Abstract
Objective
Autophagy serves as a protective mechanism in response to mechanical stress during OTM. However, the role of ATG7, a key regulatory gene in autophagy, in modulating periodontium remodeling during OTM remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the potential modulation of periodontium remodeling by ATG7 under compression force.
Materials and Methods
HPDLSCs and a rat OTM model were used as in vitro and in vivo systems to study the effect of compressive stress on autophagy and osteoclast-related markers. To investigate the role of ATG7, hPDLSCs with ATG7 knockdown and ATG7+/− rats were used in this study.
Results
Compression force activates autophagy and increases the RANKL/OPG ratio. ATG7 knockdown significantly suppresses autophagy in hPDLSCs, while the RANKL/OPG ratio is markedly elevated. Under compression stress, hPDLSCs-siATG7 markedly enhanced RANKL/OPG expression. In the rat OTM model, autophagy was significantly activated in the periodontium on the compression side. Compared to wild-type SD rats, ATG7+/− rats exhibit reduced autophagy-related protein expression, an increased RANKL/OPG ratio, and accelerated tooth movement.
Conclusions
Under compression force, inhibition of ATG7 expression significantly increases the RANKL/OPG ratio both in vivo and in vitro, which is accompanied by an increased rate of orthodontic tooth movement.
1 Introduction
Orthodontic treatment is gaining popularity due to the increasing public demand for oral care [1]. However, the extended duration of orthodontic treatment remains a major obstacle, discouraging many patients from seeking interventions. Clinically, prolonged orthodontic therapy may lead to iatrogenic complications, including root resorption, gingival recession, or demineralization of enamel [2,3]. Consequently, expediting the movement of teeth during orthodontic therapy emerges as a shared objective for both practitioners and patients. To effectively control tooth movement, it is essential to understand the underlying mechanisms of orthodontic tooth movement (OTM). OTM involves the application of mechanical forces to periodontal tissues, which are then converted into biological signals within cells. This process induces tissue remodeling through cell activation and differentiation, with bone resorption occurring on the compressed side and bone formation on the tension side, ultimately facilitating the movement of teeth [4]. During this cascade, mechanical signals are converted into intracellular biological signals, triggering responses such as inflammation [5], hypoxia [6], and autophagy [7]. Among these responses, autophagy plays a crucial role in regulating OTM, marking it one of the prominent research areas in recent years.
Autophagy encompasses cellular degradation and recycling processes, which maintain cell homeostasis by removing damaged and dysfunctional organelles. In mammals, autophagy can be divided into three types based on the different ways substrates are transported to lysosomes: macroautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and microautophagy [8]. In this study, the term “autophagy” primarily refers to macroautophagy. Autophagy, as an important regulatory factor in tooth movement, plays a significant role in the process of OTM. Numerous studies related to autophagy and OTM have been reported [9,10,11,12,13], suggesting that physiological tooth movement can induce increased autophagic activity on the pressure side of the tooth. This process is associated with a significant upregulation of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, as well as an increase in the ratio of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) to osteoprotegerin (OPG), which in turn promotes bone resorption. These events contribute to alveolar bone remodeling, ultimately facilitating tooth movement. During this process, both in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that the application of autophagy inhibitors significantly enhances the expression of inflammatory factors, promotes the recruitment of osteoclasts, reduces bone density, and accelerates tooth movement. Conversely, excessive autophagy activation after using autophagy activators may suppress tooth movement by dampening the inflammatory cascade reaction and interfering with osteoclast recruitment, ultimately resulting in a slowing down of the tooth movement speed.
Autophagy related 7 (ATG7) serves as an E1 activating enzyme for conjugation, ultimately forming the ATG12–ATG5–ATG16L1 complex, which participates in membrane elongation of the phagophore. At the same time, ATG7 also promotes lipidation of protein LC3-I to generate LC3-II. LC3-II is present on the inner and outer membranes of autophagosomes, and directly or through selective autophagy receptor proteins sequesters cytoplasmic targets into autophagosomes [14,15]. It is evident that ATG7 is an indispensable component of the autophagy process, and autophagy is closely associated with bone homeostasis. Conditional knockout of ATG7 in mice (autophagy-deficient mice) has been shown to impair the functions of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, disturb bone metabolic homeostasis, and result in a pronounced phenotype characterized by reduced bone mass [16,17,18]. Moreover, ATG7 can influence the differentiation of BMSCs toward bone formation [19]. However, it remains unclear whether ATG7 influences the differentiation potential of human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs), which are key seed cells involved in alveolar bone remodeling under mechanical stress. Furthermore, its potential role in regulating OTM in vivo has not been fully elucidated.
In summary, in this study, we plan to investigate the role of ATG7 in regulating autophagy, and its downstream effects on osteoclastogenesis and OTM speed, providing scientific evidence for the mechanism regulating tooth movement. This study may offer new insights into optimizing orthodontic treatment by targeting autophagy-related pathways involved in periodontal remodeling.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Isolation and characterization of hPDLSCs
The experiments were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Kunming Medical University (Approval number: KYKQ2023MEC026), and all involved patients and their guardians provided consent. The volunteers in the project were patients aged 12–18 years whose healthy premolars were to be extracted for orthodontic treatment. The harvested teeth were separated and rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, Beyotime, Shanghai, China) three times, and periodontal ligament tissues were scraped from the middle 1/3 of the root with a scalpel. They were then incubated in Dulbecco's modified Eagle’s medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12 (DMEM/F12; Biological Industries, Beit Haemek, Israel) medium containing 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at 37°C under 5% CO2. The media was changed every 3 days, and the cells of passage 3–5 were used for the experiment.
After three passages, the cells were harvested for identification. For osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation, the cells were cultured in 6-well plates (1 × 105 cells/well). After reaching 80% confluency, the cells were oriented and induced using osteogenic differentiation medium (Cyagen, Suzhou, China) and adipogenic differentiation medium (Cyagen, Suzhou, China) for 2 or 3 weeks, respectively. After differentiation, cells were stained with Alizarin red or Oil Red O and observed under an inverted microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect cell surface markers. Briefly, cells were inoculated at 1 × 105 cells/well on a 6-well. At 80% confluence, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, washed with PBS, and stained with the following antibodies: anti-Vimentin (Zen-Bio, Chengdu, China) and anti-Nestin (Zen-Bio, Chengdu, China), according to the manufacturer's protocols, and then visualized with Fluorescein-Conjugated Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (ZSGB-Bio, Beijing, China). 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, Beyotime, Shanghai, China) solution was used for the staining of nuclei. Images were obtained using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). For flow cytometric analysis, the cells were resuspended in cold PBS containing 2% FBS at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells/mL prior to adding the following monoclonal antibodies: CD29-PE, CD44-PE, CD90-PE, CD105-PE, CD34-FITC, and CD45-FITC (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). The unmarked cells were used as a negative control. Finally, the stained cells were analysed using BD Accuri® C6 (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) and FloMax® software (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). Cell clone formation ability was tested using the plate clone formation assay.
2.2 Application of compressive stress
HPDLSCs were seeded into 6-well plates at 105 cells/well and cultured to confluence. The cells were continuously compressed using a uniform compression method similar to that previously described [20]. Briefly, a circular industrial glass plate with a diameter of 33 mm and a weight of approximately 17 g was placed over the cell layer to apply a constant mechanical pressure. When the glass was placed vertically in the 6-well plate, it generated a compressive stress of about 2 g/cm2. Cells were immediately collected after applied stress for 0, 6, 12, 18, and 24 h.
2.3 Cell transfection
HPDLSCs were seeded into 6-well plates at 105 cells/well and cultured in medium without antibiotics. Upon reaching 60–70% confluence, a final concentration of 50 nM siRNA (Zixi Biotechnology, Beijing, China) was transfected into each group of cells. The siRNA and transfection reagent Lipofectamine™ 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) were diluted with Opti-MEM (Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) separately, then combined them gently, and allowed to incubate for 20 min at room temperature. The resulting transfection complex was added to the 6-well plate and cultured at 37°C under 5% CO2 for 5 h. Then the transfection mixture was replaced with fresh culture medium, and the cells were further incubated for at least 24 h before subsequent experiments. The primer sequences corresponding to siRNA1 targeting ATG7 are F: GACAUUAAGGGUUAUUACU (dT)(dT), R: AGUAAUAACCCUUAAUGUC (dT)(dT).
