Abstract
In this study, we prepared a silica nanoparticle from South African fly ash (SAFA), using a facile microwave (MW)-assisted sol–gel template free syntheses method. Prepared silica nanoparticles (SNPMW) were characterized using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transition electron microscope (TEM), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (S BET) surface area analysis, and ultraviolet visible diffuse reflection spectroscopy. XRF analysis suggests SAFA as fly ash class F. The XRD pattern reveals the structural composition of SAFA and the amorphous nature of extracted SNP, while the FTIR assay shows the presence of silanol and siloxane groups. SEM and TEM analyses revealed primary silica nanoparticles were roughly spherical with sizes of about <200 nm. EDX spectra confirm the presence of SiO2. The optical bandgap of SNPMW was established to be 4.67 eV. The application of SNPMW demonstrated that it can be used to remove Pb2+ from an aqueous solution. Test results show the optimum treatment time as 60 minutes, while removal efficiency increases from 66.76 to 96.64% as the pH rises from 3 to 5, but as the pH rises above 5, the efficiency decreases. The use of an MW-assisted sol–gel preparation method gave rise to an elevated reaction rate with minimal contamination and thinner particle size SNPMW, which was utilized for the removal of Pb2+ in an aqueous solution.
1 Introduction
Coal is used across the globe as a major energy source [1,2,3]. Coal provided 29% of the world’s electricity in 2015; the share of coal is still projected to be 24% by 2035, reflecting rises in the use of renewables. However, global energy demand is projected to rise by 28% between 2015 and 2040 [4]. Coal burning has historically been connected with environmental pollution, and soil degradation concerns, extending from water and air pollution to human health concerns [5,6,7]. The sweltering of coal in a power plant at high temperatures and pressures produces multiple ash types [8,9,10,11,12,13]. The “fine” ash portion is transported together with the flue gases upwards and collected by highly powerful electrostatic precipitators before meeting the atmosphere. This substance is referred to as fly ash. It is primarily made of very fine, glassy spheres which look like clay. The coarse ash fraction slides under the boilers onto the grates, where it is combined and pumped with water and into lagoons [5]. Depending on the oxide content of Al, Fe, and Si, ASTM C618 has graded fly ash into two groups [14]. Those fly ash rich in silica material is graded as class F, while class C fly ash is considered to have higher calcium content [14]. Nevertheless, because of its heterogeneous structure and physical characteristics, it becomes more difficult to classify the character of coal fly ash (CFA). However, the differing composition of CFA differs on the coal source, type of boiler, working state, post-combustion technology, and technology of the power plant [15]. South Africa’s electricity power company (Eskom) absorbs over 120 million tons of coal per year, producing over 34 million tons of CFA. Just about 5% of this fly ash is exploited, mainly in building and cement industries [16]. In many applications, CFA is used to replace naturally occurring minerals and aggregates. Around 40–65% of the total ash is silica, so one of the primary benefits of modern technologies is the possibility of silica recovery and refining into silicate products is one of the main advantages of modern developments [17].
Microwave (MW) synthesis provides benefits that are accomplished in a small reaction time cycle [17,18,19,20]. MW irradiation is an in-situ way of energy conversion, which differs dramatically from conventional heating methods; MW-assisted sol–gel synthesis is a comparatively novel approach for processing metal oxide nanoparticles [19]. More recently, due to its various advantages of generating compact, the MW-assisted sol–gel process has piqued attention due to its ordered particle size, high specific surface area, precise morphology, and higher purity due to shorter reaction time. Phase simplicity, energy saving, high yield, clean, and inexpensive are some of the advantages of MW processing [21]. Researchers have reported the use of MW sol–gel synthesis methods for silica nanoparticle preparation [22,23]. Mily et al. prepared silica nanoparticles using MW-assisted sol–gel reaction of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and reported that this technology as opposed to ordinary heating allows for smaller particle size distribution with a quicker response time [24]. Inada et al. prepared submicrometer spheres of SiO2 and SiO2–TiO2 using MW-assisted sol–gel reaction of TEOS and Ti(OC2H5)4 using stearyltrimethylammonium chloride (C18TAC) as a template and reported a quicker response time with smaller particle size distribution [25].
When acceptable levels of heavy metals like Pb2+ in the aqueous environment are exceeded, they have the potential to harm both human physiology and biological systems [26]. Metal pollutants have been removed from water using a variety of methodologies, including precipitation, adsorption, membrane filtration, and ion exchange [27]. On the other hand, adsorption has been demonstrated to be a cost-efficient and resourceful method of eradicating heavy metals, organic pollutants, and dyes from contaminated waters [27,28,29,30]. Various adsorbents, such as activated carbon, have greater adsorption capability but cannot be used on an industrial scale for wastewater treatment due to their high cost. The development of inexpensive adsorbents that can effectively eliminate organic pollutants and toxic heavy metals from wastewater is always in demand [30]. From previous research, agrarian derivatives and agricultural products are utilized as affordable adsorbents to remove metal ions from aqueous streams [31]. Applications of silica particles are common in industry, nanotechnology, and medicine [30]. From previous research, silica nanoparticles have been utilized for the elimination of Pb2+ from aqueous solution [31,32,33,34,35].
Preparation of South African fly ash silica nanoparticles is limited to a single analysis by Mathibela et al., synthesizing silica nanoparticles using H2SO4 as catalyst and polyethylene glycol as surfactant through a sol–gel process and achieving a 99.3% SiO2 purity and 26% yield [36]. Chinese fly ash yield was estimated at 37.3% [37] and approximately 62% purity of SiO2 [38]. To the author’s best knowledge, there has been no exposition of the MW-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis method for SAFA. In this analysis, the MW-assisted sol–gel technique was employed for the synthesis of amorphous nano-silica from South African fly ash (SAFA). X-Ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), S BET, ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflection spectroscopy (UV–vis DRS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) were utilized for the characterization of the isolated nano-silica. The extracted SNPMW was utilized for the elimination of Pb2+ in an aqueous solution.
2 Experimental
2.1 Extraction of silica
Samples of CFA were collected from a South African thermal power plant. The samples were pre-treated by froth floatation to remove unburned carbon and floating beads [39]. Silica extraction from SAFA was carried out using the MW-assisted sol–gel, template-free method; 50 g of SAFA (Figure 1a) was added to a 500 mL solution of 3 M NaOH and boiled for 60 min using a water bath with incessant agitation to dissolve SiO2 present in SAFA and generate a solution of sodium silicate (NaSiO3). The residue was rinsed with hot deionized water, thereafter the hot solution was filtered using ash-free filter paper. The filtrate solution was then allowed to cool before being titrated with 1 M HCl to a pH of 7.0–7.5. The resulting solution was left to stand for 30 min to allow for the formation of aqua gel (Figure 1b). The silica aqua gel was placed in an MW oven (LG Electronics Model No. MS2596OB) with 1,000 W power and 2,450 MHz for 90 s. The MW equipment was pre-set at 80°C with on–off cycle (20 s on–40 s off) [18]. The samples were cool and centrifuged. The resulting white xerogel (Figure 1c) was dried at 80°C and subjected to successive washing cycles using warm water (40°C), and finally dried at 105oC to constant weight (Figure 1d). This way, minerals and impurities are easily separated from the silica. This is because it is more effective to wash the dried silica (xerogel) with deionized water than to wash the silica gel (aqua gel) before drying, to extract the silica minerals [31,32,40,41]. The material mass was reported to estimate the yield of silica nanoparticles and the purity of the extracted SNPMW.
