Abstract
The present work addresses the optimal design of sandwich panels made of flax fabric (FF)/vinyl ester (VE) composite face sheets and honeycomb VE core. The sandwich structures are first optimized in terms of flammability by obtaining the best combination of ammonium polyphosphate (APP), halloysite nanotube (HNT), and magnesium hydroxide (MH) as three flame retardants (FRs). Using the Taguchi method and horizontal burning test, it is shown that [6, 3, and 3%] and [1, 0.5, and 0%] are the optimal combinations of APP, HNT, and MH for the face sheets and core, respectively. Cone calorimeter test results indicate that the optimal FR combinations significantly decrease the mass lost rate (MLR), heat rate release (HRR), total smoke release (TSR), and maximum average release heat emission (MARHE). The FR sandwich structures are then geometrically optimized under compressive loads based on their weight. Different failure modes are considered as the design constraints of the optimization problem. Imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA), as a powerful meta-heuristic algorithm, is implemented to considerably reduce the computational cost of the optimization process. The results of this study show that proper combinations of FR additives can increase the flame retardancy while decreasing the weight of sandwich panels.
1 Introduction
With increasing global public awareness and concerns about environmental pollutants, as well as the overproduction of nonrenewable petroleum-based products, the use of natural fiber-reinforced composites has gained significant attention in recent years [1,2,3,4]. Flax is one of these natural materials that can be used in different configurations such as mats, rovings, fabrics, monofilament fibers, and yarns [5]. Owing to their low environmental impact, lightweight, low energy consumption, cost effectiveness, recyclability, and biodegradability, flax-reinforced composites have been successfully used in real applications such as automotive parts, construction, consumer goods, furniture, pipes, tanks, and rotor blades [6,7,8,9,10]. In particular, these natural fibers are a good alternative for conventional synthetic fibers used in sandwich structures [11,12,13,14,15].
Despite the excellent properties of flax fibers, their use in composite structures can be challenging. One of the most important issues is their low flame resistance [16,17,18,19,20]. Concerning the flax-reinforced sandwich structures, Kandare et al. [21] studied the fire retardancy of eco-friendly sandwich components composed of balsa core and flax-reinforced epoxy face sheets. They established the idea of using glass fiber/ammonium polyphosphate (APP) coating and presented the results of their research using a cone calorimeter. It was found that the flammable properties of the biodegradable sandwich structures can be significantly improved in the presence of the fire protective coating. Prabhakaran et al. [22] comprehensively explored the thermal conductivity, thermal expansion, flammability, and thermal stability of the environmental-friendly cork/flax/poxy sandwich structures. Manobala et al. [23] compared the thermomechanical behavior of four types of sandwich panels obtained from a combination of flax-reinforced face sheets, glass-reinforced face sheets, coir cores, and polyurethane cores. They measured and compared the thermal conductivity, flammability, and tensile strength of the structures. The experimental results indicated that the renewable sandwich structures consisting of flax/epoxy in face sheets and coir as core possess lower thermal conductivity and higher limiting oxygen index.
Honeycomb sandwich structures are lightweight engineering structures consisting of a thick and light honeycomb core covered by two relatively thin but stiff layers. Owing to their high efficiency, these sandwich structures have found extensive applications in diverse industries, including aerospace, automotive, railway, marine, and civil [24,25,26]. In this regard, numerous studies have addressed the physical, mechanical, and thermal properties of honeycomb structures [27,28,29] to optimize them for different purposes such as weight, deflection, impact, and sound transmission loss [30,31,32,33,34].
The present study is aimed to investigate the synergistic effects of APP, halloysite nanotube (HNT), and magnesium hydroxide (MH) additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with flax fabric (FF)/vinyl ester (VE) composite face sheets and VE honeycomb core based on flame retardancy and weight. The design of the structures consists of two main parts: the design or selection of proper constituent materials and the geometrical design. Therefore, the optimal flame retardant (FR) materials are first determined for the face sheets and the core in Section 2. The main goal of this section is to optimize the amounts of three FR additives, namely APP, HNT, and MH, to maximize the flame retardancy of the structure regardless of its geometry and weight. The results of this section are obtained based on the horizontal test, cone calorimeter test, and compression test. Then, in Section 3, weight minimization of FR honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to compressive loads is investigated by considering various possible failure modes. The effects of optimal FR combinations (obtained from Section 2) on the minimum weight of sandwich panels are studied. Analytical approaches are used to predict the failure modes as the design constraints, and the optimization process is performed by imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) that has been successfully implemented in many engineering optimization problems [35,36,37,38].
2 Flame retardancy optimization of sandwich panels
As mentioned earlier, the focus of the present work is on the design of sandwich panels, whose face sheets and the honeycomb core are made of FF/VE and VE, respectively. It should be mentioned that the FF was purchased from Sungchang Industries (Korea) and the VE was supplied by CCP composites (Korea). To remove the greasy material on the fabrics, 2 wt% sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution was used. The NaOH was obtained from Samchun Chemical Co., Korea. Since both the core and face sheets are flammable, FR additives were used to reduce the flammability of the structures. Among the various available FR additives, APP, HNT, and MH (from Samchun Pure Chemical, Korea) were selected. APP is an inorganic salt of polyphosphoric acid and ammonia whose flame resistance can be assigned to its high phosphorus and nitrogen contents. APP is an effective FR for thermoset resin such as epoxy and VE due to the involvement of both APP and resin in the charring during the combustion process. HNT is an efficient and popular FR among inorganic nanofillers due to tubular nanostructure, high aspect ratio, and natural availability [39]. The incorporation of HNT has a positive effect on the thermal degradation of VE-based intumescent FR systems. MH is an environmentally friendly and nontoxic FR mineral additive. Upon exposure to high temperatures, it experiences an endothermic decomposition, absorbs combustion heat, releases water vapor and nonflammable gas, and suppresses smoke. MgO is its main decomposition product with few effects in promoting polymer charring and low ability to form an effective barrier.
The following subsections briefly describe the optimization steps of FR sandwich panels.
2.1 Optimal FR face sheets
Taguchi design of experiment (DOE) is one the most popular and well-known statistical techniques that can significantly reduce the time and cost of experiments by decreasing the number of required tests. To this end, the factors (APP, HNT, and MH) and their levels (0, 3, and 6%) were defined. An L9 orthogonal array was selected to design the experiments for different combinations of the FRs, as shown in Table 1.
L9 orthogonal array of Taguchi DOE for the face sheets at three levels of 0, 3, and 6% and for the core at three levels of 0, 0.5, and 1%
| Sample | Face sheets | Core | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APP (%) | HNT (%) | MH (%) | APP (%) | HNT (%) | MH (%) | |
| A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| B | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| C | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| D | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 |
| E | 3 | 3 | 6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 |
| F | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 |
| G | 6 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| H | 6 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 |
| I | 6 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 |
The FR composites were fabricated using the vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) technique considering different concentrations of APP, HNT, and MH. The FRs were spread between the layers of FFs before resin infusion. After preparing the nine composites proposed by Taguchi, horizontal flammability test was carried out according to the U94 standard test. This test determines the burning time and consequently the burning rate for the specimens. The digital pictures of one of the composite specimens (H) before, during, and after the horizontal burning test are presented in Figure 1. Furthermore, Table 2 depicts the burning time (the time required for the flame to reach from the initial reference point to the terminal reference point) and burning rate of the nine composites. As observed, all combinations of APP, HNT, and MH prolong the burning time or decrease the burning rate of the pure composite (sample A). Note that specimen H is the composite with the highest flame retardancy (highest burning time) among the nine specimens.