2.4 Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
The TEM was performed on hPDLSCs cultured on coverslips to observe autophagosome generation. The samples were fixed overnight at 4°C using 2.5% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M PBS, pH 7.2 (Powerful Biology, Wuhan, China), then washed with 0.1M PBS three times. Afterwards, samples were postfixed with 1% OsO4 for 2 h at 4°C, then washed with ddH2O three times, followed by 30, 50, 70, 90, and 100% ethanol dehydration and acetone transition for 5 min, then embedded in SPI pon 812 resin, and polymerization at 60°C for 48 h. After polymerization, 60 nm ultrathin sections were made using a Leica EM UC7 ultramicrotome. Ultrathin sections were then loaded onto Cu grids and double-stained with 2% uranyl acetate (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany) and lead citrate (Sigma-Aldrich, St.Louis, MO, USA) before observations employing a JEM-1400 Plus transmission electron microscope (JEOL Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) at 80 kV.
2.5 Western blotting
Western blotting was performed as previously described [21]. Briefly, hPDLSCs were lysed with radioimmuno-precipitation assay lysis buffer (Solarbio, Beijing, China). The protein levels were quantified using a Bradford assay kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). The antibodies used were the following: ATG7 (10088-2-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Beclin-1 (11306-1-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), LC3 (14600-1-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Anti-SQSTM1/p62 (GB11531, Servicebio, Wuhan, China), RANKL (23408-1-AP, Proteintech, Wuhan, China), OPG (GXP366016, GenXspan, Alabama, USA), and GAPDH (60004-1-lg, Proteintech, Wuhan, China).
2.6 RT-qPCR
According to the manufacturer's protocol, total RNA was isolated using the TaKaRa MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit (Takara, Osaka, Japan). Total RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using the PrimeScript™ RT Master Mix (Perfect Real Time) (Takara, Osaka, Japan), and qRT-PCR was conducted using a QuantStudio™ Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with the Taq Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Takara, Osaka, Japan). Relative expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech (China, Table 1).
Primers for RT-qPCR
| Sequence | Name | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| CGGTGATAATAGAACGATACAA | LC3 (H)-F | 75 |
| GGTCAGGTACAAGGAACT | LC3 (H)-R | 75 |
| TACAGAGTATCTTCAACTAATG | RANKL (H)-F | 164 |
| CTCCAGACCGTAACTTAA | RANKL (H)-R | 164 |
| AATGTGGAATAGATGTTACC | OPG (H)-F | 94 |
| TCTACCAAGACACTAAGC | OPG (H)-R | 94 |
| CAGATGGAGTCGGATAAC | p62 (H)-F | 90 |
| CTGGAGTTCACCTGTAGA | p62 (H)-R | 90 |
| GCTCTTCCTTACTTCTTA | ATG7 (H)-F | 104 |
| ATTGTTATCTTCGTCCTT | ATG7 (H)-R | 104 |
| GTGGAATGGAATGAGATTA | beclin-1 (H)-F | 107 |
| TAAGGAACAAGTCGGTAT | beclin-1 (H)-R | 107 |
| TTGCCCTCAACGACCACTTT | GAPDH (H)-F | 120 |
| TGGTCCAGGGGTCTTACTCC | GAPDH (H)-R | 120 |
2.7 Establishment of the OTM model in SD rats
The animal experiment was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Kunming Medical University (Approval number: KMMU20231513), and the animal studies adhered to the international guidelines of ARRIVE. A total of 48 SD rats (male, 6–7 weeks old) divided into 6 groups were used in this study. A tooth movement model was established on the left maxillary first molar. The molar tooth movement was established as previously described [22]. All rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium, and a 50 g orthodontic force was applied using a nickel–titanium coil spring (Smart Advanced Material Tech Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China), with the force measured by a force gauge (Xihu Biom, Hangzhou, China) prior to securing the spring with light-cured composite resin (3M, St. Paul, MN, USA). During the experiment, the behavioral changes of the rats were observed and recorded daily. Then, the rats were euthanized by over injection of pentobarbital sodium on days 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 14, and the specimens were collected.
2.8 Identification of the ATG7+/− rats
The genetically modified rats used in the experiment were established by Syagen Biotechnology Company (Syagen Technology, Inc., Tustin, CA, USA) using CRISPR/Cas-mediated genetic engineering technology to generate the ATG7+/−rat model. The gRNA and Cas9 mRNA targeting the ATG7 gene of SD rats were co-injected into zygotes, and the zygotes were then transferred to pseudopregnant rats. Positive F0 heterozygous rats were identified by PCR and sequencing. F0 heterozygous rats were bred with wild-type rats to obtain identified positive F1 heterozygous rats. F1 rats from the same F0 rat with consistent genotypes were selected and bred to obtain F2 rats. Offspring were genotyped by PCR using primer sequences, and the primer sequences are listed in Table 2. In wild-type ATG7+/+ rats, only the 592-bp PCR product can be detected, and in homozygous ATG7−/− rats, only the 840-bp PCR product can be detected. Both 592-bp and 840-bp PCR products were detected in heterozygous ATG7+/− rats. The heterozygous ATG7+/− rats were selected for the experiment. A total of six heterozygous ATG7+/− SD rats and six wild-type ATG7+/+ SD rats were used in this study.
Primer sequences for the identification of genotype
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Rat Atg7-F | ACACTGATATACGGTTAGCCGTTTAGAGAAA |
| Rat Atg7-R | GGTTGGTGGAGAGACCTATAAGGATGC |
| Rat Atg7-He/Wt-F | ACCATCGATTTGAAACTTAAACTTC |
2.9 Micro-CT analysis
The collected samples were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h. Next, a NEMO® NMC-100 micro-CT system (PINGSENG Healthcare Inc., Kunshan, China) was used to scan the maxillary molar regions with the following parameters: 90 kV source voltage and 60 μA source current. The data were reconstructed, and the tooth movement distance was measured from the distal surface of the first molar to the mesial surface of the second molar in each specimen using the Avatar 1.5.0 software (PINGSENG Healthcare Inc., Kunshan, China).
2.10 Histological analysis
The samples were fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h, decalcified for 4 weeks, dehydrated using a graded series of ethanol, and embedded in paraffin wax. Embedded sections were prepared for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining, and immunohistochemistry staining. The TRAP staining was performed according to the test kit instructions (tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase Assay, Beyotime, China). The immunohistochemical staining was performed according to a previously published method [23]. Sections were incubated with the following antibodies: ATG7 (10088-2-AP; Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Beclin-1 (11306-1-AP; Proteintech, Wuhan, China), LC3 (14600-1-AP; Proteintech, Wuhan, China), Anti-SQSTM1/p62 (GB11531; Servicebio, Wuhan, China), RANKL (23408-1-AP; Proteintech, Wuhan, China), and OPG (GXP366016; GenXspan, Alabama, USA). Immunohistochemical-stained sections, positive staining sites, were analyzed by the Image-Pro Plus version 6.0 software. Although eight or six animals per group were initially enrolled, only three samples per group were ultimately included in the statistical analysis. The remaining samples were excluded due to predefined technical criteria such as tissue damage, poor section quality, or loss during processing. Importantly, data exclusion was not based on experimental outcomes, and only samples meeting objective quality standards were analyzed.
2.11 Statistical analysis
All experimental data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 19.0 and GraphPad Prism 9.0.0. Independent sample t-test was used for comparison between two groups, one-way ANOVA was used for comparing three or more groups, and normality tests were performed before performing statistical analysis. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Application of mechanical stress upregulated ATG7 and autophagy-related proteins on the compressive side of the OTM-rat model
A tooth movement model was established on the left maxillary first molar (Figure 1a), and the application of mechanical force induces both tension and compression zones around the tooth roots. Consequently, the periodontal ligament space was stretched on the tension side and constricted on the compression side (Figure 1b). TRAP staining demonstrated that red-stained multinucleated giant cells began to appear on the compressive side by the third day, peaking between days 5 and 7 (Figure 1c). Immunohistochemical results showed that under the application of orthodontic force, autophagy-related proteins LC3B, ATG7, and Beclin-1 were significantly upregulated on the pressure side of the periodontal ligament tissues, while P62 was downregulated. The expression of ATG7 fluctuated and attained its first peak at day 3 (Figure 1c and d).
