Abstract
Mechanical metamaterials with negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR) have emerged as a novel class of engineering material, and have attracted increasing attention in various engineering sectors. Most studies available on the buckling problem of laminated plates with positive or NPR are those under uniaxial compression. Here, we report that the buckling phenomenon may occur for auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates under uniaxial tension when the unloaded edges of the plates are immovable. Two types of nanocomposites are considered, including graphene/Cu and carbon nanotube/Cu composites. Governing equations of the auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates are formulated based on the framework of Reddy’s higher-order shear deformation theory. In modeling, the von Kármán nonlinear strain–displacement relationship, temperature-dependent material properties, thermal effects, and the plate–substrate interaction are considered. The explicit analytical solutions for postbuckling of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates subjected to uniaxial tension are obtained for the first time by employing a two-step perturbation approach. Numerical investigations are performed for tension buckling and postbuckling behaviors of auxetic nanocomposite laminated rectangular plates with in-plane NPR rested on an elastic substrate under temperature environments.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Buckling is an important problem for the thin plates subjected to uniaxial or biaxial compression [1]. Under tensile loads, thin plates usually do not experience buckling. However, according to the literature survey, there are two special cases, in which buckling can occur under tensile loads, namely “tension buckling,” for the thin plates/sheets. One case is if a plate contains a hole [2,3,4] or a crack [5,6,7], the compressive stresses arise locally near the hole or the crack under a uniaxial tensile load, where these compressive stresses may cause local buckling. Another case is wrinkling (i.e., local short-wavelength buckling), which is commonly observed in stretched-thin sheets [8,9,10,11,12] and single-layer graphene sheets [13,14,15,16] due to the variation of Poisson’s effect. For nanocomposite structures, which are generally considered as the next-generation composite structures, although much research has been done on the buckling and postbuckling analyses of nanocomposite plates under uniaxial or biaxial compression, no attention is paid to the buckling of nanocomposite plates when they are subjected to a tensile load. The buckling of nanocomposite plates under tensile load represents a unique and crucial failure mode in the design of these structures, which has not been reported in the literature. To guide the design and optimization of nanocomposites for future engineering applications, it is of great significance to establish a scientific and theoretical tool to predict the critical tension buckling load, and hence, the factor of safety under this unique buckling failure mode.
Auxetic laminated composites with negative Poisson’s ratio (NPR) are one class of mechanical metamaterials. With the development of nanotechnology and additive manufacturing technology [17,18], nanofillers such as graphene sheets [19] or carbon nanotubes (CNTs) [20] can be embedded in a single-crystal copper matrix to achieve auxetic nanocomposite laminates [21,22]. Owing to their special properties and characteristics, auxetic nanocomposite materials have shown better performance in certain aspects than those of conventional materials and are expected to have a wide range of technological applications [23,24].
Recently, Shen et al. [25] combined the functionally graded (FG) concept with the auxetic concept to design the FG-GRMMC (graphene-reinforced metal-matrix composite) laminates. Considering the auxetic effect of GRMMCs, Shen and his co-authors [25,26] investigated the impact of in-plane NPR on the compressive postbuckling behaviors of FG-GRMMC laminated and sandwich plates subjected to uniaxial compression. Unlike fiber-reinforced composite (FRC), graphene-reinforced composite (GRC) and carbon nanotube-reinforced composite (CNTRC) laminated plates with positive Poisson’s ratios [27,28,29] where the buckling loads and initial postbuckling load–deflection curves for the plate with unloaded edges that are movable (i.e., displacement is unconstrained in the in-plane direction) are higher than those of the same plate with unloaded edges that are immovable (i.e., displacement is constrained in the direction perpendicular to the loaded edges), the auxetic GRMMC laminated plates showed the opposite behavior. Specifically, for auxetic laminated plates, the buckling loads and postbuckling load–deflection curves with unloaded edges that are movable in the in-plane direction are lower than those of the same plate under immovable unloaded edges. This indicates that the unique lateral contraction of the auxetic laminates under uniaxial compressive load locally enhanced the buckling strength. Such an exceptional behavior leads us to believe that auxetic laminated plates with unloaded edges that are immovable may buckle under a uniaxial tensile load as compressive reaction force will be produced on unloaded edges to restrict the lateral expansion of the auxetic plates under uniaxial tension. This provides the motivation for the present investigation.
The present research is to investigate the buckling and postbuckling behavior of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates with unloaded edges that are immovable and subjected to the uniaxial tensile load under thermal environmental conditions. In the current study, we chose two types of auxetic nanocomposite laminates. One is a graphene/Cu laminated plate with in-plane NPR and the other is a CNT/Cu laminated plate with in-plane NPR. The material properties of both graphene/Cu and CNT/Cu composites are temperature-dependent. The governing equations of the auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates are established based on the framework of Reddy’s higher-order shear deformation theory (HSDT). In modeling, the von Kármán nonlinear strain–displacement relationship, the effect of temperature, the interaction between the plate and substrate, and the effect of the plate's initial geometric imperfection are also taken into consideration. The explicit analytical solutions for buckling and postbuckling of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates subjected to uniaxial tension are obtained for the first time by employing a two-step perturbation approach. The impacts of the plate aspect ratio, the plate width-to-thickness ratio, temperature variation, and foundation stiffness on tension buckling and postbuckling behavior of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates are discussed in the numerical investigation.
2 Modeling
Consider an N-ply laminated rectangular plate, where each ply is made of nanocomposites having an in-plane NPR. As shown in Figure 1, a is the length, b is the width, and h is the total thickness of the plate. The coordinate system (X, Y, Z) is located on the middle surface of the plate with its origin placed at one corner of the plate, where the X and Y axes are set along the length and the width directions, respectively, while the Z-axis is set along the thickness direction pointing downward. The plate is rested on an elastic substrate that is idealized as a Pasternak-type foundation model with two stiffnesses, where
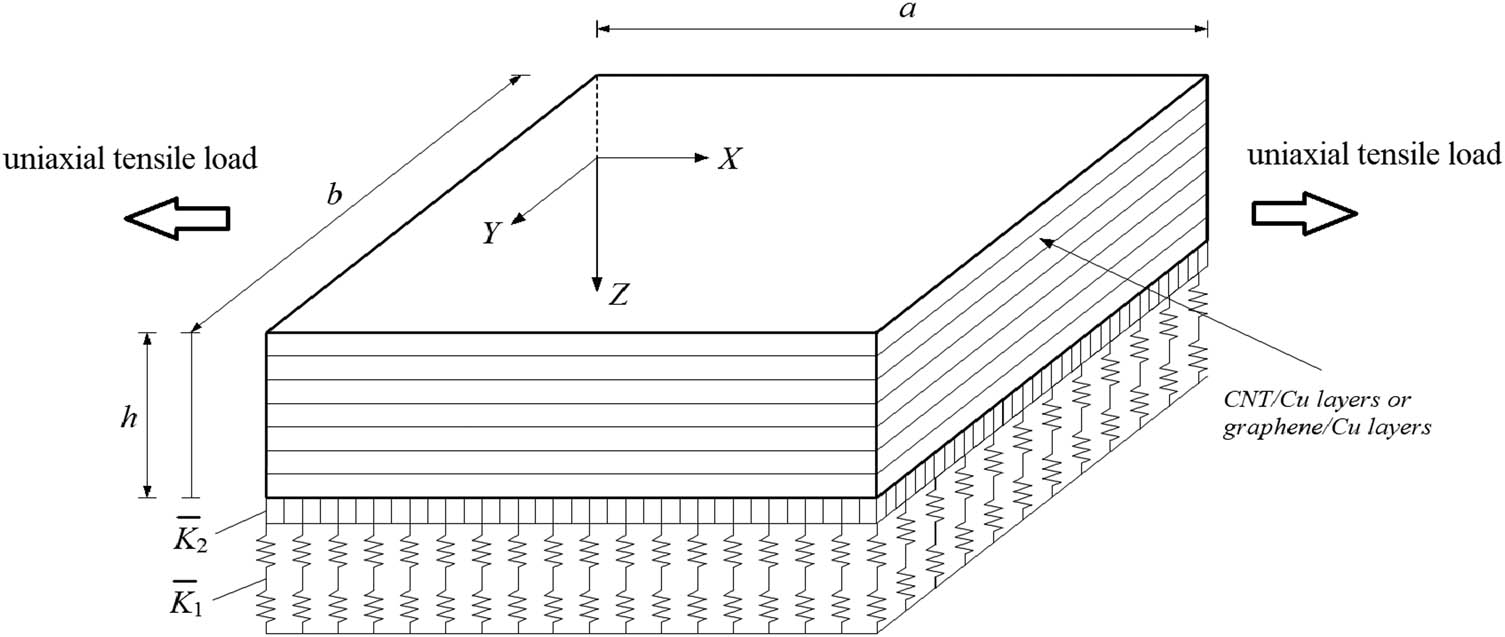
Auxetic nanocomposite laminated rectangular plate rests on an elastic substrate under uniaxial tensile load.
The plate is exposed to elevated temperature and is subjected to uniaxial tensile load. Based on the framework of HSDT of Reddy [30] and that coupled with the von Kármán nonlinear strain–displacement relationships, the governing equations for the postbuckling of the nanocomposite laminated plate with in-plane NPR are given by Shen [1]
where
Meanwhile, the interaction of the plate foundation defined by
and
In equation (3a),
where
where
where E
11, E
22, G
12, G
13, G
23,
Besides the governing equations (1a)–(1d), for the boundary-value problem, we require the boundary conditions for the auxetic laminated plate. In order to derive the theoretical solution, the four edges of the auxetic laminated plate are assumed to be SSSS (i.e., simply supported on all four edges). Specifically, on the X = 0 and X = a edges,
and on the Y = 0 and Y = b edges,
where
The tensile loads are applied on the X = 0 and X = a edges and the two loaded edges are freely movable (i.e., the displacement can move in the X-direction), while the other two unloaded edges are immovable (i.e., the displacement is constrained in the Y-direction). The in-plane boundary condition on the Y = 0 and Y = b edges is
where
or
Although the governing equations (1a)–(1d) have the same forms for the compressive buckling and tension buckling problems, unlike the compressive buckling problem [25,26], in the current study, the equilibrium of force in the X-direction is expressed as
where
In equation (8b), the reduced stiffness coefficients are contained in the reduced stiffness matrices, including [
where the plate stiffness coefficients A ij , B ij , etc., are expressed as
3 Solution procedure
In order to solve the buckling and postbuckling problems of nanocomposite structures analytically, the Ritz and Galerkin methods are usually employed [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. The accuracy of applying the Ritz and Galerkin methods depends strongly on the chosen modal shape functions. Shen [39] developed a two-step perturbation approach that gives explicit analytical expressions of all the variables in the large deflection region. The advantage of this method is that it is unnecessary to guess the form of the modal shape function, which can be obtained step by step, and such solutions satisfy both the governing equations and the boundary conditions accurately in the asymptotic sense. This approach has been applied to successfully solve various plate nonlinear boundary-value problems by other research teams [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. To employ this approach for solving the postbuckling problem of auxetic laminated plates with in-plane NPR, the governing equations (1a)–(1d) are first converted into the non-dimensional forms as
where the non-dimensional operators L ij ( ) and L( ) are given in the study of Shen [1]. Note that the operators L 15( ), L 25( ), L 35( ), and L 45( ) vanish due to the uniform temperature field. The dimensionless parameters are defined by
where k
1 and k
2 are only utilized for numerical examples in Section 4, E
0 is the reference value of Young’s modulus for the single-crystal copper matrix at T = 300 K, and is set to be E
0 = 101.14 GPa [22].
