Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
-
Yue Qin
, Nan Jiang
and Jinhong Yu
Abstract
To deal with the heat dissipation problem produced by a high integrated circuit, the preparation of heat spreaders with excellent heat transportation performance is increasing in demand. The Ti3C2 MXene sheets and copper particles were fully contacted with cellulose nanofibers by a high-speed mixer, and the composite film was prepared as a heat spreader under the action of the vacuum-assisted filtration. The MXene sheets are connected by the esterification of the carboxyl group in MXene and the hydroxyl group in cellulose nanofibers to form a chemical bond and consist of the main skeleton of the composite film. Due to the synergistic effects of MXene and copper particles, the in-plane and out-of-plane thermal conductivities of the composite film reach 24.96 and 2.46 W m−1 K−1, respectively. Compared with the pure cellulose nanofiber films, the thermal conductivity of composite films increased by 2819.2 and 187.6%, respectively. By designing two applications of composite films in the actual use process, the excellent heating conduction abilities in two directions have been proved. This measure to improve the thermal conductivities of composite films by MXene-copper binary fillers also provides ideas for the novel heat spreader.
Graphical abstract
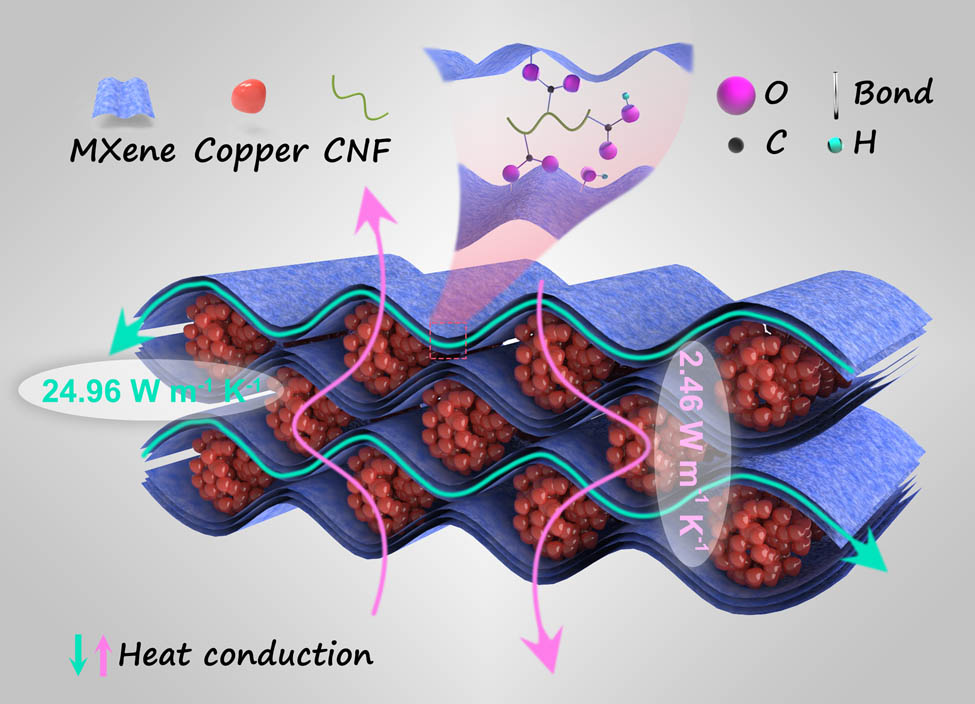
1 Introduction
With the electronic equipment tend to be integrated and lightweight in the fields of aerospace and aviation and microelectronics, higher temperature will result in a decline of the lifetime of electronic equipment and a decrease in work efficiency. Therefore, it is urgent to prepare a suitable heat spreader to dissipate the heat generated from the sustained working electronic equipment. In practical applications, the heat spreader used for heat dissipation needs excellent thermal conduction ability not only in the in-plane direction but also in the through-plane direction. Polymers with their advantages of low weight, low cost, and simple preparation process are widely used in thermal management [1–4]. But their thermal conductivities of about 0.1–0.5 W m−1 K-1 restrict their use in the thermal management field [5–8]. Thermal conductivities of polymer composite films are usually enhanced by adding fillers, which include graphene [9–13], boron nitride (BN) sheets [14–16], and few-layer Ti3C2 MXene [17–19].
MXene is a two-dimensional transition metal carbide, which has been applied in many fields by its excellent electromagnetic shielding, energy storage, high thermal conductivity, and other properties [20–22]. The intrinsic thermal conductivity is still in the theoretical calculation stage, and the thermal conductivity of monomolecular Ti3C2F x reaches 108 W m−1 K−1 at the room temperature [23]. There are many methods for preparing polymer composite films, such as vacuum-assisted filtration [24,25], hot-pressing process [26,27], layer-by-layer spraying technique [28], multiple casting [29], and spin coating process [30]. Zhu et al. fabricated MXene and polyamide (PI) solution into a three-dimensional structure by freeze-drying, for the sake of making MXene sheets fully in contact with polymer macromolecules [27]. And then, the MXene/PI films with the thermal conductivity of 5.12 W m−1 K−1 is prepared by the hot-pressing process. Gao et al. successfully fabricated MXene/thermoplastic polyurethane films using the layer-by-layer spraying technique, which exhibit the thermal conductivities of 6.31 W m−1 K−1 in the in-plane direction and 0.42 W m−1 K−1 in the through-plane direction [28]. Jiao et al. prepared the MXene/CNF films using the vacuum-assisted filtration method, which achieves thermal conductivity of 14.93 W m−1 K−1 in the in-plane direction [25]. It can be found that the MXene as the single filler to fabricate polymer composite films do not achieve the expected high thermal conductivity. Furthermore, the enhancement of thermal conductivity in the through-plane direction is very limited.
The synergistic effect of fillers has a significant impact on the thermal conductivity of polymer composites [31–37]. Compared with the single filler, the distribution of fillers in the polymer matrix is more complex. If the structure is orderly, it will be more conducive to heat transfer. He et al. reported a work on the synergistic effect of GO and BN for enhanced thermal conductivity of the composite films [31]. With the filler content of GO being 1 wt%, the thermal conductivities of the polymer composite films increase from 6.12 to 11.20 W m−1 K−1 as the filler content of BN increases from 0 to 20 wt%. Barani et al. prepared an isotropic polymer composite of an epoxy matrix using graphene and copper particles, which exhibits a thermal conductivity of 13.5 W m−1 K−1 with the synergistic effect of 40 wt% graphene and 35 wt% copper particles [32]. Hence, we are trying to find a way by using the synergistic effect to improve the thermal conductivities of polymer composite films not only in the in-plane direction but also in the through-plane direction.
Herein, the few-layer Ti3C2 MXene sheets and copper particles with high thermal conductivities were utilized to fabricate polymer composite films. MXene sheets, copper particles, and cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) were sheer mixing by a high-speed mixer, and then the composite films were obtained after the vacuum-assisted filtration process. CNF can not only provide a certain bonding effect to combine the MXene layer with the layer (the possible bonding principle is shown in Figure 1) but also has a slightly higher thermal conductivity compared with other amorphous polymers, which also contributes more to the improvement of thermal conductivity of composite films [38]. In comparison to composite films under the synergistic effect of copper particles in different diameters and MXene sheets, it can be seen that composite film with copper particles in 1 μm diameter possesses the highest thermal conductivities of 24.96 W m−1 K−1 in the in-plane direction and 2.46 W m−1 K−1 in the through-plane direction, respectively.
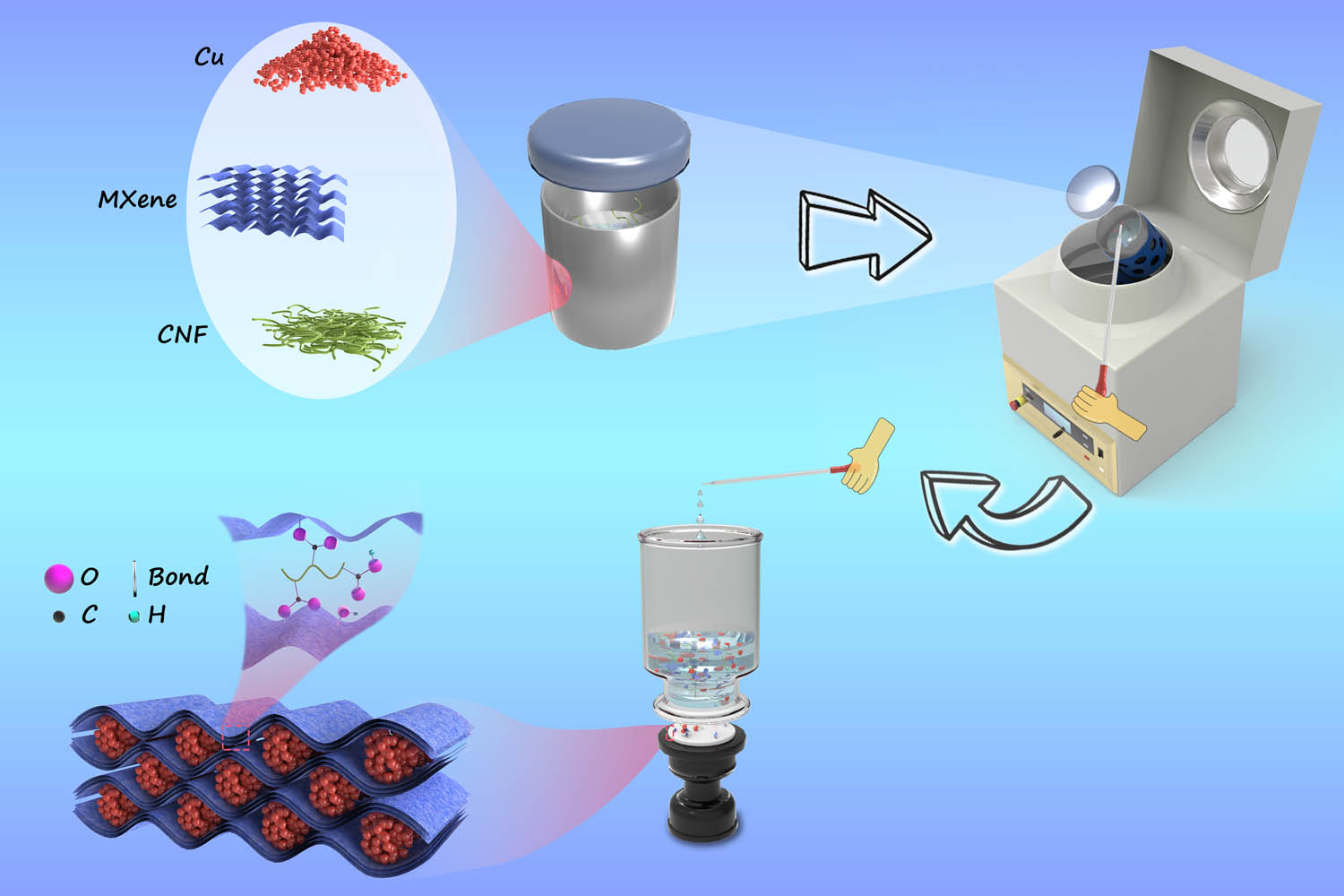
Schematic diagram of the preparation of the MXene/Cu/CNF films.
2 Experimental section
2.1 Materials
Few layer Ti3C2 MXene colloid solution (concentration of 5 mg mL−1) was purchased by Xiyan New Material Technology Co., Ltd (Shandong, China). Copper powders (0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 μm in diameter, purity of 99.999%) were supplied by Nangong Lijia Metal Materials Co., Ltd. (Hebei, China). Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) solution (1.0 wt%, 4–10 nm in diameter, 1–3 μm in length) was offered by Qihong Technology Co., Ltd. (Guangxi, China).
2.2 Preparation of composite films
MXene colloid solution and copper powders were blended and dispersed in deionized water. The mixed dispersion was put into the SpeedMixer (DAC 150.1 FVZ-K, FlackTek SpeedMixerTM, USA) at 3,500 rpm for 5 min. Afterward, the CNF solution was added to the blended solution, and the action was repeated using the SpeedMixer. The obtained dispersion was placed in the ultrasonic cleaner all the time to render the copper powders standing at a dispersing state. The obtained MXene/Cu/CNF dispersion was dropped onto a polycarbonate (PC) filter membrane by a vacuum filtration after the former layer of dropped dispersion dried. The 3 mL dispersion absorbed by a disposable drop tube was dropped into the vacuum filtration glass. After the solution in the glass dried up, the other 3 mL dispersion was dropped into it. Repeat the above process until all the solution is completely moved into the vacuum filtration device, the MXene/Cu/CNF film was formed on the filter membrane. Especially, the filler content of the MXene and copper particles is 27.94 and 23.74 vol%, respectively. The schematic diagram of the preparation of the MXene/Cu/CNF films is shown in Figure 1. The film-forming mechanism is depicted in the bottom left corner of Figure 1. During the whole vacuum filtration process, the carboxyl of CNF and the hydroxyl of the MXene sheet were dehydrated and esterified, which constituted the skeleton of the MXene film [39,40].
