Abstract
Background
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are important structures to maintain knee stability. The present study aimed to further enrich understandings of the morphology of the cruciate ligaments and explore the relationship between the diameter of ACL and PCL.
Method
This study collected valid MRI samples of 50 male and 50 female normal right knee joints and measured the diameter of each point of the ACL and PCL through the 3D Slicer.
Results
The diameter of the ACL in the sagittal MRI of the normal right knee joint was significantly different from the diameter of each point of the PCL. The average diameter of each point of the ACL was larger than the diameter of the corresponding point of the PCL. Males and females had statistical differences in their PCL origin point, PCL midpoint, ACL origin point, ACL midpoint, and ACL insertion point diameters under sagittal MRI examination. The average diameter of males was greater than the average diameter of females at the above corresponding sites. In sagittal MRI scans of the normal right knee joint, we observed that only the origin point of the PCL exhibited a moderate correlation with the midpoint and insertion point of the ACL in terms of their respective diameters.
Conclusion
The correlation between diameters of normal ACL and PCL in knee joint MRI was moderate and may help clinicians determine appropriate graft for cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery quickly for severe cruciate ligament injuries.
1 Introduction
The knee joint, pivotal for weight-bearing and mobility, is central to everyday activities such as walking and stair climbing. Cruciate ligaments within the knee are instrumental in maintaining its stability [1]. A growing body of medical research underscores the significance of graft cross-sectional area selection in knee cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Such a choice can profoundly influence postoperative knee function recovery and graft longevity [2–5]. A multitude of studies delve into the cross-sectional area and anchoring positions of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) on the femur and tibia [6,7]. Given that contemporary cruciate ligament reconstruction predominantly employs the patient’s autologous ligament as a graft [8], the patellar and hamstring tendons emerge as the preferred graft choices [8,9]. Against this backdrop, researchers are intensifying efforts to accurately measure both the cross-sectional area of the ligament set for reconstruction and the suitable autologous ligament [2–5].
The employment of computerized three-dimensional software offers a nuanced lens for evaluating cruciate ligament morphology, aiding clinicians in their preoperative graft selection decisions [10]. MRI, an emergent radiological technique, has garnered widespread acceptance, particularly in developed regions, for knee joint examinations. This modality has enabled researchers to assess the cross-sectional area of various knee structures [11]. Several studies have leveraged MRI to gauge the cross-sectional areas of the hamstring or semitendinosus tendons, facilitating more precise autologous tendon graft choices for ACL reconstruction surgeries [2,11]. While MRI-based anatomical studies of the knee’s ACL and PCL are not rare, comparative investigations focusing solely on the diameters of the ACL and PCL using MRI remain strikingly scant.
MRI is an indispensable tool in the clinical evaluation of the knee joint. By assessing the diameter of the ACL and PCL using MRI, clinicians can gain a more profound insight into the imaging characteristics of these ligaments in their normal state. This knowledge is particularly salient when dealing with significant injuries or intense physical activities that may compromise either the ACL, the PCL, or both. Such severe injuries can lead to a segmental loss of these ligaments, rendering cross-sectional measurements unfeasible. Therefore, we speculate whether the diameter of the residual injured cruciate ligament, or the diameter of the intact ACL or PCL, can be utilized as indicators for inferring and assessing the diameter of another severely damaged cruciate ligament.
This study aims to elucidate the relationship between ACL and PCL diameters in knee MRI scans to enhance clinical understanding and inform cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery decisions. By examining these morphological ties, clinicians can optimize graft selection in cruciate ligament reconstruction surgeries, with the hope of improving patient outcomes. In this investigation, we utilized state-of-the-art knee MRI images sourced from the NYU School of Medicine Langone Health fastMRI database [12] to delineate the interrelationship between the ACL and PCL in MRI diagnostics.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source and study population
This study entailed a retrospective analysis of anonymized radiographic data sourced from the public domain. The imaging corpus for this endeavor was derived from the NYU Langone Health fastMRI [12], a repository maintained by the Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research within the Department of Radiology at NYU School of Medicine and NYU Langone Health. This repository encompasses a spectrum of sub-datasets, including raw k-space data. We uniformly selected MRI images of the right knee joint for analysis.
For this investigation, Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) metadata from subjects within the NYU Langone Health fastMRI database [12], supplied by NYU Langone, were meticulously selected based on specific inclusion criteria. We incorporated individuals aged between 20 and 60 who exhibited normal right knee joint function, presented no conspicuous history of ACL and PCL injuries, and had not undergone knee surgeries. Exclusion criteria encompassed subjects: (1) exhibiting congenital abnormalities or absent/partially missing ACL and/or PCL; (2) where the origin, midpoint, and insertion points of the ACL and PCL were indiscernible; and (3) presenting torn or inflamed ACL and PCL.
The dataset under investigation was parsed to distinctly classify subjects based on gender into male and female cohorts. Subsequent to this demarcation, 88 DICOM metadata entries were indiscriminately chosen from each cluster, aggregating to 176 selected entries for this research. These entries, when processed via 3D Slicer, were meticulously assessed with a spotlight on Sagittal Proton Density with Fat Suppression (SAG PD FS) images, integral for comprehensive MRI analysis. Of the original 176 DICOM metadata entries, 175 passed the inclusion protocol. However, upon application of the exclusion criteria, 71 of these were deemed unsuitable and were subsequently removed. Delving into specifics, 48 were excluded due to discernible injuries to the ACL and/or PCL, evidenced by inflammation, mutation, or outright tears. Meanwhile, the origin, midpoint, and insertion of the ACL and PCL were ambiguous in 23 cases, leading to their exclusion. The refined dataset comprised 50 male and 54 female entries. However, to institute a balanced comparative analysis between male and female ACL and PCL relationships, the clearest 50 entries from each gender were earmarked for precise measurement. It is pivotal to note that the MRI imagery for this study was sourced from unidentified, fully sampled knee MRI datasets courtesy of NYU Langone. Further technical specifics reveal that the deployed 3.0 Tesla MRI scans were characterized by sagittal proton density with an SAG PD FS, a parameter tailored for imaging normally functioning knee joints.
2.2 Measurement points of the cruciate ligaments and their appearance under MRI images
Image processing, analysis, measurement, and collection were performed using 3D Slicer version. The ACL and PCL of the right knee joint were found through the SAG PD FS images of the subjects using the 3D Slicer version. For this project, to study the relationship between the diameter of the ACL and the PCL of the right knee joint, three representative positions of the ACL and PCL (origin point, midpoint, and insertion point of the cruciate ligament) were selected for measurement.
In the sagittal MRI, the ACL originates on the medial surface of the lateral femoral condyle, passes antero-inferiorly, and terminates at the bone surface in front of the tibial intercondylar bulge. The normal ACL in the MRI of the knee joint appears as a relatively loose mid-to-low signal shadow. There is a line-like, stripe-like medium or high shadow separation at its attachment. The origin point of the ACL was selected to be measured obliquely below the posterior part of the lateral femoral condyle of the ligament. The midpoint diameter of the ACL was measured at the midpoint of the ACL perpendicular to the cruciate ligament. The insertion point of the ACL measured was selected to be 2 mm above the bone surface in front of the tibial intercondylar bulge. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the measurement of the diameter of the ACL.
