Abstract
The importance and aim of this experimental study is that raw artificial anterior cruciate ligament samples were produced with various 3-D braiding constructions with various technical yarns using the 3-D braiding method. Later, it is aimed to determine the chemical bond changes between raw samples with ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization and bio-chemical finishing samples by applying padding process and EtO sterilization processes for all samples with 3-D braiding structures, due to the cross-linking of biocompatible chitosan (CHI) with biological cross-linker glutaraldehyde (GA). The importance of this experimental study is that it is the first experimental chemical analysis in this field in the world scientific study. Padding and EtO sterilization processes were applied on all samples and compared to various technical yarns with 3-D braiding structures thanks to biocompatible CHI. Chemical analysis was interpreted for all samples. It was determined that the applied temperature, concentration, pH, yarn types, characteristic bonds in the chemical structure of the technical yarns, applied bio-chemical finishing process and EtO sterilization had effect on the formation, shifting and breaking of chemical bonds. It was determined that the yarn number, braiding geometry, braiding angle (°) and braid construction had no effect on the formation or shifting of chemical bonds. New bonds were formed thanks to CHI and GA due to their extremely reactive between 5 and 5.5 pH. They reacted quickly with Schiff base bond in all samples. CHI was ionized in all samples. It was determined that new bonds were formed in UHMWPE, PPD-T and HT PET structures. The most common bond formations were HT PET > PPD-T > UHMWPE. The reasons for these chemical structure changes in all samples depended on their chemical structures, bond types, molecular weights, reactivities, ease and speed of diffusions, crystallinities of technical yarns and all chemicals used. In order to increase the formation of new chemical bonds the pH should be between 5 and 5.5. GA concentration should be a minimum of 25% or higher. The dissolution time of CHI should be minimum 3 h or more. The dissolution process temperature of CHI should be minimum of 70°C or higher. The absorption, adsorption and chelation properties of CHI on all samples will also be evident successfully as in this experimental chemical study.
1 Introduction
Around 100,000–250,000 anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries occur each year. In the USA, the cost of surgery for female athletes involved in athletics reaches US$650 million each year [1]. Ligaments are solid and fibrous band structures that cover the joint and are parallel to each other [2]. They have fibroblast cells and extracellular matrix, which form the most common collagen I and collagen III types in the structure of the ligaments [2,3]. Ligaments vary in length from 25 to 35 mm. The cross-sections have a triangular cross-section from the ends to the midpoint and have a diameter ranging from 4 to 10 mm [3,4]. In young people aged 16–26 years, the percent elongation at break is 44.3 ± 8.5 (%) and the maximum breaking force is 1,730 ± 660 N. In the elderly aged 48–85 years, the percent elongation at break is 30 ± 10 (%) and the maximum breaking force is 734 ± 266 N [5]. The design criteria of artificial ACL ligaments are it should be biocompatible, high tensile strength, high radial strength, high dimensional stability, easy to process, similar to the natural ACL ligament tension–strain graph, lumen diameter between 9 and 11 mm. They should also have low hysteresis and dense structures [5].
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is a semi-crystalline polymer composed of large number of transvinylene monomers. It also has a very high molecular weight of 3.1 million g/mol, very high orientation, very high crystallinity and polymerization degree of 110,000. In a biomedical study, the cross-linking density of UHMWPE increases depending on the large number of vinylidene monomers. As the radiation dose increases, the number and cross-linking of transvinylene monomers increases [6].
Para aramid (PPD-T) is a lyotropic liquid crystalline organic polymer. It has unique structure with very high crystallinity connected to each other in the para position with 85% amide bonds between the two aromatic benzene rings. It also has low density, high specific modulus of elasticity, high specific strength and high thermal resistance. Surface modifications such as chemical grafting, plasma treatment, coating method and surface construction of nanostructures can be applied. Its reactivity and surface roughness increase due to these surface modifications [7]. It has been determined that –OH, C═O and –NH2 groups are rapidly hydrolyzed by increasing the reactivity in acid or alkaline environment in some chemical study on PPD-T. The interfacial bond strength between the fiber and matrix elements increases significantly due to the diffusion of polar groups. It improved its UV resistance, surface activity, thermal and mechanical properties by reducing its number of –NH2 groups because of its chemical treatment with hyperbranched polysiloxane [7].
Polyester (PET) is a highly linear macromolecule with high crystalline synthetic chemical structure containing more than 85% ester diol and benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid (terephthalic acid) or dimethyl terephthalate. It contains methylene, carbonyl and ester groups in its chemical structure. It is hydrophobic due to its high crystallinity [8]. PET has been widely used in biomedical applications. It is successfully coated with biological chemicals such as collagen or fibronectin to improve cell–polymer interaction [8,9].
Chitosan (CHI, poly-β-(1 → 4)-2-amino-2-deoxy-d-glucose) is a nitrogenous (–NH2 based) polysaccharide. It is produced by N-deacetylation process in large quantities, thanks to chitin. It is the second most abundant natural biopolymer in the world. It is produced by passing chitin, which is extracted from shellfish, through various chemical processes (by N-deacetylation). Many properties of these biopolymers are similar to each other. It is a potential alternative biopolymer to other natural and synthetic biopolymers for environmental applications due to its ease of processing, non-toxicity, natural antibacterial and biodegradable properties. It enables to form various new compounds with various organic and inorganic compounds by chemical processes due to its highly reactive groups such as –OH and –NH2. It has a very high, tight and effective chelation feature with organic and inorganic compounds. Films, membranes, beads and composite structures can be also created [10]. It has poor adsorption due to its non-porous structure and low surface area. Particularly, chemicals with large molecular sizes cannot easily diffuse into it, which has a reticulated structure. It is easily hydrolyzed in an acidic environment and has a high swelling tendency. It has low adsorption capacity below pH 5. Due to this disadvantage, various physical or chemical surface modifications are applied. The cross-linking method increases its chemical resistance in both acidic and alkaline environments. Cross-linked CHI has higher mechanical properties, dimensional stability, hydrophilicity and larger pore size. The longer the polymer chain the greater the surface area and the number of pores. This reduces its crystallinity and increases the adsorption of its functional groups. Solvent or solvent-free solution concentrations affect its bead adsorption behavior [11].
Glutaraldehyde (GA) is widely applied as a cross-linking agent due to its low cost, high reactivity and high solubility in water solution. Schiff bases, which are formed as a result of the reaction between GA and the free –NH2 groups of lysine or hydroxylysine, are formed easily and quickly at the beginning of cross-linking. In the next stage these Schiff bases are stabilized by further reactions leading to the formation of different products. Biomechanical tests showed also that GA bio-treated collagen is suitable for in vivo studies and can be used for tissue engineering applications. GA provides homogeneous distribution on forms such as film, microcapsule, granule and fiber [12]. In an experimental study aldehyde, mono, dihydrate, cyclic cis and trans isomer structures were observed in free and equal amounts in coated CHI with GA due to the presence of 25 and 50% aqueous solution GA [12]. However, its structures in different forms were not much affected by the concentration of GA but temperature is a very important factor and increases the amount of aldehyde. According to pH dependence the cross-linking of proteins in GA was high due to a decrease in the reactivity of protonated –NH2 groups in CHI to react with C═O groups. Reaction did not occur practically in a very high acidic environment. Cross-linking was just observed at pH > pI due to the –NH2 groups of the deprotonated proteins in CHI. Degree of protonation of –NH2 groups of CHI, which had a polysaccharide, also determined the water solubility [12].
Its pH values ranged from 3.5 to 4.5 depending on its molecular mass, degree of deacetylation and concentration of the solution for its pH value in acetic acid solution. Moreover, cross-linking reaction proceeded at a high speed [12]. An imine group (–RC═N) from Schiff base bond occurred by the condensation reaction between primary –NH2 from CHI and an active aldehyde from salicylaldehyde as their fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) results [13]. CHI and GA were cross-linked at a rate of 80.8% in another experimental study. High antibacterial activity was detected. The degree of cross-linking was important as the degree of deacetylation on its features [14]. Aldehyde groups in GA solutions diffused easily and reacted with the –NH2 groups in the wet CHI microspheres. –NH2 groups in CHI can be formed by cross-linking mechanism with GA, which had aldehyde groups. –N–H and O–H bending vibrations shifted from 3,439 to 3,417 cm−1, –CH3 symmetric stretch shifted from 2,925 to 2,937 cm−1, C═O bending vibration shifted from 1,666 to 1,645 cm−1, C–N bending vibration shifted from 1,438 to 1,406 cm−1, C–OH bending vibration shifted from 1,073 to 1,037 cm−1, –CH3 bending vibration was not at 1,363 cm−1 and C–O–C bending vibration is not observed at 1,155 cm−1 but amide(ii) bonding was observed at 1,559 cm−1 due to the detailed FT-IR test results. The chemical bonding mechanism included –NH2 groups in CHI and abundant amount of aldehyde groups in GA as a cross-linking, and were experimentally investigated for a long time. pH, ionic strength, temperature, concentration of CHI and degree of cross-linking of CHI were some of the important chemical parameters on its chemical gelation rate with coated GA [14].
The applications of braiding structures are generally used in the biomedical field such as surgical yarns and artificial veins. It can be also used as electromagnetic shielding and cables in industrial field because of its high mechanical strength and flexibility [15].
Ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization is the most widely used sterilization method in biomaterials due to its high penetration capacity and high efficiency at low temperatures. The relative humidity of EtO can vary between 40 and 80%, its gas concentration is between 450 and 1,200 mg/L, its temperature is between 40 and 65°C and its exposure time varies from few hours to few days [16,17]. The chemical structures of all technical yarns and their main chemicals as a single image are presented in Figure 1 [10,18–21].
