Abstract
The flexible polymers have an outstanding impact-resistant performance because of the improved stiffness upon a high speed loading. At the aspect of microstructure, the soft segments make an important contribution. In this article, molecular dynamics simulation is carried out to reveal the dynamic mechanical behavior of a mono helical soft segment. The tensile loadings at various strain rates are conducted. The stress–strain relations and strain rate dependencies of mechanical properties are derived. The evolution of potential energy with straining accompanied by the disentanglement of molecular chain is characterized. The characteristic molecular chain of dynamic mechanical response is determined. The intrinsic physical origins of straightening of characteristic molecular chain and bond angle expansion are explored. New parameters are defined to quantitatively analyze the micro mechanisms and their rate dependencies, which are linked to the dynamic mechanical properties. This work is full of interest to fill a knowledge gap of the physical origins of dynamic mechanical behavior of flexible polymers.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the flexible polymers have been widely used in constructions, transportations, automobiles, aerospace and other engineering fields due to the outstanding impact-resistant performance [1,2,3,4,5,6]. With the further research, many kinds of flexible polymer materials, such as spray film, adhesive gel, flexible wearable and nano composite, have been developed. With their superior properties, they gradually replace the traditional small molecule materials [7,8,9,10]. Generally, they are composed of the hard segments and soft segments in microstructure. The hard segments are comprised of diisocyanate and chain extender, and the soft segments are comprised of oligomeric polyol. Between them, the thermodynamic incompatibility is presented. It makes that the polymer materials have an obvious microstructure of phase separation, in which the soft phases provide elasticity and the hard phases serve to enhance the filling and crosslinking [11,12,13,14]. Studies have suggested that the multi-phase structure is the intrinsic reason of the excellent performance of materials [15,16]. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the phases and microstructure for well knowing the flexible polymers [17,18,19,20,21].
As we know, there are a large number of C–C single bonds in the soft segment of polymer. When the internal rotation degree of freedom is large enough, the change of molecular chain conformation provides “flexibility” for the polymer. Therefore, in the molecular chain of the flexible polymers, the mass proportion of soft segments is usually higher than hard segments, which can be up to 90% [22,23]. Some research results have shown that the structures of soft segments have considerable effects on the mechanical properties of flexible polymers related to low temperature resistance [24,25,26]. Furthermore, several researches have indicated that as polyols’ relative molecular weight increases, tensile strength and tear strength decrease while tensile elongation increases [27,28,29]. They illustrates that the soft segments have an key effect on the mechanical properties of flexible polymers. Therefore, studying the soft segments is valuable for understanding the physical mechanisms linking to mechanical behavior of flexible polymers.
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations based on Newtonian mechanics theory have a capability to predict the microstructure and mechanical properties of materials under a certain condition. It is helpful to clarify the microlevel mechanisms for understanding the mechanical behavior of flexible polymers [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. MD simulations can observe the polymers at atomic scale and explain the macrolevel dynamic mechanical behavior through the microlevel physical origins. Also, they have the advantages of less testing period, lower cost and so on, which can constantly polish the results through a fast iteration. The mechanisms of mechanical performance of flexible polymers as well as their self-healing behavior have been studied by MD simulations [38,39,40]. The proportion of soft segments and hard segments was obtained to address the self-healing capability of flexible polymers [41]. The method of MD simulations can well elucidate the physical origins of mechanical behavior through describing the soft segments and hard segments. As a result, uncovering the physical mechanisms of impact resistance of flexible polymers is critical.
In this work, the mono soft segment of flexible polymers is studied through using MD simulations and the evolution of mechanical behavior with the increase in strain rate is clarified. By sampling the molecular systems at different strain states, monitoring the atomic motion process and revealing the characteristics of structures and properties, the mechanical behavior is ultimately achieved. The polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMG) is selected as the research objective, which is a typical soft segment of flexible polymers. The physical mechanisms at molecular scale are revealed and the intrinsic parameters are accompanyingly defined. This work not only describes the evolution process of molecular chain motion upon dynamic tensile loading but also explores the microlevel origins of mechanical behavior at different strain rates. This study plays an important role on improving the knowledge impact on rate dependent mechanical behavior of flexible polymers.
2 Material model and MD simulation method
Materials Studio is used to build the material model of the mono soft segment of flexible polymers. The open-source code of LAMMPS is employed for calculation [42]. The OVITO is implemented to realize the visualization of atomic structure [43]. The applicable COMPASS force field is carried out. Herein, COMPASS means “condensed-phase optimized molecular potential for atomistic simulation studies.” It is the first molecular force field that can unify the force fields of organic molecular system and inorganic molecular system. Generally, the COMPASS force field is able to achieve the simulations of polymer materials [44]. The governing function of COMPASS [45] force field can be expressed as:
In this formula, the bonding term is composed as: the energy of bond stretching (
Among these atoms, the bond increment (
In this work, the PTMG that can represent the soft segment of flexible polymers is selected for study. A typical microstructure of flexible polymers is shown in Figure 1a. The monomer of butanediol is constructed by adding atoms in Materials Studio [46,47]. Then, the repeating unit in material model is used to construct a single molecular chain of PTMG and a typical molecular structure of soft segment with helical structure is shown in Figure 1b. It is a mono soft segment for study in this work and its molecular formula is OH(C4H8O) n H (see Figure 1c).

Material model of MD simulations: (a) microstructural composition of a flexible polymer; (b) a typical molecular structure of soft segment with helical structure; and (c) molecular formula of the mono soft segment.
Herein, a regular helical structure is built for the calculation and research. The degree of polymerization is set as n = 43 that contains 562 atoms and the total molecular weight is 3,114. Afterwards, the structure of the PTMG is optimized. A reasonable and stable molecular structure can be obtained by the method of energy minimization. Finally, the material model with molecular structure is outputted by coordinate conversion and is turned into an initial configuration file that will be used by LAMMPS. The visual model that is processed by OVITO.
LAMMPS can optimize the simulation data for avoiding the failure of calculation due to unreasonable local structure of material model or excessively high system energy and the rationality of modeling can be achieved. The calculation system is simulated for 1,000 ps using an isothermal–isobaric ensemble (NPT) at 300 K under atmospheric pressure. The environmental conditions are held. The increase in temperature is processed at a step of 25 K from 300 to 1,000 K followed by cooling down to 300 K. Such the treating cycles are conducted for 10 times and a balance state of material system is reached. To study the tensile properties, the material system of PTMG was uniaxial stretched at room temperature (T = 300 K), and the model was relaxed for 1,000 ps at 300 K before loading. Periodic boundary conditions are applied in y- and z-directions while the boundary condition in x-direction is free for deformation. Time step Δt = 1 fs is set during loading process. The different impact velocities are conducted, which are (n) km/s (n = 1, 2 … 20). They correspond to the strain rates of (0.88n) × 1011/s (n = 1, 2 … 20), respectively.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Mechanical properties at various strain rates
The tensile tests within a wide range of strain rates are simulated by using LAMMPS. The mechanical responses under dynamic tensions are characterized. Yielding stress and maximum stress at various strain rates are collected to investigate the effect of strain rate on dynamic mechanical properties, which reveals the strain rate dependency. Besides, according to the simulation results, the effects of strain rate on mechanical behavior are well studied.
Figure 2 shows the representative engineering stress–strain curves of PTMG material model at different strain rates. To ensure that the simulation results can comprehensively analyze the mechanical behavior under tensile loadings, multiple simulations are conducted in the velocity range of 1–20 km/s, that corresponds the strain rate range of (0.88–17.6) × 1011/s. The engineering stress–strain curves show a similar characteristic under different strain rates. They exhibit a linear elastic behavior at beginning of deformation and then present a nonlinear transition to global yielding followed by a large strain and final failure. It is a typical mechanical characteristic of glass-like behavior. It can also be noted that in the process of yielding, with the increase of strain rate, the transition of stress–strain relation tends to be indistinct and the hardening phenomenon becomes obvious. In addition, the strength, stiffness and maximum stress increase with the increase of strain rate. The specific quantitative analysis is shown in Figures 3 and 4, respectively. It means that the material properties have an outstanding rate dependency. Likewise, the material system exhibits dynamic hardening behavior, which contributes to high impact resistance [48,49,50,51].

Stress–strain relations under dynamic tensions at different strain rates.
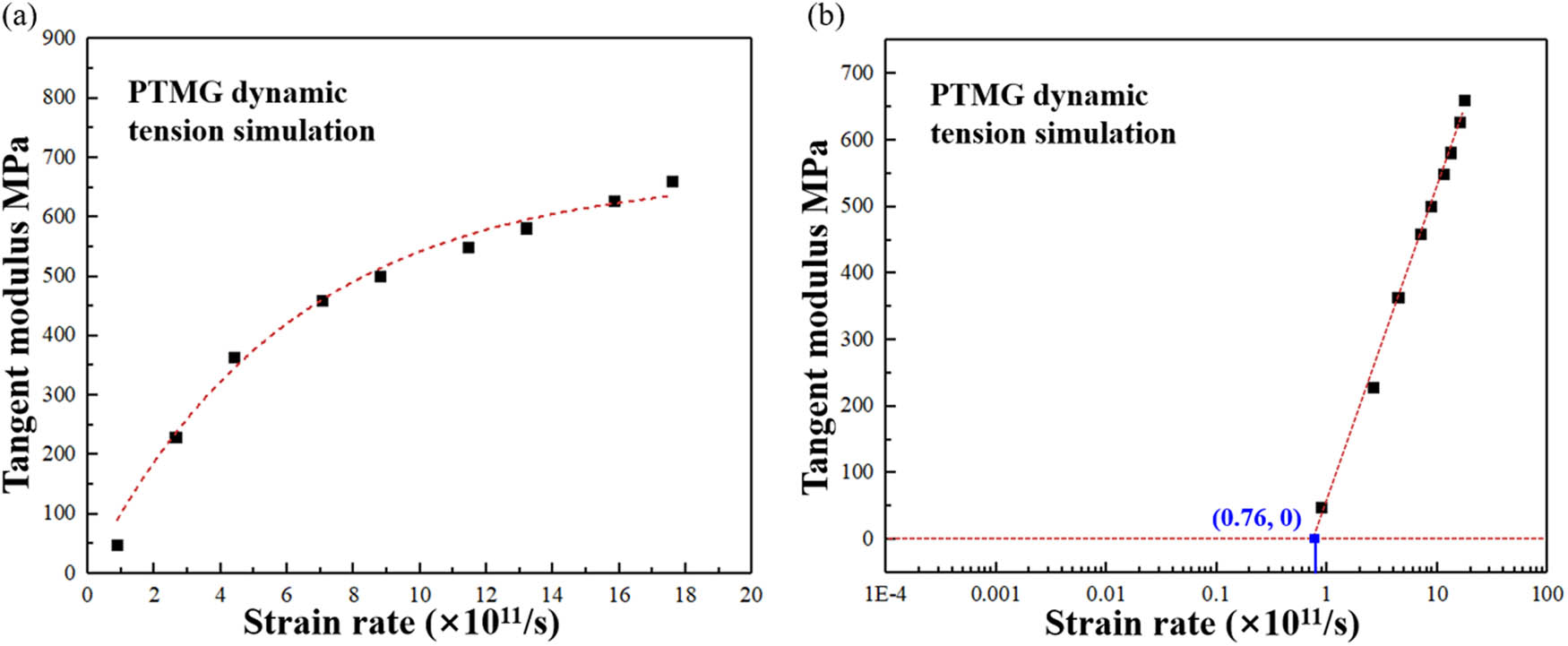
Relation between strain rate and tangent modulus of the PTMG material model: (a) positive strain rate dependency of tangent modulus and (b) critical strain rate to induce the transition of mechanical behavior of a material from rubber-like behavior at low strain rate to glass-like behavior at high strain rate.

Quantitative analysis on the strain rate dependencies of the maximum stress and yield stress.