2.3 Characterization
The morphologies of Ti3C2 MXene, copper particle, the pure CNF film, and the prepared MXene/Cu/CNF films were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, S4800, Hitachi, Japan) working at an accelerating voltage of 4 kV. High-resolution image of Ti3C2 MXene was characterized by a transmission electron microscope (TEM, Talos F200X, Thermo Fisher, USA) with an accelerated voltage of 200 kV. X-ray diffraction patterns (XRD, D8 Advance, Bruker AXS, Germany) were used to analyze the diffraction peaks of the Ti3C2 MXene and copper particles. The thermal conductivity
3 Results and discussions
The Ti3C2 MXene solution presents a strong Tyndall effect as shown in Figure 2(a), indicating well dispersion of the MXene. The SEM and TEM images of the MXene sheets are exhibited in Figure 2(b) and (c), respectively. The size of a single-layer MXene sheet is about 1 μm obtained by the SEM image, which is also identified by the TEM image. In addition, it can be seen from the TEM image that the number of layers of the MXene sheets is small verifying the existence of few-layer MXene sheets. The XRD spectra of MXene and copper are displayed in Figure 2(d). The MXene of the XRD curve described by the upper image of Figure 2(d) presents the character peak located at 6.86° corresponding to the (002) plane [40,41]. The XRD spectrum of copper particles includes three sharp peaks that are located at 43.32°, 50.45°, and 74.12°, corresponding to the (111), (200), and (220) planes of copper, respectively [42,43]. The morphological images of copper particles with the sizes of 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 μm are shown in Figure 2(e) and Figure S1 (available in the Supplementary Materials). The digital pictures of composite films prepared with the copper in 1 μm diameter and in bending and folding states are exhibited in Figure 2(f), respectively. And it can be proved that the composite film has a certain process capability.
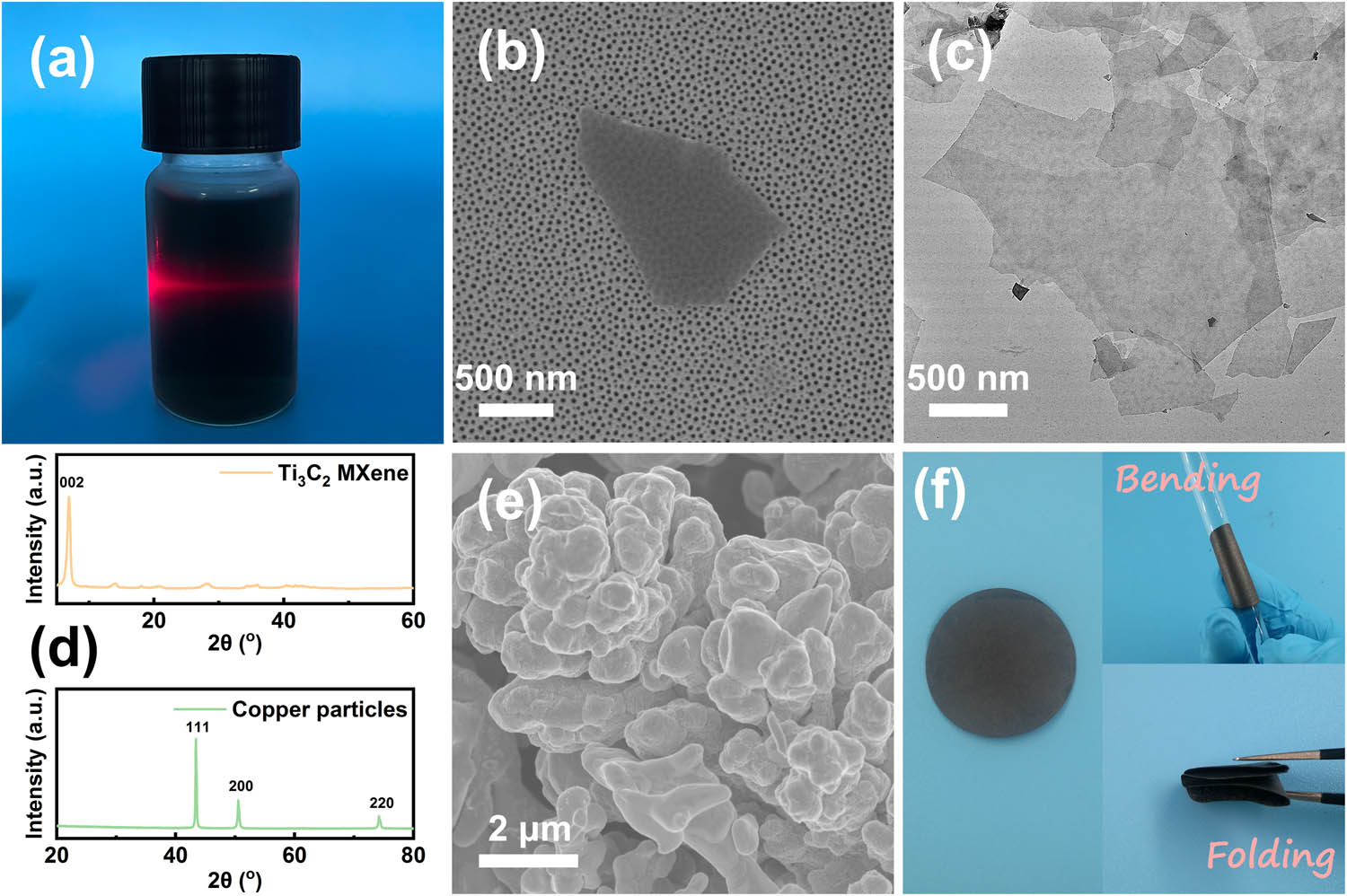
(a) Digital picture of Tyndall phenomenon of MXene colloidal solution. (b) SEM and (c) TEM images of MXene. (d) XRD curves of MXene and copper powders. (e) SEM image of copper powders in 1 μm diameter. (f) Digital pictures of the MXene/CU/CNF film and bending and folding abilities of the composite film.
