Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
-
Xinhang Hu
Abstract
Purpose
Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) is a rare subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and its diagnosis primarily relies on pathological biopsy. The study aims to investigate the causal relationships between 41 inflammatory cytokines and MZL using a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) approach, providing new insights and methodologies for rapid differential diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Methods
Causal associations between 41 inflammatory cytokines and MZL were examined using genetic variant data from two large-scale genome-wide association studies. The inverse variance weighting method was employed, and multiple sensitivity analyses, including MR-Egger, weighted median, simple model, and weighted model methods, were conducted to strengthen the robustness of the findings.
Results
Elevated levels of MIG and IL-10 were associated with an increased risk of MZL (MIG: OR = 1.57, p = 0.035; IL-10: OR = 1.69, p = 0.021), while higher B-NGF levels exhibited a protective effect (OR = 0.46, p = 0.027). Reverse MR analysis revealed a negative correlation between MZL and IFN-γ levels (OR = 0.97, p = 0.015).
Conclusions
MIG, IL-10, B-NGF, and IFN-γ are potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for MZL. IFN-γ likely acts as a downstream molecule in MZL pathogenesis, offering novel insights into MZL-related research, clinical diagnosis, and treatment strategies.
1 Introduction
Marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) is an indolent subtype of non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma [1], comprising three related subtypes: mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma, and splenic MZL with or without villous lymphocytes [2–4]. There are two main clinical manifestations of MZL: extranodal and intranodal. Extranodal MALT lymphoma is the most common, accounting for 5–8% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas, with the gastrointestinal tract being the most frequently affected site. Nodal and splenic MZL s are less common, each accounting for less than 1% of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cases [5]. With advances in medical science and technology, the diagnosis of MZL now typically involves a combination of clinical, morphological, immunophenotypic, and genetic criteria. However, a definitive diagnosis still often requires confirmation through pathological biopsy. Differentiating MZL from other tumors can be challenging. For example, MALT lymphoma has frequently been misdiagnosed as lung adenocarcinoma before pathological confirmation. Specific biomarkers for MZL, which could assist in its initial diagnosis, remain lacking [4–6]. Treatment for MZL traditionally includes surgical resection and chemotherapy [6–8]. Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (such as Rituximab) and CAR-T cell therapy in managing MZL [6,9,10]. The development of new drugs, including the covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib [11], the B-cell lymphoma-2 inhibitor venetoclax [12], and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitors [13] offers promising therapeutic options. However, no effective, clinically applicable targeted therapy strategies have been developed specifically for MZL-related biomarkers.
Although certain risk factors for extranodal MZL have been identified, such as autoimmune or chronic inflammatory diseases inducing MALT lymphoma [14] and Helicobacter pylori infection as a risk factor for gastric MALT lymphoma [15], the underlying etiology of MZL remains unclear. The role of inflammatory cytokines in cancer has garnered increasing attention recently. Inflammatory cytokines, which serve as important regulators, exhibit dual functions in cancer progression, from initiation to metastasis [16,17]. They can trigger immune responses that inhibit tumor growth, while also potentially promoting malignant processes such as cell transformation, growth, invasion, and metastasis [18]. In B-cell lymphomas, elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-10, VEGF, and IL-8 have been observed in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [19,20]. However, these studies are primarily retrospective and subject to confounding factors, making it difficult to determine whether these cytokines have independent effects or to establish the direction and sequence of their interactions. Mendelian randomization (MR) offers a robust approach to address these limitations by assessing causality. Some research has suggested that MIG, PDGFbb, and MIP-1α may increase the risk of DLBCL, while IL-13 could serve as a protective factor [21,22]. The association between inflammatory cytokines and non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma has been reported exclusively in DLBCL, based on both retrospective analyses and MR-based studies. However, MZL, another subtype of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma, has not been investigated for potential associations with inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, no MR studies have confirmed a causal relationship between inflammatory cytokines and MZL. As a result, the potential role of inflammatory cytokines as biomarkers or therapeutic targets for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of MZL remains unclear. A two-sample bidirectional MR study was conducted to explore the causal relationship between inflammatory cytokines and MZL. The study aims to identify and validate biomarkers related to MZL and potential therapeutic targets within inflammatory cytokines, providing novel insights and strategies for MZL research, diagnosis, and treatment.
MR utilizes single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as genetic instrumental variables (IVs), offering a unique approach to establish causal relationships between exposures and clinical outcomes by leveraging genetic variation in nonexperimental data. MR effectively addresses confounding factors and minimizes reverse-causation bias [23,24]. Unlike traditional observational studies, MR benefits from the random allocation of alleles during meiosis, providing stronger causal inferences and more precise determination of causal directions [25,26]. Increasing evidence suggests that human genetic data related to inflammatory cytokine levels can offer valuable insights for clinical research [21]. Consequently, MR has emerged as a robust approach for investigating the causal role of inflammatory cytokines in the development of MZL. In this study, we conducted a two-sample bidirectional MR. First, we selected suitable genetic instruments for 41 inflammatory cytokines using genome-wide association study (GWAS) data. Then, we explored the association between these cytokines and MZL, followed by reverse MR analysis to assess causality direction. This study aims to identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for MZL, providing a novel approach to its clinical diagnosis and treatment, while also offering fresh insights into the pathogenic factors and mechanisms underlying MZL.
2 Methods
2.1 MR hypothesis
Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual framework of a two-sample bidirectional MR study. The analysis relies on three key assumptions: correlation, independence, and exclusion restrictions. The correlation assumption requires a strong association between the genetic variant used as an IV and the exposure. Independence ensures that the genetic variant is not influenced by confounding factors. Exclusion restrictions state that the genetic variant affects the outcome only through its influence on the exposure, without any alternative pathways of effect [27]. In this study, significant SNPs related to 41 inflammatory cytokines and MZL were selected from data obtained from two previously published GWAS. Initially, genetic instruments for each cytokine were identified to explore their causal effects on MZL. Subsequently, genetic IVs associated with MZL were used to infer causality between MZL and each inflammatory cytokine, aiming to clarify the upstream and downstream causal relationships between these cytokines and MZL.
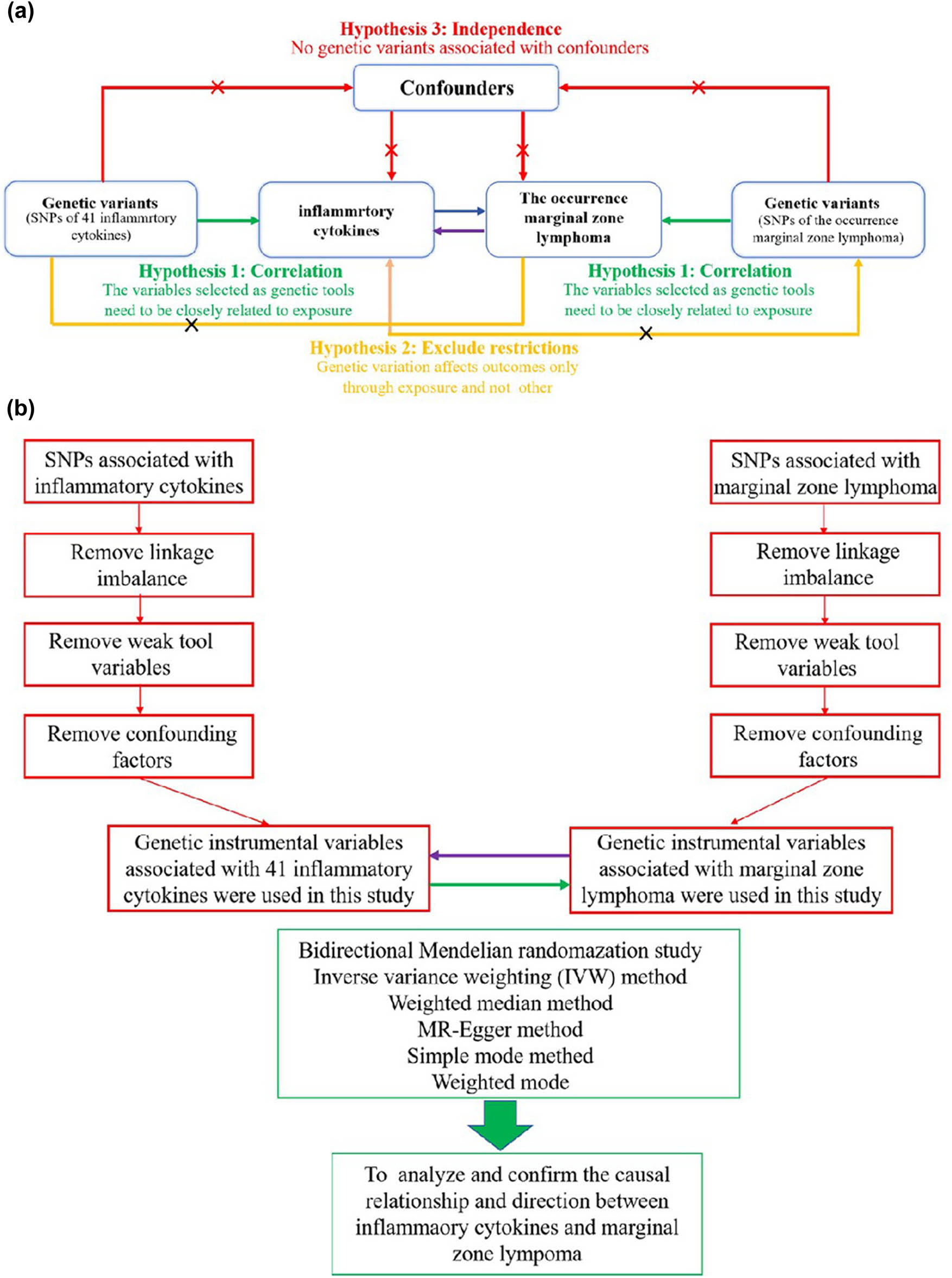
Bidirectional two-sample MR study structure. (a) The diagram outlines the foundational principles for MR analysis, emphasizing the key assumptions: (1) correlation, genetic variants are significantly associated with the exposure; (2) independence, genetic instruments should not be related to confounders; (3) exclusion restrictions, genetic variants affect the outcome only through the exposure, without alternative pathways. (b) The conceptual design and analysis approach of the bidirectional MR used in this study.