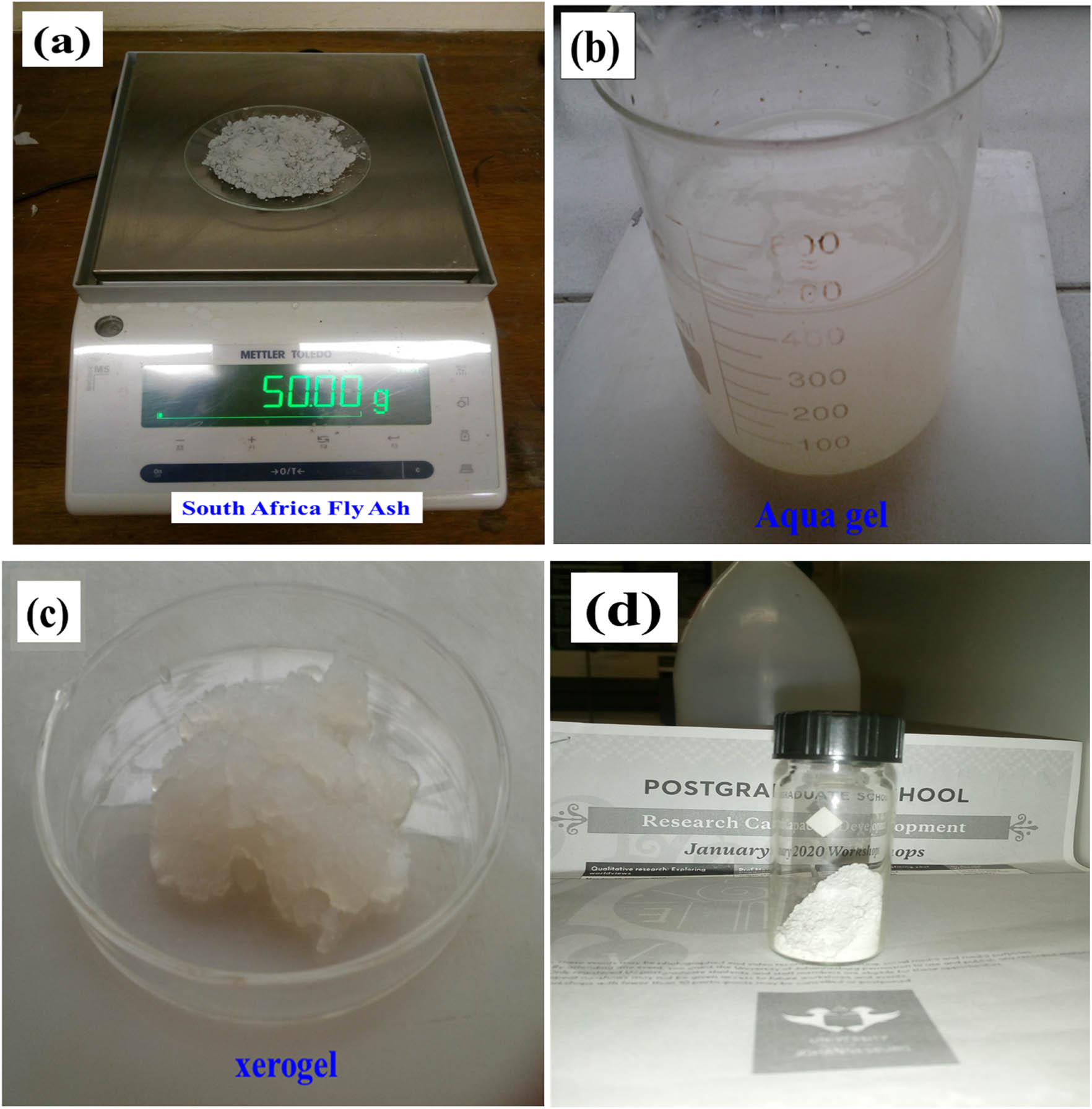
(a) South African fly ash, (b) aqua gel, (c) xerogel, and (d) extracted SNPMW.
2.2 Materials characterizations
Elemental composition was determined by “MagiX PRO” wavelength dispersive XRF spectrometer from PANalytical. XRD analysis of crystal structure was analysed using powdered sample by a Philips/PANalytical X´Pert Powder Diffractometer at 40 kV acceleration voltage, 40 mA current from two theta (2θ) 15–55°. Surface morphology was analysed using a TESCAN VEGA3 SEM microscope attached with Oxford X-Max for EDX analysis. The samples were first placed on a carbon substrate in the sample holder and then sputter coated with carbon and placed in the SEM chamber, and the samples were analysed under vacuum. The samples for the TEM analysis were first sonicated in absolute ethanol for 5 min, and a few drops of the sample solution were placed on a carbon-coated copper grid (Sample holder) and used for the analysis in a JEM-2100 JEOL electron attached with EDX. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (S BET) was utilized for surface area analysis, fine powdered samples were first placed in 6 mm cells and degassed before analysis using a micrometric Trista II Plus. Absorption/desorption was carried out in N2 at 77 K, using powdered samples. Particle size was examined using Scanning Probe Image Processor (MountainsSPIP 8). The optical bandgap was determined by the Tauc plot employing UV-Vis DRS (Cary 5000).
2.3 Application of extracted SiO2 nanoparticle in removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution
The influence of reaction time and pH on the removal efficiency of Pb2+ in an aqueous solution was investigated. Five Erlenmeyer flasks (250 mL) were filled with 100 mL of a solution containing 10 mg/L Pb2+ and adjusted to pH 4, pH 5, pH 6, pH 7, and pH 8, respectively, with 0.01 N HNO3 and NaOH. About 0.1 g of SNPMW was weighed, filled into each Erlenmeyer flask, and then agitated at 200 rpm for 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 min, respectively. The remaining Pb2+ concentration in the solution was determined using an ICP-OES iCAP 6000 machine. The effect of Pb2+ initial concentration (10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, and 40 mg/L) and SNPs absorbent dosage (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 g/L) at pH of 5 was also studied. The adsorption equilibrium data of Pb2+ on silica nanoparticles obtained from South Africa CFA were computed using Langmuir isotherm models.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 XRF analysis
XRF analysis of SAFA and extracted silica nanoparticles using MW-assisted sol–gel (SNPMW) are shown in Table 1. SAFA contains mainly Al2O3 CaO, Fe2O3 SiO2, and other minor elements. After extraction, the SNPMW yield was 30.35%. This can be attributed to the synthesis method employed in the extraction process. This was slightly higher than the 26% yield previously reported by SAFA [36]. As per ASTM C618, this SAFA is classified as fly ash class F because of its high silica and alumina concentration [10,14].
Chemical composition of SAFA and SNPMW using XRF analysis
| Mineral composition | Concentration (wt%) | |
|---|---|---|
| SAFA | SNPMW | |
| Al2O3 | 32.66 | 0.11 |
| BaO | 0.13 | 0.00 |
| CaO | 0.93 | 0.02 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Fe2O3 | 2.42 | 0.04 |
| K2O | 0.43 | 0.03 |
| MgO | 1.53 | 0.00 |
| Na2O | 4.30 | 0.01 |
| P2O5 | 0.61 | 0.00 |
| SiO2 | 52.63 | 98.91 |
| SO3 | 0.35 | 0.00 |
| TiO2 | 1.72 | 0.00 |
| LOI | 2.23 | 0.88 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
3.2 XRD analysis
XRD Analysis for both fly ash and SNPMW samples is displayed in Figure 2. SAFA samples consist of crystalline phases of Anhydrite [CaSO4], Mullite (Al6Si2O13), Quartz (SiO2), and Hydrosodalite [Na8(AlSiO4)6(OH)2·nH2O]. These data were consistent with those of previously published literature [42,43,44]. A broad diffraction peak was observed for SNPMW at 2θ = 19–25o, which confirms the extracted silica nanoparticles to be amorphous [21,22,30,36,37]; this was consistent with ICDD database PDF # 01-089-8935.
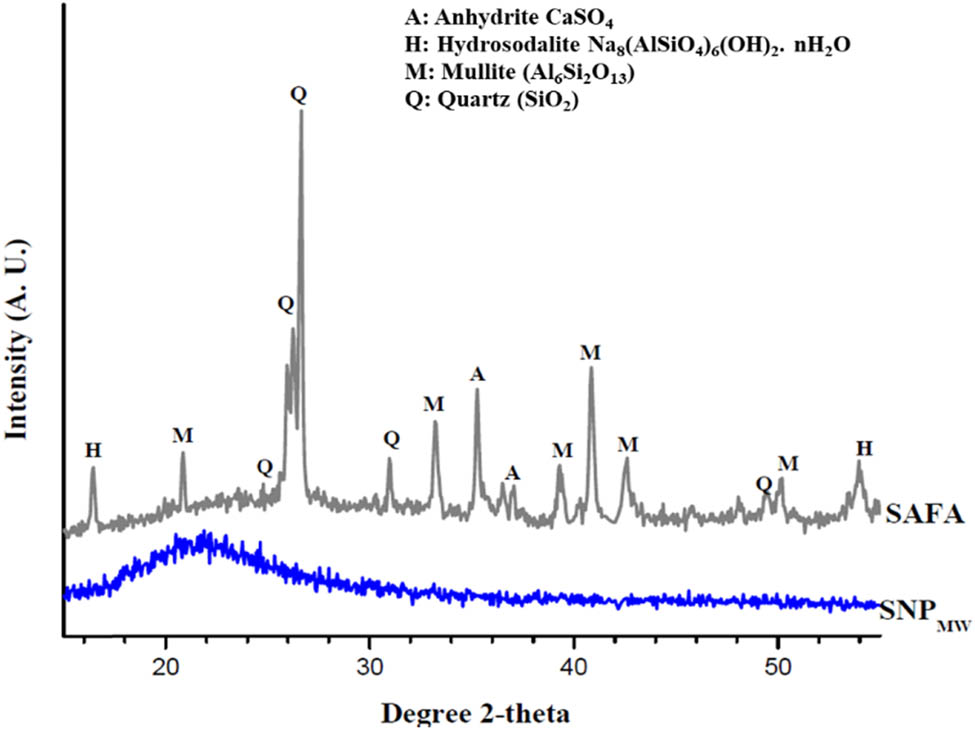
XRD Analysis of SAFA and extracted SNPMW.