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
T1 and T2 samples were produced from UHMWPE technical yarn with 445 dtex yarn number, 45° braid angle, 1 center and 16 braid yarns. The only difference between T1 and T2 samples was the braiding construction. T1 was produced with diamond and T2 was produced with double braided in braiding constructions. T3 and T4 samples were produced from PPD-T technical yarn with 1670 dtex yarn number, 45° braid angle, 1 center and 16 braid yarns. The only difference between T3 and T4 samples was the braiding construction. T3 was produced with diamond and T4 was produced with double braided in braiding constructions. T5 and T6 samples were produced from HT PET technical yarn with 1670 dtex yarn number, 45° braid angle, 1 center and 16 braid yarns. The only difference between T5 and T6 samples was the braiding construction. T5 was produced with diamond and T6 was produced with double braided in braiding constructions. EtO sterilization was applied on all samples. The meanings of the samples with the R and T symbols on the FT-IR charts are as follows: R1 was the raw sample form of T1. F1 was the form of T1 in which bio-chemical finishing process has been applied. R2 was the raw sample form of T2. F2 was the form of T2 with bio-chemical finishing process applied. R3 was the raw sample form of T3. F3 was the form of T3 with bio-chemical finishing process applied. R4 was the raw sample form of T4. F4 was the form of T4 with bio-chemical finishing process applied. R5 was the raw sample form of T5. F5 was the form of T5 in which bio-chemical finishing process has been applied. R6 was the raw sample form of T6. F6 was the form of T6 with bio-chemical finishing process applied. UHMWPE and PPD-T technical yarns were purchased from Durak Tekstil A.Ş in Bursa, Turkey. HT PET technical yarn was purchased from KordSA Technical Textile A.Ş in Kocaeli, Turkey. The bio-chemical finishing process was applied based on the following bio-finishing recipe and the liquid (flotte) ratio was 1:10, CHI (85%) with powder form at 2%, N-acetyl d-glucosamine (2%) with liquid form at 7%, GA (100%) with liquid form at 25% and acetic acid (80%) with liquid form at 1%. CHI (85%) and N-acetyl d-glucosamine (2%) were purchased from ADAGA A.Ş in Antalya, Turkey. GA (100%) was purchased from Kimbiotek Kimyevi Mad. San. and Tic. A.Ş in İstanbul, Turkey. Acetic acid (80%) was purchased from Bursa Teknik Kimya A.Ş in Bursa, Turkey.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Braiding production process
In the braiding production preparation, some technical yarns such as UHMWPE, PPD-T and HT PET bobbins in the creel were transferred to the braid bobbins by passing the control of the yarn tension meter. PPD-T, UHMWPE and HT PET technical yarns were also used as core and braid yarns with different yarn counts (dtex) in its manufacturing process. Braiding production preparation process and braiding production process were actualized in Bursa Bağcı Elyaf and Apparel Materials Construction Industry Trade Limited Company in Bursa. They are shown in Figure 2.
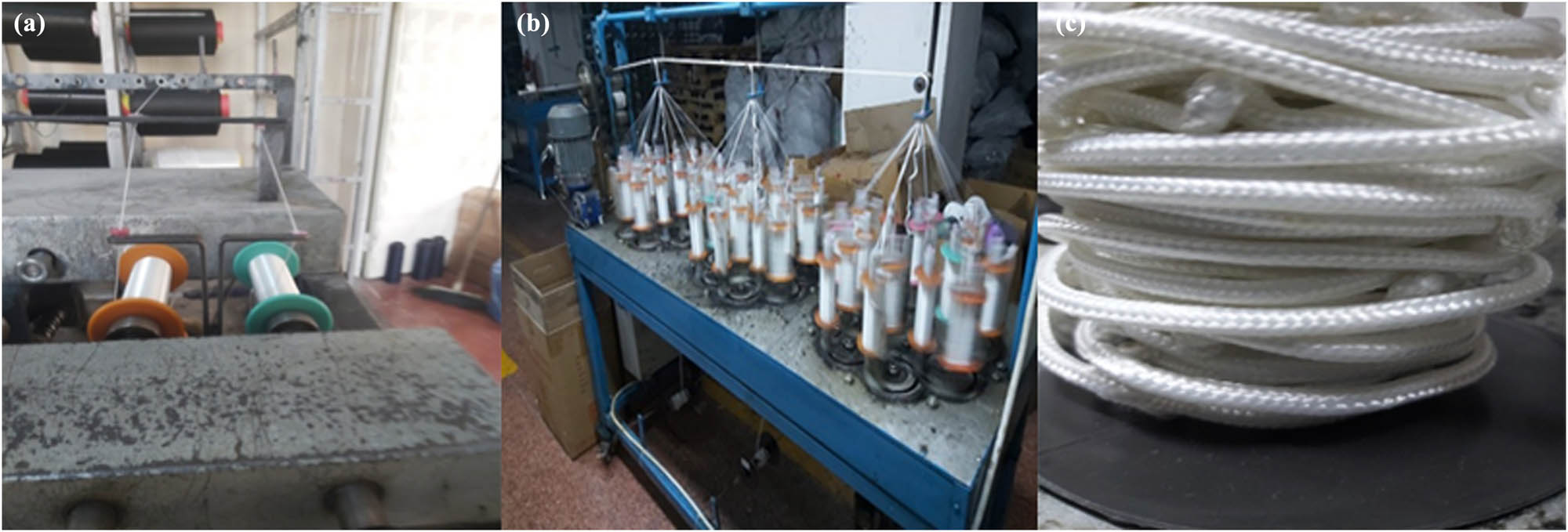

(a) Yarn preparation for braiding, (b) braiding production process, and (c) 3-D braiding yarn product.
2.2.2 Bio-chemical finishing process
The pH values of the solution were measured by P-510 portable pH meter of Peak Instruments INC. Solution ambient temperature was also measured with the helping of a mercury thermometer (maximum operating temperature was 115°C). All in one method was applied for the preparation of bio-chemical solution. All biological chemicals that have chemicals in liquid forms were prepared in accordance with the bath (flotte) recipe with the help of beakers. Weight measurements were taken with the help of a weight device for chemicals in powder forms and then added to the solution with the help of beakers where the liquid volume was 1 L. All chemicals were prepared in accordance with the bio-chemical finishing process recipe. Time (t) at 3 h, temperature (T ort) at 70°C and pH at 5–5.5 were applied as process parameters of the bio-chemical finishing chemical recipe. Bio-chemical finishing process was carried out in Bursa Uludağ University in Bursa. Color change state of the bio-chemical solution was observed from light yellow to dark brown in the solution depending on time. Impregnation of the braiding samples with a continuous method in a foulard made of high density polyethylene material, which was a chemically inert and light polymeric material, was applied as post-process. It was applied as impregnation process in ten passages for 30 min for bio-chemical bonding of the braiding textile structures and the biological chemical solution.
2.2.3 After operations are PBS bio-chemical (in vitro condition) process and EtO sterilization process
PBS bio-chemical was used to provide pH 7.2 for the in vitro condition. Twenty tablets were used for a 2 L solution volume with one tablet equivalent to 100 mL of water. This post-treatment process was applied on all samples. In totally, EtO sterilization process was applied separately on all samples for six raw samples and six bio-chemical finishing samples. It was also subjected to thermal drying and fixation in an oven with temperature as 115°C for 10 minutes at Bursa Uludağ University. As a last operation EtO sterilization was applied with 1 atm as pressure, 50°C as temperature for 16 hours on all samples at the Çekirge State Hospital in Bursa.
2.2.4 FT-IR chemical analysis
In order to determine the comparative chemical analyses of all samples, FT-IR chemical analysis was applied to all samples. The ambient conditions of the test were 20 ± 2℃, rH 65%, under 1 atm pressure after conditioning for 24 h. FT-IR chemical analysis was performed for all samples on a Thermo Scientific Nicolet IS50 FT-IR branded device in Bursa Technical University Fiber and Polymer Engineering-2 laboratory.
3 Results and discussion
The results of FT-IR chemical graphics were presented in Figures 3–5. Results of FT-IR chemical graphics were determined for all bio-composite materials with applied EtO process. They had as raw materials from R1 to R6 and had as bio-chemical finishing processes from F1 to F6. FT-IR chemical analysis had y-axis was transmittance from 0 to 100% and x-axis was wavenumbers from 500 to 4,000 cm−1 was used for all bio-composite materials (artificial ACL ligaments).
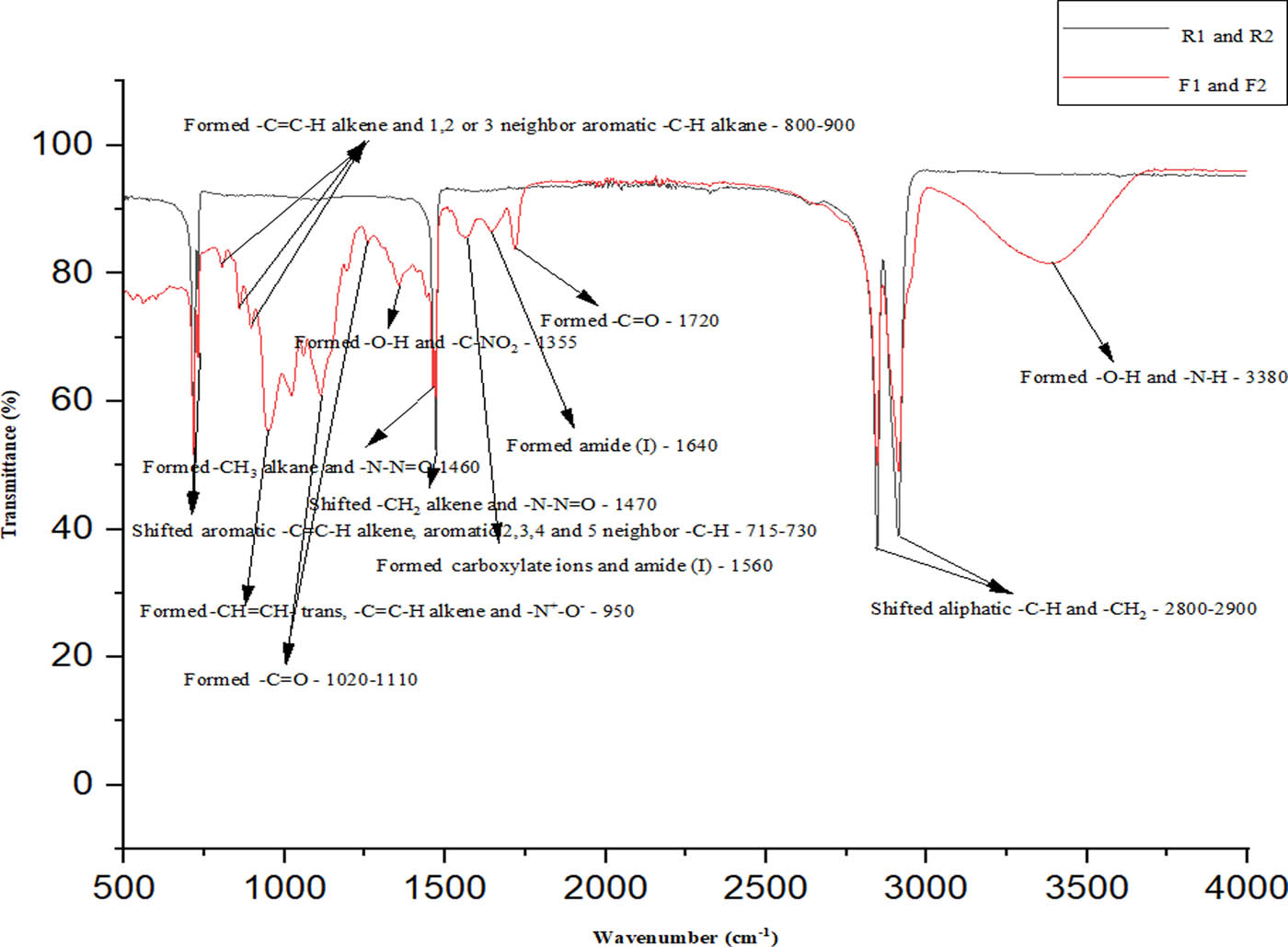
(R): raw biomaterial and (F): bio-chemical finishing biomaterial of artificial ACL ligaments for T1 and T2.