2.2 Data sources
The datasets used in this analysis were obtained from publicly available GWAS summary data, negating the need for additional ethical approval. Data on 41 inflammatory cytokines were retrieved by reanalyzing GWAS results related to serum cytokines [28], available at https://doi.org/10.5523/bris.3g3i5smgghp0s2uvm1doflkx9x. Data on MZL were extracted from C3_MARGINAL_ZONE_LYMPHOMA_EXALLC dataset in the R11_manifest Finnish database, which included 256 cases of European origin and 345,118 healthy controls. All cases were diagnosed through pathological examination. The FinnGen project, launched in 2017 in Finland, integrates genetic data from the Finnish Biobank with disease outcomes from the Finnish Health Registry, enabling the study of genotype–phenotype associations in the Finnish population. Genotyping of FinnGen participants was performed using Illumina and Affymetrix chip arrays (Illumina Inc., San Diego and Thermo Fisher Scientific, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Imputation was conducted with 3,775 genome-wide SISu v3 imputation reference panels, resulting in 16,962,023 variants. Stringent quality control measures were applied to exclude individuals with unclear sex, high deletion rates (>5%), abnormal heterozygosity, or non-Finnish ancestry. Variants with deletion rates exceeding 2%, low Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium p-values (<10⁻⁶), or minor allele counts below 3 were also excluded [25]. The exposure and outcome data used in the two-sample MR analysis were derived from separate databases and research projects, ensuring no overlap of study participants.
2.3 Selection of genetic IVs
A rigorous quality control process was applied to ensure that the chosen IVs satisfied the key assumptions of MR analysis: (1) a strong association between genetic variants and the exposure, (2) independence from confounding factors, and (3) the IVs affecting the outcome exclusively through the exposure. Initially, SNPs strongly associated with MZL and inflammatory cytokines were selected using a significance threshold of p < 5 × 10⁻⁸. Given the limited number of SNPs meeting this threshold for some exposures, the threshold was adjusted to p < 5 × 10⁻⁶ for forward exposure factors and p < 5 × 10⁻⁵ for reverse exposure factors. To minimize linkage disequilibrium (LD) effects, we applied a threshold of r 2 < 0.001 for LD, with a genetic distance of 10,000 kb [29]. Next, we calculated the proportion of variance explained by each SNP using the following formula for R 2: R 2 = (2 × EAF × (1 − EAF) × Beta2)/[(2 × EAF × (1 − EAF) × Beta2) + (2 × EAF × (1 − EAF) × N × SE2)] [30]. The F-statistic was computed to assess the potential for weak IV bias using the formula: F = R 2(N − K − 1)/K(1 − R 2). An F-statistic greater than 10 indicated no weak instrument bias, and data meeting this criterion were retained. Furthermore, we used the Phenoscanner database (http://www.phenoscanner.medschl.cam.ac.uk/) to screen SNPs and exclude those associated with confounding factors or the outcome (P < 5 × 10⁻⁸), reducing the risk of pleiotropy. The SNPs that passed this screening were selected as genetic IVs for the analysis [31].
2.4 MR analysis
Data analysis was conducted using R 4.3.2 software, with the “TwosampleMR” and “MR-PRESSO” packages employed to ensure a comprehensive and rigorous MR approach.
The primary analytical method utilized was the classical inverse variance weighting (IVW) method, known for its efficiency and strong statistical power, even in the presence of heterogeneity [32]. Weighted median, MR-Egger method, simple mode, and weighted mode approaches were utilized to perform supplementary auxiliary analyses to ensure the confidence of causal relationship. MR-Egger regression can detect and adjust for pleiotropy, although it produces estimates with lower precision [33]. The weighted median method provides accurate estimates if at least 50% of the IVs are valid [34]. The simple mode method, while less powerful than IVW, offers robustness against pleiotropy [35], and weighted mode estimation is sensitive to bandwidth choices, making it more challenging [36]. Sensitivity analyses were also performed utilizing MR-Egger regression, which incorporates an additional intercept term (α) to test for directional pleiotropy, assuming that the direct effect of a genetic variant on the outcome (not through exposure) is independent of its effect on the exposure [33]. The MR-PRESSO method was used to detect and remove outlier SNPs that could introduce bias due to confounding variables. Heterogeneity among SNPs was assessed using Cochran’s Q test. A Q value larger than the number of instruments minus one indicates heterogeneity and invalid instruments, while a Q statistic with a p-value <0.05 suggests the presence of heterogeneity. Given that heterogeneity may violate the assumptions of MR and compromise the reliability of results, datasets exhibiting heterogeneity were excluded [37–40]. The IVW method, grounded in conventional meta-analysis principles, offers a robust statistical foundation, enhancing result reliability. Its superior statistical efficiency, power, applicability, and transparency make it a preferred methodology. Thus, significant results (p < 0.05) from IVW analysis were considered reliable, even if supplementary methods like weighted or simple modes did not yield significant outcomes (p < 0.05), as long as the direction of the β-value remained consistent and there were no signs of horizontal pleiotropy, confounding bias, or heterogeneity. The MR-Egger method was employed to address potential horizontal pleiotropy, and no heterogeneity was found. In cases of heterogeneity, the weighted median and random-effects IVW methods were used, provided that no polymorphisms were detected [41–46]. Additionally, leave-one-out analyses were conducted to determine whether any single SNP influenced the causal estimates, further ensuring the robustness of the findings [47].
-
Ethical approval: The datasets utilized in this analysis were derived from publicly available genome-wide association study (9GWAS) summary data, eliminating the need for additional ethical approval.
3 Results
3.1 Genetic predictors related to 41 circulating inflammatory factors and MZL
To ensure an adequate number of SNPs for MR analysis, a significance threshold of p < 5 × 10⁻⁶ was applied for SNPs associated with the 41 inflammatory cytokines, and a threshold of p < 5 × 10⁻⁵ was set for SNPs associated with MZL. After filtering out SNPs exhibiting LD, weak IVs, and those related to confounding factors, a total of 456 SNPs associated with inflammatory cytokines were identified, with F-statistic values ranging from 20.77 to 782.3. Additionally, 13 MZL-related SNPs were identified, with F-statistic values ranging from 19.57 to 34.45. All IVs had F-statistics above 10, indicating no weak instrument bias. Detailed information is provided in Tables S1 and S2.
3.2 Effects of 41 inflammatory cytokines on the occurrence of MZL
The results of the forward MR analysis are presented in Figure 2 and further detailed in Table S3. This analysis assessed 41 inflammatory cytokines as exposure factors and MZL as the outcome. The primary focus was determining whether a positive causal relationship exists between each cytokine and the increased risk of MZL, with statistical significance indicated by a p-value <0.05 derived from the IVW) method. Additionally, the odds ratio (OR) value was used to assess whether the exposure factor acts as a risk or protective factor (OR > 1 suggests a risk factor, while OR < 1 indicates a protective factor). The p-value from the Q test was employed to evaluate heterogeneity (p < 0.05 suggests the presence of heterogeneity, while p > 0.05 suggests no heterogeneity). The IVW analysis revealed that genetically predicted higher levels of MIG and IL-10 were significantly associated with an increased risk of MZL (MIG: OR = 1.57, 95% CI = 1.03–2.40, p = 0.035; IL-10: OR = 1.69, 95% CI = 1.08–2.65, p = 0.021). In contrast, higher genetically predicted levels of B-NGF were associated with a decreased likelihood of MZL (OR = 0.46, 95% CI = 0.23–0.92, p = 0.027). The visualization results are shown in Figures 3 and S1–S3. The MR-Egger analysis showed no evidence of pleiotropy for MIG (p = 0.30), IL-10 (p = 0.96), or B-NGF (p = 0.29). The heterogeneity test also indicated no significant heterogeneity (MIG: p = 0.45; IL-10: p = 0.54; B-NGF: p = 0.32). MR-PRESSO analysis did not identify any outliers among the SNPs for the 41 inflammatory cytokines. The robustness of these findings was further confirmed through leave-one-out analysis, with β values from MR-Egger, weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode analyses consistent with the IVW results. No other inflammatory cytokines were found to have a significant association with the development of MZL (Figure 4).