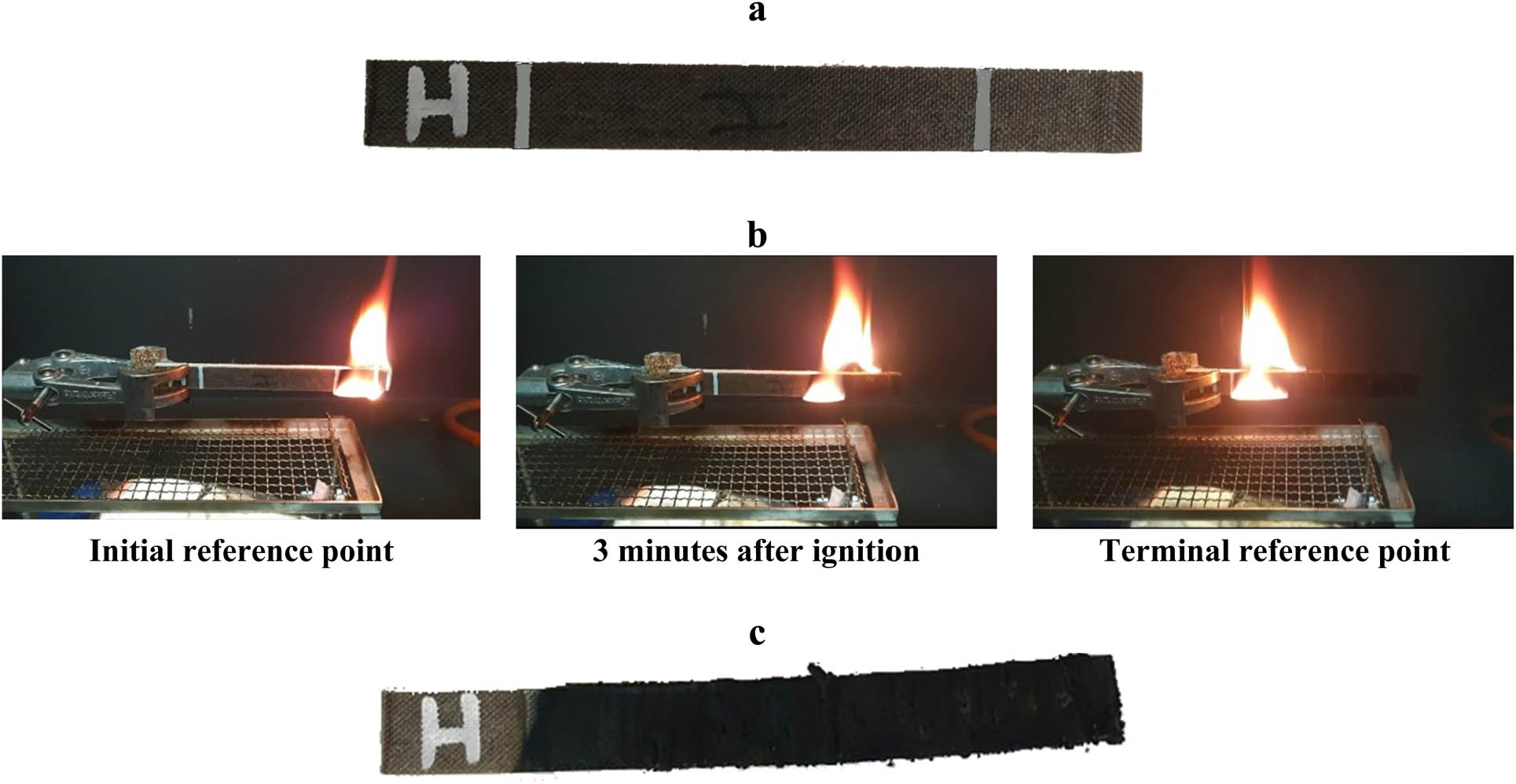
Schematic representation of specimen H for the face sheets: (a) before, (b) during, and (c) after burning in the horizontal burning test.
L9 Horizontal burning test results for FF/VE composites used in the face sheets
| Sample | Burning time (s) | Burning rate (mm/s) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 338 | 0.370 |
| B | 362 | 0.345 |
| C | 368 | 0.340 |
| D | 407 | 0.307 |
| E | 408 | 0.306 |
| F | 344 | 0.363 |
| G | 397 | 0.315 |
| H | 428 | 0.292 |
| I | 417 | 0.300 |
The S/N ratios of the experimental data were then evaluated. Based on this analysis, the effect of each FR additive on the flammability of the composites can be evaluated, as shown in Figure 2. Accordingly, the incorporation of APP additive promotes the flame retardancy of the VE/FF composites whose effect increases at higher loadings. It is speculated that APP, which is liable for the formation of dense char via intumescent mechanism by producing phosphoric acid during combustion, can react with carbon agents (VE/FF), thereby, delay the burning time and resist further flame propagation. Moreover, the ammonium functional group present in the APP can serve as a blowing agent to enhance intercomponent space or dilute the oxygen content of the air and promote the flame retardancy.
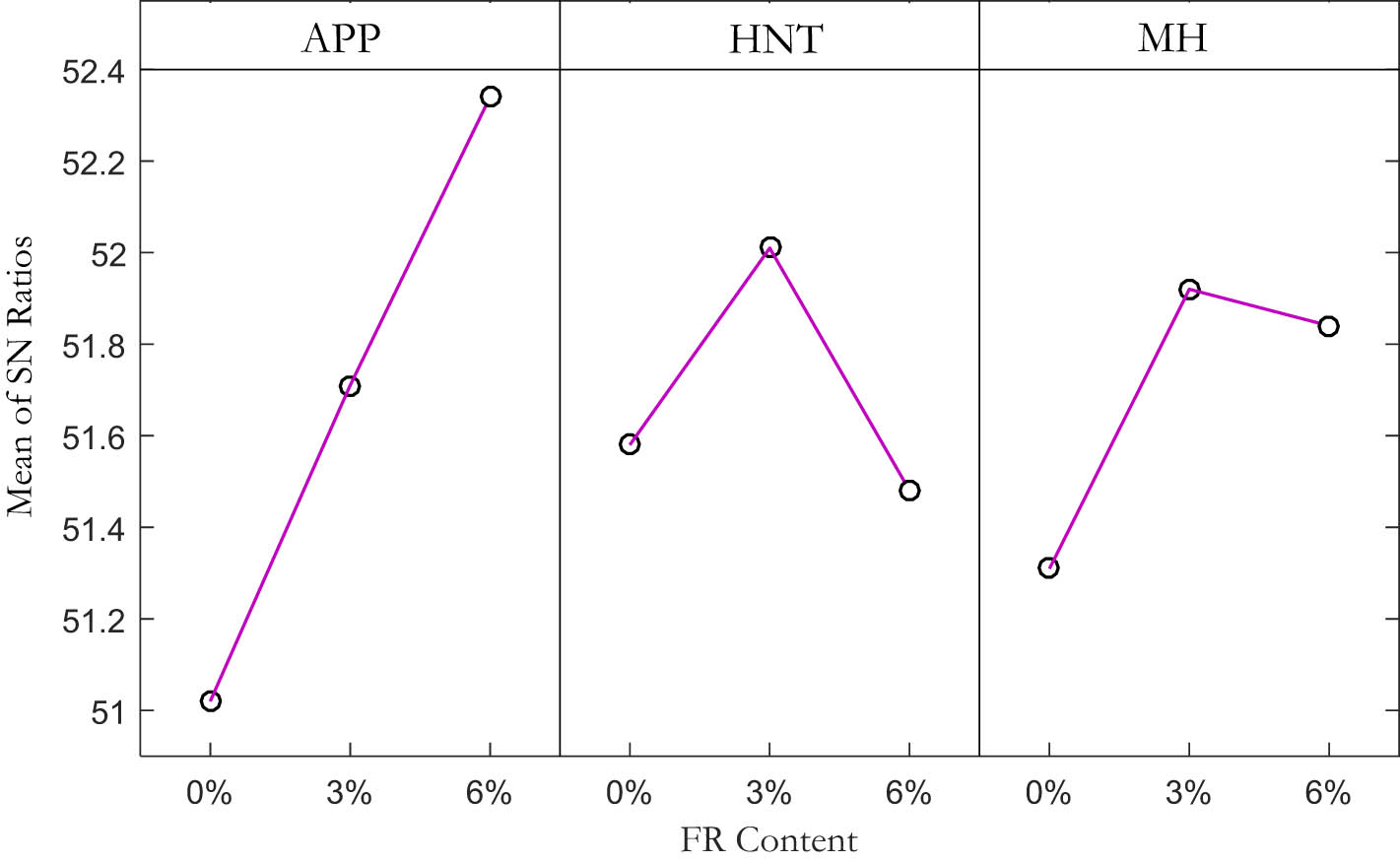
Main effects plot for S/N ratios for burning time.
In the case of HNT, the addition of 3% HNT into the VE/FF composites delays the burning time by increasing flame retardancy. HNT can produce stable cohesive char, which is responsible for trapping the flammable volatiles and forming solid barriers on the composites’ surface, reducing the decomposition rate while increasing the decomposition temperature. However, homogeneous dispersion of particles in the composites plays a vital role in the maintenance of the char layer. Hence, the higher loadings of HNT may deteriorate the fire resistance due to nonuniform distribution and agglomeration of the nanofillers.
Similarly, MH contents up to 3% lead to a significant flame retardancy. During decomposition of MH, the released magnesium oxide moiety and water serve as an insulator on the surface of the polymer composites and weakens the flame intensity, respectively. High MH loadings also decline the fire resistance due to the nonsynergistic effect with other additives as well as the agglomeration phenomenon.
S/N ratio analysis can also predict the best combination of the FRs for synergistic maximization of the flame retardancy of the VE/FF face sheets. Based on Figures 2, 6, 3, and 3% are the optimal values for APP, HNT, and MH to yield the maximum flame resistance in VE/FF face sheets, respectively. Therefore, further research was done by manufacturing a new composite coded as the J sample, with the optimal combination of FR additives. The horizontal burning test was carried out on the J sample to confirm its optimal flame retardancy behavior in terms of the burning time. The experiment showed that the burning time of the J sample reached a delay time of 462 s, almost 37% higher than the A sample and even 8% more than the H samples, indicating its superior flame retardancy behavior, as expected.