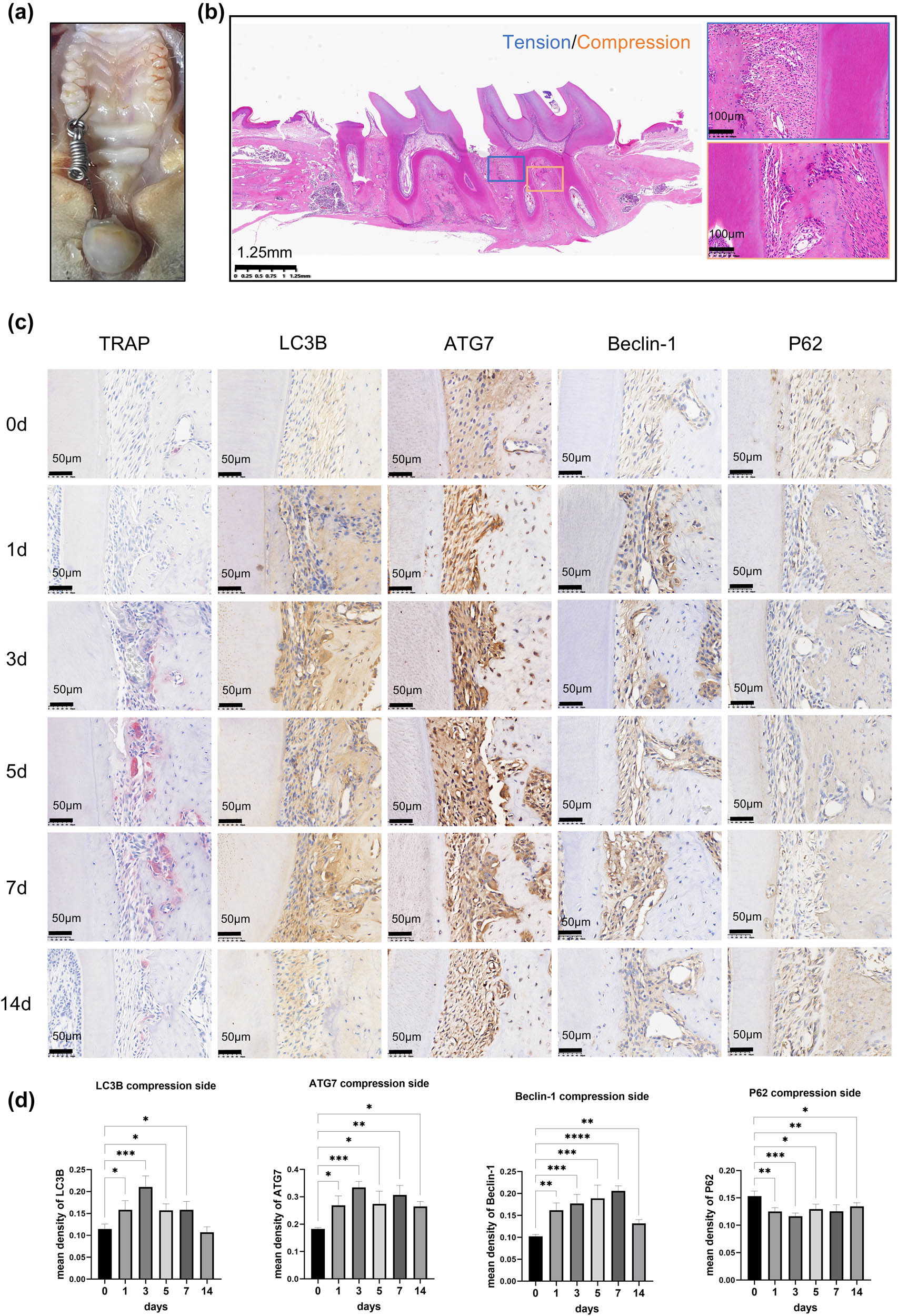
The application of mechanical stress upregulated autophagy-related proteins in the compression side of the OTM-rat model. (a) The model of tooth movement was established on the left maxillary first molar in rats. (b) H&E staining of OTM tissue section. The blue box represents the tension stress side, and the yellow box represents the compressive stress side of OTM. (c) and (d) The OTM model of SD rats was established for 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, and 14 days. The TRAP staining results showed that the red-stained multinucleated giant cells expressed the highest at days 5 and 7. Immunohistochemistry staining of autophagy-related proteins LC3B, ATG7, and Beclin-1 was significantly upregulated, while P62 was downregulated on the compression side of the periodontal ligament tissues. n = 3 per group; samples were selected based on the technical quality for histological analysis. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
3.2 Effect of compressive stress on the autophagy and RANKL/OPG expression in hPDLSCs
We isolated and cultured primary cells from detached periodontal ligament tissue (Figure 2a), and osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation results showed that the cells possessed good osteogenic ability (Figure 2b) and adipogenic ability (Figure 2c). Through cloning formation experiments, we demonstrated that the obtained cells had good cloning formation ability (Figure 2d). Subsequently, we conducted flow cytometry analysis, which revealed that the obtained cells positively expressed CD29 (99.98%), CD90 (98.75%), CD105 (99.99%), and CD44 (99.97%), which were markers of mesenchymal stem cells, while markers CD34 (0.06%) and CD45 (0.02%) for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells were negative (Figure 2e). Vimentin and Nestin showed positive expression in immunofluorescence detection (Figure 2f).
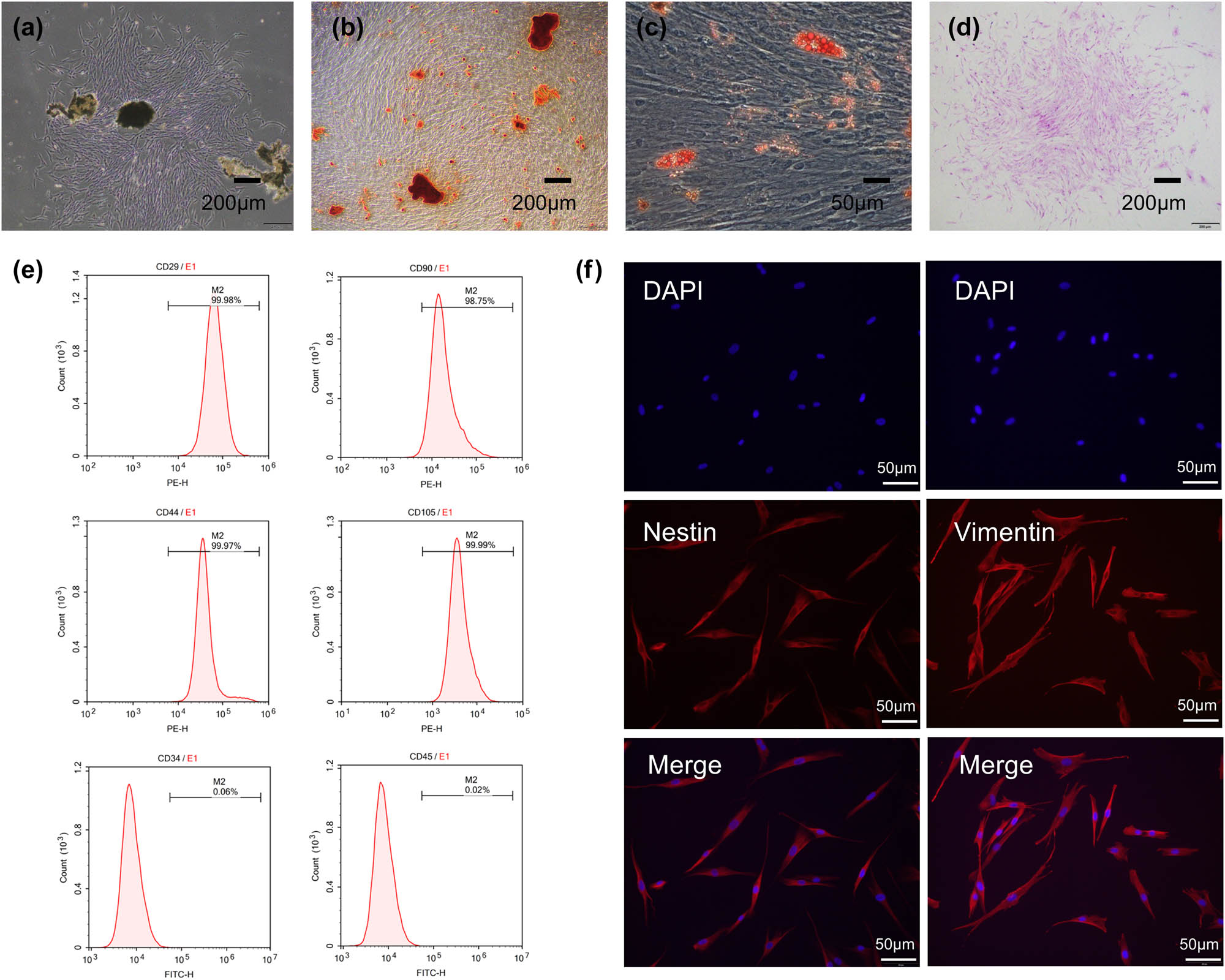
Culture and identification of hPDLSCs. (a) Primary cells cultured by periodontal ligament tissue. (b) Alizarin Red S staining of hPDLSCs after being cultured in osteogenic differentiating medium. (c) Oil Red O staining of hPDLSCs after being cultured in adipocytic differentiating medium. (d) Cell colony formation was observed after crystal violet staining. (e) Flow cytometric analysis of surface markers in hPDLSCs, CD29-PE (99.98%), CD90-PE (98.75%), CD105-PE (99.99%), CD44-PE (99.97%), CD34-FITC (0.06%), and CD45-FITC (0.02%). (f) Vimentin expression and Nestin expression in hPDLSCs.
