Abstract
Since it is difficult for manual recording to track the rapid change of indication of the power meter, the power meter images are collected by the camera and automatically recognized and recorded to effectively overcome the disadvantages of manual recording. However, the complex scene lighting environment and smearing character shadows make it difficult to transfer captured images directly to convolutional neural networks for character recognition. A smear character recognition method of side-end power meter under complex lighting conditions is proposed in this article. First, the uneven illumination image enhancement algorithm is studied. Through the estimation of the illumination component of the image, the fusion weight is calculated by the principal component analysis for multiscale fusion, and the up-sampling and down-sampling are adopted to reduce the calculation of the algorithm and achieve the rapid image enhancement. A convolution neural network framework based on deep learning is proposed to realize the segmentation of smear characters, and the final segmented individual characters are fed into a network to identify the meter readings. The experimental results show that the proposed smear character recognition method has fast recognition speed, and the recognition rate of samples with the smear character and complex illumination reaches 99.8%, which meets the requirements of power meter character recognition and is better than other algorithms.
1 Introduction
With the expansion of power consumption and the increase in the number of substations, more and more measuring instruments need to be monitored [1]. Accurate meter reading of measuring instruments is crucial to the operation of the substation [2]. In addition, the electric power inspection basically adopts the inspection robot to shoot and extract the data of the meter through the camera. However, there is a certain deviation in the recognition of the electric power meter under the complex illumination of the camera [3]. The character recognition accuracy of electric power meters needs to be improved under the complex illumination environment of the substations [4,5].
Currently, most of the instruments at the stations use LCD screens, but because the LCD screen has reflective characteristics, it is easy to cause uneven illumination of the collected images [6]. Moreover, the long black-and-white response time of some LCD screens causes serious shadows when the characters are quickly refreshed, that is, when one character does not completely disappear, another character has appeared, resulting in the superposition of two characters with different brightness in the collected image. In addition, the scene lighting environment is different, and sunlight is different indoor and outdoor, which makes the collected images vary greatly. Therefore, how to accurately identify instrument characters with serious shadow under the conditions of uneven illumination is a challenging problem [7].
Character recognition using neural networks has been a research focus in recent years. The algorithms [8,9] detect single characters before using the DCNN model to identify them. This approach often requires the implementation of an efficient character detector capable of precisely detecting and cutting each character from the original word picture. Other methods [10] treat scene character recognition as an image classification issue, requiring each English word to be assigned to a category label (90k words). Traditional character recognition approaches that are not based on neural networks have also contributed to new concepts and representations. Almazán et al. [11] and Rodriguez-Serrano et al. [12] proposed embedding word images and text strings in public-oriented quantum space and turning word recognition into a retrieval issue. Lee et al. [13] suggested a method for identifying feature pools that can learn the character information subregion. For character recognition, Bai et al. [14] and Gordo [15] used mid-level features. By exchanging features across two tasks, Yao et al. [16] unified character recognition and detection.
This article aims to design a fast image recognition method for smear characters under different illumination conditions, including image enhancement and trailing shadow character image segmentation to improve the accuracy of automatic recognition of power meter reading.
This article is divided into four sections. Section 1 presents the introduction. The status and development of power instrument character recognition are comprehensively expounded. In Section 2, a method for smear character recognition of edge power meter under complex illumination interference is proposed. First, the overall process of the algorithm is introduced. Then, the image enhancement algorithm for uneven illumination is studied to realize the rapid enhancement of instrument images. Finally, a convolutional neural network framework based on deep learning is designed to realize the perfect segmentation of instrument shadow characters. Section 3 presents the experimental results and analysis, including data collection and calibration, binary segmentation experiments, and character recognition experiments. Section 4 presents the conclusion, which summarizes the research content.
2 Method
2.1 Overall process
To achieve accurate and stable recognition of smear characters of power meters under complex lighting, improvements are mainly made in three aspects: image enhancement, binarization and character segmentation, and character recognition [17]. The overall process is shown in Figure 1. Among them, the fully convolutional network (FCN) [18] and the VGG [19] instrument character segmentation model were trained in advance, which are not marked in the flowchart. The major steps are as follows:
Camera images acquisition;
The fast adaptive image enhancement method based on PCA [20] fusion is used to correct uneven illumination, and then the binarization is carried out based on FCN and VGG instrument character segmentation method;
Remove small connected domains and noise by opening and closing operations;
Tilt correction;
Segmentation of single character;
Single characters are normalized and input to smear character recognition model for recognition.

Character recognition flow chart of power meter.
2.2 Fast adaptive image enhancement based on PCA fusion
The original RGB image is converted into HSV color space, and the V component is extracted and down-sampled. The illumination component of the image is extracted by multiscale Gaussian filtering and up-sampled to the size before down-sampling. Then, the illumination component is refined by guided filtering, and the illumination component is adaptively adjusted by different correction coefficients to obtain two images. The weights of the two images are calculated by PCA and fused to enhance the V component. Finally, the image is converted from HSV space to RGB space to obtain the final enhanced image. The specific process is shown in Figure 2.