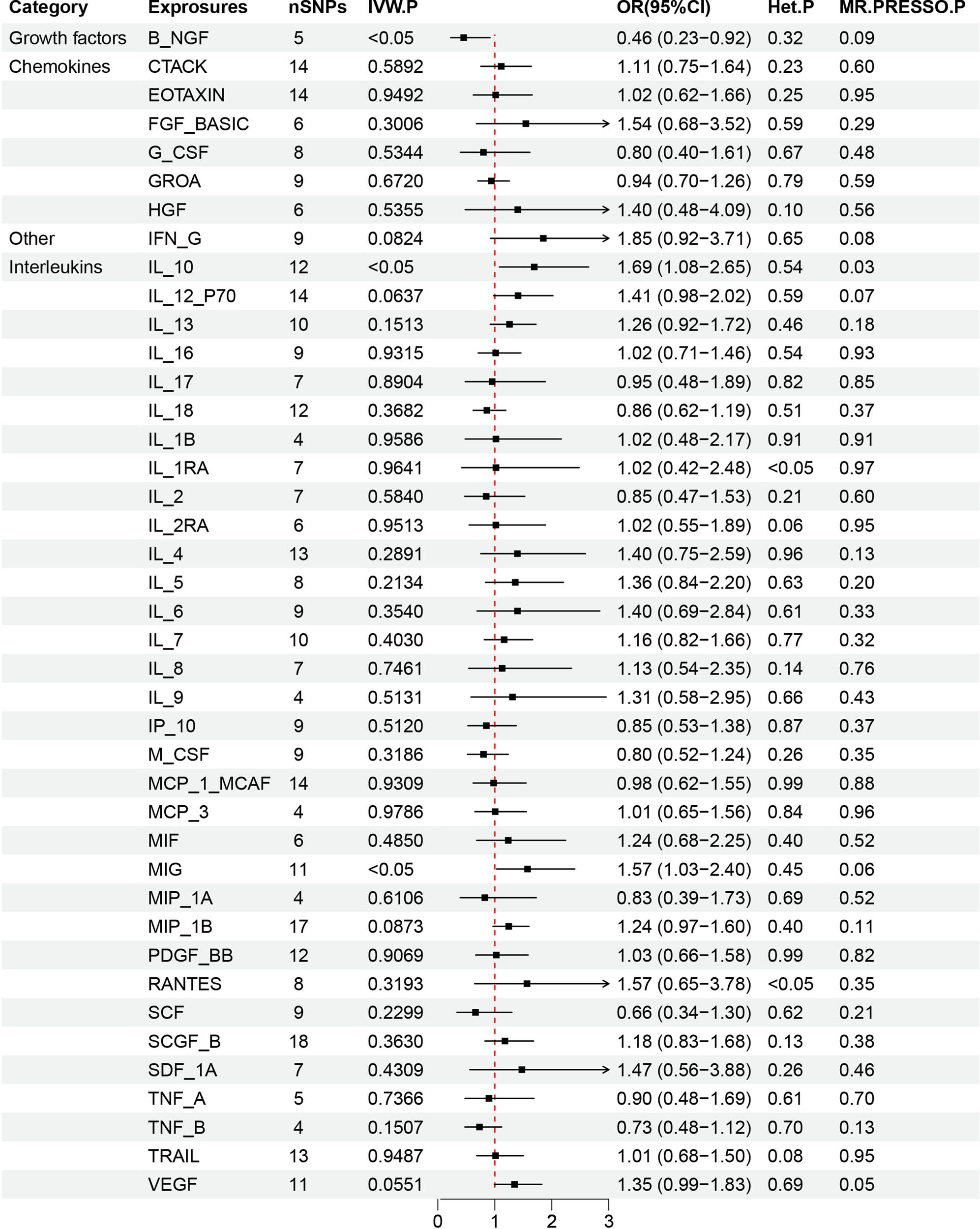
Forest plot of forward MR results for 41 inflammatory cytokines associated with MZL. This forest plot presents the results of IVW analysis to assess the potential causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines as the exposure factors and the risk of MZL as the outcome. Using a significance threshold of P < 0.05, the plot reveals that higher genetically predicted levels of MIG and IL-10 are positively correlated with an increased likelihood of MZL (MIG: OR = 1.57, 95% CI = 1.03–2.40, p = 0.035; IL-10: OR = 1.69, 95% CI = 1.08–2.65, p = 0.021). In contrast, higher genetically predicted levels of B-NGF are negatively associated with the likelihood of MZL (OR = 0.46, 95% CI = 0.23–0.92, p = 0.027). The heterogeneity test showed no evidence of heterogeneity (MIG: p = 0.45; IL-10: p = 0.54; B-NGF: p = 0.32).
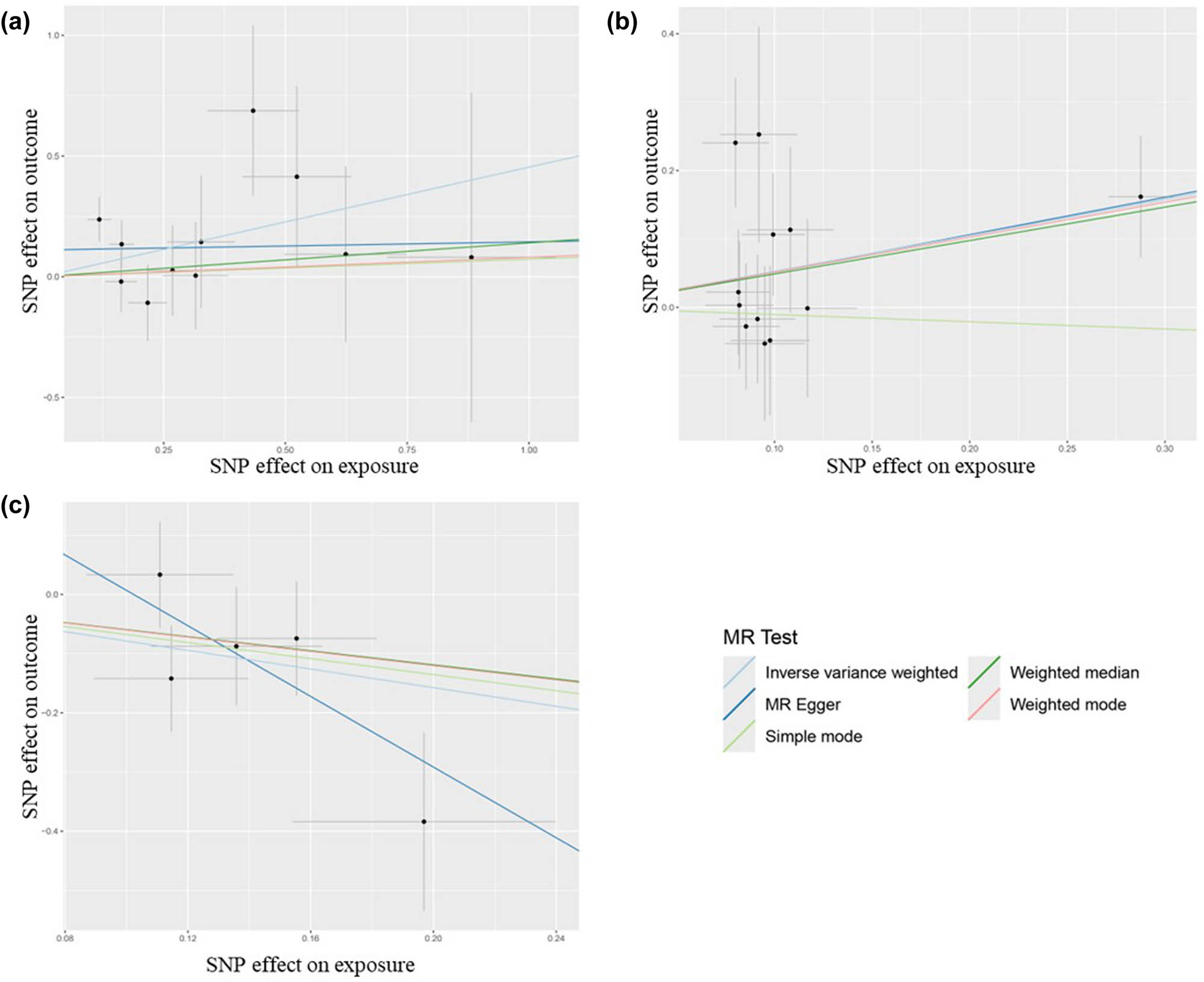
Scatter plot for positive MR analysis of MIG, IL-10, B-NGF, and MZL. (a) Funnel plot of forward MR analysis of the effects of MIG on MZL. (b) Funnel plot of forward MR analysis of the effects of IL-10 on MZL. (c) Funnel plot of forward MR analysis of the effects of B-NGF on MZL.