hPDLSCs were subjected to physiologic sustained mechanical load of 2 g/cm2 (Figure 3a). To evaluate the effects of the stress on the autophagy and RANKL/OPG expression of hPDLSCs, we detected the expression of autophagy-related factors, including LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, Beclin-1, and P62 by performing Western blotting (Figure 3b and c) and RT-qPCR (Figure 3d), as well as the expression of osteoclast-related factors RANKL and OPG (Figure 3e–g, e and f represent Western blot, while g represents RT-qPCR). The results showed that under stress, autophagy-related factors LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, and Beclin-1 were significantly upregulated, while P62 was significantly downregulated, and the overall autophagy flux of cells increased at 6 and 12 h. Under mechanical stress, the expression of RANKL and OPG demonstrated an initial increase followed by a decline. The RANKL/OPG ratio significantly increased at 6 h, indicating that under compression force, hPDLSCs tend to modulate osteoclast differentiation.
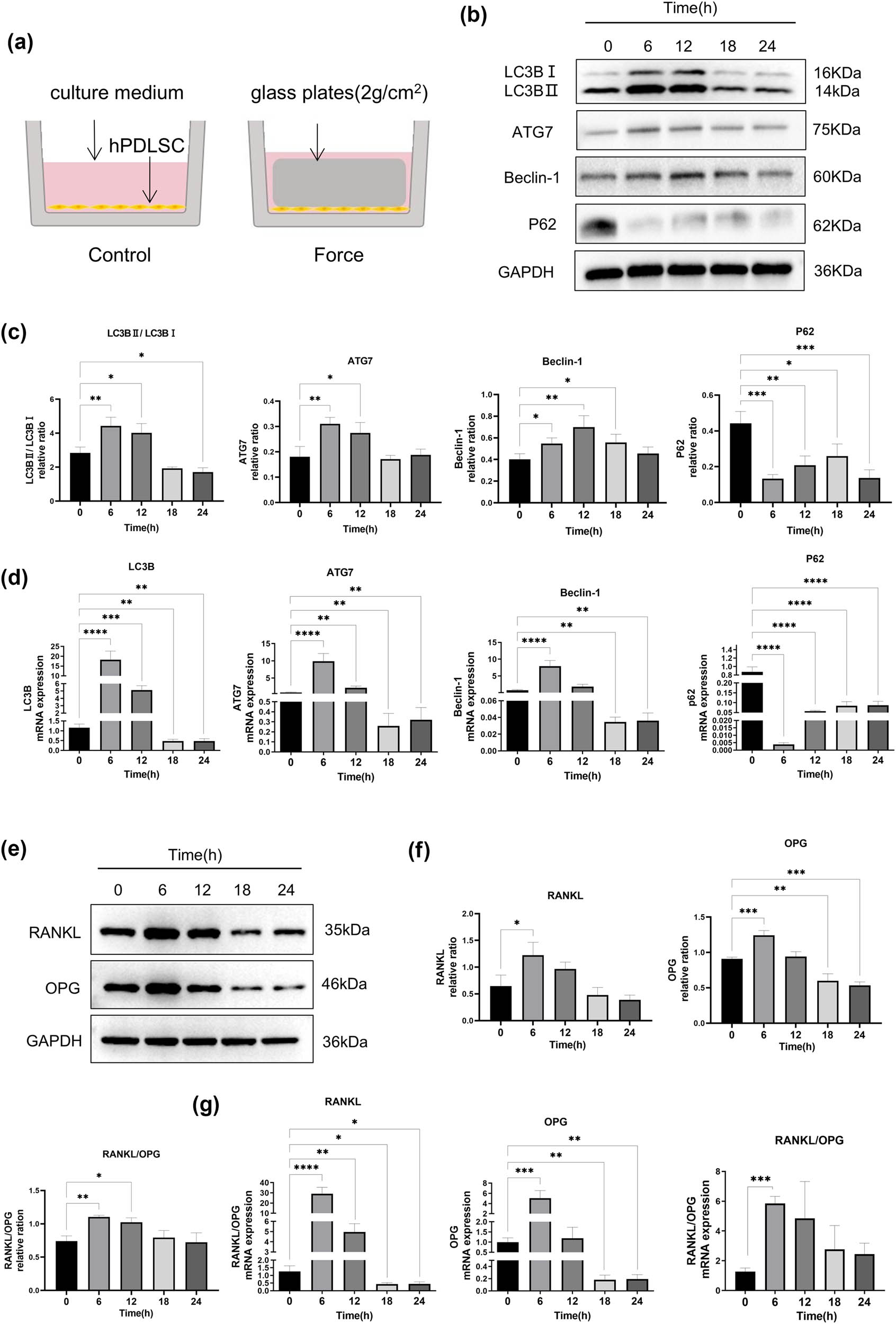
Effects of compressive stress on autophagy and RANKL/OPG expression in hPDLSCs. (a) Cell compressive stress model. (b)–(d) Western blot and RT-qPCR results of autophagy-related proteins, including LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, Beclin-1, and P62 after being cultured in the medium with a mechanical loading force of 2 g/cm2 for 0, 6, 12, 18, and 24 h. Autophagy-related proteins and mRNA were significantly activated at 6 and 12 h, and decreased at 18 and 24 h, with the first expression peak at 6 h. (e)–(g) Western blot and RT-qPCR results of RANKL and OPG expression after being cultured in the medium with a mechanical loading force of 2 g/cm2 for 0, 6, 12, 18, and 24 h. The RANKL and OPG expression significantly increased at 6 h, then decreased gradually, and the ratio of RANKL/OPG increased significantly at 6 h. n = 3; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
3.3 Effect of knockdown ATG7 gene on compressive stress-induced autophagy and RANKL/OPG expression in hPDLSCs
To investigate the impact of ATG7 on hPDLSCs, we designed three pairs of primer sequences of siRNAs for screening the transfection efficiency of siATG7. Finally, we selected siRNA1, which showed the highest inhibition of ATG7 protein expression in the WB results for the subsequent experiment. The screening results are shown in Figure S1. We conducted immunofluorescence detection of LC3B expression. As shown in the results (Figure 4a and b), the protein expression of LC3B increased after 6 h of compressive stress, and decreased in the hPDLSDs-siATG7 group. When stress was applied to the hPDLSCs-siATG7 group, the intensity of immunofluorescence increased again. Transmission electron microscopy observation (Figure 4c) of autophagosomes in cells further confirmed that stress significantly increased the number of autophagosomes, while ATG7 knockdown significantly reduced the number of autophagosomes. After 6 h of continued stress, the number of autophagosomes in hPDLSCs-siATG7 increased again. The Western blotting (Figure 4d and e) results showed that after 6 h of compressive stress, autophagy-related factors in hPDLSCs were significantly upregulated, including LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, and Beclin-1. Notably, these markers showed an opposite trend in hPDLSCs-siATG7. In contrast, the expression level of P62 is downregulated in compressive stress and upregulated in hPDLSCs-siATG7. When stress was applied to the hPDLSCs-siATG7, the results indicate that compressive stress may partially reverse the effects of siATG7 transfection, characterized by a certain degree of upregulation of LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, and Beclin-1 and downregulation of P62.
