Abstract
Background
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDL), a member of malignant mesenchymal tumors, has a high local recurrence rate and poor prognosis. Pyroptosis, a newly discovered programmed cell death, is tightly connected with the progression and outcome of tumor.
Objective
The aim of this study was to explore the role of pyroptosis in DDL.
Methods
We obtained the RNA sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Genotype-Tissue Expression databases to identify different pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs) expression pattern. An unsupervised method for clustering based on PRGs was performed. Based on the result of cluster analysis, we researched clinical outcomes and immune microenvironment between clusters. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two clusters were used to develop a prognosis model by the LASSO Cox regression method, followed by the performance of functional enrichment analysis and single-sample gene set enrichment analysis. All of the above results were validated in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset.
Results
Forty-one differentially expressed PRGs were found between tumor and normal tissues. A consensus clustering analysis based on PRGs was conducted and classified DDL patients into two clusters. Cluster 2 showed a better outcome, higher immune scores, higher immune cells abundances, and higher expression levels in numerous immune checkpoints. DEGs between clusters were identified. A total of 5 gene signatures was built based on the DEGs and divided all DDL patients of the TCGA cohort into low-risk and high-risk groups. The low-risk group indicates greater inflammatory cell infiltration and better outcome. For external validation, the survival difference and immune landscape between the two risk groups of the GEO cohort were also significant. Receiver operating characteristic curves implied that the risk model could exert its function as an outstanding predictor in predicting DDL patients’ prognoses.
Conclusion
Our findings revealed the clinical implication and key role in tumor immunity of PRGs in DDL. The risk model is a promising predictive tool that could provide a fundamental basis for future studies and individualized immunotherapy.
1 Introduction
Soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) are a series of rare tumors composed of more than 70 histological subtypes [1], accounting for almost 1% of all diagnosed cancers [2]. Liposarcoma, constituting approximately 20% of STSs, is the most common type [3]. Furthermore, the largest subgroup of liposarcoma is divided into dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDL) and well-differentiated liposarcoma (WDL) [4]. Unlike WDL, DDL behaves more aggressively, with significantly higher local recurrence rates (40%), higher metastatic rate (15–30%), and poorer prognosis [5]. DDL is characterized by a high-level amplified chromosomal region 12q13–15, including amplification of MDM2 and CDK4. Retroperitoneum is the most common location of DDL, while it can also occur in extremities and trunk [6]. Within the past decade, systemic treatments including chemotherapy and molecular targeted agents become all the rage, but surgical resection remains the fundamental method of curing DDL [7], whose recurrence and prognosis have not been markedly improved.
Pyroptosis is a highly specific type of inflammatory cell death that is largely dependent on Gasdermin family [8]. Caspase-1 and caspase-4/5/11 cleave gasdermins, which then lead to cell swelling, lysis, and release inflammatory cytokines, thus triggering a strong inflammatory response [9,10,11]. Moderate pyroptosis is conducive to maintaining a stable intracellular environment and effectively preventing excessive proliferation of cells [12]. Pyroptosis also plays a crucial role in multiple tumors. GSDMD, of which the expression was decreased in gastric cancer (GC) cells compared with adjacent normal cells, acts as a tumor suppressor [13]. However, GSDMD can induce invasion and tumor progression in lung cancer [14]. The same dual roles were also observed in other Gasdermin proteins, including GSDME, a molecule that is extensively studied in pyroptosis [15]. The role of pyroptosis in cancer may act as a double-edged sword, as pyroptosis creating an environment that inhibits tumor growth while accelerating tumor growth by weakening the immunity of patients [16,17]. Pyroptosis can also regulate malignant phenotypes and chemotherapy resistance, affecting tumor progression and patients’ prognosis [18]. Several previous studies have confirmed that GSDME-mediated pyroptosis can promote the toxin side effects of chemotherapy [19,20]. Furthermore, GSDME switches caspase-3-dependent apoptosis induced by 5-FU into pyroptosis in GC cells [21].
Although pyroptosis has been observed in a variety of tumors, its potential role in DDL is poorly understood. STSs are deemed to a group of various subtypes, and the treatment and prognosis of each type were different. In clinical work, we have observed that the prognosis of DDL is extremely poor [22], so we hope to investigate the role of pyroptosis in DDL and its impact on patient outcomes and establish a prognostic model related to pyroptosis in DDL to provide help for clinical work and further research. In the present study, with DDL patients divided into two pyroptosis-related subtypes, the prognosis and immune infiltration differed in terms of subtypes. We further established a scoring system through the LASSO-Cox method. This scoring system can be a convincing way to predict prognosis and immune infiltration. Our research marked the dawn of potential association between pyroptosis, the immune microenvironment, and outcomes of DDL patients.
2 Methods
2.1 Data acquisition
RNA sequencing profile of 56 DDL patients of TCGA-SARC and 515 adipose tissues of Genotype-Tissue Expressions cohort were downloaded from the UCSC browser (https://xenabrowser.net) on 12 October 2021. The corresponding clinical data of DDL patients were extracted from the cBioPortal (http://www.cbioportal.org/) (Table 1). The somatic mutation information and copy number variation (CNV) information of DDL were downloaded from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) dataset. The “maftools” package was applied to present the mutation landscape by waterfall plots and calculate the CNV frequency of pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs) by lollipop charts. The location of PRGs with CNV information on chromosomes was presented by the “RCircos” package. We also obtained the gene expression profiling and corresponding clinical information of GSE30929 from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) as a validation cohort, which includes totally 40 DDL patients.
Characteristics of DDL patients
| Characteristic | Overall (N = 56) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| >65 | 25 (44.64%) |
| ≤65 | 31 (55.36%) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 19 (33.93%) |
| Male | 37 (66.07%) |
| Surgical margin | |
| R0 | 24 (42.86%) |
| ≥R1 | 32 (57.14%) |
| Tumor tissue site | |
| Chest | 1 (1.79%) |
| Intraabdominal | 5 (8.93%) |
| Lower extremity | 3 (5.36%) |
| Pelvic | 4 (7.14%) |
| Retroperitoneum | 42 (75.00%) |
| Upper extremity | 1 (1.79%) |
2.2 Construction of pyroptosis-related clusters
We collected totally 52 PRGs those are proved by previous studies [18,23]. The “limma” package was used to identify different expression of PRGs between DDL and adipose tissues. A PPI network for the PRGS was constructed by the online tools on the STRING website (http://string-db.org). We used eight algorithms, namely Bottleneck, EPC, Degree, Cloness, Maximal Clique Centrality, Maximum Neighborhood Component, Density of Maximum Neighborhood Component, and EcCentricity, to calculate the top 10 hub genes using cytoscape. Then, we used “ConsensusClusterPlus” R package to identify distinct patterns based on PRGs by the k-means method. We repeated this process 50 times to ensure our classification’s stability. Then, we also used the “limma” package to obtain differentially expressed genes (DEGs) by comparing the different clusters.
2.3 Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
GSEA was performed using the Java GSEA desktop application. In this study, GSEA v4.1.0 software was used to identify immunological features in clusters. Nominal (NOM) p value <0.05 and false discovery rate <0.05 were considered significant enrichment.
2.4 Gene set variation analysis (GSVA)
GSVA enrichment analysis was performed in heatmap by the use of “GSVA” R packages [24]. “c2.cp.kegg.v7.4.symbols.gmt” and “h.all.v7.4.symbols.gmt” were downloaded from MSigDB. Differences were believed as statistically significant if adjusted p-values <0.05.
2.5 Immune correlation analysis
We used the CIBERSORT algorithm to evaluate 22 human immune cell subsets of each group sample. R software package “ESTIMATE” was used to assess the “Immunescore,” “Stromalscore,” and “Estimatescore” [25]. Single-sample gene-set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) was used to determine the levels of immune cell infiltration in different clusters and risk groups. Furthermore, Quantiseq, Timer, Mcp_counter, and Xcell [26,27] were also used to calculate the prevalence of immune cells in different cluster samples. In addition, we collected information about 122 immunomodulators, including Chemokines, Receptors, MHC, Immunoinhibitor, and Immunostimulants [28,29]. Cancer immunity and anti-cancer immune system response were reflected by analyzing the differential expression of immunomodulators in different clusters.
We also extracted 23 N6-methyladenosine (m6A) regulatory genes (METTL3, METTL14, METTL16, WTAP, VIRMA, ZC3H13, RBM15, RBM15B, YTHDC1, YTHDC2, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, HNRNPC, FMR1, LRPPRC, HNRNPA2B1, IGFBP1, IGFBP2, IGFBP3, RBMX, FTO, ALKBH5) from previous studies [30,31] and compared the different expression levels of these genes in clusters.
2.6 The establishment and validation of the prognostic gene model
In the TCGA cohort, we established an efficient prediction model using LASSO-Cox analysis. Five survival-related genes were used to construct the model, calculating the risk score for each patient. Risk score = (Exp gene1 × coefficient gene1) + (Exp gene2 × coefficient gene2) + ⋯ + (Exp gene5 × coefficient gene5). Fifty-six DDL patients were divided into high- and low-risk groups according to the median risk score, and the Kaplan–Meier analysis of overall survival (OS) time, 1-, 3-, and 5-year receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, principal component analysis (PCA), and t-SNE was performed. Following the same procedure, GSE30929 was used as a testing dataset to calculate the patient’s risk score for external validation.
2.7 Independent prognostic analysis of the risk score
We obtained the DDL patients’ clinical data (age, gender, Surgical Margin) of the TCGA cohort from cBioPortal. These clinical data together with the risk score were analyzed through the univariate and multivariable Cox regression models. Cox regression model was not analyzed in the GEO cohort due to the lack of clinical data.
2.8 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed by R software version 3.6.3. Differences between two groups were assessed by using the Wilcox test. Kaplan–Meier method with a two-sided log-rank test was used to compare the OS of patients between subgroups. LASSO Cox regression analysis was derived by using the “glmnet” packages. Time-dependent ROC curves and the area under curves (AUC) were derived by using the “timeROC” packages. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
-
Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable.
-
Human and animal rights: No animals/humans were used for studies that are the basis of this research.
3 Results
3.1 Expression variation and genetic changes of PRGs in DDL
This study included a total of 52 PRGs, and we found that 41 PRGs were expressed significantly different between cancer and normal tissues (p < 0.005) (Figure 1a). Among them, 18 genes (CHMP4A, GSDMB, PJVK, IL6, CHMP4C, NLRP1, CASP4, NOD1, HMGB1, CASP8, PLCG1, IRF1, CHMP3, SCAF11, GSDMD, GPX4, NLRP2, CHMP2A) were downregulated and 23 genes (PRKACA, PYCARD, BAX, IRF2, CHMP2B, CHMP7, IL1B, NLRP3, CASP6, CHMP4B, CHMP6, TP53, GZMB, GSDMC, CASP3, BAK1, NLRC4, GSDMA, GZMA, IL1A, CASP5, AIM2, NLRP7) were upregulated, we also constructed the PPI network and correlation network containing those different expressed PRGs (Figure 1b and c). Next, we identified hub genes by using the cytoHubba plugin. Ten hub genes (IL1A, IL1B, IL6, CASP3, CASP5, CASP8, AIM2, PYCARD, NLRC4, NLRP) were identified by intersecting the results from the eight algorithms of cytohubba (Figure 1d).

Overview of genetic and expression variation of PRGs in DDL. (a) Heatmap of the PRGs between the normal and the tumor tissues. (b) PPI network showing the interactions of the PRGs. (c) The correlation network of the PRGs (red line: positive correlation; blue line: negative correlation). (d) UpSet plot shows the hub genes from the eight algorithms of cytohubba. (e) The mutation frequency of PRGs in DDL patients from the TCGA dataset. Numbers on the right represent frequencies. Different colors in the bottom annotation represent different mutation types. (f) Frequencies of CNV gain, loss, and non-CNV among PRGs. (g) Locations of CNV alterations in PRGs on 23 chromosomes. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
At the genetic level, 6 of the 45 DDL samples (about 13.33%) showed PRG mutations, and TP53 showing the highest frequency (9%), followed by CHMP4B and GSDMC (Figure 1e). Then, we explored somatic copy number alterations in these PRGs and found that PRGs displayed prevalent CNV alterations (Figure 1f). The locations of the CNV alterations on chromosomes are shown in Figure 1g.
3.2 Immune infiltration analyses between DDL and controls
CIBERSORT was applied to explore the features of totally 22 types of immune cells’ distribution in DDL samples. The corheatmap (Figure 2a) result showed that Neutrophils and Mast cells activated had a positive correlation (value = 0.55). Mast cells resting had a negative correlation with Mast cells activated (value = −0.56). Except for B cells naive, plasma cells, macrophage M0, macrophage M2, and eosinophil immune cells, the remaining 17 immune cells are infiltrated statistically less or more in DDL compared with the adipose group (Figure 2b). PCA depicted no overlap of these two elliptical clusters in immune cell infiltration between the DDL and control groups (Figure 2c).
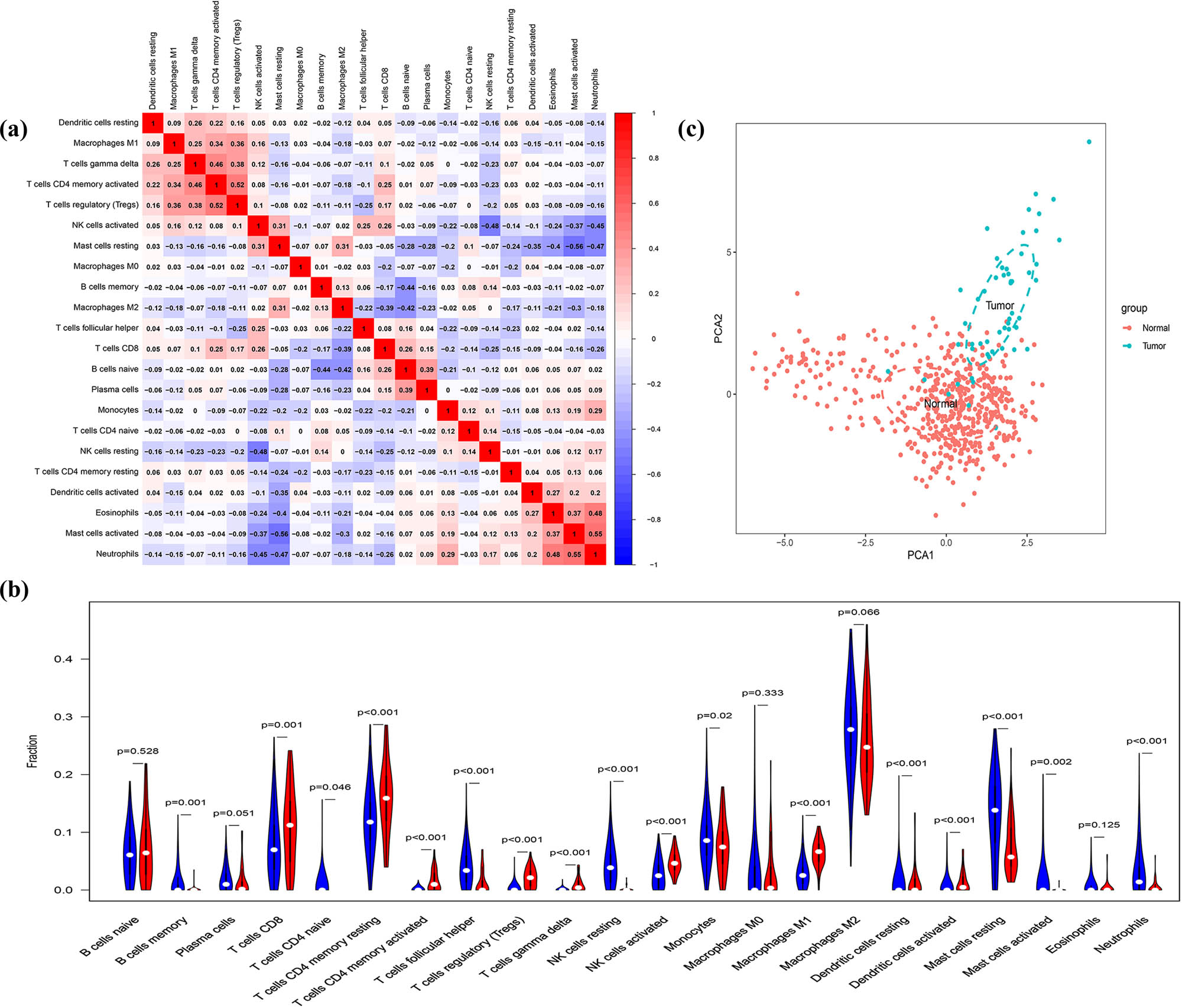
Results of CIBERSORT analysis and immune infiltration between DDL and adipose groups. (a) Correlation matrix of infiltration degree of immune cells in DDL samples. Red indicates trends consistent with the positive correlation and blue indicates trends consistent with the negative correlation between two immune cells. The bigger size of the numbers statistics data represents the more positive or negative correlation. (b) Violin diagram of immune cell proportions in two groups. The blue fusiform fractions on the left represent the adipose group and the red fusiform fractions on the right represent the DDL group. (c) PCA was performed in two groups.
3.3 PRG-related clusters identified in DDL
We used the R package “ConsensusClusterPlus” to cluster TCGA DDL patients according to the expression level of 52 PRG quantities and ultimately identified 2 clusters. Cluster 1 consisted of 21 samples, while cluster 2 was composed of 35 samples, respectively (Figure 3a). Subsequently, a survival analysis was performed and showed that the prognosis of cluster 2 was remarkably better than cluster 1 (Figure 3b). Ten PRGS (NOD2, NLRC4, IL18, NLRP3, GSDMA, CASP5, AIM2, GZMB, IL1B, IL6), expressed notably different between two clusters, were all upregulated in cluster 2 (Figure 3c). To explore the differences in biological behavior between two clusters, a GSVA enrichment analysis was performed. The results revealed (Figure 4a) that all pathways were enriched in cluster 2 and some were associated with immune activation, including antigen processing and presentation, B-cell receptor signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, and Toll-like receptor signaling. Moreover, considerable differences in these pathways were confirmed by GSEA (NOM p-value < 0.05, |NES| > 1). However, the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway and thyroid cancer were enriched in cluster 1 (Figure 4b).

Tumor classification based on the PRGs. (a) DDL patients were divided into two clusters by the consensus clustering matrix (k = 2). (b) Kaplan–Meier curves for the OS of these two clusters. (c) Heatmap and the clinicopathologic characters of the two clusters classified by these differentially expressed PRGs.
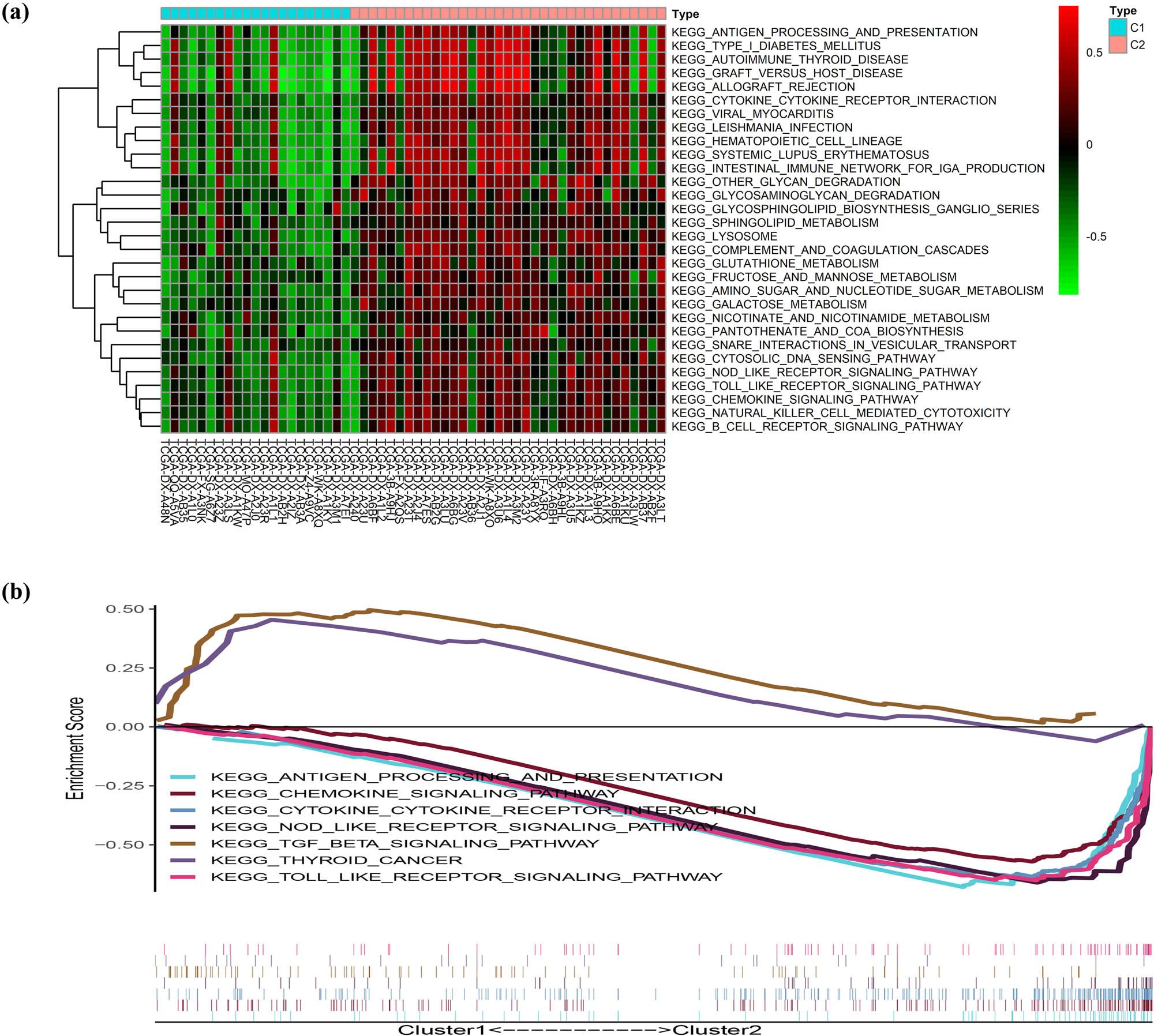
The differences in biological features in pyroptosis-associated clusters. (a) The results of a GSVA enrichment analysis. (b) The results of a GSEA.
3.4 Characteristics of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in distinct clusters
The results of GSVA and GSEA all suggest that PRG-related clusters may have a different immune status in DDLs. We first explored the various immune markers’ expression in different clusters, which included immune stimulatory or inhibitory genes, chemokine, chemokine receptors, and MHC genes. We found that 70 of 122 immune markers expressed differently in subcluster (Figure S1). In Figure 5a, we showed the significantly expressed immune markers, and most of MHC complex and part of chemokines and chemokine receptors were more highly expressed in cluster 2, including CXCL6, CXCL14, and CXCL12, which attracted dendritic cells (DCs) and CD8+ T cells and promote immune cell migration. Next, we used Timer, Cibersort, Quantiseq, Xcell, Epic, and Mcp_counter to calculate the level of immune cell infiltration in DDL samples. Additionally, more infiltration of T cells, cytotoxic lymphocytes, neutrophil, and macrophage was found in cluster 2 (Figure 5b).
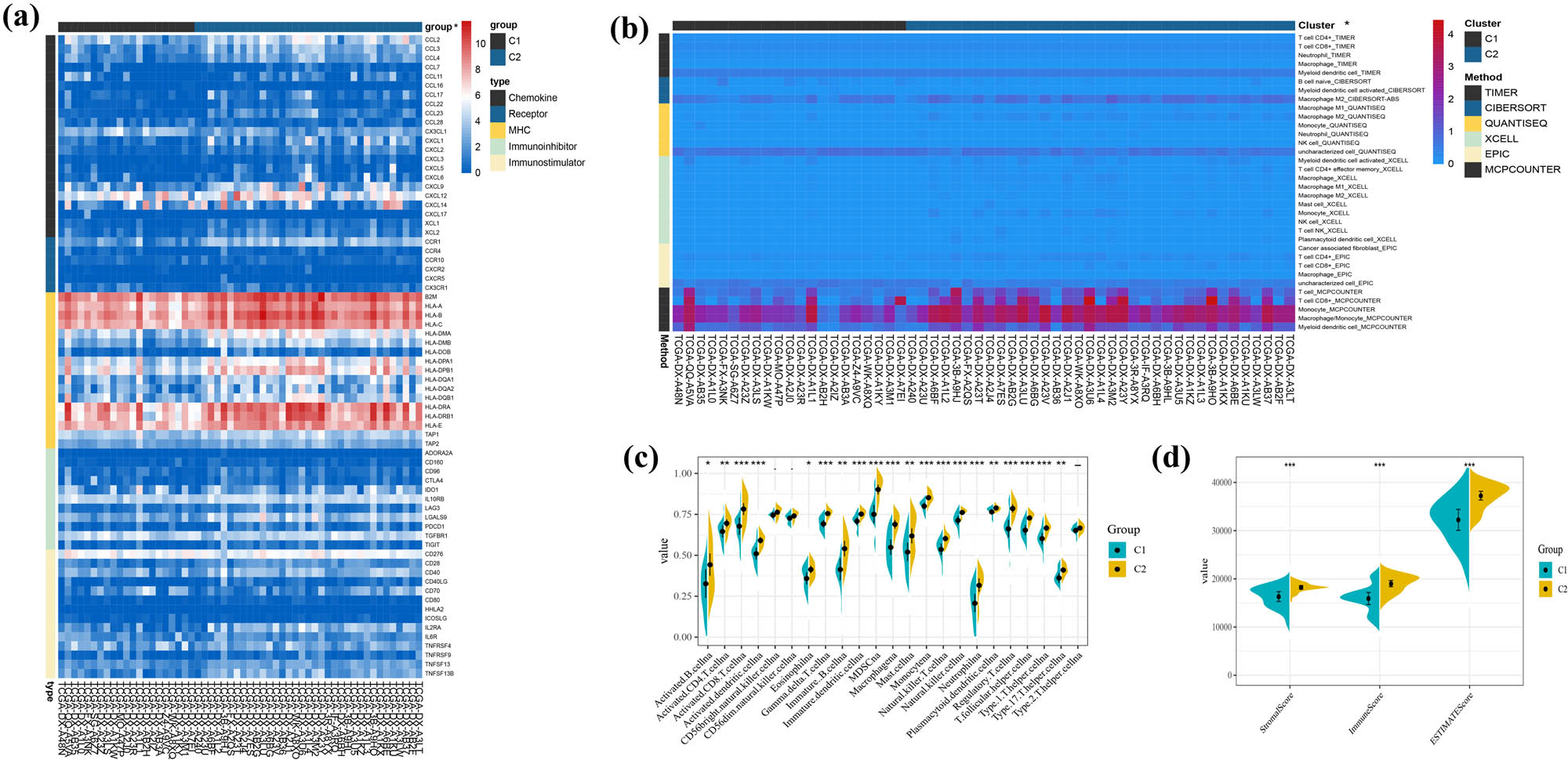
Variations in immune-related genes and the infiltration characteristics of TME cells in the pyroptosis-related clusters. (a) The thermogram shows variations in mRNA expression of chemokines, interleukins, alterons, and other cytokines among the two clusters. *p < 0.05. (b) The thermogram shows the frequency of TME-infiltrating cells among the two clusters. *p < 0.05. (c) The results of ssGSEA scores among the two clusters. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (d) Correlations between the two clusters and TME score. ***p < 0.001.
We further applied ssGSEA to make a comparison of the enrichment scores of immune cells between subclusters. Through ssGSEA, we have observed significant differences in the infiltration of most immune cells between cluster 1 and cluster 2, except for NK cells and Th2 cells. The level of immune cells’ infiltration in cluster 2 was significantly higher than in cluster 1 (Figure 5c). Otherwise, we evaluated the TME score of each cluster by using the ESTIMATE package. Just as Figure 5d shows, the StromalScore, ImmuneScore, and ESTIMATEScore of cluster 2 were significantly higher than cluster 1.
As one of the most common RNA modifications, M6A plays a role in regulating the initiation and progression of cancer. We also analyzed the expression levels of m6A regulatory genes in different clusters (Figure 6a). More expression of METTL16, ZC3H13, YTHDC1, YTHDC2, and FMR1 was found in cluster 1, while higher expression levels of WTAP, YTHDF2, HNRNPC, HNRNPA2B1, and ALKBH5 were found in cluster 2. With the use of checkpoint inhibitors, Immunotherapy is in full swing nowadays, prolonging patients’ survival in many types of tumors. We found immune checkpoint genes were expressed impressively different in clusters, including HAVCR2 (p < 0.001), PDCD1 (p < 0.05), PDCD1LG2 (p < 0.001), TIGIT (p < 0.05), SIGLEC15 (p < 0.05), BTN2A1 (p < 0.05), BTN3A2 (p < 0.05), CD209 (p < 0.001), CD28 (p < 0.001), and CD40 (p < 0.05) (Figure 6b), which indicated that these two clusters may respond differently to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
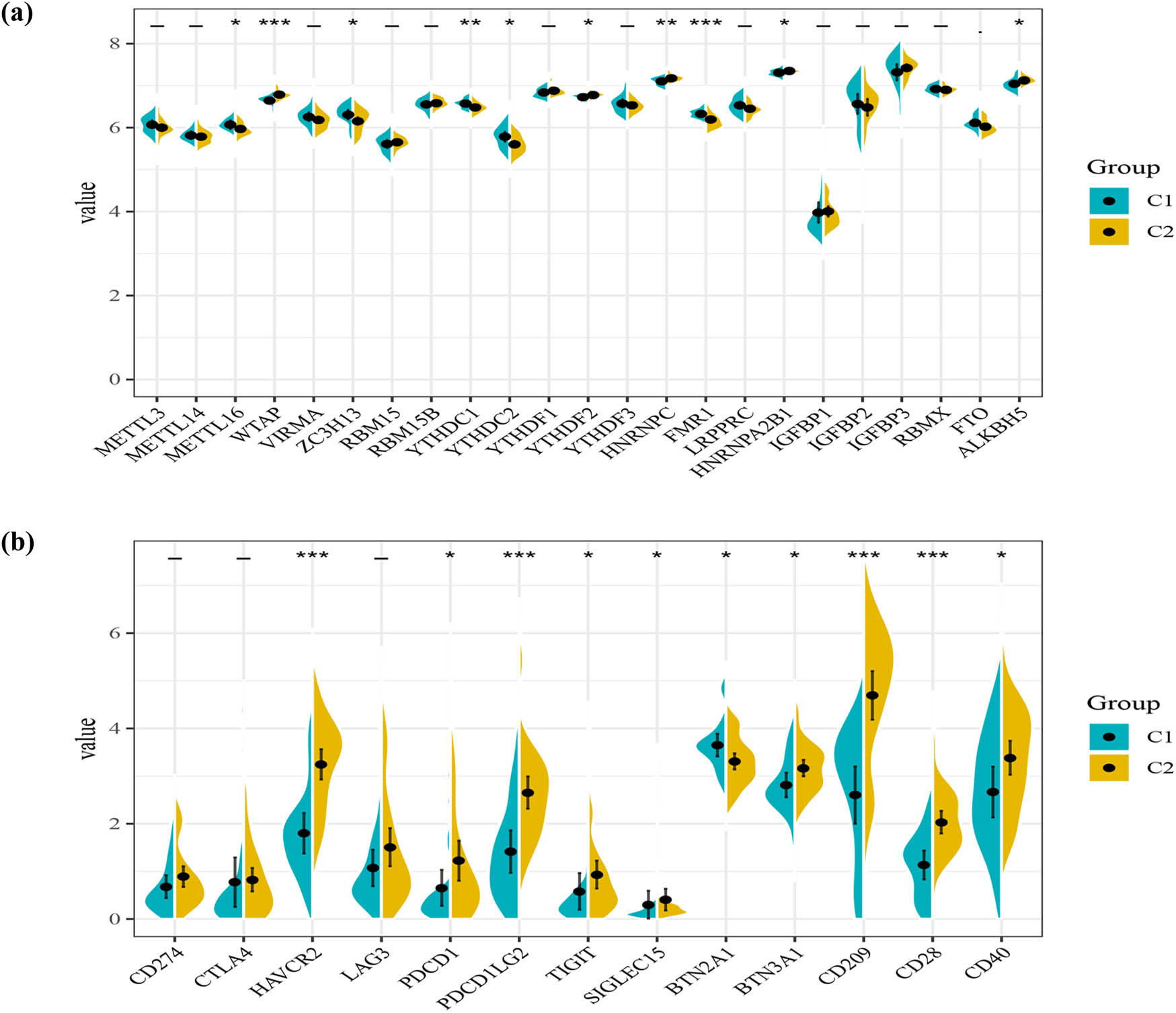
The relationship between clusters and m6A regulators and immune checkpoints. (a) Differences in expression of m6A regulators among the two clusters. (b) Differences in expression of immune checkpoint blockade genes among the two clusters. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
3.5 Development of a prognostic gene model based on pyroptosis-related clusters
For the better application of pyroptosis-related clusters in the treatment of DDL, we built a model that referred to the different genes between the two clusters next. A total of 1463 DEGs were identified, with an absolute value of |log2FC| ≥ 0.585 and p < 0.05 (Figure 7a). Seventy-seven genes were identified by univariate Cox regression analysis and all of those genes were regarded as survival-related genes (Figure 7b). By performing the LASSO-Cox regression analysis, a five-gene signature was constructed according to the optimum λ value (Figure S2a and b). We used these to build a risk score = (0.212 × SHROOM2) + (−0.403 × TTC12) + (−0.11 × IGF1) + (−0.027 × NAALADL1) + (−0.308 × SLC22A18AS). Then, 56 DDL patients were divided into low- and high-risk groups according to the median score (−2.25) (Figure 7c). The PCA and t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) showed that patients separated into two clusters showed different risks (Figure S2c and d). High-risk patients have a shorter survival time, just as Figure 7d and e proved. We applied time-dependent ROC analysis to evaluate the prognostic model’s specificity and sensitivity, and we found that the 1-year AUC was 0.747, 3-year AUC was 0.859, and the 5-year AUC was 0.920, respectively (Figure 7f). Then, we combined the risk score with age, gender, and Surgical Margin to stepwise Cox regression analysis. The results of univariate and multivariable Cox regression analyses consistently implied that risk score was an independent prognostic factor (Figure 8a and b). The alluvial diagram (Figure 8c) illustrated the distribution of patients in the two pyroptosis subclusters and two risk groups with clinical message. Most low-risk patients belonged to cluster 2 had a better prognosis. The decision curve analysis results and nomogram are shown in Figure S3.