2.2 Optimal FR core
Here, similar to the previous subsection, the optimal combination of FR additives was obtained for the VE honeycomb core. Noteworthy, the face sheets are much more important than the core in the design of a flame-resistant sandwich composite structure due to their higher chance of exposure to fire. Therefore, in the present study, smaller amounts of FR additives (at three levels of 0, 0.5, and 1%) were used for the core compared to the face sheets to be cost effective. Similarly, nine different combinations of APP, HNT, and MH were suggested based on the Taguchi technique (Table 1). The proposed specimens were prepared and subjected to the horizontal burn test, based on the UL94 standard. Figure 3 shows the digital snapshot of the specimens after the test. All composite specimens burned completely except composite H, in which the flame did not reach the terminal reference point. In this case, S/N analysis cannot be performed accurately. Therefore, the specimen H was selected as the optimal specimen.

Schematic representation of nine different specimens for the core after burning in the horizontal burning test.
2.3 Optimal FR adhesive layer
One of the main factors with significant influence on the thermal and mechanical performances of sandwich structures is the adhesive layer between face sheets and core. Despite the existence of different types of adhesives, in the present study, VE with the optimal FR combination for the core (obtained in Section 2.2) was used to bond the face sheets and core due to its compatibility with core materials and flame retardancy.
2.4 Optimal FR sandwich panels
In the previous three subsections, the optimal FR materials for the face sheets, core, and adhesive layer were selected. In this subsection, the effects of FRs on the flammability of sandwich panels are addressed. To this end, two types of sandwich panels were prepared. The first panel consisted of FF/VE composite face sheets, VE honeycomb core, and VE adhesive layer without any FR additives, whereas the second one was composed of the optimal FR flax-reinforced face sheets, optimal FR honeycomb core, and optimal FR adhesive layer. The process of making FR sandwich panels is briefly illustrated in Figure 4. First, two very thin J combination-based face sheets were fabricated using VARTM. Then, the honeycomb cores were made through four main steps: (1) designing a mold in design software, (2) making a plastic mold composed of PLA using a 3-D printer, (3) making a negative silicone mold, and (4) preparing the H combination-based VE composite and pouring it in the silicone honeycomb mold. Finally, the prepared face sheets were attached to the core by H combination-based adhesive layer and subjected to the 5 MPa pressure for 1 day.
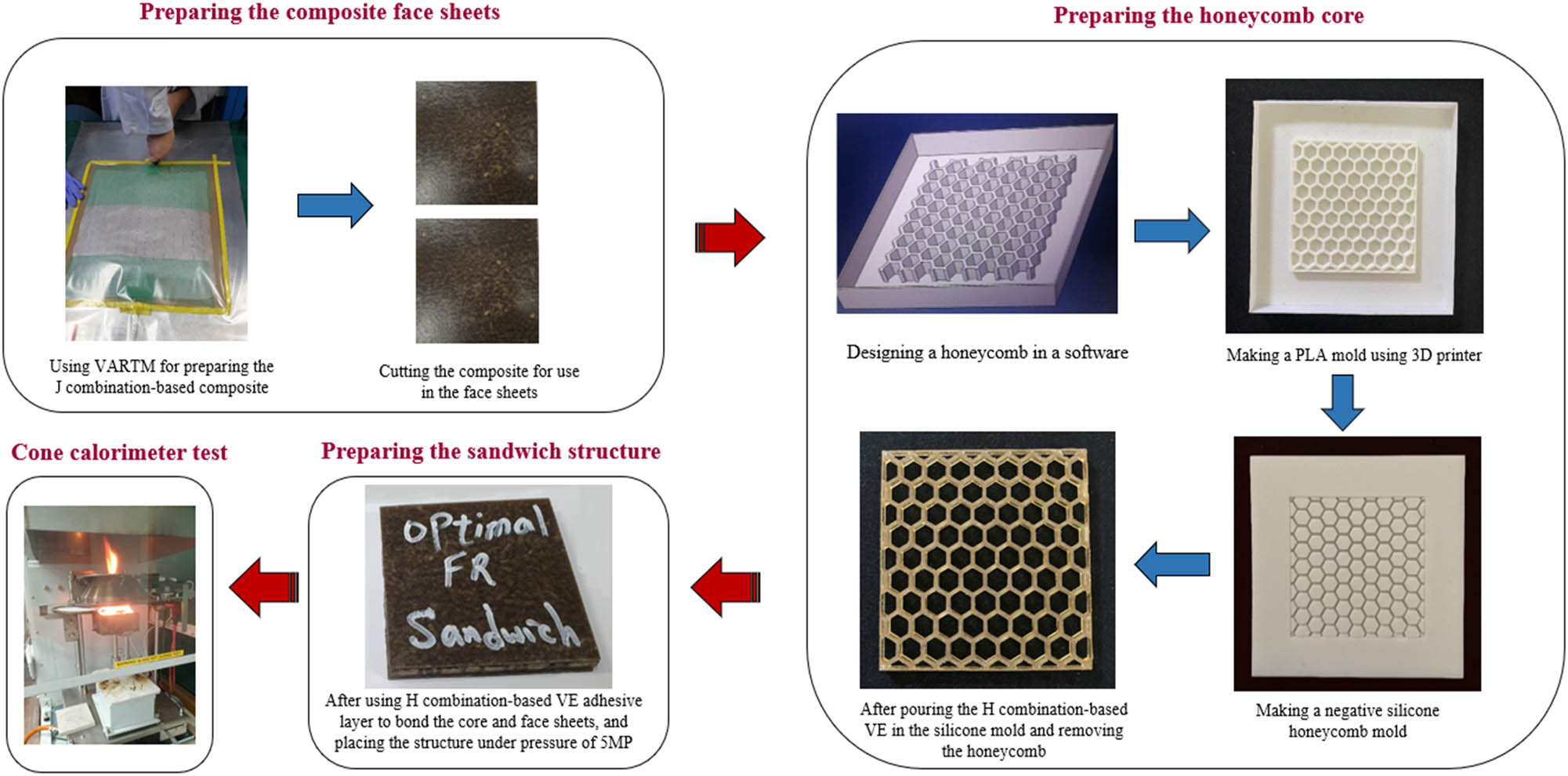
The main steps of preparing the optimal FR sandwich panel for the cone calorimeter test.
After preparing the FR and non-FR sandwich panels, cone calorimeter test was carried out to provide an accurate and detailed comparison between their fire properties. Mass lost rate (MLR) is one of the most important flammability properties of the sandwich structures, especially in the early stages of burning. This is because in these structures, the thin face sheets bear almost all applied loads; moreover, they are first exposed to fire. Thus, structures possessing face sheets with high MLR will soon fail upon exposure to fire. The variations of this parameter during the first 6 min of the burning process are listed in Table 3. As observed, FR additives can considerably (18–32%) decrease the MLR for the sandwich panel. Furthermore, during the first 4 min from the ignition, the MLR of the non-FR sandwich panel gradually decreased; but then it began to increase. The reason was that after this time, the structure core was exposed to the flame, and due to its higher flammability relative to the face sheets, the MLR increased. Similar behavior was observed for the burning of the FR-containing sandwich panels. The difference was in the longer time duration for core exposure to the flame, that is, the MLR began to increase 5 min after ignition. Heat rate release (HRR) is another prominent parameter in the flammability of composite structures. The cone calorimeter test data revealed that a proper FR combination can significantly decrement the HRR of sandwich structures (34–39%) in the first 6 min of the burning process. Again, a decrease–increase pattern was observed for both FR-containing and non-FR sandwich specimens due to the differences in flammability of composite face sheets and core. One more crucial parameter to evaluate the flammability of structures is the maximum average release heat emission (MARHE). The cone calorimeter machine showed MARHE values of 357.97 and 221.46 kW/m2 for the non-FR and FR-containing sandwich panels, respectively. It implies the FR additives could decrease the MARHE of the sandwich composite by ∼38%. Finally, the effects of FR additives on the amount of smoke production were examined. Total smoke release (TSR) of the non-FR specimen was 5495.6 m2/m2, which decremented to 4629.0 m2/m2 in the FR-containing sandwich composite. Overall, the cone calorimeter test showed the successful use of optimal combinations of APP, HNT, and MH to promote flame retardancy in the sandwich panels.
Cone calorimeter test data for the FR and non-FR honeycomb sandwich panels
| Property | Unit | Sandwich type | Time after ignition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 min | 2 min | 3 min | 4 min | 5 min | 6 min | |||
| MLR |
|
Non-FR | 19.18 | 15.74 | 12.85 | 12.25 | 12.74 | 13.36 |
| FR | 15.78 | 12.40 | 9.93 | 8.83 | 8.71 | 9.32 | ||
| HRR |
|
Non-FR | 421.15 | 326.53 | 270.96 | 265.29 | 276.48 | 289.35 |
| FR | 271.18 | 216.58 | 179.23 | 163.94 | 168.21 | 182.52 | ||
2.5 Compressive properties of the FR materials in the face sheets and core
So far, proper flame-resistant compositions were found. In the next step, an investigation was made to examine the effects of the optimal FR combinations on the compressive properties of materials used in the face sheets and core. This is because in Section 3, geometric design of FR and non-FR sandwich panels under compressive loads based on their weight is investigated, for which the values of compressive Young’s modulus and strength of the face sheets’ materials as well as the compressive Young’s modulus of the core materials are required. To this end, compression test was conducted on four different types of specimens: (1) FF/VE composites without FRs, (2) FF/VE with [6, 3, and 3%] FRs, (3) pure VE, and (4) pure VE with [1, 0.5, and 0%] FRs. The experimental data obtained from the tests are presented in Table 4. As this table shows, the optimal FR combinations led to 6.35, 5.64 and 7.28% increase in the face sheets’ modulus, face sheets’ strength, and core modulus. In addition, the Poisson’s ratio was measured, the value of which was approximately 0.26 for FF/VE composite specimens and 0.31 for VE.
Compression test results for the FR and non-FR materials used in the face sheets and core
| Property | Materials | Type | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive young modulus | FF/VE (face sheets) | Without FRs |
|
| With optimal FR combination* |
|
||
| VE (honeycomb core) | Without FRs |
|
|
| With optimal FR combination** |
|
||
| Compressive strength | FF/VE (face sheets) | Without FRs |
|
| With optimal FR combination* |
|
* 6% App, 3% HNT, and 3% MH.
** 1% App, 0.5% HNT, and 0% MH.
3 Weight minimization of sandwich panels
In this section, the effect of FR additives on the minimum required weight of sandwich panels is explored. A beam-shaped sandwich structure composed of FF/VE composite face sheets and VE honeycomb core is considered (see Figure 5). In this figure,
where
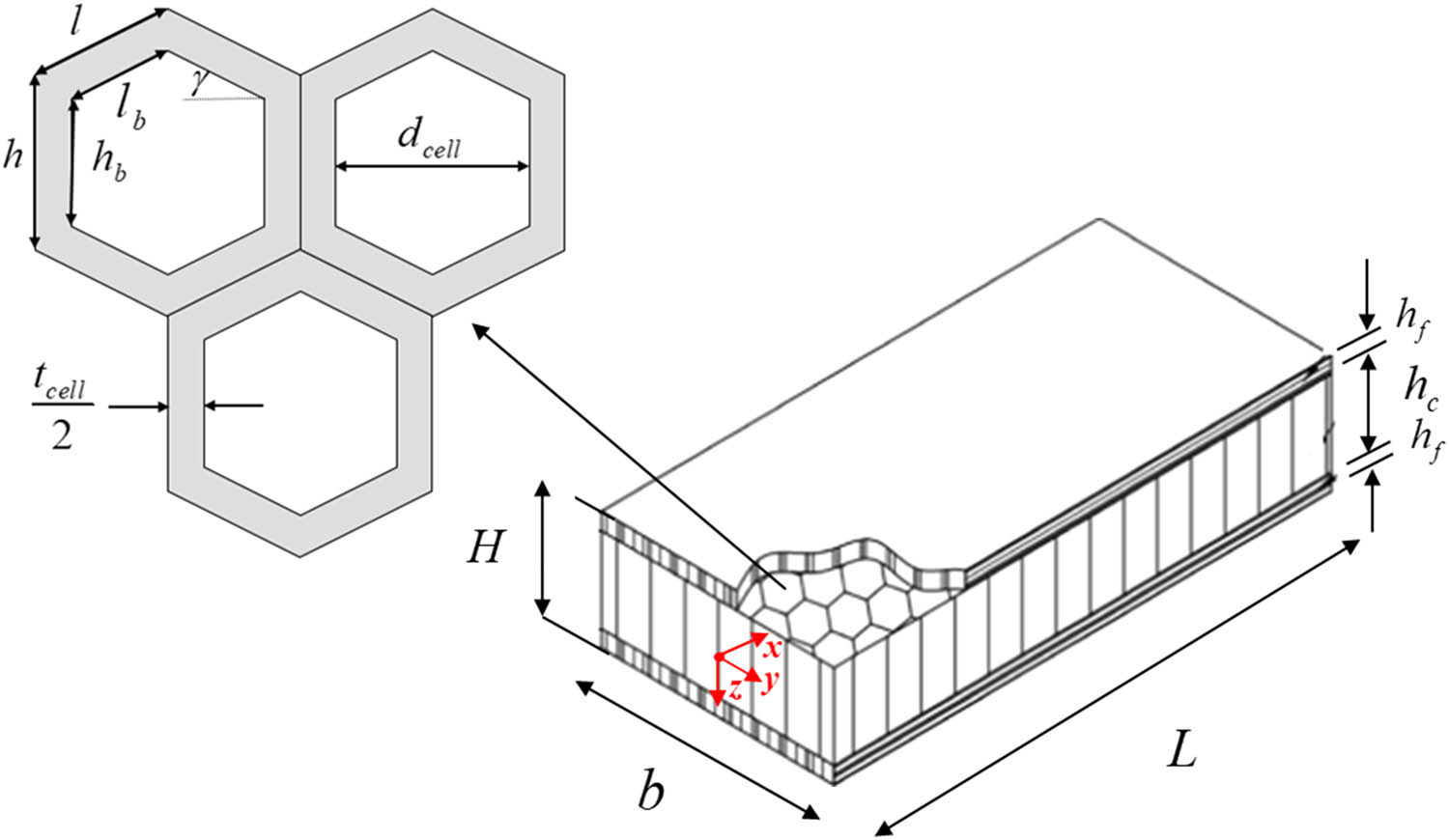
Schematic of a sandwich beam with honeycomb core and composite face sheets.
In the following subsections, the analytical models of the failure modes are first briefly described. Then, ICA and its main steps are summarized. Finally, the optimization results are presented for different load amplitudes.
3.1 Failure modes
3.1.1 Global buckling equations
The first possible failure mode in sandwich beams under compressive loads is global buckling that shows the global instability of the structure. Consider a sandwich beam with honeycomb core and laminated composite face sheets, as shown in Figure 5. The sandwich beam is assumed to be under compressive in-plane loads at its ends. Based on piecewise low-order shear deformation theory [40], the displacement fields for the sandwich beam in the face sheets and core are expressed in the following forms:
where subscripts
The stress components in the kth layer of the top composite face sheet (
where
where
Therefore, the strain energy (
In the next step, the external work done by the compressive load with amplitude
According to the principle of virtual work [42], we have:
Two out-of-plane buckling equations can be obtained by combining equations (8–10) for the sandwich beam with immovable simply supported boundaries:
in which
Moreover, the related boundary conditions can be derived as follows:
The following solution is proposed for the buckling equations of simply supported sandwich beams:
where
By setting the determinant of the above matrix of coefficients to zero, the following solution is obtained to predict the critical buckling loads of sandwich beams.
3.1.2 Face sheet dimpling (or monocell buckling)
Face sheet dimpling is a type of instability of honeycomb sandwich panels in which a face sheet over one cell buckles like a small plate supported by the cell walls. The critical stress for face sheet dimpling can be calculated by the following equation [43]:
where
3.1.3 Face sheet wrinkling
Wrinkling is a type of instability that may appear across many cells of the honeycomb core of sandwich panels in the direction of the applied load. In the present work, the following criterion is considered for this instability [43].
3.1.4 Core shear instability
The fourth constraint for designing honeycomb sandwich panels under in-plane compressive load is core shear stability. The critical stress for this instability can be calculated by the following equation [44]:
where
in which,
3.1.5 Face sheet failure
When the stress created by the applied external force exceeds the equivalent strength of the face sheets, a failure may occur in them. Here, the Tsai–Wu criterion is used for determining the equivalent strength for the face sheets, the details can be found in an earlier study [45].
3.2 ICA
As a global search heuristic algorithm, ICA uses imperialism and imperialistic competition processes for optimization steps. Similar to other evolutionary algorithms, ICA begins with an initial population known as countries classified into two major groups: imperialists (i.e., stronger countries) and colonies (the rest of countries). Stronger imperialists possess more colonies. The major steps of the ICA can be listed as follows [46]:
Step 1: Selecting some random points of the function and initializing the empires.
Step 2: Moving the colonies to their most relevant imperialist (assimilating).
Step 3: If an empire possesses a colony stronger than the imperialist, the colony will substitute the imperialist (revolution).
Step 4: Computing the total power of empires (sum of the powers of imperialist and its colonies).
Step 5: Selecting the weakest colony (colonies) from the weakest empire and transferring it (them) to the empire with the highest likelihood of its (their) possession (imperialistic competition).
Step 6: Elimination of the weak empires.
Step 7: Stopping the process if only one empire remains, otherwise starting from Step 2.
For a detailed description of the proposed algorithm, see literature [46].
3.3 Verification study
3.3.1 Verification of global buckling results
Among the mentioned failure modes, the formulation proposed in Section 3.1.1 for global buckling of sandwich beams is new and has not been developed before, to the best of the authors’ knowledge. Therefore, a comparison study is required to verify the accuracy of the present analytical method. A comparison example is presented to evaluate the mechanical buckling loads of a sandwich beam made of aluminum face sheets and an orthotropic core. In this example, the material properties of the face sheets and core are as follows [47,48]:
The dimensionless buckling loads of the structure are listed in Table 5 for different values of
The non-dimensional critical buckling loads (
|
|
|
Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | MLWT [47] | ZZT [48] | GLHT [48] | ||
| 5 | 5 | 0.014876 | 0.01432 | 0.01486 | 0.01484 |
| 10 | 0.041844 | 0.041084 | 0.04182 | 0.04182 | |
| 50 | 0.364936 | 0.34319 | 0.3648 | 0.3648 | |
| 25 | 5 | 0.009144 | 0.009031 | 0.009143 | 0.009142 |
| 10 | 0.031691 | 0.031096 | 0.03168 | 0.03168 | |
| 50 | 0.155846 | 0.14385 | 0.1558 | 0.1558 | |
| 50 | 5 | 0.008694 | 0.008555 | 0.008692 | 0.008692 |
| 10 | 0.027580 | 0.026762 | 0.02756 | 0.02756 | |
| 50 | 0.090749 | 0.083230 | 0.09072 | 0.09072 | |
3.3.2 Verification of ICA optimization results
As the second part of the verification study, the performance of the applied ICA is evaluated in weight minimization of non-FR honeycomb sandwich beam under 200 kN/m compressive loads when the length of beam is 0.3 m. The values of design variables are assumed to vary in the following ranges.
The increments of the design variable are considered to be 0.3 mm for the face sheet thickness, 0.2 mm for the core thickness, and 0.1 mm for the other variables. First, all possible solutions (around
Parameters of ICA for the optimization process
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of initial countries | 100 |
| Number of initial imperialists | 6 |
| Number of decades | 40 |
| Revolution rate | 0.3 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
0.1 |
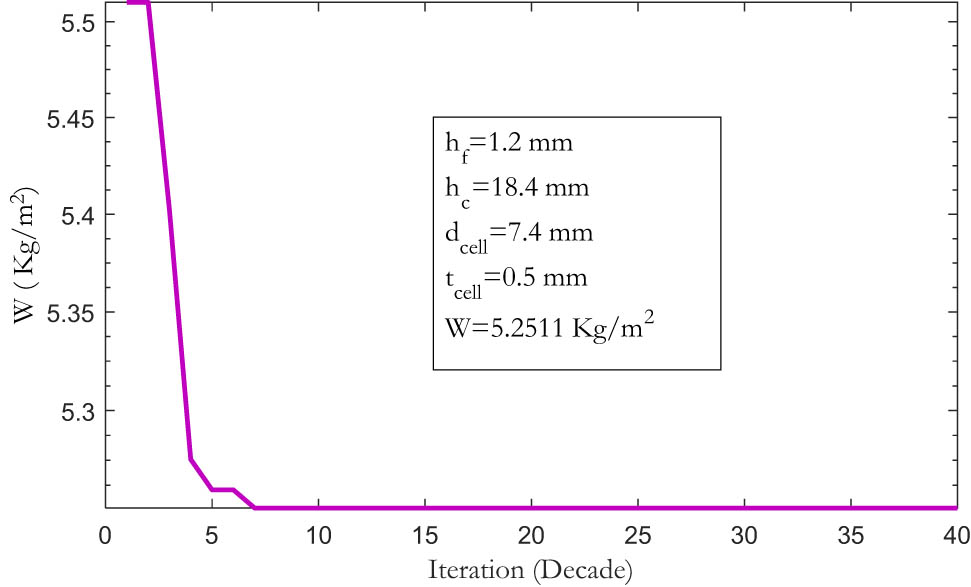
Convergence of the ICA to the optimal solution for a sandwich beam without FR additives (
From this comparison, two conclusions can be drawn: (1) ICA is sufficiently powerful to handle the optimization problems, especially for the weight minimization of honeycomb sandwich beams and (2) ICA significantly reduces the computational costs. This confirms the reliability of the ICA results of the present study.
3.4 Optimization results
The main goal of the optimization problem here is to investigate the effects of FRs on the geometric design of honeycomb sandwich beams. For this purpose, the sandwich beam is presumed to be subjected to compressive loads with different amplitudes (
The increment is assumed to be 0.3 mm for the thickness of the face sheets while 0.2 mm for the core thickness and 0.1 mm for the cell wall thickness and cell size. ICA is implemented 10 times for each sandwich beam, and the best solution is selected as the optimal answer. Table 7 provides the optimization results for FR-containing and non-FR sandwich beams subjected to different compressive loads when
ICA results for the optimal design of FR and non-FR simply supported sandwich beams in terms of weight (
|
|
Optimum variables |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
| 50 | Non-FR | 0.6 | 13.2 | 6.4 | 0.3 | 2.6543 |
| FR | 0.6 | 12.8 | 4.5 | 0.2 | 2.5622 | |
| 100 | Non-FR | 0.9 | 15.0 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 3.7024 |
| FR | 0.9 | 14.6 | 6.1 | 0.3 | 3.5728 | |
| 200 | Non-FR | 1.2 | 18.4 | 7.4 | 0.5 | 5.2511 |
| FR | 1.2 | 18.0 | 9.5 | 0.6 | 5.0653 | |
4 Conclusion
The present study addressed the synergistic effects of APP, HNT, and MH additives on the optimal design of honeycomb sandwich panels made of FF and VE in terms of flammability and weight. The flammability of the structure was first optimized by applying the best combinations of FR additives in the face sheets, core, and adhesive layer, using the Taguchi method and performing experimental tests. In the second step, the weight of sandwich structures was minimized by optimizing its geometric parameters including the thickness of the face sheet, core and cell wall and the size of the honeycomb cell. The following conclusions can be drawn:
[6, 3, and 3%] and [1, 0.5, and 0%] were the best FR combinations of APP, HNT, and MH in the face sheets and core, respectively.
Cone calorimeter test showed that the optimum amount of FRs in the sandwich structures led to an 18–32% decrease in MLR and a 34–39% decline in HRR during the first 6 min of the burning process.
The experimental data obtained from the cone calorimeter test revealed that optimal FR combinations can decrement the MARHE and TSR in the burning process of the sandwich structure by 38 and 16%, respectively.
Optimal FR combinations can also enhance the compressive modulus and strength of both FF/VE composite face sheets and VE honeycomb core.
ICA is a powerful meta-heuristic optimization algorithm capable of predicting the optimum answers for engineering optimization problems, especially for weight minimization of honeycomb sandwich beams, with high accuracy. It can also significantly reduce the CPU time and consequently the computational costs of the optimization process.
Using optimum amounts of APP, HNT, and MH, it is possible to design a sandwich panel with higher flame resistance and lighter weight.
-
Funding information: This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science Education (2018R1A6A1A03024509 and 2021R1A2B5B03002355).
