women undergoing IVF. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016;14:57. 10.1186/s12958-016-0184-7.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Shao R, Wang Y, He C, Chen L. Melatonin and its emerging physiological role in reproduction: a review and update. Curr Mol Med. 2024;24:449–56. 10.2174/1566524023666230417103201.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Mousavi R, Alizadeh M, Asghari Jafarabadi M, Heidari L, Nikbakht R, Babaahmadi Rezaei H, et al. Effects of melatonin and/or magnesium supplementation on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled trial. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200:1010–9. 10.1007/s12011-021-02725-y.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Pacchiarotti A, Carlomagno G, Antonini G, Pacchiarotti A. Effect of myo-inositol and melatonin versus myo-inositol, in a randomized controlled trial, for improving in vitro fertilization of patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2016;32:69–73. 10.3109/09513590.2015.1101444.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Harsini R, Zavareh S, Nasiri M, Seyfi S. The effect of coenzyme q10 on mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse ovarian follicles during in vitro culture. Zygote. 2024;32:14–20. 10.1017/S0967199423000461.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Ben-Meir A, Burstein E, Borrego-Alvarez A, Chong J, Wong E, Yavorska T, et al. Coenzyme Q10 restores oocyte mitochondrial function and fertility during reproductive aging. Aging Cell. 2015;14:887–95. 10.1111/acel.12368.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Giannubilo SR, Orlando P, Silvestri S, Cirilli I, Marcheggiani F, Ciavattini A, et al. CoQ10 supplementation in patients undergoing IVF-ET: the relationship with follicular fluid content and oocyte maturity. Antioxidants. 2018;7:141. 10.3390/antiox7100141.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Xu Y, Nisenblat V, Lu C, Li R, Qiao J, Zhen X, et al. Pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 improves ovarian response and embryo quality in low-prognosis young women with decreased ovarian reserve: a randomized controlled trial. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16:29. 10.1186/s12958-018- 0343-0.Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Salek M, Clark CCT, Taghizadeh M, Jafarnejad S. N-3 fatty acids as preventive and therapeutic agents in attenuating PCOS complications. EXCLI J. 2019;18:558–75. 10.17179/excli2019-1534.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Arentz S, Smith CA, Abbott J, Bensoussan A. Nutritional supplements and herbal medicines for women with polycystic ovary syndrome; a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17:500. 10.1186/s12906-017-2011-x.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Zadeh Modarres S, Asemi Z, Heidar Z. The effects of selenium supplementation on glycemic control, serum lipoproteins and biomarkers of oxidative stress in infertile women diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing in vitro fertilization: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022;51:92–6. 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.07.017.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[57] Albolino S, Bellandi T, Cappelletti S, Di Paolo M, Fineschi V, Frati P, et al. New rules on patient’s safety and professional liability for the italian health service. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20:615–24. 10.2174/1389201020666190408094016.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Graziano S, Zaami S, Tittarelli R, Pichini S, Sciotti M, Berretta P, et al. The complex and constantly evolving public health threat of new psychoactive substances in italy: addressing the main functions of a national observatory of drugs. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2021;57:144–50. 10.4415/ANN_21_02_06.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[59] Napoletano G, Paola LD, Rinaldi R. COVID-19-shaped substance abuse and adulteration dynamics: lasting beyond the pandemic? Acta Biomed. 2024;95:e2024181. 10.23750/abm.v95i6.16577.Suche in Google Scholar
[60] Martínez-Sanz JM, Sospedra I, Ortiz CM, Baladía E, Gil-Izquierdo A, Ortiz-Moncada R. Intended or unintended doping? a review of the presence of doping substances in dietary supplements used in sports. Nutrients. 2017;9:1093. 10.3390/nu9101093.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Jędrejko K, Catlin O, Stewart T, Anderson A, Muszyńska B, Catlin DH. Unauthorized ingredients in “nootropic” dietary supplements: a review of the history, pharmacology, prevalence, international regulations, and potential as doping agents. Drug Test Anal. 2023;15:803–39. 10.1002/dta.3529.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Jędrejko K, Lazur J, Muszyńska B. Risk associated with the use of selected ingredients in food supplements. Chem Biodiversity. 2021;18:e2000686. 10.1002/cbdv.202000686.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) Available online: https://www.unodc.org/wdr2013/en/nps.html (accessed on 7 March 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[64] Brewer Eberly J, Frush BW. First, Do No Harm (to the One You Train). Linacre Q. 2025;00243639241311315. 10.1177/00243639241311315.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Martines V, Magnaldi S, Fazio ND, Volonnino G, Marinelli E, Paola LD. Enhancing patient safety and delineate professional responsibility in radiological procedures involving contrast medium administration. La Clin Ter. 2025;176(1):42–6. 10.7417/CT.2025.5163.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Medenica S, Abazovic D, Ljubić A, Vukovic J, Begovic A, Cucinella G, et al. The role of cell and gene therapies in the treatment of infertility in patients with thyroid autoimmunity. Int J Endocrinol. 2022;2022:4842316. 10.1155/2022/4842316.