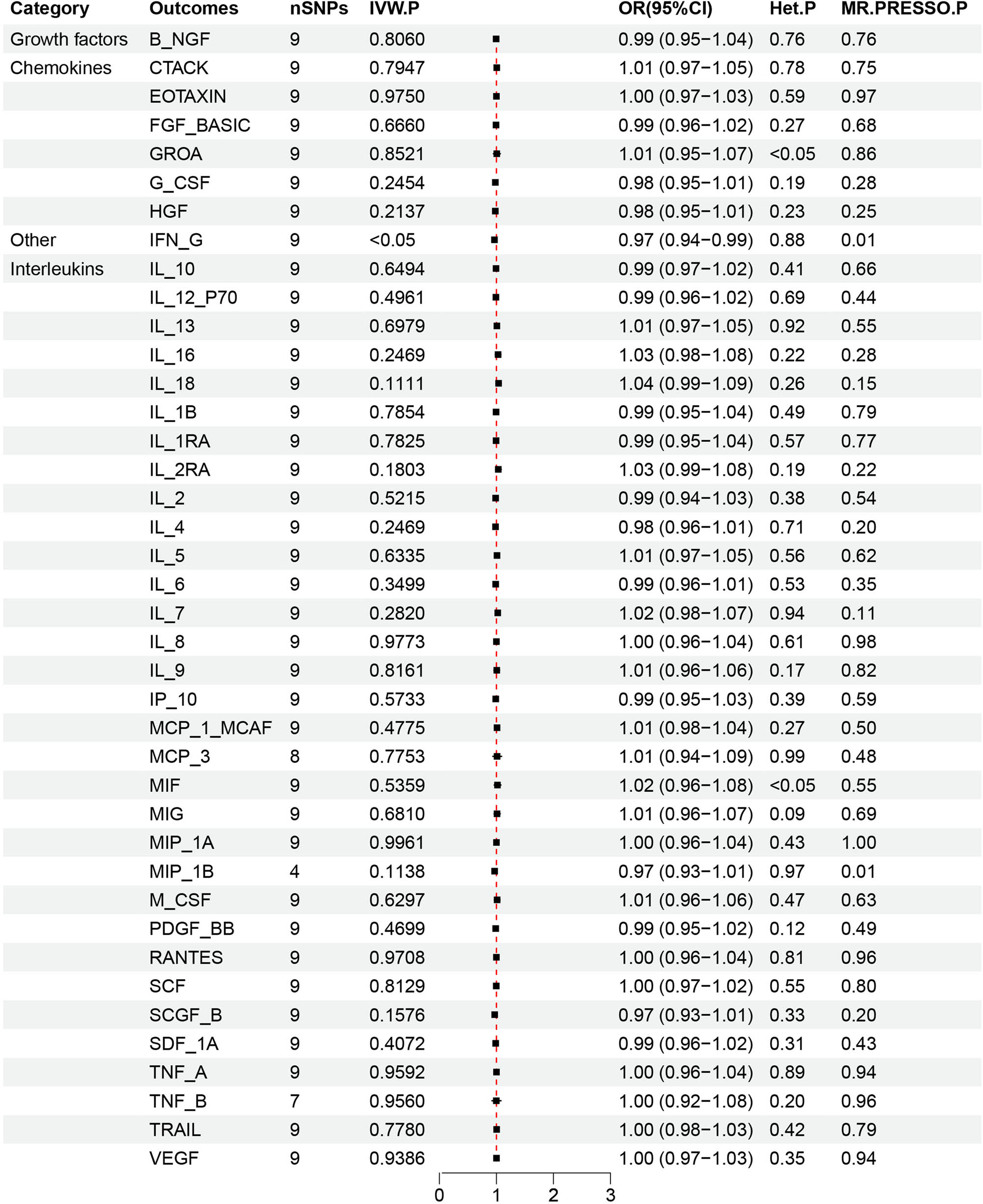
Forest plot of reverse MR data for 41 inflammatory cytokines associated with MZL. This forest plot highlights the use of IVW analysis to explore the potential causal relationship between the risk of MZL as the exposure factor and the levels of inflammatory cytokines as the outcome. At a significance threshold of P < 0.05, the results demonstrated that an increased likelihood of MZL was inversely associated with IFN-γ levels (OR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.94–0.99, p = 0.015). The strength of this evidence was further supported by MR-PRESSO analysis (p = 0.01). The heterogeneity test showed no evidence of heterogeneity (p = 0.88).
3.3 Effects of MZL on 41 inflammatory cytokines
A reverse MR analysis was conducted to provide additional evidence and clarify the causal direction between inflammatory cytokines and MZL. MZL was used as the exposure factor, with the 41 inflammatory cytokines as the outcomes. The analysis focused on evaluating the causal relationship between each cytokine and MZL, specifically assessing whether increased levels of cytokines were associated with a higher risk of MZL. Causal relationships were determined based on p-values from the IVW method, with p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance. The OR was used to assess whether each cytokine acted as a risk or protective factor, where OR > 1 indicates a risk factor, and OR < 1 indicates a protective factor. The p-value from the Q test was also used to assess heterogeneity, with p < 0.05 indicating heterogeneity and p > 0.05 suggesting no significant heterogeneity. The IVW analysis found that higher levels of IFN-G were inversely associated with MZL risk (OR = 0.97, 95% CI = 0.94–0.99, p = 0.015). No horizontal pleiotropy was detected for IFN-G (p = 0.94) in the MR-Egger analysis, and no heterogeneity was observed (p = 0.88). MR-PRESSO analysis also identified no outlier SNPs among the exposure factors. The robustness of these findings was confirmed through leave-one-out analysis, with β values from MR-Egger, simple mode, weighted median, and weighted mode methods consistent with the IVW results. Figure 5 illustrates the causal relationship between MZL and changes in IFN-γ levels. No significant evidence was found to suggest that MZL influences the levels of other inflammatory cytokines.
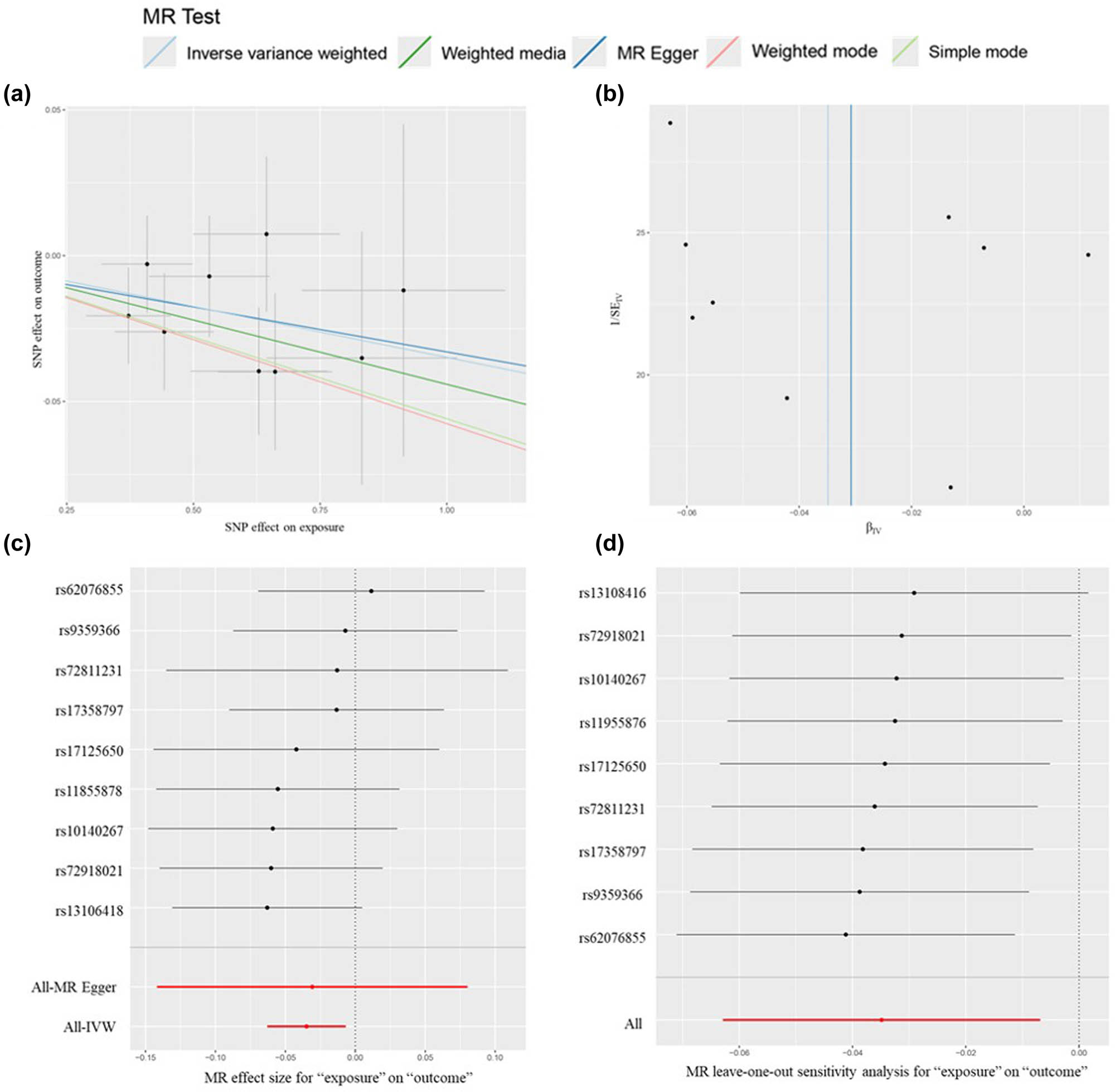
Visual results for reverse MR analysis of IFN-G and MZL. (a) Scatter plot of reverse MR analysis of IFN-G and MZL. (b) Funnel plot of reverse MR analysis of IFN-G and MZL. (c) Forest plot of reverse MR analysis of IFN-G and MZL. (d) Leave-one-out analyses of reverse MR analysis of IFN-G and MZL.
4 Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and MZL using a two-sample bidirectional MR approach to elucidate the directionality of this relationship and their roles in MZL development. Our results suggest that monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) may act as risk factors for MZL, while brain-derived neurotrophic factor (B-NGF) could serve as a protective factor against MZL Reverse MR analysis excluded MIG, IL-10, and B-NGF as downstream molecules of MZL. Furthermore, when MZL was considered an exposure factor, a decrease in interferon-gamma (IFN-G) levels was observed, highlighting potential pathogenic pathways and molecular mechanisms. These findings offer valuable insights and provide a clinical foundation for early diagnosis and further investigation into the pathogenesis of MZL.
MIG, located on human chromosome 4 [48], is involved in leukocyte chemotaxis, differentiation, proliferation, and tissue migration [49]. Induced by IFN-γ, MIG acts as a chemoattractant for T cells, with elevated circulating levels serving as markers of the host immune response, particularly in Th1 cells [50]. The role of MIG in the lymphoma microenvironment, particularly its involvement in B-cell lymphoma development, has been highlighted in several studies. Yu et al. [22] identified MIG as a contributing risk factor for DLBCL. Zhou et al. [51] found significantly higher MIG levels in DLBCL tissues compared to normal tissues. However, most research on MIG and lymphoma has focused on DLBCL. Jiang et al. [21] proposed that MIG may increase DLBCL risk by influencing the gut microbiome, particularly the genus Ruminococcus UCG-002. Ruiduo et al. [52] demonstrated that MIG promotes DLBCL progression via β-catenin upregulation. Despite these findings, there is limited research on MIG’s involvement in MZL. To date, no studies have explored the relationship between MIG and MZL or their interaction mechanisms. Our study addresses this gap by providing direct evidence of a causal relationship between MIG and MZL. However, the precise molecular mechanisms by which MIG influences MZL remain unclear, and further experimental studies are needed to investigate whether MIG affects MZL through interactions with the intestinal microbiota or β-catenin regulation.
IL-10 produced by various immune cells and encoded by the IL-10 gene on chromosome 1q32, is crucial in regulating the inflammatory response [53]. IL-10 exerts a dual regulatory effect on the immune system, promoting immune responses through CD8+ T cells while negatively regulating them via regulatory T cells [54]. Most studies on IL-10 in B-cell lymphomas have focused on DLBCL, consistently linking high IL-10 expression with poor prognosis. Shen et al. [19] and Bao et al. [55] found that IL-10 is highly expressed in DLBCL and associated with poor prognosis. Wu et al. [56] and Mishina et al. [57] recognized IL-10 as a factor that increases the risk of DLBCL and proposed it as a potential biomarker for diagnosing. Stirm et al. further explored the biological mechanisms of IL-10 in promoting DLBCL growth, suggesting that IL-10 induces tumor immune evasion, thereby driving progression [58]. However, most research on IL-10 in B-cell lymphoma has concentrated on DLBCL, with limited studies examining the relationship between IL-10 and MZL, another form of non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. A recent study proposed IL-10 as a risk factor for gastric MALT lymphoma [59], a subtype of MZL, which supports the hypothesis that IL-10 plays a significant role in MZL development. This finding provides a theoretical foundation for further exploration of how IL-10 influences MZL pathogenesis, particularly in relation to tumor immune escape mechanisms.
B-NGF, a key nerve growth factor (NGF) family member, shares biological functions with NGF. As an essential neurotrophic factor, NGF is crucial for the survival and differentiation of neurons, significantly contributing to the growth and maintenance of the nervous system [60]. However, research on the relationship between B-NGF and tumors is limited. Existing studies suggest that NGF and B-NGF jointly participate in angiogenesis, promoting cancer progression [61,62]. In various cancers, including breast, prostate, pancreatic, and liver cancers, B-NGF has been implicated in tumor initiation, development, and metastasis [62–65]. These findings contradict our conclusion that B-NGF acts as a protective factor for MZL. However, most research on B-NGF has primarily focused on solid tumors, with little attention given to its role in hematological malignancies. The effects of B-NGF on hematological tumors remain largely unexplored. While B-NGF may promote the growth and metastasis of solid tumors, it likely functions as a protective factor against hematologic tumors, particularly MZL. Based on our analysis, this hypothesis requires further experimental validation to confirm these findings and elucidate the mechanisms through which B-NGF influences the pathogenesis and development of MZL.
No significant association between IFN-γ levels and the risk of MZL was observed in the forward MR analysis. However, reverse MR results suggested that the onset of MZL may reduce IFN-γ levels. After accounting for potential confounding factors, heterogeneity, and pleiotropy, our bidirectional MR analysis indicates that changes in IFN-γ levels are likely a consequence of MZL, positioning IFN-γ as a potential downstream effector molecule. MZL may contribute to tumor progression by downregulating IFN-γ expression. IFN-γ is a protein consisting of two antiparallel polypeptide chains [66]. In innate immunity, IFN-γ production is primarily controlled by natural killer and natural killer T cells, whereas in adaptive immunity, CD8+ and CD4+ T cells are the main producers of this cytokine [67]. The biological effects of IFN-γ are thought to inhibit tumor progression through various pathways. IFN-γ has been shown to activate the JAK-STAT1-caspase signaling pathway, promoting tumor cell apoptosis and inhibiting tumor growth [68–71]. Liu et al. [72] reported that IFN-γ indirectly enhances tumor immunity by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis and suppressing immunosuppressive M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Additionally, IFN-γ interacts with various cytokines in the tumor microenvironment (TME), inducing tumor growth arrest. For instance, IFN-γ and TNF stabilize the p16INK4a-Rb pathway, promoting tumor cell senescence and dormancy [73]. Recent studies have identified IFN-γ as a marker for immune checkpoint inhibitors [67]. Based on these findings, it is evident that IFN-γ can promote inflammatory responses through multiple mechanisms within the TME, contributing to tumor suppression and inhibiting tumor growth. Therefore, IFN-γ functions as a protective cytokine against tumors. Several studies have shown that IFN-γ expression is downregulated in the solid TME of cancer patients [74–76], suggesting its potential role as a tumor suppressor, particularly in colorectal and breast cancers [76,77]. The IFN-γ signaling pathway is crucial in mediating host responses to infection, inflammation, and anti-tumor immunity, aiding in anti-tumor defense. In hematological malignancies, IFN-γ + T cells have been shown to effectively kill tumor cells, aligning with our observations [78]. However, the interaction between IFN-γ and MZL remains unexplored. Based on the physiological mechanisms of IFN-γ, its interactions with various tumors, and our MR analysis of GWAS data, we hypothesize that IFN-γ may be a downstream effector of MZL and a potential therapeutic target. Specifically, MZL may reduce circulating IFN-γ levels, inhibiting tumor cell apoptosis and senescence-induced quiescence, while promoting immune suppression and evasion, further facilitating tumor progression. However, these conclusions are based on theoretical analysis, and further experimental validation is needed to clarify the relationship between IFN-γ and MZL and to understand its biological role in MZL development.
Based on the analysis results, we propose that elevated levels of MIG and IL-10 and reduced levels of B-NGF and IFN-γ may serve as potential biomarkers for diagnosing MZL. The interaction between MIG, IL-10, B-NGF, IFN-γ, and MZL, along with the proposed mechanisms of action, is summarized in Figure 6. It is important to note that distinguishing pulmonary and gastric MZL from lung and gastric cancer can be clinically challenging. Our previous research identified high circulating levels of IL-1RA as a diagnostic marker for lung adenocarcinoma. Elevated IL-10, IL-13, and TERT levels and reduced MCP-1/MCAF levels are associated with lung squamous cell carcinoma. High levels of SDF-1α and B-NGF are indicative of small-cell lung cancer [46]. The study by Chen et al. suggests that elevated levels of circulating IL-16 and reduced levels of TRAIL serve as diagnostic markers for gastric cancer [79]. Inflammatory cytokine-related biomarkers for MZL, lung, and gastric cancer differ, highlighting their potential as auxiliary diagnostic tools to distinguish MZL from these cancers. Our findings also suggest that inflammatory cytokines could aid in differentiating MZL from other non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. Previous studies identified high levels of MIG, MIP1A, PDGFbb, and low levels of IL-13 as diagnostic markers for DLBCL [21], which differ from those associated with MZL. These differences lead to the hypothesis that inflammatory cytokines could serve as supplementary references to distinguish between MZL and DLBCL. However, these conclusions are based on theoretical analysis, and further clinical trials are needed to validate whether inflammatory cytokine characteristics can serve as diagnostic standards for MZL. Incorporating these markers into clinical practice could improve the accuracy of MZL diagnosis.
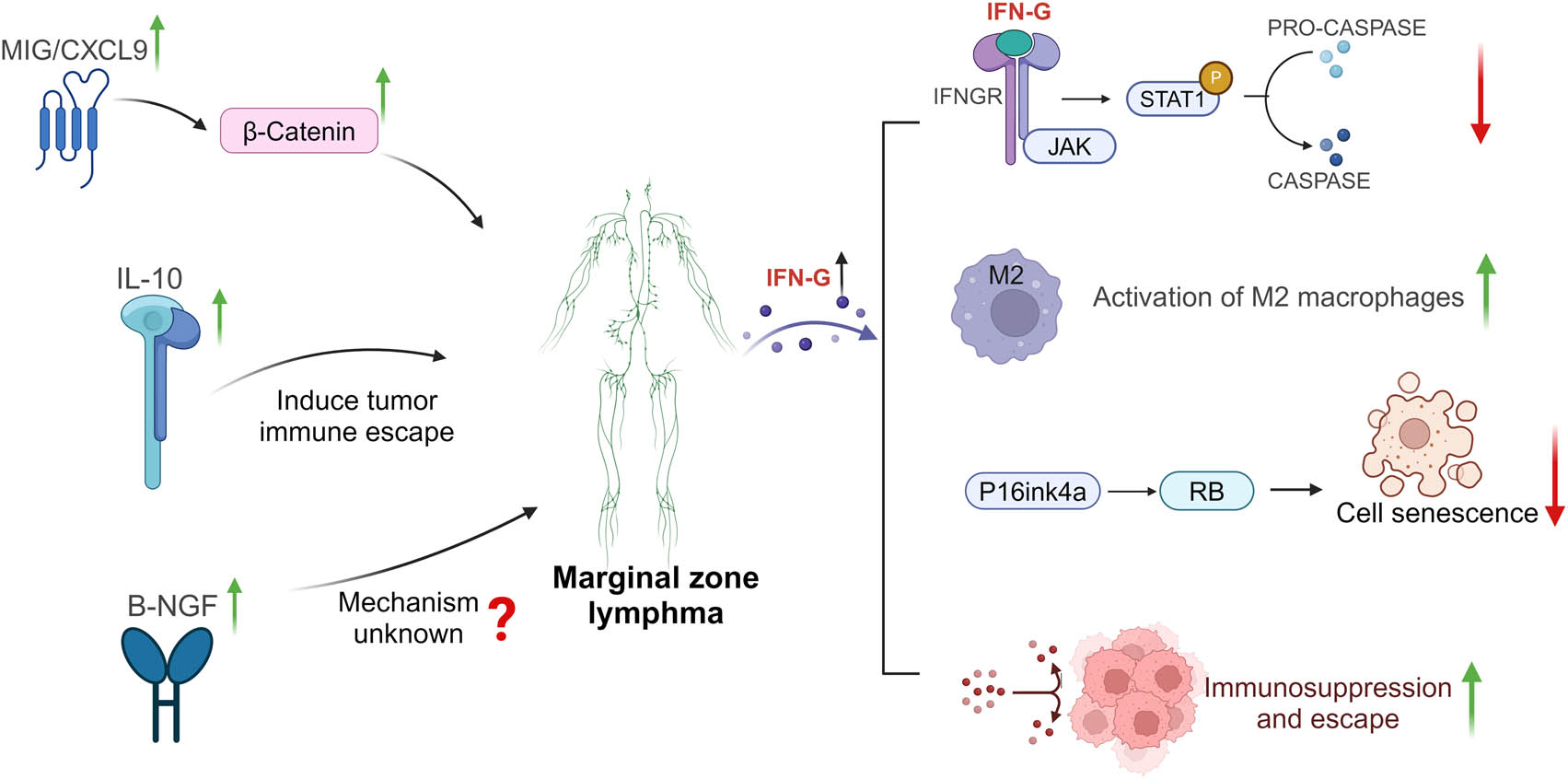
Molecular mechanisms for the causal interaction between MIG, IL10, B-NGF, IFN-G, and MZL: MIG/CXCL9 may promote MZL progression by upregulating β-catenin, while IL-10 likely facilitates tumor immune evasion, contributing to MZL development. The molecular mechanism through which B-NGF inhibits MZL progression remains unclear. MZL may reduce IFN-γ levels, potentially suppressing tumor cell apoptosis by inhibiting the JAK-STAT1-caspase signaling pathway. This reduction could enhance the activity of immunosuppressive M2-like TAMs and weaken the synergistic effect of TNF. Furthermore, through the p16INK4a-Rb pathway, it may inhibit tumor cell senescence and dormancy, leading to immune suppression and evasion, thereby promoting MZL progression.
With the advancement of immunotherapy, cytokine antibodies have increasingly been used in clinical and scientific studies. Recent animal research has shown that IL-10 antibodies can alleviate immune suppression and significantly enhance anti-tumor immunity in cancers such as melanoma and cervical cancer [80,81]. Building on these findings, we aim to explore whether elevated levels of MIG and IL-10, identified as risk factors for MZL, could be targeted therapeutically. Specifically, we seek to determine whether blocking the biological functions of MIG and IL-10 with specific antibodies can inhibit MZL progression. However, no clinical trials or treatments targeting these cytokines have been conducted for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. We expect that MIG and IL-10 antibodies could offer novel therapeutic strategies for MZL, potentially improving treatment efficacy.
However, several limitations of this study should be recognized. First, the data were derived from two large public GWAS, but the lack of detailed demographic and clinical information limited our ability to perform subgroup analyses. Additionally, the MZL dataset contained only 256 MZL cases and 345,118 healthy controls. Given the rarity of MZL, the sample size imbalance between cases and controls may impact the internal and external consistency of our MR analysis. Although we prioritized the use of IVW analysis, known for its stability, and employed multiple statistical strategies to ensure robustness, the data imbalance remains a potential limitation. Future studies should explore more robust data processing methods or incorporate external controls to further validate our conclusions. Second, we utilized a significance threshold of p < 5 × 10⁻⁶ for SNPs correlated with the 41 inflammatory biomarkers and p < 5 × 10−5 for the MZL SNPs. The scarcity of genome-wide significant SNPs at the more stringent p < 5 × 10⁻⁸ threshold limited further MR analyses. While the adjustment remains within MR principles, it introduces some risk by potentially including weak IVs, which could compromise causal inference robustness. However, multiple methods were applied to strengthen the reliability of our results. To address the limitations of this adjustment, we plan to expand the sample size in future studies to improve the robustness and reliability of our research. Third, we relied on the IVW method for data analysis and interpretation. Although results from MR-Egger, weighted average, simple, and weighted models did not reach high significance, the IVW method’s statistical power and the consistent direction of β values support the validity of our findings. However, due to the rarity of MZL, which accounts for about 5% of B-cell lymphoma cases, obtaining a sufficient number of MZL samples was challenging. Consequently, we were unable to validate our conclusions experimentally. In future studies, we aim to collect adequate blood and tissue samples from MZL patients and use ELISA, qPCR, and immunohistochemistry to detect and compare the levels of MIG, IL-10, B-NGF, and IFN-γ in these samples versus healthy controls. These experiments will help test our hypotheses regarding the underlying molecular mechanisms and strengthen the scientific rigor of our conclusions. Lastly, the GWAS data used in this study were exclusively from European populations, limiting the generalizability of the findings to other racial and ethnic groups. Genetic variation varies significantly among populations, and data from European populations may not accurately reflect the genetic landscape of global or non-European populations. Furthermore, the genetic structure of European populations is closely linked with specific environmental factors and lifestyle patterns, which may influence the study’s outcomes. A genetic variant associated with a disease in European populations may show no or weak associations in other populations, potentially reducing the external validity of our results. Additionally, the genetic polymorphisms observed in European populations may not fully capture the entire spectrum of genetic effects, as some variants may be rare or absent in these populations. Even within Europe, significant genetic heterogeneity exists across countries, which can influence study outcomes. Thus, caution is necessary when extrapolating these findings to non-European populations. Future research should include diverse ethnic groups and more comprehensive clinical data to validate these findings. Integrating basic experimental and clinical studies will help assess the relevance and feasibility of these results in clinical practice.
5 Conclusion
Using a two-sample two-way MR approach, we found that elevated levels of IL-10 and MIG are associated with an increased risk of MZL, while genetically predicted higher levels of B-NGF may act as a protective factor. The data also suggest that IFN-γ is likely a downstream molecule in MZL pathogenesis and its reduction due to MZL may further promote disease progression. No significant associations were observed between other inflammatory biomarkers and MZL. MIG, IL-10, B-NGF, and IFN-γ represent potential biomarkers for MZL, offering new and reliable strategies for its clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82172879), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province for Distinguished Young Scholars (2022JJ10096), Clinical Technology Innovation and Guidance Project of Hunan Province (2021SK53520), Hunan Provincial Key Area R&D Program (2021SK2020), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ40871).
-
Author contributions: X.H.H. and F.L.Y. conceived and supervised the project; L.W., M.Y.P., Z.Y., and X.Y.Y. collected the clinical data; H.L.H. performed the analysis of the clinical data; Y.F.Y.O. conducted the GWAS data analysis; Z.Z. and W.C.Z analyzed the genomic data; X.C.H. wrote the original draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to reviewing and revising the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The dataset on MZL involved in this study is available in the FinnGen (https://storage.googleapis.com/finngen-public-data-r11/summary_stats/finngen_R11_C3_MARGINAL_ZONE_LYMPHOMA_EXALLC.gz). The dataset on 41 inflammatory cytokines were obtained by reanalysis outcomes of GWAS associated with serum cytokines (https://doi.org/10.5523/bris.3g3i5smgghp0s2uvm1doflkx9x).
References
[1] Juárez-Salcedo LM, Castillo JJ. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2019;33:639–56. 10.1016/j.hoc.2019.03.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Alderuccio JP, Kahl BS. Current treatments in marginal zone lymphoma. Oncology (Williston Park). 2022;36:206–15. 10.46883/2022.25920956.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Laurent C, Cook JR, Yoshino T, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Jaffe ES. Follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma: how many diseases? Virchows Arch. 2023;482:149–62. 10.1007/s00428-022-03432-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Zucca E, Rossi D, Bertoni F. Marginal zone lymphomas. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(Suppl 1):88–91. 10.1002/hon.3152.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Ferreri AJ, Zucca E. Marginal-zone lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;63:245–56. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2007.04.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Cheah CY, Seymour JF. Marginal zone lymphoma: 2023 update on diagnosis and management. Am J Hematol. 2023;98:1645–57. 10.1002/ajh.27058.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Sindel A, Al-Juhaishi T, Yazbeck V. Marginal zone lymphoma: state-of-the-art treatment. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2019;20:90. 10.1007/s11864-019-0687-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Thieblemont C. Clinical presentation and management of marginal zone lymphomas. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2005;2005(1):307–13. 10.1182/asheducation-2005.1.307.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Martinelli G, Laszlo D, Ferreri AJ, Pruneri G, Ponzoni M, Conconi A, et al. Clinical activity of Rituximab in gastric marginal zone non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma resistant to or not eligible for anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1979–83. 10.1200/jco.2005.08.128.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Herold M, Hoster E, Janssens A, McCarthy H, Tedeschi A, Pocock C, et al. Immunochemotherapy and maintenance with obinutuzumab or rituximab in patients with previously untreated marginal zone lymphoma in the randomized GALLIUM trial. Hemasphere. 2022;6:e699. 10.1097/hs9.0000000000000699.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Noy A, de Vos S, Thieblemont C, Martin P, Flowers CR, Morschhauser F, et al. Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. 2017;129:2224–32. 10.1182/blood-2016-10-747345.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Jäger G, Neumeister P, Brezinschek R, Hinterleitner T, Fiebiger W, Penz M, et al. Treatment of extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type with cladribine: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3872–7. 10.1200/jco.2002.05.117.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Gopal AK, Kahl BS, de Vos S, Wagner-Johnston ND, Schuster SJ, Jurczak WJ, et al. PI3Kδ inhibition by idelalisib in patients with relapsed indolent lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1008–18. 10.1056/NEJMoa1314583.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Wotherspoon AC, Doglioni C, de Boni M, Spencer J, Isaacson PG. Antibiotic treatment for low-grade gastric MALT lymphoma. Lancet. 1994;343:1503.10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92613-1Search in Google Scholar
[15] Salar A. Gastric MALT lymphoma and Helicobacter pylori. Med Clin (Barc). 2019;152:65–71. 10.1016/j.medcli.2018.09.006.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Bouras E, Karhunen V, Gill D, Huang J, Haycock PC, Gunter MJ, et al. Circulating inflammatory cytokines and risk of five cancers: a Mendelian randomization analysis. BMC Med. 2022;20:3. 10.1186/s12916-021-02193-0.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Chen J, Li X, Huang C, Lin Y, Dai Q. Change of serum inflammatory cytokines levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pneumonia and lung cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020;19:1533033820951807. 10.1177/1533033820951807.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Gaur P, Bhattacharya S, Kant S, Kushwaha R, Garg R, Singh G, et al. Association of inflammatory biomarkers with lung cancer in North Indian population. Afr Health Sci. 2019;19:2147–55. 10.4314/ahs.v19i2.39.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Shen N, Yu Y, Zhang R, Guo Y, Liu M, Tan M, et al. Expression and prognostic value of PIK3CA, VEGF, IL-8, IL-10, and RIP2 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Clin Pract. 2022;2022:2637581. 10.1155/2022/2637581.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Man Y, Ge CQ, Li ZZ, Yang TH, Wang YJ. Expression and prognostic value of cytokines in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023;31:1050–5. 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2023.04.019.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Jiang P, Yu F, Zhou X, Shi H, He Q, Song X. Dissecting causal links between gut microbiota, inflammatory cytokines, and DLBCL: a Mendelian randomization study. Blood Adv. 2024;8:2268–78. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012246.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Yu J, Fu L, Zhang Z, Ding L, Hong L, Gao F, et al. Causal relationships between circulating inflammatory cytokines and diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Clin Exp Med. 2023;23:4585–95. 10.1007/s10238-023-01221-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Wootton RE, Richmond RC, Stuijfzand BG, Lawn RB, Sallis HM, Taylor GMJ, et al. Evidence for causal effects of lifetime smoking on risk for depression and schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomisation study. Psychol Med. 2020;50:2435–43. 10.1017/s0033291719002678.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Richmond RC, Davey Smith G. Mendelian randomization: concepts and scope. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12. 10.1101/cshperspect.a040501.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Liu H, Liu Z, Huang Y, Ding Q, Lai Z, Cai X, et al. Exploring causal association between circulating inflammatory cytokines and functional outcomes following ischemic stroke: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Neurol. 2024;31:e16123. 10.1111/ene.16123.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:R89–98. 10.1093/hmg/ddu328.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA. 2017;318:1925–6. 10.1001/jama.2017.17219.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Ahola-Olli AV, Würtz P, Havulinna AS, Aalto K, Pitkänen N, Lehtimäki T, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 27 loci influencing concentrations of circulating cytokines and growth factors. Am J Hum Genet. 2017;100:40–50. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.11.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Pierce BL, Ahsan H, Vanderweele TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40:740–52. 10.1093/ije/dyq151.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Wu M, Liao Z, Zeng K, Jiang Q. Exploring the causal role of gut microbiota in giant cell arteritis: a Mendelian randomization analysis with mediator insights. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1280249. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1280249.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Xiang M, Wang Y, Gao Z, Wang J, Chen Q, Sun Z, et al. Exploring causal correlations between inflammatory cytokines and systemic lupus erythematosus: a Mendelian randomization. Front Immunol. 2022;13:985729. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.985729.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Li N, Wang Y, Wei P, Min Y, Yu M, Zhou G, et al. Causal effects of specific gut microbiota on chronic kidney diseases and renal function – -a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023;15:360. 10.3390/nu15020360.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Burgess S, Thompson SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32:377–89. 10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S. Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40:304–14. 10.1002/gepi.21965.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Xu J, Zhang S, Tian Y, Si H, Zeng Y, Wu Y, et al. Genetic causal association between iron status and osteoarthritis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization. Nutrients. 2022;14(18). 10.3390/nu14183683.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Hartwig FP, Davey Smith G, Bowden J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46:1985–98. 10.1093/ije/dyx102.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Cao Z, Wu Y, Li Q, Li Y, Wu J. A causal relationship between childhood obesity and risk of osteoarthritis: results from a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Ann Med. 2022;54:1636–45. 10.1080/07853890.2022.2085883.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Greco MF, Minelli C, Sheehan NA, Thompson JR. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med. 2015;34(21):2926–40. 10.1002/sim.6522.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Long Y, Tang L, Zhou Y, Zhao S, Zhu H. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and cancers: a two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):66. 10.1186/s12916-023-02761-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Bowden J, Del Greco MF, Minelli C, Zhao Q, Lawlor DA, Sheehan NA, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(3):728–42. 10.1093/ije/dyy258.