Accordingly, the plate boundary conditions on the x = 0 and x = π edges can be nondimensionalized as
and those on the y = 0 and y = π edges can be nondimensionalized as
And, hence, the in-plane boundary condition for the plate becomes
where
For the auxetic laminated plate subjected to uniaxial tension, equation (9) becomes
The initial geometric imperfection of the auxetic laminated plate in the dimensionless form is given by
where
By employing the two-step perturbation approach, the asymptotic solutions of equations (12a)–(12d) along with the boundary conditions (15a) and (15b) are obtained as follows:
Note that to restrict the lateral expansion of the auxetic laminated plate subjected to uniaxial tensile loads, compressive stresses are produced in two unloaded edges that are immovable, so that
It is worth noting that solution (22) is different from that obtained for the compressive postbuckling problem, as reported in the study of Shen et al. [25]. Thereafter, by substituting equation (22) into equation (17), one has
Similarly, we have
From perturbation procedure, we can obtain the expressions for
and substituting W,
From equations (25) and (26), we obtain
where (
In the current study, buckling is caused by compressed stress on the unloaded edges. By minimizing the compressive stress in equation (27) with respect to m and n, the buckling load of a perfect plate can readily be numerically obtained by setting
After the buckling mode (m, n) and buckling loads are determined, the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curve can be obtained as
All symbols used in equations (27)–(29) are explained in Appendix.
4 Numerical results
In this section, we will present numerical studies for tension buckling and postbuckling behavior of perfect and imperfect auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates with in-plane NPR that are rested on elastic foundations. Two types of nanocomposite materials are selected for each ply of the laminated plate. One is the graphene/Cu composite with the graphene weight fraction w G = 3%, while another is the CNT/Cu composite with the CNT weight fraction w CNT = 3%. The material properties of the two composites are both temperature-dependent and are taken from the molecular dynamics simulation results of Fan et al. [21] and Zhang et al. [22], respectively, which are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively.
Temperature-dependent properties of graphene/Cu composites (w G = 3%) [21]
| T = 300 K | T = 500 K | T = 700 K | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E 11 (GPa) | 207.55 | 193.15 | 180.50 |
| E 22 (GPa) | 196.69 | 183.94 | 171.58 |
| E 33 (GPa) | 61.454 | 55.773 | 47.192 |
| G 12 (GPa) | 66.389 | 62.092 | 58.314 |
| G 13 (GPa) | 33.617 | 31.536 | 28.928 |
| G 23 (GPa) | 32.327 | 31.009 | 28.200 |
| ν 12 | −0.0649 | −0.0721 | −0.0751 |
| ν 13 | 0.6297 | 0.6298 | 0.6826 |
| ν 23 | 0.6512 | 0.6617 | 0.6742 |
| α 11 (×10−6 K−1) | 1.4224 | 1.5037 | 1.6222 |
| α 22 (×10−6 K−1) | 1.4194 | 1.5006 | 1.6278 |
Temperature-dependent properties of CNT/Cu composites (w CNT = 3%) [22]
| T = 300 K | T = 500 K | T = 700 K | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E 11 (GPa) | 226.24 | 216.70 | 209.84 |
| E 22 (GPa) | 96.918 | 89.186 | 81.311 |
| E 33 (GPa) | 68.336 | 63.629 | 59.185 |
| G 12 (GPa) | 15.496 | 14.090 | 12.584 |
| G 13 (GPa) | 48.932 | 45.508 | 42.145 |
| G 23 (GPa) | 49.838 | 46.357 | 43.688 |
| ν 12 | −0.1537 | −0.1637 | −0.1762 |
| ν 13 | 0.7508 | 0.7677 | 0.7833 |
| ν 23 | 0.8121 | 0.8215 | 0.8316 |
| α 11 (×10−6 K−1) | 8.3366 | 8.3227 | 8.3089 |
| α 22 (×10−6 K−1) | 12.649 | 13.000 | 13.349 |
In the current research, symmetric (0/90/0)S and anti-symmetric (10/−10)3T laminated rectangular plates are considered. The thickness of each ply is identical and the total thickness of the plate is h = 1.2 mm. The plate aspect ratios are selected as a/b = 2, 3, 4, and 5. To avoid cases where stresses increase beyond the elastic range, the plate width-to-thickness ratio is set as b/h = 50, 100, and 200. The in-plane effective Poisson’s ratio (EPR)
Effective Poisson’s ratios
| T (K) | CNT/Cu laminates | Graphene/Cu laminates | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0/90/0)S | (0/90/0)S | (10/−10)3T | |
| 300 | −0.111 | −0.064 | −0.040 |
| 500 | −0.115 | −0.071 | −0.047 |
| 700 | −0.120 | −0.074 | −0.050 |
The buckling load is of practical concern of the nanocomposite laminated plates and, therefore, we need to determine the buckling tensile load and the corresponding buckling mode for the auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates first. Since the tension buckling of the auxetic laminated plates is investigated for the first time, no experimental data are currently available for model validation. In order to validate the accuracy and reliability of the present solution method, the finite element analysis is performed and the results are depicted in Figure 2. The buckling load associated with the buckling mode agrees well in each case, which clearly shows the validity and accuracy of the current solution for the tension buckling analysis of auxetic laminated plates.
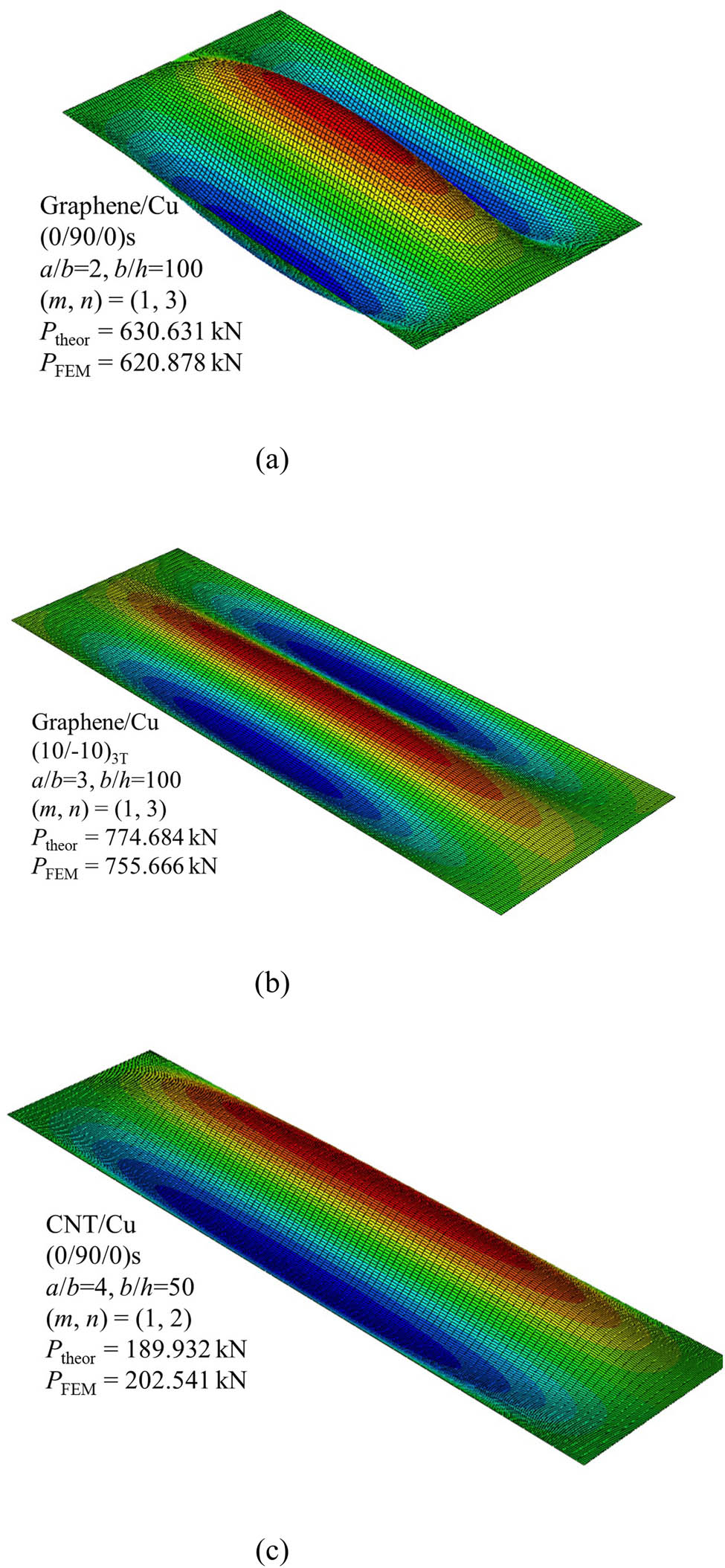
Comparisons of buckling loads of nanocomposite laminated plates under uniaxial tension: (a) a/b = 2, (m, n) = (1,3); (b) a/b = 3, (m, n) = (1,3); and (c) a/b = 4, (m, n) = (1,2).
Buckling tensile loads P cr (kN) of the (0/90/0)S and (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plates and (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu laminated plates, with different values of plate aspect ratios (a/b = 2, 3, and 4) rested on the elastic foundations under temperature conditions are presented in Tables 4–6. The thermal environments are set as T = 300, 500, and 700 K. Two foundation models with (k 1, k 2) = (10, 0) for the Winkler foundation and (k 1, k 2) = (10, 1) for the Pasternak foundation are considered. Owing to the NPR effect, the applied tensile load acting in the longitudinal direction produces a compressive reaction force and, hence, compressive stress, when the transverse displacement is constrained. Buckling occurs when the compressive stress reaches a critical value. As can be observed, the buckling tensile loads for the (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plates are larger than those of the (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu laminated plates, whereas the buckling tensile loads of the (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu laminated plates are lower than those of the (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu laminated plates, even if the (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu laminated plate is relatively thicker (i.e., lower b/h) than the (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu laminated plate. This is because the (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plate has the lowest negative EPR, while the (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu laminated plate has the highest negative EPR among the three. In other words, a higher negative EPR will exacerbate the compressive stress caused by the reaction force, and hence, make the composites more prone to buckle. We also observe that the buckling mode (m, n) changes from (1, 3) to (1, 2) for the (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu and graphene/Cu laminated plates, whereas the buckling mode (m, n) changes from (1, 4) to (1, 2) for the (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plates when the plate aspect ratio a/b changes from 2 to 4. The changes in the buckling mode can also be observed when the temperature increases from 300 to 700 K. These simulation results indicate that changing the aspect ratio of the plates and applying the temperature condition significantly affect the distribution of the compressive stress along the unloaded edges, thereby resulting in shifts in the buckling mode. Additionally, similar to cases of compressive buckling [25], the buckling tensile loads decrease when the temperature increases and increase when the foundation stiffnesses are increased.
Buckling tensile loads P cr (kN) of (0/90/0)S laminated plates made of graphene/Cu with unloaded edges that are immovable [h = 1.2 mm, b/h = 100]
| T (K) | a/b = 2 | a/b = 3 | a/b = 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (0, 0) | |||
| 300 | 630.6308 (1, 3)a | 281.1347 (1, 2) | 205.3563 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 199.6882 (1, 2) | 209.9876 (1, 3) | 189.8835 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 62.7413 (1, 3) | 40.8513 (1, 3) | 35.6539 (1, 3) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 0) | |||
| 300 | 635.3398 (1, 3) | 291.7302 (1, 2) | 213.2104 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 250.4258 (1, 2) | 212.8428 (1, 3) | 192.4932 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 66.4007 (1, 3) | 43.5732 (1, 3) | 38.1518 (1, 6) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 1) | |||
| 300 | 678.3310 (1, 3) | 334.7214 (1, 2) | 244.7016 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 335.6300 (1, 3) | 238.5179 (1, 3) | 215.8357 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 99.8081 (1, 3) | 68.0491 (1, 3) | 60.4938 (1, 3) |
-
aBuckling mode (m, n).
Buckling tensile loads P cr (kN) of (±10)3T laminated plates made of graphene/Cu with unloaded edges that are immovable [h = 1.2 mm, b/h = 100]
| T (K) | a/b = 2 | a/b = 3 | a/b = 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (0, 0) | |||
| 300 | 1569.6150 (1, 4)a | 774.6838 (1, 3) | 395.1861 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 658.9609 (1, 3) | 345.4806 (1, 3) | 294.1510 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 131.6798 (1, 3) | 65.4747 (1, 3) | 53.8327 (1, 3) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 0) | |||
| 300 | 1573.5280 (1, 4) | 780.7916 (1, 3) | 410.8407 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 667.8953 (1, 3) | 350.3338 (1, 3) | 298.3353 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 139.4096 (1, 3) | 69.9492 (1, 3) | 57.7324 (1, 3) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 1) | |||
| 300 | 1636.2960 (1, 4) | 835.7136 (1, 3) | 473.6080 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 749.4606 (1, 3) | 393.9758 (1, 3) | 335.7609 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 209.9779 (1, 3) | 110.1851 (1, 3) | 92.6123 (1, 3) |
aBuckling mode (m, n).
Buckling tensile loads P cr (kN) of (0/90/0)S laminated plates made of CNT/Cu with unloaded edges that are immovable [h = 1.2 mm, b/h = 50]
| T (K) | a/b = 2 | a/b = 3 | a/b = 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (0, 0) | |||
| 300 | 523.3330 (1, 3)a | 233.8883 (1, 2) | 189.9320 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 118.3289 (1, 3) | 91.2130 (1, 3) | 84.3524 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 86.4904 (1, 4) | 75.9266 (1, 4) | 72.7877 (1, 4) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 0) | |||
| 300 | 529.4551 (1, 3) | 247.6630 (1, 2) | 201.1594 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 176.8505 (1, 3) | 95.8015 (1, 3) | 88.6184 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 89.1192 (1, 4) | 78.2660 (1, 4) | 75.0403 (1, 4) |
| ( k 1 , k 2 ) = (10, 1) | |||
| 300 | 585.3463 (1, 3) | 303.5543 (1, 2) | 246.1761 (1, 2) |
| 500 | 230.2771 (1, 3) | 137.0625 (1, 3) | 126.7755 (1, 3) |
| 700 | 131.2807 (1, 4) | 115.4652 (1, 4) | 110.7512 (1, 4) |
aBuckling mode (m, n).
Figure 3 shows the effect of plate aspect ratio a/b ( = 3, 4 and 5) on the postbuckling behavior of (0/90/0)S and (
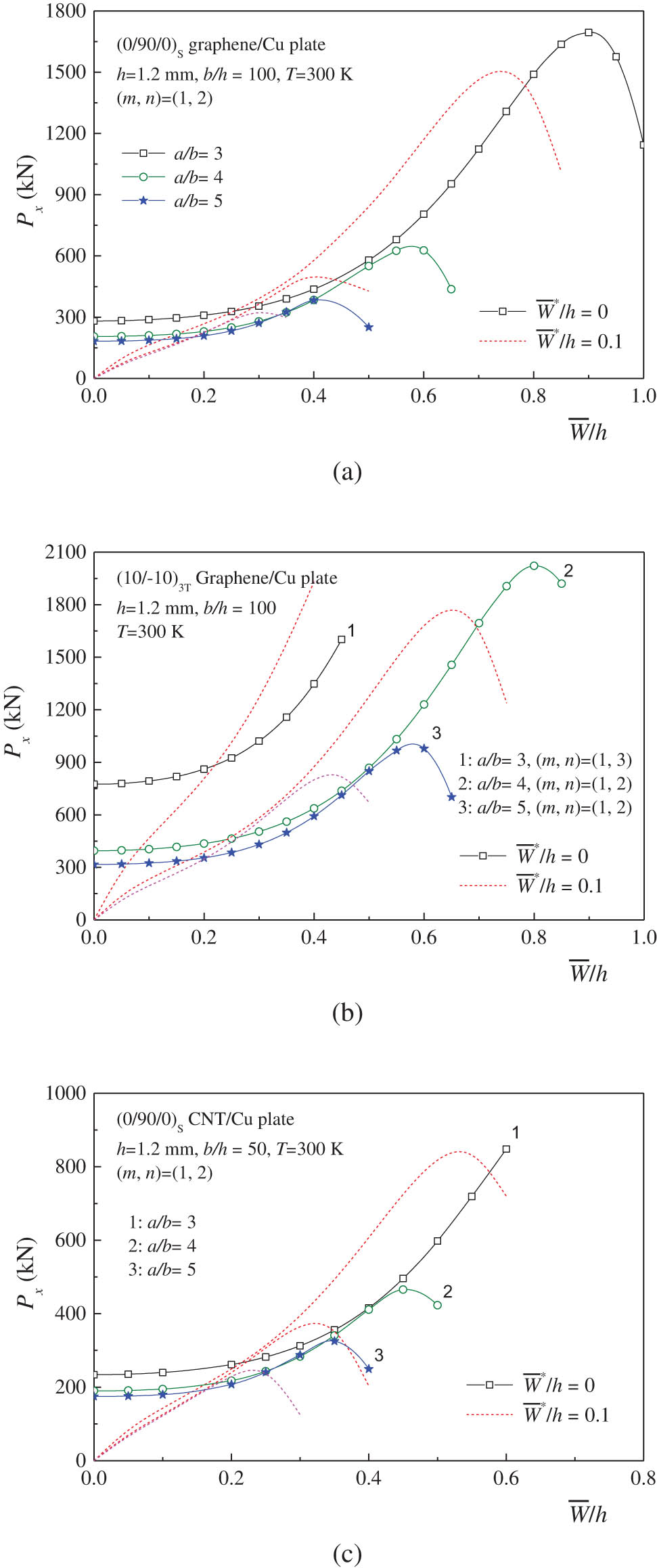
Effect of the plate aspect ratio on the postbuckling behavior of auxetic laminated plates under tension: (a) (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu plate; (b) (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu plate; and (c) (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu plate.
The effect of plate width-to-thickness ratio on the postbuckling behavior of the three configurations of auxetic laminated plates with a/b = 3 under tension at 300 K is illustrated in Figure 4. Three cases of b/h = 50, 100, and 200 are chosen for the (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu and graphene/Cu laminated plates, while b/h is set as 100, 150, and 200 for the (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plates. Such choices of the b/h ratios for the two types of laminates have ensured that the compressive or tensile stresses stay within the elastic range. As a result, no peak can be observed on the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curves for b/h = 50 for the (0/90/0)S laminated plates and b/h = 100 for the (10/−10)3T laminated plates. It is found that the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curves are reduced when the plate becomes thinner.

Effect of the plate width-to-thickness ratio on the postbuckling behavior of auxetic laminated plates under tension: (a) (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu plate; (b) (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu plate; and (c) (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu plate.
The effect of temperature change on the postbuckling behavior of three configurations of auxetic laminated plates with a/b = 3 is depicted in Figure 5. Three thermal environmental conditions, T = 300, 500, and 700 K, are considered. The temperature effect is included in the simulations by using the temperature-dependent material properties of both graphene/Cu and CNT/Cu composites. As the temperature increases, the elastic moduli reduce and the strength degrades for nanocomposites. As a result, the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curves are decreased as the temperature increases. Note that the initial geometric imperfection is set as
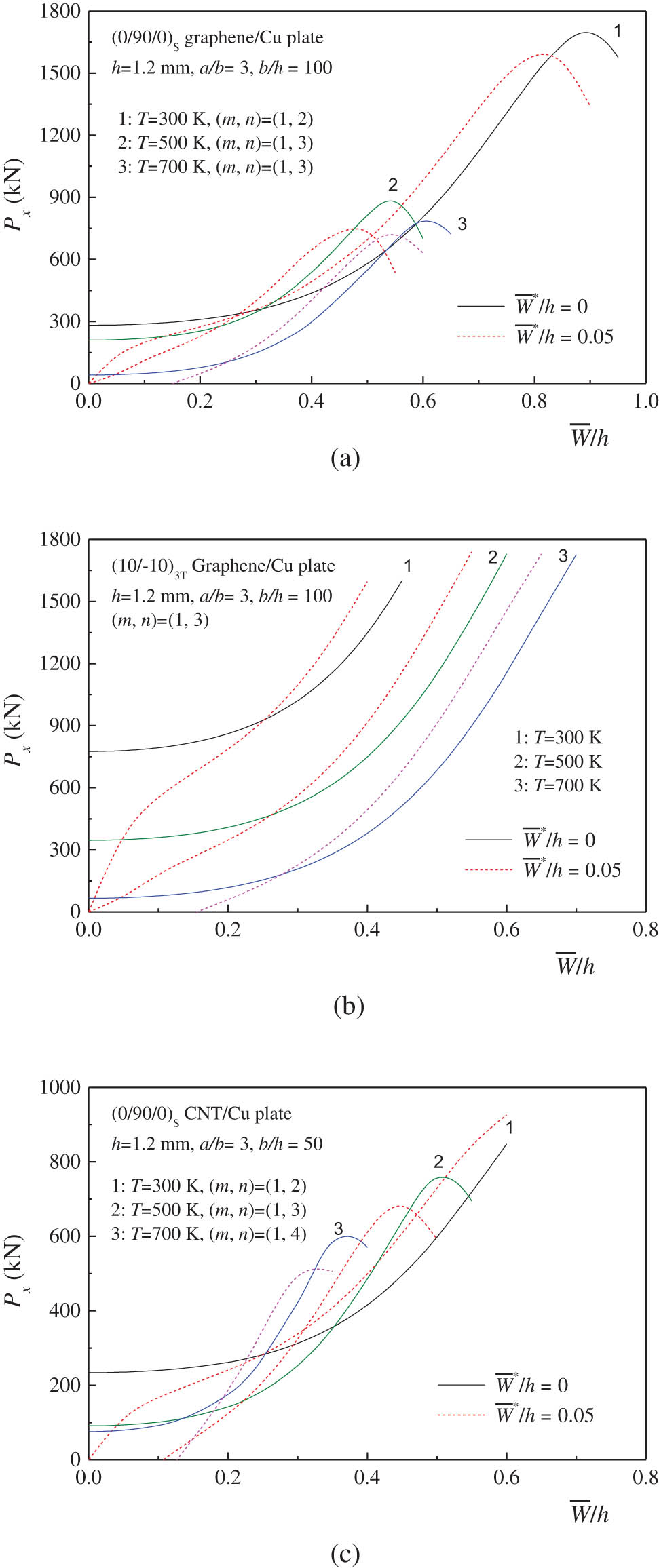
Effect of temperature variation on the postbuckling behavior of auxetic laminated plates under tension: (a) (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu plate; (b) (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu plate; and (c) (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu plate.
Figure 6 illustrates the effect of foundation stiffnesses on the postbuckling behavior of three configurations of auxetic laminated plates with a/b = 3 rested on elastic foundations at T = 300 K. In this example, two foundation models with (k 1, k 2) = (50, 0) for the Winkler foundation and (k 1, k 2) = (50, 5) for the Pasternak foundation are considered. Similar to conventional observations in laminated plates [25], the postbuckling curves of tensile load vs deflection increase with higher foundation stiffnesses. This implies that the tensile buckling could be mitigated by using a stiffer foundation as a substrate. Furthermore, no change in the buckling mode is observed when the auxetic laminated plate is supported by either the Winkler foundation or the Pasternak foundation.
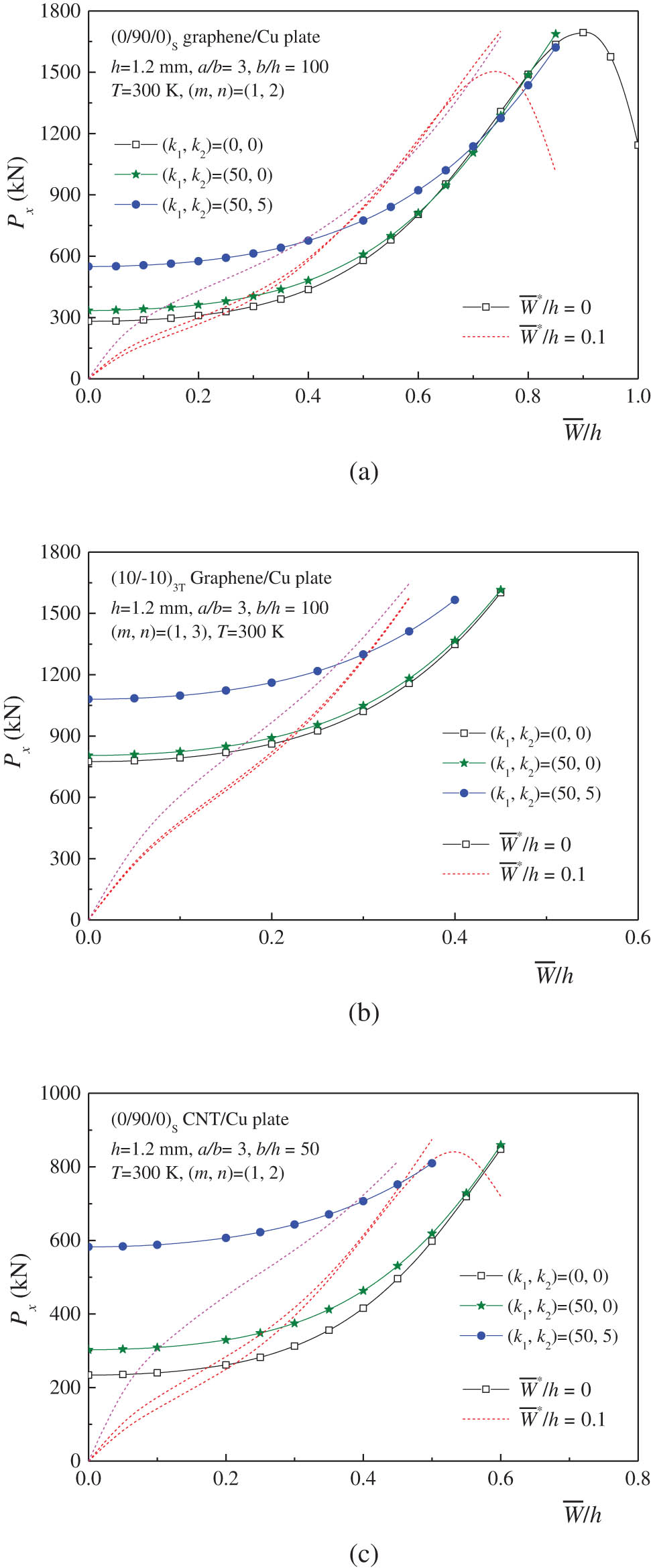
Effect of substrate stiffnesses on the postbuckling behavior of auxetic laminated plates under tension: (a) (0/90/0)S graphene/Cu plate; (b) (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu plate; and (c) (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu plate.
5 Conclusion
Tension buckling and postbuckling phenomena of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates with immovable unloaded edges are presented. The material properties of the two nanocomposites considered in this study, CNT/Cu and graphene/Cu composites, are both dependent on temperature. Based on the two-step perturbation method, the explicit analytical solutions are obtained for the first time. The numerical studies have been presented for three configurations of laminated plates, including (0/90/0)S and (10/−10)3T graphene/Cu laminated plates and (0/90/0)S CNT/Cu laminated plates, with or without an elastic substrate under temperature environments. The buckling tensile loads and associated buckling modes have been verified by FE simulation. The results presented explore for the first time the important issue of auxetic nanocomposite laminated plates, and thus are greatly useful in the engineering design of the novel nanocomposite structures. The findings are summarized as follows:
Due to the impact of in-plane NPR, the buckling tensile loads exist for the auxetic laminated rectangular plates with unloaded edges that are “immovable” under uniaxial tension. The tensile loads on “movable” ends lead to compressive stress on “immovable” ends, which is exactly the origin of tension buckling and postbuckling.
Unlike the traditional compressive postbuckling case where the postbuckling load–deflection curve rises slowly, in the tension postbuckling case, the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curve rises rapidly, in particular for cases when the temperature variation is under consideration.
In the postbuckling range, the increase of the amplitude of the plate deflection will counteract the lateral expansion displacement of the auxetic plate. The stress on the unloaded edges may shift from compressive stress to tensile stress when the amplitude of the plate deflection reaches a certain value. In most cases, a peak point exists on the postbuckling tensile load–deflection curves.
Funding information
Y. Fan would like to acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 12102255. Y. Wang would like to acknowledge financial support provided by the National Science Foundation under Award No. CMMI-2202737.
-
Funding information: Y. Fan would like to acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 12102255. Y. Wang would like to acknowledge financial support provided by the National Science Foundation under Award No. CMMI-2202737.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
where (with other symbols being defined as in the study of Shen [1])
References
[1] Shen H-S. Postbuckling Behavior of Plates and Shells. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd; 2017.10.1142/10208Search in Google Scholar
[2] Shimizu S, Yoshida S, Enomoto N. Buckling of plates with a hole under tension. Thin-Walled Struct. 1991;12:35–49.10.1016/0263-8231(91)90025-ESearch in Google Scholar
[3] Shimizu S. Tension buckling of plate having a hole. Thin-Walled Struct. 2007;45:827–33.10.1016/j.tws.2007.08.033Search in Google Scholar
[4] Kremer T, Schurmann H. Buckling of tension-loaded thin-walled composite plates with cut-outs. Compos Sci Technol. 2008;68:90–7.10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.05.035Search in Google Scholar
[5] Fujimoto T, Sumi S. Postbuckling behavior of centrally cracked plates under tension. JSME Int J. 1987;30:1714–23.10.1299/jsme1987.30.1714Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shaw D, Huang YH. Buckling behavior of a central cracked thin plate under tension. Eng Fract Mech. 1990;35:1019–27.10.1016/0013-7944(90)90129-5Search in Google Scholar
[7] Biks E, Bankin CC, Brogan FA. The buckling behavior of a central crack in a plate under tension. Eng Fract Mech. 1992;43:529–48.10.1016/0013-7944(92)90197-MSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Segedin RH, Collins IF, Segedin CM. The elastic wrinkling of rectangular sheets. Int J Mech Sci. 1988;30:719–32.10.1016/0020-7403(88)90037-9Search in Google Scholar
[9] Cerda E, Ravi-Chandar K, Mahadevan L. Wrinkling of an elastic sheet under tension. Nature. 2002;419:579–80.10.1038/419579bSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Nayyar V, Ravi-Chandar K, Huang R. Stretch-induced stress patterns and wrinkles in hyperelastic thin sheets. Int J Solids Struct. 2011;48:3471–83.10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2011.09.004Search in Google Scholar
[11] Puntel E, Deseri L, Fried E. Wrinkling of a stretched thin sheet. J Elast. 2011;105:137–70.10.1007/s10659-010-9290-5Search in Google Scholar
[12] Silvestre N. Wrinkling of stretched thin sheets: Is restrained Poisson’s effect the sole cause? Eng Struct. 2016;106:195–208.10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.09.035Search in Google Scholar
[13] Shen H-S, Xu Y-M, Zhang C-L. Graphene: why buckling occurs? Appl Phys Lett. 2013;102:131905.10.1063/1.4799673Search in Google Scholar
[14] Xiang Y, Shen H-S. Tension buckling of graphene: a new phenotype. Solid State Commun. 2014;192:20–3.10.1016/j.ssc.2014.04.021Search in Google Scholar
[15] Wang C, Lan L, Tan H. The physics of wrinkling in graphene membranes under local tension. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15:2764–73.10.1039/c2cp44033dSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Huang J, Han Q. Wrinkling in graphene subjected to gradient tension. Nano. 2015;10:53–61.10.1142/S179329201550037XSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Dahiya M, Bansal SA. Graphene-reinforced nanocomposites: synthesis, micromechanics models, analysis and applications – a review. Proc IMechE Part C-J Mech Eng Sci. 2022;236:9218–40.10.1177/09544062221091773Search in Google Scholar
[18] Soni SK, Thomas B, Kar VR. A comprehensive review on CNTs and CNT-reinforced composites: syntheses, characteristics and applications. Mater Today Commun. 2020;25:101546.10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101546Search in Google Scholar
[19] Fan Y, Xiang Y, Shen H-S. Temperature-dependent negative Poisson’s ratio of monolayer graphene: Prediction from molecular dynamics simulations. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8:415–21.10.1515/ntrev-2019-0037Search in Google Scholar
[20] Zhang H-N, Fan Y, Shen H-S. Chirality-dependent and intrinsic auxeticity for single-walled carbon nanotubes. Materials. 2022;15:8720.10.3390/ma15248720Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Fan Y, Xiang Y, Shen H-S. Temperature-dependent mechanical properties of graphene/Cu nanocomposites with in-plane negative Poisson’s ratios. Research. 2020;2020:5618021.10.34133/2020/5618021Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Zhang H-N, Fan Y, Shen H-S. Prediction of temperature-dependent mechanical properties for SWCNT/Cu nanocomposite metamaterials: A molecular dynamics study. Nanomaterials. 2023;13:1885.10.3390/nano13121885Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Ren X, Das R, Tran P, Ngo TD, Xie YM. Auxetic metamaterials and structures: a review. Smart Mater Struct. 2018;27:023001.10.1088/1361-665X/aaa61cSearch in Google Scholar
[24] Fan Y, Wang Y. The effect of negative Poisson’s ratio on the low-velocity impact response of an auxetic nanocomposite laminate beam. Int J Mech Mater Des. 2021;17:153–69.10.1007/s10999-020-09521-xSearch in Google Scholar
[25] Shen H-S, Xiang Y, Reddy JN. Effect of negative Poisson’s ratio on the post-buckling behavior of FG-GRMMC laminated plates in thermal environments. Compos Struct. 2020;253:112731.10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112731Search in Google Scholar
[26] Chen XH, Shen H-S, Huang X-H. Thermo-mechanical postbuckling analysis of sandwich plates with functionally graded auxetic GRMMC core on elastic foundations. Compos Struct. 2022;279:114796.10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114796Search in Google Scholar
[27] Librescu L, Stein M. A geometrically nonlinear theory of transversely isotropic laminated composite plates and its use in the post-buckling analysis. Thin-Walled Struct. 1991;11:177–201.10.1016/0263-8231(91)90016-CSearch in Google Scholar
[28] Shen H-S, Xiang Y, Lin F, Hui D. Buckling and postbuckling of functionally graded graphene-reinforced composite laminated plates in thermal environments. Compos Part B-Eng. 2017;119:67–78.10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.020Search in Google Scholar
[29] Shen H-S, Zhu ZH. Buckling and postbuckling behavior of functionally graded nanotube-reinforced composite plates in thermal environments. CMC-Comput Mater Continua. 2010;18:155–82.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Reddy JN. A refined nonlinear theory of plates with transverse shear deformation. Int J Solids Struct. 1984;20:881–96.10.1016/0020-7683(84)90056-8Search in Google Scholar
[31] Sofiyev AH, Tornabene F, Dimitri R, Kuruoglu N. Buckling behavior of FG-CNT reinforced composite conical shells subjected to a combined loading. Nanomaterials. 2020;10:419.10.3390/nano10030419Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Sofiyev AH, Fantuzzi N. Stability analysis of shear deformable inhomogeneous nanocomposite cylindrical shells under hydrostatic pressure in thermal environment. Materials. 2023;16:4887.10.3390/ma16134887Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Mirzaei M, Kiani Y. Thermal buckling of temperature dependent FG-CNT reinforced composite plates. Meccanica. 2016;51:2185–201.10.1007/s11012-015-0348-0Search in Google Scholar
[34] Kiani Y. Thermal post-buckling of FG-CNT reinforced composite plates. Compos Struct. 2017;159:299–306.10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.09.084Search in Google Scholar
[35] Kiani Y. Shear buckling of FG-CNT reinforced composite plates using Chebyshev-Ritz method. Compos Part B-Eng. 2016;105:176–87.10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.09.001Search in Google Scholar
[36] Zeverdejani MK, Beni YT, Kiani Y. Multi-scale buckling and post-buckling analysis of functionally graded laminated composite plates reinforced by defective graphene sheets. Int J Struct Stab Dyn. 2020;20:2050001.10.1142/S0219455420500017Search in Google Scholar
[37] Abbaspour F, Arvin H, Kiani Y. Mechanical buckling analysis of functionally graded composite laminated plates reinforced with temperature dependent graphene sheets resting on elastic foundation. ZAMM. 2022;102:e202100097.10.1002/zamm.202100097Search in Google Scholar
[38] Guo H, Zur KK, Ouyang X. New insights into the nonlinear stability of nanocomposite cylindrical panels under aero-thermal loads. Compos Struct. 2023;303:116231.10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116231Search in Google Scholar
[39] Shen H-S. A two-step perturbation method in nonlinear analysis of beams. Plates and Shells. Singapore: John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2013.10.1002/9781118649893Search in Google Scholar
[40] Li ZM. Thermal postbuckling behavior of 3D braided rectangular plates. J Therm Stresses. 2011;34:626–49.10.1080/01495739.2011.581050Search in Google Scholar
[41] Wang Z-X, Xu J, Qiao P. Nonlinear low-velocity impact analysis of temperature-dependent nanotube-reinforced composite plates. Compos Struct. 2014;108:423–34.10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.09.024Search in Google Scholar
[42] Fu Y, Zhong J, Shao X, Tao C. Analysis of nonlinear dynamic stability for carbon nanotube-reinforced composite plates resting on elastic foundations. Mech Adv Mater Struct. 2016;23:1284–9.10.1080/15376494.2015.1068404Search in Google Scholar
[43] Fallah F, Nosier A, Sharifi M, Ghezelbash F. On perturbation method in mechanical, thermal and thermo-mechanical loadings of plates: cylindrical bending of FG plates. ZAMM. 2016;96:217–32.10.1002/zamm.201400136Search in Google Scholar
[44] Najafi F, Shojaeefard MH, Googarchin HS. Nonlinear low-velocity impact response of functionally graded plate with nonlinear three-parameter elastic foundation in thermal field. Compos Part B-Eng. 2016;107:123–40.10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.09.070Search in Google Scholar
[45] Fan Y, Wang H. Thermal postbuckling and vibration of postbuckled matrix cracked hybrid laminated plates containing carbon nanotube reinforced composite layers on elastic foundation. Compos Struct. 2016;157:386–97.10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.08.040Search in Google Scholar
[46] Fan Y, Wang H. Nonlinear dynamics of matrix-cracked hybrid laminated plates containing carbon nanotube-reinforced composite layers resting on elastic foundations. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016;84:1181–99.10.1007/s11071-015-2562-7Search in Google Scholar
[47] Fan Y, Wang H. Nonlinear low-velocity impact analysis of matrix cracked hybrid laminated plates containing CNTRC layers resting on visco-Pasternak foundation. Compos Part B-Eng. 2017;117:9–19.10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.02.010Search in Google Scholar
[48] Huang X-H, Yang J, Azim I, Ren X, Wang X. Static and dynamic analyses of auxetic hybrid FRC/CNTRC laminated plates. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9:1625–42.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0106Search in Google Scholar
[49] Huang X-H, Yang J, Wang X, Azim I. Combined analytical and numerical approach for auxetic FG-CNTRC plate subjected to a sudden load. Eng Comput. 2022;38:S55–70.10.1007/s00366-020-01106-8Search in Google Scholar
[50] Huang X-H, Yu N-T, Azim I, Zhu J, Wu M-J. A comparative analysis of thermos-mechanical behavior of CNT-reinforced composite plates: Capturing the effects of thermal shrinkage. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2022;38:102347.10.1016/j.csite.2022.102347Search in Google Scholar
[51] Shen H-S, Li C, Huang X-H. Assessment of negative Poisson’s ratio effect on the postbuckling of pressure-loaded FG-CNTRC laminated cylindrical shells. Mech Based Des Struct Mach. 2023;51:1856–80.10.1080/15397734.2021.1880934Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Tension buckling and postbuckling of nanocomposite laminated plates with in-plane negative Poisson’s ratio
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone-stabilised gold nanoparticle coatings inhibit blood protein adsorption
- Energy and mass transmission through hybrid nanofluid flow passing over a spinning sphere with magnetic effect and heat source/sink
- Surface treatment with nano-silica and magnesium potassium phosphate cement co-action for enhancing recycled aggregate concrete
- Numerical investigation of thermal radiation with entropy generation effects in hybrid nanofluid flow over a shrinking/stretching sheet
- Enhancing the performance of thermal energy storage by adding nano-particles with paraffin phase change materials
- Using nano-CaCO3 and ceramic tile waste to design low-carbon ultra high performance concrete
- Numerical analysis of thermophoretic particle deposition in a magneto-Marangoni convective dusty tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow – Thermal and magnetic features
- Dual numerical solutions of Casson SA–hybrid nanofluid toward a stagnation point flow over stretching/shrinking cylinder
- Single flake homo p–n diode of MoTe2 enabled by oxygen plasma doping
- Electrostatic self-assembly effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on performance of carbon nanotubes in cement-based materials
- Multi-scale alignment to buried atom-scale devices using Kelvin probe force microscopy
- Antibacterial, mechanical, and dielectric properties of hydroxyapatite cordierite/zirconia porous nanocomposites for use in bone tissue engineering applications
- Time-dependent Darcy–Forchheimer flow of Casson hybrid nanofluid comprising the CNTs through a Riga plate with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation
- Durability prediction of geopolymer mortar reinforced with nanoparticles and PVA fiber using particle swarm optimized BP neural network
- Utilization of zein nano-based system for promoting antibiofilm and anti-virulence activities of curcumin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Antibacterial effect of novel dental resin composites containing rod-like zinc oxide
- An extended model to assess Jeffery–Hamel blood flow through arteries with iron-oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles and melting effects: Entropy optimization analysis
- Comparative study of copper nanoparticles over radially stretching sheet with water and silicone oil
- Cementitious composites modified by nanocarbon fillers with cooperation effect possessing excellent self-sensing properties
- Confinement size effect on dielectric properties, antimicrobial activity, and recycling of TiO2 quantum dots via photodegradation processes of Congo red dye and real industrial textile wastewater
- Biogenic silver nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera leaf extract: Characterization and photocatalytic application
- Novel integrated structure and function of Mg–Gd neutron shielding materials
- Impact of multiple slips on thermally radiative peristaltic transport of Sisko nanofluid with double diffusion convection, viscous dissipation, and induced magnetic field
- Magnetized water-based hybrid nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretching sheet with thermal convective and mass flux conditions: HAM solution
- A numerical investigation of the two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic water-based hybrid nanofluid flow composed of Fe3O4 and Au nanoparticles over a heated surface
- Development and modeling of an ultra-robust TPU-MWCNT foam with high flexibility and compressibility
- Effects of nanofillers on the physical, mechanical, and tribological behavior of carbon/kenaf fiber–reinforced phenolic composites
- Polymer nanocomposite for protecting photovoltaic cells from solar ultraviolet in space
- Study on the mechanical properties and microstructure of recycled concrete reinforced with basalt fibers and nano-silica in early low-temperature environments
- Synergistic effect of carbon nanotubes and polyvinyl alcohol on the mechanical performance and microstructure of cement mortar
- CFD analysis of paraffin-based hybrid (Co–Au) and trihybrid (Co–Au–ZrO2) nanofluid flow through a porous medium
- Forced convective tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow subject to heat source/sink and Lorentz force over a permeable wedge: Numerical exploration
- Physiochemical and electrical activities of nano copper oxides synthesised via hydrothermal method utilising natural reduction agents for solar cell application
- A homotopic analysis of the blood-based bioconvection Carreau–Yasuda hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with convective conditions
- In situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/SnIn4S8 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance for pollutant degradation
- A coarse-grained Poisson–Nernst–Planck model for polyelectrolyte-modified nanofluidic diodes
- A numerical investigation of the magnetized water-based hybrid nanofluid flow over an extending sheet with a convective condition: Active and passive controls of nanoparticles
- The LyP-1 cyclic peptide modified mesoporous polydopamine nanospheres for targeted delivery of triptolide regulate the macrophage repolarization in atherosclerosis
- Synergistic effect of hydroxyapatite-magnetite nanocomposites in magnetic hyperthermia for bone cancer treatment
- The significance of quadratic thermal radiative scrutinization of a nanofluid flow across a microchannel with thermophoretic particle deposition effects
- Ferromagnetic effect on Casson nanofluid flow and transport phenomena across a bi-directional Riga sensor device: Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Performance of carbon nanomaterials incorporated with concrete exposed to high temperature
- Multicriteria-based optimization of roller compacted concrete pavement containing crumb rubber and nano-silica
- Revisiting hydrotalcite synthesis: Efficient combined mechanochemical/coprecipitation synthesis to design advanced tunable basic catalysts
- Exploration of irreversibility process and thermal energy of a tetra hybrid radiative binary nanofluid focusing on solar implementations
- Effect of graphene oxide on the properties of ternary limestone clay cement paste
- Improved mechanical properties of graphene-modified basalt fibre–epoxy composites
- Sodium titanate nanostructured modified by green synthesis of iron oxide for highly efficient photodegradation of dye contaminants
- Green synthesis of Vitis vinifera extract-appended magnesium oxide NPs for biomedical applications
- Differential study on the thermal–physical properties of metal and its oxide nanoparticle-formed nanofluids: Molecular dynamics simulation investigation of argon-based nanofluids
- Heat convection and irreversibility of magneto-micropolar hybrid nanofluids within a porous hexagonal-shaped enclosure having heated obstacle
- Numerical simulation and optimization of biological nanocomposite system for enhanced oil recovery
- Laser ablation and chemical vapor deposition to prepare a nanostructured PPy layer on the Ti surface
- Cilostazol niosomes-loaded transdermal gels: An in vitro and in vivo anti-aggregant and skin permeation activity investigations towards preparing an efficient nanoscale formulation
- Linear and nonlinear optical studies on successfully mixed vanadium oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique
- Analytical investigation of convective phenomena with nonlinearity characteristics in nanostratified liquid film above an inclined extended sheet
- Optimization method for low-velocity impact identification in nanocomposite using genetic algorithm
- Analyzing the 3D-MHD flow of a sodium alginate-based nanofluid flow containing alumina nanoparticles over a bi-directional extending sheet using variable porous medium and slip conditions
- A comprehensive study of laser irradiated hydrothermally synthesized 2D layered heterostructure V2O5(1−x)MoS2(x) (X = 1–5%) nanocomposites for photocatalytic application
- Computational analysis of water-based silver, copper, and alumina hybrid nanoparticles over a stretchable sheet embedded in a porous medium with thermophoretic particle deposition effects
- A deep dive into AI integration and advanced nanobiosensor technologies for enhanced bacterial infection monitoring
- Effects of normal strain on pyramidal I and II 〈c + a〉 screw dislocation mobility and structure in single-crystal magnesium
- Computational study of cross-flow in entropy-optimized nanofluids
- Significance of nanoparticle aggregation for thermal transport over magnetized sensor surface
- A green and facile synthesis route of nanosize cupric oxide at room temperature
- Effect of annealing time on bending performance and microstructure of C19400 alloy strip
- Chitosan-based Mupirocin and Alkanna tinctoria extract nanoparticles for the management of burn wound: In vitro and in vivo characterization
- Electrospinning of MNZ/PLGA/SF nanofibers for periodontitis
- Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by Nd-doped titanium dioxide thin films
- Shell-core-structured electrospinning film with sequential anti-inflammatory and pro-neurogenic effects for peripheral nerve repairment
- Flow and heat transfer insights into a chemically reactive micropolar Williamson ternary hybrid nanofluid with cross-diffusion theory
- One-pot fabrication of open-spherical shapes based on the decoration of copper sulfide/poly-O-amino benzenethiol on copper oxide as a promising photocathode for hydrogen generation from the natural source of Red Sea water
- A penta-hybrid approach for modeling the nanofluid flow in a spatially dependent magnetic field
- Advancing sustainable agriculture: Metal-doped urea–hydroxyapatite hybrid nanofertilizer for agro-industry
- Utilizing Ziziphus spina-christi for eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Antimicrobial activity and promising application in wound healing
- Plant-mediated synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of a copper oxide/silicon dioxide nanocomposite by an antimicrobial study
- Effects of PVA fibers and nano-SiO2 on rheological properties of geopolymer mortar
- Investigating silver and alumina nanoparticles’ impact on fluid behavior over porous stretching surface
- Potential pharmaceutical applications and molecular docking study for green fabricated ZnO nanoparticles mediated Raphanus sativus: In vitro and in vivo study
- Effect of temperature and nanoparticle size on the interfacial layer thickness of TiO2–water nanofluids using molecular dynamics
- Characteristics of induced magnetic field on the time-dependent MHD nanofluid flow through parallel plates
- Flexural and vibration behaviours of novel covered CFRP composite joints with an MWCNT-modified adhesive
- Experimental research on mechanically and thermally activation of nano-kaolin to improve the properties of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete
- Analysis of variable fluid properties for three-dimensional flow of ternary hybrid nanofluid on a stretching sheet with MHD effects
- Biodegradability of corn starch films containing nanocellulose fiber and thymol
- Toxicity assessment of copper oxide nanoparticles: In vivo study
- Some measures to enhance the energy output performances of triboelectric nanogenerators
- Reinforcement of graphene nanoplatelets on water uptake and thermomechanical behaviour of epoxy adhesive subjected to water ageing conditions
- Optimization of preparation parameters and testing verification of carbon nanotube suspensions used in concrete
- Max-phase Ti3SiC2 and diverse nanoparticle reinforcements for enhancement of the mechanical, dynamic, and microstructural properties of AA5083 aluminum alloy via FSP
- Advancing drug delivery: Neural network perspectives on nanoparticle-mediated treatments for cancerous tissues
- PEG-PLGA core–shell nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of picoplatin–hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in triple-negative breast cancer: In vitro and in vivo study
- Conduction transportation from graphene to an insulative polymer medium: A novel approach for the conductivity of nanocomposites
- Review Articles
- Developments of terahertz metasurface biosensors: A literature review
- Overview of amorphous carbon memristor device, modeling, and applications for neuromorphic computing
- Advances in the synthesis of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) of proteins extracted from nature
- A review of ternary polymer nanocomposites containing clay and calcium carbonate and their biomedical applications
- Recent advancements in polyoxometalate-functionalized fiber materials: A review
- Special contribution of atomic force microscopy in cell death research
- A comprehensive review of oral chitosan drug delivery systems: Applications for oral insulin delivery
- Cellular senescence and nanoparticle-based therapies: Current developments and perspectives
- Cyclodextrins-block copolymer drug delivery systems: From design and development to preclinical studies
- Micelle-based nanoparticles with stimuli-responsive properties for drug delivery
- Critical assessment of the thermal stability and degradation of chemically functionalized nanocellulose-based polymer nanocomposites
- Research progress in preparation technology of micro and nano titanium alloy powder
- Nanoformulations for lysozyme-based additives in animal feed: An alternative to fight antibiotic resistance spread
- Incorporation of organic photochromic molecules in mesoporous silica materials: Synthesis and applications
- A review on modeling of graphene and associated nanostructures reinforced concrete
- A review on strengthening mechanisms of carbon quantum dots-reinforced Cu-matrix nanocomposites
- Review on nanocellulose composites and CNFs assembled microfiber toward automotive applications
- Nanomaterial coating for layered lithium rich transition metal oxide cathode for lithium-ion battery
- Application of AgNPs in biomedicine: An overview and current trends
- Nanobiotechnology and microbial influence on cold adaptation in plants
- Hepatotoxicity of nanomaterials: From mechanism to therapeutic strategy
- Applications of micro-nanobubble and its influence on concrete properties: An in-depth review
- A comprehensive systematic literature review of ML in nanotechnology for sustainable development
- Exploiting the nanotechnological approaches for traditional Chinese medicine in childhood rhinitis: A review of future perspectives
- Twisto-photonics in two-dimensional materials: A comprehensive review
- Current advances of anticancer drugs based on solubilization technology
- Recent process of using nanoparticles in the T cell-based immunometabolic therapy
- Future prospects of gold nanoclusters in hydrogen storage systems and sustainable environmental treatment applications
- Preparation, types, and applications of one- and two-dimensional nanochannels and their transport properties for water and ions
- Microstructural, mechanical, and corrosion characteristics of Mg–Gd–x systems: A review of recent advancements
- Functionalized nanostructures and targeted delivery systems with a focus on plant-derived natural agents for COVID-19 therapy: A review and outlook
- Mapping evolution and trends of cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A bibliometric analysis and scoping review
- Nanoparticles and their application in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- In situ growth of carbon nanotubes on fly ash substrates
- Structural performance of boards through nanoparticle reinforcement: An advance review
- Reinforcing mechanisms review of the graphene oxide on cement composites
- Seed regeneration aided by nanomaterials in a climate change scenario: A comprehensive review
- Surface-engineered quantum dot nanocomposites for neurodegenerative disorder remediation and avenue for neuroimaging
- Graphitic carbon nitride hybrid thin films for energy conversion: A mini-review on defect activation with different materials
- Nanoparticles and the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials and Composites for Energy Conversion and Storage - Part II
- Highly safe lithium vanadium oxide anode for fast-charging dendrite-free lithium-ion batteries
- Recent progress in nanomaterials of battery energy storage: A patent landscape analysis, technology updates, and future prospects
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Carbon Capture, Environment and Utilization for Energy Sustainability - Part II
- Calcium-, magnesium-, and yttrium-doped lithium nickel phosphate nanomaterials as high-performance catalysts for electrochemical water oxidation reaction
- Low alkaline vegetation concrete with silica fume and nano-fly ash composites to improve the planting properties and soil ecology
- Mesoporous silica-grafted deep eutectic solvent-based mixed matrix membranes for wastewater treatment: Synthesis and emerging pollutant removal performance
- Electrochemically prepared ultrathin two-dimensional graphitic nanosheets as cathodes for advanced Zn-based energy storage devices
- Enhanced catalytic degradation of amoxicillin by phyto-mediated synthesised ZnO NPs and ZnO-rGO hybrid nanocomposite: Assessment of antioxidant activity, adsorption, and thermodynamic analysis
- Incorporating GO in PI matrix to advance nanocomposite coating: An enhancing strategy to prevent corrosion
- Synthesis, characterization, thermal stability, and application of microporous hyper cross-linked polyphosphazenes with naphthylamine group for CO2 uptake
- Engineering in ceramic albite morphology by the addition of additives: Carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide for energy applications
- Nanoscale synergy: Optimizing energy storage with SnO2 quantum dots on ZnO hexagonal prisms for advanced supercapacitors
- Aging assessment of silicone rubber materials under corona discharge accompanied by humidity and UV radiation
- Tuning structural and electrical properties of Co-precipitated and Cu-incorporated nickel ferrite for energy applications
- Sodium alginate-supported AgSr nanoparticles for catalytic degradation of malachite green and methyl orange in aqueous medium
- An environmentally greener and reusability approach for bioenergy production using Mallotus philippensis (Kamala) seed oil feedstock via phytonanotechnology
- Micro-/nano-alumina trihydrate and -magnesium hydroxide fillers in RTV-SR composites under electrical and environmental stresses
- Mechanism exploration of ion-implanted epoxy on surface trap distribution: An approach to augment the vacuum flashover voltages
- Nanoscale engineering of semiconductor photocatalysts boosting charge separation for solar-driven H2 production: Recent advances and future perspective
- Excellent catalytic performance over reduced graphene-boosted novel nanoparticles for oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil
- Special Issue on Advances in Nanotechnology for Agriculture
- Deciphering the synergistic potential of mycogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles and bio-slurry formulation on phenology and physiology of Vigna radiata
- Nanomaterials: Cross-disciplinary applications in ornamental plants
- Special Issue on Catechol Based Nano and Microstructures
- Polydopamine films: Versatile but interface-dependent coatings
- In vitro anticancer activity of melanin-like nanoparticles for multimodal therapy of glioblastoma
- Poly-3,4-dihydroxybenzylidenhydrazine, a different analogue of polydopamine
- Chirality and self-assembly of structures derived from optically active 1,2-diaminocyclohexane and catecholamines
- Advancing resource sustainability with green photothermal materials: Insights from organic waste-derived and bioderived sources
- Bioinspired neuromelanin-like Pt(iv) polymeric nanoparticles for cancer treatment
- Special Issue on Implementing Nanotechnology for Smart Healthcare System
- Intelligent explainable optical sensing on Internet of nanorobots for disease detection
- Special Issue on Green Mono, Bi and Tri Metallic Nanoparticles for Biological and Environmental Applications
- Tracking success of interaction of green-synthesized Carbopol nanoemulgel (neomycin-decorated Ag/ZnO nanocomposite) with wound-based MDR bacteria
- Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using genus Inula and evaluation of biological therapeutics and environmental applications
- Biogenic fabrication and multifunctional therapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles synthesized from rose petal extract
- Metal oxides on the frontlines: Antimicrobial activity in plant-derived biometallic nanoparticles
- Controlling pore size during the synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles using CTAB by the sol–gel hydrothermal method and their biological activities
- Special Issue on State-of-Art Advanced Nanotechnology for Healthcare
- Applications of nanomedicine-integrated phototherapeutic agents in cancer theranostics: A comprehensive review of the current state of research
- Smart bionanomaterials for treatment and diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease
- Beyond conventional therapy: Synthesis of multifunctional nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Tension buckling and postbuckling of nanocomposite laminated plates with in-plane negative Poisson’s ratio
- Polyvinylpyrrolidone-stabilised gold nanoparticle coatings inhibit blood protein adsorption
- Energy and mass transmission through hybrid nanofluid flow passing over a spinning sphere with magnetic effect and heat source/sink
- Surface treatment with nano-silica and magnesium potassium phosphate cement co-action for enhancing recycled aggregate concrete
- Numerical investigation of thermal radiation with entropy generation effects in hybrid nanofluid flow over a shrinking/stretching sheet
- Enhancing the performance of thermal energy storage by adding nano-particles with paraffin phase change materials
- Using nano-CaCO3 and ceramic tile waste to design low-carbon ultra high performance concrete
- Numerical analysis of thermophoretic particle deposition in a magneto-Marangoni convective dusty tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow – Thermal and magnetic features
- Dual numerical solutions of Casson SA–hybrid nanofluid toward a stagnation point flow over stretching/shrinking cylinder
- Single flake homo p–n diode of MoTe2 enabled by oxygen plasma doping
- Electrostatic self-assembly effect of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on performance of carbon nanotubes in cement-based materials
- Multi-scale alignment to buried atom-scale devices using Kelvin probe force microscopy
- Antibacterial, mechanical, and dielectric properties of hydroxyapatite cordierite/zirconia porous nanocomposites for use in bone tissue engineering applications
- Time-dependent Darcy–Forchheimer flow of Casson hybrid nanofluid comprising the CNTs through a Riga plate with nonlinear thermal radiation and viscous dissipation
- Durability prediction of geopolymer mortar reinforced with nanoparticles and PVA fiber using particle swarm optimized BP neural network
- Utilization of zein nano-based system for promoting antibiofilm and anti-virulence activities of curcumin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Antibacterial effect of novel dental resin composites containing rod-like zinc oxide
- An extended model to assess Jeffery–Hamel blood flow through arteries with iron-oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles and melting effects: Entropy optimization analysis
- Comparative study of copper nanoparticles over radially stretching sheet with water and silicone oil
- Cementitious composites modified by nanocarbon fillers with cooperation effect possessing excellent self-sensing properties
- Confinement size effect on dielectric properties, antimicrobial activity, and recycling of TiO2 quantum dots via photodegradation processes of Congo red dye and real industrial textile wastewater
- Biogenic silver nanoparticles of Moringa oleifera leaf extract: Characterization and photocatalytic application
- Novel integrated structure and function of Mg–Gd neutron shielding materials
- Impact of multiple slips on thermally radiative peristaltic transport of Sisko nanofluid with double diffusion convection, viscous dissipation, and induced magnetic field
- Magnetized water-based hybrid nanofluid flow over an exponentially stretching sheet with thermal convective and mass flux conditions: HAM solution
- A numerical investigation of the two-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic water-based hybrid nanofluid flow composed of Fe3O4 and Au nanoparticles over a heated surface
- Development and modeling of an ultra-robust TPU-MWCNT foam with high flexibility and compressibility
- Effects of nanofillers on the physical, mechanical, and tribological behavior of carbon/kenaf fiber–reinforced phenolic composites
- Polymer nanocomposite for protecting photovoltaic cells from solar ultraviolet in space
- Study on the mechanical properties and microstructure of recycled concrete reinforced with basalt fibers and nano-silica in early low-temperature environments
- Synergistic effect of carbon nanotubes and polyvinyl alcohol on the mechanical performance and microstructure of cement mortar
- CFD analysis of paraffin-based hybrid (Co–Au) and trihybrid (Co–Au–ZrO2) nanofluid flow through a porous medium
- Forced convective tangent hyperbolic nanofluid flow subject to heat source/sink and Lorentz force over a permeable wedge: Numerical exploration
- Physiochemical and electrical activities of nano copper oxides synthesised via hydrothermal method utilising natural reduction agents for solar cell application
- A homotopic analysis of the blood-based bioconvection Carreau–Yasuda hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet with convective conditions
- In situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/SnIn4S8 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic performance for pollutant degradation
- A coarse-grained Poisson–Nernst–Planck model for polyelectrolyte-modified nanofluidic diodes
- A numerical investigation of the magnetized water-based hybrid nanofluid flow over an extending sheet with a convective condition: Active and passive controls of nanoparticles
- The LyP-1 cyclic peptide modified mesoporous polydopamine nanospheres for targeted delivery of triptolide regulate the macrophage repolarization in atherosclerosis
- Synergistic effect of hydroxyapatite-magnetite nanocomposites in magnetic hyperthermia for bone cancer treatment
- The significance of quadratic thermal radiative scrutinization of a nanofluid flow across a microchannel with thermophoretic particle deposition effects
- Ferromagnetic effect on Casson nanofluid flow and transport phenomena across a bi-directional Riga sensor device: Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Performance of carbon nanomaterials incorporated with concrete exposed to high temperature
- Multicriteria-based optimization of roller compacted concrete pavement containing crumb rubber and nano-silica
- Revisiting hydrotalcite synthesis: Efficient combined mechanochemical/coprecipitation synthesis to design advanced tunable basic catalysts
- Exploration of irreversibility process and thermal energy of a tetra hybrid radiative binary nanofluid focusing on solar implementations
- Effect of graphene oxide on the properties of ternary limestone clay cement paste
- Improved mechanical properties of graphene-modified basalt fibre–epoxy composites
- Sodium titanate nanostructured modified by green synthesis of iron oxide for highly efficient photodegradation of dye contaminants
- Green synthesis of Vitis vinifera extract-appended magnesium oxide NPs for biomedical applications
- Differential study on the thermal–physical properties of metal and its oxide nanoparticle-formed nanofluids: Molecular dynamics simulation investigation of argon-based nanofluids
- Heat convection and irreversibility of magneto-micropolar hybrid nanofluids within a porous hexagonal-shaped enclosure having heated obstacle
- Numerical simulation and optimization of biological nanocomposite system for enhanced oil recovery
- Laser ablation and chemical vapor deposition to prepare a nanostructured PPy layer on the Ti surface
- Cilostazol niosomes-loaded transdermal gels: An in vitro and in vivo anti-aggregant and skin permeation activity investigations towards preparing an efficient nanoscale formulation
- Linear and nonlinear optical studies on successfully mixed vanadium oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique
- Analytical investigation of convective phenomena with nonlinearity characteristics in nanostratified liquid film above an inclined extended sheet
- Optimization method for low-velocity impact identification in nanocomposite using genetic algorithm
- Analyzing the 3D-MHD flow of a sodium alginate-based nanofluid flow containing alumina nanoparticles over a bi-directional extending sheet using variable porous medium and slip conditions
- A comprehensive study of laser irradiated hydrothermally synthesized 2D layered heterostructure V2O5(1−x)MoS2(x) (X = 1–5%) nanocomposites for photocatalytic application
- Computational analysis of water-based silver, copper, and alumina hybrid nanoparticles over a stretchable sheet embedded in a porous medium with thermophoretic particle deposition effects
- A deep dive into AI integration and advanced nanobiosensor technologies for enhanced bacterial infection monitoring
- Effects of normal strain on pyramidal I and II 〈c + a〉 screw dislocation mobility and structure in single-crystal magnesium
- Computational study of cross-flow in entropy-optimized nanofluids
- Significance of nanoparticle aggregation for thermal transport over magnetized sensor surface
- A green and facile synthesis route of nanosize cupric oxide at room temperature
- Effect of annealing time on bending performance and microstructure of C19400 alloy strip
- Chitosan-based Mupirocin and Alkanna tinctoria extract nanoparticles for the management of burn wound: In vitro and in vivo characterization
- Electrospinning of MNZ/PLGA/SF nanofibers for periodontitis
- Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by Nd-doped titanium dioxide thin films
- Shell-core-structured electrospinning film with sequential anti-inflammatory and pro-neurogenic effects for peripheral nerve repairment
- Flow and heat transfer insights into a chemically reactive micropolar Williamson ternary hybrid nanofluid with cross-diffusion theory
- One-pot fabrication of open-spherical shapes based on the decoration of copper sulfide/poly-O-amino benzenethiol on copper oxide as a promising photocathode for hydrogen generation from the natural source of Red Sea water
- A penta-hybrid approach for modeling the nanofluid flow in a spatially dependent magnetic field
- Advancing sustainable agriculture: Metal-doped urea–hydroxyapatite hybrid nanofertilizer for agro-industry
- Utilizing Ziziphus spina-christi for eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Antimicrobial activity and promising application in wound healing
- Plant-mediated synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of a copper oxide/silicon dioxide nanocomposite by an antimicrobial study
- Effects of PVA fibers and nano-SiO2 on rheological properties of geopolymer mortar
- Investigating silver and alumina nanoparticles’ impact on fluid behavior over porous stretching surface
- Potential pharmaceutical applications and molecular docking study for green fabricated ZnO nanoparticles mediated Raphanus sativus: In vitro and in vivo study
- Effect of temperature and nanoparticle size on the interfacial layer thickness of TiO2–water nanofluids using molecular dynamics
- Characteristics of induced magnetic field on the time-dependent MHD nanofluid flow through parallel plates
- Flexural and vibration behaviours of novel covered CFRP composite joints with an MWCNT-modified adhesive
- Experimental research on mechanically and thermally activation of nano-kaolin to improve the properties of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete
- Analysis of variable fluid properties for three-dimensional flow of ternary hybrid nanofluid on a stretching sheet with MHD effects
- Biodegradability of corn starch films containing nanocellulose fiber and thymol
- Toxicity assessment of copper oxide nanoparticles: In vivo study
- Some measures to enhance the energy output performances of triboelectric nanogenerators
- Reinforcement of graphene nanoplatelets on water uptake and thermomechanical behaviour of epoxy adhesive subjected to water ageing conditions
- Optimization of preparation parameters and testing verification of carbon nanotube suspensions used in concrete
- Max-phase Ti3SiC2 and diverse nanoparticle reinforcements for enhancement of the mechanical, dynamic, and microstructural properties of AA5083 aluminum alloy via FSP
- Advancing drug delivery: Neural network perspectives on nanoparticle-mediated treatments for cancerous tissues
- PEG-PLGA core–shell nanoparticles for the controlled delivery of picoplatin–hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex in triple-negative breast cancer: In vitro and in vivo study
- Conduction transportation from graphene to an insulative polymer medium: A novel approach for the conductivity of nanocomposites
- Review Articles
- Developments of terahertz metasurface biosensors: A literature review
- Overview of amorphous carbon memristor device, modeling, and applications for neuromorphic computing
- Advances in the synthesis of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) of proteins extracted from nature
- A review of ternary polymer nanocomposites containing clay and calcium carbonate and their biomedical applications
- Recent advancements in polyoxometalate-functionalized fiber materials: A review
- Special contribution of atomic force microscopy in cell death research
- A comprehensive review of oral chitosan drug delivery systems: Applications for oral insulin delivery
- Cellular senescence and nanoparticle-based therapies: Current developments and perspectives
- Cyclodextrins-block copolymer drug delivery systems: From design and development to preclinical studies
- Micelle-based nanoparticles with stimuli-responsive properties for drug delivery
- Critical assessment of the thermal stability and degradation of chemically functionalized nanocellulose-based polymer nanocomposites
- Research progress in preparation technology of micro and nano titanium alloy powder
- Nanoformulations for lysozyme-based additives in animal feed: An alternative to fight antibiotic resistance spread
- Incorporation of organic photochromic molecules in mesoporous silica materials: Synthesis and applications
- A review on modeling of graphene and associated nanostructures reinforced concrete
- A review on strengthening mechanisms of carbon quantum dots-reinforced Cu-matrix nanocomposites
- Review on nanocellulose composites and CNFs assembled microfiber toward automotive applications
- Nanomaterial coating for layered lithium rich transition metal oxide cathode for lithium-ion battery
- Application of AgNPs in biomedicine: An overview and current trends
- Nanobiotechnology and microbial influence on cold adaptation in plants
- Hepatotoxicity of nanomaterials: From mechanism to therapeutic strategy
- Applications of micro-nanobubble and its influence on concrete properties: An in-depth review
- A comprehensive systematic literature review of ML in nanotechnology for sustainable development
- Exploiting the nanotechnological approaches for traditional Chinese medicine in childhood rhinitis: A review of future perspectives
- Twisto-photonics in two-dimensional materials: A comprehensive review
- Current advances of anticancer drugs based on solubilization technology
- Recent process of using nanoparticles in the T cell-based immunometabolic therapy
- Future prospects of gold nanoclusters in hydrogen storage systems and sustainable environmental treatment applications
- Preparation, types, and applications of one- and two-dimensional nanochannels and their transport properties for water and ions
- Microstructural, mechanical, and corrosion characteristics of Mg–Gd–x systems: A review of recent advancements
- Functionalized nanostructures and targeted delivery systems with a focus on plant-derived natural agents for COVID-19 therapy: A review and outlook
- Mapping evolution and trends of cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A bibliometric analysis and scoping review
- Nanoparticles and their application in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- In situ growth of carbon nanotubes on fly ash substrates
- Structural performance of boards through nanoparticle reinforcement: An advance review
- Reinforcing mechanisms review of the graphene oxide on cement composites
- Seed regeneration aided by nanomaterials in a climate change scenario: A comprehensive review
- Surface-engineered quantum dot nanocomposites for neurodegenerative disorder remediation and avenue for neuroimaging
- Graphitic carbon nitride hybrid thin films for energy conversion: A mini-review on defect activation with different materials
- Nanoparticles and the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials and Composites for Energy Conversion and Storage - Part II
- Highly safe lithium vanadium oxide anode for fast-charging dendrite-free lithium-ion batteries
- Recent progress in nanomaterials of battery energy storage: A patent landscape analysis, technology updates, and future prospects
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Carbon Capture, Environment and Utilization for Energy Sustainability - Part II
- Calcium-, magnesium-, and yttrium-doped lithium nickel phosphate nanomaterials as high-performance catalysts for electrochemical water oxidation reaction
- Low alkaline vegetation concrete with silica fume and nano-fly ash composites to improve the planting properties and soil ecology
- Mesoporous silica-grafted deep eutectic solvent-based mixed matrix membranes for wastewater treatment: Synthesis and emerging pollutant removal performance
- Electrochemically prepared ultrathin two-dimensional graphitic nanosheets as cathodes for advanced Zn-based energy storage devices
- Enhanced catalytic degradation of amoxicillin by phyto-mediated synthesised ZnO NPs and ZnO-rGO hybrid nanocomposite: Assessment of antioxidant activity, adsorption, and thermodynamic analysis
- Incorporating GO in PI matrix to advance nanocomposite coating: An enhancing strategy to prevent corrosion
- Synthesis, characterization, thermal stability, and application of microporous hyper cross-linked polyphosphazenes with naphthylamine group for CO2 uptake
- Engineering in ceramic albite morphology by the addition of additives: Carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide for energy applications
- Nanoscale synergy: Optimizing energy storage with SnO2 quantum dots on ZnO hexagonal prisms for advanced supercapacitors
- Aging assessment of silicone rubber materials under corona discharge accompanied by humidity and UV radiation
- Tuning structural and electrical properties of Co-precipitated and Cu-incorporated nickel ferrite for energy applications
- Sodium alginate-supported AgSr nanoparticles for catalytic degradation of malachite green and methyl orange in aqueous medium
- An environmentally greener and reusability approach for bioenergy production using Mallotus philippensis (Kamala) seed oil feedstock via phytonanotechnology
- Micro-/nano-alumina trihydrate and -magnesium hydroxide fillers in RTV-SR composites under electrical and environmental stresses
- Mechanism exploration of ion-implanted epoxy on surface trap distribution: An approach to augment the vacuum flashover voltages
- Nanoscale engineering of semiconductor photocatalysts boosting charge separation for solar-driven H2 production: Recent advances and future perspective
- Excellent catalytic performance over reduced graphene-boosted novel nanoparticles for oxidative desulfurization of fuel oil
- Special Issue on Advances in Nanotechnology for Agriculture
- Deciphering the synergistic potential of mycogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles and bio-slurry formulation on phenology and physiology of Vigna radiata
- Nanomaterials: Cross-disciplinary applications in ornamental plants
- Special Issue on Catechol Based Nano and Microstructures
- Polydopamine films: Versatile but interface-dependent coatings
- In vitro anticancer activity of melanin-like nanoparticles for multimodal therapy of glioblastoma
- Poly-3,4-dihydroxybenzylidenhydrazine, a different analogue of polydopamine
- Chirality and self-assembly of structures derived from optically active 1,2-diaminocyclohexane and catecholamines
- Advancing resource sustainability with green photothermal materials: Insights from organic waste-derived and bioderived sources
- Bioinspired neuromelanin-like Pt(iv) polymeric nanoparticles for cancer treatment
- Special Issue on Implementing Nanotechnology for Smart Healthcare System
- Intelligent explainable optical sensing on Internet of nanorobots for disease detection
- Special Issue on Green Mono, Bi and Tri Metallic Nanoparticles for Biological and Environmental Applications
- Tracking success of interaction of green-synthesized Carbopol nanoemulgel (neomycin-decorated Ag/ZnO nanocomposite) with wound-based MDR bacteria
- Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using genus Inula and evaluation of biological therapeutics and environmental applications
- Biogenic fabrication and multifunctional therapeutic applications of silver nanoparticles synthesized from rose petal extract
- Metal oxides on the frontlines: Antimicrobial activity in plant-derived biometallic nanoparticles
- Controlling pore size during the synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles using CTAB by the sol–gel hydrothermal method and their biological activities
- Special Issue on State-of-Art Advanced Nanotechnology for Healthcare
- Applications of nanomedicine-integrated phototherapeutic agents in cancer theranostics: A comprehensive review of the current state of research
- Smart bionanomaterials for treatment and diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease
- Beyond conventional therapy: Synthesis of multifunctional nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy

