Abstract
Background
The immune system is closely related to hypertension. Hypertension is an immune disorder to a certain extent, and inflammation is the basis of abnormally elevated blood pressure (BP). The accumulation of T cells and their cytokines can increase BP and end organ damage. T cells are activated by antigen-presenting cells of the innate immune system or by the influence of a high-sodium diet, the self-environment, or the gut microbiota. These cells produce inflammatory factors and cytokines, such as interleukin-17A (IL-17A) in T helper 17 cells, causing vascular inflammation, hypertension, and target organ damage
Methods
In this article, we provide an insightful review of the research progress regarding the role of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of hypertension and its effects on different organs while emphasizing the role of IL-17A and its mediated functions in the kidneys, brain, intestines, and vascular system in the development and progression of hypertension.
Results
At the organ level, IL-17A is involved in the development and progression of hypertension in the kidneys, brain, intestines, and blood vessels, interacting with multiple signal pathway.
Conclusions
These findings have significant implications for developing future immunomodulatory therapies, which may lead to the development of potential treatments for hypertension.
1 Introduction
Recent studies have demonstrated the involvement of interleukin-17A (IL-17A) in the progression of autoimmune diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis [1] and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) [2] with anti-IL-17A treatment found to mitigate autoimmune disease progression [3] Moreover, IL-17A is also closely associated with cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis [4,5] and heart failure [6,7], and prostate cancer [8,9]. Thus, elevated IL-17A levels may serve as a marker for cardiovascular event risk assessment. There is limited information on the mechanism underlying the association between IL-17A and hypertension, and there are no comprehensive reviews of the effects of IL-17A on different systems in the pressor response. The present article systematically analyzes the relationship between IL-17A and hypertension in terms of the source, production, and actions of IL-17A, together with an analysis of the underlying mechanism, current research status, and cutting-edge applications of IL-17A in the pressor response in multiple systems.
2 Source and regulatory pathways of IL-17A
2.1 General biology of IL-17A
In 2005, the T helper 17 (Th17) cell emerged as a new T cell subset that can produce a unique proinflammatory cytokine, interleukin-17 (IL-17) [10]. Unlike other IL-17 isoforms, IL-17A is currently considered the member of the IL-17 family that is most involved in autoimmune diseases and the most deeply studied member in various diseases. In the state of autoimmune activation or excessive dietary sodium, peroxidation caused by aseptic inflammatory injury causes professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including dendritic cells, macrophages, and monocytes, to secrete prohypertensive cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). APCs process exogenous proteins and modified self-proteins into peptides, leading to the formation of modified proteins, such as IsoLG protein adducts, and interactions between CD28/B7 ligands and CD27/CD70 [11]. This process stimulates the proliferation of T cells and the polarization of Th17 cells to produce IL-23 and interferon gamma.
The differentiation of mature Th17 cells from naive Th17 cells is normally controlled by master transcriptional regulators – retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor gamma (RORγt) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) [12]. Th17 cell differentiation is induced by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and IL-6. TGF-β promotes RORγt expression of Th17 cells, while IL-6 and IL-1β amplify the Th17 lineage. IL-23 induces RORγt maturation and expansion. IL-21 is produced by Th17 cells and drives IL-17A production in a STAT3-dependent manner. The presence of IL-1β and IL-23 maximizes the expression of IL-17A [13]. IL-17A regulates downstream cells by interacting with the IL-17A receptor. Upon binding of IL-17A to its receptor, signal proteins downstream of the IL-17A receptor are activated, leading to the activation of transcription factors, such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), activator protein 1 (AP-1), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein.
2.2 Regulation of IL-17A in hypertensive states
Chronic elevated circulating levels of IL-17A could contribute to organ damage and hypertension. Intravenous injection of IL-17A was found to increase blood pressure (BP) and heart rate, and similar results occurred after paraventricular nucleus (PVN) microinjection or intracerebroventricular (ICV) [14]. The results of kidney biopsies of hypertensive nephrosclerosis patients showed that Th17 and γδT lymphocytes existed in kidney tissue, which were IL-17A-positive cells [15].
IL-17A promotes the elevation of BP through three intracellular signaling pathways: Janus kinase 1 [16], Janus kinase 2 [17], and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) [18]. The major T cell sources of IL-17A in hypertensive target organs are CD4+ Th17 cells and γδT cells. It should be noted that IL-17A can also be produced by other cells under certain conditions, including natural killer cells, lymphoid tissue inducer cells, and group 3 innate lymphoid cells [19], but the relative contribution of these cells to total IL-17A production in the development of hypertension is unknown. IL-17A can activate and recruit neutrophils in blood vessels and central glial cells, upregulate the expression of inflammatory mediators, promote inflammation, damage the vascular endothelium, and cause vascular dysfunction. IL-17A induces oxidative stress injury and endothelial dysfunction, which contributes to hypertension.
In addition, IL-17A is also reported to affect other cardiovascular risk factors. Increased serum IL-17A is regarded as a risk factor for autoimmune type 1 diabetes for the Chinese population [20]. Depletion of IL-17A ameliorated retinal inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular leakage in diabetic retinopathy [21]. Il-17A is also reported to be an independent risk factor for dyslipidemia among AR patients. Apparently, IL-17A is an important factor that not only regulates hypertension but also affects other disease factors that may cause hypertension.
3 Mechanisms of IL-17A-induced hypertension through multiple pathways
3.1 Renal mechanisms
The kidney is the most commonly affected end-target organ of hypertension and is closely related to the development and progression of hypertension. The kidney is not only an organ for excreting metabolites, but also an endocrine organ that regulates water and electrolyte balance, regulates BP, and maintains homeostasis in the internal environment. Therefore, the kidneys play an important role in the regulation of BP.
3.1.1 By regulating sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 3 (NHE3), sodium/chloride cotransporter (NCC), and Na+−K+−2Cl− cotransporter 1 (NKCC1) activity
IL-17A produced by immune cells was found to induce serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1)-dependent expression and activity of proximal and distal sodium transporters (including NHE3 and NCC) in the kidneys, resulting in increased sodium and water retention. In addition, IL-17A also impairs glomerular selectivity and tubular secretory activity, thereby contributing to increased BP and impaired renal function. At present, IL-17A is the only IL-17 family member that has a unique regulatory effect on NHE3 and NCC in the proximal and distal tubules [22]. This may be related to the activation of the Rac1-mineralocorticoid receptor (MR)-SGK1-NCC and beta-2 adrenergic and glucocorticoid receptor-with-no-lysine kinase 4-NCC pathways after excessive activation of the renal sympathetic nervous system following upregulation of salt loading [23,24]. Rac1 is a member of Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate (Rac) GTPases, acting as a molecular switch regulating different cellular functions. It is associated with reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, apoptosis, etc. [25]. The MR is a ligand-activated transcription factor, which is reported to be activated by Rac1 [26]. Researchers found that constitutively active Rac1 promoted gene transcription dependent on the MR and the nuclear translocation of the MR, finally aggravating podocyte injury. The serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) is a significant molecule regulating signal transduction pathways and cell phosphorylation cascades [20]. It is also reported that SGK1 was able to phosphorylate NEDD4 and induce inflammatory fibrosis and hinder Treg development [27]. In the salt-sensitive hypertension animal model, Rac-1 was also found to amplify MR activation and promote its nuclear translocation [28]. The abnormal activation of the Rac-1-MR pathway led to sodium reabsorption via NCC in distal convoluted tubule 2 segment [29]. Correspondingly, when the uptake of sodium increases, SGK is also upregulated by MR [30] Under salt-sensitive conditions, sympathetic nervous system overactivation increases NCC activity, renal sodium reabsorption, and BP by upregulating SGK1, a renal NCC and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activator, and downregulating WNK4, whose activation leads to renal sodium excretion. Meanwhile, Norlander et al. [22] found that in addition to the production of IL-17A by T cell stimulation, human renal cortical proximal tubular epithelial cells and mouse distal convoluted tubule 15 (mDCT15) cells in the kidney also produce IL-17A.