Figure 3(a) and (d) exhibits sectional SEM of pure CNF film at low and high magnifications. It can be found that the surface of the pure CNF is smooth and the stripes formed by brittle fracture are obviously arranged in order. The sectional morphologies of MXene/Cu/CNF films with different copper particle diameters are shown in Figure 3(b, c, g, h, and i), in which enlarged SEM images are located under them. When the copper particles are 0.1 μm in diameter, as displayed in Figure 3(b) and (e), the agglomeration of copper particles is serious, due to the particle size attaining nanometer level. Under the action of vacuum filtration equipment, MXene sheets are propped up with many flat holes with thick middle and thin sides. As the sizes of copper particles increase, the number of copper particles in agglomeration status decreases. But the diameter of the copper particles after agglomeration increases, the holes propped by particles become round and more ordered. When the particle size increases to 1 μm, the shape of the propped holes is closest to the circle, and the distribution of holes is more uniform. As the sizes of copper particles increase to more than 1 μm, the agglomeration phenomena have been alleviated. Because the sizes of particles become bigger, the diameters of the holes propped up by the particles become longer and larger, and the distribution of the holes becomes more disordered. In summary, as exhibited from the sectional SEM images, the holes obtained and propped by copper particles in 1 μm diameter have the best morphological structure in shape and distribution.
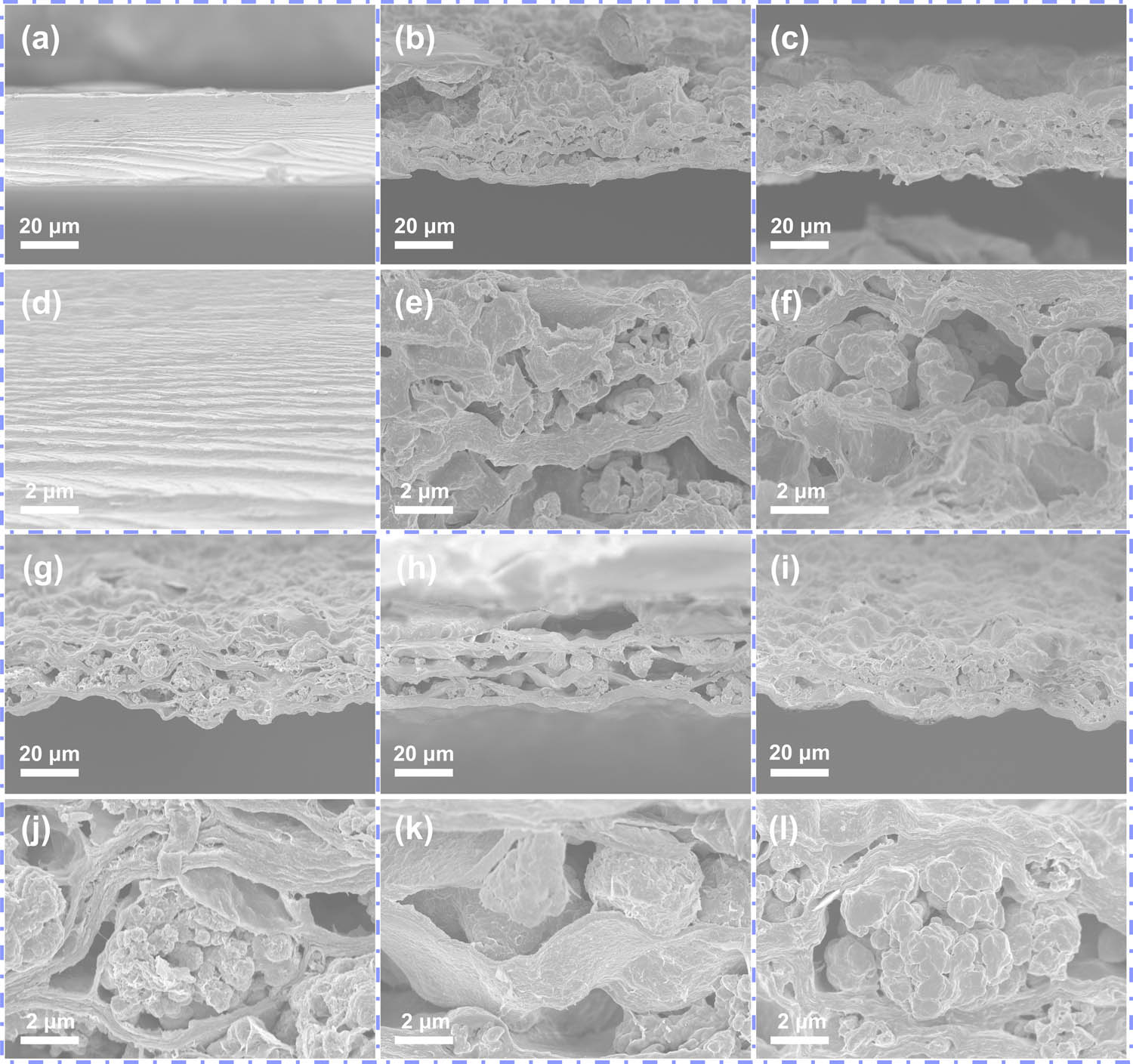
Sectional and their enlarged SEM images of (a and d) pure CNF film and MXene/Cu/CNF films with different copper powder diameters of (b and e) 0.1, (c and f) 0.5, (g and j) 1, (h and k) 2 and (i and l) 5 μm, respectively.
The model of heat conduction of the composite films is shown in Figure 4(a). The effect of synergistic filler was reported by the previous works. Two or more kinds of filler to the composite were introduced, and the mutual effect of which can lead to higher thermal conductivity. For the in-plane direction, MXene sheets play a dominant effect on the thermal conductivity because of forming an orientation continuous pathway using the vacuum filtration method. Meanwhile, for the through-plane direction, copper particles play a main role in thermal conductivity after agglomeration and the formation of the heating conduction pathway. The thermal diffusivities and conductivities of the pure CNF film and the MXene/Cu/CNF films with different copper particles diameters at the in-plane direction are exhibited in Figure 4(b), in which it can be seen that the thermal diffusivities and conductivities in the in-plane direction both present the trend of first rising and then falling. The thermal diffusivities and conductivities in the in-plane direction achieve a summit at 1 μm with 13.64 mm2 s−1 and 24.96 W m−1 K−1, respectively. A similar trend for the through-plane direction is displayed in Figure 4(c), in which the thermal diffusivity and conductivity are 1.35 mm2 s−1 and 2.46 W m−1 K−1, respectively. Compared with the reported thermal conductivity of the MXene/CNF films [17,34,44,45], the composite films with the synergistic effect of MXene sheets and copper particles of 0.1–5 μm show a higher heating conduction ability. Although the MXene sheets and the copper particles play dominant effects on thermal conductivities in the in-plane and through-plane directions, respectively, the more excellent heating conduction abilities of the MXene/Cu/CNF films are led by their synergistic effects and formation of continuous heating conduction networks. To quantify the difference between the thermal conductivities of the pure polymer and the polymer composite, the thermal conductivity enhancement (TCE) rates of the composite films with different copper particles diameters are introduced and shown in Figure 4(d). The TCE rate is calculated by the following equation,
where
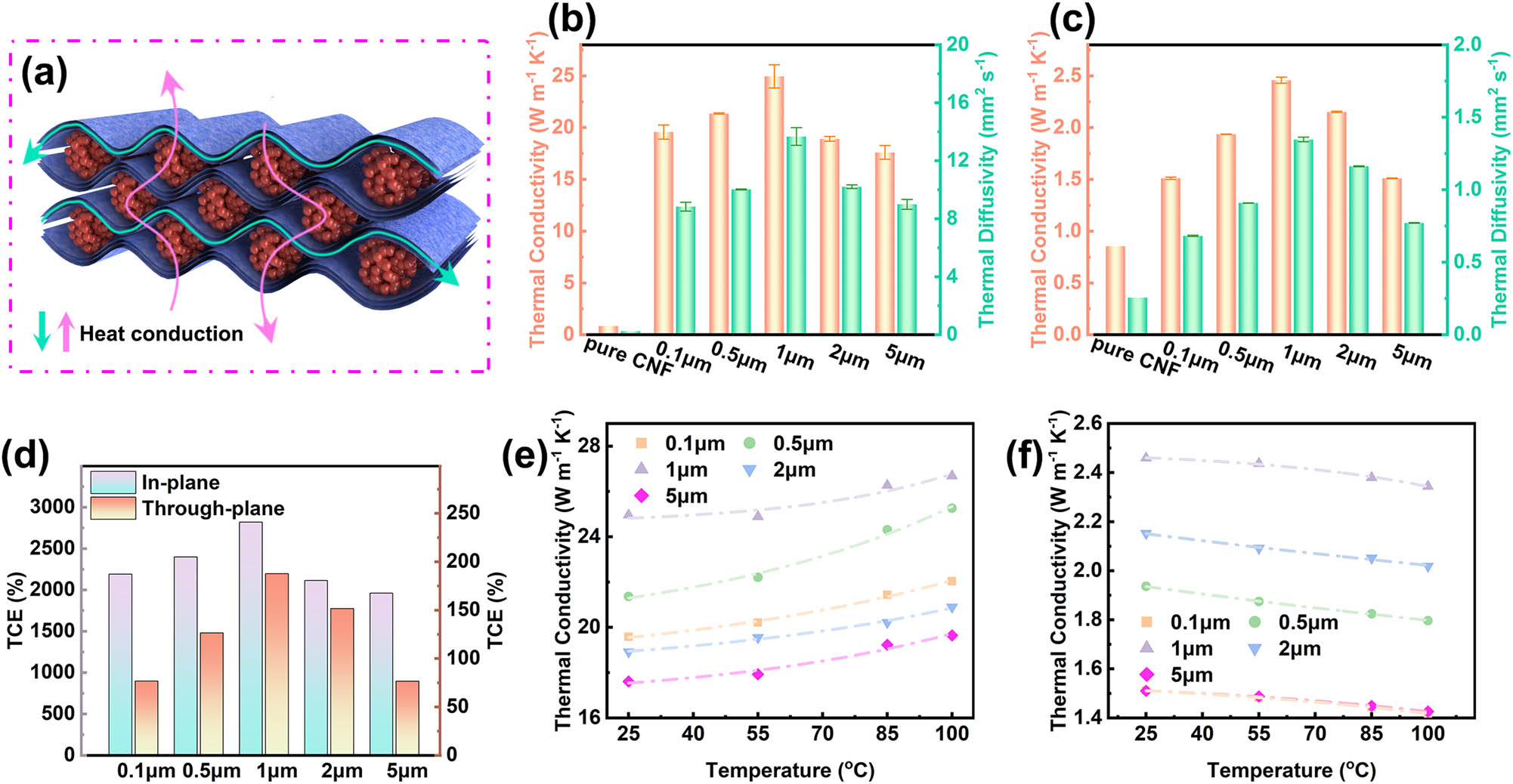
(a) Mechanism diagram of heating conduction of composite films. Thermal conductivity of the pure CNF film and the MXene/Cu/CNF films with different copper powder diameters with 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 μm in the (b) in-plane and (c) through-plane directions. (d) Thermal conductivity enhancement (TCE) and thermal conductivity in the (e) in-plane and (f) through-plane directions as a function of the temperature of the MXene/Cu/CNF films with different copper powder diameters with 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 μm, respectively.
To exhibit the excellent thermal conductivity of the MXene/Cu/CNF films with copper particles in 1 μm diameter, two types of instrumentation were used to characterize the heating conduction abilities of the in-plane and through-plane directions, respectively. Figure 5(a) shows the mechanism diagram of the heated device that was utilized to test the thermal conduction ability of the in-plane direction. A direct-current power was linked to an annular heated ceramic plate, which was under the texted composite films. Above them, another annular ceramic plate of the same size was used to fix the composites films, and an infrared (IR) camera was used for capturing the surface temperature and IR images. The temperatures of margin and center points captured by the films as a function of time are shown in Figure 5(b) and (c), respectively. As presented in Figure 5(d), the IR images of the MXene/Cu/CNF films and the pure CNF film are located in the first and second rows, respectively. Every image was the temperature contour-line image drawn from the temperature under and after heating captured by the IR image in the upper left corner of the image. With an increase in the heating time, the temperatures of the unheated part of the CNF film, the MXene/Cu/CNF films have a higher contour line of the films rose from the margin to the center, forming clear contour lines. In comparison to the pure at the same time, the composite film at the same position possesses a higher temperature after the same heating time. It can be seen that the temperature increasement rate of the MXene/Cu/CNF films is higher than that of the pure CNF film at either the margin point or center point, as shown in Figure 5(b) and (c). After heating for 120 s, the temperatures of the composites film at a margin point of 57.4°C and a center point of 74.7°C are 14.9 and 21.0°C higher than that of the pure CNF film, respectively. A cooling radiator model presented in Figure 5(e) was used to exhibit the heating conduction ability in the through-plane direction. The films to be texted were placed between the CPU and a cooling fan, and then, the power capacity of the CPU was promoted to the apex. The CPU temperature curves as a function of time, which is revealed in Figure 5(f), are the confidence intervals and curves calculated by the temperature points, and the mean temperature during the whole CPU operating time is located in the bottom right corner of the picture. As the CPU began to work with a full load, the temperatures of the two films rose sharply and tend to be steady at about 300 s. The steady temperature under the action of the MXene/Cu/CNF films is lower than that of the pure CNF film obviously. And, the mean temperature under the action of the composite film is 5.2°C lower than that of the pure CNF film.
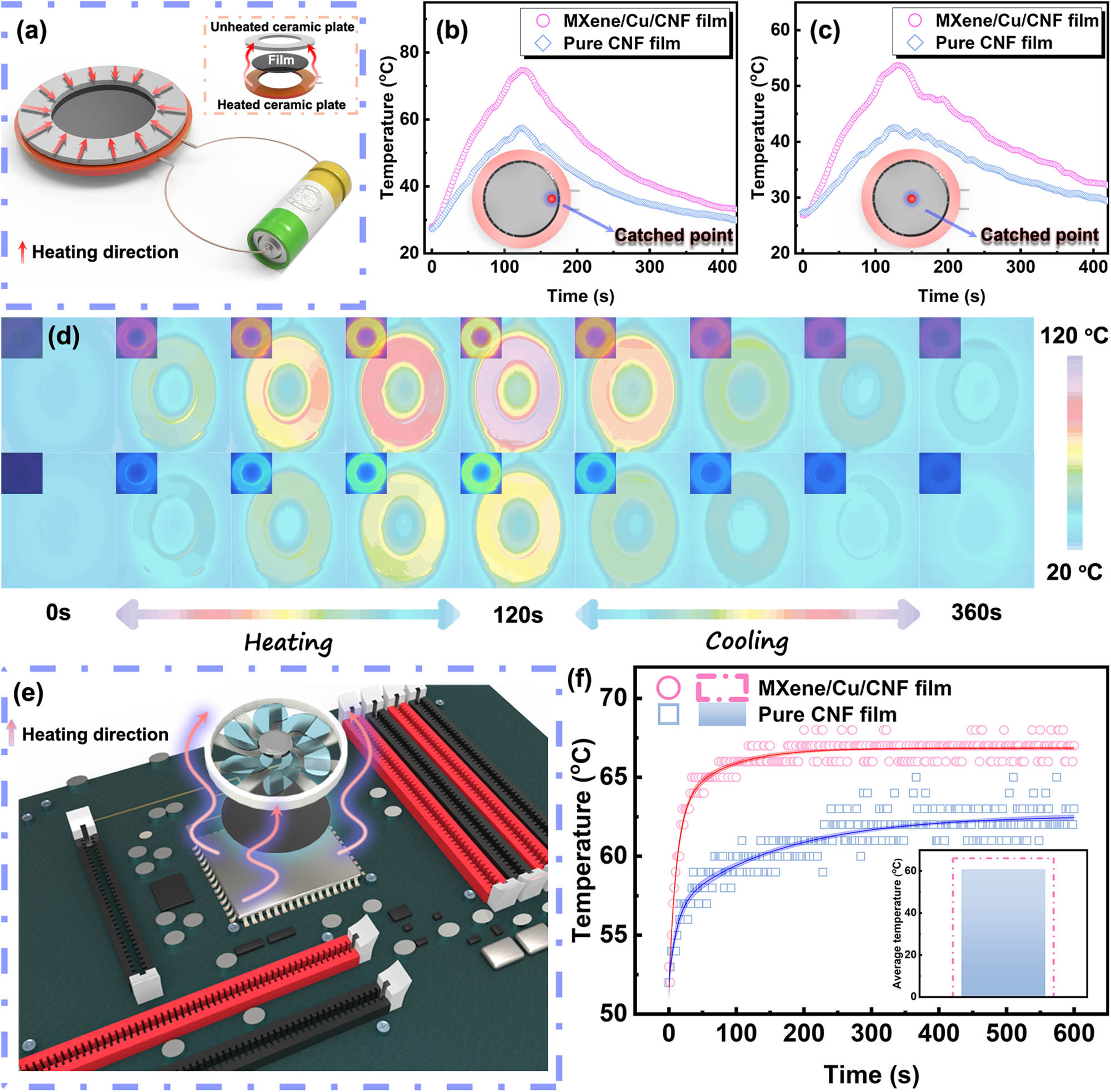
(a) Mechanism diagram of the heated device. The time-temperature curve of (b) margin and (c) center points captured from the (d) corresponding temperature contour-line images of the MXene/Cu/CNF films with copper powders in 1 μm diameter and pure CNF film. The temperature contour-line images were drawn by the temperature date of the inset infrared images photographed by an infrared camera. (e) Mechanism diagram of a cooling radiator and (f) corresponding time-temperature curves of CPU.
4 Conclusion
In this paper, the MXene/Cu/CNF films were prepared by high-speeding shear mixing and vacuum-assisted filtration of MXene sheets and copper particles of different sizes. The basic skeleton of the film was formed by dehydration and esterification of hydroxyl groups in MXene and carboxyl groups in CNF. Under the synergistic effect of two different fillers, the maximum in-plane thermal conductivity of 24.96 W m−1 K−1 and through-plane thermal conductivity of 2.46 W m−1 K−1 are obtained by composite films with the copper particles in 1 μm diameter. By calculating the TCE of the in-plane and through-plane directions with the formula, it can be found that the thermal conductivity of the composite films increased by 2819.2 and 187.6% at two thermal conduction directions, respectively. A heated device and a cooling radiator are utilized to visualize the thermal conductivities of the MXene/Cu/CNF films in the in-plane and through-plane directions. From the results of the designed test, the MXene/Cu/CNF film has an excellent thermal transfer performance in both the directions. In summary, by adding two kinds of fillers with a synergistic effect, the thermal conductivities of the polymer composite film in the in-plane and through-plane directions can be effectively increased simultaneously. This also provides a way for the preparation of thermally conductive polymer films with excellent thermal conductivity.
-
Funding information: The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51573201, 52075527, and U1709205).
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Tarawneh MA, Saraireh SA, Chen RS, Ahmad SH, Al-Tarawni MAM, Yu LJ, et al. Mechanical reinforcement with enhanced electrical and heat conduction of epoxy resin by polyaniline and graphene nanoplatelets. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):1550–61.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0118Search in Google Scholar
[2] Alhijazi M, Zeeshan Q, Qin Z, Safaei B, Asmael M. Finite element analysis of natural fibers composites: A review. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):853–75.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0069Search in Google Scholar
[3] Qin Y, Wang B, Hou X, Li L, Guan C, Pan Z, et al. Constructing Tanghulu-like Diamond@Silicon carbide nanowires for enhanced thermal conductivity of polymer composite. Compos Commun. 2022;29:101008.10.1016/j.coco.2021.101008Search in Google Scholar
[4] Roy S, Petrova RS, Mitra S. Effect of carbon nanotube (CNT) functionalization in Epoxy-CNT composites. Nanotechnol Rev. 2018;7(6):475–85.10.1515/ntrev-2018-0068Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Song W-L, Veca LM, Anderson A, Cao M-S, Cao L, Sun Y-P. Light-weight nanocomposite materials with enhanced thermal transport properties. Nanotechnol Rev. 2012;1(4):363–76.10.1515/ntrev-2012-0023Search in Google Scholar
[6] Xiong S, Qin Y, Li L, Yang G, Li M, Wei X, et al. Constructing a three-dimensional nano-crystalline diamond network within polymer composites for enhanced thermal conductivity. Nanoscale. 2021;13(44):18657–64.10.1039/D1NR05481CSearch in Google Scholar
[7] Lapčík L, Vašina M, Lapčíková B, Staněk M, Ovsík M, Murtaja Y. Study of the material engineering properties of high-density poly(ethylene)/perlite nanocomposite materials. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):1491–9.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0113Search in Google Scholar
[8] Wang X, Chen Z, Huang Y, Ye X, Wang J, Yang Y, et al. Liquid crystallinity and thermal properties of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/side-chain azobenzene hybrid copolymer. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):886–95.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0068Search in Google Scholar
[9] Chen Y, Hou X, Kang R, Liang Y, Guo L, Dai W, et al. Highly flexible biodegradable cellulose nanofiber/graphene heat-spreader films with improved mechanical properties and enhanced thermal conductivity. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6(46):12739–45.10.1039/C8TC04859BSearch in Google Scholar
[10] Chen F, Yu P, Mao l, Wang J. Simple large-scale method of recycled graphene films vertical arrangement for superhigh through-plane thermal conductivity of epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol. 2021;215:109026.10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109026Search in Google Scholar
[11] Wang Y, Pang H, Guo Q, Tsujii N, Baba T, Baba T, et al. Flexible n-Type Abundant Chalcopyrite/PEDOT:PSS/Graphene Hybrid Film for Thermoelectric Device Utilizing Low-Grade Heat. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(43):51245–54.10.1021/acsami.1c15232Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Behdinan K, Moradi-Dastjerdi R, Safaei B, Qin Z, Chu F, Hui D. Graphene and CNT impact on heat transfer response of nanocomposite cylinders. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):41–52.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0004Search in Google Scholar
[13] Liu X, Chen L, Liu Z, Song Q, Liu C. Optimization of thermal and hydrophobic properties of GO-doped epoxy nanocomposite coatings. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10(1):1236–52.10.1515/ntrev-2021-0078Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhao L-H, Wang L, Jin Y-F, Ren J-W, Wang Z, Jia L-C. Simultaneously improved thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of boron nitride nanosheets/aramid nanofiber films by constructing multilayer gradient structure. Compos Pt B Eng. 2022;229:109454.10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109454Search in Google Scholar
[15] Li M, Wang M, Hou X, Zhan Z, Wang H, Fu H, et al. Highly thermal conductive and electrical insulating polymer composites with boron nitride. Compos Pt B Eng. 2020;184:107746.10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107746Search in Google Scholar
[16] Wu X, Liu A, Wang W, Ye R, Enhanced thermal conductivity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/boron nitride nanosheet composites at low filler content. Compos Pt A Appl Sci Manuf. 2018;109:321–9.10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.03.023Search in Google Scholar
[17] Song G, Kang R, Guo L, Ali Z, Chen X, Zhang Z, et al. Highly flexible few-layer Ti3C2 MXene/cellulose nanofiber heat-spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity. N J Chem. 2020;44(17):7186–93.10.1039/D0NJ00672FSearch in Google Scholar
[18] Song G, Deng Q, Wang B, Liu Z, Ye C, Wei X, et al. Thermal and corrosion behavior of Ti3C2/Copper composites. Compos Commun. 2020;22:100498.10.1016/j.coco.2020.100498Search in Google Scholar
[19] Zhan Y, Nan B, Liu Y, Jiao E, Shi J, Lu M, et al. Multifunctional cellulose-based fireproof thermal conductive nanocomposite films assembled by in-situ grown SiO2 nanoparticle onto MXene. Chem Eng J. 2021;421:129733.10.1016/j.cej.2021.129733Search in Google Scholar
[20] Nguyen VP, Lim M, Kim K-S, Kim J-H, Park JS, Yuk JM, et al. Drastically increased electrical and thermal conductivities of Pt-infiltrated MXenes. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(17):10739–46.10.1039/D1TA00331CSearch in Google Scholar
[21] Liu Y, Wu K, Lu M, Jiao E, Zhang H, Shi J, et al. Highly thermal conductivity and flame retardant flexible graphene/MXene paper based on an optimized interface and nacre laminated structure. Compos Pt A Appl Sci Manuf. 2021;141:106227.10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106227Search in Google Scholar
[22] Lee S, Kim J. Incorporating MXene into Boron Nitride/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Films to enhance Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Polymers. 2021;13(3):379.10.3390/polym13030379Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Gholivand H, Fuladi S, Hemmat Z, Salehi-Khojin A, Khalili-Araghi F. Effect of surface termination on the lattice thermal conductivity of monolayer Ti3C2Tz MXenes. J Appl Phys. 2019;126(6):065101.10.1063/1.5094294Search in Google Scholar
[24] Sun K, Wang F, Yang W, Liu H, Pan C, Guo Z, et al. Flexible conductive polyimide fiber/MXene composite film for electromagnetic interference shielding and joule heating with excellent harsh environment tolerance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(42):50368–80.10.1021/acsami.1c15467Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Jiao E, Wu K, Liu Y, Lu M, Hu Z, Chen B, et al. Ultrarobust MXene-based laminated paper with excellent thermal conductivity and flame retardancy. Compos Pt A-Appl Sci Manuf. 2021;146:106417.10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106417Search in Google Scholar
[26] Cao Y, Deng Q, Liu Z, Shen D, Wang T, Huang Q, et al. Enhanced thermal properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) composites with ultrathin nanosheets of MXene. RSC Adv. 2017;7(33):20494–501.10.1039/C7RA00184CSearch in Google Scholar
[27] Zhu Y, Zhao X, Peng Q, Zheng H, Xue F, Li P, et al. Flame-retardant MXene/polyimide film with outstanding thermal and mechanical properties based on the secondary orientation strategy. Nanoscale Adv. 2021;3(19):5683–93.10.1039/D1NA00415HSearch in Google Scholar
[28] Gao Q, Pan Y, Zheng G, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X. Flexible multilayered MXene/thermoplastic polyurethane films with excellent electromagnetic interference shielding, thermal conductivity, and management performances. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. 2021;4(2):274–85.10.1007/s42114-021-00221-4Search in Google Scholar
[29] Jin X, Wang J, Dai L, Liu X, Li L, Yang Y, et al. Flame-retardant poly(vinyl alcohol)/MXene multilayered films with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal conductive performances. Chem Eng J. 2020;380:122475.10.1016/j.cej.2019.122475Search in Google Scholar
[30] Liu H, Fu R, Su X, Wu B, Wang H, Xu Y, et al. Electrical insulating MXene/PDMS/BN composite with enhanced thermal conductivity for electromagnetic shielding application. Compos Commun. 2021;23:100593.10.1016/j.coco.2020.100593Search in Google Scholar
[31] He X, Wang Y. Highly thermally conductive polyimide composite films with excellent thermal and electrical insulating properties. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2020;59(5):1925–33.10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05939Search in Google Scholar
[32] Barani Z, Mohammadzadeh A, Geremew A, Huang CY, Coleman D, Mangolini L, et al. Thermal properties of the binary‐filler hybrid composites with graphene and copper nanoparticles. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;30(8):1904008.10.1002/adfm.201904008Search in Google Scholar
[33] Zhou S, Xu T, Jiang F, Song N, Shi L, Ding P. High thermal conductivity property of polyamide-imide/boron nitride composite films by doping boron nitride quantum dots. J Mater Chem C. 2019;7(44):13896–903.10.1039/C9TC04381KSearch in Google Scholar
[34] Jiao E, Wu K, Liu Y, Lu M, Zhang H, Zheng H, et al. Robust bioinspired MXene-based flexible films with excellent thermal conductivity and photothermal properties. Compos Pt A Appl Sci Manuf. 2021;143:106290.10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106290Search in Google Scholar
[35] Liu C, Chen F, Wu Y, Zheng Z, Yang J, Yang B, et al. Research progress on individual effect of graphene oxide in cement-based materials and its synergistic effect with other nanomaterials. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10(1):1208–35.10.1515/ntrev-2021-0080Search in Google Scholar
[36] Wang Y, Wang J, Wang J, Hui D. Experimental and multiscale numerical investigations on low-velocity impact responses of syntactic foam composites reinforced with modified MWCNTs. Nanotechnol Rev. 2021;10(1):883–903.10.1515/ntrev-2021-0064Search in Google Scholar
[37] Zuo H-M, Li D-S, Hui D, Jiang L. The multiscale enhancement of mechanical properties of 3D MWK composites via poly(oxypropylene) diamines and GO nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):587–99.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0052Search in Google Scholar
[38] Uetani K, Okada T, Oyama HT. Crystallite size effect on thermal conductive properties of nonwoven nanocellulose sheets. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(7):2220–7.10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00617Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Zhang Y, Ruan K, Shi X, Qiu H, Pan Y, Yan Y, et al. Ti3C2Tx/rGO porous composite films with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Carbon. 2021;175:271–80.10.1016/j.carbon.2020.12.084Search in Google Scholar
[40] Ma Z, Kang S, Ma J, Shao L, Zhang Y, Liu C, et al. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano. 2020;14(7):8368–82.10.1021/acsnano.0c02401Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Zhang Y, Ruan K, Gu J. Flexible sandwich-structured electromagnetic interference shielding nanocomposite films with excellent thermal conductivities. Small. 2021;17(42):e2101951.10.1002/smll.202101951Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Chen S, Fu S, Liang D, Chen X, Mi X, Liu P, et al. Preparation and properties of 3D interconnected CNTs/Cu composites. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):146–54.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0013Search in Google Scholar
[43] Roy K, Sarkar CK, Ghosh CK. Antibacterial mechanism of biogenic copper nanoparticles synthesized using Heliconia psittacorum leaf extract. Nanotechnol Rev. 2016;5(6):529–36.10.1515/ntrev-2016-0040Search in Google Scholar
[44] Zhou B, Li Q, Xu P, Feng Y, Ma J, Liu C, et al. An asymmetric sandwich structural cellulose-based film with self-supported MXene and AgNW layers for flexible electromagnetic interference shielding and thermal management. Nanoscale. 2021;13(4):2378–88.10.1039/D0NR07840ASearch in Google Scholar
[45] Chen L, Shi X, Yu N, Zhang X, Du X, Lin J. Measurement and analysis of thermal conductivity of Ti3C2Tx MXene films. Materials. 2018;11(9):1701.10.3390/ma11091701Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2022 Yue Qin et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption