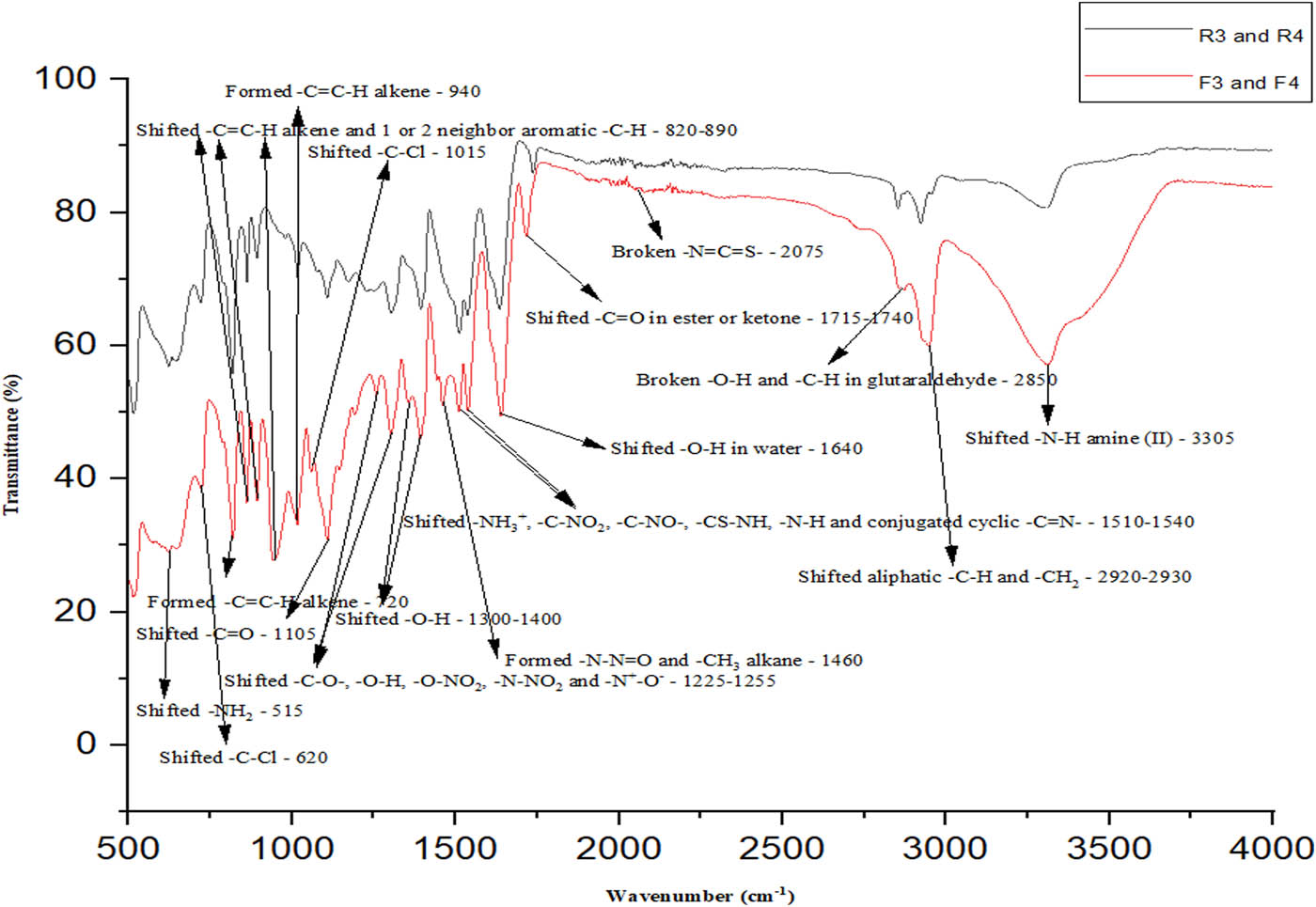
(R): raw biomaterial and (F): bio-chemical finishing biomaterial of artificial ACL ligaments for T3 and T4.
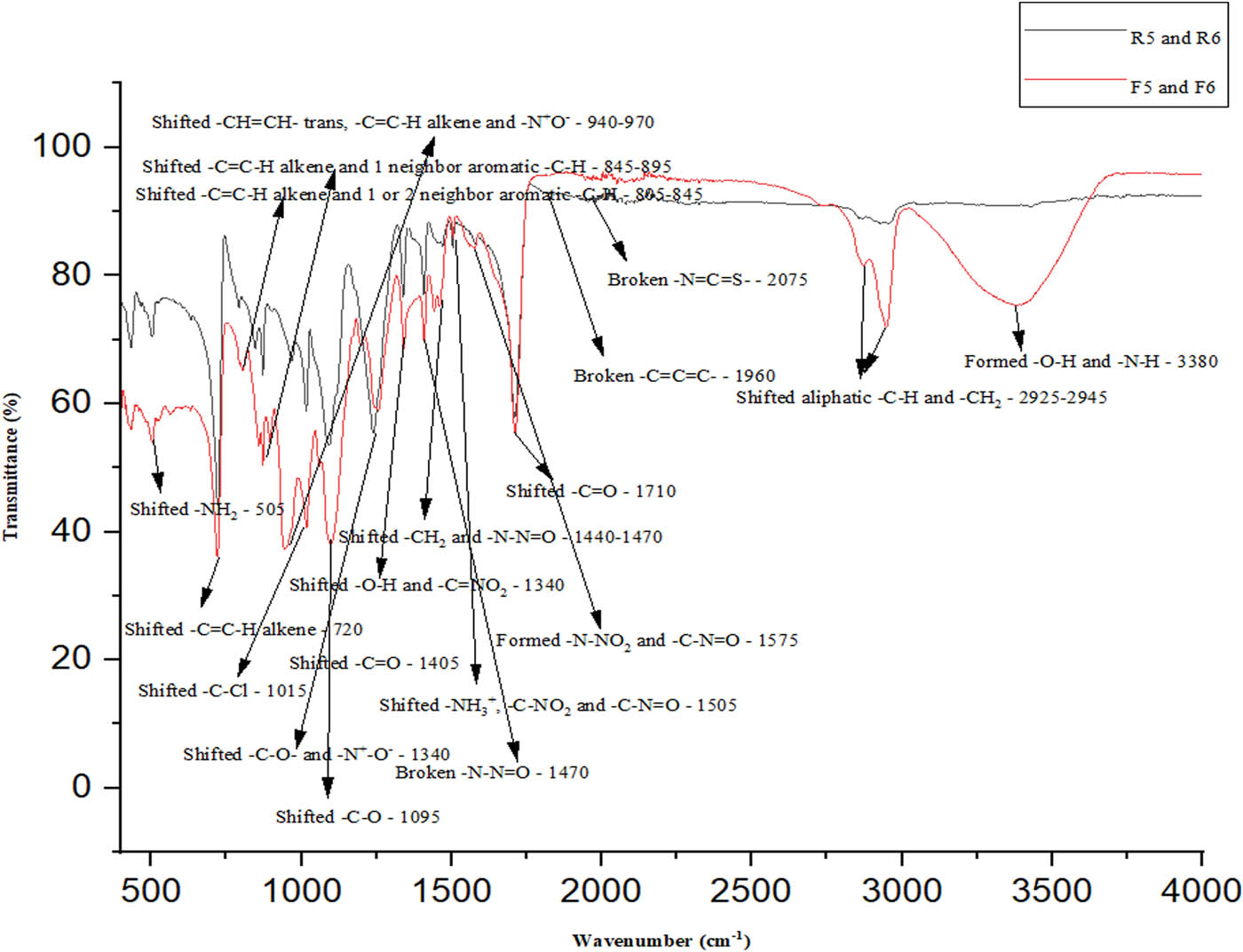
(R): raw biomaterial and (F): bio-chemical finishing biomaterial of artificial ACL ligaments for T5 and T6.
3.1 Results of FT-IR chemical analyses
Chemical analysis results of UHMWPE structured T1 and T2 samples were presented in Table 1. Chemical analysis results of PPD-T structured T3 and T4 samples were presented in Table 2. Chemical analysis results of HT PET structured T5 and T6 samples were presented in Table 3. They were also presented as supporting information.
Chemical analysis results of UHMWPE structured T1 and T2 samples
| Bond status | Bond types | Wavelength (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Formed | –O–H and –N–H | 3,380 |
| Shifted | Aliphatic –C–H and –CH2 | Between 2,800 and 2,900 |
| Formed | –C═O | 1,720 |
| Formed | Amide(i) | 1,640 |
| Formed | Carboxylate ions and amide(i) | 1,560 |
| Shifted | –CH2 alkene and –N–N═O | 1,470 |
| Formed | –CH3 alkane and –N–N═O | 1,460 |
| Formed | –O–H and –C–NO2 | 1,355 |
| Formed | –C═O | Between 1,020 and 1,110 |
| Formed | –CH═CH– trans, –C═C–H alkene and –N+–O– | 950 |
| Formed | –C═C–H alkene, 1, 2 or 3 neighbor aromatic –C–H alkane | Between 800 and 900 |
| Shifted | Aromatic –C═C–H alkene and aromatic 2,3,4 and 5 neighbor –C–H | 730 |
| Formed |
|
560 |
The general summary for T1 and T2 was that reactive and aliphatic –OH and –NH2 groups in CHI formed many new, complex and aromatic bonds with the aliphatic CH2 groups of UHMWPE due to the aliphatic C═O groups of GA. N+–O– in CHI was ionization. The aliphatic structure of UHMWPE was partially converted to aromatic ring structure. New, complex and aromatic C═C–H alkene bonds and many adjacent CH3 alkane bonds ranging from 1 to 5 were formed. No bond break was detected.
Chemical analysis results of PPD-T structured T3 and T4 samples
| Bond status | Bond types | Wavelength (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Shifted | –N–H amine(ii) | 3,305 |
| Shifted | Aliphatic C–H and C–H2 | Between 2,920 and 2,930 |
| Broken | –O–H and C–H in GA | 2,850 |
| Broken | –N═C═S | 2,075 |
| Shifted | –C═O in ester or ketone | Between 1,715 and 1,740 |
| Shifted | –O–H in water | 1,640 |
| Shifted | –
|
Between 1,510 and 1,540 |
| Formed | –N–N═O and –CH3 alkane | 1,460 |
| Shifted | –O–H | Between 1,300 and 1,400 |
| Shifted | –C–O, –O–H, –O–NO2, –N–NO2 and –N+–O– | Between 1,225 and 1,255 |
| Shifted | –C–O | 1,105 |
| Shifted | –C–Cl | 1,015 |
| Formed | –C═C–H alkene | 940 |
| Shifted | –C═C–H alkene and 1 or 2 neighbor aromatic –C–H | Between 820 and 890 |
| Formed | –C═C–H alkene | 720 |
| Shifted | –C–Cl | 620 |
| Shifted | –NH2 | 515 |
The general summary for T3 and T4 was that the aliphatic CH2, N–H, C═O and aromatic benzene ring groups of PPD-T and the aliphatic O–H and NH2 groups of CHI reacted with each other to form new and complex bonds such as N–N═O, CH3 alkane and C═C–H. N+–O– in CHI was ionization. PPD-T’s and CHI’s bonds such as
Chemical analysis results of HT PET structured T5 and T6 samples
| Bond status | Bond types | Wavelength (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Formed | –O–H and –N–H | 3,380 |
| Shifted | Aliphatic –C–H and –CH2 | Between 2,925 and 2,945 |
| Broken | –N═C═S | 2,075 |
| Broken | –C═C═C– | 1,960 |
| Shifted | –C═O | 1,710 |
| Formed | –N–NO2 and –C–N═O | 1,575 |
| Shifted | –
|
1,505 |
| Broken | –N–N═O | 1,470 |
| Shifted | –CH2 and –N–N═O | Between 1,440 and 1,470 |
| Shifted | –C═O | 1,405 |
| Shifted | –O–H and –C–NO2 | 1,340 |
| Shifted | –C–O and –N+–O− | Between 1,240 and 1,255 |
| Shifted | –C–O | 1,095 |
| Shifted | –C–Cl | 1,015 |
| Shifted | –CH═CH– trans, –C═C–H alkene and –N+–O– | Between 940 and 970 |
| Shifted | –C═C–H alkene and 1 neighbor aromatic –C–H | Between 870 and 895 |
| Shifted | –C═C–H alkene, 2 neighbor aromatic –C–H and 1 neighbor aromatic –C–H | Between 805 and 845 |
| Shifted | –C═C–H alkene | 720 |
| Shifted | –NH2 | 505 |
The general summary for T5 and T6 was that the aliphatic CH2, C═O and aromatic benzene ring groups of HT PET and the aliphatic O–H and NH2 groups of CHI reacted with each other to form new and complex O–H, N–H–N–NO2, C–N═, C═C–H alkene and 1-neighbor aromatic C–H bonds. CHI’s N+–O– was ionization. Aliphatic C–H, CH2, C═O, –
4 Conclusions
General chemical analysis was interpreted for all samples as follows.
It was determined that the applied temperature, concentration, pH, yarn types, characteristic bonds in the chemical structure of the yarns, applied bio-chemical finishing process and EtO sterilization had effect on the formation or shifting of chemical bonds.
It was determined that the yarn number, braiding geometry, braiding angle (°) and braid construction had no effect on the formation or shifting of chemical bonds.
New bonds were formed thanks to CHI and GA due to their extremely reactive between 5 and 5.5 pH. They reacted quickly with Schiff base bond in all samples. CHI was ionized in all samples.
In addition, the surface area and porosity of CHI cross-linked with GA increased while decreasing its crystallinity. This situation facilitated and accelerated the adsorption in all samples. In this way, CHI’s excellent chelation property was ensured.
–OH and –NH2 groups of CHI provided a fast and easy diffusion in all processed samples. Moreover, swelling was observed in the structures of all processed samples. Mechanical properties and dimensional stability for GA cross-linked CHI were higher than those with non-cross-linked CHI in all samples. Its crystallinity decreased, but its adsorption increased because as the DD of CHI increased, the surface area and the number of pores increased. Aliphatic structures turned into aromatic and complex structures.
The aliphatic structure of UHMWPE was partially converted to aromatic ring structure. The aromatic structure of PPD-T was preserved. The aromatic structure of HT PET was not preserved and was partially converted to aliphatic structure. No bond breaks had been detected in the UHMWPE structure. It was determined that new bonds were formed in UHMWPE, PPD-T and HT PET structures. The most common bond formations were HT PET > PPD-T > UHMWPE.
In order to increase the formation of new chemical bonds in all samples the following should be actualized:
The pH should be 5–5.5. GA concentration should be a minimum of 25% or higher. The dissolution time of CHI should be a minimum of 3 h or more. The process temperature should be a minimum of 70°C or higher. In this way, the molecular size of CHI will be reduced so that it will facilitate easier and faster diffusion and adsorption. The chelation property of CHI on all samples will be also evident successfully.
In the future studies about various artificial ACL ligament experimental studies to be actualized, the chemical analyses of CHI cross-linked with GA on technical yarns used in this experimental study can be based. In addition, in future experimental studies on artificial ACL ligament it is thought that more comprehensive in vitro or in vivo experimental studies will be actualized by using different biocompatible biopolymers by changing and comparing various process parameters such as pH, temperature, time, concentration, textile form, production method, construction, yarn type, yarn count and bio-finishing process.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Mr. İnal Kaan Duygun, assistant of Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering at T.C Bursa Technical University for assistance in using the FT-IR device. All raw samples were collected from Bursa Bağcı Elyaf and Apparel Materials Construction Industry Trade Limited Company in Bursa with the help of Mr. Fedahi KILIÇAY who is the head of manufacturing department.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the T.C Bursa Uludağ University registered under the number: T.C B.U.Ü BAP OUAP (MH) 2020/9.
-
Author contributions: Ömer Fırat Turşucular – conceptualization, manuscript writing, data acquisition, technical data analysis and manuscript spell check. Yusuf Ulcay – conceptualization and manuscript spell check.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
-
Ethical approval: This experimental study was not related to human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and supplementary information files).
References
[1] Timothy EH, Myer GD. The mechanistic connection between the trunk, knee and anterior cruciate ligament injury. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2011;39(4):161–6. 10.1097/JES.0b013e3182297439.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Prado M, Nazario S, Bergamima JSSP, Nasrala MLS, Neto EN, Felippe LA, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament: anatomy and biomechanics. J Health Sci. 2019;21(2):166–9. 10.17921/2447-8938.2019v21n2p166-169.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Marieswaran M, Jain I, Garg B, Sharma V, Kalyanasundaram DA. Review on biomechanics of anterior cruciate ligament and materials for reconstruction. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2018;1:4657824. 10.1155/2018/4657824.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Boden BP, Dean GS, Feagin JA, Garnett WE. Mechanisms of anterior cruciate ligament injury. Orthopedics. 2000;23(6):573–8. 10.3928/0147-7447-20000601-15.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Gloy RYS, Loehrer M, Lang B, Rongen L, Gries T, Jockenhoevel S. Tubular woven narrow fabrics for replacement of cruciate ligaments. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(9):1950–6. 10.1007/s10439-013-0806-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Hussain M, Naqvi RA, Abbas N, Khan SM, Nawaz S, Hussain A, et al. Ultra-high-molecular-weight-polyethylene (UHMWPE) as a promising polymer material for biomedical applications: a concise review. Polymers. 2020;12(2):32, 1–28. 10.3390/polym12020323.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Zhang B, Jia L, Tian M, Ning N, Zhang L, Wang W. Surface and interface modification of aramid fiber and its reinforcement for polymer composites: a review. Eur Polym J. 2021;147(1):110352, 1–11. 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2021.110352.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Ketema A, Worku A. Review on intermolecular forces between dyes used for polyester dyeing and polyester fiber. J Chem. 2020;1:6628404, 1–7. 10.1155/2020/6628404.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sun L, Huang L, Wang X, Hu H, Guo J, Zhu R, et al. Synthesis and structural characterization of sequential structure and crystallization properties for hydrophilic modified polyester. Polymers. 2020;12(8):1733, 1–18. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/160943.10.3390/polym12081733Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Kyzas GZ, Bikiaris DN. Recent modifications of chitosan for adsorption applications: a critical and systematic review. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(1):312–37. 10.3390/md13010312.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Vakili M, Mojiri A, Zwain HM, Yuan J, Giwa AS, Wang W, et al. Effect of beading parameters on cross-linked chitosan adsorptive properties. Reactive Funct Polym. 2019;144:104354, 1–9. 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2019.104354.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Kildeeva NR, Perminov PA, Vladimirov LV, Novikov VV, Mikhailov SN. On the Mechanism of the reaction of glutaraldehyde with chitosan. Rus J Bioorg Chem. 2009;35(3):360–9. 10.1134/S106816200903011X.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Chan MY, Koay SC, Husseinsyah S, Sam ST. Cross-linked chitosan/corn cob biocomposite films with salicylaldehyde on tensile, thermal, and biodegradable properties: a comparative study. Adv Polym Technol. 2018;37(4):21784. 10.1002/adv.21784. (1 of 11)10.1002/adv.21784© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Li B, Shan CL, Zhou Q, Fang Y, Wang YL, Xu F, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan–glutaraldehyde. Mar Drugs. 2013;11:1534–52. 10.3390/md11051534.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Bilisik K. Three-dimensional braiding for composites: a review. Tex Res J. 2013;83(13):1414–36. 10.1177/0040517512450766.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Williams FD, Cahn RW, Bever MB. Concise Encyclopedia of Medical & Dental Materials. Oxford UK: Pergamon Press; 1990. Corpus ID: 136849050.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Morais JM, Papadimitrakopoulos F, Burgess DJ. Biomaterials/tissue interactions: possible solutions to overcome foreign body response. AAPS J. 2010;12(2):188–96. 10.1208/s12248-010-9175-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Sherazi TA, Rehman T, Naqvi SAR, Shaikh AJ, Shahzad SA, Abbas G, et al. Surface functionalization of solid state ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene through chemical grafting. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;359(1):593–601. 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.10.080.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Dong A, Wang YJ, Gao Y, Gao T, Gao G. Chemical insights into antibacterial N-halamines. Chem Rev. 2017;117(10):1021. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00687.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Hu Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Qian J, Xing X, Wang X. Synthesis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) based on glycolysis of waste PET fiber. J Macromol Sci Part A. 2020;57(6):430–8. 10.1080/10601325.2019.1709498.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Price SA, McDorman K, Chan C, Rojko J, Raymond JT, Brown D, et al. Haschek and Rousseaux’s handbook of toxicologic pathology. 4th edn. Glutaraldehyde (GLUT) is one key fixative since it provides improved molecular cross-linking and the other fixative usually is methanol-free formaldehyde. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Academic Press; Vol. 1; 2022; p. 335–93. 10.1177/10915818221099126.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Characteristics, source, and health risk assessment of aerosol polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the rural and urban regions of western Saudi Arabia
- Regular Articles
- A network-based correlation research between element electronegativity and node importance
- Pomegranate attenuates kidney injury in cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by suppressing oxidative stress
- Ab initio study of fundamental properties of XInO3 (X = K, Rb, Cs) perovskites
- Responses of feldspathic sandstone and sand-reconstituted soil C and N to freeze–thaw cycles
- Robust fractional control based on high gain observers design (RNFC) for a Spirulina maxima culture interfaced with an advanced oxidation process
- Study on arsenic speciation and redistribution mechanism in Lonicera japonica plants via synchrotron techniques
- Optimization of machining Nilo 36 superalloy parameters in turning operation
- Vacuum impregnation pre-treatment: A novel method for incorporating mono- and divalent cations into potato strips to reduce the acrylamide formation in French fries
- Characterization of effective constituents in Acanthopanax senticosus fruit for blood deficiency syndrome based on the chinmedomics strategy
- Comparative analysis of the metabolites in Pinellia ternata from two producing regions using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry
- The assessment of environmental parameter along the desalination plants in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Effects of harpin and carbendazim on antioxidant accumulation in young jujube leaves
- The effects of in ovo injected with sodium borate on hatching performance and small intestine morphology in broiler chicks
- Optimization of cutting forces and surface roughness via ANOVA and grey relational analysis in machining of In718
- Essential oils of Origanum compactum Benth: Chemical characterization, in vitro, in silico, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities
- Translocation of tungsten(vi) oxide/gadolinium(iii) fluoride in tellurite glasses towards improvement of gamma-ray attenuation features in high-density glass shields
- Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, and gamma ray attenuation competencies of some TeO2–WO3–GdF3 glasses: Tailoring WO3–GdF3 substitution toward optimum behavioral state range
- Comparison between the CIDR or sponge with hormone injection to induce estrus synchronization for twining and sex preselection in Naimi sheep
- Exergetic performance analyses of three different cogeneration plants
- Psoralea corylifolia (babchi) seeds enhance proliferation of normal human cultured melanocytes: GC–MS profiling and biological investigation
- A novel electrochemical micro-titration method for quantitative evaluation of the DPPH free radical scavenging capacity of caffeic acid
- Comparative study between supported bimetallic catalysts for nitrate remediation in water
- Persicaline, an alkaloid from Salvadora persica, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in MCF-7 cells
- Determination of nicotine content in locally produced smokeless tobacco (Shammah) samples from Jazan region of Saudi Arabia using a convenient HPLC-MS/MS method
- Changes in oxidative stress markers in pediatric burn injury over a 1-week period
- Integrated geophysical techniques applied for petroleum basins structural characterization in the central part of the Western Desert, Egypt
- The impact of chemical modifications on gamma-ray attenuation properties of some WO3-reinforced tellurite glasses
- Microwave and Cs+-assisted chemo selective reaction protocol for synthesizing 2-styryl quinoline biorelevant molecules
- Structural, physical, and radiation absorption properties of a significant nuclear power plant component: A comparison between REX-734 and 316L SS austenitic stainless steels
- Effect of Moringa oleifera on serum YKL-40 level: In vivo rat periodontitis model
- Investigating the impact of CO2 emissions on the COVID-19 pandemic by generalized linear mixed model approach with inverse Gaussian and gamma distributions
- Influence of WO3 content on gamma rays attenuation characteristics of phosphate glasses at low energy range
- Study on CO2 absorption performance of ternary DES formed based on DEA as promoting factor
- Performance analyses of detonation engine cogeneration cycles
- Sterols from Centaurea pumilio L. with cell proliferative activity: In vitro and in silico studies
- Untargeted metabolomics revealing changes in aroma substances in flue-cured tobacco
- Effect of pumpkin enriched with calcium lactate on iron status in an animal model of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Energy consumption, mechanical and metallographic properties of cryogenically treated tool steels
- Optimization of ultra-high pressure-assisted extraction of total phenols from Eucommia ulmoides leaves by response surface methodology
- Harpin enhances antioxidant nutrient accumulation and decreases enzymatic browning in stored soybean sprouts
- Physicochemical and biological properties of carvacrol
- Radix puerariae in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: A network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation
- Anti-Alzheimer, antioxidants, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase effects of Taverniera glabra mediated ZnO and Fe2O3 nanoparticles in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
- Experimental study on photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of ZnS/CdS-TiO2 nanotube array thin films
- Epoxy-reinforced heavy metal oxides for gamma ray shielding purposes
- Black mulberry (Morus nigra L.) fruits: As a medicinal plant rich in human health-promoting compounds
- Promising antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of essential oils extracted from fruits of Juniperus thurifera: In vitro and in silico investigations
- Chloramine-T-induced oxidation of Rizatriptan Benzoate: An integral chemical and spectroscopic study of products, mechanisms and kinetics
- Study on antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of chemically profiled essential oils extracted from Juniperus phoenicea (L.) by use of in vitro and in silico approaches
- Screening and characterization of fungal taxol-producing endophytic fungi for evaluation of antimicrobial and anticancer activities
- Mineral composition, principal polyphenolic components, and evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant properties of Cytisus villosus Pourr leaf extracts
- In vitro antiproliferative efficacy of Annona muricata seed and fruit extracts on several cancer cell lines
- An experimental study for chemical characterization of artificial anterior cruciate ligament with coated chitosan as biomaterial
- Prevalence of residual risks of the transfusion-transmitted infections in Riyadh hospitals: A two-year retrospective study
- Computational and experimental investigation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of Nicotiana tabacum extracts
- Reinforcement of cementitious mortars with hemp fibers and shives
- X-ray shielding properties of bismuth-borate glass doped with rare earth ions
- Green supported silver nanoparticles over modified reduced graphene oxide: Investigation of its antioxidant and anti-ovarian cancer effects
- Orthogonal synthesis of a versatile building block for dual functionalization of targeting vectors
- Thymbra spicata leaf extract driven biogenic synthesis of Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its bio-application in the treatment of different types of leukemia
- The role of Ag2O incorporation in nuclear radiation shielding behaviors of the Li2O–Pb3O4–SiO2 glass system: A multi-step characterization study
- A stimuli-responsive in situ spray hydrogel co-loaded with naringenin and gentamicin for chronic wounds
- Assessment of the impact of γ-irradiation on the piperine content and microbial quality of black pepper
- Antioxidant, sensory, and functional properties of low-alcoholic IPA beer with Pinus sylvestris L. shoots addition fermented using unconventional yeast
- Screening and optimization of extracellular pectinase produced by Bacillus thuringiensis SH7
- Determination of polyphenols in Chinese jujube using ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
- Synergistic effects of harpin and NaCl in determining soybean sprout quality under non-sterile conditions
- Field evaluation of different eco-friendly alternative control methods against Panonychus citri [Acari: Tetranychidae] spider mite and its predators in citrus orchards
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biologically synthesized zero valent iron nanoparticles
- NaCl regulates goldfish growth and survival at three food supply levels under hypoxia
- An exploration of the physical, optical, mechanical, and radiation shielding properties of PbO–MgO–ZnO–B2O3 glasses
- A novel statistical modeling of air pollution and the COVID-19 pandemic mortality data by Poisson, geometric, and negative binomial regression models with fixed and random effects
- Treatment activity of the injectable hydrogels loaded with dexamethasone In(iii) complex on glioma by inhibiting the VEGF signaling pathway
- An alternative approach for the excess lifetime cancer risk and prediction of radiological parameters
- Panax ginseng leaf aqueous extract mediated green synthesis of AgNPs under ultrasound condition and investigation of its anti-lung adenocarcinoma effects
- Study of hydrolysis and production of instant ginger (Zingiber officinale) tea
- Novel green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Salvia rosmarinus extract for treatment of human lung cancer
- Evaluation of second trimester plasma lipoxin A4, VEGFR-1, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Antidiabetic, antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities of ortho- and para-substituted Schiff bases derived from metformin hydrochloride: Validation by molecular docking and in silico ADME studies
- Antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiglaucoma, and anticholinergic effects of Tayfi grape (Vitis vinifera): A phytochemical screening by LC-MS/MS analysis
- Identification of genetic polymorphisms in the stearoyl CoA desaturase gene and its association with milk quality traits in Najdi sheep
- Cold-acclimation effect on cadmium absorption and biosynthesis of polyphenolics, and free proline and photosynthetic pigments in Spirogyra aequinoctialis
- Analysis of secondary metabolites in Xinjiang Morus nigra leaves using different extraction methods with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS/MS technology
- Nanoarchitectonics and performance evaluation of a Fe3O4-stabilized Pickering emulsion-type differential pressure plugging agent
- Investigating pyrolysis characteristics of Shengdong coal through Py-GC/MS
- Extraction, phytochemical characterization, and antifungal activity of Salvia rosmarinus extract
- Introducing a novel and natural antibiotic for the treatment of oral pathogens: Abelmoschus esculentus green-formulated silver nanoparticles
- Optimization of gallic acid-enriched ultrasonic-assisted extraction from mango peels
- Effect of gamma rays irradiation in the structure, optical, and electrical properties of samarium doped bismuth titanate ceramics
- Combinatory in silico investigation for potential inhibitors from Curcuma sahuynhensis Škorničk. & N.S. Lý volatile phytoconstituents against influenza A hemagglutinin, SARS-CoV-2 main protease, and Omicron-variant spike protein
- Physical, mechanical, and gamma ray shielding properties of the Bi2O3–BaO–B2O3–ZnO–As2O3–MgO–Na2O glass system
- Twofold interpenetrated 3D Cd(ii) complex: Crystal structure and luminescent property
- Study on the microstructure and soil quality variation of composite soil with soft rock and sand
- Ancient spring waters still emerging and accessible in the Roman Forum area: Chemical–physical and microbiological characterization
- Extraction and characterization of type I collagen from scales of Mexican Biajaiba fish
- Finding small molecular compounds to decrease trimethylamine oxide levels in atherosclerosis by virtual screening
- Prefatory in silico studies and in vitro insecticidal effect of Nigella sativa (L.) essential oil and its active compound (carvacrol) against the Callosobruchus maculatus adults (Fab), a major pest of chickpea
- Polymerized methyl imidazole silver bromide (CH3C6H5AgBr)6: Synthesis, crystal structures, and catalytic activity
- Using calcined waste fish bones as a green solid catalyst for biodiesel production from date seed oil
- Influence of the addition of WO3 on TeO2–Na2O glass systems in view of the feature of mechanical, optical, and photon attenuation
- Naringin ameliorates 5-fluorouracil elicited neurotoxicity by curtailing oxidative stress and iNOS/NF-ĸB/caspase-3 pathway
- GC-MS profile of extracts of an endophytic fungus Alternaria and evaluation of its anticancer and antibacterial potentialities
- Green synthesis, chemical characterization, and antioxidant and anti-colorectal cancer effects of vanadium nanoparticles
- Determination of caffeine content in coffee drinks prepared in some coffee shops in the local market in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia
- A new 3D supramolecular Cu(ii) framework: Crystal structure and photocatalytic characteristics
- Bordeaux mixture accelerates ripening, delays senescence, and promotes metabolite accumulation in jujube fruit
- Important application value of injectable hydrogels loaded with omeprazole Schiff base complex in the treatment of pancreatitis
- Color tunable benzothiadiazole-based small molecules for lightening applications
- Investigation of structural, dielectric, impedance, and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-modified barium titanate composites for biomedical applications
- Metal gel particles loaded with epidermal cell growth factor promote skin wound repair mechanism by regulating miRNA
- In vitro exploration of Hypsizygus ulmarius (Bull.) mushroom fruiting bodies: Potential antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory agent
- Alteration in the molecular structure of the adenine base exposed to gamma irradiation: An ESR study
- Comprehensive study of optical, thermal, and gamma-ray shielding properties of Bi2O3–ZnO–PbO–B2O3 glasses
- Lewis acids as co-catalysts in Pd-based catalyzed systems of the octene-1 hydroethoxycarbonylation reaction
- Synthesis, Hirshfeld surface analysis, thermal, and selective α-glucosidase inhibitory studies of Schiff base transition metal complexes
- Protective properties of AgNPs green-synthesized by Abelmoschus esculentus on retinal damage on the virtue of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in diabetic rat
- Effects of green decorated AgNPs on lignin-modified magnetic nanoparticles mediated by Cydonia on cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis
- Treatment of gastric cancer by green mediated silver nanoparticles using Pistacia atlantica bark aqueous extract
- Preparation of newly developed porcelain ceramics containing WO3 nanoparticles for radiation shielding applications
- Utilization of computational methods for the identification of new natural inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase in inflammation therapy
- Some anticancer agents as effective glutathione S-transferase (GST) inhibitors
- Clay-based bricks’ rich illite mineral for gamma-ray shielding applications: An experimental evaluation of the effect of pressure rates on gamma-ray attenuation parameters
- Stability kinetics of orevactaene pigments produced by Epicoccum nigrum in solid-state fermentation
- Treatment of denture stomatitis using iron nanoparticles green-synthesized by Silybum marianum extract
- Characterization and antioxidant potential of white mustard (Brassica hirta) leaf extract and stabilization of sunflower oil
- Characteristics of Langmuir monomolecular monolayers formed by the novel oil blends
- Strategies for optimizing the single GdSrFeO4 phase synthesis
- Oleic acid and linoleic acid nanosomes boost immunity and provoke cell death via the upregulation of beta-defensin-4 at genetic and epigenetic levels
- Unraveling the therapeutic potential of Bombax ceiba roots: A comprehensive study of chemical composition, heavy metal content, antibacterial activity, and in silico analysis
- Green synthesis of AgNPs using plant extract and investigation of its anti-human colorectal cancer application
- The adsorption of naproxen on adsorbents obtained from pepper stalk extract by green synthesis
- Treatment of gastric cancer by silver nanoparticles encapsulated by chitosan polymers mediated by Pistacia atlantica extract under ultrasound condition
- In vitro protective and anti-inflammatory effects of Capparis spinosa and its flavonoids profile
- Wear and corrosion behavior of TiC and WC coatings deposited on high-speed steels by electro-spark deposition
- Therapeutic effects of green-formulated gold nanoparticles by Origanum majorana on spinal cord injury in rats
- Melanin antibacterial activity of two new strains, SN1 and SN2, of Exophiala phaeomuriformis against five human pathogens
- Evaluation of the analgesic and anesthetic properties of silver nanoparticles supported over biodegradable acacia gum-modified magnetic nanoparticles
- Review Articles
- Role and mechanism of fruit waste polyphenols in diabetes management
- A comprehensive review of non-alkaloidal metabolites from the subfamily Amaryllidoideae (Amaryllidaceae)
- Discovery of the chemical constituents, structural characteristics, and pharmacological functions of Chinese caterpillar fungus
- Eco-friendly green approach of nickel oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications
- Advances in the pharmaceutical research of curcumin for oral administration
- Rapid Communication
- Determination of the contents of bioactive compounds in St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum): Comparison of commercial and wild samples
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: The protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α”
- Topical Issue on Phytochemicals, biological and toxicological analysis of aromatic medicinal plants
- Anti-plasmodial potential of selected medicinal plants and a compound Atropine isolated from Eucalyptus obliqua
- Anthocyanin extract from black rice attenuates chronic inflammation in DSS-induced colitis mouse model by modulating the gut microbiota
- Evaluation of antibiofilm and cytotoxicity effect of Rumex vesicarius methanol extract
- Chemical compositions of Litsea umbellata and inhibition activities
- Green synthesis, characterization of silver nanoparticles using Rhynchosia capitata leaf extract and their biological activities
- GC-MS analysis and antibacterial activities of some plants belonging to the genus Euphorbia on selected bacterial isolates
- The abrogative effect of propolis on acrylamide-induced toxicity in male albino rats: Histological study
- A phytoconstituent 6-aminoflavone ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress mediated synapse and memory dysfunction via p-Akt/NF-kB pathway in albino mice
- Anti-diabetic potentials of Sorbaria tomentosa Lindl. Rehder: Phytochemistry (GC-MS analysis), α-amylase, α-glucosidase inhibitory, in vivo hypoglycemic, and biochemical analysis
- Assessment of cytotoxic and apoptotic activities of the Cassia angustifolia aqueous extract against SW480 colon cancer
- Biochemical analysis, antioxidant, and antibacterial efficacy of the bee propolis extract (Hymenoptera: Apis mellifera) against Staphylococcus aureus-induced infection in BALB/c mice: In vitro and in vivo study
- Assessment of essential elements and heavy metals in Saudi Arabian rice samples underwent various processing methods
- Two new compounds from leaves of Capparis dongvanensis (Sy, B. H. Quang & D. V. Hai) and inhibition activities
- Hydroxyquinoline sulfanilamide ameliorates STZ-induced hyperglycemia-mediated amyleoid beta burden and memory impairment in adult mice
- An automated reading of semi-quantitative hemagglutination results in microplates: Micro-assay for plant lectins
- Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry assessment of essential and toxic trace elements in traditional spices consumed by the population of the Middle Eastern region in their recipes
- Phytochemical analysis and anticancer activity of the Pithecellobium dulce seed extract in colorectal cancer cells
- Impact of climatic disturbances on the chemical compositions and metabolites of Salvia officinalis
- Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant and antifungal activities of essential oils of Urginea maritima and Allium sativum
- Phytochemical analysis and antifungal efficiency of Origanum majorana extracts against some phytopathogenic fungi causing tomato damping-off diseases
- Special Issue on 4th IC3PE
- Graphene quantum dots: A comprehensive overview
- Studies on the intercalation of calcium–aluminium layered double hydroxide-MCPA and its controlled release mechanism as a potential green herbicide
- Synergetic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis by zinc ferrite-anchored graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet for the removal of ciprofloxacin under visible light irradiation
- Exploring anticancer activity of the Indonesian guava leaf (Psidium guajava L.) fraction on various human cancer cell lines in an in vitro cell-based approach
- The comparison of gold extraction methods from the rock using thiourea and thiosulfate
- Special Issue on Marine environmental sciences and significance of the multidisciplinary approaches
- Sorption of alkylphenols and estrogens on microplastics in marine conditions
- Cytotoxic ketosteroids from the Red Sea soft coral Dendronephthya sp.
- Antibacterial and biofilm prevention metabolites from Acanthophora spicifera
- Characteristics, source, and health risk assessment of aerosol polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the rural and urban regions of western Saudi Arabia
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part II
- Green synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antibacterial activities of cobalt nanoparticles produced by marine fungal species Periconia prolifica
- Combustion-mediated sol–gel preparation of cobalt-doped ZnO nanohybrids for the degradation of acid red and antibacterial performance
- Perinatal supplementation with selenium nanoparticles modified with ascorbic acid improves hepatotoxicity in rat gestational diabetes
- Evaluation and chemical characterization of bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytic fungi associated with the ethnomedicinal plant Bergenia ciliata
- Enhancing photovoltaic efficiency with SQI-Br and SQI-I sensitizers: A comparative analysis
- Nanostructured p-PbS/p-CuO sulfide/oxide bilayer heterojunction as a promising photoelectrode for hydrogen gas generation
Articles in the same Issue
- Characteristics, source, and health risk assessment of aerosol polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the rural and urban regions of western Saudi Arabia
- Regular Articles
- A network-based correlation research between element electronegativity and node importance
- Pomegranate attenuates kidney injury in cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by suppressing oxidative stress
- Ab initio study of fundamental properties of XInO3 (X = K, Rb, Cs) perovskites
- Responses of feldspathic sandstone and sand-reconstituted soil C and N to freeze–thaw cycles
- Robust fractional control based on high gain observers design (RNFC) for a Spirulina maxima culture interfaced with an advanced oxidation process
- Study on arsenic speciation and redistribution mechanism in Lonicera japonica plants via synchrotron techniques
- Optimization of machining Nilo 36 superalloy parameters in turning operation
- Vacuum impregnation pre-treatment: A novel method for incorporating mono- and divalent cations into potato strips to reduce the acrylamide formation in French fries
- Characterization of effective constituents in Acanthopanax senticosus fruit for blood deficiency syndrome based on the chinmedomics strategy
- Comparative analysis of the metabolites in Pinellia ternata from two producing regions using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–tandem mass spectrometry
- The assessment of environmental parameter along the desalination plants in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Effects of harpin and carbendazim on antioxidant accumulation in young jujube leaves
- The effects of in ovo injected with sodium borate on hatching performance and small intestine morphology in broiler chicks
- Optimization of cutting forces and surface roughness via ANOVA and grey relational analysis in machining of In718
- Essential oils of Origanum compactum Benth: Chemical characterization, in vitro, in silico, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities
- Translocation of tungsten(vi) oxide/gadolinium(iii) fluoride in tellurite glasses towards improvement of gamma-ray attenuation features in high-density glass shields
- Mechanical properties, elastic moduli, and gamma ray attenuation competencies of some TeO2–WO3–GdF3 glasses: Tailoring WO3–GdF3 substitution toward optimum behavioral state range
- Comparison between the CIDR or sponge with hormone injection to induce estrus synchronization for twining and sex preselection in Naimi sheep
- Exergetic performance analyses of three different cogeneration plants
- Psoralea corylifolia (babchi) seeds enhance proliferation of normal human cultured melanocytes: GC–MS profiling and biological investigation
- A novel electrochemical micro-titration method for quantitative evaluation of the DPPH free radical scavenging capacity of caffeic acid
- Comparative study between supported bimetallic catalysts for nitrate remediation in water
- Persicaline, an alkaloid from Salvadora persica, inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest in MCF-7 cells
- Determination of nicotine content in locally produced smokeless tobacco (Shammah) samples from Jazan region of Saudi Arabia using a convenient HPLC-MS/MS method
- Changes in oxidative stress markers in pediatric burn injury over a 1-week period
- Integrated geophysical techniques applied for petroleum basins structural characterization in the central part of the Western Desert, Egypt
- The impact of chemical modifications on gamma-ray attenuation properties of some WO3-reinforced tellurite glasses
- Microwave and Cs+-assisted chemo selective reaction protocol for synthesizing 2-styryl quinoline biorelevant molecules
- Structural, physical, and radiation absorption properties of a significant nuclear power plant component: A comparison between REX-734 and 316L SS austenitic stainless steels
- Effect of Moringa oleifera on serum YKL-40 level: In vivo rat periodontitis model
- Investigating the impact of CO2 emissions on the COVID-19 pandemic by generalized linear mixed model approach with inverse Gaussian and gamma distributions
- Influence of WO3 content on gamma rays attenuation characteristics of phosphate glasses at low energy range
- Study on CO2 absorption performance of ternary DES formed based on DEA as promoting factor
- Performance analyses of detonation engine cogeneration cycles
- Sterols from Centaurea pumilio L. with cell proliferative activity: In vitro and in silico studies
- Untargeted metabolomics revealing changes in aroma substances in flue-cured tobacco
- Effect of pumpkin enriched with calcium lactate on iron status in an animal model of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Energy consumption, mechanical and metallographic properties of cryogenically treated tool steels
- Optimization of ultra-high pressure-assisted extraction of total phenols from Eucommia ulmoides leaves by response surface methodology
- Harpin enhances antioxidant nutrient accumulation and decreases enzymatic browning in stored soybean sprouts
- Physicochemical and biological properties of carvacrol
- Radix puerariae in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy: A network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation
- Anti-Alzheimer, antioxidants, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase effects of Taverniera glabra mediated ZnO and Fe2O3 nanoparticles in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
- Experimental study on photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of ZnS/CdS-TiO2 nanotube array thin films
- Epoxy-reinforced heavy metal oxides for gamma ray shielding purposes
- Black mulberry (Morus nigra L.) fruits: As a medicinal plant rich in human health-promoting compounds
- Promising antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of essential oils extracted from fruits of Juniperus thurifera: In vitro and in silico investigations
- Chloramine-T-induced oxidation of Rizatriptan Benzoate: An integral chemical and spectroscopic study of products, mechanisms and kinetics
- Study on antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of chemically profiled essential oils extracted from Juniperus phoenicea (L.) by use of in vitro and in silico approaches
- Screening and characterization of fungal taxol-producing endophytic fungi for evaluation of antimicrobial and anticancer activities
- Mineral composition, principal polyphenolic components, and evaluation of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antioxidant properties of Cytisus villosus Pourr leaf extracts
- In vitro antiproliferative efficacy of Annona muricata seed and fruit extracts on several cancer cell lines
- An experimental study for chemical characterization of artificial anterior cruciate ligament with coated chitosan as biomaterial
- Prevalence of residual risks of the transfusion-transmitted infections in Riyadh hospitals: A two-year retrospective study
- Computational and experimental investigation of antibacterial and antifungal properties of Nicotiana tabacum extracts
- Reinforcement of cementitious mortars with hemp fibers and shives
- X-ray shielding properties of bismuth-borate glass doped with rare earth ions
- Green supported silver nanoparticles over modified reduced graphene oxide: Investigation of its antioxidant and anti-ovarian cancer effects
- Orthogonal synthesis of a versatile building block for dual functionalization of targeting vectors
- Thymbra spicata leaf extract driven biogenic synthesis of Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its bio-application in the treatment of different types of leukemia
- The role of Ag2O incorporation in nuclear radiation shielding behaviors of the Li2O–Pb3O4–SiO2 glass system: A multi-step characterization study
- A stimuli-responsive in situ spray hydrogel co-loaded with naringenin and gentamicin for chronic wounds
- Assessment of the impact of γ-irradiation on the piperine content and microbial quality of black pepper
- Antioxidant, sensory, and functional properties of low-alcoholic IPA beer with Pinus sylvestris L. shoots addition fermented using unconventional yeast
- Screening and optimization of extracellular pectinase produced by Bacillus thuringiensis SH7
- Determination of polyphenols in Chinese jujube using ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
- Synergistic effects of harpin and NaCl in determining soybean sprout quality under non-sterile conditions
- Field evaluation of different eco-friendly alternative control methods against Panonychus citri [Acari: Tetranychidae] spider mite and its predators in citrus orchards
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biologically synthesized zero valent iron nanoparticles
- NaCl regulates goldfish growth and survival at three food supply levels under hypoxia
- An exploration of the physical, optical, mechanical, and radiation shielding properties of PbO–MgO–ZnO–B2O3 glasses
- A novel statistical modeling of air pollution and the COVID-19 pandemic mortality data by Poisson, geometric, and negative binomial regression models with fixed and random effects
- Treatment activity of the injectable hydrogels loaded with dexamethasone In(iii) complex on glioma by inhibiting the VEGF signaling pathway
- An alternative approach for the excess lifetime cancer risk and prediction of radiological parameters
- Panax ginseng leaf aqueous extract mediated green synthesis of AgNPs under ultrasound condition and investigation of its anti-lung adenocarcinoma effects
- Study of hydrolysis and production of instant ginger (Zingiber officinale) tea
- Novel green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Salvia rosmarinus extract for treatment of human lung cancer
- Evaluation of second trimester plasma lipoxin A4, VEGFR-1, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Antidiabetic, antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities of ortho- and para-substituted Schiff bases derived from metformin hydrochloride: Validation by molecular docking and in silico ADME studies
- Antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiglaucoma, and anticholinergic effects of Tayfi grape (Vitis vinifera): A phytochemical screening by LC-MS/MS analysis
- Identification of genetic polymorphisms in the stearoyl CoA desaturase gene and its association with milk quality traits in Najdi sheep
- Cold-acclimation effect on cadmium absorption and biosynthesis of polyphenolics, and free proline and photosynthetic pigments in Spirogyra aequinoctialis
- Analysis of secondary metabolites in Xinjiang Morus nigra leaves using different extraction methods with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS/MS technology
- Nanoarchitectonics and performance evaluation of a Fe3O4-stabilized Pickering emulsion-type differential pressure plugging agent
- Investigating pyrolysis characteristics of Shengdong coal through Py-GC/MS
- Extraction, phytochemical characterization, and antifungal activity of Salvia rosmarinus extract
- Introducing a novel and natural antibiotic for the treatment of oral pathogens: Abelmoschus esculentus green-formulated silver nanoparticles
- Optimization of gallic acid-enriched ultrasonic-assisted extraction from mango peels
- Effect of gamma rays irradiation in the structure, optical, and electrical properties of samarium doped bismuth titanate ceramics
- Combinatory in silico investigation for potential inhibitors from Curcuma sahuynhensis Škorničk. & N.S. Lý volatile phytoconstituents against influenza A hemagglutinin, SARS-CoV-2 main protease, and Omicron-variant spike protein
- Physical, mechanical, and gamma ray shielding properties of the Bi2O3–BaO–B2O3–ZnO–As2O3–MgO–Na2O glass system
- Twofold interpenetrated 3D Cd(ii) complex: Crystal structure and luminescent property
- Study on the microstructure and soil quality variation of composite soil with soft rock and sand
- Ancient spring waters still emerging and accessible in the Roman Forum area: Chemical–physical and microbiological characterization
- Extraction and characterization of type I collagen from scales of Mexican Biajaiba fish
- Finding small molecular compounds to decrease trimethylamine oxide levels in atherosclerosis by virtual screening
- Prefatory in silico studies and in vitro insecticidal effect of Nigella sativa (L.) essential oil and its active compound (carvacrol) against the Callosobruchus maculatus adults (Fab), a major pest of chickpea
- Polymerized methyl imidazole silver bromide (CH3C6H5AgBr)6: Synthesis, crystal structures, and catalytic activity
- Using calcined waste fish bones as a green solid catalyst for biodiesel production from date seed oil
- Influence of the addition of WO3 on TeO2–Na2O glass systems in view of the feature of mechanical, optical, and photon attenuation
- Naringin ameliorates 5-fluorouracil elicited neurotoxicity by curtailing oxidative stress and iNOS/NF-ĸB/caspase-3 pathway
- GC-MS profile of extracts of an endophytic fungus Alternaria and evaluation of its anticancer and antibacterial potentialities
- Green synthesis, chemical characterization, and antioxidant and anti-colorectal cancer effects of vanadium nanoparticles
- Determination of caffeine content in coffee drinks prepared in some coffee shops in the local market in Jeddah City, Saudi Arabia
- A new 3D supramolecular Cu(ii) framework: Crystal structure and photocatalytic characteristics
- Bordeaux mixture accelerates ripening, delays senescence, and promotes metabolite accumulation in jujube fruit
- Important application value of injectable hydrogels loaded with omeprazole Schiff base complex in the treatment of pancreatitis
- Color tunable benzothiadiazole-based small molecules for lightening applications
- Investigation of structural, dielectric, impedance, and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-modified barium titanate composites for biomedical applications
- Metal gel particles loaded with epidermal cell growth factor promote skin wound repair mechanism by regulating miRNA
- In vitro exploration of Hypsizygus ulmarius (Bull.) mushroom fruiting bodies: Potential antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory agent
- Alteration in the molecular structure of the adenine base exposed to gamma irradiation: An ESR study
- Comprehensive study of optical, thermal, and gamma-ray shielding properties of Bi2O3–ZnO–PbO–B2O3 glasses
- Lewis acids as co-catalysts in Pd-based catalyzed systems of the octene-1 hydroethoxycarbonylation reaction
- Synthesis, Hirshfeld surface analysis, thermal, and selective α-glucosidase inhibitory studies of Schiff base transition metal complexes
- Protective properties of AgNPs green-synthesized by Abelmoschus esculentus on retinal damage on the virtue of its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in diabetic rat
- Effects of green decorated AgNPs on lignin-modified magnetic nanoparticles mediated by Cydonia on cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis
- Treatment of gastric cancer by green mediated silver nanoparticles using Pistacia atlantica bark aqueous extract
- Preparation of newly developed porcelain ceramics containing WO3 nanoparticles for radiation shielding applications
- Utilization of computational methods for the identification of new natural inhibitors of human neutrophil elastase in inflammation therapy
- Some anticancer agents as effective glutathione S-transferase (GST) inhibitors
- Clay-based bricks’ rich illite mineral for gamma-ray shielding applications: An experimental evaluation of the effect of pressure rates on gamma-ray attenuation parameters
- Stability kinetics of orevactaene pigments produced by Epicoccum nigrum in solid-state fermentation
- Treatment of denture stomatitis using iron nanoparticles green-synthesized by Silybum marianum extract
- Characterization and antioxidant potential of white mustard (Brassica hirta) leaf extract and stabilization of sunflower oil
- Characteristics of Langmuir monomolecular monolayers formed by the novel oil blends
- Strategies for optimizing the single GdSrFeO4 phase synthesis
- Oleic acid and linoleic acid nanosomes boost immunity and provoke cell death via the upregulation of beta-defensin-4 at genetic and epigenetic levels
- Unraveling the therapeutic potential of Bombax ceiba roots: A comprehensive study of chemical composition, heavy metal content, antibacterial activity, and in silico analysis
- Green synthesis of AgNPs using plant extract and investigation of its anti-human colorectal cancer application
- The adsorption of naproxen on adsorbents obtained from pepper stalk extract by green synthesis
- Treatment of gastric cancer by silver nanoparticles encapsulated by chitosan polymers mediated by Pistacia atlantica extract under ultrasound condition
- In vitro protective and anti-inflammatory effects of Capparis spinosa and its flavonoids profile
- Wear and corrosion behavior of TiC and WC coatings deposited on high-speed steels by electro-spark deposition
- Therapeutic effects of green-formulated gold nanoparticles by Origanum majorana on spinal cord injury in rats
- Melanin antibacterial activity of two new strains, SN1 and SN2, of Exophiala phaeomuriformis against five human pathogens
- Evaluation of the analgesic and anesthetic properties of silver nanoparticles supported over biodegradable acacia gum-modified magnetic nanoparticles
- Review Articles
- Role and mechanism of fruit waste polyphenols in diabetes management
- A comprehensive review of non-alkaloidal metabolites from the subfamily Amaryllidoideae (Amaryllidaceae)
- Discovery of the chemical constituents, structural characteristics, and pharmacological functions of Chinese caterpillar fungus
- Eco-friendly green approach of nickel oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications
- Advances in the pharmaceutical research of curcumin for oral administration
- Rapid Communication
- Determination of the contents of bioactive compounds in St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum): Comparison of commercial and wild samples
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Two mixed-ligand coordination polymers based on 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid and flexible N-donor ligands: The protective effect on periodontitis via reducing the release of IL-1β and TNF-α”
- Topical Issue on Phytochemicals, biological and toxicological analysis of aromatic medicinal plants
- Anti-plasmodial potential of selected medicinal plants and a compound Atropine isolated from Eucalyptus obliqua
- Anthocyanin extract from black rice attenuates chronic inflammation in DSS-induced colitis mouse model by modulating the gut microbiota
- Evaluation of antibiofilm and cytotoxicity effect of Rumex vesicarius methanol extract
- Chemical compositions of Litsea umbellata and inhibition activities
- Green synthesis, characterization of silver nanoparticles using Rhynchosia capitata leaf extract and their biological activities
- GC-MS analysis and antibacterial activities of some plants belonging to the genus Euphorbia on selected bacterial isolates
- The abrogative effect of propolis on acrylamide-induced toxicity in male albino rats: Histological study
- A phytoconstituent 6-aminoflavone ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress mediated synapse and memory dysfunction via p-Akt/NF-kB pathway in albino mice
- Anti-diabetic potentials of Sorbaria tomentosa Lindl. Rehder: Phytochemistry (GC-MS analysis), α-amylase, α-glucosidase inhibitory, in vivo hypoglycemic, and biochemical analysis
- Assessment of cytotoxic and apoptotic activities of the Cassia angustifolia aqueous extract against SW480 colon cancer
- Biochemical analysis, antioxidant, and antibacterial efficacy of the bee propolis extract (Hymenoptera: Apis mellifera) against Staphylococcus aureus-induced infection in BALB/c mice: In vitro and in vivo study
- Assessment of essential elements and heavy metals in Saudi Arabian rice samples underwent various processing methods
- Two new compounds from leaves of Capparis dongvanensis (Sy, B. H. Quang & D. V. Hai) and inhibition activities
- Hydroxyquinoline sulfanilamide ameliorates STZ-induced hyperglycemia-mediated amyleoid beta burden and memory impairment in adult mice
- An automated reading of semi-quantitative hemagglutination results in microplates: Micro-assay for plant lectins
- Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry assessment of essential and toxic trace elements in traditional spices consumed by the population of the Middle Eastern region in their recipes
- Phytochemical analysis and anticancer activity of the Pithecellobium dulce seed extract in colorectal cancer cells
- Impact of climatic disturbances on the chemical compositions and metabolites of Salvia officinalis
- Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant and antifungal activities of essential oils of Urginea maritima and Allium sativum
- Phytochemical analysis and antifungal efficiency of Origanum majorana extracts against some phytopathogenic fungi causing tomato damping-off diseases
- Special Issue on 4th IC3PE
- Graphene quantum dots: A comprehensive overview
- Studies on the intercalation of calcium–aluminium layered double hydroxide-MCPA and its controlled release mechanism as a potential green herbicide
- Synergetic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis by zinc ferrite-anchored graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet for the removal of ciprofloxacin under visible light irradiation
- Exploring anticancer activity of the Indonesian guava leaf (Psidium guajava L.) fraction on various human cancer cell lines in an in vitro cell-based approach
- The comparison of gold extraction methods from the rock using thiourea and thiosulfate
- Special Issue on Marine environmental sciences and significance of the multidisciplinary approaches
- Sorption of alkylphenols and estrogens on microplastics in marine conditions
- Cytotoxic ketosteroids from the Red Sea soft coral Dendronephthya sp.
- Antibacterial and biofilm prevention metabolites from Acanthophora spicifera
- Characteristics, source, and health risk assessment of aerosol polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the rural and urban regions of western Saudi Arabia
- Special Issue on Advanced Nanomaterials for Energy, Environmental and Biological Applications - Part II
- Green synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antibacterial activities of cobalt nanoparticles produced by marine fungal species Periconia prolifica
- Combustion-mediated sol–gel preparation of cobalt-doped ZnO nanohybrids for the degradation of acid red and antibacterial performance
- Perinatal supplementation with selenium nanoparticles modified with ascorbic acid improves hepatotoxicity in rat gestational diabetes
- Evaluation and chemical characterization of bioactive secondary metabolites from endophytic fungi associated with the ethnomedicinal plant Bergenia ciliata
- Enhancing photovoltaic efficiency with SQI-Br and SQI-I sensitizers: A comparative analysis
- Nanostructured p-PbS/p-CuO sulfide/oxide bilayer heterojunction as a promising photoelectrode for hydrogen gas generation

![Figure 1
Chemical structures of technical yarns and their main chemicals [10,18–21].](/document/doi/10.1515/chem-2022-0324/asset/graphic/j_chem-2022-0324_fig_001.jpg)