IL-17A increases NCC activity in mDCT15 cells through the SGK1/Nedd4-2-dependent pathway. Meanwhile, it increases sodium/hydrogen exchange protein activity by increasing SGK1 expression and phosphorylation in the proximal tubule. It is involved in angiotensin II-induced hypertension and kidney damage. In addition, loss of SGK1 can slow down hypertension, eliminate renal and vascular inflammation, protect the hypertensive kidney, and mitigate vascular damage. However, NKCC1 was found to be upregulated in Th17 cells in salt-induced hypertensive mice, and it mediated the salt-induced increase in SGK1 and IL-23 receptors [31].
3.1.2 By inducing renal fibrosis and elevated BP
Renal inflammation, subsequent fibrosis, and impaired function lead to the development of hypertension [32]. Orejudo et al. [33] found that IL-17A is involved in inflammatory cell accumulation in the kidneys and that injection of anti-IL-17A antibodies can reduce the nephritic state of pre-clinical renal injury. First, inhibition of IL-17A reduced renal inflammation. Saleh et al. [34] found that staining for the cell surface markers CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, and F4/80 on leukocytes in the kidneys of Ang II-induced hypertensive mice that had been treated with monoclonal antibodies to IL-17A and IL-17 receptor A subunit revealed significantly decreased levels of total T cells, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells. On the other hand, the accumulation of total leukocytes, T cells, and both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the kidney was decreased after angiotensin II-induced hypertension was blunted, which was induced by phenol application in bilateral renal denervation [35]. Collectively, those data revealed IL-17A might promote renal hypertension via inducing immune cells accumulation like CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells.
In addition, IL-17A regulates renal fibrosis (Figure 1), further influencing BP. Anti-IL-17A or anti-IL-17 receptor A subunit monoclonal antibodies significantly reduced TGF-β levels in TGF-β-mediated renal fibrosis. Naive T-cells develop into Th17 cells under the stimulation of TGF-β and IL-6 and secrete IL-17A [36], which can create a vicious cycle leading to increased fibrosis. More than this, renal fibrosis is caused by the aggregation and activation of fibroblasts regulated by IL-17A, as well as a significant increase in the production of fibrocyte-related chemokine CXCL12 and activating factors Semaphorin7A and PDGF-BB, which significantly induce and participate in the pathogenesis of renal fibrosis [37].
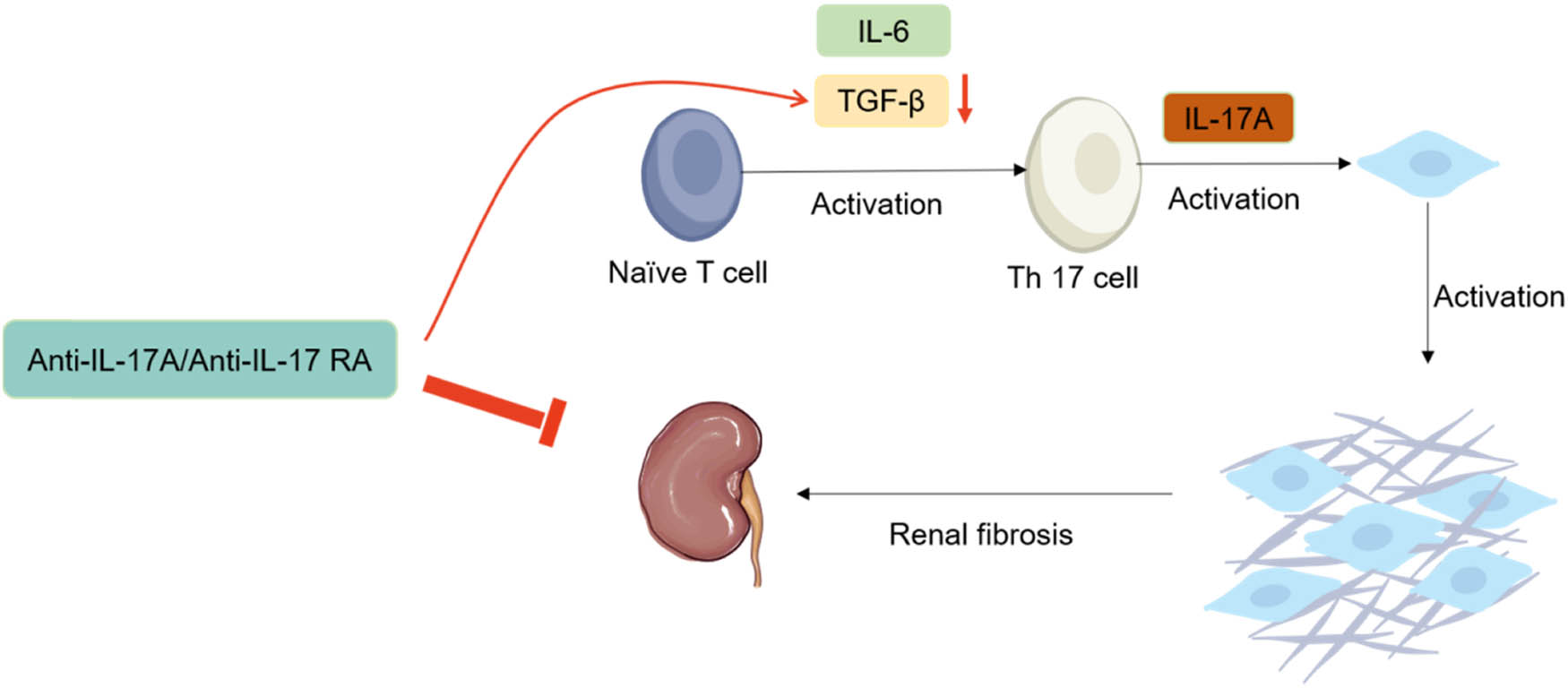
Interaction between IL-17A and other cytokines in renal fibrosis. Naive T-cells develop into Th17 cells under the stimulation of TGF-β and IL-6 and secrete IL-17A. On the other hand, anti-IL-17A or anti-IL-17 receptor A subunit monoclonal antibodies significantly reduced TGF-β levels in renal fibrosis.
However, there are different perspectives on the role of IL-17A in renal injury. It was found that IL17−/− deficient mice exerted less vascular dysfunction as per Madhur et al. [38]. In this study, the mouse hypertension model was induced only by Angiotensin II. And at the first 2 weeks, there was no significant change in BP between wild-type mice and IL17−/− mice. And by 3–4 weeks of angiotensin II infusion, the BP of IL17−/− mice began to obviously decline. Likewise, the application of IL-17A neutralizing antibody did not show obvious effect on BP or albuminuria [39]. In contrast, Krebs et al. [40] discovered that there was no apparent change in hypertensive response between IL-17–/– and wild-type mice, which was not in line with the previous study. While, more albuminuria and glomerular injury in IL-17–/– mice were found, which was probably induced by γδ T cell infiltration. The increased γδ T cell infiltration was considered as compensatory changes in other immune cell populations. After weeks, the BP was found lower in IL-17–/– mice than in wild-type mice. In this study, the hypertension mouse model was induced by deoxycorticosterone acetate and angiotensin II, which is regarded as inducing substantial hypertensive renal and cardiac injury. Different from the literature mentioned above, the relevant indicators were detected in this study on the 4th and 14th day, which was much earlier than the detection time of the previous study. Compared with those research studies, the difference in model, the frequency and administration of antibodies, and observation period length all contributed to the difference, which needs more samples and long-term observation to confirm.
3.2 Central nervous system (CNS)
Numerous studies have shown that inflammation significantly promotes the development of hypertension and heart failure by driving sympathetic hyperactivity and neurohumoral activation; microglia-mediated neuroinflammation plays an important role in this process. In addition, researchers have found that peripheral IL-17A can increase the permeability of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) by reducing the gene expression of tight junction proteins (such as ZO-1, claudin-5, and occludin) and modifying the underlying actin cytoskeleton, which allows IL-17A to enter the brain by damaging the integrity of the BBB [41]. Moreover, studies have also found that IL-17RA and IL-17RC are highly expressed in the CNS, especially in the PVN of the hypothalamus, which lays the foundation for IL-17A to play a role in the brain [14]. Studies have shown that peripheral IL-17A plays a role in promoting chronic inflammation, leading to a pressor response and end-organ damage. There is also strong evidence that brain IL-17A mediates neuroinflammation, and sympathetic outflow also aggravates hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
3.2.1 An increase in peripheral IL-17A damages the BBB, activates glial cells in the brain, and promotes an increase in BP
Cao et al. [14] found that in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats, intravenous and ICV injections of IL-17A resulted in a significant and sustained increase in BP and excitatory responses, and heart rate and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) were also maintained at high levels. Systemic administration of IL-17A significantly increased the levels of IL-17A in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid and upregulated the mRNA expression of IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-17RA in the PVN of the hypothalamus in normal rats. Moreover, the mRNA levels of the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and chemokines CCL2, CCL3, CXCL8, and CXCL12 in the PVN were significantly elevated. In addition, microglia and astrocytes in the PVN showed elevated expression of the surface markers CD11b and glial fibrillary acidic protein. In summary, increased peripheral IL-17A could promote the production of large amounts of IL-17A in the CNS, activate glial cells in the brain, and produce new cytokines or chemokines by these activated glial cells in response to increased IL-17A, which may lead to further BBB damage.
3.2.2 Synergistic effect of IL-17A increases BP and myocardial infarction risk through the CNS
More directly, it was found that injecting trace amounts of IL-17RA small interfering RNA into the PVN significantly reduced BP, heart rate, RSNA, and gene expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The same effect was also observed in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats pretreated with the microglial or astrocyte inhibitors minocycline and fluorouracil [42,43]. IL-17A cooperates with chemokines to amplify its inflammatory effect, and this effect may be the key to promoting sympathetic nerve excitation. The subsequent immune response and tissue inflammation cause a positive feedback loop centered on IL-17A, which aggravates CNS neuroinflammation. ICV administration of IL-17A increased the expression of phosphorylated (p) 44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), p-TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), and phospho-I-kappa B-alpha (IκB-α), and the rapid degradation of IκB-α promoted NF-κB activity [44]. These results suggest that IL-17A activates the TAK1, p44/42 MAPK, and NF-κB signaling pathways in the PVN to promote neuroinflammation, which in turn promotes sympathetic activation and hypertension.
The discovery of the synergistic effects of IL-17A has important implications for cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension and myocardial infarction. In an experimental study by Yu et al. [45], it was found that in rats with heart failure induced by myocardial infarction, peripheral IL-17A entered the brain and activated autonomic nerve and neuroendocrine neurons in the brain, especially in the PVN, triggering the production of broad spectrum proinflammatory factors and chemokines, thereby activating sympathetic nerve and hormone activation and ultimately leading to the deterioration of cardiac function in heart failure.
3.2.3 Brain–kidney interaction of IL-17A
In line with the above, excessive activation of RSNA promotes the opening of ion channel proteins. Moreover, IL-17A promotes excessive and sustained RSNA by acting on the CNS, which suggests that a brain–kidney interaction may explain the pathogenesis of IL-17A-induced hypertension.
3.3 Vascular system
Hypertension is associated with vascular changes that are characterized by endothelial dysfunction, maladaptive vasomotor function, and arterial remodeling. IL-17A plays a key role in the development and progression of hypertension by impairing vascular function through vascular inflammation, promoting an increase in ROS, increasing aortic stiffness, causing vascular fibrosis, and leading to vascular remodeling.
3.3.1 By increasing ROS, vascular fibrosis, arterial stiffness, and arterial remodeling
This ROS-induced mitochondrial ROS release process is directly involved in the prohypertensive response induced by angiotensin II in hypertensive mice [46]. Schuler et al. [47] found an increase in peripheral ROS and significant vascular dysfunction in CD4−IL-17Aind/+ mice. Moreover, it was found that overexpression of IL-17A alone led to the formation and increase of peripheral oxidative stress and impaired vascular function. First, IL-17A could disrupt the oxidation-antioxidant balance and downregulate the intravascular soluble guanylate cyclase-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway through IL-17A and myeloid cell-mediated oxidative stress, which would impair nitric oxide signaling and increase peripheral vascular resistance. Second, IL-17A is ubiquitously expressed in the vascular wall. It directly induces fibroblast proliferation and vascular collagen deposition through the NF-κB pathway downstream of IL-17A/IL-17RA [48]. Moreover, IL-17A-mediated redox activation activates tyrosine kinase 2 in perivascular adipose tissue, which promotes vascular fibrosis and induces vascular dysfunction. In addition, overexpression of IL-17A also upregulates the profibrotic transcriptional marker matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) [49]. MMP2 causes fibrosis and hypertrophy of arteries, as well as degradation and expansion of elastic fibers, leading to arterial stiffness and remodeling. VCAM-1 promotes the adhesion and migration of macrophages to the endothelium, leading to the production of various proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6, in addition to ROS, which ultimately leads to hypertension [50,51].