3.3 FTIR analysis
FTIR Spectra are shown in Figure 3. Broadband observed at 3450.34–2925.25 cm−1 is owing to O–H bond stretching vibration from the Si–OH silanol groups, which is due to silica surface adsorbed H2O molecules [21,31,32,36]. It was observed that SAFA contains more absorbed water molecules than SNPMW. Banding vibration at 1650.37–1420.24 cm−1 is the result of O–H bond bending vibration, suggesting that the samples consist of absorbed water. However, absorbed water shows a reduction after silica extraction [45–47]. FTIR spectral that is typical of silica nanoparticles was observed at 1070.48 cm−1; this is due to intermittent stretch vibration caused by Si–O–Si [36,48,49]. Si–O–Si symmetric stretching vibration network was assigned to 805.43 cm−1 [50]. The O–Si–O vibrational modes characteristic peak was detected at 580.24–471.64 cm−1 [51].
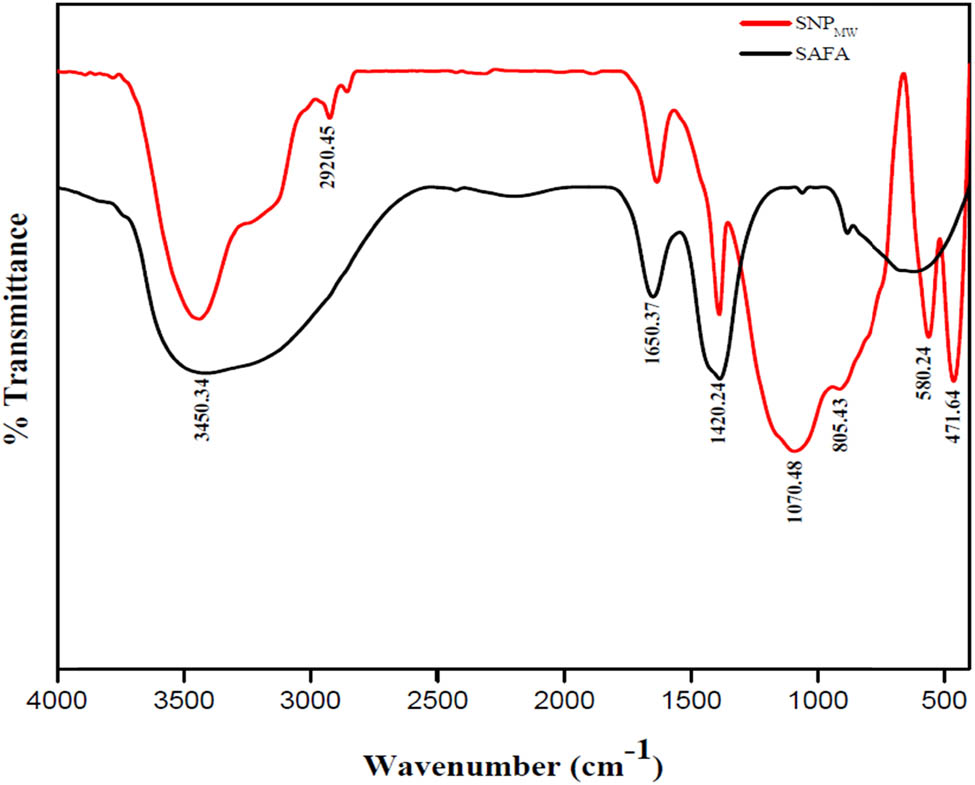
FTIR Spectra of SAFA and SNPMW.
3.4 SEM-EDX analysis
The morphology of SAFA particles is shown in Figure 4. From the SEM illustration Figure 4(a), SAFA appears like a group of ellipsoidal and spheroidal bodies of differing dimensions as well as fragments of peculiar forms. Similar results were published by Kutchko et al. [15] and Zhu et al. [52]. These earlier studies revealed that the length of SAFA particles is not constant and that small particles do cling to the surfaces of certain spheroidal particles, as was also detected in this research. Figure 4(b) displays the EDX of SAFA. SiO2 was observed as the most prominent element present followed by Al2O3; these results correlate with the XRF analysis of SAFA. SEM image of extracted SNPMW is shown in Figure 5(a). It was revealed that primary silica nanoparticles formed agglomeration. The SNPMW particle size diameter ranges from 48 to 87 nm and an average particle size diameter of 67 nm, according to the scanning probe image processor (MountainsSPIP 8) analysis. EDX spectral 5(b) shows negligible impurities that are usually associated with the process of sol–gel extraction.
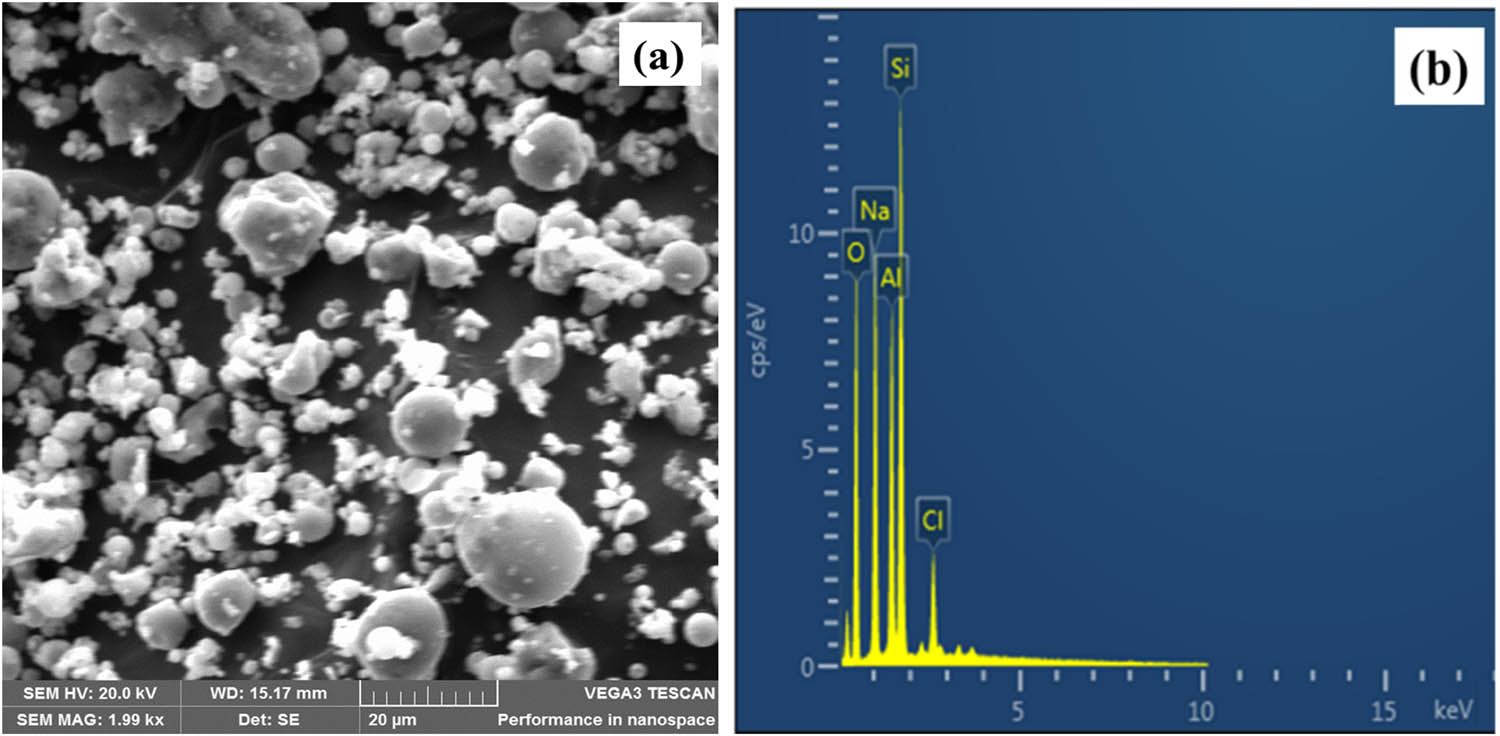
Morphology of SAFA: (a) SEM and (b) EDX.