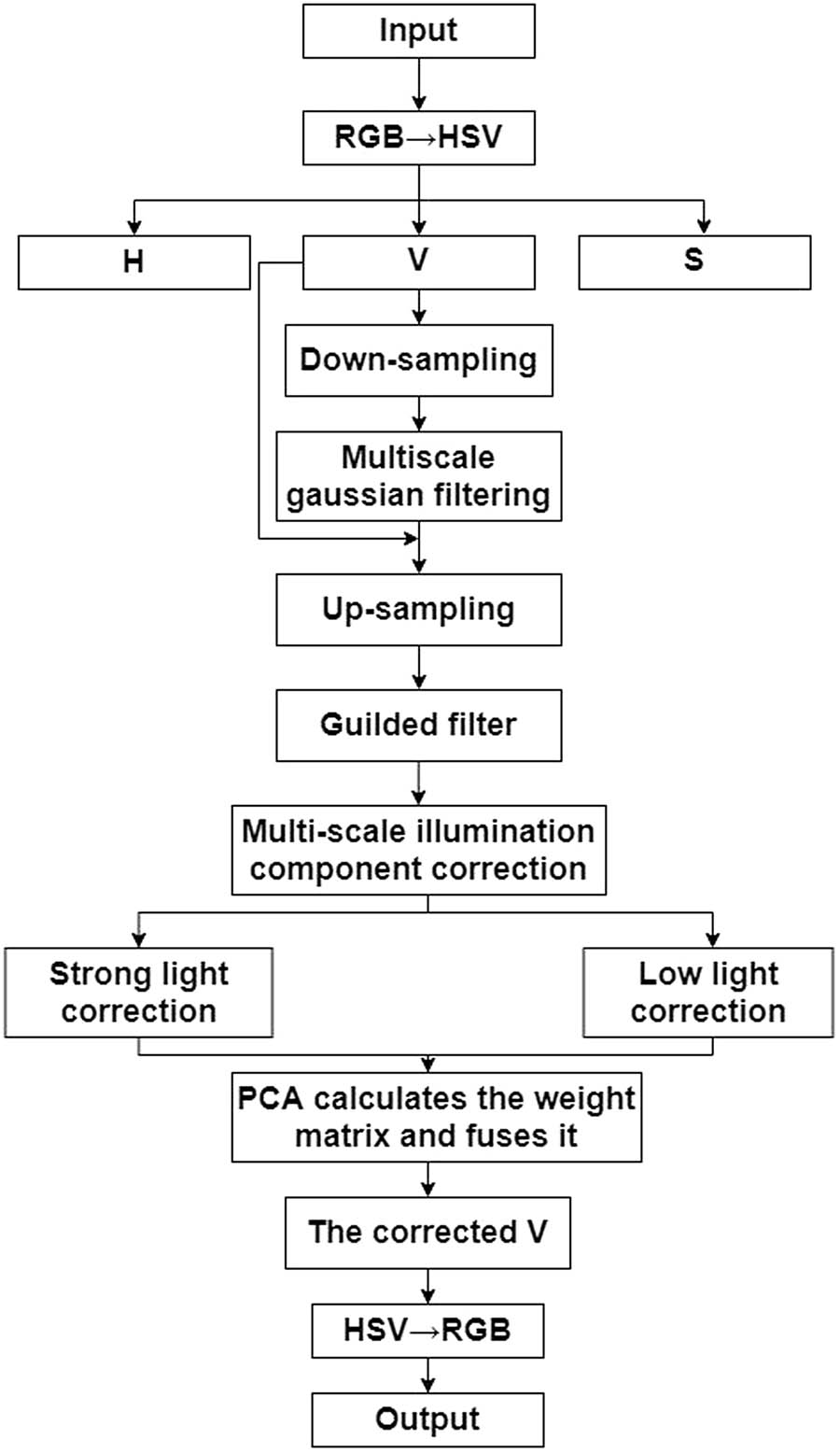
Fast adaptive image enhancement algorithm flow based on PCA fusion.
The calculation amount of multiscale Gaussian filtering increases with the increase of the input image size [21], which affects the real-time performance of the algorithm. Down-sampling and up-sampling can well reduce the calculation amount, and guided filtering can refine the up-sampling results and retain the local characteristics of the illumination component. To avoid the small down-sampling size and excessive loss of image details, the linear interpolation method is used for down-sampling, and the down-sampling size is a quarter of the input size.
To balance the global and local characteristics of the extracted illumination components, the multiscale two-dimensional discrete Gaussian function is used to extract the illumination components in the scene, and each component is weighted. Finally, the estimated illumination components are obtained. The calculation is as follows:
where
To reduce the amount of fusion computation, a simple source image weighted fusion is adopted without multiscale decomposition to avoid the bias of fusion results to a certain source image. PCA is used to determine the weight coefficient of each source image as the key to image fusion. The specific process and result are shown in Figure 3, and it can be seen that the image process by fast adaptive image enhancement algorithm is significantly improved in terms of color, brightness, and detail.
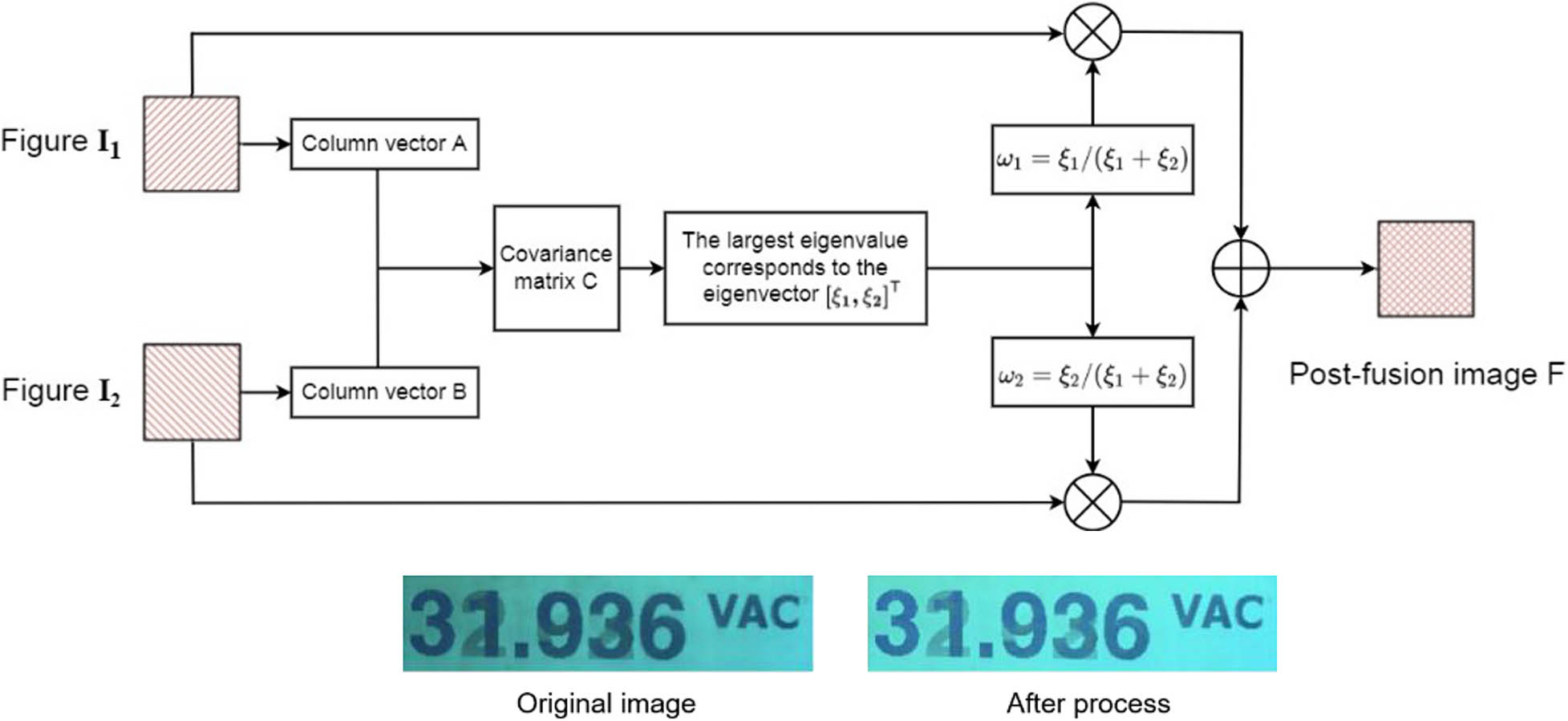
Image fusion based on PCA.
2.3 FCN- and VGG-based smear character segmentation
Combining FCN and VGG16 network, the input is the original RGB image and the output is a binary map without the smear. The network consists of two parts: feature extraction and image recombination. The feature extraction is a down-sampling composed of five convolutional blocks, each convolutional block includes a convolutional layer and a maximum pooling layer, and the Relu activation function is chosen behind the convolutional layer to alleviate overfitting. The number of convolutional kernels in the convolutional layer is 256, the size is 3 × 3, the step size is 1, and the pad is 1. The pooling layer has a pooling window size of 2 × 2 and a step size of 2.
The image reconstruction is performed by five deconvolution blocks to reduce the extracted information to images. The deconvolution block includes a deconvolution layer and a connection layer, where the convolution kernel of the deconvolution layer is 4 × 4 with a step size of 2. The overall structure of the network is shown in Figure 4, and the mean square error (MSE) is used as the loss function, which is defined as follows:
where n is the number of samples,
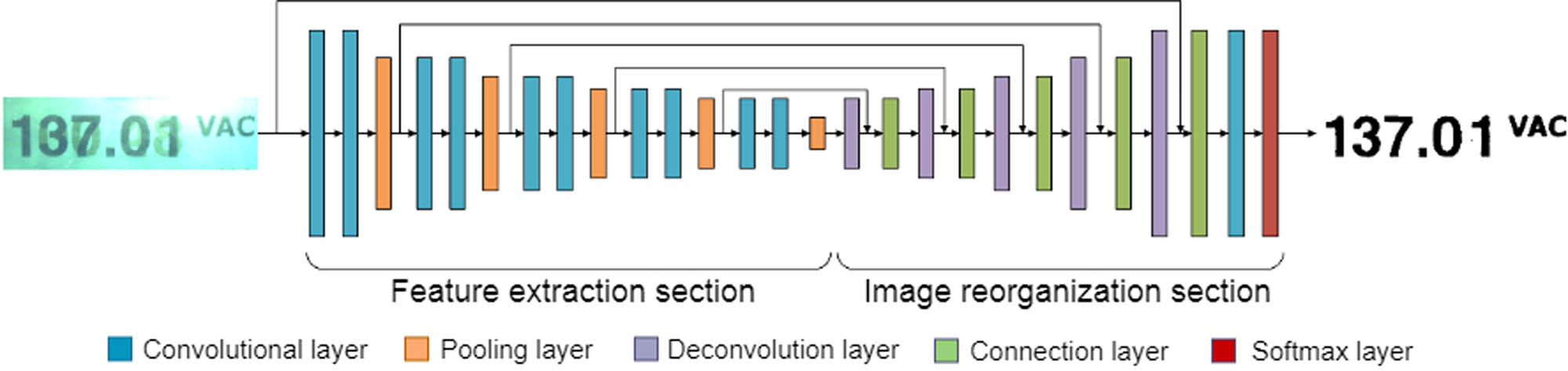
The structure of a fully convolutional neural network.
3 Experimental results and analysis
3.1 Collection and calibration of data sets
The samples were collected in the instrument working environment. The light sources were placed in the left, right, and median positions of the instrument and combined with a 30 degree angle deflection between the camera and the instrument. A total of 7,600 color images were collected.
Label production is divided into two stages: preparation and production. In the preparation stage, the accurate position of the characters in the instrument image is mainly counted. The image with good illumination is selected, and the approximate region of the characters is manually calibrated. The minimum circumscribed rectangle is determined, and the angle θ between the long edge of the minimum circumscribed rectangle and the horizontal x-axis is calculated. The binary image is rotated and corrected to make all the characters on the same horizontal line. The center P1(x 1, y 1), P2(x 2, y 2), and P3(x 3, y 3) of the three calibration circles are determined by circle detection as the three points corresponding to the affine transformation in the label production stage. The position of each character is recorded by the vertical projection method, and the characters with complete segmentation and no shadow are selected as the standard single character, as shown in Figure 5.

Label preparation phase. (a) Original image, (b) binary graph, (c) calculate rotation angle, and (d) location of each character.
In the label production stage, Wolf algorithm is used to binarize the instrument image and detect the center of three calibration circles P1́
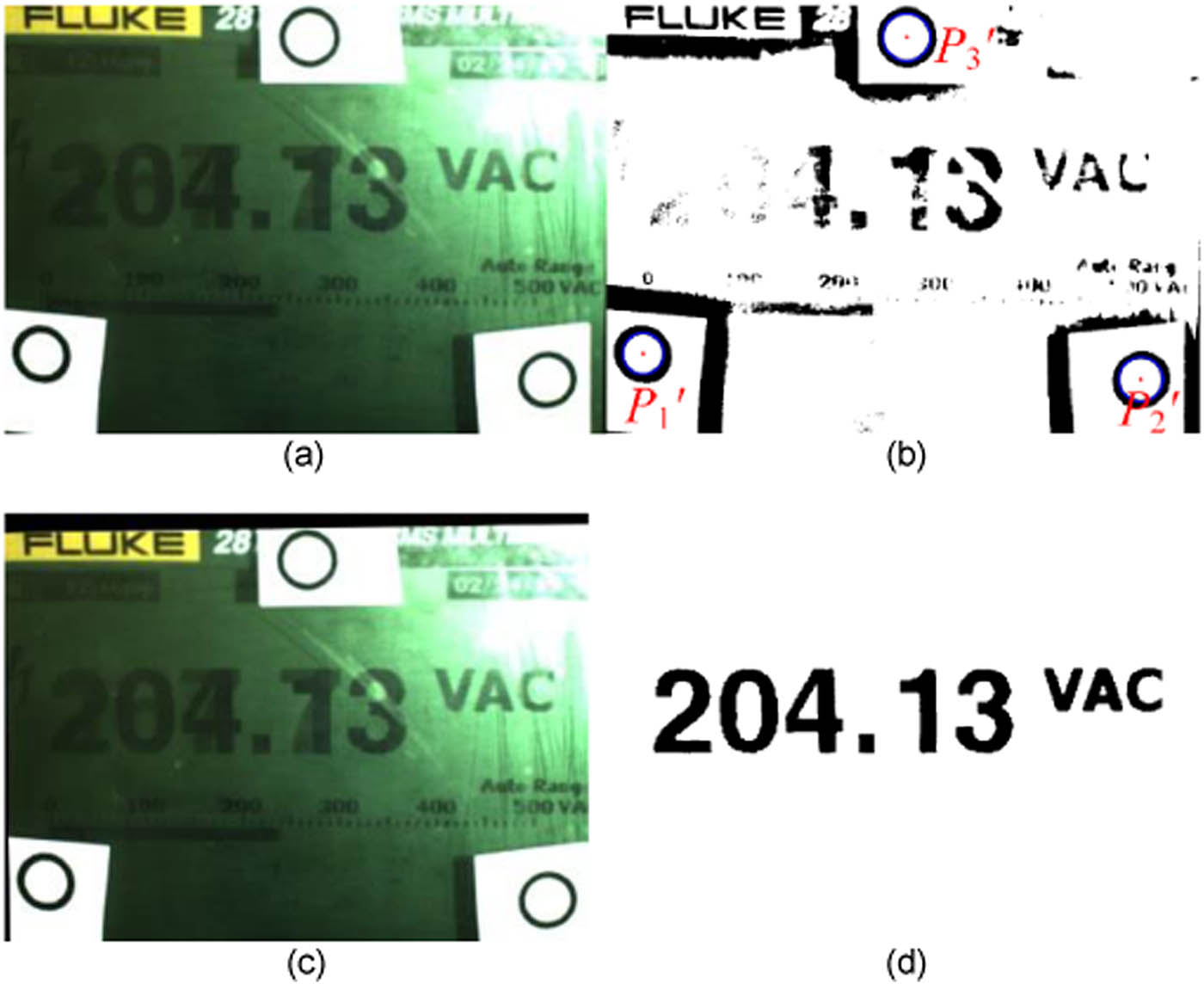
The label production phase. (a) Original image, (b) binary graph, (c) affine transformation result, and (d) label after character replacement.
To reduce the training time, the sample only represents the number of parts by the interceptor, and each sample is randomly rotated and shifted to expand three samples. Through this method, the total number of samples is 30,400, and 80% of the samples are randomly selected for training, and the remaining samples are used as testing samples.
3.2 Binary segmentation experiment
The experimental environment is Intel (R) Xeon (R) 2.4 GHz CPU E5-2640, GPU NVIDIA RTX 2080Ti, Python3.6 programming in TensorFlow framework. Without other pretraining models, batch size is 16, initial learning rate is 1 × 10−4, period is 100. Compared with local threshold binarization algorithms such as Bernsen [22] black, Sauvola [23] Bradley [24], Wellner [25], and Wolf et al. [26], IoU and SNR are used as evaluation indexes.
The running time, IoU, and SNR mean of each algorithm are presented in Table 1. Some of the operation results are shown in Figure 7. The uneven illumination has a great influence on the binarization effect, and the binarization effect of the traditional methods on the smear is very poor. Niblack algorithm generally divides the target area, but with a lot of noise, it cannot remove the smear character. Because most of the local region of the instrument image is the background, uneven illumination causes Bernsen, Sauvola and Bradley algorithm to divide part of the background into target pixels and do not eliminate the smear character. Wellner algorithm cannot segment strong light region and smear character. Wolf algorithm overcomes the influence of uneven illumination to some extent, but cannot smear character. The network designed in this article has a clear and no smear character on the binarization effect of uneven illumination and shadow images. The IoU and SNR values are higher than those of other methods. It is suitable for images with different light intensities and rotations. It has a strong generalization ability and fast processing speed, only slightly higher than Wellner.
Comparison of results of various algorithms
| Algorithm | Running time (s) | IoU | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bernsen | 0.85 | 0.33 | 8.93 |
| Niblack | 1.06 | 0.51 | 6.74 |
| Sauvola | 0.28 | 0.66 | 10.17 |
| Bradley | 1.87 | 0.71 | 10.11 |
| Wellner | 0.07 | 0.70 | 10.97 |
| Wolf | 0.81 | 0.69 | 10.24 |
| Ours | 0.10 | 0.95 | 20.53 |
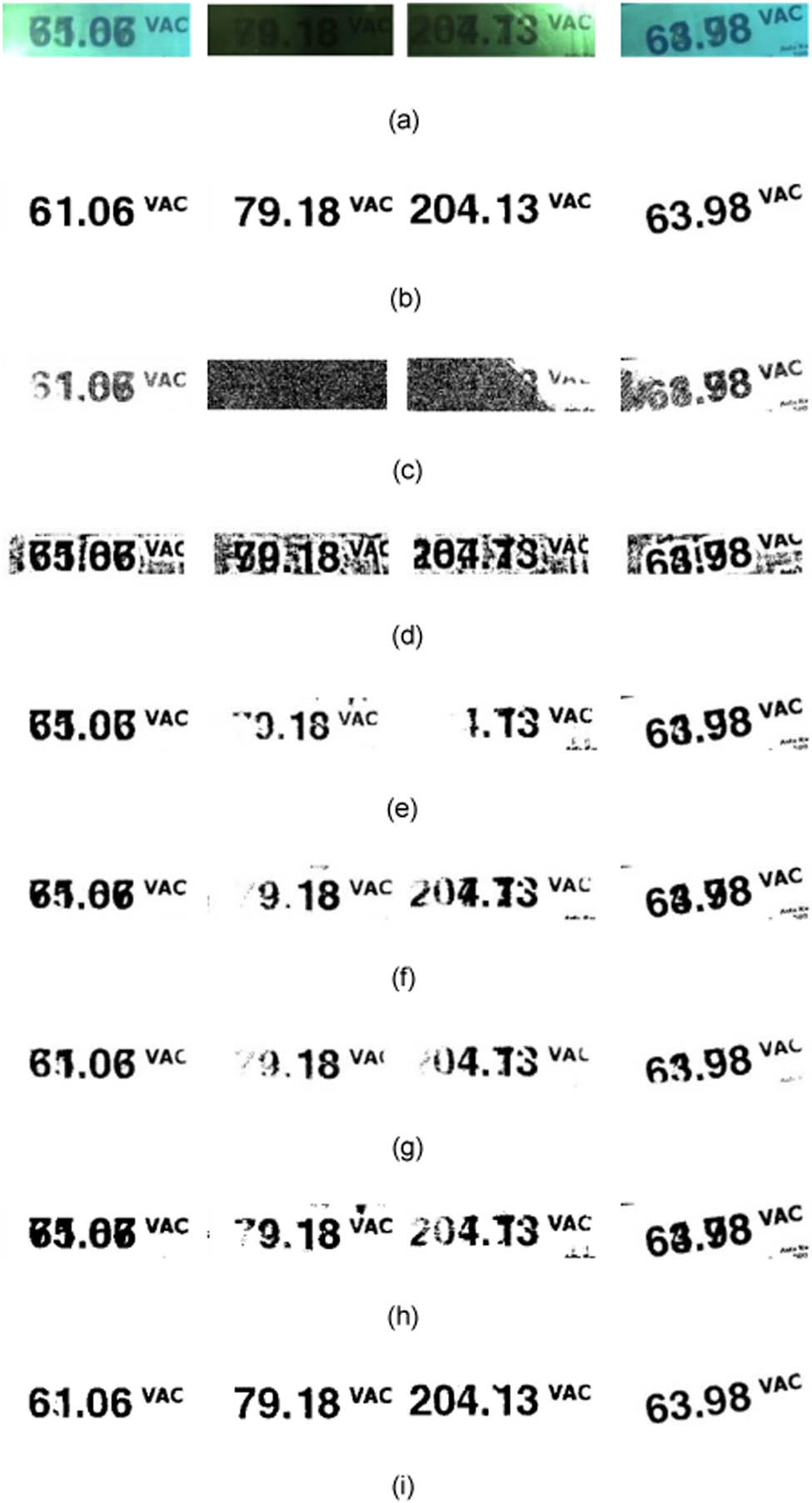
Processing results of different algorithms. (a) Original image, (b) ideal binary label, (c) Bernsen algorithm, (d) Niblack algorithm, (e) Sauvola algorithm, (f) Bradley algorithm, (g) Wellner algorithm, (h) Wolf algorithm, and (i) the method of this article.
3.3 Character recognition experiment
Smear characters are segmented for character recognition [27]. Character segmentation includes tilt correction, affine transformation, vertical projection, and horizontal projection. The specific effect is shown in Figure 8. Because the horizontal projection intervals of numbers, decimals and “VAC” characters are different, and “VAC” characters remain unchanged, decimals can be judged directly by the horizontal projection interval, so only numbers are reserved in segmentation. The single character is segmented by this algorithm, as shown in Figure 9, where the smear character is basically eliminated.
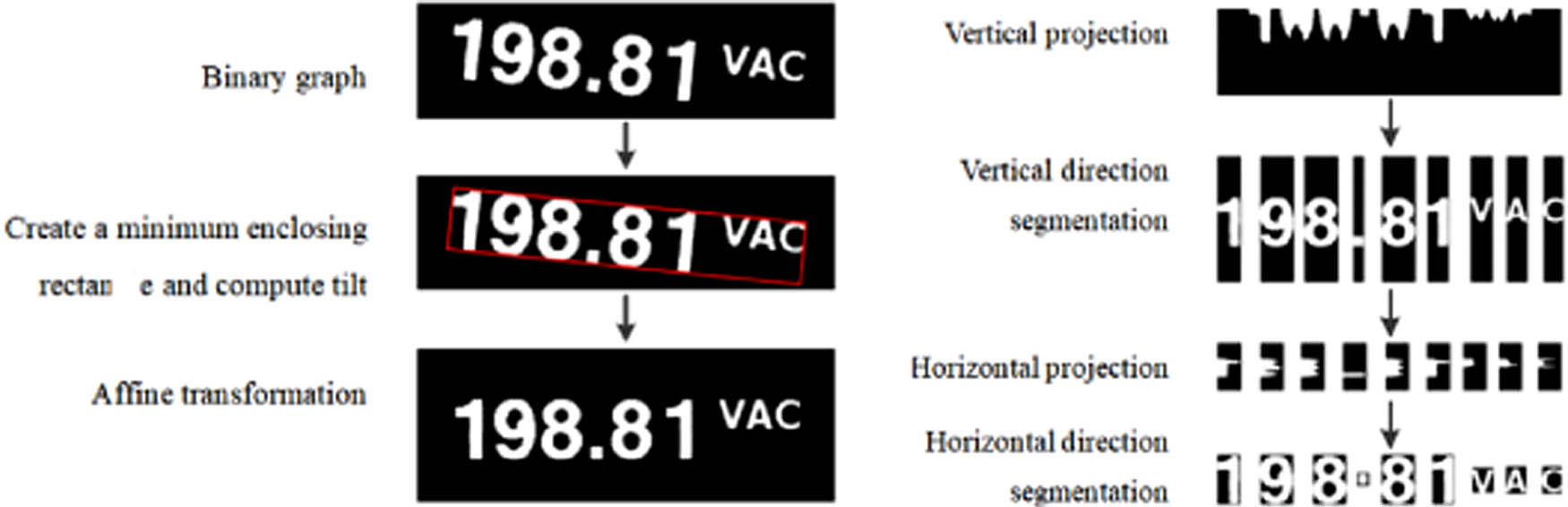
Segmentation effect of the projection method.

Single-character samples segmented by the proposed algorithm.
The individual characters after sample segmentation are categorized to make numerical labels, which are input into the CRNN model for training and testing, respectively.
To verify the effectiveness of the algorithms in this article, HOG + SVM [28], KNN [29], and CRNN [30] algorithms are used for character recognition. The CRNN algorithm parameters are as follows: input image size is 32 × 32, batch size is 64, training cycle is 3000, and learning rate is 0.0001. SVM uses linear kernel function, and HOG feature unit size is 3 × 3.
The experimental results are presented in Table 2. Compared with the direct recognition of characters, the recognition rate of all algorithms is higher after the processing of the proposed character segmentation algorithm, and the recognition rate of CRNN algorithm is improved by 21.71%, indicating that the proposed binarization algorithm provides a better basis for character recognition.
Instrument character recognition results
| Method | Training time (s) | Single-sample test time (ms) | Test recognition rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRNN (original) | — | — | 78.09 |
| HOG + SVM | 32.18 | 5.7 | 98.95 |
| KNN | — | 12.6 | 98.75 |
| LeNet-5 | 98.54 | 1.4 | 96.45 |
| CRNN | 90.16 | 2.16 | 99.80 |
4 Conclusions
In this article, we design a fast recognition method for power meter characters by combining adaptive image enhancement, smear character segmentation based on FCN and VGG for the problem of difficult recognition of meter smear characters under complex illumination. The experimental results show that the proposed smear character segmentation network can achieve adaptive binary segmentation of meter images, effectively remove the effects of digital trailing, offset or rotation under severe illumination uneven conditions, with high recognition rate and fast recognition speed of the whole method, meeting the requirements of fast meter character recognition.
-
Funding information: The work was supported by State Grid Science and Technology Project (kj2020-055): Research on Development Aligned Access Gateway and Networking Technology of Heterogeneous Sensor Network Based on Cloud-edge Computing Collaboration.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Tang X. Research and design of electric energy online metering device for high voltage transmission line based on electric field coupling method. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE); 2021 Jan 15–17; Guangzhou, China. IEEE; 2021. p. 222–6.10.1109/ICCECE51280.2021.9342120Search in Google Scholar
[2] Liu C, Fan H, Tian Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Yang W. research on analysis method of current loop fault in high voltage electric energy metering device. 2021 International Conference on Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy (ATEEE); 2021 Dec 24–26; Qingdao, China. IEEE; 2022. p. 41–5.10.1109/ATEEE54283.2021.00017Search in Google Scholar
[3] Zheng C, Wang S, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Zhao Y. A robust and automatic recognition system of analog instruments in power system by using computer vision. Measurement. 2016;92:413–20.10.1016/j.measurement.2016.06.045Search in Google Scholar
[4] Dai DX, Wang W, Yang Y, Chen Y. Calibration device of high voltage capacitance bridge. 2020 Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements (CPEM); 2020 Aug 24–28; Denver (CO), USA. IEEE; 2020. p. 1–2.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Ilić D, Lüddecke C, Heinrich A, Meisner J, Behr R. Calibration of a precision current measurement system for high AC voltages using an AC Quantum Voltmeter. 2020 Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements (CPEM); 2020 Aug 24–28; Denver (CO), USA. IEEE; p. 1–2.10.1088/1681-7575/ac8482Search in Google Scholar
[6] Miranda Filho J, de Carvalho Filho JM, Paiva AP, de Souza PV, Tomasin S. A PCA-based approach for substation clustering for voltage sag studies in the Brazilian new energy context. Electr Power Syst Res. 2016;136:31–42.10.1016/j.epsr.2016.02.012Search in Google Scholar
[7] Wu C, Wu Q, Yuan C, Li P, Zhang Y, Xiao Y. Multimeter digital recognition based on feature coding detection. 2017 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI); 2017 Oct 14–16; Shanghai, China. IEEE; 2018. p. 1–6.10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2017.8302009Search in Google Scholar
[8] Wang T, Wu DJ, Coates A, Ng AY. End-to-end text recognition with convolutional neural networks. Proceedings of the 21st international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR2012); 2012 Nov 11–15; Tsukuba, Japan. IEEE; 2013. p. 3304–8.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Bissacco A, Cummins M, Netzer Y, Neven H. PhotoOCR: Reading text in uncontrolled conditions. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision; 2013 Dec 1–8; Sydney, Australia. IEEE; 2014. p. 785–92.10.1109/ICCV.2013.102Search in Google Scholar
[10] Jaderberg M, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A. Reading text in the wild with convolutional neural networks. Int J Comput Vis. 2016;116(1):1–20.10.1007/s11263-015-0823-zSearch in Google Scholar
[11] Almazán J, Gordo A, Fornés A, Valveny E. Word spotting and recognition with embedded attributes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2014;36(12):2552–66.10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2339814Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Rodriguez-Serrano JA, Gordo A, Perronnin F. Label embedding: A frugal baseline for text recognition. Int J Comput Vis. 2015;113(3):193–207.10.1007/s11263-014-0793-6Search in Google Scholar
[13] Lee CY, Bhardwaj A, Di W, Jagadeesh V, Piramuthu R. Region-based discriminative feature pooling for scene text recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2014 Jun 23–28; Columbus (OH), USA. IEEE; 2014. p. 4050–7.10.1109/CVPR.2014.516Search in Google Scholar
[14] Bai X, Yao C, Liu W. Strokelets: A learned multi-scale mid-level representation for scene text recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2016;25(6):2789–802.10.1109/TIP.2016.2555080Search in Google Scholar
[15] Gordo A. Supervised mid-level features for word image representation. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015 Jun 7–12; Boston (MA), USA. IEEE; 2015. p. 2956–64.10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298914Search in Google Scholar
[16] Yao C, Bai X, Liu W. A unified framework for multioriented text detection and recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2014;23(11):4737–49.10.1109/TIP.2014.2353813Search in Google Scholar
[17] Sarika N, Sirisala N, Velpuru MS. CNN based Optical Character Recognition and Applications. 2021 6th International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT); 2021 Jan 20–22; Coimbatore, India. IEEE; 2021. p. 666–72.10.1109/ICICT50816.2021.9358735Search in Google Scholar
[18] Su W, Wang Z. Regularized fully convolutional networks for RGB-D semantic segmentation. 2016 Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP); 2016 Nov 27–30; Chengdu, China. IEEE; 2016. p. 1–4.10.1109/VCIP.2016.7805508Search in Google Scholar
[19] Raja J, Shanmugam P, Pitchai R. An Automated Early Detection of Glaucoma using Support Vector Machine Based Visual Geometry Group 19 (VGG-19) Convolutional Neural Network. Wirel Pers Commun. 2021;118(1):523–34.10.1007/s11277-020-08029-zSearch in Google Scholar
[20] Anzai Y, Minoshima S, Wolf GT, Wahl RL. Head and neck cancer: detection of recurrence with three-dimensional principal components analysis at dynamic FDG PET. Radiology. 1999;212(1):285–90.10.1148/radiology.212.1.r99jl02285Search in Google Scholar
[21] Choi MJ, Willsky AS, editors. Multiscale Gaussian graphical models and algorithms for large-scale inference. 2007 IEEE/SP 14th Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing; 2007 Aug 26–29; Madison (MI), USA. IEEE; 2007. p. 229–33.10.1109/SSP.2007.4301253Search in Google Scholar
[22] Bernsen J. Dynamic thresholding of gray-level images. Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition; 1986 Oct 27–31; Paris, France. The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Press; 1986. p. 1251–5.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Sauvola J, Pietikäinen M. Adaptive document image binarization. Pattern Recognit. 2000;33(2):225–36.10.1016/S0031-3203(99)00055-2Search in Google Scholar
[24] Bradley PS, Bennett KP, Demiriz A. Constrained K-Means clustering. Microsoft. Research, Redmond. 2000;1–8.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Wellner PD. Adaptive thresholding for the DigitalDesk. Xerox, EPC1993-110. 1993. p. 1–19.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Wolf C, Jolion JM, Chassaing F. Text localization, enhancement and binarization in multimedia documents. Object recognition supported by user interaction for service robots. 2002 International Conference on Pattern Recognition. 2002 Aug 11–15; Quebec City, Canada. IEEE; 2002. p. 1037–40.10.1109/ICPR.2002.1048482Search in Google Scholar
[27] Qin Y, Zhang Z. Summary of scene text detection and recognition. 2020 15th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA); 2020 Nov 9–13; Kristiansand, Norway. IEEE; 2020. p. 85–9.10.1109/ICIEA48937.2020.9248121Search in Google Scholar
[28] Yao C, Wu F, Chen, HJ, Hao, XL, Shen Y. Traffic sign recognition using HOG-SVM and grid search. 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP); 2014 Oct 19–23; Hangzhou, China. IEEE; 2015. p. 962–5.10.1109/ICOSP.2014.7015147Search in Google Scholar
[29] Keller JM, Gray MR, Givens JA. A Fuzzy K-nearest Neighbor Algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1985;SMC-15(4):580–5.10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313426Search in Google Scholar
[30] Shi B, Bai X, Yao C. An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2016;39(11):2298–304.10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2646371Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Peng Luo et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Fractal approach to the fluidity of a cement mortar
- Novel results on conformable Bessel functions
- The role of relaxation and retardation phenomenon of Oldroyd-B fluid flow through Stehfest’s and Tzou’s algorithms
- Damage identification of wind turbine blades based on dynamic characteristics
- Improving nonlinear behavior and tensile and compressive strengths of sustainable lightweight concrete using waste glass powder, nanosilica, and recycled polypropylene fiber
- Two-point nonlocal nonlinear fractional boundary value problem with Caputo derivative: Analysis and numerical solution
- Construction of optical solitons of Radhakrishnan–Kundu–Lakshmanan equation in birefringent fibers
- Dynamics and simulations of discretized Caputo-conformable fractional-order Lotka–Volterra models
- Research on facial expression recognition based on an improved fusion algorithm
- N-dimensional quintic B-spline functions for solving n-dimensional partial differential equations
- Solution of two-dimensional fractional diffusion equation by a novel hybrid D(TQ) method
- Investigation of three-dimensional hybrid nanofluid flow affected by nonuniform MHD over exponential stretching/shrinking plate
- Solution for a rotational pendulum system by the Rach–Adomian–Meyers decomposition method
- Study on the technical parameters model of the functional components of cone crushers
- Using Krasnoselskii's theorem to investigate the Cauchy and neutral fractional q-integro-differential equation via numerical technique
- Smear character recognition method of side-end power meter based on PCA image enhancement
- Significance of adding titanium dioxide nanoparticles to an existing distilled water conveying aluminum oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles: Scrutinization of chemical reactive ternary-hybrid nanofluid due to bioconvection on a convectively heated surface
- An analytical approach for Shehu transform on fractional coupled 1D, 2D and 3D Burgers’ equations
- Exploration of the dynamics of hyperbolic tangent fluid through a tapered asymmetric porous channel
- Bond behavior of recycled coarse aggregate concrete with rebar after freeze–thaw cycles: Finite element nonlinear analysis
- Edge detection using nonlinear structure tensor
- Synchronizing a synchronverter to an unbalanced power grid using sequence component decomposition
- Distinguishability criteria of conformable hybrid linear systems
- A new computational investigation to the new exact solutions of (3 + 1)-dimensional WKdV equations via two novel procedures arising in shallow water magnetohydrodynamics
- A passive verses active exposure of mathematical smoking model: A role for optimal and dynamical control
- A new analytical method to simulate the mutual impact of space-time memory indices embedded in (1 + 2)-physical models
- Exploration of peristaltic pumping of Casson fluid flow through a porous peripheral layer in a channel
- Investigation of optimized ELM using Invasive Weed-optimization and Cuckoo-Search optimization
- Analytical analysis for non-homogeneous two-layer functionally graded material
- Investigation of critical load of structures using modified energy method in nonlinear-geometry solid mechanics problems
- Thermal and multi-boiling analysis of a rectangular porous fin: A spectral approach
- The path planning of collision avoidance for an unmanned ship navigating in waterways based on an artificial neural network
- Shear bond and compressive strength of clay stabilised with lime/cement jet grouting and deep mixing: A case of Norvik, Nynäshamn
- Communication
- Results for the heat transfer of a fin with exponential-law temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and power-law temperature-dependent heat transfer coefficients
- Special Issue: Recent trends and emergence of technology in nonlinear engineering and its applications - Part I
- Research on fault detection and identification methods of nonlinear dynamic process based on ICA
- Multi-objective optimization design of steel structure building energy consumption simulation based on genetic algorithm
- Study on modal parameter identification of engineering structures based on nonlinear characteristics
- On-line monitoring of steel ball stamping by mechatronics cold heading equipment based on PVDF polymer sensing material
- Vibration signal acquisition and computer simulation detection of mechanical equipment failure
- Development of a CPU-GPU heterogeneous platform based on a nonlinear parallel algorithm
- A GA-BP neural network for nonlinear time-series forecasting and its application in cigarette sales forecast
- Analysis of radiation effects of semiconductor devices based on numerical simulation Fermi–Dirac
- Design of motion-assisted training control system based on nonlinear mechanics
- Nonlinear discrete system model of tobacco supply chain information
- Performance degradation detection method of aeroengine fuel metering device
- Research on contour feature extraction method of multiple sports images based on nonlinear mechanics
- Design and implementation of Internet-of-Things software monitoring and early warning system based on nonlinear technology
- Application of nonlinear adaptive technology in GPS positioning trajectory of ship navigation
- Real-time control of laboratory information system based on nonlinear programming
- Software engineering defect detection and classification system based on artificial intelligence
- Vibration signal collection and analysis of mechanical equipment failure based on computer simulation detection
- Fractal analysis of retinal vasculature in relation with retinal diseases – an machine learning approach
- Application of programmable logic control in the nonlinear machine automation control using numerical control technology
- Application of nonlinear recursion equation in network security risk detection
- Study on mechanical maintenance method of ballasted track of high-speed railway based on nonlinear discrete element theory
- Optimal control and nonlinear numerical simulation analysis of tunnel rock deformation parameters
- Nonlinear reliability of urban rail transit network connectivity based on computer aided design and topology
- Optimization of target acquisition and sorting for object-finding multi-manipulator based on open MV vision
- Nonlinear numerical simulation of dynamic response of pile site and pile foundation under earthquake
- Research on stability of hydraulic system based on nonlinear PID control
- Design and simulation of vehicle vibration test based on virtual reality technology
- Nonlinear parameter optimization method for high-resolution monitoring of marine environment
- Mobile app for COVID-19 patient education – Development process using the analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation models
- Internet of Things-based smart vehicles design of bio-inspired algorithms using artificial intelligence charging system
- Construction vibration risk assessment of engineering projects based on nonlinear feature algorithm
- Application of third-order nonlinear optical materials in complex crystalline chemical reactions of borates
- Evaluation of LoRa nodes for long-range communication
- Secret information security system in computer network based on Bayesian classification and nonlinear algorithm
- Experimental and simulation research on the difference in motion technology levels based on nonlinear characteristics
- Research on computer 3D image encryption processing based on the nonlinear algorithm
- Outage probability for a multiuser NOMA-based network using energy harvesting relays
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Fractal approach to the fluidity of a cement mortar
- Novel results on conformable Bessel functions
- The role of relaxation and retardation phenomenon of Oldroyd-B fluid flow through Stehfest’s and Tzou’s algorithms
- Damage identification of wind turbine blades based on dynamic characteristics
- Improving nonlinear behavior and tensile and compressive strengths of sustainable lightweight concrete using waste glass powder, nanosilica, and recycled polypropylene fiber
- Two-point nonlocal nonlinear fractional boundary value problem with Caputo derivative: Analysis and numerical solution
- Construction of optical solitons of Radhakrishnan–Kundu–Lakshmanan equation in birefringent fibers
- Dynamics and simulations of discretized Caputo-conformable fractional-order Lotka–Volterra models
- Research on facial expression recognition based on an improved fusion algorithm
- N-dimensional quintic B-spline functions for solving n-dimensional partial differential equations
- Solution of two-dimensional fractional diffusion equation by a novel hybrid D(TQ) method
- Investigation of three-dimensional hybrid nanofluid flow affected by nonuniform MHD over exponential stretching/shrinking plate
- Solution for a rotational pendulum system by the Rach–Adomian–Meyers decomposition method
- Study on the technical parameters model of the functional components of cone crushers
- Using Krasnoselskii's theorem to investigate the Cauchy and neutral fractional q-integro-differential equation via numerical technique
- Smear character recognition method of side-end power meter based on PCA image enhancement
- Significance of adding titanium dioxide nanoparticles to an existing distilled water conveying aluminum oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles: Scrutinization of chemical reactive ternary-hybrid nanofluid due to bioconvection on a convectively heated surface
- An analytical approach for Shehu transform on fractional coupled 1D, 2D and 3D Burgers’ equations
- Exploration of the dynamics of hyperbolic tangent fluid through a tapered asymmetric porous channel
- Bond behavior of recycled coarse aggregate concrete with rebar after freeze–thaw cycles: Finite element nonlinear analysis
- Edge detection using nonlinear structure tensor
- Synchronizing a synchronverter to an unbalanced power grid using sequence component decomposition
- Distinguishability criteria of conformable hybrid linear systems
- A new computational investigation to the new exact solutions of (3 + 1)-dimensional WKdV equations via two novel procedures arising in shallow water magnetohydrodynamics
- A passive verses active exposure of mathematical smoking model: A role for optimal and dynamical control
- A new analytical method to simulate the mutual impact of space-time memory indices embedded in (1 + 2)-physical models
- Exploration of peristaltic pumping of Casson fluid flow through a porous peripheral layer in a channel
- Investigation of optimized ELM using Invasive Weed-optimization and Cuckoo-Search optimization
- Analytical analysis for non-homogeneous two-layer functionally graded material
- Investigation of critical load of structures using modified energy method in nonlinear-geometry solid mechanics problems
- Thermal and multi-boiling analysis of a rectangular porous fin: A spectral approach
- The path planning of collision avoidance for an unmanned ship navigating in waterways based on an artificial neural network
- Shear bond and compressive strength of clay stabilised with lime/cement jet grouting and deep mixing: A case of Norvik, Nynäshamn
- Communication
- Results for the heat transfer of a fin with exponential-law temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and power-law temperature-dependent heat transfer coefficients
- Special Issue: Recent trends and emergence of technology in nonlinear engineering and its applications - Part I
- Research on fault detection and identification methods of nonlinear dynamic process based on ICA
- Multi-objective optimization design of steel structure building energy consumption simulation based on genetic algorithm
- Study on modal parameter identification of engineering structures based on nonlinear characteristics
- On-line monitoring of steel ball stamping by mechatronics cold heading equipment based on PVDF polymer sensing material
- Vibration signal acquisition and computer simulation detection of mechanical equipment failure
- Development of a CPU-GPU heterogeneous platform based on a nonlinear parallel algorithm
- A GA-BP neural network for nonlinear time-series forecasting and its application in cigarette sales forecast
- Analysis of radiation effects of semiconductor devices based on numerical simulation Fermi–Dirac
- Design of motion-assisted training control system based on nonlinear mechanics
- Nonlinear discrete system model of tobacco supply chain information
- Performance degradation detection method of aeroengine fuel metering device
- Research on contour feature extraction method of multiple sports images based on nonlinear mechanics
- Design and implementation of Internet-of-Things software monitoring and early warning system based on nonlinear technology
- Application of nonlinear adaptive technology in GPS positioning trajectory of ship navigation
- Real-time control of laboratory information system based on nonlinear programming
- Software engineering defect detection and classification system based on artificial intelligence
- Vibration signal collection and analysis of mechanical equipment failure based on computer simulation detection
- Fractal analysis of retinal vasculature in relation with retinal diseases – an machine learning approach
- Application of programmable logic control in the nonlinear machine automation control using numerical control technology
- Application of nonlinear recursion equation in network security risk detection
- Study on mechanical maintenance method of ballasted track of high-speed railway based on nonlinear discrete element theory
- Optimal control and nonlinear numerical simulation analysis of tunnel rock deformation parameters
- Nonlinear reliability of urban rail transit network connectivity based on computer aided design and topology
- Optimization of target acquisition and sorting for object-finding multi-manipulator based on open MV vision
- Nonlinear numerical simulation of dynamic response of pile site and pile foundation under earthquake
- Research on stability of hydraulic system based on nonlinear PID control
- Design and simulation of vehicle vibration test based on virtual reality technology
- Nonlinear parameter optimization method for high-resolution monitoring of marine environment
- Mobile app for COVID-19 patient education – Development process using the analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation models
- Internet of Things-based smart vehicles design of bio-inspired algorithms using artificial intelligence charging system
- Construction vibration risk assessment of engineering projects based on nonlinear feature algorithm
- Application of third-order nonlinear optical materials in complex crystalline chemical reactions of borates
- Evaluation of LoRa nodes for long-range communication
- Secret information security system in computer network based on Bayesian classification and nonlinear algorithm
- Experimental and simulation research on the difference in motion technology levels based on nonlinear characteristics
- Research on computer 3D image encryption processing based on the nonlinear algorithm
- Outage probability for a multiuser NOMA-based network using energy harvesting relays