3.3.2 By mediating oxidative stress, vascular inflammation, and smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation in a TRAF3IP2-dependent manner
As a potent pro-oxidant and proinflammatory cytokine, IL-17A promotes IL-17A/TRAF3 interacting protein 2 (TRAF3IP2)-mediated oxidative stress, NF-κB, AP-1, and p38MAPK-induced NLRP3 expression, caspase-1 activation, IL-1β and IL-18 secretion, and human primary aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation in a TRAF3IP2-dependent manner [52]. In addition, TRAF3IP2 overexpression impairs insulin signaling in endothelial cells and attenuates endothelial-dependent relaxation in isolated arteries; this inhibition of aortic vasodilation is consistent with the downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in aortic endothelial cells. However, whether the expression of TRAF31P2 has a significant effect on BP requires more experimental evidence to confirm this finding [53]. Previous studies have shown that IL-17A induces a variety of inflammatory mediators, including IL-6, TNF-α, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and TGF-β through TRAF3IP2 to produce and maintain vascular inflammation and damage the vascular endothelium [54].
Clinical data indicated that patients with higher concentrations of IL-17A exerted more severe HF. Subsequent analysis showed elevated activation of lymphocyte-mediated immunity and leukocyte activation pathways in patients with elevated IL-17A [7]. On the other hand, the character of HF is the production and release of proinflammatory cytokines induced by immune activation [55], which will lead to a vicious cycle. In addition, Li et al. discovered that IL-17A damaged cardiac function by cardiac remodeling and calcium handling mediated by NF-κB [6]. More than this, Il-17A also exerted a significant role in ischemic stroke. First, IL-17A accelerated the progress of atherosclerotic plaques and hypertension, which are ischemic stroke risk factors [56]. Second, IL-17A accelerated neuronal injury via mediating neutrophil chemotaxis to the site of injury, the induction of neuronal apoptosis, causing further damage to neurons [57]. Therefore, targeting IL-17A is beneficial not only for the treatment of hypertension, but also for the treatment of complications such as heart failure and stroke.
3.3.3 By regulating Th17/Treg balance
In angiotensin II-infused mice, serum levels of IL-17A, IL-23, and TNF-α, which have roles in maintaining hypertension, were shown to be significantly increased, while serum levels of the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10, which has cardiovascular protective effects, were significantly decreased [58]. Expression of RORγt, a Th17-related transcription factor, was significantly increased, while in contrast, expression of Treg-related transcription factor Foxp3 was significantly decreased. Among these, the SGK1-FoxO1 signaling pathway was shown to be involved in Th17/Treg imbalance and target organ damage in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice, and it was also involved in renal/cardiac inflammation and fibrosis induced by vascular endothelial cells in hypertensive mice [59]. Bu-Shen-He-Mai (BSHM) granuleswere found to significantly increase the density of Foxp3, circulating Tregs, and IL-10 in the spleen but decrease the density of RORγt in the spleen, circulating Th17 lymphocytes, IL-6, and IL-17A. BSHM inhibits the inflammatory response and improves the Th17/Treg balance, thereby inhibiting the development and progression of hypertension [60].
3.4 Gut microbiota
The gastrointestinal tract is the largest immune organ in the human body, and the gut and gut microbiota are closely related to immune activation and immune regulation. In one study, three-dimensional principal component analysis of fecal bacterial communities in normotensive Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats revealed significant differences in microbial community composition between the two groups [61]. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota contributes to the development of hypertension [62]. Gut microbiota dysbiosis occurs before the development of hypertension, and the gut microbiota has a direct impact on host BP.
3.4.1 By regulating gut microbial immunity
Recent studies have found that as an important part of the gut microbial immune response, IL-17A drives the infiltration and inflammation of vascular immune cells and promotes sodium- and angiotensin II-mediated vascular dysfunction and hypertension [63]. Toral et al. [64] found that transplantation of spontaneously hypertensive rats with fecal microbiota from normotensive WKY rats reduced BP and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase activities, ameliorated IL-17A-mediated immune cell infiltration, and improved angiotensin II-induced endothelial dysfunction and cardiorenal hypertrophy. The Th17/Treg balance in mesenteric lymph nodes and the aorta was restored in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive germ-free mice, which exhibited attenuated IL-17A-induced leukocyte adhesion, reduced vascular and renal inflammatory infiltration, and decreased BP compared with conventional mice [65]. In summary, increased intestinal permeability allows bacteria, as well as IL-17A and other inflammatory factors, to enter the systemic circulation and reach the kidneys, which aggravates renal inflammation and renal damage under hypertension, resulting in impaired glomerular selectivity and tubular secretory activity and an imbalance in internal environmental homeostasis.
3.4.2 By affecting intestinal probiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics can prevent the occurrence of dysbiosis and vascular endothelial dysfunction and alleviate hypertension in hypertensive patients [66]. A high-sodium diet can significantly reduce the survival rate of the Lactobacillus intestinal population and increase intestinal permeability. Supplementation with Lactobacillus as a probiotic can prevent the development of salt-sensitive hypertension by reducing the polarization of Th17 cells and the production of IL-17A through Lactobacillus-induced indole-3-lactic acid [67]. In addition, lactulose can be added to the diet as a prebiotic to maintain a healthy intestinal microenvironment. Compared with untreated high-salt diet mice, high-salt diet mice treated with lactulose showed significant reductions in IL-17A mRNA levels in the small intestine, serum IL-17A and IL-22 levels, inflammatory cytokine levels, and inflammatory cell infiltration. They also showed increased fecal sodium excretion, relieved constipation, regulated intestinal flora, and reduced intestinal permeability. Lactulose also alleviated salt-sensitive hypertension [68].
3.4.3 Pressor role of IL-17A in the interaction between the gut and brain
Recent studies have found that the gut microbiota and CNS regulate BP through two-way communication. Increased neural activity in the CNS promotes enhanced intestinal sympathetic drive, gut dysbiosis, and increased intestinal permeability and inflammatory states. In contrast, fecal transplantation from normotensive WKY rats in the spontaneously hypertensive rat group significantly reduced BP, PVN inflammation, and central sympathetic excitation [37]. IL-17A can directly act on sympathetic nerve axons and nerve endings, promote growth, and increase the permeability of the BBB and the small intestinal epithelial barrier [69]. The immunosuppressive agent mycophenolate mofetil can reduce immune cell infiltration and NADPH oxidase activity in the PVN of the hypothalamus, reduce IL-17A-induced neuroinflammation and sympathetic remodeling during inflammation, improve intestinal integrity, dysbiosis, and aortic endothelial function, and reduce arterial BP in hypertensive rats [70].
Collectively, the gut microbiota activates immune cells, leading to low-grade inflammation that circulates, affecting the brain, autonomic nervous system, and kidneys (Figure 2). The amplified cascade of sympathetic nerve activity and vascular immune inflammation in the nervous system connects the kidneys, CNS, intestines, and blood vessels and then participates in the development and progression of hypertension through target organs, such as the kidneys, brain, intestines, and blood vessels. The role of IL-17A in the treatment of hypertension still needs to be proven by a large number of experiments. The mechanism of hypertension induced by organs such as the kidneys, CNS, intestines, and blood vessels is not a one-to-one connection but a mutual interaction among several organs to promote an increase in BP.