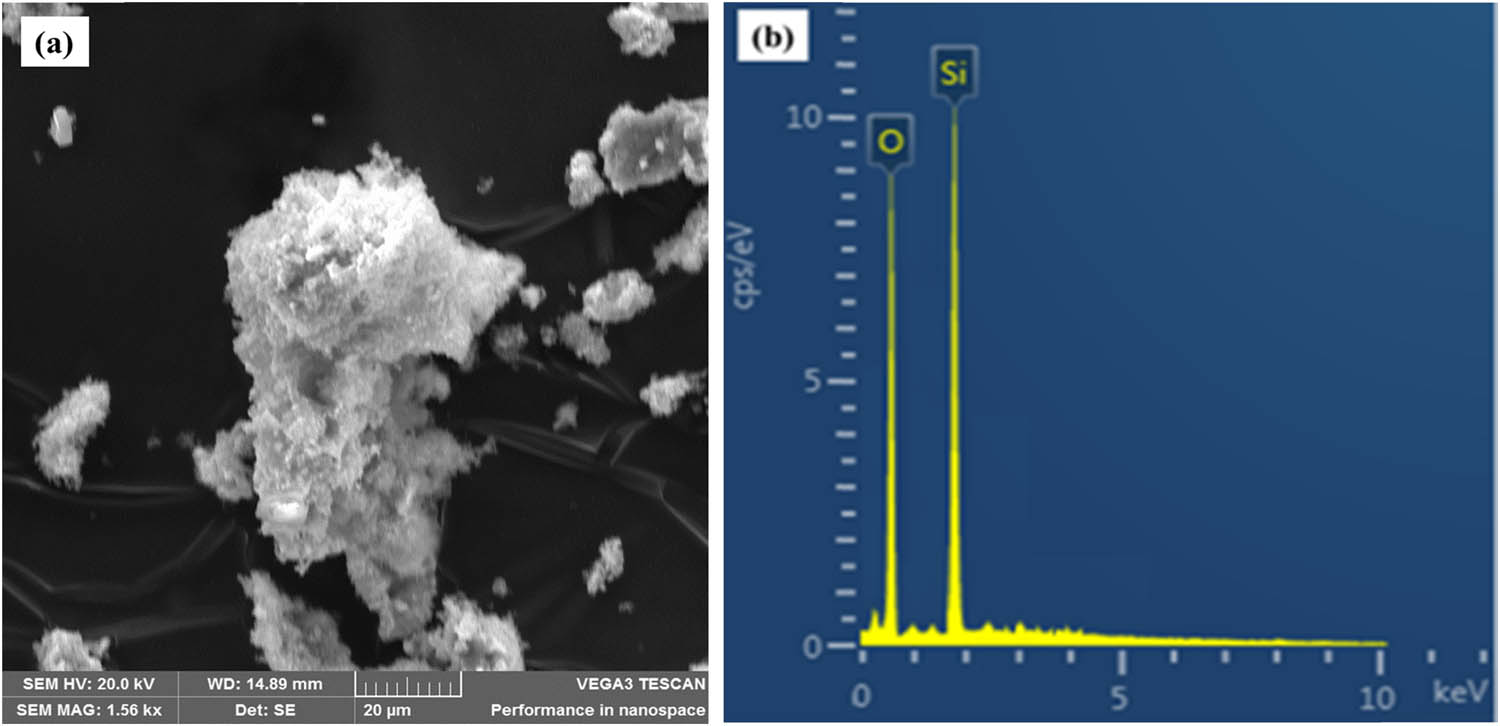
Morphology of SNPMW: (a) SEM and (b) EDX.
3.5 TEM–EDX analysis
The TEM image of SNPMW is displayed in Figure 6(a). Primary SiO2 nanoparticles were discovered to be approximately spherical with diameters of around <200 nm and accumulated to create an agglomeration of nanoparticles. TEM–EDX is also displayed in Figure 6(b), indicating the presence of SiO2 with negligible impurities, while the presence of C and Cu in the spectral is from the carbon-coated copper grids used in the TEM analysis.
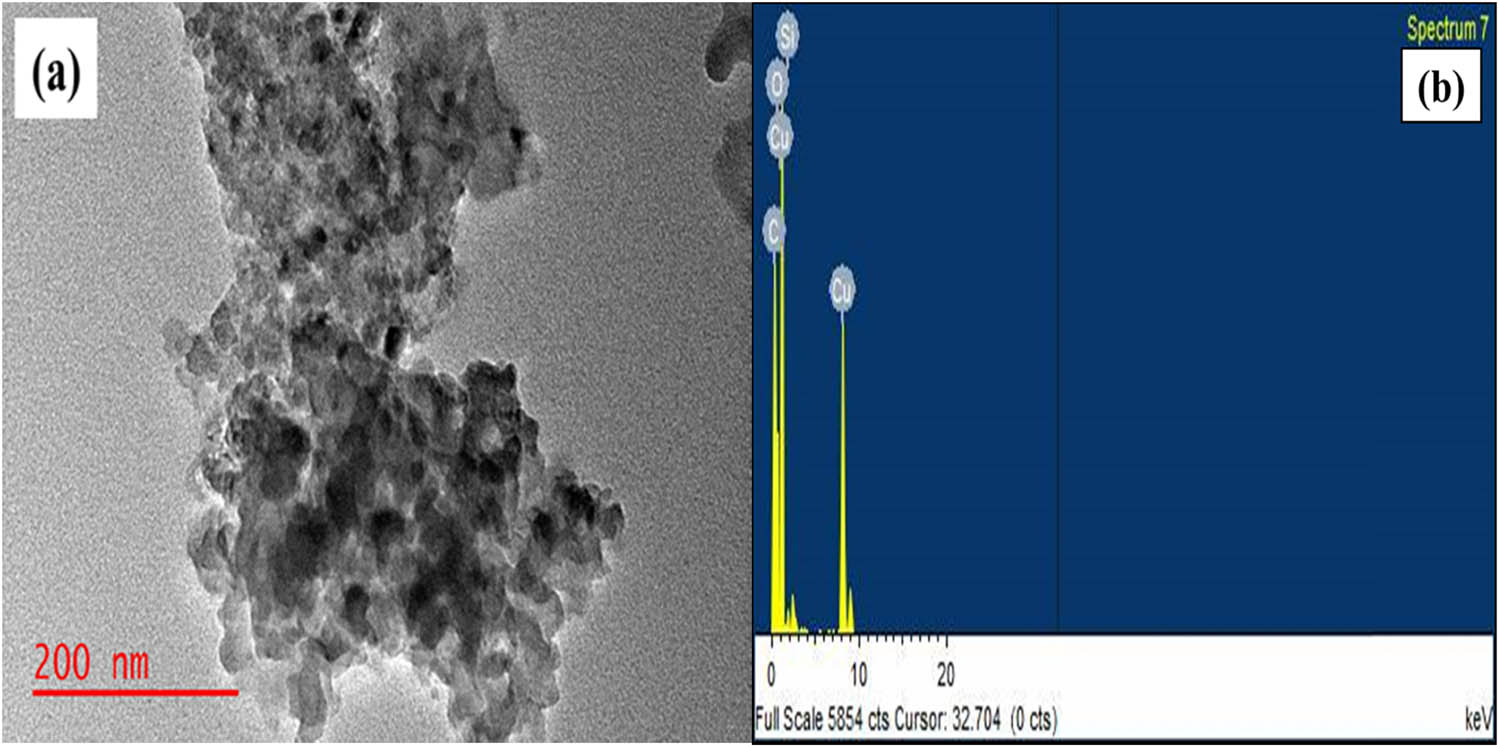
TEM image (a) EDX (b) of SNPMW.
3.6 BET analysis
Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms of extracted SNPMW prepared from SAFA are displayed in Figure 7. The isotherm displayed an apparent type IV isotherm and hysteresis curve type H1, with a well-defined peak at high P/P0, which are typical of mesoporous materials [53,54,55].
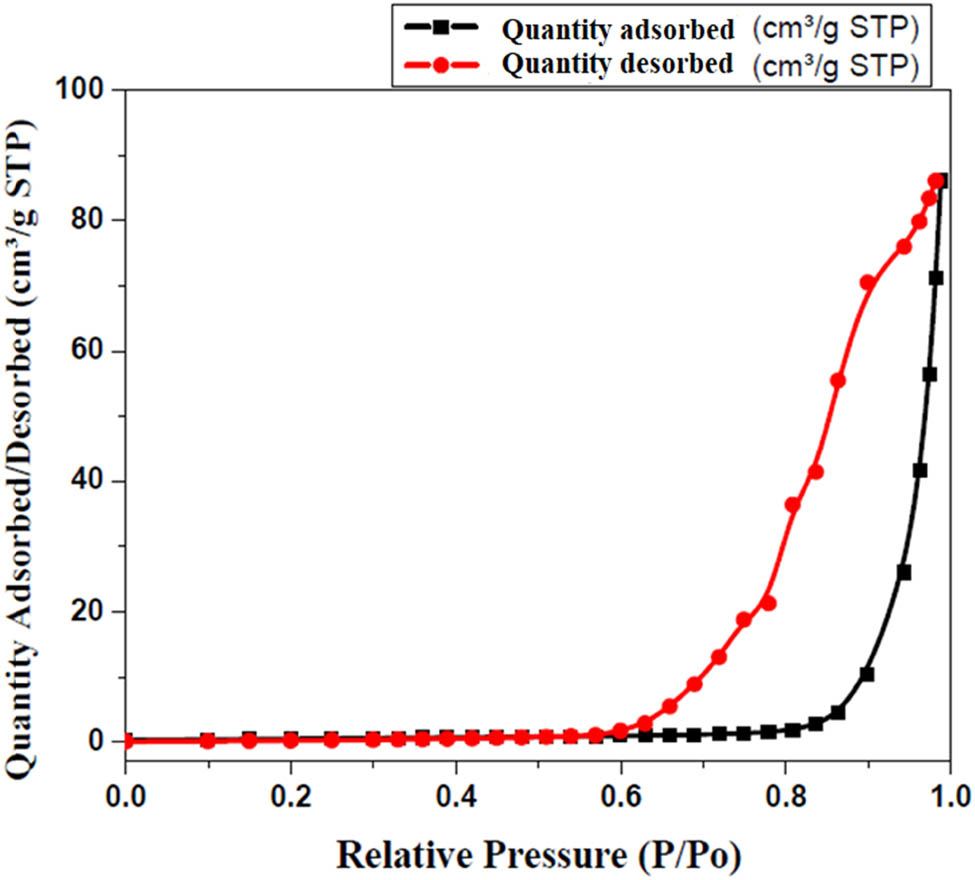
Adsorption/desorption isotherms of prepared SNPMW.
Figure 8 exhibits the Pore size distributions of produced SNPMW. As observed, the average pore diameter ranging between 7.56 and 92.68 nm exhibited a bimodal distribution. BET surface area was 1,865 m2/g.
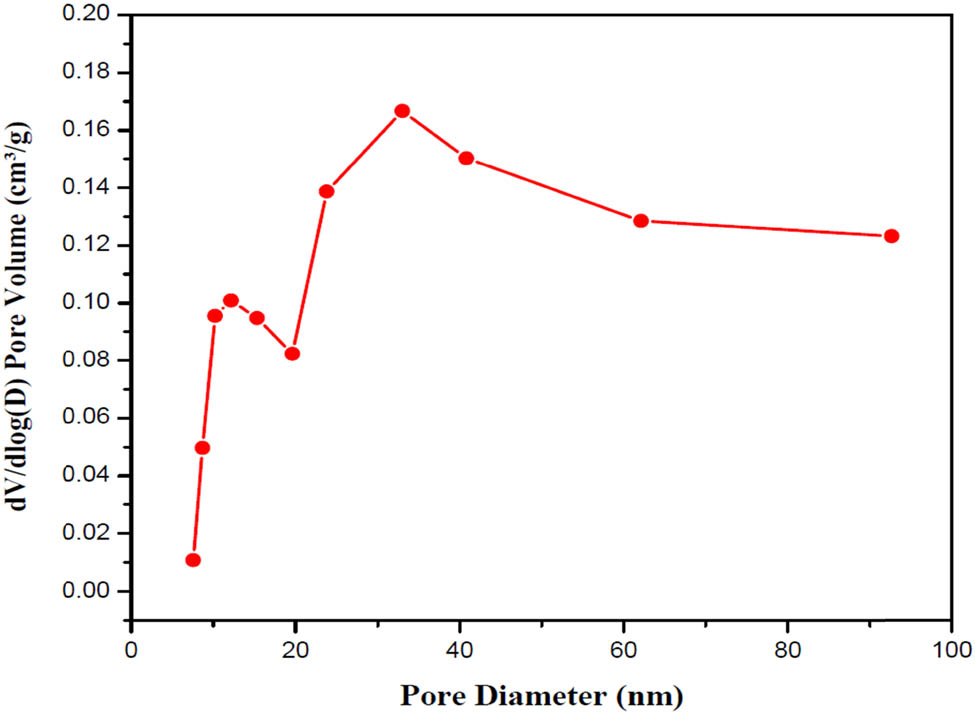
Pore size distributions of prepared SNPMW.
3.7 Optical bandgap
Figure 9 shows the energy bandgap of the SNPMW sample as measured using UV–DRS spectrophotometer. The linear intercept of the curve of (αhυ)2 versus energy (hυ) was used to evaluate the optical bandgap energy of the material [56]. SNPMW optical bandgap was discovered to be 4.67 eV, indicating that the produced sample is insulating, and similar results have been recorded previously [57].
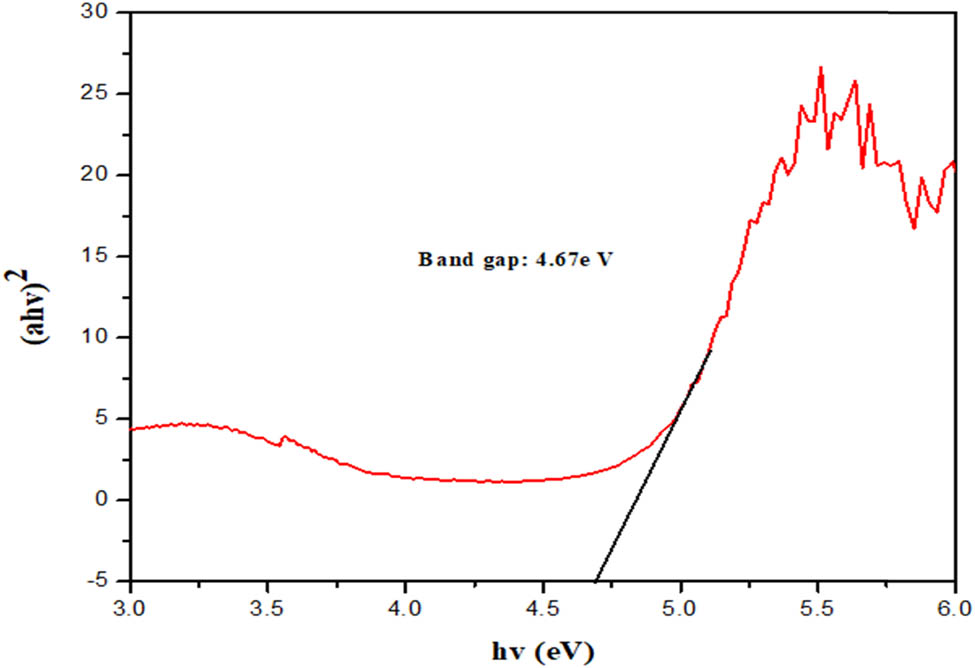
Energy band gap of SNPMW.
3.8 Removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution using prepared SNPMW
As shown in Figure 10, the efficiency rises quickly in the first 20 min after treatment, reaching 91.87%. After 60 min, the treatment efficiency has increased to 96.64%, with a residual Pb2+ concentration of 0.336 mg Pb2+/L. However, after 90 min, practically all the Pb2+ has been adsorbed, leaving a concentration of 0.122 mg Pb2+/L. As a result, the ideal time frame is between 60 and 90 min. Similar rests were previously reported [58].
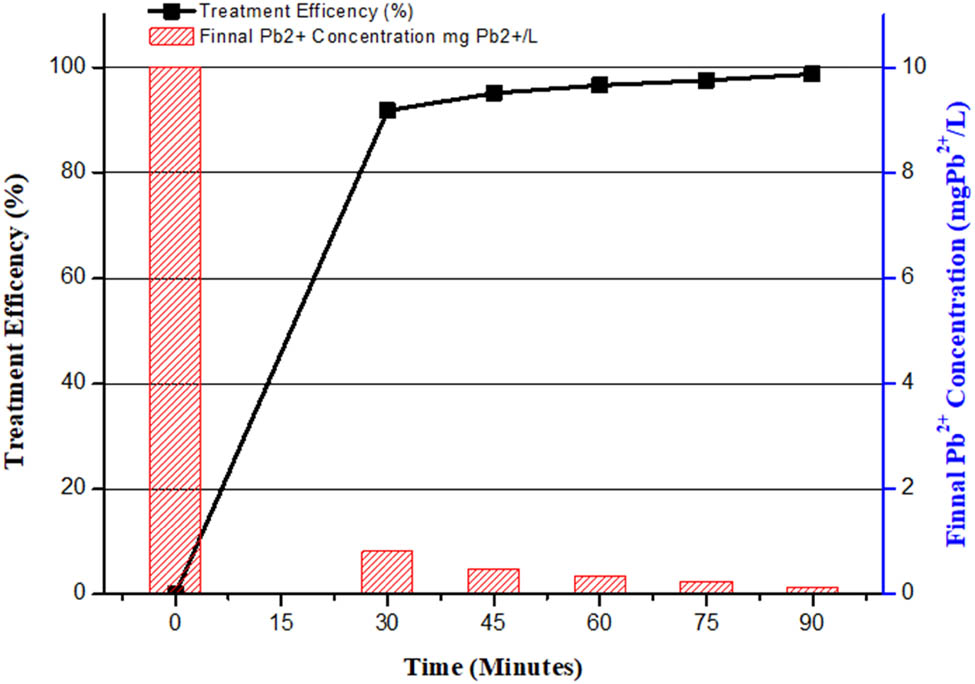
Effect of Pb2+ concentration and removal efficiency at different times.
The consequence of pH on the removal efficiency was demonstrated in Figure 11. When the pH is between 5 and 6, the treatment efficiency does not change much. The efficiency reaches 96.64% at pH = 5. According to previous research, SiO2 hydroxyl groups occur at acid-base balance as shown in equations (1) and (2) [59].
Equations (1) and (2) demonstrate that as pH rises, the balance shifts towards a more negative charge on the SiO2 (>SiO−) surface. This increases the capacity and adsorption efficiency by causing a strong electrostatic attraction between the positive charge Pb2+-adsorbed material and the negatively charged SiO2 adsorbent. When pH is lower, the balance shifts due to an increase in the positively charged SiO2 (
Figure 12 demonstrates that treatment efficiency improves after adding SNPMW. When SNPMW concentration reaches 1 g/L, almost Pb2+ concentration is removed at efficiency 96.64%, and Pb2+ remaining concentration is 0.482 mg Pb2+/L. SNPMW concentration in the range of 1–2.0 g/L leads to a negligible change in Pb2+ treatment efficiency. From Figure 13, the findings suggest that increasing the concentration of Pb2+ reduces its removal. It could be due to metal ions occupying active sites in the adsorbent. Additional ions are produced as the metal ion concentration rises, and at a certain point, the adsorbent sites can no longer pick up more ions from the solution.
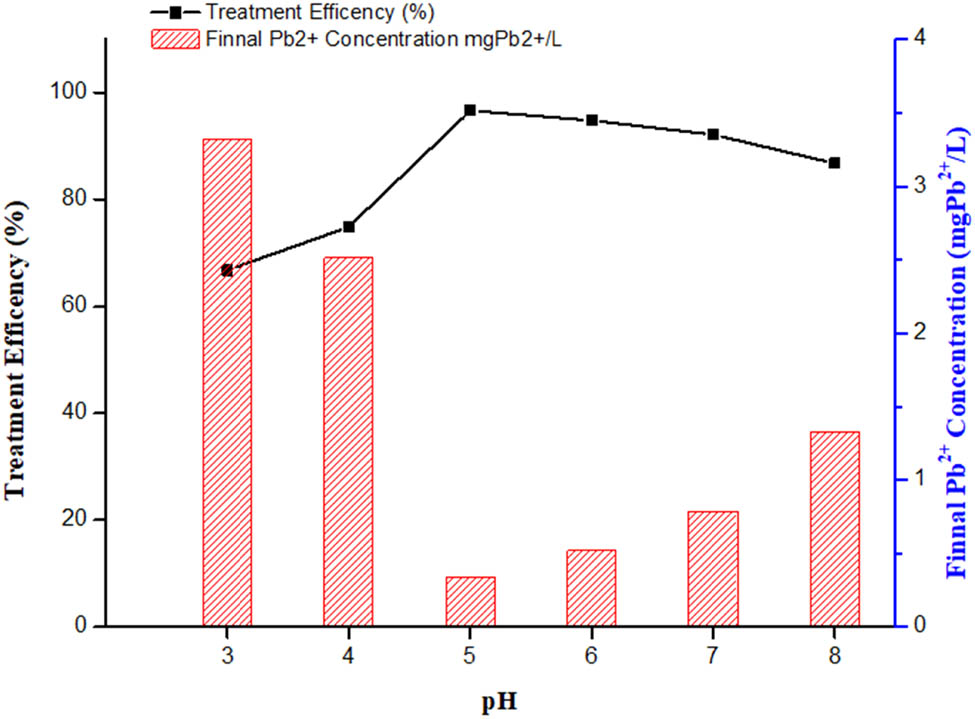
Effect of Pb2+ concentration and removal efficiency at different pH.
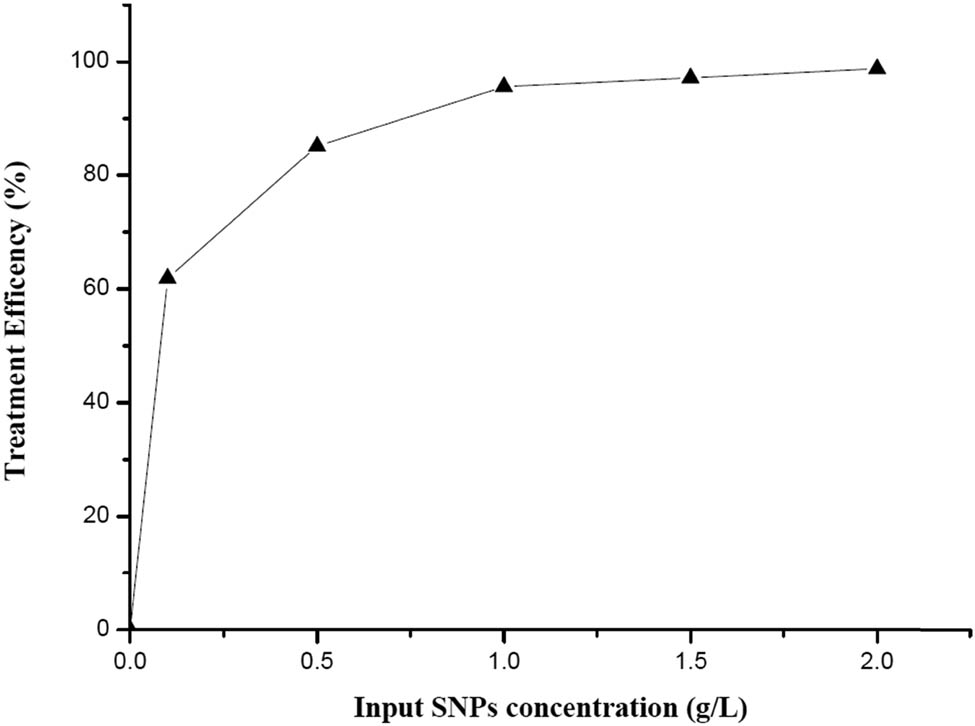
Effect of SNPMW absorbent concentration on Pb2+ treatment efficiency.
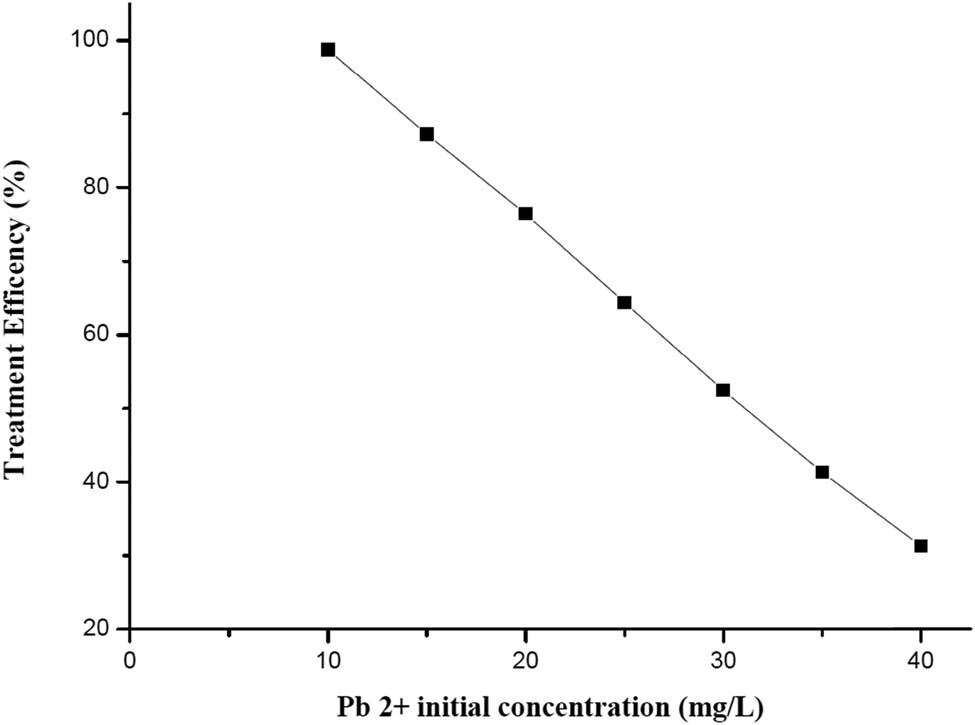
Effect of Pb2+ initial concentration on treatment efficiency.
The relationship between the amount of solute adsorbed and the concentration of the solute in the liquid phase is expressed by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm equation.
where Q e is the volume of metal ions adsorbed at equilibrium (mg/g), C e is the equilibrium concentrations of metal ions in aqueous solution (mg/L), θ is the measure of monolayer adsorption capacity under the experimental conditions and b is the Langmuir adsorption constant related to the energy of adsorption. The plot of C e/Q e against (C e) can be used to derive these values (Figure 14) [60]. The correlation coefficient (R 2 = 0.9985) for SNPMW adsorbents indicated that the Langmuir model fitted the experimental data very well.