Therefore, the material system presents a mechanical characteristic of glass-like behavior under dynamic loading. To study the origins of this characteristic, the tangent modulus of the material at different strain rates is quantitatively analyzed and the simulation data are fitted. Since yielding occurs under dynamic stress equilibrium of atomic structure, tensile modulus can be roughly estimated by a stress–strain curve. The curve slope is the tangent modulus that can indicate the material stiffness at a corresponding strain rate. Figure 3a shows the relation between the tangent modulus of the material system and strain rate. It is found that tangent modulus increases with the increase of strain rate, which is a positive strain rate sensitivity. By fitting the data points, it can be seen that the increase speed becomes slow and even the tangent modulus becomes a constant when strain rate is high enough. It means that the rate independency of tangent modulus emerges at a high strain rate. Furthermore, a logarithmical abscissa axis of strain rate is transformed and the data points of tangent modulus are fitted into a straight line (see Figure 3b). By extending the fitting line, a point of (0.76, 0) is attained. It indicates that when strain rate is lower than 0.76 × 1011/s, tangent modulus becomes 0, which is a typical mechanical behavior of soft matter. Thus, the strain rate of 0.76 × 1011/s is determined as the transition of mechanical behavior of a material from rubber-like behavior to glass-like behavior with the increase of strain rate [52,53,54,55,56]. The mechanical characteristics upon loading remain similar in the range of the simulated strain rate and occur to transition with the increase of strain rate.
Based on the stress–strain curves in Figure 2, yield stress and maximum stress at different strain rates are measured and their rate dependencies are analyzed quantitatively (see Figure 4). Herein, the point of the minimum stress after linear elastic deformation is taken as yield stress. In general, the strain rate dependency of material properties can be calculated by a formula of
The quantitative analysis shows that both the maximum stress and yield stress have a positive correlation with strain rate and they increase with the increase in strain rate. By comparing, the strain rate dependency of yield stress is higher than that of the maximum stress. The yield stress corresponds to the yielding resistance of a material, which can indicate a material stiffness. It is consistent with the relation between tangent modulus and strain rate as shown in Figure 3. And, the maximum stress corresponds to the fracture resistance of a material, which is related to the strength and cracking resistance of a material. Thus, with the increase in strain rate, the material stiffness, strength, and cracking resistance are significantly increased, which illustrates a high impact-resistant performance.
3.2 Physical mechanisms of strain rate dependency
According to the study in literatures [57,58,59], the potential energy is strongly related to the mechanical properties of a material. To explore the physical mechanisms of the strain rate dependency of mechanical properties, the relation between potential energy and strain rate is analyzed, which is shown in Figure 5. The potential energy evolution with straining at different strain rates is given in Figure 5a. The curves of potential energy and engineering strain also show a similar trend at different strain rates. The potential energy increases rapidly with straining at a given strain rate. In addition, according to the growth rate of the potential energy with straining, two turning points, marked by round and square black dots, can be obviously seen at each strain rate. This phenomenon is similar with that which occurs in the stress–strain relations, as shown in Figure 2. Through linking with the engineering strain, it is found that the engineering strains at these two turning points of potential energy are consistent with the strains, which correspond to yield stress and maximum stress, respectively, as shown in Figure 6. Thus, we can derive that these two turning points of potential energy correspond to the yield stress point and maximum stress point, respectively. Then, the potential energies at yield stress point and maximum stress point are measured at different strain rates (see Figure 5a) and their strain rate dependencies are analyzed quantitatively by curve fitting (see Figure 5b).
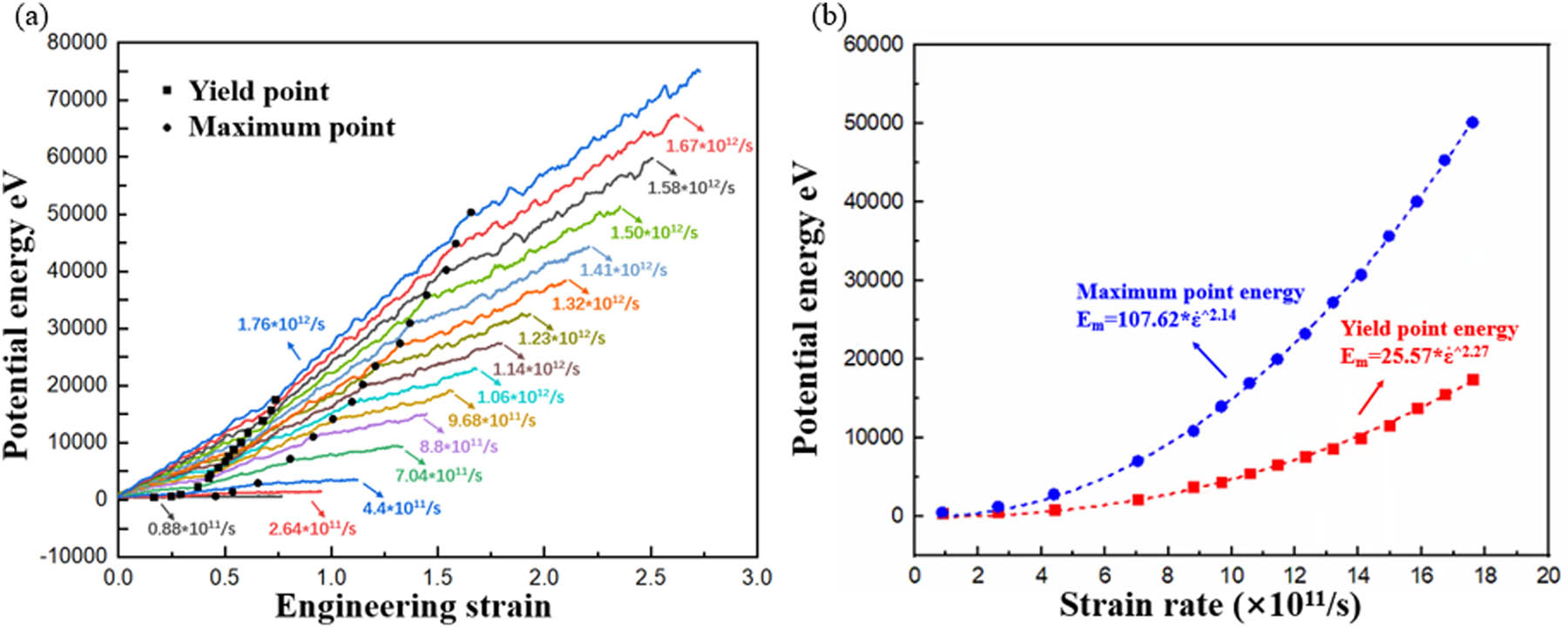
Relation between potential energy and strain rate: (a) potential energy with straining at different strain rates and (b) quantitative analysis of strain rate dependencies of the potential energies at yield stress point and maximum stress point.

Evolutions of potential energy and stress with straining at a representative strain rate of 1.32 × 1012/s.
A power function is employed to characterize the strain rate dependencies. They are
In addition, to explore the evolution details of potential energy with stress and strain, one typical loading case at a strain rate of 1.32 × 1012/s is investigated as shown in Figure 6. At the beginning of deformation, a linear stress–strain behavior is processed and the potential energy increases linearly at a lower speed with straining, which is Stage I. When strain reaches 0.53, the stress–strain curve shows yielding behavior and yield stress point is obtained here. Meantime, the curve of potential energy and strain reaches the first turning point. Afterwards, with the continuous increase in strain, the increase in stress becomes faster and, accompanyingly, the increase of potential energy also becomes faster, which is Stage II. Then, a large deformation is processed and the strain reaches 1.31. At this time, the maximum stress point is obtained here. Finally, at Stage III, with the increase in strain, the stress shows a downward trend, while the potential energy continues to increase, but the increase rate slows down. Herein, the failure of material maybe occurs. Therefore, with the increase in strain, the evolutions of stress and potential energy are given in detail.
Along with the above illustrations, the configuration of molecular chain is furthermore studied for exploring the physical mechanisms at atomic scale, as shown in Figure 7. Herein, three representative loading cases at the strain rates of 0.88 × 1011, 7.04 × 1011 and 1.32 × 1012/s are presented and the configurations of molecular chain at the initial, yield and maximum stress points in each loading case are investigated. At the initial state, strain is 0 and the material system is not affected by external force. That means the configuration of molecular chain keeps the original state without any tension and relaxation. When the stress–strain relation arrives at yield point, tensile deformation makes an effect on the configuration of molecular chain. Disentanglement occurs and it is localized at the ending part of the molecular chain, which is determined as the characteristic molecular chain for carrying the dynamic mechanical behavior. Herein, the disentanglement is carried out by the change in bond length and bond angle as well as the straightening of molecular chain rearrangement [21,24,30,38]. The medium position of the molecular chain, on the other hand, appears to have no or very little modification. The relative motion of the segments is observed at both ends of the molecular chain, and this phenomenon becomes more obvious at the maximum stress point. So, the performance of molecular chain upon dynamic loadings at different strain rates is the same, which indicates the intrinsic physical mechanism is the same. However, through comparison, it is found that with the increase in strain rate, the characteristic molecular chains become “straighter” and “longer.” This means the disentanglement of molecular chain becomes more obvious with the increase in loading rate.

Configurations of molecular chain at the initial, yield stress and maximum stress points at different strain rates of 0.88 × 1011, 7.04 × 1011 and 1.32 × 1012/s, respectively.
To further study the disentanglement phenomenon of a molecular chain upon dynamic loading as well as the intrinsic physical mechanisms, some new parameters are defined and accordingly a quantitative analysis is conducted. Under dynamic loading, a molecular chain is divided into two parts of disentanglement at the ending part and non-disentanglement at the medium part, which are schematically shown in Figure 8a. This performance is caused by the inertia behavior of matter. They are defined as
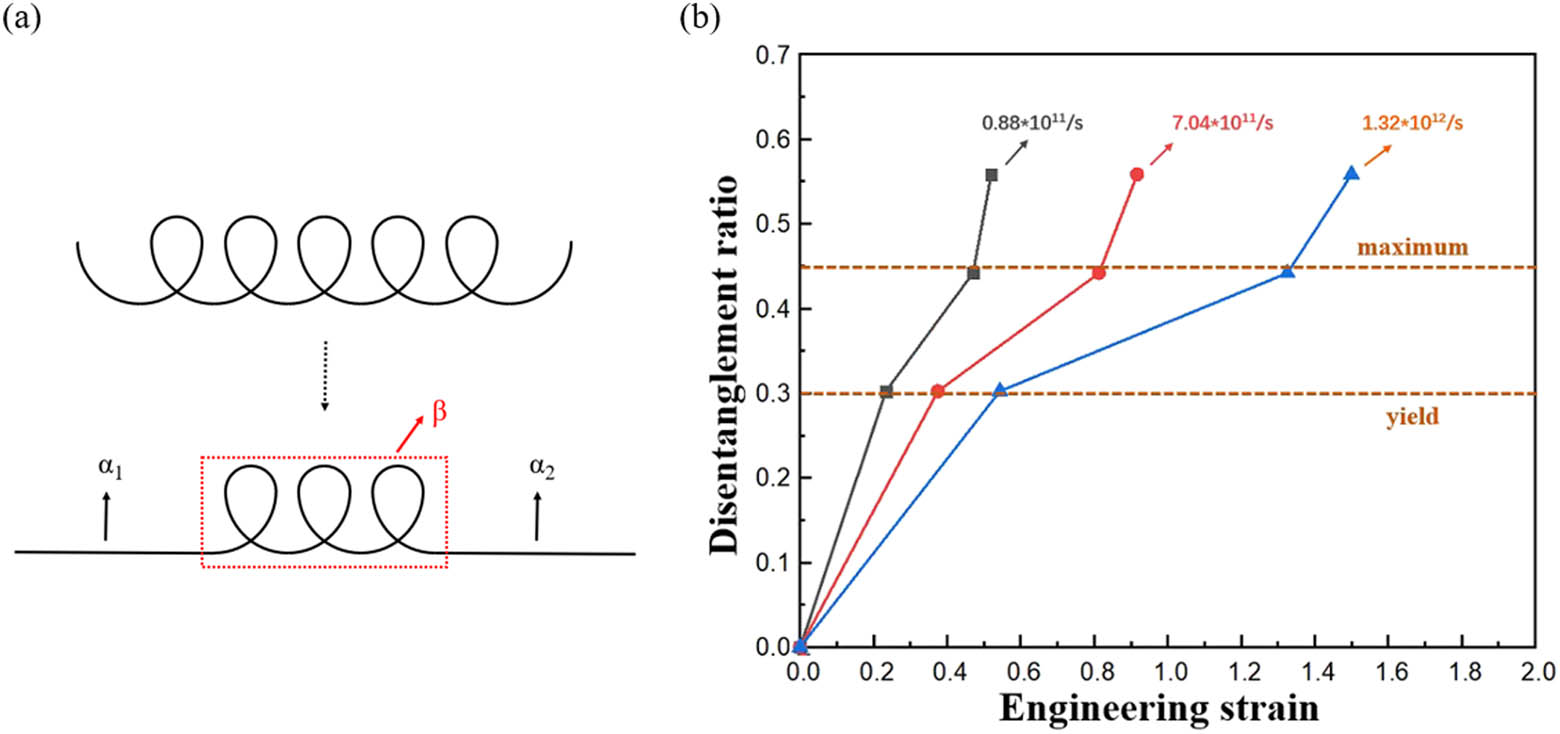
Relation between disentanglement ratio and strain rate of the PTMG system: (a) schematic illustration of a molecular chain under dynamic tension loading including the disentanglement part,
Besides, it is interesting to find that for these three loading cases, the disentanglement ratio is the same at yield stress point as well as at the maximum stress point. That means the disentanglement ratio is not changed by the loading rate, which is strain rate independency. So, 0.3 and 0.45, as the data of disentanglement ratio, are determined to be the characteristic parameters of the mono helical soft PTMG segment for describing the rearrangement of molecular chain at yield stress point and maximum stress point at various strain rates. However, the strain at yield stress point and maximum stress point becomes large with the increase in strain rate (see Figures 2 and 5). Thus, we can derive that the disentanglement degree of molecular chain becomes high with the increase in strain rate, which is mainly operated by the change in bond length and bond angle.
As above illustrations, disentanglement is a natural carrier at micro level as the response of molecular chain upon dynamic loading. The disentanglement part,

Zoomed-in observation on the disentanglement part,
The initial configuration at the end of molecular chain is U shape. And, the rearrangements at yield stress point and maximum stress point are also given at the three representative loading cases where strain rates are 0.88 × 1011, 7.04 × 1011 and 1.32 × 1012/s, respectively. By comparison, the U-shape part becomes straighter at maximum stress point than that at yield stress point for a certain loading case. And, at both yield stress point and maximum stress point, the U-shape part also becomes straighter for the loading case at a higher strain rate. So, both straining and strain rate can lead to the straightening of characteristic molecular chain, which results in the increase in disentanglement degree at the ending part of a whole molecular chain. Herein, the straightening of characteristic molecular chain is operated by the motion of atoms, which is the physical origin of the increased stress with the increase in strain and strain rate [60]. So, the stress–strain relations at various strain rates as well as the strain rate dependencies of tangent modulus and strength are produced, as shown in Figures 2–4.
To quantitatively analyze the straightening of characteristic molecular chain upon dynamic loading, the parameters of straightening ratio and bond angle–expansion ratio are defined as shown in Figure 10. A schematic diagram of the straightening of characteristic molecular chain is given in Figure 10a. The straightening ratio,
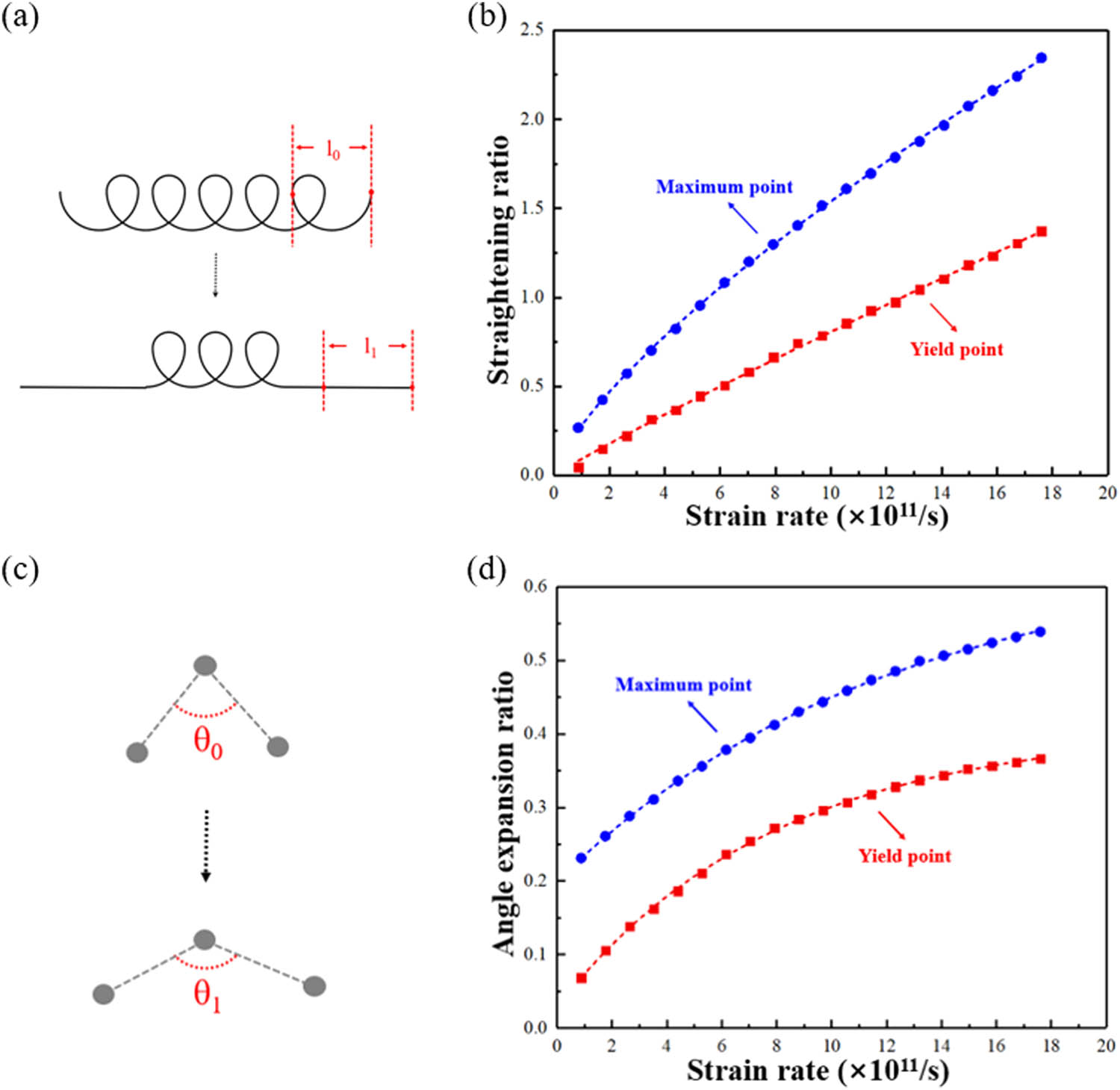
Quantitative analysis on the straightening of characteristic molecular chain in the disentanglement part upon dynamic loading: (a) schematic diagram of the straightening of characteristic molecular chain; (b) strain rate dependences of straightening ratio,
The same, the angle–expansion ratio,
According to the quantitative analysis in Figure 10b and d, with the increase in strain rate, both straightening ratio and bond angle–expansion ratio increase, which contributes to the disentanglement of molecular chain upon dynamic loading. That means the loading at a higher strain rate can lead to a greater degree of disentanglement, which is mainly conducted by the straightening of characteristic molecular chain and bond angle expansion. Herein, the increase in bond length is deemed to make less effect on the material deformation and it will cause the material failure.
4 Conclusions
The physical origins of dynamic mechanical behavior of flexible polymers are revealed by studying a mono helical soft segment at various strain rates using MD simulation. The stress–strain relations show yield stress point and maximum stress point and both of them as well as the tangent modulus, which can indicate the material stiffness, has a positive strain rate dependency. The evolution of potential energy of atoms with straining is also given and it is in line with the stress–strain relation. A similar strain rate dependency is produced.
Furthermore, disentanglement of molecular chain upon dynamic loading is observed. The disentanglement ratio is defined and found that at the yield stress point and the maximum stress point, it is independent of strain rates, which are 0.3 and 0.45, respectively. Through the quantitative analysis of the straightening and the inherent bond angle expansion of the characteristic molecular chain under different strain rates, it is proved that the bond length and bond angle of the chain segment at the yield stress point and the maximum stress point change more distinctly with the increase in strain rate. When the strain rate is up to 1.76 × 1012/s, the straightening rate and the inherent bond angle expansion at the yield stress point are 1.35 and 0.35, respectively. They are 1.3 and 0.28, respectively, higher than those at a strain rate of 8.8 × 1010/s. The same, at the maximum stress points, they are 2.05 and 0.3 higher, respectively, when comparing the data at these two different strain rates. Thus, the disentanglement degree of the characteristic molecular chain increases with the increase in strain rate. Then, we can deduce the increase in the interaction force between atoms, which can result in the improved strain and stress. Therefore, through the step-by-step exploration and investigation, the physical mechanisms of dynamic mechanical behavior of flexible polymers are clarified.
-
Funding information: The authors acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant No. 11602024 and the “111” Project of China with Grant No. G20012017001.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this article and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: David Hui, who is the co-author of this article, is a current Editorial Board member of Nanotechnology Reviews. This fact did not affect the peer-review process. The authors declare no other conflict of interest.
References
[1] Alves P, Kaiser JP, Haack J, Salk N, Bruinink A, Sousa HC, et al. Surface modification of thermoplastic polyurethane in order to enhance reactivity and avoid cell adhesion. Colloid Polym Sci. 2009;287(12):1469–74.10.1007/s00396-009-2116-ySuche in Google Scholar
[2] Shan CL. Analysis of collision performance of anticollision box made of steel-polyurethane sandwich plates. J Constr Steel Res. 2020;175:106357.10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106357Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Zhang XS, Chen YJ, Hu JL. Recent advances in the development of aerospace materials. Prog Aerosp Sci. 2018;97:22–34.10.1016/j.paerosci.2018.01.001Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Xu T, Shen W, Lin XS, Xie YM. Mechanical properties of additively manufactured thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) material affected by various processing parameters. Polymers. 2020;12(12):3010.10.3390/polym12123010Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Sun Y, Chen HJ, Yin H, Sun BZ, Gu BH, Zhang W. A flexible, high-strength, conductive shape memory composite fabric based on continuous carbon fiber/polyurethane yarn. Smart Mater Struct. 2020;29(8):085044.10.1088/1361-665X/ab9f4aSuche in Google Scholar
[6] Engels HW, Pirkl HG, Albers R, Albach RW, Krause J, Hoffmann A, et al. Polyurethanes: Versatile materials and sustainable problem solvers for today’s challenges. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52(36):9422–41.10.1002/anie.201302766Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Li D, Lai ZC, Liu CJ, Guo JT, Yang XQ, Guan MS. Random vibration of pretensioned rectangular membrane structures under heavy rainfall excitation. Thin-Walled Struct. 2021;164(9):107856.10.1016/j.tws.2021.107856Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Li D, Zheng ZL, Todd M. Nonlinear vibration of orthotropic rectangular membrane structures including modal coupling. J Appl Mech Trans ASME. 2018;85(6):061004.10.1115/1.4039620Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Jiang BK, Chen AY, Gu JF, Fan JT, Liu Y, Wang P, et al. Corrosion resistance enhancement of magnesium alloy by N-doped graphene quantum dots and polymethyltrimethoxysilane composite coating. Carbon. 2020;157:537–48.10.1016/j.carbon.2019.09.013Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Lin M, Chen QY, Wang ZW, Fang YC, Liu JF, Yang YC, et al. Flexible polymer device based on parylene-C with memory and temperature sensing functionalities. Polymers. 2017;9(8):310.10.3390/polym9080310Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Yanagisawa Y, Nan YL, Okuro K, Aida T. Mechanically robust, readily repairable polymers via tailored noncovalent cross-linking. Science. 2018;359(6371):72–6.10.1126/science.aam7588Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Wu CH, Huang YC, Chen WL, Lin YY, Dai SA, Tung SH, et al. Size-dependent phase separation and thermomechanical properties of thermoplastic polyurethanes. Polymer. 2020;210:123075.10.1016/j.polymer.2020.123075Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Gogolewski S. Selected topics in biomedical polyurethanes. A review. Colloid Polym Sci. 1989;267(9):757–85.10.1007/BF01410115Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Špírková M, Machová L, Kobera L, Brus J, Poreba R, Serkis M, et al. Multiscale approach to the morphology, structure, and segmental dynamics of complex degradable aliphatic polyurethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;132(10):41590–n/a.10.1002/app.41590Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Cipriani E, Zanetti M, Brunella V, Costa L, Bracco P. Thermoplastic polyurethanes with polycarbonate soft phase: Effect of thermal treatment on phase morphology. Polym Degrad Stab. 2012;97(9):1794–800.10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.06.004Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Li YJ, Ren ZY, Zhao M, Yang HC, Chu B. Multiphase structure of segmented polyurethanes: effects of hard-segment flexibility. Macromolecules. 1993;26:612–22.10.1021/ma00056a010Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Yoshihara N, Enomoto M, Doro M, Suzuki Y, Shibaya M, Ishihara H. Effect of soft segment components on mechanical properties at low temperatures for segmented polyurethane elastomers. J Polym Eng. 2007;27(4):291–311.10.1515/POLYENG.2007.27.4.291Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Shibaya M, Suzuki Y, Doro M, Ishihara H, Yoshihara N, Enomoto M. Effect of soft segment component on moisture-permeable polyurethane films. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys. 2006;27(4):291–311.10.1002/polb.20720Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Kultys A, Rogulska M, Głuchowska H. The effect of soft‐segment structure on the properties of novel thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers based on an unconventional chain extender. Polym Int. 2011;60(4):652–9.10.1002/pi.2998Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Eceiza A, Larranaga M, de la Caba K, Kortaberria G, Marieta C, Corcuera MA, et al. Structure-property relationships of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers based on polycarbonate diols. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;108(5):3092–103.10.1002/app.26553Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Lee DK, Tsai HB, Tsai RS, Chen PH. Preparation and properties of transparent thermoplastic segmented polyurethanes derived from different polyols. Polym Eng Sci. 2007;47(5):695–701.10.1002/pen.20742Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Fan JT, Weerheijm J, Sluys LJ. High-strain-rate tensile mechanical response of a polyurethane elastomeric material. Polymer. 2015;65:72–80.10.1016/j.polymer.2015.03.046Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Lee YM, Lee JC, Kim BK. Effect of soft segment length on the properties of polyurethane anionomer dispersion. Polymer. 1994;35(5):1095–9.10.1016/0032-3861(94)90958-XSuche in Google Scholar
[24] Mokeev MV, Ostanin SA, Saprykina NN, Zuev VV. Microphase structure of polyurethane-polyurea copolymers as revealed by solid-state NMR: Effect of molecular architecture. Polymer. 2018;150:72–83.10.1016/j.polymer.2018.07.014Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Jie OU, Tian LY, Wang XL. Effect of hard and soft segment on structure-property of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer. J Funct Polym. 2010;23(2):160–5.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Kull KL, Bass RW, Craft G, Julien T, Marangon E, Marrouat C, et al. Synthesis and characterization of an ultra-soft poly(carbonate urethane). Eur Polym J. 2015;71:510–22.10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.08.015Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Amrollahi M, Sadeghi GMM, Kashcooli Y. Investigation of novel polyurethane elastomeric networks based on polybutadiene-ol/polypropyleneoxide mixture and their structure-properties relationship. Mater Des. 2011;32(7):3933–41.10.1016/j.matdes.2011.02.039Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Liu N, Zhao Y, Kang M, Wang JW, Wang XK, Feng YL, et al. The effects of the molecular weight and structure of polycarbonatediols on the properties of waterborne polyurethanes. Prog Org Coat. 2015;82:46–56.10.1016/j.porgcoat.2015.01.015Suche in Google Scholar
[29] Mishra VK, Patel RH. Processing and characterizations: Effect of PPG molecular weight on properties of phosphate based polyurethanes. Prog Org Coat. 2020;147:105868.10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105868Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Luo YL, Liu HB, Xiang B, Chen XL, Yang W, Luo ZY. Temperature dependence of the interfacial bonding characteristics of silica/styrene butadiene rubber composites: A molecular dynamics simulation study. RSC Adv. 2019;9:40062–71.10.1039/C9RA08325ASuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Wang MD, Gu Q, Luo YL, Bukhvalov D, Ma XF, Zhu LJ, et al. Understanding mechanism of adsorption in the decolorization of aqueous methyl violet (6B) solution by okra polysaccharides: Experiment and theory. ACS Omega. 2019;4(18):17880–9.10.1021/acsomega.9b02768Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Wang YH, Yang G, Wang WH, Zhu SY, Guo LH, Zhang ZQ, et al. Effects of different functional groups in graphene nanofiber on the mechanical property of polyvinyl alcohol composites by the molecular dynamic simulations. J Mol Liq. 2019;277:261–8.10.1016/j.molliq.2018.12.089Suche in Google Scholar
[33] Deng SD, Zhou H, Wang YB, Leng S, Zhuang GL, Zhong X, et al. Multiscale simulation on product distribution from pyrolysis of styrene-butadiene rubber. Polymers. 2019;11(12):1967.10.3390/polym11121967Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Zhu R, Zhang ZW, Li YL. Advanced materials for flexible solar cell applications. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):452–8.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0040Suche in Google Scholar
[35] Liang YJ, Huang JZ, Qin HF, Huan S, Hui D. Mechanical properties of boron nitride sheet with randomly distributed vacancy defects. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):210–7.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0019Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Jiang Q, Tallury SS, Qiu YP, Pasquinelli MA. Interfacial characteristics of a carbon nanotube-polyimide nanocomposite by molecular dynamics simulation. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):136–45.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0012Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Fan Y, Xiang Y, Shen HS. Temperature-dependent negative Poisson’s ratio of monolayer graphene: Prediction from molecular dynamics simulations. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):415–21.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0037Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Yildirim E, Yurtsever M, Yilgör E, Yilgör I, Wilkes G. Temperature‐dependent changes in the hydrogen bonded hard segment network and microphase morphology in a model polyurethane: Experimental and simulation studies. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys. 2018;56(2):182–92.10.1002/polb.24532Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Chen J, Li FZ, Lou YL, Shi YJ, Ma XF, Zhang M, et al. A self-healing elastomer based on an intrinsic non-covalent cross-linking mechanism. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7(25):15207–14.10.1039/C9TA03775FSuche in Google Scholar
[40] Miao YG, He H, Li ZH. Strain hardening behaviors and mechanisms of polyurethane under various strain rate loading. Polym Eng Sci. 2020;60(5):1083–92.10.1002/pen.25364Suche in Google Scholar
[41] Chen XL, Zhu J, Luo YL, Chen J, Ma XF, Bukhvalov D, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation insight into the temperature dependence and healing mechanism of an intrinsic self-healing polyurethane elastomer. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2020;22(31):17620–31.10.1039/D0CP03013ASuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Plimpton S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J Comput Phys. 1995;117(1):1–19.10.2172/10176421Suche in Google Scholar
[43] Stukowski A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO-the open visualization tool. Model Simul Mater Sci Eng. 2010;18(1):015012.10.1088/0965-0393/18/1/015012Suche in Google Scholar
[44] Ma SJ, Chen P, Xu JL, Chen GZ, Xiong XH. Directional control of the mechanical properties of a resin-cross-linking system: A molecular dynamics study. Ind & Eng Chem Res. 2021;60:11621–26.10.1021/acs.iecr.1c01811Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Sun HJ. COMPASS: An ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J Phys Chem B. 1998;102:7338–64.10.1021/jp980939vSuche in Google Scholar
[46] Wei T, Zhang L, Zhao HY, Ma H, Sajib MSJ, Jiang H, et al. Aromatic polyamide reverse-osmosis membrane: An atomistic molecular dynamics simulation. J Phys Chem B. 2016;120(39):10311–8.10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b06560Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Jaidann M, Abou-Rachid H, Lafleur-Lambert X, Lussier LS, Gagnon N, Brisson J. Modeling and temperatures measurement of glass transition of energetic and inert systems. Polym Eng Sci. 2008;48(6):1141–50.10.1002/pen.21062Suche in Google Scholar
[48] Fan JT, Chen A. Studying a flexible polyurethane elastomer with improved impact-resistant performance. Polymers. 2019;11:467–78.10.3390/polym11030467Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Mulliken AD, Boyce MC. Mechanics of the rate-dependent elastic-plastic deformation of glassy polymers from low to high strain rates. Int J Solids Struct. 2006;43(5):1331–56.10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2005.04.016Suche in Google Scholar
[50] Ali SF, Fan JT. Capturing dynamic behaviors of a rate sensitive elastomer with strain energy absorptions and dissipation effects. Int J Appl Mech. 2021;31:13–628.10.1142/S1758825121501040Suche in Google Scholar
[51] Omar MF, Akil HM, Ahmad ZA. Effect of molecular structures on dynamic compression properties of polyethylene. Mater Sci Eng A. 2012;538:125–34.10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.111Suche in Google Scholar
[52] Ali SF, Fan JT. Elastic-viscoplastic constitutive model for capturing the mechanical response of polymer composite at various strain rates. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020;57:12–7.10.1016/j.jmst.2020.05.013Suche in Google Scholar
[53] Kendall MJ, Siviour CR. Rate dependence of poly(vinyl chloride), the effects of plasticizer and time-temperature superposition. Proc R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2014;470(2167):20140012.10.1098/rspa.2014.0012Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Yi J, Boyce MC, Lee GF, Balizer E. Large deformation rate-dependent stress–strain behavior of polyurea and polyurethanes. Polymer. 2006;47(1):319–29.10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.107Suche in Google Scholar
[55] Fan JT, Wang C. Dynamic compressive response of a developed polymer composite at different strain rates. Compos Part B Eng. 2018;152:96–101.10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.06.025Suche in Google Scholar
[56] Ali SF, Fan JT, Feng JQ, Wei XQ. A macro-mechanical study for capturing the dynamic behaviors of a rate-dependent elastomer and clarifying the energy dissipation mechanisms at various strain rates. Acta Mech Solida Sin. 2021;35:228–38.10.1007/s10338-021-00263-7Suche in Google Scholar
[57] Song JH, Li JC, Li ZB. Molecular dynamics simulations of uniaxial deformation of bimodal polyethylene melts. Polymer. 2020;213:123210.10.1016/j.polymer.2020.123210Suche in Google Scholar
[58] Fujinami A, Ogata S, Shibutani Y. Ab initio study of the tensile behavior of single polyimide molecular chain. Polymer. 2004;45:9023–8.10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.058Suche in Google Scholar
[59] Yang LQ, Fan JT, Vu-Bac N, Rabczuk T. A nanoscale study of the negative strain rate dependency of the strength of metallic glasses by molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018;20:26552–7.10.1039/C8CP05557BSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Nouraniana S, Gwaltney SR, Baskes MI, Tschoppd MA, Horstemeyer MF. Simulations of tensile bond rupture in single alkane molecules using reactive interatomic potentials. Chem Phys Lett. 2015;635:278–84.10.1016/j.cplett.2015.06.071Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 Fengxiao Chen et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption

