Abstract
The cost-effective and environmental friendly biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles is becoming increasingly important in biomedical science. This study biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) from pumpkin seed extract and assessed its anticancer activity by using different molecular biology experiments in human breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cell lines. The well-known analytical techniques, such as UV-visible spectrophotometry, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), were used to confirm the synthesis and characterize the morphological and structural features of biogenic ZnO NPs. The formation of spherical nanoparticles with an average size of 50–60 nm was recorded using scanning electron microscopy and TEM. We observed the dose-dependent increase in cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs in the MDA-MB-231 cell line with a 50% inhibitory concentration of 10 µg/mL. Moreover, the ZnO NPs also showed significant cell morphology changes, apoptosis induction, and reactive oxygen species production at the highest tested concentration. The cellular adhesion and migration assay indicated cell death and inhibition in the migration of breast cancer cells in response to ZnO NPs’ treatment. These results clearly demonstrated the significant anticancer potential of ZnO NPs against the studied breast cancer cell line. However, an extension of this study is recommended in different cancer models and, based on the results, in vivo validation should be done.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most frequent cancers and the leading cause of death in women, with 2.26 million recorded cases in 2020 worldwide [1,2]. It is a heterogeneous condition with a wide range of molecular characteristics, clinical outcomes, and therapeutic resistance levels [3,4,5]. The onset and progression of breast cancer are influenced by a complex interplay of regulatory signaling networks that are still being unraveled. Despite significant advancements in breast cancer prognosis, more comprehensive treatment modalities are required, especially for drug-resistant patients [6]. Advanced research has recommended various adjuvants, complementary medicine, and alternative therapies for breast cancer patients and highlighted the importance of multidisciplinary therapeutic approaches.
Recent developments in science and technology significantly impacted human health and life [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Among those developments, nanotechnology has sparked much interest to the scientific community in the past few decades, owing to its numerous applications [17,18]. Due to unique characteristics, such as shape, size, compatibility, surface charge, chemical stability, catalytic activity, and small size to the higher surface area, NP-based therapeutics are most sought after [19,20,21]. Traditional chemical and physical approaches may produce nanoparticles in a quick time; however, these techniques leave hazardous compounds adsorbed on the NPs’ surface, which could be harmful in medical applications [22,23]. Lately, the scientific community has emphasized and encouraged the biogenic approach of nanoparticle synthesis, producing nontoxic and environmentally friendly NPs. The plant extract’s biomolecules operate as effective capping agents, assisting in NPs synthesis and increasing its life, and overcoming the limitations of traditional chemical approaches [24]. The green synthesis of NPs is a clean, low-cost, ecologically friendly, and safe method that can help humans in several real-world applications [19,20,25]. This method produces nanoparticles that are useful in the textile industry, wastewater treatment, paper preservation, food industry, cosmetics, optics, smart devices, pharmaceuticals, and biomedical sciences, such as diagnostics, targeted delivery, biosensing, and bioimaging [18,26,27].
The inorganic compound zinc oxide (ZnO) is rarely found in nature, has a crystalline in form, has limited solubility in water, low detrimental effect, and is responsible for the unique red or orange color [28]. In terms of the significance and biological importance, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) are widely used in a variety of applications, such as textiles, cosmetics, diagnostics, and micro-electronics, because of their antimicrobial activity and strong interaction with infectious diseases in humans and animals. The clinical significance of ZnO NPs is due to their strong potential and decisiveness compared to other metal NPs obtained through the green-synthesized methods [29,30,31]. Recently, several studies have come to light on the formation of ZnO NPs from vegetable seeds [32,33,34]. The scientific literature revealed that the extracts of plants, such as leaves, peel roots, flowers, fruits, and seeds, act as reducing and stabilizing agents for synthesizing ZnO NPs [35,36,37]. The green approach of ZnO NPs’ synthesis has produced better outcomes in textile industries, boosting antibacterial capability, antibiofilm, and anti-quorum sensing potentialities while maintaining environmentally friendly conditions [38]. The current study synthesized cost-effective and ecofriendly ZnO NPs using pumpkin seed extracts, characterized using several spectroscopic techniques, and evaluated their anticancer efficacy in the human breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB 231).
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
Pumpkin seeds were collected from Jaipur’s Jagatpura market, Rajasthan, India. Zinc acetate (GR) and NaOH were purchased from Merck and Sigma-Aldrich. All the other reagents used in this study were procured locally.
2.2 Preparation of plant extract
The pumpkin seeds were cleaned with tap water to remove debris, and other undesired items were washed with double-distilled water and air-dried at room temperature. In a 250 mL round bottom flask, 5.0 g of fine-powdered pumpkin seeds were added to 100 mL of double-distilled water and refluxed for 45 min. The extracts were cooled at room temperature and filtered through Whatman filter paper no. 1 for the downstream processing.
2.3 Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs
In a 250 mL conical flask, 20 mL of pumpkin seed extracts were heated at 50°C for 10 min and, then, 50 mL of 91 mM zinc acetate solution was added dropwise with continuous stirring. The reaction mixture turned yellowish, and a cream-colored precipitate of zinc hydroxide was formed. The reaction mixture was allowed to stand for 30 min to complete the reduction to zinc hydroxide and then centrifuged at 16,000 rpm for 10 min. The residue was vacuum dried at 40–50°C and preserved for further investigations. The reduction of Zn2+ to Zn0 was confirmed by the change in color of the solution from light yellow to cream. The UV-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy (Shimadzu, USA) showed a peak in the range of 272 nm, indicating the formation of ZnO NPs.
2.4 Characterization of ZnO NPs
The biogenic synthesis of ZnO NPs were confirmed by several spectral techniques, such as Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). FTIR spectra (Perkin Elmer 1750) were recorded to identify bioactive functional groups present in the seed extract, a peak at 563 cm−1 confirmed the formation of ZnO NPs. A broad rise at 3,452 cm−1 indicates aliphatic −OH of carboxylic acid. The X-ray diffraction, SEM, and TEM of ZnO NPs showed spherical shape and size in the range of 50–60 nm. X-ray diffractometer with a Cu Kα radiation was applied to acquire an XRD pattern of nanoparticles that suggested the crystalline nature of ZnO NPs. The size distribution of particles was determined using dynamic light scattering (Malvern).
2.5 Cell culture maintenance
The MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line was obtained from the National Centre for Cell Sciences, Pune, India. The cell line was maintained in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C using DMEM high glucose media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, penicillin (100 U/mL), and streptomycin (100 g/mL).
2.6 Cytotoxicity (MTT) assay
The MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with different concentrations of ZnO NPs (2.5–17.5 µg/mL) for 24 h to assess the cytotoxicity. After treatment, each well was added with 10 µL of MTT (5 mg/mL), followed by 2 h of incubation at 37°C. By adding 100 µL of DMSO to the purple-precipitated formazan, the absorbance was measured at 540 nm using a multi-well plate reader (BioTek, USA). The percentage of viable cells after the treatment compared to control cells was used to calculate the viability of the cells.
The ZnO NPs’ dose–responsive curve calculated the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50). The optimum concentrations for future experiments were chosen based on the IC50 value.
2.7 Measurement of apoptotic induction
The method adopted by Baskić et al. [39], was used to perform a microscopic fluorescence examination of apoptotic cell death in a six-well plate treated with different concentrations of ZnO NPs (7.5, 10, and 12.5 µg/mL) for 24 h. After the treatment, the cells were washed in cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and stained with acridine orange/ethidium bromide (1:1 ratio; 100 µg/mL) for 5 min before visualizing under a fluorescence microscope (40× magnification). The number of cells exhibiting apoptosis was calculated as a percentage of the total number of cells.
2.8 Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production
The dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate test detected intracellular ROS levels [40]. MDA-MB-231 cells (2 × 106 cells/well) were treated with different concentrations of ZnO NPs (7.5, 10, and 12.5 µg/mL) for 24 h at 37°C. The fluorescence was measured using a spectrofluorometer (Shimadzu, Columbia, USA) every 5 min for up to 30 min (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm). A mean slope/min was used to calculate the increase in ROS production, which was then normalized to the unexposed control.
2.9 Cell adhesion assay
Cells were separated at 0-, 15-, 30-, 45-, and 60-min intervals in six-well plates, and wells were rinsed with PBS to remove weakly attached/unattached cells. The seeded cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde (5%) and crystal violet (1%) and fostered for 15 min. After 15 min, crystal violet was bounded to the cellular proteins, and excess crystal violet dye was washed with PBS. The amount of crystal violet destained to protein was proportional to the number of cells in the well.
2.10 Scratch assay
The cells were scratched by a sterile 200 μL pipette tip to make a straight line. After two cleanses with PBS, the cells were treated with different doses of ZnO NP (7.5, 10, and 12.5 µg/mL) and maintained at 37°C for 36 h. The distances among the two edges of the wound were determined as the reference points and analyzed.
2.11 Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent values (wherever applicable). One-way analysis of variance was used to compare control and treated cells. The size distribution histogram of ZnO NPs was calculated using ImageJ and OriginPro 2018 software, and a total of 135 nanoparticles were counted in the study.
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs
Recently, green-synthesized plant-based NPs have been recognized as a potential weapon in cancer therapy [41,42]. The advantage of the green method of NP formulations is the limited use of toxic reagents and byproducts along with minimum invasiveness and maximum biocompatibility [42]. Several studies reported the synthesis of different metallic NPs from various natural sources and observed anticancer activity in different cancer models [19,20,43]. Owing to the multifunctional properties of green-synthesized NPs, we exploited this methodology to biosynthesize ZnO NPs from pumpkin seed extract and evaluated its anticancer potential in breast cancer cell lines. Earlier studies also revealed broader applicability of ZnO NPs that have shown effective interactions with biological membranes and exhibited antibacterial and anticancer behaviors [24]. Depending on its nanostructure characteristics and levels of treatment, the ZnO NPs have demonstrated detrimental effects on various human malignancies, including lung, hepatocytes, alveolar, ovarian, colon, and breast cancers [44]. The current method of ZnO NPs production is a phytochemically driven process in which the pumpkin seed extracts that contain a variety of reducing substances, such as terpenoid, α-, and β-carotene, flavonoid, saponin, vitamins, and phenol moieties, perhaps convert zinc cations into ZnO NPs. Thus, the presence of phytochemicals is thought to encourage the reduction of zinc cations to zerovalent zinc, which leads to the clustering of zinc atoms into NPs. In addition, the richly accessible alkaloids and flavonoids present in the pumpkin seed extracts could function as stabilizers and capping agents [48]. In the current green synthesis protocol, the reduction of Zn2+ to Zn0 was confirmed by the change in color of the solution from light yellow to cream. The reaction mixture of pumpkin seed extract with zinc acetate solvent enabled the intense color shift that confirmed the formation of ZnO NPs.
3.2 Characterization of ZnO NPs
3.2.1 UV-vis spectroscopy
The biosynthesis of ZnO NPs and their stability were confirmed by UV-vis spectra. The light brown powder identified that the UV-vis spectrum of the synthesized ZnO NPs conducting electrons start oscillating at a specific wavelength due to the surface plasmon resonance effect. Figure 1 displays the UV-vis spectra of ZnO NPs, where the peak at 272 nm confirms the formation of biogenic NPs. The oscillation of more electrons after 4 h describes the continuous synthesis of ZnO NPs. Earlier studies also reported an absorption peak at 272 nm for the ZnO NPs synthesized from other sources [45,46].

UV-vis spectra of ZnO NPs synthesized from the extract of pumpkin seeds.
3.2.2 FTIR analysis
FTIR analysis is one of the most reliable and sensitive methods to identify the biomolecules involved in the green synthesis of NPs from metal ions [47]. The pumpkin seed extract was found to be rich in bioactive metabolites, as shown by IR spectrum peaks (Figure 2), which may have supported the synthesis of biogenic ZnO NPs. Our FTIR spectra displayed a strong vibration at around 671–482 cm−1 showing the Zn–O stretching vibration frequencies [48]. FT-IR spectra and functional group identification found a peak in the range of 500–4,000 cm−1 (Figure 2). Broad signals observed at 3,498 cm−1 (−NH), 3,259 (−OH), amines, hydroxyl, 1,751 (ester), and 1,689 (carbonyl) may be attributed to green extract. The peak at 1,581 indicates the C═C stretch in the aromatic ring and C═O stretch in polyphenols. On the other hand, the peak at 1,488 cm−1 indicates the C–N stretch of amide. Moreover, a peak at 563 cm−1 showed Zn–O stretching and confirmed the formation of ZnO NPs [49]. Our findings concur with earlier research that reports that the hydroxyl and carbonyl groups of algal biomass act as reducing and capping agents to effectively synthesize metal NPs [50].

(a) FTIR of pumpkin seeds’ extract and (b) FTIR of ZnO NPs derived from the extract of pumpkin seeds.
3.2.3 XRD analysis
The crystalline lattice of biogenic ZnO NPs was determined by the XRD technique. XRD was recorded in the range of 2θ (10–80°) at a scanning rate of 2°/min (Figure 3). Close observation of the XRD revealed that the biosynthesized ZnO NPs have 2θ intensity peaks at 31.72, 34.32, 36.16, 47.35, 56.38, 62.87, and 67.91° with Miller indices of orientation plans (1 0 0), (0 0 2), (1 0 1), (1 0 2), (1 1 0), (1 0 3), and (1 1 2) matching with the hexagonal phase having a wurtzite structure (JCPDS no. 36-1451). A similar pattern was observed for ZnO NPs synthesized from other sources [51].

XRD data of biogenic ZnO NPs.
3.2.4 Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) analysis
The morphology of biosynthesized ZnO NPs was characterized by the FESEM technique. The SEM analysis confirmed the distribution of ZnO NPs on the surface (Figure 4a). A statistical analysis of the particle size histogram of ZnO NPs reveals the particle size in the range of 10–130 nm, with an average size of 58 ± 23 nm (Figure 4b). Some small particles (5–10 nm) were also observed, which could be attributed to vigorous shaking. The frequency distribution of the particles in the histogram shows that nearly 80% are in the 50–60 nm range. The particle size and dispersion stability are critical considerations to avoid adverse events such as venous thrombosis during in vivo application [52]. Our biogenic ZnO NPs were developed with a size of <100 nm to maximize the effective delivery and reduced danger of venous thrombosis [53].

(a) FESEM image of biosynthesized ZnO NPs. (b) Particle size distribution histogram of ZnO NPs.
3.2.5 TEM analysis
The particle size and structural morphology of the biosynthesized ZnO NPs were described by TEM analysis (Figure 5). The TEM data clarify that most of the base ZnO NPs are spherical and hexagonal in shape, with a 48–50 nm diameter range. Due to the large specific area and high surface energy, the same NPs accumulate during the process of drying.

HR-TEM image of biogenic ZnO NPs.
3.3 Cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs
3.3.1 Cytotoxicity and morphological alterations
We observed a significant decrease in the viability of MDA-MB-231 cells with an increasing concentration of ZnO NPs compared to the untreated solvent control (Figure 6). The viability of cells started declining from the lowest tested concentration (2.5 µg/mL) and decreased up to 20% at 17.5 µg/mL of ZnO NP after 24 h of treatment. The IC50 concentrations of biosynthesized ZnO NPs were found to be 10 µg/mL. Several studies also reported significant cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs in MDA-MB-231 cell line, which corroborates well with our findings [54,55]. Bangroo et al. observed significantly decreased cell viability of MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner by ZnO NPs prepared from Catharanthus roseus leaves extract [55]. Similarly, Kc et al. reported dose-dependent cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs in MDA-MB-231 cell lines with IC50 of 38.44 µg/mL [56]. On the other hand, Aalami et al. observed significantly reduced cell viability of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with ZnO NPs biosynthesized from Saponaria officinalis with an IC50 concentration of 60.08 μg/mL [54]. The release of zinc into the cell culture atmosphere with the help of CO2, high solubility, and oxidative stress promotion ability might be the reasons for the observed cytotoxicity of ZnO NPs [57]. One study also reported that the toxicity of ZnO NPs is caused by the breakdown of ZnO NPs, which results in the formation of Zn2+ ions [58]. Our results show the better anticancer potential of green-synthesized ZnO NPs, with a significantly lower IC50 concentration.

Dose-dependent decrease in the cell viability of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with ZnO NPs.
Concentration-dependent changes in the cell morphology, such as shrinkage, detachment, membrane blebbing, and distorted shape, were observed by ZnO NPs’ treatment in MDA-MB-231 cells (Figure 7). However, the control cells showed normal intact cell morphology. One study also reported significant changes in cancer cell morphology due to ZnO NPs’ treatment [56].

Morphological alterations in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with ZnO NPs.
3.3.2 Effect of ZnO NPs on apoptosis induction
The characteristic hallmarks of apoptotic cells include cell shrinkage, chromatin cleavage, nuclear condensation, disintegration, formation of pyknotic bodies, etc. [56,59]. MDA-MB-231 cells treated with different concentrations of ZnO NPs showed a significant increase in early apoptotic cells. Living cells showed a normal green nucleus, early apoptotic cells showed yellow fluorescence, indicating a condensed or fragmented nucleus with chromatin, and late apoptotic cells showed orange fluorescence, indicating chromatin condensation or fragmentation and cell necrosis (Figure 8). The morphological alteration caused by nuclear material fragmentation of the treated cells suggests possible activation of caspase cascades and induction of apoptosis. One study observed inhibition in the proliferation of cancer cells by inducing the activity of caspases and triggering apoptosis by synthesized ZnO NPs from Cucumis melo inodorus [60]. ZnO NPs also increase the number of cells in the sub-G1 phase, causing damage to the DNA and apoptosis. The DNA damage in cancer cells results in the significant expression of p53 protein [58]. The p53 pathway selectively triggers apoptosis in cancer cells and activates other genes involved in cell cycle checkpoint activation [61]. In addition to the cell cycle regulation, the p53 protein is known to trigger the transcription of the pro-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma protein 2 (Bcl-2)-associated X (Bax) gene, which in turn neutralizes the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and triggers the induction of apoptotic pathways [44,62]. Bcl-2 encodes a protein that prevents cell death, enhances cellular survival against many toxins and drugs by blocking the apoptosis pathway, and ultimately results in the cancer phenotype [63]. In one study, Aalami et al. reported the modulation in the expression of apoptosis effector genes, caspase-3 and caspase-8, in response to green-synthesized ZnO NPs in breast cancer cells [54]. Boskabadi et al. suggested green-synthesized ZnO NPs as a natural apoptosis inducer [44].

Induction in apoptosis as a result of ZnO NPs’ treatment in MDA-MB-231 cells.
3.3.3 Effect of ZnO NPs on ROS production
The induction in apoptosis by chemotherapeutic agents leads to ROS production and plays a critical role in cancer cell death. We observed a significant dose-dependent increase in intracellular ROS production in response to ZnO NPs’ treatment, which enhanced DCF fluorescent intensity in treated MDA-MB-231 cells (Figure 9). The untreated control cells showed dull green fluorescence; however, bright DCF-stained green fluorescence was observed in ZnO NP-treated cells. Despite its vital role in cell development and differentiation, the accumulation of intracellular ROS above the threshold level results in irreversible damage to several cellular processes and their further accretion leads to cell death [64]. Zn ionization and subsequent scavenging of free radicals by the NP’s surface are essential for ZnO NPs to carry out their biological functions, which causes numerous metabolic changes in the cells [65]. Conversely, Zn O NPs induce oxidative stress by increasing the production of ROS in cells [66]. Earlier studies also suggested a decreased expression of antioxidant enzymes (GSH, CAT, and SOD) after oral exposure to ZnO NPs in rodent models, highlighting a rise in ROS levels [67,68]. In addition, the excess production of ROS could lead endoplasmic reticulum dysfunctions, which also causes cell death [69]. These generalized mechanisms could explain ROS-dependent oxidative stress, leading to apoptosis. In one study, Bai et al. reported the proapoptotic effects of ZnO NPs by inducing ROS production and ensuing oxidative stress in human ovarian cancer cells [58]. Our results are concurrent with earlier studies that reported an increase in ROS production as one of the main cytotoxicity approaches of green-synthesized ZnO NPs [54,61,70].

Effect of ZnO NPs on the intracellular ROS generation in MDA-MB-231 cells.
3.3.4 Effect of ZnO NPs on cell adhesion
The cell adhesion experiment showed cell growth inhibition compared with the untreated control. The maximum inhibition was recorded at the highest tested concentration, where cancer cells were minimally adhered at the bottom of the plate (Figure 10).

Effect of ZnO NPs on cell adhesion in MDA-MB-231 cells.
3.3.5 Effect of ZnO NPs on cellular migration by scratch assay
Cellular migration is an essential phenomenon in cancer progression. In this assay, the assessment of the anti-migration ability of anticancer compounds are measured without promoting cell death [71]. As observed in Figure 11, treatment with different doses of ZnO NPs (7.5, 10, and 12.5 μg/mL) decreased cell motility and migration of cancer cells where the complete closure of the scratched area was inhibited. The results obtained in this assay indicate a generally positive trend in the inhibiting potential of ZnO NPs for cell migration. The relative inhibition was calculated by comparing the residual scar areas after 24-h edge progression vs the initial gap area. The untreated control cells promoted wound healing and completely migrated after 24 h of incubation. However, we observed the inhibited cell migration and non-closure of a gap at the highest concentration after 24 h. The cancer cells exhibit the ability to form a colony, and the treatment with anticancer agents results in reduced colony formation [72,73]. The anti-migratory effect of anticancer drugs could prevent cancer-related mortality without progressing to the metastatic stage [73]. Recently, one study also reported the inhibition in the migratory property of MDA-MB-231 cells by the treatment of ZnO NPs [64]. We also observed a similar pattern in response to biogenic AgNPs in HCT-116 and MCF-7 cell lines [43]. The above results indicate that inhibiting migratory signaling could be an efficient approach to control the invasion and migration of cancer cells [64,73]. To summarize our article, a schematic diagram depicting the proposed mechanism of ZnO NPs anticancer activity has also been included in Figure 12.

Effect of ZnO NPs on cell migration in MDA-MB-231 cells.
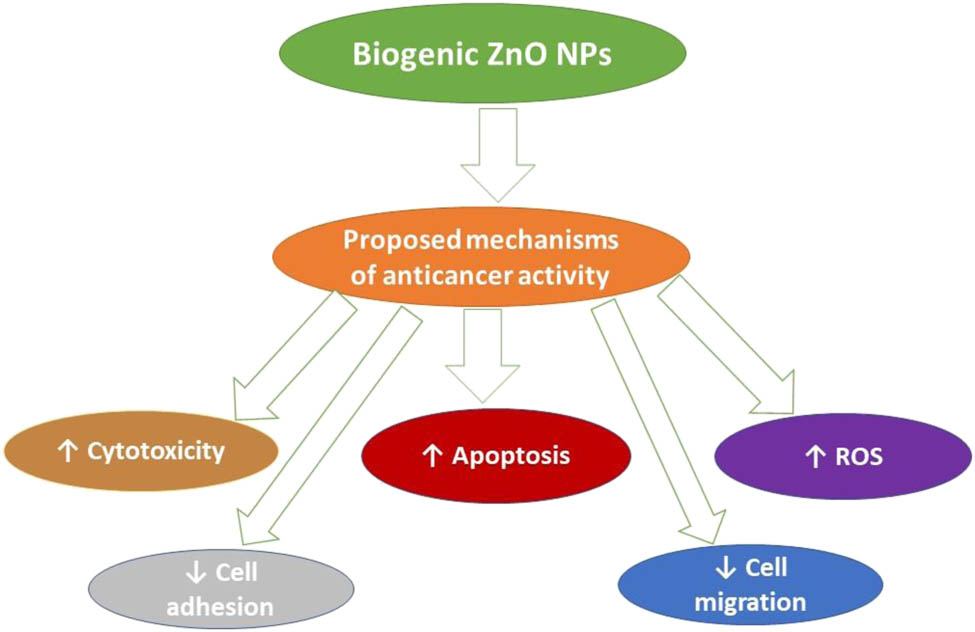
Proposed mechanism of the anticancer activity of ZnO NPs.
4 Conclusion
We employed pumpkin seed extract to synthesize ZnO NPs in a green and ecofriendly way. The first indicator of ZnO NPs biosynthesis was a change in the color of the reaction solution from light yellow to cream with an average particle size of 50–60 nm. In MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, our biogenic ZnO NPs revealed considerable cytotoxicity, apoptotic induction, generation of ROS, inhibition, and migration, demonstrating their anticancer potential. The bioactive compounds, such as carotenoids, flavonoids, vitamins, and other phenolics, in pumpkin seed extract might have role in the observed anticancer activity. The mechanism of action appears to be the induction of apoptosis and increased production of ROS. However, more research in different in vitro models is needed to determine the exact mechanism of action and best cancer model so that this novel nano-formulation could be validated in a specific in vivo model and further exploited for the benefit of humanity.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the research facilities provided by King Fahd Medical Research Center, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
-
Funding information: The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, for funding this research work through the project number “IFPRC-146-141-2020” and King Abdulaziz University, DSR, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Cipriani C, Pacheco MP, Kishk A, Wachich M, Abankwa D, Schaffner-Reckinger E, et al. Bruceine D identified as a drug candidate against breast cancer by a novel drug selection pipeline and cell viability assay. Pharm (Basel). 2022;15(2):179.10.3390/ph15020179Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.10.3322/caac.21660Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Paz MFCJ, Gomes ALJ, Islam MT, Tabrez S, Jabir NR, Alam MZ, et al. Assessment of chemotherapy on various biochemical markers in breast cancer patients. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3):2923–8.10.1002/jcb.26487Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Paz MFCJ, Gomes Júnior AL, de Alencar MVOB, Tabrez S, Islam MT, Jabir NR, et al. Effect of diets, familial history, and alternative therapies on genomic instability of breast cancer patients. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;188(1):282–96.10.1007/s12010-018-2918-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Assidi M, Buhmeida A, Al-Zahrani MH, Al-Maghrabi J, Rasool M, Naseer MI, et al. The prognostic value of the developmental gene FZD6 in young saudi breast cancer patients: a biomarkers discovery and cancer inducers oncoscreen approach. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:783735.10.3389/fmolb.2022.783735Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Malik JA, Ahmed S, Jan B, Bender O, Al Hagbani T, Alqarni A, et al. Drugs repurposed: an advanced step towards the treatment of breast cancer and associated challenges. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;145:112375.10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112375Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Chen J, Zou Q, Li J. DeepM6ASeq-EL: prediction of human N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites with LSTM and ensemble learning. Front Comput Sci. 2021;16(2):162302.10.1007/s11704-020-0180-0Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Lai W-F, Wong W-T. Use of graphene-based materials as carriers of bioactive agents. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2021;16(5):577–88.10.1016/j.ajps.2020.11.004Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Li B, Li C, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Jia D, Yang M. Grinding temperature and energy ratio coefficient in MQL grinding of high-temperature nickel-base alloy by using different vegetable oils as base oil. Chin J Aeronaut. 2016;29(4):1084–95.10.1016/j.cja.2015.10.012Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Wang X, Li C, Zhang Y, Ding W, Yang M, Gao T, et al. Vegetable oil-based nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication turning: Academic review and perspectives. J Manuf Process. 2020;59:76–97.10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.09.044Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Yang L, Wu X, Luo M, Shi T, Gong F, Yan L, et al. Na+/Ca2+ induced the migration of soy hull polysaccharides in the mucus layer in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;199:331–40.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Huang K, Lin Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Cai S, Pang L, et al. Predictive model for minimum chip thickness and size effect in single diamond grain grinding of zirconia ceramics under different lubricating conditions. Ceram Int. 2019;45(12):14908–20.10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.226Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Zhang J, Li C, Zhang Y, Yang M, Jia D, Liu G, et al. Experimental assessment of an environmentally friendly grinding process using nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication with cryogenic air. J Clean Prod. 2018;193:236–48.10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.009Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Zou Q, Xing P, Wei L, Liu B. Gene2vec: gene subsequence embedding for prediction of mammalian N 6-methyladenosine sites from mRNA. RNA. 2019;25(2):205–18.10.1261/rna.069112.118Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Ejaz A, Babar H, Ali HM, Jamil F, Janjua MM, Fattah IMR, et al. Concentrated photovoltaics as light harvesters: outlook, recent progress, and challenges. Sustain Energy Technol Assess. 2021;46:101199.10.1016/j.seta.2021.101199Suche in Google Scholar
[16] ShuMing G, ChangHe L, YanBin Z, YaoGang W, BenKai L, Min Y, et al. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication performance of mixtures of castor oil with other vegetable oils in MQL grinding of nickel-based alloy. J Clean Prod. 2017;140(Part 3):1060–76.10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.073Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Tabrez S, Jabir NR, Adhami VM, Khan MI, Moulay M, Kamal MA, et al. Nanoencapsulated dietary polyphenols for cancer prevention and treatment: successes and challenges. Nanomed (Lond). 2020;15(11):1147–62.10.2217/nnm-2019-0398Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Alserihi RF, Mohammed MRS, Kaleem M, Khan MI, Sechi M, Sanna V, et al. Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment. Nanotechnol Rev. 2022;11(1):298–311.10.1515/ntrev-2022-0013Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Tabrez S, Khan AU, Mirza AA, Suhail M, Jabir NR, Zughaibi TA, Alam M. Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) and its efficacy against colon cancer. Nanotechnol Rev. 2022;11:1322–31.10.1515/ntrev-2022-0081Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Zughaibi TA, Mirza AA, Suhail M, Jabir NR, Zaidi SK, Wasi S, et al. Evaluation of anticancer potential of biogenic copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) against breast cancer. J Nano Mater. 2022;2022:1–7.10.1155/2022/5326355Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Gowd V, Ahmad A, Tarique M, Suhail M, Zughaibi TA, Tabrez S, et al. Advancement of cancer immunotherapy using nanoparticles-based nanomedicine. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;S1044-579X(22)00081-5.10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.03.026Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Shait Mohammed MR, Ahmad V, Ahmad A, Tabrez S, Choudhry H, Zamzami MA, et al. Prospective of nanoscale metal organic frameworks [NMOFs] for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;69:129–39.10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.12.015Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Khashan KS, Badr BA, Sulaiman GM, Jabir MS, Hussain SA. Antibacterial activity of Zinc Oxide nanostructured materials synthesis by laser ablation method. J Phys Conf Ser. 2021;1795(1):012040.10.1088/1742-6596/1795/1/012040Suche in Google Scholar
[24] Alyamani AA, Albukhaty S, Aloufi S, AlMalki FA, Al-Karagoly H, Sulaiman GM. Green fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using phlomis leaf extract: characterization and in vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity and antibacterial properties. Molecules. 2021;26(20):6140.10.3390/molecules26206140Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Hano C, Abbasi BH. Plant-based green synthesis of nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Biomolecules. 2021;12(1):31.10.3390/biom12010031Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Hassan SE, Fouda A, Saied E, Farag MMS, Eid AM, Barghoth MG, et al. Rhizopus oryzae-mediated green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs): a promising tool for antimicrobial, mosquitocidal action, and tanning effluent treatment. J Fungi. 2021;7(5):372.10.3390/jof7050372Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Khan AU, Malik N, Khan M, Cho MH, Khan MM. Fungi-assisted silver nanoparticle synthesis and their applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2018;41(1):1–20.10.1007/s00449-017-1846-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Naseer M, Aslam U, Khalid B, Chen B. Green route to synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9055.10.1038/s41598-020-65949-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Sushma NJ, Mahitha B, Mallikarjuna K, Raju BDP. Bio-inspired ZnO nanoparticles from Ocimum tenuiflorum and their in vitro antioxidant activity. Appl Phys A. 2016;5(122):1–10.10.1007/s00339-016-0069-9Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Zare E, Pourseyedi S, Khatami M, Darezereshki E. Simple biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using nature’s source, and it’s in vitro bio-activity. J Mol Struct. 2017;1146:96–103.10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.05.118Suche in Google Scholar
[31] Cao Y, Dhahad HA, El-Shorbagy MA, Alijani HQ, Zakeri M, Heydari A, et al. Green synthesis of bimetallic ZnO–CuO nanoparticles and their cytotoxicity properties. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):23479.10.1038/s41598-021-02937-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Xu J, Huang Y, Zhu S, Abbes N, Jing X, Zhang L. A review of the green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using plant extracts and their prospects for application in antibacterial textiles. J Eng Fibers Fabr. 2021;16:15589250211046242.10.1177/15589250211046242Suche in Google Scholar
[33] Low DYS, Mahendra CK, Supramaniam J, Tan LTH, Lee LH, Manickam S, et al. Ultrasound-enhanced biosynthesis of uniform ZnO nanorice using Swietenia macrophylla seed extract and its in vitro anticancer activity. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10(1):572–85.10.1515/ntrev-2021-0044Suche in Google Scholar
[34] AlSalhi MS, Devanesan S, Atif M, AlQahtani WS, Nicoletti M, Serrone PD. Therapeutic potential assessment of green synthesized Zinc Oxide nanoparticles derived from fennel seeds extract. IJN. 2020;15:8045–57.10.2147/IJN.S272734Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Liu D, Liu L, Yao L, Peng X, Li Y, Jiang T, et al. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using radish root extract for effective wound dressing agents for diabetic foot ulcers in nursing care. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol. 2020;55:101364.10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101364Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Chakraborty S, Farida JJ, Simon R, Kasthuri S, Mary NL. Averrhoe carrambola fruit extract assisted green synthesis of zno nanoparticles for the photodegradation of congo red dye. Surf Interfaces. 2020;19:100488.10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100488Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Durmuş A, Çolak H, Karaköse E. Production and examination of ZnO thin film for first time using green synthesized method from aqueous Citrus reticulata peel extract. J Alloy Compd. 2019;809:151813.10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151813Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Zubair N, Akhtar K. Morphology controlled synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for in-vitro evaluation of antibacterial activity. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2020;30(6):1605–14.10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65323-7Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Baskić D, Popović S, Ristić P, Arsenijević NN. Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: fluorescence microscopy using annexin V/propidium iodide versus acridin orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol Int. 2006;30(11):924–32.10.1016/j.cellbi.2006.06.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Aranda A, Sequedo L, Tolosa L, Quintas G, Burello E, Castell JV, et al. Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay: a quantitative method for oxidative stress assessment of nanoparticle-treated cells. Toxicol Vitro. 2013;27(2):954–63.10.1016/j.tiv.2013.01.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Medina Cruz D, Mostafavi E, Vernet-Crua A, Barabadi H, Shah V, Cholula-Díaz JL, et al. Green nanotechnology-based zinc oxide (ZnO) nanomaterials for biomedical applications: a review. J Phys Mater. 2020;3(3):034005.10.1088/2515-7639/ab8186Suche in Google Scholar
[42] Ahmed Rather G, Nanda A, Ahmad Pandit M, Yahya S, sofi MA, Barabadi H, et al. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles using Bergenia ciliate aqueous extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic and antioxidant potential. Inorg Chem Commun. 2021;134:109020.10.1016/j.inoche.2021.109020Suche in Google Scholar
[43] Khan MS, Alomari A, Tabrez S, Hassan I, Wahab R, Bhat SA, et al. Anticancer potential of biogenic silver nanoparticles: a mechanistic study. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(5):707.10.3390/pharmaceutics13050707Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Boskabadi SH, Balanezhad SZ, Neamati A, Tabrizi MH. The green-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticle as a novel natural apoptosis inducer in human breast (MCF7 and MDA-MB231) and colon (HT-29) cancer cells. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem. 2021;51(5):733–43.10.1080/24701556.2020.1808991Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Goutam SP, Yadav AK, Das AJ. Coriander extract mediated green synthesis of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. J Nanosci Technol. 2017;249–52.Suche in Google Scholar
[46] Khan AU, Khan M, Malik N, Parveen A, Sharma P, Min K, et al. Screening of biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for their effect on Daucus carota pathogen and molecular docking. Microsc Res Tech. 2022. 10.1002/jemt.24191.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Al-Zahrani S, Astudillo-Calderón S, Pintos B, Pérez-Urria E, Manzanera JA, Martín L, Gomez-Garay A. Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles with aqueous extract of green algae Chaetomorpha ligustica and its anticancer potential. Green Process Synth. 2021;10(1):711–21.10.1515/gps-2021-0067Suche in Google Scholar
[48] Ali SG, Ansari MA, Jamal QMS, Almatroudi A, Alzohairy MA, Alomary MN, et al. Butea monosperma seed extract mediated biosynthesis of ZnO NPs and their antibacterial, antibiofilm and anti-quorum sensing potentialities. Arab J Chem. 2021;14(4):103044.10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103044Suche in Google Scholar
[49] Yedurkar S, Maurya C, Mahanwar P. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles using ixora coccinea leaf extract – a green approach. Open J Synth Theory Appl. 2016;5(1):1–14.10.4236/ojsta.2016.51001Suche in Google Scholar
[50] Chugh D, Viswamalya VS, Das B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with algae and the importance of capping agents in the process. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021;19(1):126.10.1186/s43141-021-00228-wSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Loganathan K, Kumar VP, Ahamed J. Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Phyllanthus Emblica seed powder and its structural and optical characterization studies. J Environ Nanotechnol. 2018;7(3):1–4.10.13074/jent.2018.09.183320Suche in Google Scholar
[52] Tanino R, Amano Y, Tong X, Sun R, Tsubata Y, Harada M, et al. Anticancer activity of ZnO nanoparticles against human small-cell lung cancer in an orthotopic mouse model. Mol Cancer Therapeutics. 2020;19(2):502–12.10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0018Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Wilhelm S, Tavares AJ, Dai Q, Ohta S, Audet J, Dvorak HF, et al. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;1(5):1–12.10.1038/natrevmats.2016.14Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Aalami AH, Mesgari M, Sahebkar A. Synthesis and characterization of green zinc oxide nanoparticles with antiproliferative effects through apoptosis induction and microrna modulation in breast cancer cells. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2020;2020:e8817110–17.10.1155/2020/8817110Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Bangroo A, Malhotra A, Sharma U, Jain A, Kaur A. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles using Catharanthus Roseus leaves and their therapeutic response in breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells. Nutr Cancer. 2021;74:1489–96.10.1080/01635581.2021.1952622Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Kc B, Paudel SN, Rayamajhi S, Karna D, Adhikari S, Shrestha BG, et al. Enhanced preferential cytotoxicity through surface modification: synthesis, characterization and comparative in vitro evaluation of TritonX-100 modified and unmodified zinc oxide nanoparticles in human breast cancer cell (MDA-MB-231). Chem Cent J. 2016;10:16.10.1186/s13065-016-0162-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Yang S-T, Liu J-H, Wang J, Yuan Y, Cao A, Wang H, et al. Cytotoxicity of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles: importance of microenvironment. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2010;10(12):8638–45.10.1166/jnn.2010.2491Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Bai D-P, Zhang X-F, Zhang G-L, Huang Y-F, Gurunathan S. Zinc Oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells. IJN. 2017;12:6521–35.10.2147/IJN.S140071Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Alharthy S, Tabrez S, Mirza A, Zughaibi T, Firoz C, Dutta M. Sugiol suppresses the proliferation of human U87 glioma cells via induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med. 2022;2022:7658899.10.1155/2022/7658899Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[60] Mahdizadeh R, Homayouni-Tabrizi M, Neamati A, Seyedi SMR, Tavakkol Afshari HS. Green synthesized-zinc oxide nanoparticles, the strong apoptosis inducer as an exclusive antitumor agent in murine breast tumor model and human breast cancer cell lines (MCF7). J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):17984–93.10.1002/jcb.29065Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] Anjum S, Hashim M, Malik SA, Khan M, Lorenzo JM, Abbasi BH, et al. Recent advances in zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) for cancer diagnosis, target drug delivery, and treatment. Cancers. 2021;13(18):4570.10.3390/cancers13184570Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[62] Reisman D, Takahashi P, Polson A, Boggs K. Transcriptional regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in S-phase of the cell-cycle and the cellular response to DNA damage. Biochem Res Int. 2012;2012:e808934.10.1155/2012/808934Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[63] Singh R, Letai A, Sarosiek K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(3):175–93.10.1038/s41580-018-0089-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[64] Banupriya SK, Kavithaa K, Poornima A, Sumathi S. Mechanistic study on thymoquinone conjugated ZnO nanoparticles mediated cytotoxicity and anticancer activity in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(2):313–27.10.2174/1871520621666210412104731Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[65] Song W, Zhang J, Guo J, Zhang J, Ding F, Li L, et al. Role of the dissolved zinc ion and reactive oxygen species in cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett. 2010;199(3):389–97.10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.10.003Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Namvar F, Rahman HS, Mohamad R, Azizi S, Tahir PM, Chartrand MS, et al. Cytotoxic effects of biosynthesized Zinc Oxide nanoparticles on murine cell lines. Evidence-Based Complementary Alternative Med. 2015;2015:e593014.10.1155/2015/593014Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Attia H, Nounou H, Shalaby M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induced oxidative DNA damage, inflammation and apoptosis in rat’s brain after oral exposure. Toxics. 2018;6(2):29.10.3390/toxics6020029Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Negahdary M, Chelongar R, Zadeh SK, Ajdary M. The antioxidant effects of silver, gold, and zinc oxide nanoparticles on male mice in in vivo condition. Adv Biomed Res. 2015;4(1):69.10.4103/2277-9175.153893Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[69] Sadhukhan P, Kundu M, Chatterjee S, Ghosh N, Manna P, Das J, et al. Targeted delivery of quercetin via pH-responsive zinc oxide nanoparticles for breast cancer therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;100:129–40.10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.096Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[70] Karimzadeh MR, Soltanian S, Sheikhbahaei M, Mohamadi N. Characterization and biological activities of synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using the extract of Acantholimon serotinum. Green Process Synth. 2020;9(1):722–33.10.1515/gps-2020-0058Suche in Google Scholar
[71] Ovejero Paredes K, Díaz-García D, García-Almodóvar V, Lozano Chamizo L, Marciello M, Díaz-Sánchez M, et al. Multifunctional silica-based nanoparticles with controlled release of organotin metallodrug for targeted theranosis of breast cancer. Cancers. 2020;12(1):E187.10.3390/cancers12010187Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[72] Sabzichi M, Ramezani M, Mohammadian J, Ghorbani M, Mardomi A, Najafipour F, et al. The synergistic impact of quinacrine on cell cycle and anti-invasiveness behaviors of doxorubicin in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Process Biochem. 2019;81:175–81.10.1016/j.procbio.2019.03.007Suche in Google Scholar
[73] Jia T-T, Yang G, Mo S-J, Wang Z-Y, Li B-J, Ma W, et al. Atomically precise gold–levonorgestrel nanocluster as a radiosensitizer for enhanced cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13(7):8320–8.10.1021/acsnano.9b03767Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Shams Tabrez et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption