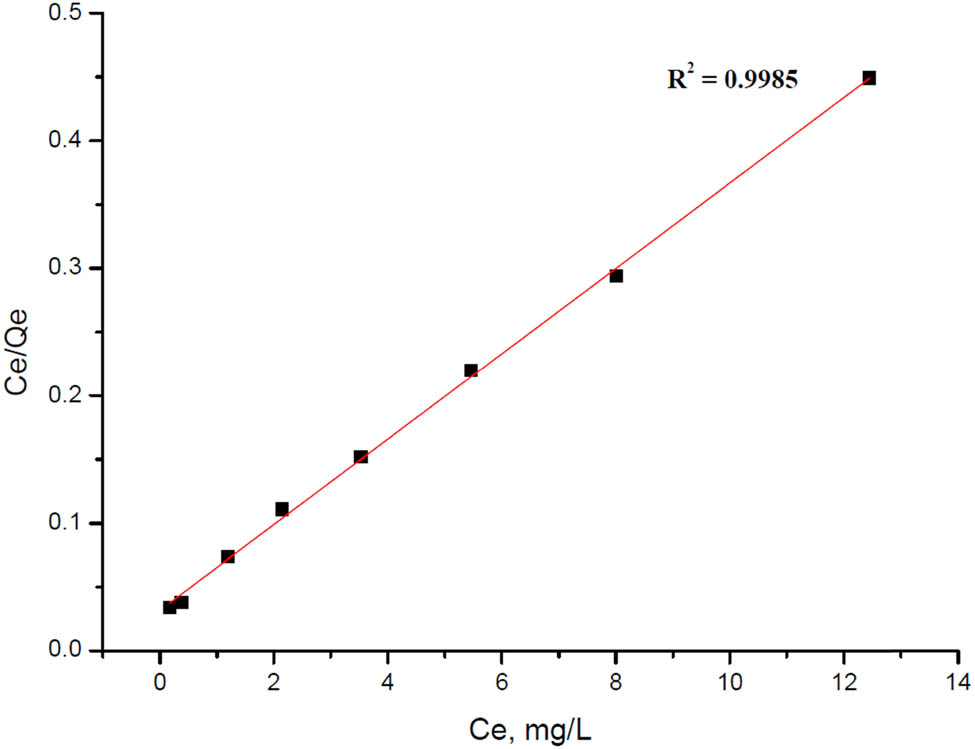
Langmuir’s adsorptive isotherm equation on Pb2+ removal by SNPMW.
4 Conclusions
SNPMW was successfully prepared from SAFA, using an MW-assisted sol–gel method. The findings indicate that after preparation, SNPMW yield was 31.35 with 98.81% purity recorded. The occurrence of silica in SAFA and derived silica have been discovered using XRF studies. FTIR data show the primary chemical group present in the samples, crystalline phase of SAFA, and the amorphous nature of SNPMW was determined using XRD analysis. SEM of SAFA showed ellipsoidal and spheroidal particles of various sizes and unusual forms, while SEM of extracted SNPMW shows agglomerations, and TEM revealed primary silica nanoparticles were roughly spherical with sizes of about <200 nm. EDX confirmed the presence of SiO2. SNPMW particle size varies between 48 and 87 nm in diameter, with 67 nm as the average diameter, while S BET surface area was 1,865 m2/g. The average pore diameter ranges between 7.56 and 92.68 nm exhibiting a bimodal distribution. The optical bandgap of SNPMW was established to be 4.67 eV. SiO2 nanoparticles can be produced with a faster reaction rate, smaller particle size, 98.81%, pure, and negligible impurities utilizing an MW-assisted sol–gel preparation technique, as demonstrated in this work. The potential application of prepared SNPMW for the elimination of Pb2+ in an aqueous solution has been demonstrated. Results show that treatment efficiency increases with time and the optimum time obtained were 60 min. An increase in pH from 3 to 5 increases the removal efficiency from 66.76 to 96.64%. However, at pH above 5, efficiency decreases. The Langmuir isotherm model fits the adsorption data perfectly, according to the isotherm analysis. This research suggests that there will be more innovation in the use of South African CFA for high-tech and sophisticated materials preparation and applications.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate funding of URC the University of Johannesburg, and NRF of South Africa.
-
Funding information: The authors would like to appreciate funding from URC the University of Johannesburg and NRF of South Africa.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Zhaoa Y, Suna Y, Yuana L, Xue Q. Impact of nanopore structure on coal strength: A study based on synchrotron radiation nano-CT. Results Phys. 2020;7:103029. 10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103029.Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Li Zenga B, Suna H-J, Penga T-J, Zhenga W-M. The sintering kinetics and properties of sintered glass-ceramics from coal fly ash of different particle size. Results Phys. 2019;15:102774. 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102774.Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Liu J, Dong Y, Dong X, Hampshire S, Zhu L, Zhu Z, et al. Feasible recycling of industrial waste coal fly ash for preparation of anorthite-cordierite based porous ceramic membrane supports with addition of dolomite. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2016;4:1059–71. 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.11.012.Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Liu J, Wang K, Zou J, Kong Y. The implications of coal consumption in the power sector for China’s CO2 peaking target. Appl Energy. 2019;253:113518. 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113518.Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Koloa MT, Khandakera MU, Amina YM, Abdullah WHB, Bradley DA, Alzimami KS. Assessment of health risk due to the exposure of heavy metals in soil around mega coal-fired cement factory in Nigeria. Results Phys. 2018;11:755–62. 10.1016/j.rinp.2018.10.003.Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Lu X, Liu W, Zhao C, Chen C. Environmental assessment of heavy metal and natural radioactivity in soil around a coal-fired power plant in China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2013;295:1845–54. 10.1007/s10967-012-2241-9.Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Çayır A, Belivermiş M, Kılıç Ö, Coşkun M, Coşkun M. Heavy metal and radionuclide levels in soil around Afsin-Elbistan coal-fired thermal power plants. Turk Environ Earth Sci. 2012;67(4):1183–90. 10.1007/s12665-012-1561-y.Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Li J, Zhuang X, Querol X, Font O, Moreno N, Zhou J. Environmental geochemistry of the feed coals and their combustion by-products from two coal-fired power plants in Xinjiang Province, Northwest China. Fuel. 2012;95:446–56. 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.10.025.Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Wu H, Bryant G, Wall T. The effect of pressure on ash formation during pulverized coal combustion. Energy Fuels. 2000;14(4):745–50. 10.1021/ef990080w.Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Ćwik A, Casanova I, Rausis K, Koukouzas N, Zarębska K. Carbonation of high-calcium fly ashes and its potential for carbon dioxide removal in coal fired power plants. J Clean Prod. 2018;202:1026–34. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.234.Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Muriithi GN, Petrik LF, Doucet FJ. Synthesis, characterisation and CO2 adsorption potential of NaA and NaX zeolites and hydrotalcite obtained from the same coal fly ash. J CO2 Utilization. 2020;36:220–30. 10.1016/j.jcou.2019.11.016.Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Wu X, Liu W, Gao H, Alfaro D, Sun S, Lei R, et al. Coordinated effects of air pollution control devices on PAH Emissions in coal-fired power plants and industrial boilers. Sci Total Environ. 2021;756:144063. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144063.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Abdulkareem AO, Al Bakri Abdullah MM, Kamarudin H, Khairul Nizar I. Alteration in the microstructure of fly ash geopolymers upon exposure to elevated temperatures. Adv Mater Res. 2013;795:201–5. 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.795.201.Suche in Google Scholar
[14] American Society for Testing and Materials. ASTM C618. West Conshohocken, US.: Annual Book of ASTM Standard; 2004.Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Kutchko BG, Kim AG. Fly ash characterization by SEM–EDS. Fuel. 2006;85(17–18):2537–44. 10.1016/j.fuel.2006.05.016.Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Imoisili PE, Jen TC. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of zeolite prepared from south africa coal fly ash. Key Eng Mater. 2022;917:154–9. 10.4028/p-2oxfw6.Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Nile SH, Baskar V, Selvaraj D, Nile A, Xiao J, Kai G. Nanotechnologies in food science: applications, recent trends, and future perspectives. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020;12(1):45. 10.1007/s40820-020-0383-9.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Imoisili PE, Jen TC, Safaei B. Microwave-assisted sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-mixed metal oxide nanocatalyst for degradation of organic pollutant. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10:1–11. 10.1515/ntrev-2021-0016.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Mohajerani A, Burnett L, Smith JV, Kurmus H, Milas J, Arulrajah A, et al. Nanoparticles in construction materials and other applications, and implications of nanoparticle use. Materials. 2019;12(19):3052. 10.3390/ma12193052.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] El-Sayed A, Kamel M. Advanced applications of nanotechnology in veterinary medicine. Env Sci Pollut Res. 2020;27:19073–86. 10.1007/s11356-018-3913-y.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Naiara IV, Zoilo G, Begoña F, Yolanda C. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles by sol–gel as nanocontainer for future drug delivery applications. Boletín Soc Española Cerámica Vidrio. 2017;56(3):139–45. 10.1016/j.bsecv.2017.03.002.Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Corradi AB, Bondioli F, Ferrari AM, Focher B, Leonelli C. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles in a continuous-flow microwave reactor. Powder Technol. 2006;167(1):45–8. 10.1016/j.powtec.2006.05.009.Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Celer EB, Jaroniec M. Temperature-programmed microwave-assisted synthesis of SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silica. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(44):14408–14. 10.1021/ja065345h.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Mily E, Gonza´lez A, Iruin JJ, Irusta L, Ferna´ndez-Berridi MJ. Silica nanoparticles obtained by microwave assisted sol–gel process: multivariate analysis of the size and conversion dependence. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. 2010;53:667–2. 10.1007/s10971-010-2148-2.Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Inada M, Nishinosono A, Kamada K, Enomoto N, Hojo J. Microwave-assisted sol–gel process for production of spherical mesoporous silica materials. J Mater Sci. 2008;43(7):2362–6. 10.1007/s10853-007-2022-y.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Hua M, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q. Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: A review. J Hazard Mater. 2012;211:317–31. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.016.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Chingombe P, Saha B, Wakeman R. Surface modification and characterization of a coal-based activated carbon. Carbon. 2005;43(15):3132–43. 10.1016/j.carbon.2005.06.021.Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Ntobeng MK, Imoisili PE, Jen TC. Facile fabrication of vanadium sensitized silver titanium oxides (V–Ag/TiO2) photocatalyst nanocomposite for pollutants removal in river water. Mater Sci Semiconductor Process. 2021;123:105569. 10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105569.Suche in Google Scholar
[29] Ali A, Alharthi S, Ahmad B, Naz A, Khan I, Mabood F. Efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous medium using chemically modified silica monolith. Molecules. 2021;26:6885. 10.3390/molecules26226885.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Jeelani PG, Mulay P, Venkat R, Ramalingam C. Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A Review. Silicon. 2020;12:1337–54. 10.1007/s12633-019-00229-y.Suche in Google Scholar
[31] Raji F, Saraeian A, Pakizeh M, Attarzadeh F. Removal of Pb (ii) from aqueous solution by mesoporous silica MCM-41 modified by ZnCl2: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and isotherms. RSC Adv. 2015;5:37066–77. 10.1039/C5RA01192B.Suche in Google Scholar
[32] Manyangadze M, Chikuruwo NM, Narsaiah TB, Chakra CS, Charis G, Danha G, et al. Adsorption of lead ions from wastewater using nano silica spheres synthesized on calcium carbonate templates. Heliyon. 2020;6:e05309. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05309.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Trewyn BG, Slowing II, Giri S, Chen HT, Lin VSY. Synthesis and functionalization of a mesoporous silica nanoparticle based on the sol–gel process and applications in controlled release. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40(9):846–53. 10.1021/ar600032u.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Soltani RDC, Khorramabadi GS, Khataee A, Jorfi S. Silica nanopowders/alginate composite for adsorption of lead (II) ions in aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45(3):973–80. 10.1016/j.jtice.2013.09.014.Suche in Google Scholar
[35] Thirumavalavan M, Wang YT, Lin LC, Lee JF. Monitoring of the structure of mesoporous silica materials tailored using different organic templates and their effect on the adsorption of heavy metal ions. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115:8165–74. 10.1021/jp200029g.Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Mathibela E, Aphane Frédéric J, Doucet RA, Kruger LP, Elizabet MV. Preparation of sodium silicate solutions and silica nanoparticles from South African coal fly ash. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020;11:4403–17. 10.1007/s12649-019-00726-6.Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Guo Y, Zhao Z, Zhao Q, Cheng F. Novel process of alumina extraction from coal fly ash by pre-desilicating – Na2CO3 activation – Acid leaching technique. Hydrometallurgy. 2017;169:418–25. 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.02.021.Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Bai G, Teng W, Wang X, Zhang H, Xu P. Processing and kinetics studies on the alumina enrichment of coal fly ash by fractionating silicon dioxide as nano particles. Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91:175–84. 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.09.010.Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Walker A, Wheelock TD. Separation of carbon from fly ash using froth flotation. Coal Prep. 2006;26(4):235–50. 10.1080/07349340601104883.Suche in Google Scholar
[40] Imoisili PE, Jen TC. Facile Extraction and characterization of silica nanoparticles from corn stalk by sol–gel hydrothermal methods. IOP Conf Series Mater Sci Eng. 2021;1107(1):012030. 10.1088/1757-899x/1107/1/012030.Suche in Google Scholar
[41] Okoronkwo EA, Imoisili PE, Olubayode SA, Olusunle SOO. Development of silica nanoparticle from corn cob ash. Adv Nanopart. 2016;5:135–9. 10.4236/anp.2016.52015.Suche in Google Scholar
[42] Yang L, Shuhua M, Chunli L, Zhenqing Z, Shili Z, Xiaohui W. Effect of particle size and alkali activation on coal fly ash and their role in sintered ceramic tiles. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2017;37(4):1847–56. 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.11.032.Suche in Google Scholar
[43] Huang Y, Dongliang J, Jingxian Z, Zhongmin C, Qingling L, Zhengren H. Sintering kinetics of YAG ceramics. J Rare Earth. 2014;32(5):416–22. 10.1016/S1002-0721(14)60087-9.Suche in Google Scholar
[44] Lin B, Li S, Hou X, Li H. Preparation of high performance mullite ceramics from high-aluminum fly ash by an effective method. J Alloy Compd. 2015;623:359–61. 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.023.Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Imoisili PE, Ukoba KO, Jen TC. Green technology extraction and characterization of silica nanoparticles from palm kernel shell ash via sol–gel. J Mater Res Technol. 2020;9(1):307–13. 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.10.059.Suche in Google Scholar
[46] Liu C-L, Zheng S-L, Ma S-H, Luo Y, Ding J, Wang X-H, et al. A novel process to enrich alumina and prepare silica nanoparticles from high-alumina fly ash. Fuel Process Technol. 2018;173:40–7. 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.01.007.Suche in Google Scholar
[47] Huffman GP, Huggins FE, Dunmyre GR. Investigation of the high-temperature behavior of coal fly ash in reducing and oxidizing atmospheres. Fuel. 1991;60:585–97. 10.1016/0016-2361(81)90158-7.Suche in Google Scholar
[48] Imoisili PE, Ukoba KO, Jen TC. Synthesis and characterization of amorphous mesoporous silica from palm kernel shell ash. Boletín Soc Española Cerámica Vidrio. 2020;59:159–64. 10.1016/j.bsecv.2019.09.006.Suche in Google Scholar
[49] Chen H, Fu S, Fu L, Yang H, Chen D. Simple synthesis and characterization of hexagonal and ordered Al–MCM–41 from natural perlite. Minerals. 2019;9(5):264. 10.3390/min9050264.Suche in Google Scholar
[50] Costa JAS, Paranhos CM. Systematic evaluation of amorphous silica production from rice husk ashes. J Clean Prod. 2018;192:688–97. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.028.Suche in Google Scholar
[51] Miricioiu MG, Niculescu VC, Filote C, Raboaca MS, Nechifor G. Coal fly ash derived silica nanomaterial for MMMs – Application in CO2/CH4 separation. Membranes. 2021;11(2):78. 10.3390/membranes11020078.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Zhu GR, Tan W, Sun JM, Gong YB, Zhang S, Zhang ZJ, et al. Effects and mechanism research of the desilication pretreatment for high-aluminum fly ash. Energy Fuel. 2013;27:6948–54. 10.1021/ef4012005.Suche in Google Scholar
[53] Zhang WH, Lu XB, Xiu JH, Hua ZL, Zhang LX, Robertson M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of biofunctionalized ordered mesoporous materials. Adv Funct Mater. 2004;14(6):544–52. 10.1002/adfm.200305001.Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Yan Z, Fu L, Yang H, Ouyang J. Amino-functionalized hierarchical porous SiO2-AlOOH composite nanosheets with enhanced adsorption performance. J Hazard Mater. 2018;344:1090–100. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.058.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Muthusami R, Kesavan A, Ramachandran V, Vasudevan V, Irena K, Rangappan R. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a lychee-like morphology and dual pore arrangement and its application towards biomimetic activity via functionalization with copper (II) complex. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020;294:109910. 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109910.Suche in Google Scholar
[56] Gutzov S, Danchova N, Karakashev S, Khristov M, Ivanova J, Ulbikas J. Preparation and thermal properties of chemically prepared nanoporous silica aerogels. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. 2014;70:511–6. 10.1007/s10971-014-3315-7.Suche in Google Scholar
[57] Khedkar MV, Somvanshi SB, Humbe AV, Jadhav KM. Surface modified sodium silicate based superhydrophobic silica aerogels prepared via ambient pressure drying process. J Non-Crystalline Solids. 2019;511:140–6. 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.02.004.Suche in Google Scholar
[58] Nguyen XH, Nam AT, Thi THN, Thi TND. Nanosilica synthesis and application for lead treatment in water. J Viet Environ. 2019;9(5):255–63. 10.13141/JVE.Suche in Google Scholar
[59] Ahmed MN, Ram RN. Removal of basic dye from waste-water using silica as adsorbent. Environ Pollut. 2019;77:79–86. 10.1016/0269-7491(92)90161-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Karnib M, Kabbani A, Holail H, Olama Z. Heavy metals removal using activated carbon, silica and silica activated carbon composite. Energy Proc. 2014;50:113–20. 10.1016/j.egypro.2014.06.014.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 Patrick Ehi Imoisili and Tien-Chien Jen, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption