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Zaami S, Melcarne R, Patrone R, Gullo G, Negro F, Napoletano G, et al. Oncofertility and reproductive counseling in patients with breast cancer: a retrospective study. J Clin Med. 2022;11:1311. 10.3390/jcm11051311.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Paola LD, Napoletano G, Gullo G, Circosta F, Vergallo GM, Marinelli S. The era of increasing cancer survivorship: trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges. Open Medicine. 2025;20(1):20251144. 10.1515/med-2025-1144.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[69] Treglia M, Pallocci M, Passalacqua P, Giammatteo J, De Luca L, Mauriello S, et al. Medical liability: review of a whole year of judgments of the civil court of rome. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:6019. 10.3390/ijerph18116019.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[70] Office of Dietary Supplements - Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/About/DSHEA_Wording.aspx (accessed on 24 April 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[71] Regulation - 1924/2006 - EN - EUR-Lex Available online: https://eur- lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/1924/oj/eng (accessed on 24 April 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[72] Regulation - 1169/2011 - EN - Food Information to Consumers Regulation - EUR-Lex Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/1169/oj/eng (accessed on 24 April 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[73] Directive - 2002/46 - EN - EUR-Lex Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2002/46/oj/eng (accessed on 24 April 2025).Suche in Google Scholar
[74] Program HF. Questions and Answers on Dietary Supplements. FDA; 2024.Suche in Google Scholar
[75] Cohen MH. Complementary and Integrative Medical Therapies, the FDA, and the NIH: Definitions and Regulation. Dermatol Ther. 2003;16:77–84. 10.1046/j.1529-8019.2003.01614.x.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] White CM. Dietary Supplements Pose Real Dangers to Patients. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54:815–9. 10.1177/1060028019900504.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[77] Brown AC. An overview of herb and dietary supplement efficacy, safety and government regulations in the united states with suggested improvements. Part 1 of 5 Series. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;107:449–71. 10.1016/j.fct.2016.11.001.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[78] Menichini D, Forte G, Orrù B, Gullo G, Unfer V, Facchinetti F. The role of vitamin D in metabolic and reproductive disturbances of polycystic ovary syndrome: a narrative mini-review. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2022;92:126–33. 10.1024/0300-9831/a000691.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[79] Thill M, Becker S, Fischer D, Cordes T, Hornemann A, Diedrich K, et al. expression of prostaglandin metabolising enzymes COX-2 and 15-PGDH and VDR in human granulosa cells. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:3611–8.Suche in Google Scholar
[80] Jukic AMZ, Steiner AZ, Baird DD. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and ovarian reserve in premenopausal women. Menopause. 2015;22:312–6. 10.1097/GME.0000000000000312.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Merhi Z, Doswell A, Krebs K, Cipolla M. Vitamin D alters genes involved in follicular development and steroidogenesis in human cumulus granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:E1137–45. 10.1210/jc.2013-4161.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[82] Dennis NA, Houghton LA, Jones GT, van Rij AM, Morgan K, McLennan IS. The level of serum anti-müllerian hormone correlates with vitamin D status in men and women but not in boys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2450–5. 10.1210/jc.2012-1213.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[83] Parikh G, Varadinova M, Suwandhi P, Araki T, Rosenwaks Z, Poretsky L, et al. Vitamin D regulates steroidogenesis and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) production in human ovarian cells. Horm Metab Res. 2010;42:754–7. 10.1055/s-0030-1262837.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[84] Morsy AA, Sabri NA, Mourad AM, Mojahed EM, Shawki MA. Randomized controlled open- label study of the effect of vitamin E supplementation on fertility in clomiphene citrate-resistant polycystic ovary syndrome. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2020;46:2375–82. 10.1111/jog.14467.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[85] Irani M, Merhi Z. Role of vitamin D in ovarian physiology and its implication in reproduction: a systematic review. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:460–8.e3. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.04.046.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[86] Arslan S, Akdevelioğlu Y. The relationship between female reproductive functions and vitamin D. J Am Coll Nutr. 2018;37:546–51. 10.1080/07315724.2018.1431160.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[87] Mohd Mutalip SS, Ab-Rahim S, Rajikin MH. Vitamin E as an antioxidant in female reproductive health. Antioxidants. 2018;7:22. 10.3390/antiox7020022.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[88] Cicek N, Eryilmaz OG, Sarikaya E, Gulerman C, Genc Y. Vitamin E effect on controlled ovarian stimulation of unexplained infertile women. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2012;29:325–8. 10.1007/s10815-012-9714-1.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[89] Bahadori MH, Sharami SH, Fakor F, Milani F, Pourmarzi D, Dalil-Heirati SF. Level of vitamin E in follicular fluid and serum and oocyte morphology and embryo quality in patients undergoing IVF treatment. J Family Reprod Health. 2017;11:74–81.Suche in Google Scholar
[90] Effects of Pentoxifylline and Vitamin E on Pregnancy Rate in Infertile Women Treated by ZIFT: A Randomized Clinical Trial. 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
[91] Ashokkumar K, Murugan M, Dhanya MK, Warkentin TD. Botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry and biological activities of cardamom [elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton] - a critical review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;246:112244. 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112244.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[92] Cheshmeh S, Ghayyem M, Khamooshi F, Heidarzadeh-Esfahani N, Rahmani N, Hojati N, et al. Green cardamom plus low-calorie diet can decrease the expression of inflammatory genes among obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Eat Weight Disord. 2022;27:821–30. 10.1007/s40519-021-01223-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[93] Daneshi-Maskooni M, Keshavarz SA, Mansouri S, Qorbani M, Alavian SM, Badri-Fariman M, et al. The effects of green cardamom on blood glucose indices, lipids, inflammatory factors, paraxonase-1, sirtuin-1, and irisin in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18:260. 10.1186/s13063- 017-1979-3.Suche in Google Scholar
[94] Fruzzetti F, Benelli E, Fidecicchi T, Tonacchera M. Clinical and metabolic effects of alpha-lipoic acid associated with two different doses of myo-inositol in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J Endocrinol. 2020;2020:2901393. 10.1155/2020/2901393.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[95] Showell MG, Mackenzie-Proctor R, Jordan V, Hodgson R, Farquhar C. Inositol for subfertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;12:CD012378. 10.1002/14651858.CD012378.pub2.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[96] Geronikolou SA, Pavlopoulou A, Cokkinos DV, Bacopoulou F, Chrousos GP. Polycystic οvary syndrome revisited: an interactions network approach. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51:e13578. 10.1111/eci.13578.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[97] Visser JA. The importance of metabolic dysfunction in polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17:77–8. 10.1038/s41574-020-00456-z.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[98] Miedziaszczyk M, Maciejewski A, Idasiak-Piechocka I, Karczewski M, Lacka K. Effects of isoflavonoid and vitamin D synergism on bone mineral density-a systematic and critical review. Nutrients. 2023;15:5014. 10.3390/nu15245014.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[99] Piskin E, Cianciosi D, Gulec S, Tomas M, Capanoglu E. Iron absorption: factors, limitations, and improvement methods. ACS Omega. 2022;7:20441–56. 10.1021/acsomega.2c01833.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[100] Hu Z, Yang X, Ho PCL, Chan SY, Heng PWS, Chan E, et al. Herb-drug interactions: A Literature Review. Drugs. 2005;65:1239–82. 10.2165/00003495-200565090- 00005.Suche in Google Scholar
[101] Pang CS, Tsang SF, Yang JC. Effects of melatonin, morphine and diazepam on formalin-induced nociception in mice. Life Sci. 2001;68:943–51. 10.1016/s0024-3205(00)00996-6.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[102] Thorsness KR, Watson C, LaRusso EM. Perinatal anxiety: approach to diagnosis and management in the obstetric setting. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;219:326–45. 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.05.017.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[103] Gougis P, Hilmi M, Geraud A, Mir O, Funck-Brentano C. Potential cytochrome P450-mediated pharmacokinetic interactions between herbs, food, and dietary supplements and cancer treatments. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021;166:103342. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103342.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[104] Nicolussi S, Drewe J, Butterweck V, Meyer Zu Schwabedissen HE. Clinical relevance of st. john’s wort drug interactions revisited. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177:1212–26. 10.1111/bph.14936.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[105] Oketch-Rabah HA, Madden EF, Roe AL, Betz JM. United states pharmacopeia (USP) safety review of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Nutrients. 2021;13:2742. 10.3390/nu13082742.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[106] Sciorio R, De Paola L, Notari T, Ganduscio S, Amato P, Crifasi L, et al. Decoding the puzzle of male infertility: the role of infection, inflammation, and autoimmunity. Diagnostics. 2025;15:547. 10.3390/diagnostics15050547.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[107] Elgayed SH, Afify EA, Amin HA, Abdellatif AAH. Estrogenic effect of salvia officinalis extract on reproductive function of female mice and identification of its phenolic content. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021;24:1654–63. 10.2174/1386207323666200811095527.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[108] Buhling KJ, Laakmann E. The effect of micronutrient supplements on male fertility. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;26:199–209. 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000063.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[109] Palmsten K, Flores KF, Chambers CD, Weiss LA, Sundaram R, Buck Louis GM. Most frequently reported prescription medications and supplements in couples planning pregnancy: the LIFE study. Reprod Sci. 2018;25:94–101. 10.1177/1933719117702249.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[110] Chiarella G, Marcianò G, Viola P, Palleria C, Pisani D, Rania V, et al. Nutraceuticals for peripheral vestibular pathology: properties, usefulness, future perspectives and medico-legal aspects. Nutrients. 2021;13:3646. 10.3390/nu13103646.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[111] Marinelli S, De Paola L, Stark M, Montanari Vergallo G. Artificial intelligence in the service of medicine: current solutions and future perspectives, opportunities, and challenges. Clin Ter. 2025;176:77–82. 10.7417/CT.2025.5192.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms