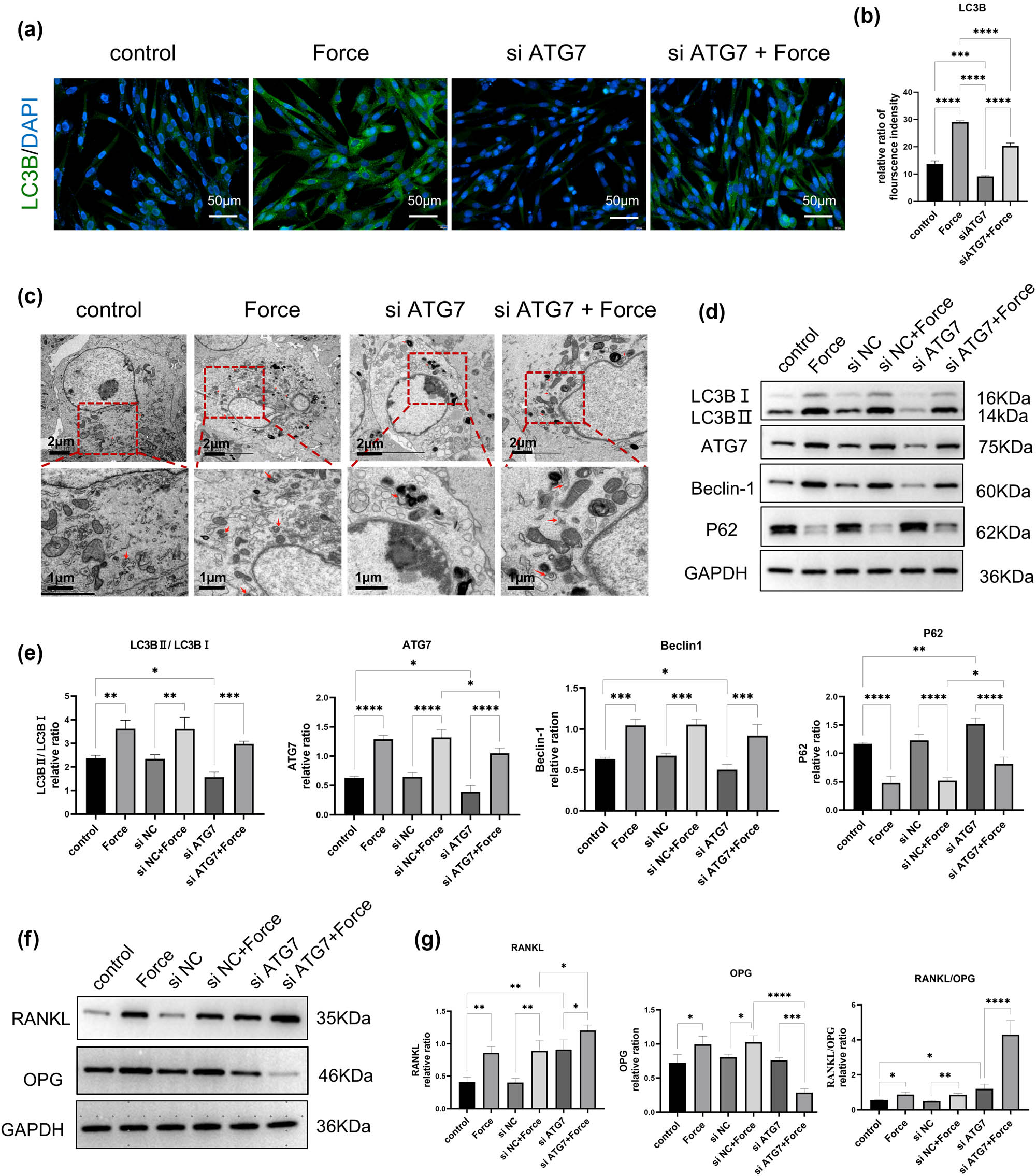
Knockdown of the ATG7 gene inhibits compressive stress-induced autophagy and promotes osteoclast differentiation in hPDLSCs. (a) and (b) The protein level of LC3B was detected by immunofluorescent staining. The immunofluorescence intensity of LC3B was enhanced under stress and decreased under siATG7 transfection. In hPDLSCs-siATG7 under the stress group, the immunofluorescence intensity enhanced again. (c) Autophagosomes were observed by TEM. The number of autophagosomes increased under stress, and decreased after ATG7 knockdown in hPDLSCs, which increased again by stress stimuli on hPDLSCs-siATG7. (d) and (e) Western blot results of autophagy-related genes and the quantitative analysis of protein expression levels. (f) and (g) Western blot results of RANKL/OPG expression and the quantitative analysis of protein expression levels. n = 3; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Western blotting (Figure 4f and g) results showed that osteoclast-related factor RANKL and OPG exhibit different expression trends in the hPDLSCs-siATG7 group and hPDLSCs-siATG7 under the stress group. Specifically, compressive stress and ATG7 knockdown in hPDLSCs can both independently lead to an increase in RANKL expression. Furthermore, when stress loading was applied to hPDLSCs with ATG7 knockdown, a more significant increase in RANKL expression was observed. However, in the hPDLSCs-siATG7 group, there was no significant difference in the expression of OPG compared with the control group, but when the stress was applied to hPDLSCs-siATG7, the expression of OPG was significantly reduced. Notably, under compressive stress, hPDLSCs transfected with siATG7 exhibited a marked increase in the RANKL/OPG ratio.
3.4 Heterozygous ATG7+/− rats enhanced OTM in the orthodontic model
To elucidate the influence of the ATG7 gene on the OTM model, heterozygous rats with positive PCR results for both 840bp and 592bp bands were utilized in this study (Figure 5a). The Micro-CT measurement and analysis results indicated that the rate of OTM was considerably accelerated in the ATG7+/− rats orthodontic model compared to that observed in wild-type rats (Figure 5b and c). The average tooth movement distance in wild-type SD rats was 0.193 mm, while the average distance in ATG7+/− SD rats was 0.295 mm, with a significant difference observed between the two groups. We detected the expression levels of autophagy-related proteins in the ATG7+/− rats group and wild-type rats group (Figure 5d and e). On the compression side, autophagy-related protein was elevated in both the wild-type group and the ATG7+/− group, as evidenced by the upregulation of LC3B, ATG7, Beclin-1, and the downregulation of P62. However, the autophagy-related protein induced by compressive force in the ATG7+/− group was significantly lower compared to the wild-type group. On the control side, although the autophagy-related protein of the ATG7+/− group was lower than that of the wild-type group, there was no significant difference between the two groups. Immunohistochemical staining (Figure 5d and e) for RANKL and OPG demonstrated that the RANKL/OPG expression increased on the compression side both in the wild-type group and the ATG7+/− group. In the ATG7+/− group, both the control and stress sides exhibited an increase of RANKL/OPG ratio compared to the wild-type group. Notably, on the compressive stress side of the ATG7+/− group, the expression of RANKL/OPG was significantly increased.
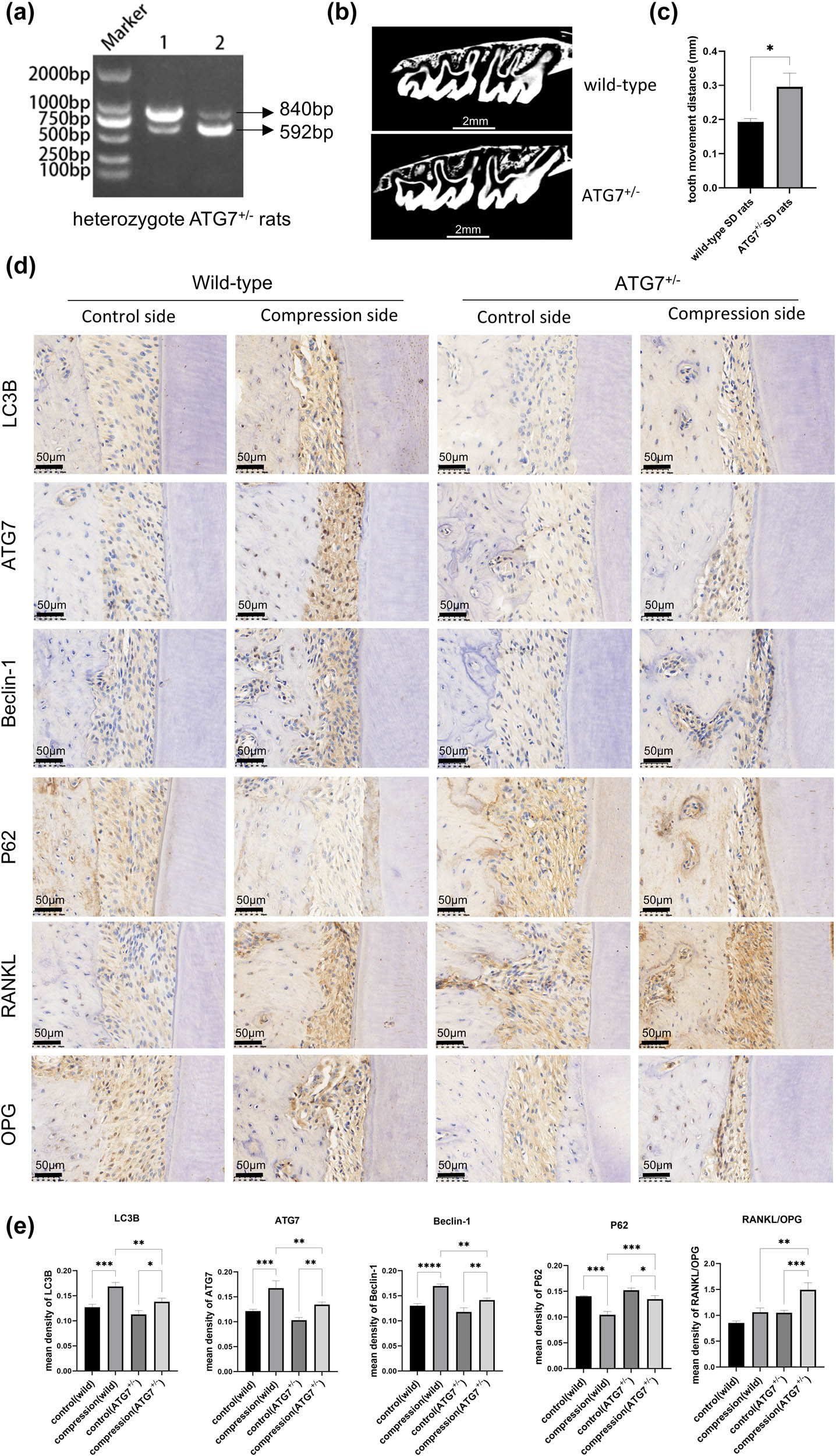
Heterozygous ATG7+/− rats enhanced OTM in the orthodontic model. (a) Rats were identified by performing PCR. (b) and (c) Micro-CT scan and analysis. The results of tooth movement data are expressed as mean ± SD; the wild-type group was 0.193 ± 0.01 mm, and the ATG7+/− group was 0.295 ± 0.04 mm. (d) and (e) Immunohistochemistry staining and its quantitative analysis for autophagy proteins, RANKL, and OPG. The autophagy-related proteins in the ATG7+/− group were lower when compared to the wild-type group on the compression side, but with a significantly increased RANKL/OPG expression. n = 3 per group; samples were selected based on the technical quality for histological analysis. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
4 Discussion
This study was designed to identify whether ATG7 modulated periodontium remodeling under compressive stress. In our experiments, mechanical compressive stress was found to upregulate autophagy-related proteins, including ATG7, and concurrently increased the RANKL/OPG ratio. Paradoxically, we also observed that knockdown of ATG7 led to a further elevation in the RANKL/OPG ratio, both in vitro and in vivo. We observed that these findings appear contradictory. However, mechanical compression is known to activate multiple cellular pathways in periodontal ligament cells, not limited to autophagy. Notably, it also triggers inflammatory and hypoxic responses [4,5,9], both of which are well-documented inducers of RANKL expression. While ATG7 and autophagy may negatively regulate osteoclastogenesis under certain conditions, this suppressive effect may be overridden by pro-inflammatory signaling cascades under mechanical load. In this context, the increase in ATG7 expression may exert a compensatory, protective role against stress but may not be sufficient to counteract the dominant RANKL-promoting effects of inflammation. As a result, despite the elevated expression of ATG7, the overall expression of RANKL/OPG under compressive stress remains increased. Conversely, suppression of ATG7 may impair autophagy and exacerbate cellular stress, potentially enhancing inflammation-driven RANKL expression through pathways such as NF-κB or MAPKs. Thus, the upregulation of RANKL/OPG observed in both ATG7 upregulation and downregulation contexts likely arises from the integration of multiple, competing signals. Consequently, when ATG7 expression is inhibited, the application of mechanical stress further amplifies RANKL/OPG expression, which may eventually affect the OTM speed (Figure 6). We acknowledge that the precise mechanistic link between ATG7 and RANKL/OPG regulation remains to be fully elucidated. In particular, overexpression studies of ATG7 in hPDLSCs may help clarify whether ATG7 directly suppresses RANKL expression. This represents an important direction for our future work.
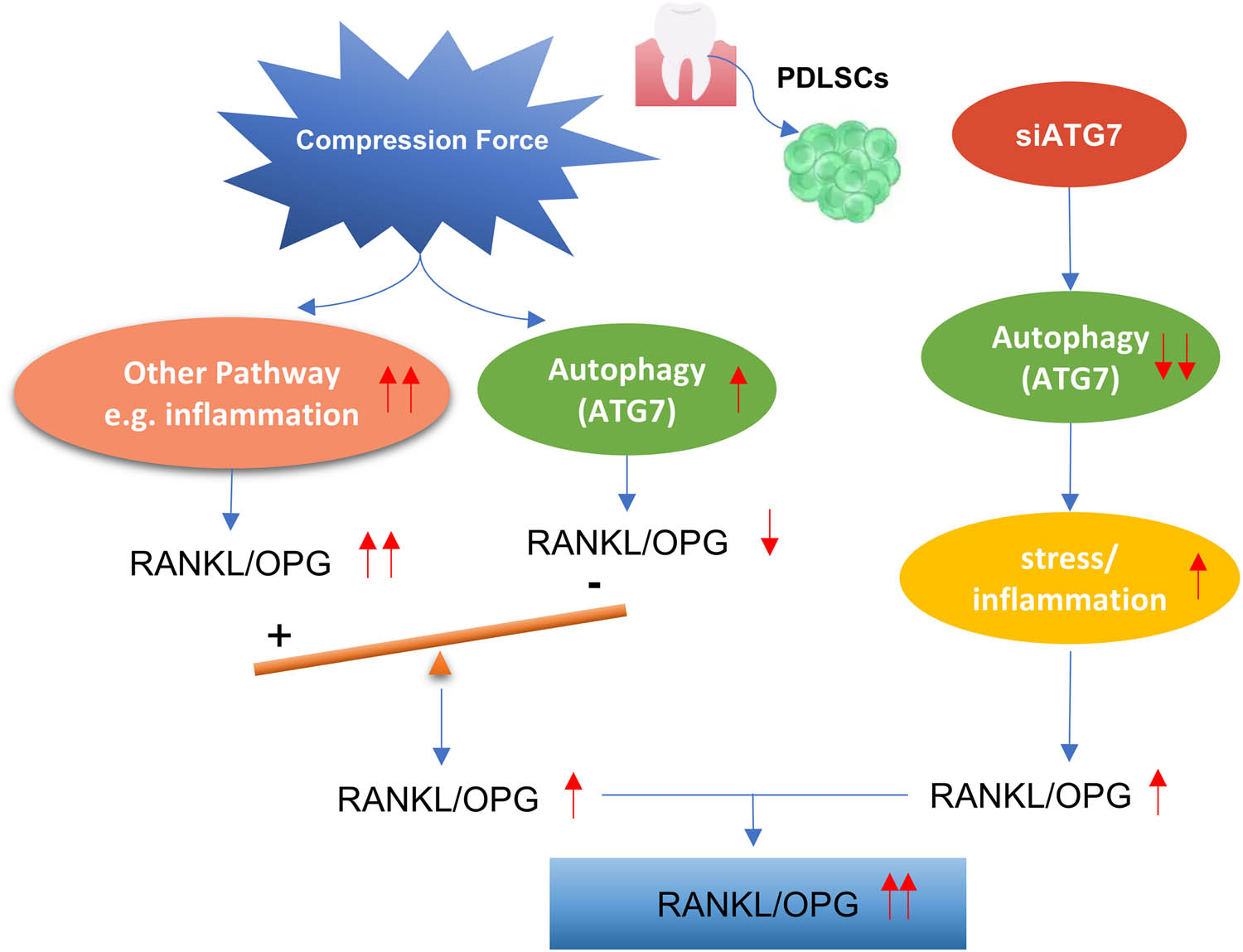
Schematic diagram of the relationship between the compression force, ATG7, and RANKL/OPG.
PDLSCs play an essential role in the formation, regeneration, and remodeling of periodontal tissue. They are recognized as a critical stem cell population for periodontal tissue repair and regenerative therapy [24,25]. To explore the effects of mechanical loading on periodontal tissue, various forces have been applied to hPDLSCs, including fluid shear stress, centrifugal force, tensile stress, and compressive stress [26–28]. Periodontal ligament cells are considered the primary cellular receptors for orthodontic mechanical signals in periodontal tissues. Applying physiological orthodontic compressive stress to human periodontal ligament cells has been shown to induce the expression of genes associated with bone remodeling, inflammation, extracellular matrix remodeling, and angiogenesis [29]. Although PDLSCs are widely used as an in vitro model to investigate cellular responses during OTM, their application has inherent limitations. The periodontal microenvironment in vivo is highly complex and involves not only PDLSCs but also osteoblasts, osteoclasts, endothelial cells, immune cells, and mechanical forces from the surrounding tissue and vasculature. PDLSC monocultures lack these dynamic interactions, which may affect the translatability of the results. Thus, while PDLSCs provide useful mechanistic insights, further validation in animal models is necessary.
In our in vitro experimental results, applying a compressive force of 2 g/cm2 to hPDLSCs significantly modulated autophagy-related factors LC3BⅡ/LC3BⅠ, ATG7, and Beclin-1 upregulated, while P62 was downregulated. The observed differential expression patterns of autophagy-related markers under orthodontic force can be attributed to their distinct functional roles in the autophagic process. Beclin-1 and ATG7 are upstream regulators essential for autophagosome initiation and expansion, respectively. LC3B, particularly its lipidated form LC3BII, associates with autophagosome membranes and serves as a marker for autophagosome number [15]. In contrast, p62 acts as a cargo receptor that is degraded during autophagy; thus, its accumulation typically indicates impaired autophagic flux, while a decrease suggests active autophagy [30]. Consistent with our findings, other studies have also demonstrated that autophagy is a rapidly activated protective physiological response to adapt to compressive stress [31,32]. As for the ATG7 expression peaks at 6 h in our study, subsequent experiments were conducted with stress loading for 6 h.
RANKL is a key cytokine that binds to its receptor RANK on osteoclast precursors, directly stimulating their differentiation, activation, and survival. OPG is a soluble decoy receptor secreted by osteoblasts and stromal cells that binds RANKL and prevents it from interacting with RANK [33]. The RANKL/OPG does not directly measure osteoclast formation or activity, but its ratio reflects the potential environmental signaling. An increased RANKL/OPG ratio is indicative of enhanced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption, which are fundamental processes that facilitate tooth movement. Therefore, we used changes in the RANKL/OPG ratio to reflect osteoclast differentiation activity in the periodontium and found that the rate of tooth movement after mechanical stress or autophagy deficiency is of great significance. In this study, we observed that compressive stress significantly increased the RANKL/OPG ratio in hPDLSCs, particularly under ATG7 knockdown conditions, suggesting that autophagy may negatively regulate pro-osteoclastic signaling. This finding is supported by previous research showing that compressive force upregulates RANKL in a time- and force-dependent manner in PDL cells, thereby enhancing osteoclastogenesis in co-culture systems with osteoclast precursors [34,35]. Our multi-modal analyses, including Western blotting, LC3B immunofluorescence, and transmission electron microscopy, confirmed that ATG7 knockdown significantly suppressed autophagy in hPDLSCs, while mechanical loading partially restored autophagic activity. This partial restoration may reflect a stress-induced compensatory mechanism that allows limited autophagic flux despite ATG7 suppression. Mechanistically, our results align with previous studies, indicating that silencing autophagy genes such as ATG5, ATG7, and Beclin-1 impairs mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and promotes osteoclastogenic environments [19,36]. In vivo, osteoblast-specific ATG7 cKO mice displayed reduced bone mass and elevated RANKL levels, confirming the dual role of ATG7 in both osteoblast formation and osteoclast inhibition [17]. Taken together, our findings and existing literature suggest that ATG7-mediated autophagy acts as a key modulator in periodontal tissue homeostasis and maintaining a balanced bone remodeling process under mechanical stress. A limitation of this study is the use of siRNA-mediated ATG7 knockdown, which may result in partial inhibition of autophagy due to suboptimal transfection efficiency. Future studies using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated ATG7 knockout models may provide more definitive insights into the mechanistic role of autophagy in hPDLSCs under mechanical stress. However, excessive activation or inhibition of autophagy can also impact bone homeostasis. It is clear that autophagy and bone homeostasis are interdependent and mutually regulated.
Orthodontic force application typically induces tooth movement through three distinct phases: the initial phase of rapid tooth movement immediately following force application (usually the first three days), the subsequent phase of slowed tooth movement, and the final phase of linear tooth movement [22,37]. In our experimental findings, the autophagic activity on the compression side exhibited a relative peak around day 3. This elevation in autophagy is considered indicative of active periodontal tissue remodeling, as autophagy plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and responding to mechanical stress, which are essential processes during OTM [7,8]. Thus, investigating molecular expression changes in periodontal ligament tissues at this time point provides representative insight into the remodeling response. Based on these observations, we conducted our subsequent in vivo OTM experiment for 3 days. Although our study primarily focused on autophagy-related markers, other indicators of periodontal remodeling, such as ALP, RUNX2, RANKL, OPG, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and TRAP, could be incorporated in future studies to provide a more comprehensive evaluation of the remodeling process.
ATG7 deficiency impairs the degradation of autophagosomal inner membranes following autophagosome-lysosome fusion [38], and this disruption of autophagy has been demonstrated in yeast, mice, and humans [39–41]. We used heterozygote rats in this study because the survival rate of homozygous rats was low. Although tissue-specific conditional knockout models are available in rats, constructing a periodontal ligament-specific cKO model remains technically challenging. Additionally, isolating sufficient PDL tissue from rats for downstream analyses is also difficult. While heterozygous rats showed no remarkable differences in physical appearance compared to wild-type rats at 7 weeks of age, their body weights were significantly lower (wild-type: 205.5 ± 9.88 g vs ATG7+/-: 171.5 ± 10.25 g), and relevant results are shown in Figure S2. The in vivo results shown in Figure 5d and e demonstrated that compared to wild-type SD rats, ATG7+/− SD rats exhibited slightly lower levels of autophagy markers, including LC3B, Beclin-1, and ATG7, as well as a slight accumulation of P62 in the periodontal tissues. However, these differences were not statistically significant. However, on the compression force side, the ATG7+/− SD rats showed a significant decline in the autophagy level, which indicated that the autophagy-related protein of heterozygote rats was affected after stress loading. Additionally, these rats showed an increased RANKL/OPG ratio on the compression side and a significantly accelerated rate of tooth movement. The absolute increase in tooth movement during the first 3 days was 0.102 mm; this degree of enhancement is comparable to that achieved by some non-invasive approaches currently under investigation or clinical use, such as low-level laser therapy or vibration devices [42,43]. A limitation of this study is the reduced number of analyzed samples (n = 3 per group), which was due to technical constraints. Specifically, during histological processing, tissue folding, sectioning artifacts, or staining inconsistencies led to the exclusion of several samples from quantitative analysis. However, a post hoc power analysis of the ooth movement result indicated that the observed effect size was sufficiently large (Cohen’s d = 3.49), yielding a statistical power of 0.996, thereby supporting the reliability of our findings. Nonetheless, we acknowledge that the high attrition rate may compromise the representativeness of the retained samples and could affect the reproducibility of the results. Future studies will aim to improve tissue preparation protocols, such as optimizing fixation, embedding orientation, and sectioning techniques, to reduce sample loss. Additionally, larger initial cohorts should be considered to ensure adequate sample availability after processing.
Nonetheless, we acknowledge that the minimal baseline differences in ATG7 expression between wild-type and ATG7+/− rats may limit the interpretation of gene dosage effects. Future studies employing conditional knockout models or more precise quantitative measurements of ATG7 protein levels under stress conditions would provide stronger validation of the biological relevance of ATG7 in OTM.
Taken together, these results provide strong evidence that ATG7 plays a regulatory role in RANKL/OPG and OTM. However, it would be better if we had sufficient homozygous rats to investigate the dynamic variations of autophagy and RANKL/OPG under different loading times. We also recognize that the ATG7+/− genotype itself is not directly translatable into a clinical intervention. To address this, we propose that our findings open up a potential avenue for targeted modulation of autophagy pathways as a therapeutic strategy. Pharmacologic or gene-based approaches that locally modulate ATG7 expression or autophagy level at the periodontal site could, in theory, replicate the effects observed in our model without systemic alteration of gene expression. Such approaches would need to be carefully controlled to avoid unwanted side effects, and future studies will be necessary to optimize delivery methods and evaluate long-term safety.
5 Conclusion
Knockdown of ATG7-modulated RANKL expression in periodontal ligament cells, under compressive force, was associated with a significant increase in the RANKL/OPG ratio both in vivo and in vitro. This was accompanied by a greater extent of OTM. Our findings suggest that ATG7-mediated autophagy may play a regulatory role in alveolar bone remodeling during orthodontic force application, providing a potential experimental basis for strategies aimed at accelerating tooth movement.
-
Funding information: This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no: 82360200), Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Team (202105AE160004), and First-Class Discipline Team of Kunming Medical University (2024XKTDTS08). We would like to express our gratitude for their financial support of this project.
-
Author contributions: YZJ, CMZ, and HJT designed the experiments. YZJ, CMZ, LXM, MLY, and LC performed experiments and collected data; LYJ, YZJ, and CMZ discussed the results and strategy; HJT supervised, directed, and managed the study; YZJ, CMZ, LXM, MLY, LC, LYJ, and HJT approved the final version to be published.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
[1] Erbe C, Heger S, Kasaj A, Berres M, Wehrbein H. Orthodontic treatment in periodontally compromised patients: A systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(1):79–89.10.1007/s00784-022-04822-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Liu Y, Li CX, Nie J, Mi CB, Li YM. Interactions between orthodontic treatment and gingival tissue. Chin J Dent Res. 2023;26(1):11–8.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Pandis N, Nasika M, Polychronopoulou A, Eliades T. External apical root resorption in patients treated with conventional and self-ligating brackets. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;134(5):646–51.10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.01.032Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Li Y, Zhan Q, Bao M, Yi J, Li Y. Biomechanical and biological responses of periodontium in orthodontic tooth movement: up-date in a new decade. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):20.10.1038/s41368-021-00125-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Yamaguchi M, Fukasawa S. Is inflammation a friend or foe for orthodontic treatment?: Inflammation in orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption and accelerating tooth movement. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2388.10.3390/ijms22052388Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Niklas A, Proff P, Gosau M, Römer P. The role of hypoxia in orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Dent. 2013;2013:841840.10.1155/2013/841840Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Xu J, Zhao X, Zeng J, Yu JH, Guan S, Xu XM, et al. Role of autophagy in the periodontal ligament reconstruction during orthodontic tooth movement in rats. J Dent Sci. 2020;15(3):351–63.10.1016/j.jds.2020.02.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Yin X, Zhou C, Li J, Liu R, Shi B, Yuan Q, et al. Autophagy in bone homeostasis and the onset of osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2019;7:28.10.1038/s41413-019-0058-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Chen L, Hua Y. Autophagy of periodontal ligament inhibits inflammation and reduces the decline of bone density during orthodontic tooth movement of mice. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;121:104960.10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104960Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Li Y, Jacox LA, Coats S, Kwon J, Xue P, Tang N, et al. Roles of autophagy in orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2021;159(5):582–93.10.1016/j.ajodo.2020.01.027Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Li W, Zhao J, Sun W, Wang H, Pan Y, Wang L, et al. Osteocytes promote osteoclastogenesis via autophagy-mediated RANKL secretion under mechanical compressive force. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020;694:108594.10.1016/j.abb.2020.108594Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Blawat K, Mayr A, Hardt M, Kirschneck C, Nokhbehsaim M, Behl C, et al. Regulation of autophagic signaling by mechanical loading and inflammation in human PDL fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9446.10.3390/ijms21249446Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Mayr A, Marciniak J, Eggers B, Blawat K, Wildenhof J, Bastos Craveiro R, et al. Autophagy induces expression of IL-6 in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts under mechanical load and overload and effects osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Front Physiol. 2021;12:716441.10.3389/fphys.2021.716441Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Collier JJ, Guissart C, Oláhová M, Sasorith S, Piron-Prunier F, Suomi F, et al. Developmental consequences of defective ATG7-mediated autophagy in humans. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(25):2406–17.10.1056/NEJMoa1915722Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ. An overview of autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20(3):460–73.10.1089/ars.2013.5371Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Onal M, Piemontese M, Xiong J, Wang Y, Han L, Ye S, et al. Suppression of autophagy in osteocytes mimics skeletal aging. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(24):17432–40.10.1074/jbc.M112.444190Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Li H, Li D, Ma Z, Qian Z, Kang X, Jin X, et al. Defective autophagy in osteoblasts induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and causes remarkable bone loss. Autophagy. 2018;14(10):1726–41.10.1080/15548627.2018.1483807Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Piemontese M, Onal M, Xiong J, Han L, Thostenson JD, Almeida M, et al. Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24262.10.1038/srep24262Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Nollet M, Santucci-Darmanin S, Breuil V, Al-Sahlanee R, Cros C, Topi M, et al. Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy. 2014;10(11):1965–77.10.4161/auto.36182Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Chen L, Mo S, Hua Y. Compressive force-induced autophagy in periodontal ligament cells downregulates osteoclastogenesis during tooth movement. J Periodontol. 2019;90(10):1170–81.10.1002/JPER.19-0049Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Liao XM, Guan Z, Yang ZJ, Ma LY, Dai YJ, Liang C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes facilitating osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):647.10.1186/s12903-022-02682-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] An J, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang R, Zhang B. A micro-CT study of microstructure change of alveolar bone during orthodontic tooth movement under different force magnitudes in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):1793–8.10.3892/etm.2017.4186Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Dai Q, Zhou S, Zhang P, Ma X, Ha N, Yang X, et al. Force-induced increased osteogenesis enables accelerated orthodontic tooth movement in ovariectomized rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3906.10.1038/s41598-017-04422-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Bartold PM, Batouli S, Brahim J, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004;364(9429):149–55.10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16627-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Tomokiyo A, Wada N, Maeda H. Periodontal ligament stem cells: Regenerative potency in periodontium. Stem Cell Dev. 2019;28(15):974–85.10.1089/scd.2019.0031Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Kanzaki H, Wada S, Yamaguchi Y, Katsumata Y, Itohiya K, Fukaya S, et al. Compression and tension variably alter Osteoprotegerin expression via miR-3198 in periodontal ligament cells. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):6.10.1186/s12860-019-0187-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Nile M, Folwaczny M, Wichelhaus A, Baumert U, Janjic Rankovic M. Fluid flow shear stress and tissue remodeling-an orthodontic perspective: evidence synthesis and differential gene expression network analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1256825.10.3389/fbioe.2023.1256825Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Wei F, Wang C, Zhou G, Liu D, Zhang X, Zhao Y, et al. The effect of centrifugal force on the mRNA and protein levels of ATF4 in cultured human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 2008;53(1):35–43.10.1016/j.archoralbio.2007.07.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Schröder A, Bauer K, Spanier G, Proff P, Wolf M, Kirschneck C. Expression kinetics of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in the early phases of orthodontic tooth movement. J Orofac Orthop. 2018;79(5):337–51.10.1007/s00056-018-0145-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Jiang P, Mizushima N. LC3- and p62-based biochemical methods for the analysis of autophagy progression in mammalian cells. Methods. 2015;75:13–8.10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.11.021Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] King JS, Veltman DM, Insall RH. The induction of autophagy by mechanical stress. Autophagy. 2011;7(12):1490–9.10.4161/auto.7.12.17924Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Kroemer G, Mariño G, Levine B. Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 2010;40(2):280–93.10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.023Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Yu X, Lv L, Zhang J, Zhang T, Xiao C, Li S. Expression of neuropeptides and bone remodeling-related factors during periodontal tissue regeneration in denervated rats. J Mol Histol. 2015;46(2):195–203.10.1007/s10735-015-9611-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Kanzaki H, Chiba M, Shimizu Y, Mitani H. Periodontal ligament cells under mechanical stress induce osteoclastogenesis by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand up-regulation via prostaglandin E2 synthesis. J Bone Min Res. 2002;17(2):210–20.10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.2.210Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Kanzaki H, Chiba M, Shimizu Y, Mitani H. Dual regulation of osteoclast differentiation by periodontal ligament cells through RANKL stimulation and OPG inhibition. J Dent Res. 2001;80(3):887–91.10.1177/00220345010800030801Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[36] Weng YM, Ke CR, Kong JZ, Chen H, Hong JJ, Zhou DS. The significant role of ATG5 in the maintenance of normal functions of Mc3T3-E1 osteoblast. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(5):1224–32.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Wise GE, King GJ. Mechanisms of tooth eruption and orthodontic tooth movement. J Dent Res. 2008;87(5):414–34.10.1177/154405910808700509Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Tsuboyama K, Koyama-Honda I, Sakamaki Y, Koike M, Morishita H, Mizushima N. The ATG conjugation systems are important for degradation of the inner autophagosomal membrane. Science. 2016;354(6315):1036–41.10.1126/science.aaf6136Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Tanida I, Mizushima N, Kiyooka M, Ohsumi M, Ueno T, Ohsumi Y, et al. Apg7p/Cvt2p: A novel protein-activating enzyme essential for autophagy. Mol Biol Cel. 1999;10(5):1367–79.10.1091/mbc.10.5.1367Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, et al. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2005;169(3):425–34.10.1083/jcb.200412022Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Luhr M, Szalai P, Engedal N. The lactate dehydrogenase sequestration assay - A simple and reliable method to determine bulk autophagic sequestration activity in mammalian cells. J Vis Exp. 2018;137:57971.10.3791/57971-vSearch in Google Scholar
[42] AlSayed Hasan MMA, Sultan K, Hamadah O. Low-level laser therapy effectiveness in accelerating orthodontic tooth movement: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Angle Orthod. 2017;87(4):499–504.10.2319/062716-503.1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Leethanakul C, Suamphan S, Jitpukdeebodintra S, Thongudomporn U, Charoemratrote C. Vibratory stimulation increases interleukin-1 beta secretion during orthodontic tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 2016;86(1):74–80.10.2319/111914-830.1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms