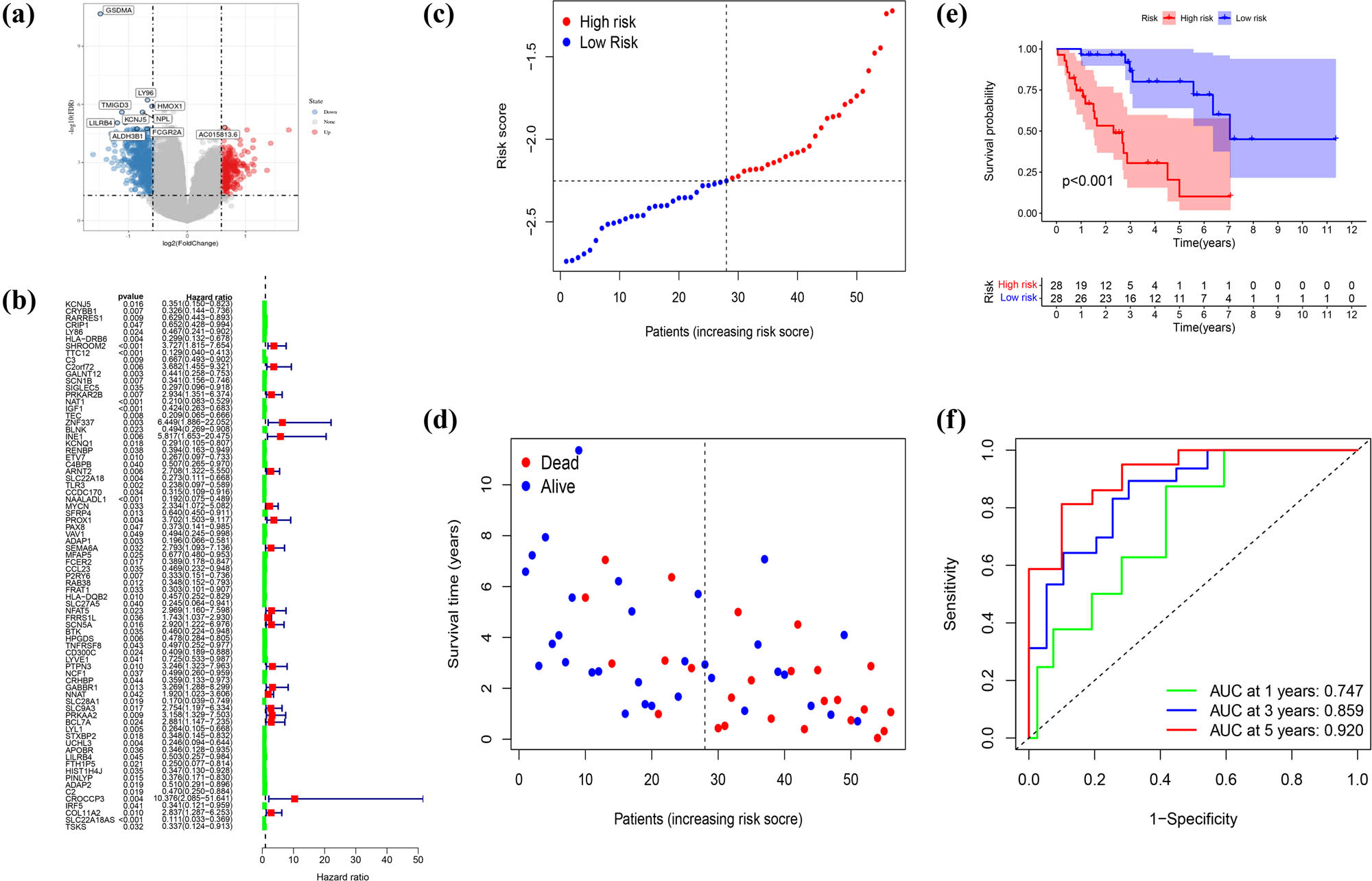
Generation of a gene expression signature to predict patient survival based on pyroptosis-related clusters in the TCGA cohort. (a) An overview of the differential gene expression between the two pyroptosis-related clusters in TCGA cohorts. (b) Univariate Cox regression analysis of OS in TCGA cohorts. (c) Distribution of patients based on the risk score. (d) The survival status for each patient (low-risk population: on the left side of the dotted line; high-risk population: on the right side of the dotted line). (e) Kaplan–Meier curves for the OS of patients in the high- and low-risk groups. (f) ROC curves demonstrated the predictive efficiency of the risk score.

Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses for the risk score. (a) Univariate analyses for the TCGA cohort. (b) Multivariate analysis for the TCGA cohort. (c) Heatmap for the connections between clinicopathologic features and the risk groups. (d) Alluvial diagram showing the changes in the age, gender, surgical margin, risk group, and pyroptosis-related clusters.
3.6 External validation of the risk signature
A validation cohort was set based on the data of 40 DDL patients from GEO database. Seventeen patients made up the low-risk group, and 23 patients composed the high-risk group, respectively (Figure 9a). Patients were well divided into two clusters through PCA and t-SNE analysis (Figure 9b and c), and patients in the low-risk group had a clear survival advantage over the high-risk group (Figure 9d). Moreover, Kaplan–Meier analysis also showed significant differences in the survival between the high-risk and low-risk groups (p = 0.01, Figure 9e). We further proved that the prognosis model was a good indicator for the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival, and AUC was 0.782, 0.683, and 0.807 separately (Figure 9f).
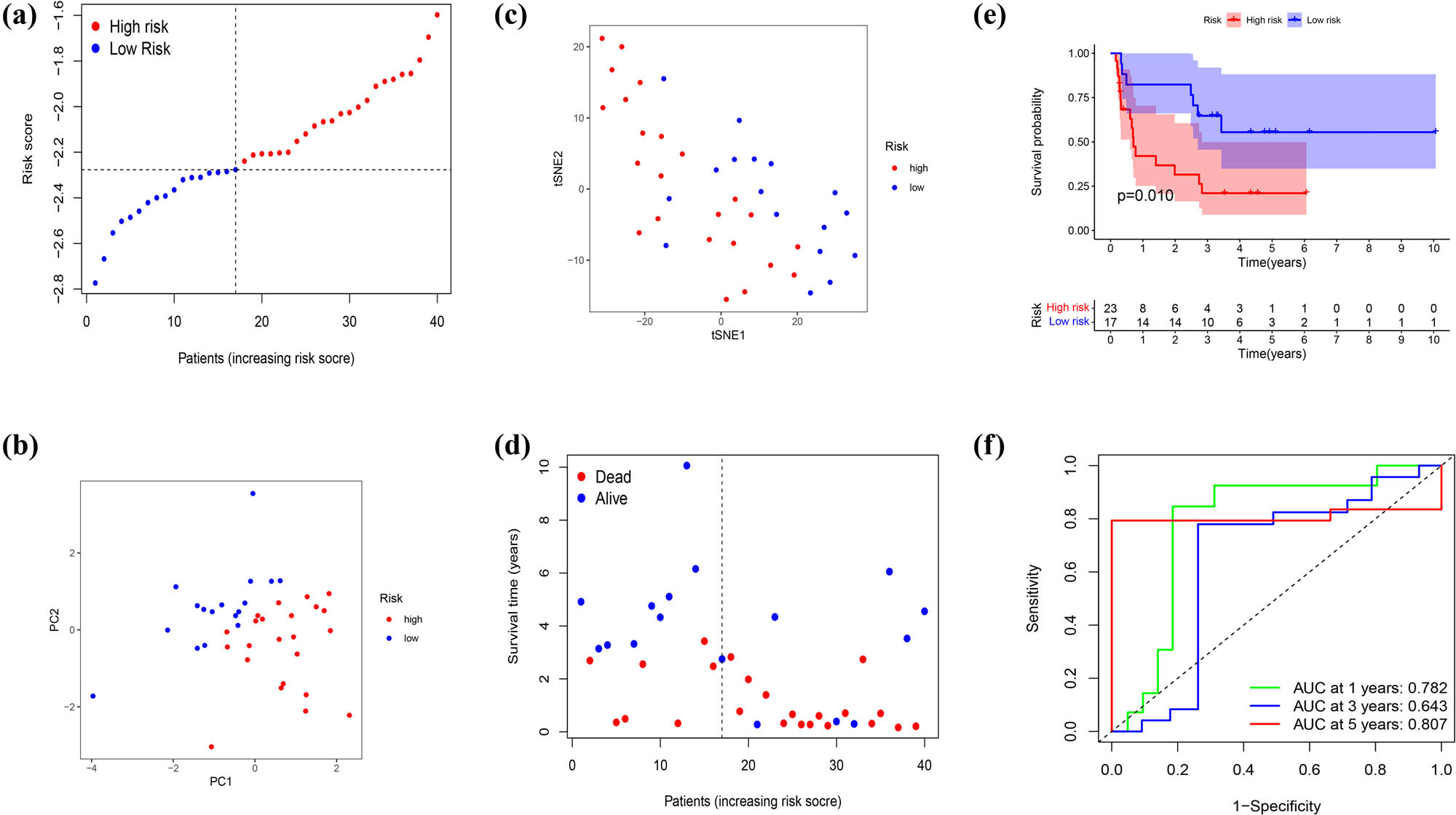
Validation of the risk model in the GEO cohort. (a) Distribution of patients in the GEO cohort based on the median risk score in the TCGA cohort. (b) PCA plot for DDL patients in the GEO cohort. (c) t-SNE plot for DDL patients in the GEO cohort based on the risk score. (d) The survival status for each patient (low-risk population: on the left side of the dotted line; high-risk population: on the right side of the dotted line). (e) Kaplan–Meier curves for comparison of the OS between the low- and high-risk groups. (f) Time-dependent ROC curves in the GEO cohort.
3.7 Functional analyses of risk model
To explore the differences in pathways and gene functions between the high-risk and low-risk groups in the TCGA cohort, the “limma” R package was used, and finally, 67 DEGs were screened out. In the high-risk group, there were 9 genes upregulated and 58 genes downregulated. Complement and coagulation cascades, chemokine signaling pathway, and Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis were enriched in KEGG pathways (Figure 10a). The top five most enriched GO-biological process terms were as follows: regulation of inflammatory response, neutrophil activation, humoral immune response, humoral immune response, regulation of immune effector process, acute inflammatory response, and humoral immune response (Figure 10b). The results of GO-cellular component and molecular function are shown in Figure S4. These results indicated that the DEGs were mainly correlated with the immune response and inflammation.
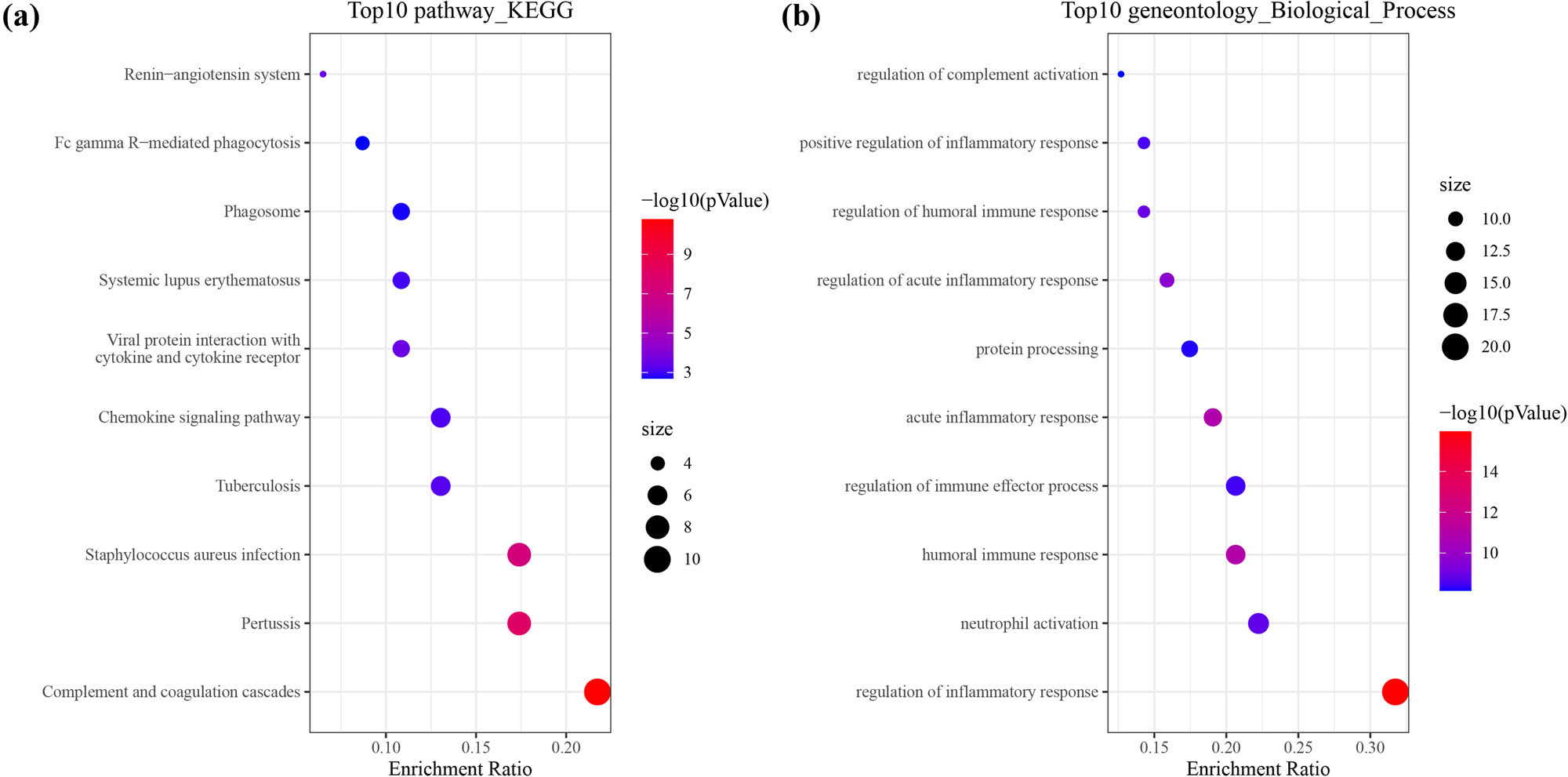
Functional analysis based on the DEGs between the two-risk groups in the TCGA cohort. (a) Bubble graph for KEGG pathways. (b) Bubble graph for GO-biological process enrichment. The bigger bubble means the more genes enriched, and the increasing depth of red means the differences were more obvious.
3.8 Evaluation of the TME and immune activity between the high- and low-risk groups
Based on the KEGG and GO analyses, we can detect the different immune status in high- and low-risk groups. We first performed ESTIMATE to evaluate the immune environment. As shown in Figure S5, Immunesocre and ESTIMATEScore of the low-risk group were significantly higher than the high-risk group, no matter in TCGA or GEO cohorts. Then, the enrichment scores of 16 types of immune cells and the activity of 13 immune-related pathways were further compared by ssGSEA. We can observe most of the immune cells less infiltrated in the high-risk group in TCGA and GEO cohorts (Figure 11a and b), especially of DCs, T helper cells, T helper (Th) 1 cells (th1 cells), and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Aside from APC co-stimulation, MHC-class-Itype-2, IFN response pathway, and the other 10 immune pathways showed lower activity in the high-risk group than in the low-risk group in the TCGA cohort (Figure 11c). The analysis of the GEO cohort disclosed similar results (Figure 11d). Though Timer, Cibersort, Quantiseq, Xcell, Epic, and Mcp_counter to evaluate the immune cell infiltration level between low-risk and high-risk groups, we found T cells, B cells, and macrophage cells were infiltrated more in low-risk samples in the TCGA cohort (Figure S6). All results together suggested that the high-risk group is in a state of immunosuppression.

Comparison of the ssGSEA scores for immune cells and immune pathways. (a and c) Comparison of the enrichment scores of 16 types of immune cells and 13 immune-related pathways between the low- (blue box) and high-risk (red box) groups in the TCGA cohort. (b and d) Comparison of the tumor immunity between the low- (blue box) and high-risk (red box) groups in the GEO cohort. p values were shown as follows: ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p<0.01; ***p < 0.001.
4 Discussion
Inflammation is a recognized hallmark of cancer that substantially contributes to the tumorigenesis and progression of malignancies [32]. Pyroptosis, known as an inflammation-related way of programmed cell death, can be triggered by long-term exposure of tissues or cells to the inflammatory environment. Wang et al. [33] reported that alcohol accumulation could promote esophagitis through active pyroptosis and release of IL-18 and IL-1β in esophageal epithelial cells. Furthermore, caspase-1-derived pyroptosis was associated with esophageal cancer. Chen et al. [34] found that NEK7–NLRP3 interaction modulated the pyroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). With increased expression in IBD, GSDMB can regulate epithelial repair [35]. As we know, IBD increases the risk of severe diseases like colon cancer [36]. However, pyroptosis plays a different role in cancers. It can be a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer [17] and skin cancer [37]. lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 can inhibit GC cell viability by activating NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis [38]. Decreased GSDME is related to lymph node metastasis and worse prognosis in breast cancer [39], but GSDMB can be a tumor promoter that induces invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells [40]. Just as those researchers have proven, pyroptosis acts as a “double-edged sword” in cancer so that we cannot evaluate the prognostic value of these gasdermins in tumors based on their expression alone.
DDL is the worst type of STS with aggressive clinical behavior, high recurrence rates, and the trend for metastasis. In recent decades, chemotherapy and target therapy have made progress in DDL. Anthracycline-based therapy is still the standard treatment for DDL [7,22,41], but recent literature suggests that eribulin [42], trabectedin [43], and pazopanib [44] may also benefit DDL patients. Since DDL highly expression of MDM2 and CDK4, the clinical trials about MDM2-targeted therapy and CDK4-targeted therapy have been conducted and demonstrated the clinical benefits and toxicity [45,46]. With the rise of immunotherapy, multicenter trials about immune-checkpoint inhibitors such as nivolumab and pembrolizumab were launched and exhibited clinical benefits [47,48]. However, the precise role of these agents remains to be elucidated, and the efficacy is still limited. The search for the new target remains imperative work for DDL patients.
TME can influence the tumor development and progression [49]. TILs were considered prognosis-related agents in numerous cancers [50]. Through the analysis of immune cell infiltration in the DDL group and the adipose group, we found that the proportion of T-cell CD8, T-cell CD4, NK cells activated, macrophages, and DC cells activated was lower in DDL tissues, which may indicate that DDL patients were in a state of immunosuppression. Emerging evidence unveils the possible association between pyroptosis and the tumor immune microenvironment [51,52]. We separated DDL patients into two completely different clusters on the ground of 52 PRGs. Our results show: (1) most PRGs showed high expression in cluster 2 and (2) cluster 2 showed a better prognosis. We also observed that expression of IL-6 and IL-18 was significantly increased in cluster 2, uncovering that cluster 2 exhibits a dramatic response of inflammatory, which is possibly mediated by pyroptosis. We further analyzed the differences of immune state in clusters. As we know, TME includes fibroblasts, immune cells, diffusible cytokines, and chemokines secreted from cancer. In our results, most of MHC complex, chemokines, and chemokine receptors were more highly expressed in cluster 2, T cells, cytotoxic lymphocytes, neutrophil, and macrophage were infiltrated more in cluster 2, and stromal score, immune score, and estimate score were higher in cluster 2. The cluster 2 was also characterized by a significant immune activation, including antigen processing and presentation, B-cell receptor signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Our study indicates that the higher infiltrating immune cells and stronger immune activation in DDL are related to a better prognosis, and pyroptosis levels were closely related to TME.
In the era of immunotherapy, positive expression of immune checkpoint molecular has been the criteria for the eligible patients. Patients with high expression of PD-L1 are generally more sensitive to immunotherapy [53]. Park et al. reported that 21.9% (7/32) of the DDL patients were PD-L1 positive [54]. Tawbi et al. also reported that the expression level of PD-L1 was increased dramatically in DDL compared with other types of STS [47]. These studies suggest the possibility of immunotherapy to treat advanced DDL. However, only a few DDL patients manifest effective response to immunotherapy, suggesting that additional strategies are needed to promote anti-tumor immunity. We found higher expression of immune checkpoint molecular in cluster 2, and pyroptosis can lead to activation of DCs and macrophages in tumor to better present tumor antigens, secrete cytokines and chemokines, enhancing T-cell recruitment and activation, so we speculate that the group of DDL patients with high expression PRGs may more fit the immunotherapy.
A wide variety of prognosis-correlated models have been built in multiple cancer types to facilitate tumor management and treatment. Considering the crucial role pyroptosis plays in the patients’ outcome and immune regulation of DDL, it is essential to establish a scoring system to evaluate the clinical outcome linked with pyroptosis in DDL patients. To make a better application in clinical works, we built a model to value the prognostic risk on the base of DEGs between the two pyroptosis-related clusters. Our study generated five signature featuring genes (SHROOM2, TTC12, IGF1, NAALADL1, SLC22A18AS) and found that they could provide benefits for clinical management and predict survival in DDL patients. IGF1, a member of the insulin superfamily, is an important regulator of tissue growth and development and is linked to the development of numerous cancers [55,56]. IGF/IGF1R was reported as an independent predictor of the malignant potential of adult STS [57]. SHROOM2 has been considered to be the carcinogenesis of colorectal cancer and esophageal squamous carcinoma [58,59]. Our risk model linked prognosis with pyroptosis but was not limited to PRGs. Moreover, this model represented DDL patients with various clinical traits and was linked to immunomodulation. The high-risk group presented a worse outcome. Chen et al. reported that positive surgical margin was an independent predictor of poor OS in primary retroperitoneal liposarcoma [60]. However, the results of other studies show that the surgical margin was only associated with DDL local recurrence-free survival, rather than the OS [61]. And our risk model casts better light on patient outcomes than surgical margins. Furthermore, immune infiltrated cells and TME score in the high-risk group were weightless, exhibiting a wide disorder of immune functions, which was verified by GEO datasets.
In our investigation, it has been observed that both cluster 1 identified through PRGs and the high-risk group established based on key genes exhibit pronounced immunosuppressive status and inferior prognostic outcomes. Numerous studies have already established a correlation between immunosuppression and adverse prognosis in tumors [62]. Patients with immunosuppressive tumor status typically demonstrate reduced immune cell infiltration, higher tumor grading and staging, elevated rates of recurrence and metastasis, as well as poorer survival rates [63]. Furthermore, immunosuppression can also impact the tumor’s sensitivity to immune therapies, diminishing its responsiveness to immunotherapeutic agents such as immune checkpoint inhibitors [64]. Understanding the influence of tumor immunosuppression on prognosis aids in guiding tumor treatment choices and optimization, with the aim of enhancing patient outcomes and survival rates [65,66]. For the high-risk group, strategies such as inhibiting immune suppressive factors, enhancing immune cell functionality, and rectifying immune evasion mutations can be employed to ameliorate the tumor’s immune response. As for the low-risk group identified by the model, exploration of immune therapies may potentially yield greater clinical benefits.
Overall, with multi-perspective and cross-validation of the database, our study classifies DDL patients into clusters, identifies DEGs, and builds a prognostic model, suggesting that pyroptosis is bound up with DDL. The development of our model enables the categorization of patients with DDL and facilitates targeted therapeutic interventions. Through the discovery of novel biomarkers, this model assists in the diagnosis, prognostic evaluation, and therapeutic monitoring of diseases, leading to the provision of more accurate and reliable clinical information. However, our study has several limitations that are worth considering. First, all data are from public databases, further research in vitro and in vivo experiments are needed for better evaluation. Second, data on some important clinical variables such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy were not available in our database. Our study is the first bioinformatics study dedicated to pyroptosis in DDL, and our findings emphasized the crucial clinical implications of pyroptosis-related genes and provided new strategies for personalized therapy, including immunotherapy, in patients with DDL.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge TCGA and GEO for providing their platforms and contributors for uploading their meaningful datasets.
-
Funding information: This study was supported by the Wenzhou Basic Scientific Research Projects (No. Y20210941).
-
Author contributions: Wenjing Chen: conceptualization, methodology, writing – original draft. Jun Cheng: software, visualization. Yiqi Cai: analyzed and interpreted the data. Pengfei Wang: review & editing. Jinji Jin: project administration.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
-
Data availability statement: The data and supportive information are available within the article.
References
[1] Brennan MF, Antonescu CR, Moraco N, Singer S. Lessons learned from the study of 10,000 patients with soft tissue sarcoma. Ann Surg. 2014;260:416–21. discussion 421–12.10.1097/SLA.0000000000000869Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.10.3322/caac.21660Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Thway K. Well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma: An updated review. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019;36:112–21.10.1053/j.semdp.2019.02.006Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Lee ATJ, Thway K, Huang PH, Jones RL. Clinical and molecular spectrum of liposarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:151–9.10.1200/JCO.2017.74.9598Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Thway K, Jones RL, Noujaim J, Zaidi S, Miah AB, Fisher C. Dedifferentiated liposarcoma: Updates on morphology, genetics, and therapeutic strategies. Adv Anat Pathol. 2016;23:30–40.10.1097/PAP.0000000000000101Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Crago AM, Dickson MA. Liposarcoma: Multimodality management and future targeted therapies. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:761–73.10.1016/j.soc.2016.05.007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Gahvari Z, Parkes A. Dedifferentiated liposarcoma: Systemic therapy options. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2020;21:15.10.1007/s11864-020-0705-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Shi J, Gao W, Shao F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42:245–54.10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Xia S, Kong Q, Li S, Liu X, et al. Gasdermin E suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2020;579:415–20.10.1038/s41586-020-2071-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Zhou Z, He H, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Su Y, et al. Granzyme A from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells. Science. 2020;368:6469.10.1126/science.aaz7548Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Broz P, Pelegrin P, Shao F. The gasdermins, a protein family executing cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:143–57.10.1038/s41577-019-0228-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Aglietti RA, Dueber EC. Recent insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis and gasdermin family functions. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:261–71.10.1016/j.it.2017.01.003Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Wang WJ, Chen D, Jiang MZ, Xu B, Li XW, Chu Y, et al. Downregulation of gasdermin D promotes gastric cancer proliferation by regulating cell cycle-related proteins. J Dig Dis. 2018;19:74–83.10.1111/1751-2980.12576Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Gao J, Qiu X, Xi G, Liu H, Zhang F, Lv T, et al. Downregulation of GSDMD attenuates tumor proliferation via the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and inhibition of EGFR/Akt signaling and predicts a good prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2018;40:1971–84.10.3892/or.2018.6634Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Wang YY, Liu XL, Zhao R. Induction of Pyroptosis and Its Implications in Cancer Management. Front Oncol. 2019;9:971.10.3389/fonc.2019.00971Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Chen LC, Wang LJ, Tsang NM, Ojcius DM, Chen CC, Ouyang CN, et al. Tumour inflammasome-derived IL-1beta recruits neutrophils and improves local recurrence-free survival in EBV-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:1276–93.10.1002/emmm.201201569Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Zaki MH, Vogel P, Body-Malapel M, Lamkanfi M, Kanneganti TD. IL-18 production downstream of the Nlrp3 inflammasome confers protection against colorectal tumor formation. J Immunol. 2010;185:4912–20.10.4049/jimmunol.1002046Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Xia X, Wang X, Cheng Z, Qin W, Lei L, Jiang J, et al. The role of pyroptosis in cancer: pro-cancer or pro-“host”? Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:650.10.1038/s41419-019-1883-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Wang Y, Gao W, Shi X, Ding J, Liu W, He H, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547:99–103.10.1038/nature22393Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Yu X, He S. GSDME as an executioner of chemotherapy-induced cell death. Sci China Life Sci. 2017;60:1291–4.10.1007/s11427-017-9142-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Wang Y, Yin B, Li D, Wang G, Han X, Sun X. GSDME mediates caspase-3-dependent pyroptosis in gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495:1418–25.10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.156Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Nishio J, Nakayama S, Nabeshima K, Yamamoto T. Biology and management of dedifferentiated liposarcoma: State of the art and perspectives. J Clin Med. 2021;10.10.3390/jcm10153230Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Ye Y, Dai Q, Qi H. A novel defined pyroptosis-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:71.10.1038/s41420-021-00451-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Hanzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinforma. 2013;14:7.10.1186/1471-2105-14-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2612.10.1038/ncomms3612Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Aran D, Hu Z, Butte AJ. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017;18:220.10.1186/s13059-017-1349-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Finotello F, Mayer C, Plattner C, Laschober G, Rieder D, Hackl H, et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med. 2019;11:34.10.1186/s13073-019-0655-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M, Mayer C, Efremova M, Rieder D, et al. Pan-cancer immunogenomic analyses reveal genotype-immunophenotype relationships and predictors of response to checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep. 2017;18:248–62.10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Xiao Y, Ma D, Zhao S, Suo C, Shi J, Xue MZ, et al. Multi-omics profiling reveals distinct microenvironment characterization and suggests immune escape mechanisms of triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:5002–14.10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3524Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Feng ZY, Gao HY, Feng TD. Immune infiltrates of m(6)A RNA methylation-related lncRNAs and identification of PD-L1 in patients with primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:672248.10.3389/fcell.2021.672248Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Wang W, Shao F, Yang X, Wang J, Zhu R, Yang Y, et al. METTL3 promotes tumour development by decreasing APC expression mediated by APC mRNA N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent YTHDF binding. Nat Commun. 2021;12:3803.10.1038/s41467-021-24860-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e493–503.10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70263-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Wang F, Li G, Ning J, Chen L, Xu H, Kong X, et al. Alcohol accumulation promotes esophagitis via pyroptosis activation. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14:1245–55.10.7150/ijbs.24347Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Chen X, Liu G, Yuan Y, Wu G, Wang S, Yuan L. NEK7 interacts with NLRP3 to modulate the pyroptosis in inflammatory bowel disease via NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:906.10.1038/s41419-019-2157-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Rana N, Privitera G, Kondolf HC, Bulek K, Lechuga S, De Salvo C, et al. GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis. Cell. 2022;185:283–98.10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.024Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Shah SC, Itzkowitz SH. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: Mechanisms and management. Gastroenterology. 2021;162:715–30.10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.035Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Ellis LZ, Liu W, Luo Y, Okamoto M, Qu D, Dunn JH, et al. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses melanoma growth by inhibiting inflammasome and IL-1beta secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414:551–6.10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.115Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Ren N, Jiang T, Wang C, Xie S, Xing Y, Piao D, et al. LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 inhibits gastric cancer (GC) development and sensitizes chemoresistant GC cells to cisplatin by regulating miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:11025–41.10.18632/aging.103314Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Croes L, de Beeck KO, Pauwels P, Vanden Berghe W, Peeters M, Fransen E, et al. DFNA5 promoter methylation a marker for breast tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:31948–58.10.18632/oncotarget.16654Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Hergueta-Redondo M, Sarrió D, Molina-Crespo Á, Megias D, Mota A, Rojo-Sebastian A, et al. Gasdermin-B promotes invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90099.10.1371/journal.pone.0090099Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Judson I, Verweij J, Gelderblom H, Hartmann JT, Schöffski P, Blay JY, et al. Doxorubicin alone versus intensified doxorubicin plus ifosfamide for first-line treatment of advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma: a randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:415–23.10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70063-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Demetri GD, Schöffski P, Grignani G, Blay JY, Maki RG, Van Tine BA, et al. Activity of eribulin in patients with advanced liposarcoma demonstrated in a subgroup analysis from a randomized phase III study of eribulin versus dacarbazine. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3433–9.10.1200/JCO.2016.71.6605Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Jones RL, Hensley ML, Schuetze SM, Staddon A, et al. Efficacy and safety of trabectedin or dacarbazine for metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma after failure of conventional chemotherapy: Results of a phase III randomized multicenter clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:786–93.10.1200/JCO.2015.62.4734Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Samuels BL, Chawla SP, Somaiah N, Staddon AP, Skubitz KM, Milhem MM, et al. Results of a prospective phase 2 study of pazopanib in patients with advanced intermediate-grade or high-grade liposarcoma. Cancer. 2017;123:4640–7.10.1002/cncr.30926Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[45] Wagner AJ, Banerji U, Mahipal A, Somaiah N, Hirsch H, Fancourt C, et al. Phase I trial of the human double minute 2 inhibitor MK-8242 in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1304–11.10.1200/JCO.2016.70.7117Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Dickson MA, Schwartz GK, Keohan ML, D'Angelo SP, Gounder MM, Chi P, et al. Progression-free survival among patients with well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma treated with CDK4 inhibitor palbociclib: A phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:937–40.10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0264Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Tawbi HA, Burgess M, Bolejack V, Van Tine BA, Schuetze SM, Hu J, et al. Pembrolizumab in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma (SARC028): A multicentre, two-cohort, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1493–501.10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30624-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] D'angelo SP, Mahoney MR, Van Tine BA, Atkins J, Milhem MM, Jahagirdar BN, et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): Two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:416–26.10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30006-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Runa F, Hamalian S, Meade K, Shisgal P, Gray PC, Kelber JA. Tumor microenvironment heterogeneity: Challenges and opportunities. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2017;3:218–29.10.1007/s40610-017-0073-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Azimi F, Scolyer RA, Rumcheva P, Moncrieff M, Murali R, McCarthy SW, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte grade is an independent predictor of sentinel lymph node status and survival in patients with cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2678–83.10.1200/JCO.2011.37.8539Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Orning P, Lien E, Fitzgerald KA. Gasdermins and their role in immunity and inflammation. J Exp Med. 2019;216:2453–65.10.1084/jem.20190545Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Erkes DA, Cai W, Sanchez IM, Purwin TJ, Rogers C, Field CO, et al. Mutant BRAF and MEK inhibitors regulate the tumor immune microenvironment via pyroptosis. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:254–69.10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0672Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2443–54.10.1056/NEJMoa1200690Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Park HK, Kim M, Sung M, Lee SE, Kim YJ, Choi YL. Status of programmed death-ligand 1 expression in sarcomas. J Transl Med. 2018;16:303.10.1186/s12967-018-1658-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Clemmons DR. Modifying IGF1 activity: An approach to treat endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:821–33.10.1038/nrd2359Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Kasprzak A, Szaflarski W. Role of alternatively spliced messenger RNA (mRNA) isoforms of the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) in selected human tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6995.10.3390/ijms21196995Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Busund LT, Ow KT, Russell P, Crowe PJ, Yang JL. Expression of insulin-like growth factor mitogenic signals in adult soft-tissue sarcomas: significant correlation with malignant potential. Virchows Arch. 2004;444:142–8.10.1007/s00428-003-0931-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Dunlop MG, Dobbins SE, Farrington SM, Jones AM, Palles C, Whiffin N, et al. Common variation near CDKN1A, POLD3 and SHROOM2 influences colorectal cancer risk. Nat Genet. 2012;44:770–6.10.1038/ng.2293Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Timme S, Ihde S, Fichter CD, Waehle V, Bogatyreva L, Atanasov K, et al. STAT3 expression, activity and functional consequences of STAT3 inhibition in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and Barrett’s adenocarcinomas. Oncogene. 2014;33:3256–66.10.1038/onc.2013.298Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Chen J, Hang Y, Gao Q, Huang X. Surgical diagnosis and treatment of primary retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Front Surg. 2021;8:672669.10.3389/fsurg.2021.672669Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Dehner CA, Hagemann IS, Chrisinger JSA. Retroperitoneal dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2021;156:920–5.10.1093/ajcp/aqab051Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Zou WP. Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:263–74.10.1038/nrc1586Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K, Arihiro K. Tumor-driven evolution of immunosuppressive networks during malignant progression. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5527–36.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4128Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[64] Guerrouahen BS, Maccalli C, Cugno C, Rutella S, Akporiaye ET. Reverting immune suppression to enhance cancer immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2020;9:1554.10.3389/fonc.2019.01554Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Cervantes-Villagrana RD, Albores-García D, Cervantes-Villagrana AR, García-Acevez SJ. Tumor-induced neurogenesis and immune evasion as targets of innovative anti-cancer therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:99.10.1038/s41392-020-0205-zSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[66] Tie Y, Tang F, Wei YQ, Wei XW. Immunosuppressive cells in cancer: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:61.10.1186/s13045-022-01282-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis