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Birney E. Mendelian randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4). 10.1101/cshperspect.a041302.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Higbee DH, Granell R, Sanderson E, Davey Smith G, Dodd JW. Lung function and cardiovascular disease: a two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. Eur Respir J. 2021;58(3):2003196. 10.1183/13993003.03196-2020.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Xiao G, He Q, Liu L, Zhang T, Zhou M, Li X, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):475. 10.1186/s12967-022-03691-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Carter AR, Sanderson E, Hammerton G, Richmond RC, Davey Smith G, Heron J, et al. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur J Epidemiol. 2021;36(5):465–78. 10.1007/s10654-021-00757-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Bowden J, Holmes MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: a review. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(4):486–96. 10.1002/jrsm.1346.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Hu X, Xie S, Yi X, Ouyang Y, Zhao W, Yang Z, et al. Bidirectional Mendelian randomization of causal relationship between inflammatory cytokines and different pathological types of lung cancer. J Cancer. 2024;15(15):4969–84. 10.7150/jca.98301.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Vaucher J, Keating BJ, Lasserre AM, Gan W, Lyall DM, Ward J, et al. Cannabis use and risk of schizophrenia: a Mendelian randomization study. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1287–92. 10.1038/mp.2016.252.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Ragusa F. Dermatomyositis and MIG. Clin Ter. 2019;170:e142–7. 10.7417/ct.2019.2124.Search in Google Scholar
[49] Tokunaga R, Zhang W, Naseem M, Puccini A, Berger MD, Soni S, et al. CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation – a target for novel cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;63:40–7. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.11.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Giuggioli D, Ferrannini E, Ferri C, Fallahi P. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:272–80. 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.010.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Zhou X, Guo S, Shi Y. Comprehensive analysis of the expression and significance of CXCLs in human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep. 2022;12:2817. 10.1038/s41598-022-06877-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Ruiduo C, Ying D, Qiwei W. CXCL9 promotes the progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma through up-regulating β-catenin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:689–95. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.171.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Chen D, Huang L, Zhou H, Zhang Y. Combining IL-10 and oncolytic adenovirus demonstrates enhanced antitumor efficacy through CD8(+) T cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:615089. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.615089.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Ferreri AJM, Calimeri T, Lopedote P, Francaviglia I, Daverio R, Iacona C, et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and interleukin-10 detection in cerebrospinal fluid are highly specific discriminating markers in patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: results from a prospective study. Br J Haematol. 2021;193:497–505. 10.1111/bjh.17357.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Bao C, Gu J, Huang X, You L, Zhou Z, Jin J. Cytokine profiles in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: IL-6 and IL-10 levels are associated with adverse clinical features and poor outcomes. Cytokine. 2023;169:156289. 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156289.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Wu H, Sun HC, Ouyang GF. Effect of T-regulatory cells and interleukin-35, interleukin-10, and transforming growth factor-beta on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11:7075–81. 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i29.7075.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Mishina T, Miyoshi H, Takeuchi M, Miyawaki K, Nakashima K, Yamada K, et al. Co-expression of regulatory B-cell markers, transforming growth factor β and interleukin-10 as a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2024;254:155117. 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155117.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Stirm K, Leary P, Bertram K, Núñez NG, Wüst D, Boudesco C, et al. Tumor cell-derived IL-10 promotes cell-autonomous growth and immune escape in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncoimmunology. 2021;10:2003533. 10.1080/2162402x.2021.2003533.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Hellmig S, Bartscht T, Fischbach W, Fölsch UR, Schreiber S. Interleukin-10 (-819 C/T) and TNF-A (-308 G/A) as risk factors for H. pylori-associated gastric MALT-lymphoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:2007–8. 10.1007/s10620-008-0231-0.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Yue XJ, Xu LB, Zhu MS, Zhang R, Liu C. Over-expression of nerve growth factor-β in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells promote tumor progression. PLoS One. 2013;8:e62024. 10.1371/journal.pone.0062024.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Emanueli C, Salis MB, Pinna A, Graiani G, Manni L, Madeddu P. Nerve growth factor promotes angiogenesis and arteriogenesis in ischemic hindlimbs. Circulation. 2002;106:2257–62. 10.1161/01.cir.0000033971.56802.c5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Adriaenssens E, Vanhecke E, Saule P, Mougel A, Page A, Romon R, et al. Nerve growth factor is a potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:346–51. 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-07-1183.Search in Google Scholar
[63] Lanki M, Mustonen H, Salmi M, Jalkanen S, Haglund C, Seppänen H. Serum cytokine profiles in patients with pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2023;23:657–62. 10.1016/j.pan.2023.07.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[64] Owusu Sekyere S, Port K, Deterding K, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H. Inflammatory patterns in plasma associate with hepatocellular carcinoma development in cured hepatitis C cirrhotic patients. U Eur Gastroenterol J. 2021;9:486–96. 10.1177/2050640620976991.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Sigala S, Bodei S, Missale C, Zani D, Simeone C, Cunico SC, et al. Gene expression profile of prostate cancer cell lines: effect of nerve growth factor treatment. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;284:11–20. 10.1016/j.mce.2007.12.015.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Jorgovanovic D, Song M, Wang L, Zhang Y. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: a review. Biomark Res. 2020;8:49. 10.1186/s40364-020-00228-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Burke JD, Young HA. IFN-γ: a cytokine at the right time, is in the right place. Semin Immunol. 2019;43:101280. 10.1016/j.smim.2019.05.002.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Song M, Ping Y, Zhang K, Yang L, Li F, Zhang C, et al. Low-dose IFNγ induces tumor cell stemness in tumor microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3737–48. 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-0596.Search in Google Scholar
[69] Bhat P, Leggatt G, Waterhouse N, Frazer IH. Interferon-γ derived from cytotoxic lymphocytes directly enhances their motility and cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2836. 10.1038/cddis.2017.67.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[70] Hao Q, Tang H. Interferon-γ and Smac mimetics synergize to induce apoptosis of lung cancer cells in a TNFα-independent manner. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18:84. 10.1186/s12935-018-0579-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[71] Ni C, Wu P, Zhu X, Ye J, Zhang Z, Chen Z, et al. IFN-γ selectively exerts pro-apoptotic effects on tumor-initiating label-retaining colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013;336:174–84. 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.029.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[72] Liu C, Chikina M, Deshpande R, Menk AV, Wang T, Tabib T, et al. Treg cells promote the SREBP1-dependent metabolic fitness of tumor-promoting macrophages via repression of CD8( +) T cell-derived interferon-γ. Immunity. 2019;51:381–97.e386. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.017.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Braumüller H, Wieder T, Brenner E, Aßmann S, Hahn M, Alkhaled M, et al. T-helper-1-cell cytokines drive cancer into senescence. Nature. 2013;494:361–5. 10.1038/nature11824.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[74] Hu X, Hu Z, Zhang H, Zhang N, Feng H, Jia X, et al. Deciphering the tumor-suppressive role of PSMB9 in melanoma through multi-omics and single-cell transcriptome analyses. Cancer Lett. 2024;581:216466. 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216466.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[75] Cai J, Zhong M, Xu J, Cheng H, Xu S. Codelivery of triptolide and IFN-γ to boost antitumor immunity for triple-negative breast cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;120:110346. 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110346.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] Yin H, Jiang Z, Wang S, Zhang P. IFN-γ restores the impaired function of RNase L and induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:642. 10.1038/s41419-019-1902-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[77] Coelho MA, Cooper S, Strauss ME, Karakoc E, Bhosle S, Gonçalves E, et al. Base editing screens map mutations affecting interferon-γ signaling in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2023;41(2):288–303.e6. 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.12.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[78] Minnie SA, Waltner OG, Zhang P, Takahashi S, Nemychenkov NS, Ensbey KS, et al. TIM-3( +) CD8 T cells with a terminally exhausted phenotype retain functional capacity in hematological malignancies. Sci Immunol. 2024;9(94):eadg1094. 10.1126/sciimmunol.adg1094.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[79] Chen SL, Zhang B, Wang S, Yang M, Shen QH, Zhang R, et al. Correlation between inflammatory cytokines and the likelihood of developing multiple types of digestive system cancers: a Mendelian randomization study. Cytokine. 2024;183:156735. 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156735.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[80] Miri SM, Pourhossein B, Hosseini SY, Keshavarz M, Shahmahmoodi S, Zolfaghari MR, et al. Enhanced synergistic antitumor effect of a DNA vaccine with anticancer cytokine, MDA-7/IL-24, and immune checkpoint blockade. Virol J. 2022;19(1):106. 10.1186/s12985-022-01842-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Gordy JT, Luo K, Francica B, Drake C, Markham RB. Anti-IL-10-mediated enhancement of antitumor efficacy of a dendritic cell-targeting MIP3α-gp100 vaccine in the B16F10 mouse melanoma model is dependent on type I interferons. J Immunother. 2018;41(4):181–9. 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000212.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms