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT, editors. Natural fibers, biopolymers, and biocomposites. Boca Raton: CRC press; 2005.10.1201/9780203508206Search in Google Scholar
[2] Pickering K, editor. Properties and performance of natural-fibre composites. Boca Raton: Elsevier; 2008.10.1201/9781439832141Search in Google Scholar
[3] John MJ, Thomas S. Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym. 2008;71(3):343–64.10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.05.040Search in Google Scholar
[4] Alhijazi M, Zeeshan Q, Qin Z, Safaei B, Asmael M. Finite element analysis of natural fibers composites: a review. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):853–75.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0069Search in Google Scholar
[5] Yan L, Chouw N, Jayaraman K. Flax fibre and its composites–a review. Compos Part B: Eng. 2014;56:296–317.10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.014Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shah DU, Schubel PJ, Clifford MJ. Can flax replace E-glass in structural composites? A small wind turbine blade case study. Compos Part B: Eng. 2013;52:172–81.10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.04.027Search in Google Scholar
[7] Khalfallah M, Abbès B, Abbès F, Guo YQ, Marcel V, Duval A, et al. Innovative flax tapes reinforced Acrodur biocomposites: A new alternative for automotive applications. Mater & Des. 2014;64:116–26.10.1016/j.matdes.2014.07.029Search in Google Scholar
[8] Ramesh M. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) fibre reinforced polymer composite materials: a review on preparation, properties and prospects. Prog Mater Sci. 2019;102:109–66.10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.12.004Search in Google Scholar
[9] Firouzsalari SE, Dizhur D, Jayaraman K, Ingham J. Experimental study of flax fabric-reinforced epoxy pipes subjected to internal pressure. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf. 2021;147:106445.10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106445Search in Google Scholar
[10] Le Duigou A, Barbé A, Guillou E, Castro M. 3D printing of continuous flax fibre reinforced biocomposites for structural applications. Mater & Des. 2019;180:107884.10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107884Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sadeghian P, Hristozov D, Wroblewski L. Experimental and analytical behavior of sandwich composite beams: Comparison of natural and synthetic materials. J Sandw Struct & Mater. 2018;20(3):287–307.10.1177/1099636216649891Search in Google Scholar
[12] Sarasini F, Tirillò J, Lampani L, Barbero E, Sanchez-Saez S, Valente T, et al. Impact behavior of sandwich structures made of flax/epoxy face sheets and agglomerated cork. J Nat Fibers. 2020;17(2):168–88. Available from 10.1080/15440478.2018.1477084.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Monti A, El Mahi A, Jendli Z, Guillaumat L. Quasi-static and fatigue properties of a balsa cored sandwich structure with thermoplastic skins reinforced by flax fibres. J Sandw Struct & Mater. 2019;21(7):2358–81.10.1177/1099636218760307Search in Google Scholar
[14] Xu J, Gao X, Zhang C, Yin S. Flax fiber-reinforced composite lattice cores: a low-cost and recyclable approach. Mater & Des. 2017;133:444–54.10.1016/j.matdes.2017.07.066Search in Google Scholar
[15] Essassi K, Rebiere JL, Mahi AE, Souf MA, Bouguecha A, Haddar M. Experimental and numerical analysis of the dynamic behavior of a bio-based sandwich with an auxetic core. J Sandw Struct & Mater. 2019. Available from 10.1177/1099636219851547.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Hajj R, El Hage R, Sonnier R, Otazaghine B, Gallard B, Rouif S, et al. Grafting of phosphorus flame retardants on flax fabrics: comparison between two routes. Polym Degrad Stab. 2018;147:25–34.10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.11.006Search in Google Scholar
[17] Zhang L, Li Z, Pan YT, Yáñez AP, Hu S, Zhang XQ, et al. Polydopamine induced natural fiber surface functionalization: a way towards flame retardancy of flax/poly (lactic acid) biocomposites. Compos Part B: Eng. 2018;154:56–63.10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.07.037Search in Google Scholar
[18] Pornwannachai W, Ebdon JR, Kandola BK. Fire-resistant natural fibre-reinforced composites from flame retarded textiles. Polym Degrad Stab. 2018;154:115–23.10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.05.019Search in Google Scholar
[19] Prabhakar MN, Song JI. Fabrication and characterisation of starch/chitosan/flax fabric green flame-retardant composites. Int J Biol Macromolecules. 2018;119:1335–43.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Lazko J, Landercy N, Laoutid F, Dangreau L, Huguet MH, Talon O. Flame retardant treatments of insulating agro-materials from flax short fibres. Polym Degrad Stab. 2013;98(5):1043–51.10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.02.002Search in Google Scholar
[21] Kandare E, Luangtriratana P, Kandola BK. Fire reaction properties of flax/epoxy laminates and their balsa-core sandwich composites with or without fire protection. Compos Part B: Eng. 2014;56:602–10.10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.090Search in Google Scholar
[22] Prabhakaran S, Krishnaraj V, Sharma S, Senthilkumar M, Jegathishkumar R, Zitoune R. Experimental study on thermal and morphological analyses of green composite sandwich made of flax and agglomerated cork. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(5):3003–12.10.1007/s10973-019-08691-xSearch in Google Scholar
[23] Manobala KS, Prabhakaran S, Ramji Gautham DR, Sathish Kumar M, Bala Ganesan A, Nithish C. Investigation of mechanical and thermal behaviour of natural sandwich composite materials for partition walls. Int J Res Rev. 2020;7(5):211–6.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Joy VA, Murthy KN, Nair CG. Technological excellence in honeycomb sandwich and composite structures for aerospace applications. Aeronaut Soc India J. 1991;43(2):101–12.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Wang S, Liu L, Huang Z, Li Z, Liu J, Hao Y. Honeycomb structure is promising for the repair of human bone defects. Mater Des. 2021;207:109832.10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109832Search in Google Scholar
[26] Shifa M, Tariq F, Chandio AD. Mechanical and electrical properties of hybrid honeycomb sandwich structure for spacecraft structural applications. J Sandw Struct & Mater. 2021;23(1):222–40.10.1177/1099636219830783Search in Google Scholar
[27] Gibson LJ. Cellular solids. Mrs Bull. 2003;28(4):270–4.10.1017/CBO9781139878326Search in Google Scholar
[28] Malek S, Gibson L. Effective elastic properties of periodic hexagonal honeycombs. Mech Mater. 2015;91:226–40.10.1016/j.mechmat.2015.07.008Search in Google Scholar
[29] Dong Z, Li Y, Zhao T, Wu W, Xiao D, Liang J. Experimental and numerical studies on the compressive mechanical properties of the metallic auxetic reentrant honeycomb. Mater Des. 2019;182:108036.10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108036Search in Google Scholar
[30] Gholami M, Alashti RA, Fathi A. Optimal design of a honeycomb core composite sandwich panel using evolutionary optimization algorithms. Compos Struct. 2016;139:254–62.10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.12.019Search in Google Scholar
[31] Galgalikar R, Thompson LL. Design optimization of honeycomb core sandwich panels for maximum sound transmission loss. J Vib Acoust. 2016;138(5):051005.10.1115/1.4033459Search in Google Scholar
[32] Hao J, Wu X, Oporto G, Liu W, Wang J. Structural analysis and strength-to-weight optimization of wood-based sandwich composite with honeycomb core under three-point flexural test. Eur J Wood Wood Products. 2020;78(6):1195–207.10.1007/s00107-020-01574-1Search in Google Scholar
[33] Wang L, Liu HT. Parameter optimization of bidirectional re-entrant auxetic honeycomb metamaterial based on genetic algorithm. Compos Struct. 2021;267:113915.10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113915Search in Google Scholar
[34] Cheng YC, Yeh HC, Lee CK. Multi-objective optimization of the honeycomb core in a honeycomb structure using uniform design and grey relational analysis. Eng Optim. 2021;1–9.10.1080/0305215X.2020.1862825Search in Google Scholar
[35] Gerist S, Maheri MR. Structural damage detection using imperialist competitive algorithm and damage function. Appl Soft Comput. 2019;77:1–23.10.1016/j.asoc.2018.12.032Search in Google Scholar
[36] Amirhosseini B, Hosseini SH. Scheduling charging of hybrid-electric vehicles according to supply and demand based on particle swarm optimization, imperialist competitive and teaching-learning algorithms. Sustain Cities Soc. 2018;43:339–49.10.1016/j.scs.2018.09.002Search in Google Scholar
[37] Maheri MR, Talezadeh M. An enhanced imperialist competitive algorithm for optimum design of skeletal structures. Swarm Evolut Comput. 2018;40:24–36.10.1016/j.swevo.2017.12.001Search in Google Scholar
[38] Yas MH, Kamarian S, Pourasghar A. Application of imperialist competitive algorithm and neural networks to optimise the volume fraction of three-parameter functionally graded beams. J Exp Theor Artif Intell. 2014;26(1):1–2.10.1080/0952813X.2013.782346Search in Google Scholar
[39] Cheng C, Song W, Zhao Q, Zhang H. Halloysite nanotubes in polymer science: Purification, characterization, modification and applications. Nanotechnol Rev. 2020;9(1):323–44.10.1515/ntrev-2020-0024Search in Google Scholar
[40] Li X, Yu K, Zhao R. Thermal post-buckling and vibration analysis of a symmetric sandwich beam with clamped and simply supported boundary conditions. Archive Appl Mech. 2018;88(4):543–61.10.1007/s00419-017-1326-xSearch in Google Scholar
[41] Emam S, Eltaher MA. Buckling and postbuckling of composite beams in hygrothermal environments. Compos Struct. 2016;152:665–75.10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.05.029Search in Google Scholar
[42] Reddy JN. Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells: theory and analysis. Boca Raton: CRC press; 2004.10.1201/b12409Search in Google Scholar
[43] Heslehurst R. Composite sandwich structure design requirements: Part 6-failure modes For honeycomb sandwich. Connection. 2016;41:16.Search in Google Scholar
[44] Vinson JR. Optimum design of composite honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to uniaxial compression. AIAA J. 1986;24(10):1690–6.10.2514/3.9502Search in Google Scholar
[45] Tsai SW, Wu EM. A general theory of strength for anisotropic materials. J Compos Mater. 1971;5(1):58–80.10.21236/ADA306350Search in Google Scholar
[46] Atashpaz-Gargari E, Lucas C. Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. 2007 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation. IEEE; 2007. p. 4661–710.1109/CEC.2007.4425083Search in Google Scholar
[47] Dafedar JB, Desai YM. Stability of composite and sandwich struts by mixed formulation. J Eng Mech. 2004;130(7):762–70.10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:7(762)Search in Google Scholar
[48] Zhen W, Wanji C. An assessment of several displacement-based theories for the vibration and stability analysis of laminated composite and sandwich beams. Compos Struct. 2008;84(4):337–49.10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.10.005Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Saeed Kamarian et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Theoretical and experimental investigation of MWCNT dispersion effect on the elastic modulus of flexible PDMS/MWCNT nanocomposites
- Mechanical, morphological, and fracture-deformation behavior of MWCNTs-reinforced (Al–Cu–Mg–T351) alloy cast nanocomposites fabricated by optimized mechanical milling and powder metallurgy techniques
- Flammability and physical stability of sugar palm crystalline nanocellulose reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/poly(lactic acid) blend bionanocomposites
- Glutathione-loaded non-ionic surfactant niosomes: A new approach to improve oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective efficacy of glutathione
- Relationship between mechano-bactericidal activity and nanoblades density on chemically strengthened glass
- In situ regulation of microstructure and microwave-absorbing properties of FeSiAl through HNO3 oxidation
- Research on a mechanical model of magnetorheological fluid different diameter particles
- Nanomechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of rubber–wood–plastic composites
- Investigative properties of CeO2 doped with niobium: A combined characterization and DFT studies
- Miniaturized peptidomimetics and nano-vesiculation in endothelin types through probable nano-disk formation and structure property relationships of endothelins’ fragments
- N/S co-doped CoSe/C nanocubes as anode materials for Li-ion batteries
- Synergistic effects of halloysite nanotubes with metal and phosphorus additives on the optimal design of eco-friendly sandwich panels with maximum flame resistance and minimum weight
- Octreotide-conjugated silver nanoparticles for active targeting of somatostatin receptors and their application in a nebulized rat model
- Controllable morphology of Bi2S3 nanostructures formed via hydrothermal vulcanization of Bi2O3 thin-film layer and their photoelectrocatalytic performances
- Development of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-loaded folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for prostate cancer treatment
- Enhancement of the mechanical properties of HDPE mineral nanocomposites by filler particles modulation of the matrix plastic/elastic behavior
- Effect of plasticizers on the properties of sugar palm nanocellulose/cinnamon essential oil reinforced starch bionanocomposite films
- Optimization of nano coating to reduce the thermal deformation of ball screws
- Preparation of efficient piezoelectric PVDF–HFP/Ni composite films by high electric field poling
- MHD dissipative Casson nanofluid liquid film flow due to an unsteady stretching sheet with radiation influence and slip velocity phenomenon
- Effects of nano-SiO2 modification on rubberised mortar and concrete with recycled coarse aggregates
- Mechanical and microscopic properties of fiber-reinforced coal gangue-based geopolymer concrete
- Effect of morphology and size on the thermodynamic stability of cerium oxide nanoparticles: Experiment and molecular dynamics calculation
- Mechanical performance of a CFRP composite reinforced via gelatin-CNTs: A study on fiber interfacial enhancement and matrix enhancement
- A practical review over surface modification, nanopatterns, emerging materials, drug delivery systems, and their biophysiochemical properties for dental implants: Recent progresses and advances
- HTR: An ultra-high speed algorithm for cage recognition of clathrate hydrates
- Effects of microalloying elements added by in situ synthesis on the microstructure of WCu composites
- A highly sensitive nanobiosensor based on aptamer-conjugated graphene-decorated rhodium nanoparticles for detection of HER2-positive circulating tumor cells
- Progressive collapse performance of shear strengthened RC frames by nano CFRP
- Core–shell heterostructured composites of carbon nanotubes and imine-linked hyperbranched polymers as metal-free Li-ion anodes
- A Galerkin strategy for tri-hybridized mixture in ethylene glycol comprising variable diffusion and thermal conductivity using non-Fourier’s theory
- Simple models for tensile modulus of shape memory polymer nanocomposites at ambient temperature
- Preparation and morphological studies of tin sulfide nanoparticles and use as efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of rhodamine B and phenol
- Polyethyleneimine-impregnated activated carbon nanofiber composited graphene-derived rice husk char for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture
- Electrospun nanofibers of Co3O4 nanocrystals encapsulated in cyclized-polyacrylonitrile for lithium storage
- Pitting corrosion induced on high-strength high carbon steel wire in high alkaline deaerated chloride electrolyte
- Formulation of polymeric nanoparticles loaded sorafenib; evaluation of cytotoxicity, molecular evaluation, and gene expression studies in lung and breast cancer cell lines
- Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders
- Influence of loading voltage, domain ratio, and additional load on the actuation of dielectric elastomer
- Thermally induced hex-graphene transitions in 2D carbon crystals
- The surface modification effect on the interfacial properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy: A molecular dynamics study
- Molecular dynamics study of deformation mechanism of interfacial microzone of Cu/Al2Cu/Al composites under tension
- Nanocolloid simulators of luminescent solar concentrator photovoltaic windows
- Compressive strength and anti-chloride ion penetration assessment of geopolymer mortar merging PVA fiber and nano-SiO2 using RBF–BP composite neural network
- Effect of 3-mercapto-1-propane sulfonate sulfonic acid and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the growth of cobalt pillar by electrodeposition
- Dynamics of convective slippery constraints on hybrid radiative Sutterby nanofluid flow by Galerkin finite element simulation
- Preparation of vanadium by the magnesiothermic self-propagating reduction and process control
- Microstructure-dependent photoelectrocatalytic activity of heterogeneous ZnO–ZnS nanosheets
- Cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of molybdenum and tungsten disulphide on human bronchial cells
- Improving recycled aggregate concrete by compression casting and nano-silica
- Chemically reactive Maxwell nanoliquid flow by a stretching surface in the frames of Newtonian heating, nonlinear convection and radiative flux: Nanopolymer flow processing simulation
- Nonlinear dynamic and crack behaviors of carbon nanotubes-reinforced composites with various geometries
- Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its therapeutic efficacy against colon cancer
- Synthesis and characterization of smart stimuli-responsive herbal drug-encapsulated nanoniosome particles for efficient treatment of breast cancer
- Homotopic simulation for heat transport phenomenon of the Burgers nanofluids flow over a stretching cylinder with thermal convective and zero mass flux conditions
- Incorporation of copper and strontium ions in TiO2 nanotubes via dopamine to enhance hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility
- Mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties of starch films incorporated with chitosan nanoparticles
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-strengthened recycled aggregate concrete
- Glucose-responsive nanogels efficiently maintain the stability and activity of therapeutic enzymes
- Tunning matrix rheology and mechanical performance of ultra-high performance concrete using cellulose nanofibers
- Flexible MXene/copper/cellulose nanofiber heat spreader films with enhanced thermal conductivity
- Promoted charge separation and specific surface area via interlacing of N-doped titanium dioxide nanotubes on carbon nitride nanosheets for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B
- Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita
- An implication of magnetic dipole in Carreau Yasuda liquid influenced by engine oil using ternary hybrid nanomaterial
- Robust synthesis of a composite phase of copper vanadium oxide with enhanced performance for durable aqueous Zn-ion batteries
- Tunning self-assembled phases of bovine serum albumin via hydrothermal process to synthesize novel functional hydrogel for skin protection against UVB
- A comparative experimental study on damping properties of epoxy nanocomposite beams reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets
- Lightweight and hydrophobic Ni/GO/PVA composite aerogels for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding
- Research on the auxetic behavior and mechanical properties of periodically rotating graphene nanostructures
- Repairing performances of novel cement mortar modified with graphene oxide and polyacrylate polymer
- Closed-loop recycling and fabrication of hydrophilic CNT films with high performance
- Design of thin-film configuration of SnO2–Ag2O composites for NO2 gas-sensing applications
- Study on stress distribution of SiC/Al composites based on microstructure models with microns and nanoparticles
- PVDF green nanofibers as potential carriers for improving self-healing and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy prepregs
- Osteogenesis capability of three-dimensionally printed poly(lactic acid)-halloysite nanotube scaffolds containing strontium ranelate
- Silver nanoparticles induce mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and late non-canonical autophagy in HT-29 colon cancer cells
- Preparation and bonding mechanisms of polymer/metal hybrid composite by nano molding technology
- Damage self-sensing and strain monitoring of glass-reinforced epoxy composite impregnated with graphene nanoplatelet and multiwalled carbon nanotubes
- Thermal analysis characterisation of solar-powered ship using Oldroyd hybrid nanofluids in parabolic trough solar collector: An optimal thermal application
- Pyrene-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for simultaneously detecting and separating Hg(ii) in aqueous media: A comprehensive comparison on interparticle and intraparticle excimers
- Fabrication of self-assembly CNT flexible film and its piezoresistive sensing behaviors
- Thermal valuation and entropy inspection of second-grade nanoscale fluid flow over a stretching surface by applying Koo–Kleinstreuer–Li relation
- Mechanical properties and microstructure of nano-SiO2 and basalt-fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete
- Characterization and tribology performance of polyaniline-coated nanodiamond lubricant additives
- Combined impact of Marangoni convection and thermophoretic particle deposition on chemically reactive transport of nanofluid flow over a stretching surface
- Spark plasma extrusion of binder free hydroxyapatite powder
- An investigation on thermo-mechanical performance of graphene-oxide-reinforced shape memory polymer
- Effect of nanoadditives on the novel leather fiber/recycled poly(ethylene-vinyl-acetate) polymer composites for multifunctional applications: Fabrication, characterizations, and multiobjective optimization using central composite design
- Design selection for a hemispherical dimple core sandwich panel using hybrid multi-criteria decision-making methods
- Improving tensile strength and impact toughness of plasticized poly(lactic acid) biocomposites by incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose
- Green synthesis of spinel copper ferrite (CuFe2O4) nanoparticles and their toxicity
- The effect of TaC and NbC hybrid and mono-nanoparticles on AA2024 nanocomposites: Microstructure, strengthening, and artificial aging
- Excited-state geometry relaxation of pyrene-modified cellulose nanocrystals under UV-light excitation for detecting Fe3+
- Effect of CNTs and MEA on the creep of face-slab concrete at an early age
- Effect of deformation conditions on compression phase transformation of AZ31
- Application of MXene as a new generation of highly conductive coating materials for electromembrane-surrounded solid-phase microextraction
- A comparative study of the elasto-plastic properties for ceramic nanocomposites filled by graphene or graphene oxide nanoplates
- Encapsulation strategies for improving the biological behavior of CdS@ZIF-8 nanocomposites
- Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs from pumpkin seeds’ extract and elucidation of its anticancer potential against breast cancer
- Preliminary trials of the gold nanoparticles conjugated chrysin: An assessment of anti-oxidant, anti-microbial, and in vitro cytotoxic activities of a nanoformulated flavonoid
- Effect of micron-scale pores increased by nano-SiO2 sol modification on the strength of cement mortar
- Fractional simulations for thermal flow of hybrid nanofluid with aluminum oxide and titanium oxide nanoparticles with water and blood base fluids
- The effect of graphene nano-powder on the viscosity of water: An experimental study and artificial neural network modeling
- Development of a novel heat- and shear-resistant nano-silica gelling agent
- Characterization, biocompatibility and in vivo of nominal MnO2-containing wollastonite glass-ceramic
- Entropy production simulation of second-grade magnetic nanomaterials flowing across an expanding surface with viscidness dissipative flux
- Enhancement in structural, morphological, and optical properties of copper oxide for optoelectronic device applications
- Aptamer-functionalized chitosan-coated gold nanoparticle complex as a suitable targeted drug carrier for improved breast cancer treatment
- Performance and overall evaluation of nano-alumina-modified asphalt mixture
- Analysis of pure nanofluid (GO/engine oil) and hybrid nanofluid (GO–Fe3O4/engine oil): Novel thermal and magnetic features
- Synthesis of Ag@AgCl modified anatase/rutile/brookite mixed phase TiO2 and their photocatalytic property
- Mechanisms and influential variables on the abrasion resistance hydraulic concrete
- Synergistic reinforcement mechanism of basalt fiber/cellulose nanocrystals/polypropylene composites
- Achieving excellent oxidation resistance and mechanical properties of TiB2–B4C/carbon aerogel composites by quick-gelation and mechanical mixing
- Microwave-assisted sol–gel template-free synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles obtained from South African coal fly ash
- Pulsed laser-assisted synthesis of nano nickel(ii) oxide-anchored graphitic carbon nitride: Characterizations and their potential antibacterial/anti-biofilm applications
- Effects of nano-ZrSi2 on thermal stability of phenolic resin and thermal reusability of quartz–phenolic composites
- Benzaldehyde derivatives on tin electroplating as corrosion resistance for fabricating copper circuit
- Mechanical and heat transfer properties of 4D-printed shape memory graphene oxide/epoxy acrylate composites
- Coupling the vanadium-induced amorphous/crystalline NiFe2O4 with phosphide heterojunction toward active oxygen evolution reaction catalysts
- Graphene-oxide-reinforced cement composites mechanical and microstructural characteristics at elevated temperatures
- Gray correlation analysis of factors influencing compressive strength and durability of nano-SiO2 and PVA fiber reinforced geopolymer mortar
- Preparation of layered gradient Cu–Cr–Ti alloy with excellent mechanical properties, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity
- Recovery of Cr from chrome-containing leather wastes to develop aluminum-based composite material along with Al2O3 ceramic particles: An ingenious approach
- Mechanisms of the improved stiffness of flexible polymers under impact loading
- Anticancer potential of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using a battery of in vitro tests
- Review Articles
- Proposed approaches for coronaviruses elimination from wastewater: Membrane techniques and nanotechnology solutions
- Application of Pickering emulsion in oil drilling and production
- The contribution of microfluidics to the fight against tuberculosis
- Graphene-based biosensors for disease theranostics: Development, applications, and recent advancements
- Synthesis and encapsulation of iron oxide nanorods for application in magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal therapy
- Contemporary nano-architectured drugs and leads for ανβ3 integrin-based chemotherapy: Rationale and retrospect
- State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
- Insights on magnetic spinel ferrites for targeted drug delivery and hyperthermia applications
- A review on heterogeneous oxidation of acetaminophen based on micro and nanoparticles catalyzed by different activators
- Early diagnosis of lung cancer using magnetic nanoparticles-integrated systems
- Advances in ZnO: Manipulation of defects for enhancing their technological potentials
- Efficacious nanomedicine track toward combating COVID-19
- A review of the design, processes, and properties of Mg-based composites
- Green synthesis of nanoparticles for varied applications: Green renewable resources and energy-efficient synthetic routes
- Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based polymer composites: Fundamentals and applications
- Recent progress and challenges in plasmonic nanomaterials
- Apoptotic cell-derived micro/nanosized extracellular vesicles in tissue regeneration
- Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review
- Framework materials for supercapacitors
- An overview on the reproductive toxicity of graphene derivatives: Highlighting the importance
- Antibacterial nanomaterials: Upcoming hope to overcome antibiotic resistance crisis
- Research progress of carbon materials in the field of three-dimensional printing polymer nanocomposites
- A review of atomic layer deposition modelling and simulation methodologies: Density functional theory and molecular dynamics
- Recent advances in the preparation of PVDF-based piezoelectric materials
- Recent developments in tensile properties of friction welding of carbon fiber-reinforced composite: A review
- Comprehensive review of the properties of fly ash-based geopolymer with additive of nano-SiO2
- Perspectives in biopolymer/graphene-based composite application: Advances, challenges, and recommendations
- Graphene-based nanocomposite using new modeling molecular dynamic simulations for proposed neutralizing mechanism and real-time sensing of COVID-19
- Nanotechnology application on bamboo materials: A review
- Recent developments and future perspectives of biorenewable nanocomposites for advanced applications
- Nanostructured lipid carrier system: A compendium of their formulation development approaches, optimization strategies by quality by design, and recent applications in drug delivery
- 3D printing customized design of human bone tissue implant and its application
- Design, preparation, and functionalization of nanobiomaterials for enhanced efficacy in current and future biomedical applications
- A brief review of nanoparticles-doped PEDOT:PSS nanocomposite for OLED and OPV
- Nanotechnology interventions as a putative tool for the treatment of dental afflictions
- Recent advancements in metal–organic frameworks integrating quantum dots (QDs@MOF) and their potential applications
- A focused review of short electrospun nanofiber preparation techniques for composite reinforcement
- Microstructural characteristics and nano-modification of interfacial transition zone in concrete: A review
- Latest developments in the upconversion nanotechnology for the rapid detection of food safety: A review
- Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks
- Molecular dynamics application of cocrystal energetic materials: A review
- Synthesis and application of nanometer hydroxyapatite in biomedicine
- Cutting-edge development in waste-recycled nanomaterials for energy storage and conversion applications
- Biological applications of ternary quantum dots: A review
- Nanotherapeutics for hydrogen sulfide-involved treatment: An emerging approach for cancer therapy
- Application of antibacterial nanoparticles in orthodontic materials
- Effect of natural-based biological hydrogels combined with growth factors on skin wound healing
- Nanozymes – A route to overcome microbial resistance: A viewpoint
- Recent developments and applications of smart nanoparticles in biomedicine
- Contemporary review on carbon nanotube (CNT) composites and their impact on multifarious applications
- Interfacial interactions and reinforcing mechanisms of cellulose and chitin nanomaterials and starch derivatives for cement and concrete strength and durability enhancement: A review
- Diamond-like carbon films for tribological modification of rubber
- Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) modified cement-based materials: A systematic review
- Recent research progress and advanced applications of silica/polymer nanocomposites
- Modeling of supramolecular biopolymers: Leading the in silico revolution of tissue engineering and nanomedicine
- Recent advances in perovskites-based optoelectronics
- Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: New production methods and applications
- A comprehensive review of nanofluids with fractional derivatives: Modeling and application
- Electrospinning of marine polysaccharides: Processing and chemical aspects, challenges, and future prospects
- Electrohydrodynamic printing for demanding devices: A review of processing and applications
- Rapid Communications
- Structural material with designed thermal twist for a simple actuation
- Recent advances in photothermal materials for solar-driven crude oil adsorption