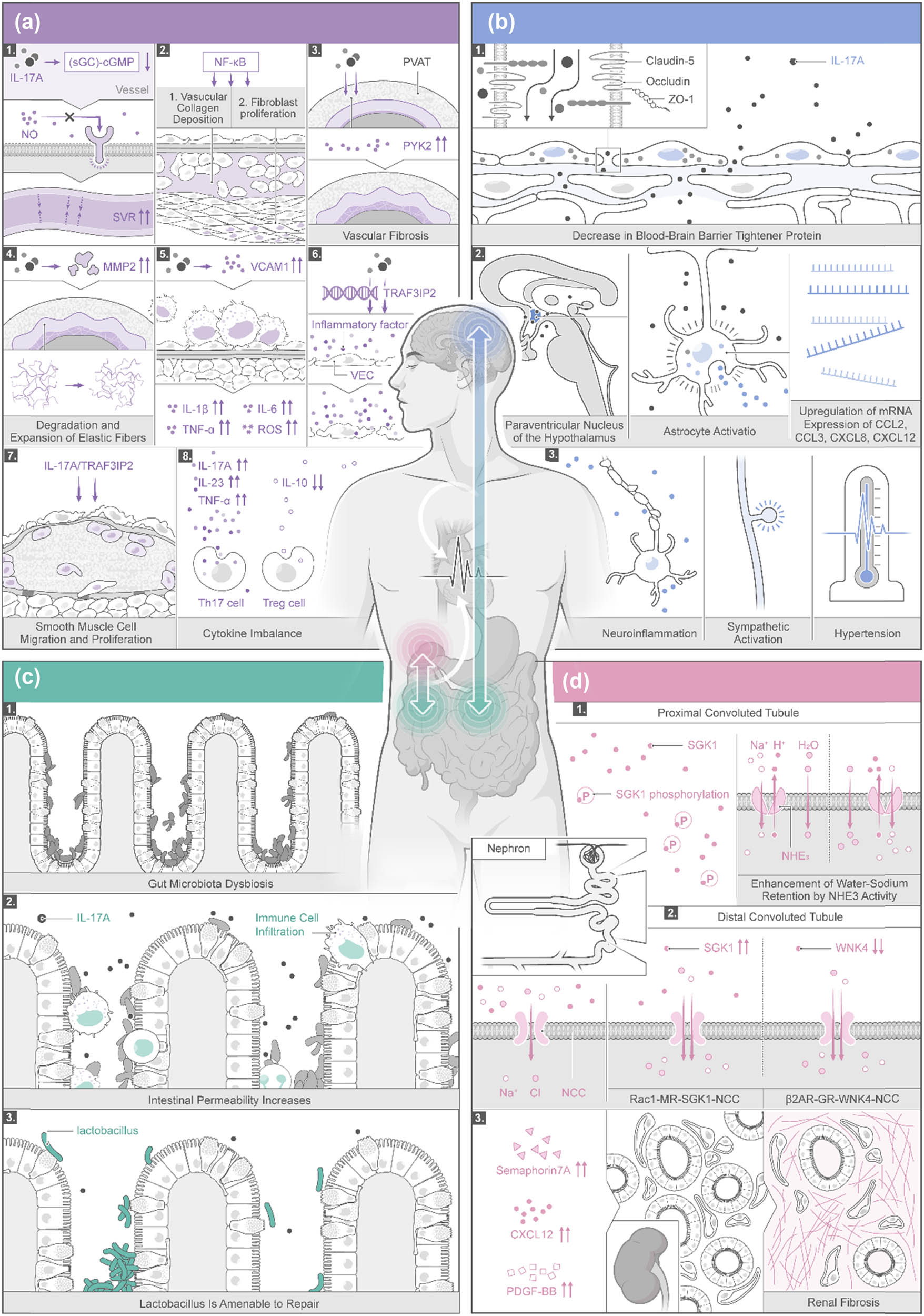
Mechanisms of IL-17A-induced hypertension through multiple pathways in the vascular system (a), brain (b), intestinal microbiota (c), and kidneys (d). When the inflammation from gut microbiota gets further into the circulating bloodstream, the brain, autonomic nervous system, and kidneys will be affected.
4 Anti-IL-17A in the treatment of hypertension
4.1 Application of IL-17A inhibitors
As a potential biological marker of cardiovascular risk, IL-17A is closely related to cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, heart failure, viral myocarditis, and hypertension. Anti-IL-17A therapy can not only improve the skin manifestations of psoriasis but also improve cardiovascular inflammation, vascular function, and metabolic factors in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis, and PsA [71]. From the perspective of clinical trials of anti-cytokine drugs, it has been found that canakinumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-1β, successfully prevented cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction [72]. IL-1 receptor antagonists have been reported to reduce BP in obese individuals [73]. Specific monoclonal antibodies directly targeting IL-17A (secukinumab and ixekizumab) and antibodies and drugs acting on IL-17A and IL-17F (bimekizumab) have been used in the clinical treatment of psoriasis with hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases, as well as other cardiovascular risk factors. They have achieved significant benefits for patients with cardiovascular diseases [74,75]. In addition, statins can reduce the proinflammatory and prothrombotic effects of IL-17A and TNF-α on endothelial cells by acting through the cholesterol pathway [76]. Metformin treatment reduced IL-17A expression, mediated redox balance, add an anti-inflammatory effect, and protected endothelial function [77,78].
In the mouse neurovascular coupling (NVC) injured model induced by angiotensin (Ang) II in the context of hypertension, IL-17A promoted the generation of cerebral superoxide anion production. While the application of neutralization of IL-17A or specific inhibition of its receptor ameliorated NVC damage [79]. However, Jiang et al. found anti-IL-17 treatment might escalate hypertension risk [80]. They conducted a meta-analysis on 9,909 patients with diverse autoimmune diseases who received anti-IL-17 agents, which revealed only secukinumab exhibited a notable association with hypertension among secukinumab, ixekizumab, bimekizumab, and brodalumab these four agents.
4.2 Safety of IL-17A inhibitors
It is well recognized that IL-17 pathway plays a significant role in defending against non-system fungal infections [81]. IL-17A inhibition usually leads to adverse events like paradoxical psoriasis [82] and atopic-like eczema [83]. At present, most of the side effects of treatment are found in the treatment of other diseases, such as ankylosing spondylitis [84], PsA [85], etc. The safety of IL-17A inhibitors needs a larger sample size and longer follow-up times to be verified. As IL-17A is rarely used in hypertensive diseases, the side effects of hypertension remain to be further explored.
In summary, anti-IL-17A therapy may provide a new perspective for the prevention of inflammatory diseases and the treatment of hypertension in the general population. Improvements in cardiovascular events may be a direct result of specific or relatively nonspecific anti-inflammatory treatments. Whereas, current research about the application of IL-17A inhibitors in hypertension is relatively rare. Whether in basic research or clinical trials, IL-17A inhibitors have not been used in hypertensive diseases. From the current research results, first, the effective and safe dose of IL-17A inhibitor is uncertain, and second, the application of the inhibitor in multiple diseases cannot be determined that it plays an effective protective role in multiple diseases.
5 Conclusions
In this review, the various ways in which IL-17A regulates BP are summarized systematically at molecule level, such as sodium and water retention, central sympathetic outflow and excitability, oxidative stress, vascular fibrosis, arterial stiffness, vascular dysfunction, and intestinal flora imbalance. At the organ level, IL-17A participates in and mediates the development and progression of hypertension in the kidneys, brain, intestines, and blood vessels. The current study suggests that IL-17A may play an important role in salt-sensitive hypertension, and remains to be studied in other types of hypertension. Novel therapies targeting IL-17A signaling have been approved for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and have shown promise in both animal models and human studies of hypertension. However, further investigation is required into these drugs to determine their specific suitability for the treatment of high BP. At present, there are clear clinical applications of successful IL-17A target therapy standards for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. However, no clinical studies have reported the therapeutic effect of targeting IL-17A in hypertensive patients, so relevant clinical cohort studies are needed to fill this gap.
Since IL-17A plays an effective role in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, hypertensive diseases, and tumor suppression, targeting it may have multiple protective effects in clinical therapy. It will also be an important research direction to apply it to other IL-17A-based cell-targeted biotherapy treatments currently under development and to target more specifically on IL-17A for the treatment of hypertension.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the numerous study investigators, fellows, and research coordinators who participated in the study.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ruiyuan Li drafted the manuscript, Lipeng Guo conceived the idea and supervised it, Bin Liang, Wei Sun, and Feng Hai revised the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data related to this article may also be requested from the corresponding authors (13889661829@163.com).
References
[1] Rosenzweig HL, Vance EE, Asare-Konadu K, Koney KV, Lee EJ, Deodhar AA, et al. Card9/neutrophil signalling axis promotes IL-17A-mediated ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83:214–22.10.1136/ard-2022-223146Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Vecellio M, Hake VX, Davidson C, Carena MC, Wordsworth BP, Selmi C. The IL-17/IL-23 axis and its genetic contribution to psoriatic arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:596086.10.3389/fimmu.2020.596086Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Berry SPD-G, Dossou C, Kashif A, Sharifinejad N, Azizi G, Hamedifar H, et al. The role of IL-17 and anti-IL-17 agents in the immunopathogenesis and management of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;102:108402.10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108402Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Nordlohne J, von Vietinghoff S. Interleukin 17A in atherosclerosis - regulation and pathophysiologic effector function. Cytokine. 2019;122:154089.10.1016/j.cyto.2017.06.016Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Liuzzo G, Trotta F, Pedicino D. Interleukin-17 in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease: the good, the bad, and the unknown. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:556–9.10.1093/eurheartj/ehs399Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Xue G-L, Li D-S, Wang Z-Y, Liu Y, Yang J-M, Li C-Z, et al. Interleukin-17 upregulation participates in the pathogenesis of heart failure in mice via NF-κB-dependent suppression of SERCA2a and Cav1.2 expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42:1780–9.10.1038/s41401-020-00580-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Baumhove L, van Essen BJ, Dokter MM, Zijlstra SN, Deiman FE, Laman JD, et al. IL-17 is associated with disease severity and targetable inflammatory processes in heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2024;11(6):3530–8.10.1002/ehf2.14968Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Zhang Q, Liu S, Parajuli KR, Zhang W, Zhang K, Mo Z, et al. Interleukin-17 promotes prostate cancer via MMP7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 2017;36:687–99.10.1038/onc.2016.240Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Liang H, Liu Y, Guo J, Dou M, Zhang X, Hu L, et al. Progression in immunotherapy for advanced prostate cancer. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1126752.10.3389/fonc.2023.1126752Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–32.10.1038/ni1254Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Ruggeri Barbaro N, Van Beusecum J, Xiao L, do Carmo L, Pitzer A, Loperena R, et al. Sodium activates human monocytes via the NADPH oxidase and isolevuglandin formation. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117:1358–71.10.1093/cvr/cvaa207Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Wang Z, Wang J, Yang P, Song X, Li Y. Elevated Th17 cell proportion, related cytokines and mRNA expression level in patients with hypertension-mediated organ damage: a case control study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022;22:257.10.1186/s12872-022-02698-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Jiang Y, Wang X, Dong C. Molecular mechanisms of T helper 17 cell differentiation: emerging roles for transcription cofactors. Adv Immunol. 2019;144:121–53.10.1016/bs.ai.2019.09.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Cao Y, Yu Y, Xue B, Wang Y, Chen X, Beltz TG, et al. IL (Interleukin)-17A acts in the brain to drive neuroinflammation, sympathetic activation, and hypertension. Hypertension. 2021;78:1450–62.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18219Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Orejudo M, Rodrigues-Diez RR, Rodrigues-Diez R, Garcia-Redondo A, Santos-Sánchez L, Rández-Garbayo J, et al. Interleukin 17A participates in renal inflammation associated to experimental and human hypertension. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1015.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Byrne EM, Llorián-Salvador M, Tang M, Margariti A, Chen M, Xu H. IL-17A damages the blood-retinal barrier through activating the janus kinase 1 pathway. Biomedicines. 2021;9:831.10.3390/biomedicines9070831Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Saleem M, Aden LA, Mutchler AL, Basu C, Ertuglu LA, Sheng Q, et al. Myeloid-specific JAK2 contributes to inflammation and salt sensitivity of blood pressure. Circ Res. 2024;135:890–909.10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.323595Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Yang J, Zhang M, Song Q, Li S, Zhao X, Kan L, et al. Integrating network pharmacological and experimental models to investigate the therapeutic effects of baicalein in glaucoma. Chin Med. 2021;16:124.10.1186/s13020-021-00537-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Raifer H, Mahiny AJ, Bollig N, Petermann F, Hellhund A, Kellner K, et al. Unlike alphabeta T cells, gammadelta T cells, LTi cells and NKT cells do not require IRF4 for the production of IL-17A and IL-22. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:3189–201.10.1002/eji.201142155Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Li J, Xu L, Zhao W, Pan J, Lu J, Lu H, et al. Serum IL-17A concentration and a IL17RA single nucleotide polymorphism contribute to the risk of autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2022;38:e3547.10.1002/dmrr.3547Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Sigurdardottir S, Zapadka TE, Lindstrom SI, Liu H, Taylor BE, Lee CA, et al. Diabetes-mediated IL-17A enhances retinal inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular permeability. Cell Immunol. 2019;341:103921.10.1016/j.cellimm.2019.04.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Norlander AE, Saleh MA, Kamat NV, Ko B, Gnecco J, Zhu L, et al. Interleukin-17A regulates renal sodium transporters and renal injury in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 2016;68:167–74.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07493Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Hirohama D, Kawarazaki W, Nishimoto M, Ayuzawa N, Marumo T, Shibata S, et al. PGI(2) analog attenuates salt-induced renal injury through the inhibition of inflammation and Rac1-MR activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4433.10.3390/ijms21124433Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Yang YS, Xie J, Yang SS, Lin SH, Huang CL. Differential roles of WNK4 in regulation of NCC in vivo. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2018;314:F999–1007.10.1152/ajprenal.00177.2017Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Nagase M, Fujita T. Role of Rac1-mineralocorticoid-receptor signalling in renal and cardiac disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9:86–98.10.1038/nrneph.2012.282Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawarazaki W, Kurihara H, Tanaka H, et al. Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase: implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:1370–6.10.1038/nm.1879Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Palmada M, Dieter M, Speil A, Böhmer C, Mack AF, Wagner HJ, et al. Regulation of intestinal phosphate cotransporter NaPi IIb by ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 and by serum- and glucocorticoid-dependent kinase 1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G143–50.10.1152/ajpgi.00121.2003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Ueda K, Nagase M. Mineralocorticoid receptor activation as an etiological factor in kidney diseases. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014;18:16–23.10.1007/s10157-013-0827-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Fujita T. Mechanism of salt-sensitive hypertension: focus on adrenal and sympathetic nervous systems. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:1148–55.10.1681/ASN.2013121258Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Mishra S, Ingole S, Jain R. Salt sensitivity and its implication in clinical practice. Indian Heart J. 2018;70:556–64.10.1016/j.ihj.2017.10.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Norlander AE, Saleh MA, Pandey AK, Itani HA, Wu J, Xiao L, et al. A salt-sensing kinase in T lymphocytes, SGK1, drives hypertension and hypertensive end-organ damage. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e92801.10.1172/jci.insight.92801Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Krishnan SM, Ling YH, Huuskes BM, Ferens DM, Saini N, Chan CT, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome reduces blood pressure, renal damage, and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115:776–87.10.1093/cvr/cvy252Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Orejudo M, Rodrigues-Diez RR, Rodrigues-Diez R, Garcia-Redondo A, Santos-Sanchez L, Randez-Garbayo J, et al. Interleukin 17A participates in renal inflammation associated to experimental and human hypertension. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1015.10.3389/fphar.2019.01015Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Saleh MA, Norlander AE, Madhur MS. Inhibition of interleukin 17-a but not interleukin-17F signaling lowers blood pressure and reduces end-organ inflammation in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2016;1:606–16.10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.07.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Xiao L, Kirabo A, Wu J, Saleh MA, Zhu L, Wang F, et al. Renal denervation prevents immune cell activation and renal inflammation in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Circ Res. 2015;117:547–57.10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306010Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Ferrantelli E, Liappas G, Vila Cuenca M, Keuning ED, Foster TL, Vervloet MG, et al. The dipeptide alanyl-glutamine ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis and attenuates IL-17 dependent pathways during peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. 2016;89:625–35.10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Li L, Luo R, Yang Y, Cheng Y, Ge S, Xu G. Tamibarotene inhibit the accumulation of fibrocyte and alleviate renal fibrosis by IL-17A. Ren Fail. 2020;42:1173–83.10.1080/0886022X.2020.1847145Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Madhur MS, Lob HE, McCann LA, Iwakura Y, Blinder Y, Guzik TJ, et al. Interleukin 17 promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension. 2010;55:500–7.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.145094Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Markó L, Kvakan H, Park J-K, Qadri F, Spallek B, Binger KJ, et al. Interferon-γ signaling inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-induced cardiac damage. Hypertension. 2012;60:1430–6.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.199265Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Krebs CF, Lange S, Niemann G, Rosendahl A, Lehners A, Meyer-Schwesinger C, et al. Deficiency of the interleukin 17/23 axis accelerates renal injury in mice with deoxycorticosterone acetate + angiotensin ii-induced hypertension. Hypertension. 2014;63:565–71.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02620Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Chen H, Tang X, Li J, Hu B, Yang W, Zhan M, et al. IL-17 crosses the blood-brain barrier to trigger neuroinflammation: a novel mechanism in nitroglycerin-induced chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. 2022;23:1.10.1186/s10194-021-01374-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Yu XJ, Liu XJ, Guo J, Su YK, Zhang N, Qi J, et al. Blockade of microglial activation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus improves high salt-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2022;35:820–7.10.1093/ajh/hpac052Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Flor AFL, de Brito Alves JL, Franca-Silva MS, Balarini CM, Elias LLK, Ruginsk SG, et al. Glial cells are involved in ANG-II-induced vasopressin release and sodium intake in awake rats. Front Physiol. 2018;9:430.10.3389/fphys.2018.00430Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Yang ZY, Yuan CX. IL-17A promotes the neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18:147.10.1186/s12871-018-0607-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Yu Y, Weiss RM, Wei SG. Brain Interleukin-17A contributes to neuroinflammation and cardiac dysfunction in rats with myocardial infarction. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:1032434.10.3389/fnins.2022.1032434Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Chen Y, Li S, Guo Y, Yu H, Bao Y, Xin X, et al. Astaxanthin attenuates hypertensive vascular remodeling by protecting vascular smooth muscle cells from oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4629189.10.1155/2020/4629189Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Schuler R, Efentakis P, Wild J, Lagrange J, Garlapati V, Molitor M, et al. T cell-derived IL-17A induces vascular dysfunction via perivascular fibrosis formation and dysregulation of (.)NO/cGMP signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6721531.10.1155/2019/6721531Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Wu J, Thabet SR, Kirabo A, Trott DW, Saleh MA, Xiao L, et al. Inflammation and mechanical stretch promote aortic stiffening in hypertension through activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Circ Res. 2014;114:616–25.10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302157Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Krishnan SM, Dowling JK, Ling YH, Diep H, Chan CT, Ferens D, et al. Inflammasome activity is essential for one kidney/deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt-induced hypertension in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173:752–65.10.1111/bph.13230Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Diaz-Canestro C, Puspitasari YM, Liberale L, Guzik TJ, Flammer AJ, Bonetti NR, et al. MMP-2 knockdown blunts age-dependent carotid stiffness by decreasing elastin degradation and augmenting eNOS activation. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118:2385–96.10.1093/cvr/cvab300Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Yin L, Bai J, Yu WJ, Liu Y, Li HH, Lin QY. Blocking VCAM-1 prevents angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular remodeling in mice. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:825459.10.3389/fphar.2022.825459Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Sukhanov S, Higashi Y, Yoshida T, Mummidi S, Aroor AR, Jeffrey Russell J, et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor Empagliflozin attenuates interleukin-17A-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by targeting TRAF3IP2/ROS/NLRP3/Caspase-1-dependent IL-1beta and IL-18 secretion. Cell Signal. 2021;77:109825.10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109825Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Grunewald ZI, Ramirez-Perez FI, Woodford ML, Morales-Quinones M, Mejia S, Manrique-Acevedo C, et al. TRAF3IP2 (TRAF3 interacting protein 2) mediates obesity-associated vascular insulin resistance and dysfunction in male mice. Hypertension. 2020;76:1319–29.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15262Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Mummidi S, Das NA, Carpenter AJ, Yoshida T, Yariswamy M, Mostany R, et al. RECK suppresses interleukin-17/TRAF3IP2-mediated MMP-13 activation and human aortic smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:22242–59.10.1002/jcp.28792Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Sandip C, Tan L, Huang J, Li Q, Ni L, Cianflone K, et al. Common variants in IL-17A/IL-17RA axis contribute to predisposition to and progression of congestive heart failure. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e4105.10.1097/MD.0000000000004105Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Boehme AK, Esenwa C, Elkind MSV. Stroke risk factors, genetics, and prevention. Circ Res. 2017;120:472–95.10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308398Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Chen X, Zhang Y, Ding Q, He Y, Li H. Role of IL-17A in different stages of ischemic stroke. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;117:109926.10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109926Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Qiu M, Shu H, Li L, Shen Y, Tian Y, Ji Y, et al. Interleukin 10 attenuates angiotensin II-induced aortic remodelling by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced activation of the vascular p38 and NF-kappaB pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8244497.10.1155/2022/8244497Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Radwan E, Mali V, Haddox S, El-Noweihi A, Mandour M, Ren J, et al. Treg cells depletion is a mechanism that drives microvascular dysfunction in mice with established hypertension. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865:403–12.10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.10.031Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Zhang P, Song XY, Li W, Wei JL, Cui YJ, Qi YZ, et al. Study on the mechanism of Bu-Shen-He-Mai granules in improving renal damage of ageing spontaneously hypertensive rats by regulating Th17 cell/tregs balance. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2022;2022:8315503.10.1155/2022/8315503Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Robles-Vera I, de la Visitacion N, Toral M, Sanchez M, Gomez-Guzman M, Jimenez R, et al. Mycophenolate mediated remodeling of gut microbiota and improvement of gut-brain axis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;135:111189.10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111189Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Jiang S, Shui Y, Cui Y, Tang C, Wang X, Qiu X, et al. Gut microbiota dependent trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Redox Biol. 2021;46:102115.10.1016/j.redox.2021.102115Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[63] Yan D, Si W, Zhou X, Yang M, Chen Y, Chang Y, et al. Eucommia ulmoides bark extract reduces blood pressure and inflammation by regulating the gut microbiota and enriching the Parabacteroides strain in high-salt diet and N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester induced mice. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:967649.10.3389/fmicb.2022.967649Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[64] Toral M, Robles-Vera I, de la Visitacion N, Romero M, Sanchez M, Gomez-Guzman M, et al. Role of the immune system in vascular function and blood pressure control induced by faecal microbiota transplantation in rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;227:e13285.10.1111/apha.13285Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[65] Karbach SH, Schonfelder T, Brandao I, Wilms E, Hormann N, Jackel S, et al. Gut microbiota promote angiotensin II-induced arterial hypertension and vascular dysfunction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016;5:e003698.10.1161/JAHA.116.003698Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[66] Robles-Vera I, Toral M, de la Visitacion N, Sanchez M, Gomez-Guzman M, Romero M, et al. Probiotics prevent dysbiosis and the rise in blood pressure in genetic hypertension: role of short-chain fatty acids. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020;64:e1900616.10.1002/mnfr.201900616Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[67] Wilck N, Matus MG, Kearney SM, Olesen SW, Forslund K, Bartolomaeus H, et al. Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates T(H)17 axis and disease. Nature. 2017;551:585–9.10.1038/nature24628Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Zhang Z, Zhao J, Tian C, Chen X, Li H, Wei X, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota to investigate the mechanism of lactulose in negating the effects of a high-salt diet on hypertension. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019;63:e1800941.10.1002/mnfr.201800941Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[69] Chisholm SP, Cervi AL, Nagpal S, Lomax AE. Interleukin-17A increases neurite outgrowth from adult postganglionic sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1146–55.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5343-11.2012Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[70] Deng J, Zhou X, Wang M, Wang M, Zhou L, Meng G, et al. The effects of interleukin 17A on left stellate ganglion remodeling are mediated by neuroimmune communication in normal structural hearts. Int J Cardiol. 2019;279:64–71.10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.01.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[71] von Stebut E, Reich K, Thaci D, Koenig W, Pinter A, Korber A, et al. Impact of secukinumab on endothelial dysfunction and other cardiovascular disease parameters in psoriasis patients over 52 weeks. J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139:1054–62.10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.042Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[72] Rothman AM, MacFadyen J, Thuren T, Webb A, Harrison DG, Guzik TJ, et al. Effects of interleukin-1beta inhibition on blood pressure, incident hypertension, and residual inflammatory risk: a secondary analysis of CANTOS. Hypertension. 2020;75:477–82.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13642Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Urwyler SA, Ebrahimi F, Burkard T, Schuetz P, Poglitsch M, Mueller B, et al. IL (Interleukin)-1 receptor antagonist increases ang (angiotensin [1-7]) and decreases blood pressure in obese individuals. Hypertension. 2020;75:1455–63.10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13982Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[74] Elnabawi YA, Dey AK, Goyal A, Groenendyk JW, Chung JH, Belur AD, et al. Coronary artery plaque characteristics and treatment with biologic therapy in severe psoriasis: results from a prospective observational study. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115:721–8.10.1093/cvr/cvz009Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[75] Egeberg A, Wu JJ, Korman N, Solomon JA, Goldblum O, Zhao F, et al. Ixekizumab treatment shows a neutral impact on cardiovascular parameters in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: results from UNCOVER-1, UNCOVER-2, and UNCOVER-3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79:104–9.e108.10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.074Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] Liu Z, Zhao Y, Wei F, Ye L, Lu F, Zhang H, et al. Treatment with telmisartan/rosuvastatin combination has a beneficial synergistic effect on ameliorating Th17/Treg functional imbalance in hypertensive patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233:291–9.10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.12.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[77] Bharath LP, Agrawal M, McCambridge G, Nicholas DA, Hasturk H, Liu J, et al. Metformin enhances autophagy and normalizes mitochondrial function to alleviate aging-associated inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020;32:44–55.e46.10.1016/j.cmet.2020.04.015Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[78] Chen C, Kassan A, Castaneda D, Gabani M, Choi SK, Kassan M. Metformin prevents vascular damage in hypertension through the AMPK/ER stress pathway. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:960–9.10.1038/s41440-019-0212-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[79] Youwakim J, Vallerand D, Girouard H. Neurovascular coupling in hypertension is impaired by IL-17A through oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:3959.10.3390/ijms24043959Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[80] Jiang K, Jia Y, Chen L, Huang F, Chen M. Association of interleukin-17 inhibitors with hypertension in patients with autoimmune diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized controlled trials. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024;83:557–64.10.1097/FJC.0000000000001547Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[81] Blauvelt A, Lebwohl MG, Bissonnette R. IL-23/IL-17A dysfunction phenotypes inform possible clinical effects from anti-IL-17A therapies. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:1946–53.10.1038/jid.2015.144Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[82] Messina F, Piaserico S. The dark side of the moon: the immune-mediated adverse events of IL-17A/IL-17R inhibition. J Dermatol Treat. 2022;33:2443–54.10.1080/09546634.2022.2062281Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[83] Tang X, Li Q, Zhou Y, Zheng X, Zhou C, Hu Y, et al. Predictive factors of atopic-like dermatitis induced by IL-17A inhibitors in patients with psoriasis: a 2-year follow-up study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:2509–16.10.1111/jdv.19394Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[84] Wang P, Zhang S, Hu B, Liu W, Lv X, Chen S, et al. Efficacy and safety of interleukin-17A inhibitors in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40:3053–65.10.1007/s10067-020-05545-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[85] Skougaard M, Søndergaard MF, Ditlev SB, Kristensen LE. Changes in inflammatory cytokines in responders and non-responders to TNFα inhibitor and IL-17A inhibitor: a study examining psoriatic arthritis patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25:3002.10.3390/ijms25053002Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms