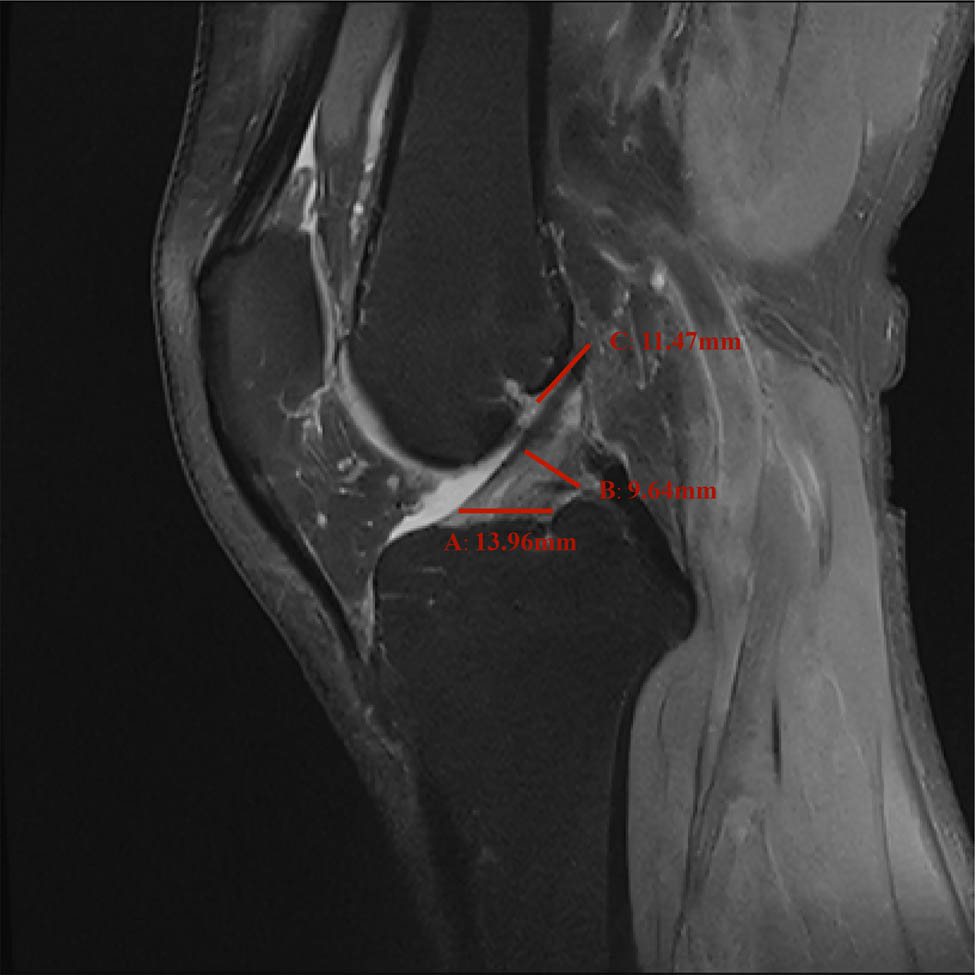
Schematic picture of the diameter measurement of each point of the ACL: A represents insertion point, B represents midpoint, and C represents origin point of the ACL.
In the sagittal MRI, the PCL originates from the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle, passes posteriorly, and terminates at the articular surface of the posterior tibia. The normal PCL in the knee joint MRI image shows low signal intensity. The sagittal PCL was arched convexly backward, with smooth edges, and at an angle of approximately 40–50° with the tibial plateau [13–15]. The origin measurement point of the PCL was chosen to be 2 mm below the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle. The midpoint measurement of the PCL was selected to be the convex point of the PCL in the sagittal MRI of the kyphotic arch, and the insertion point of the PCL was selected as the point where the ligament inserts 2 mm above the articular surface of the posterior tibia. Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of the measurement of the diameter of the PCL.

Schematic picture of the diameter measurement of each point of the PCL: D represents origin point, E represents midpoint, and F represents insertion point of the PCL.
The DICOM metadata package MRI provided in the NYU Langone Health fastMRI database mainly includes three parts: T1 weighted, T2 weighted, and proton density weighted with fat suppression. The T1 weighted image can be regarded as the mapping expression of the proton energy in human adipose tissue, and it is an image that highlights human adipose tissue [12]. The T2 weighted image is a representation of the proton energy map in the fat- and water-based tissues of the human body. By comparing with the T1 weighted image, the adipose tissue can be distinguished from the water-based tissue. Therefore, what is bright on the T2 image but dark on the T1 image is the liquid tissue in the human body. However, for images that are proton density weighted with fat suppression, when imaging human tissues, long repetition time [1] (2,000 ms) and short echo time [8] (30–40 ms) sequences are often selected for proton-density-weighted imaging. Because the long TR and short TE can reduce the influence of T1 and T2 on the imaging signal, this can highlight the proton density-related signals on the image. At the same time, fat suppression can better observe the ACL and PCL. Moreover, data analysis under the same series of MRIs can minimize the measurement error. Therefore, the measurement points that were selected (i.e., origin point, midpoint, and insertion point) of the knee joint ACLs and PCLs were all analyzed and measured under the subject’s SAG PD FS images.
2.3 Reliability and repeatability of the project
Researchers were trained in standardized cadaver dissection and imaging interpretation training. Proficient in using 3D Slicer software to segment and measure MRI parts accurately. Multiple repetitive tests were performed for each measurement, taking an average of an hour per set of data. All measurements in this study were independently conducted by two experienced orthopedic doctors, both adhering to the same standardized procedures. Subsequently, the average value derived from their independent assessments was utilized for analysis. The measured data underwent statistical analysis conducted by a third researcher.
2.4 Dataset and statistical analysis
Utilizing IBM SPSS (Version 22, Armonk, NY, USA), we administered both the Kolmogorov–Smirnov (K–S) and Shapiro–Wilk (S–W) tests to ascertain the normality of our dataset. Data adhering to a normal distribution were characterized by the mean ± standard deviation (SD). To discern differences across datasets, we employed the independent sample t-test, whereas the paired t-test was reserved for analogous measurement points. For data abiding by a normal distribution, the Pearson correlation analysis was invoked. Correlation strengths were delineated as follows: a coefficient ≥0.8 indicated a strong correlation, a coefficient between 0.5 and 0.8 signified a moderate correlation, a coefficient from 0.3 to 0.5 represented a low correlation, and a coefficient below 0.3 suggested an exceedingly weak correlation, verging on irrelevance. A p-value threshold of <0.05 was set as the marker for statistical significance.
-
Ethical approval: The study was conducted according to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. The approval of the study from the ethics review board was waived because the research relied upon publicly used, de-identified secondary data.
3 Result
The measurement values of the diameter of the ACL and PCL of the right knee joints of a group of 100 valid subjects (including 50 men and 50 women) were obtained. There were six groups in total of males and females: the diameters of the origin point, midpoint, and insertion point of the ACLs, and the diameters of the origin point, midpoint, and insertion point of the PCLs (Table 1). The units of measurement data are in millimeter [16]. Comparison was carried out as to whether the ACLs and PCLs are related in terms of diameter, comparing the size of the ACLs and PCLs at each point, and whether the male and female results are related in terms of the ACL and PCL measurements.
Diameter of the ACL and PCLa
| Diameter (male, N = 50) | Diameter (female, N = 50) | |
|---|---|---|
| PCL origin (mm) | 9.83 ± 0.88 | 8.58 ± 0.88 |
| PCL middle (mm) | 6.54 ± 0.57 | 6.27 ± 0.52 |
| PCL insertion (mm) | 9.16 ± 0.68 | 8.99 ± 0.56 |
| ACL origin (mm) | 11.74 ± 0.82 | 11.31 ± 0.78 |
| ACL middle (mm) | 9.59 ± 0.61 | 8.08 ± 0.47 |
| ACL insertion (mm) | 12.68 ± 0.89 | 10.69 ± 0.71 |
aThe values are shown as the mean ± SD. The units of measurement data are mm.
3.1 Analysis of the difference of the starting point, midpoint, and end point diameter of the ACLs and PCLs
The K–S test and S–W test were performed on the normal distributions of these six sets of data (starting point diameter, midpoint diameter, and endpoint diameter of the ACL and PCL), they all conformed to a normal distribution. According to the statistics and analysis results obtained in Table 2, by conducting t tests on the origin point diameter, midpoint diameter, and insertion point diameter of the ACLs and PCLs, the p-values of the three groups of differences were all less than 0.05. Therefore, there were significant statistical differences in the t tests for the diameters of these points of the PCL and ACL. From the mean and range values of each site, it can be concluded that the diameter of the ACL was greater than the diameter of the PCL at each of the given points.
Simple Student’s test combining male and female dataa
| Segment | PCL (N = 100) | ACL (N = 100) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | 9.21 ± 1.08 | 11.53 ± 0.83 | −19.067 | <0.001 |
| Middle | 6.40 ± 0.56 | 8.84 ± 0.93 | −25.450 | <0.001 |
| Insertion | 9.07 ± 0.63 | 11.68 ± 1.28 | −20.793 | <0.001 |
aThe values are shown as the mean ± SD. t means simple Student’s test, p means p-value. The units of measurement data are mm.
3.2 Comparison of the difference of the diameter of each point of the ACL and PCL between males and females
Using SPSS, the 12 sets of data that had passed the K–S and S–W normal distribution tests were differentiated using sexual testing. The difference between male data and the female data at the same site was detected using t tests, and the mean and SD of each group of data were counted and analyzed. As shown in Table 3, the p-values from the results of the t tests on the same site of the five sets of data for males and females, i.e., PCL origin point, PCL midpoint, ACL origin point, ACL midpoint, and ACL insertion point were all less than 0.05. Therefore, the diameters of the PCL’s origin point and midpoint, and the ACL’s origin point, midpoint, and insertion point were all statistically different between males and females. From a numerical point of view, the diameters of the male PCL origin point, the PCL midpoint, the ACL origin point, the ACL midpoint, and the ACL insertion point were all higher than those of females at the same site. The p-value was found to be 0.187 when the t tests were performed on the male and female groups of the PCL insertion point diameter. As the p-value of this group was greater than 0.05, the difference between males and females at the point of the PCL’s insertion point diameter was not statistically significant.
t-test for each group of males and femalesa
| Male (N = 50) | Female (N = 50) | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL origin | 9.83 ± 0.88 | 8.58 ± 0.88 | 7.107 | <0.001 |
| PCL middle | 6.54 ± 0.57 | 6.27 ± 0.52 | 2.456 | 0.016 |
| PCL insertion | 9.16 ± 0.68 | 8.99 ± 0.56 | 1.330 | 0.187 |
| ACL origin | 11.74 ± 0.82 | 11.31 ± 0.78 | 2.656 | 0.009 |
| ACL middle | 9.59 ± 0.61 | 8.08 ± 0.47 | 13.792 | <0.001 |
| ACL insertion | 12.68 ± 0.89 | 10.69 ± 0.71 | 12.382 | <0.001 |
aThe values are shown as the mean ± SD. t means t-test, p means p-value. The units of measurement data are mm.
3.3 Correlation between the ACL and PCL
As the datasets of each point in the male and female groups had passed the K–S and S–W normal distribution tests, and the six sets of data meet the normal distribution conditions, the correlation of each point diameter index was adopted for Pearson correlation analysis. p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 were identified as statistically significant. As shown in the results in Table 4, the correlation coefficient between the PCL origin point and ACL midpoint was r = 0.517, p < 0.05; and the correlation coefficient of the PCL origin point and the ACL insertion point was r = 0.615, p < 0.05. For the others, the correlation coefficient of each point of the PCL and the ACL was less than 0.3, and p < 0.05. In sagittal MRI scans of the normal knee joint, we observed that only the origin point of the PCL exhibited a moderate correlation with the midpoint and insertion point of the ACL in terms of their respective diameters, and those of the diameters of the other points were extremely weak and can be regarded as irrelevant. The correlation coefficient between the PCL origin point and PCL midpoint was 0.505, and p < 0.05, there was a positive but weak correlation between them.
Correlation test of each point diameter of the PCLs and ACLs
| PCL origin | PCL middle | PCL insert | ACL origin | ACL middle | ACL insert | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL origin | 1 | |||||
| PCL middle | 0.505** | 1 | ||||
| PCL insert | 0.399** | 0.377** | 1 | |||
| ACL origin | 0.202* | 0.205* | 0.174 | 1 | ||
| ACL middle | 0.517** | 0.254* | 0.246* | 0.320** | 1 | |
| ACL insert | 0.615** | 0.260** | 0.287** | 0.322** | 0.805** | 1 |
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
4 Discussion
Our study identified a nuanced relationship between the diameters of the normal ACL and PCL in sagittal MRI examinations of the right knee. Notably, a distinct correlation emerged solely at the origin point diameter of the PCL, exhibiting a moderate relationship with the midpoint and insertion point diameters of the ACL. Remarkably, correlations with other points waned to a negligible degree. Diametric comparisons between ACL and PCL in MRI scans revealed significant disparities. On average, every ACL point diameter surpassed its corresponding PCL counterpart. Gender differences presented themselves with statistical significance across various ligament points in sagittal MRI examinations of the right knee joint: the average diameter for males consistently exceeded that for females at analogous ligament locales, consistent with previous research [17]. Yet, this gender distinction proved inconsequential in the PCL insertion point diameter dataset. These findings resonate, albeit with variations, with preceding research. A cadaveric analysis posited that the ACL and PCL widths in females are comparatively slender than in males [18]. Further, this anatomical inquiry suggested an average ACL width of 6.4 ± 1.4 mm juxtaposed against an average PCL width of 10.2 ± 2.0 mm [18], a conclusion seemingly at odds with our study which determined a more prominent average diameter across ACL points than the PCL.
These discordances can be attributed primarily to two factors. First, the aforementioned cadaveric study [18] gauged the ACL and PCL widths in the coronal plane, whereas our research employed the sagittal plane. Second, the irregularly shaped cross-sections of the ACL and PCL [19] exerted influence on the findings. Typically, the PCL showcases its maximal width in the coronal plane, while the ACL tends to be broader in the sagittal plane [19]. Acknowledging these measurement orientations, coupled with the inherent morphology of the cruciate ligaments, our study’s outcomes align closely with, and are robustly corroborated by, the referenced cadaveric anatomy investigation.
In cruciate ligament reconstruction, the cross-sectional area of each ligament segment stands as a pivotal metric for graft selection [16,20,21]. Integrating our project’s data with traditional anatomical insights on the cross-sectional dimensions and morphology of the ACL and PCL could revolutionize the utilization of MRI scans, enabling accurate determinations of these ligaments’ cross-sectional areas within the patient’s knee. Such synergy promises clinicians enhanced precision in preoperative evaluations of the cruciate ligament’s cross-sectional area, facilitating optimal graft selection. Furthermore, this amalgamated understanding deepens our insights into the radiographic depictions of ACL and PCL diameters, equipping clinicians to adeptly discern these ligaments’ diameters even in pathological joints and pinpoint elusive lesions. This proficiency becomes especially pivotal when confronted with cases of acute cruciate ligament trauma, where direct measurements of the injured ligament’s cross-sectional area may be untenable. Under such scenarios, the remnant diameter of the injured ligament, or that of an intact ACL or PCL, could serve as a surrogate metric, enabling robust inferences about another grievously injured ligament’s diameter. By extrapolating these diameters to cross-sectional areas, clinicians can judiciously select grafts for reconstructive surgeries, ensuring superior restoration of knee functionality and bolstering patient outcomes.
In this investigation, we chiefly probed the interrelations between the diameters of typical ACLs and PCLs in sagittal MRI evaluations of standard knee joints. Traditional anatomical studies on three-dimensional cadavers, however, pose an inherent constraint to our project: the reliance on two-dimensional measurements. Given the inherently irregular morphology of each segment of the ACL and PCL [22–25], pinpointing the optimal point for diameter measurement within this plane proves challenging. Contemporary research brims with studies delving into the interplay between the cross-sectional areas of ACL, PCL, and grafts within the knee joint [26–28]. Yet, our approach – deriving diameters of the ACL and PCL from a two-dimensional plane – POSES hurdles in drawing correlations with the corresponding cross-sectional areas. This underscores the imperative for expanded studies, elucidating the ties between the diameters of ACLs and PCLs in standard human knee sagittal MRIs and their cross-sectional areas in conventional anatomical studies. Should a robust association between the diameter of each ligament’s point and its corresponding cross-sectional area be ascertained, one could deduce the latter simply by tracking diameter shifts in sagittal MRI examinations. Such a methodology would empower clinicians to swiftly and precisely pinpoint the requisite cross-sectional area, leveraging just the cruciate ligament diameter from a patient’s knee MRI. This study currently only includes gender as a variable, and in the future, further consideration will be given to incorporating factors such as age and weight.
5 Conclusion
In sagittal MRI evaluations of the right knee joint, the mean diameter at each location of the ACL surpassed that of its PCL counterpart. Male subjects consistently presented larger mean diameters than females across various anatomical landmarks, encompassing the PCL’s origin and midpoint as well as the ACL’s origin, midpoint, and insertion. Notably, the gender disparity in the PCL’s insertion point’s diameter lacked statistical significance in our analysis. Intriguingly, correlation analysis unveiled that only the PCL’s origin bore a moderate relationship with the ACL’s midpoint and insertion within standard knee joints in sagittal MRI of the right knee joint. Such insights could equip clinicians with a methodology to extrapolate and assess the diameter of a severely compromised cruciate ligament, leveraging data either from the remnant of an injured ligament or a relatively intact anterior cruciate ligament. This, in turn, could facilitate estimations of the cross-sectional area pertinent to each site, guiding the selection of optimal grafts for cruciate ligament reconstructive procedures.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the fastMRI database participants.
-
Funding information: This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81472106).
-
Author contributions: G.X., C.X., N.M., and K.H. conceptualized and designed the study; G.X., C.X., Z.Y., and L.M. performed the experiments and collected data; G.X. and C.X. analyzed the data and wrote the first draft; Z.Y., L.M., N.M., and K.H. provided technical assistance and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
-
Data availability statement: All data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
[1] Duthon VB, Barea C, Abrassart S, Fasel JH, Fritschy D, Ménétrey J. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumato Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA. 2006;14(3):204–13.10.1007/s00167-005-0679-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Bickel BA, Fowler TT, Mowbray JG, Adler B, Klingele K, Phillips G. Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging cross-sectional area for the measurement of hamstring autograft diameter for reconstruction of the adolescent anterior cruciate ligament. Arthrosc: J Arthrosc Relat Surg: Off Publ Arthrosc Assoc North Am Int Arthrosc Assoc. 2008;24(12):1336–41.10.1016/j.arthro.2008.07.012Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Kinugasa K, Hamada M, Yoneda K, Matsuo T, Mae T, Shino K. Cross-sectional area of hamstring tendon autograft after anatomic triple-bundle ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumato Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA. 2017;25(4):1219–26.10.1007/s00167-015-3880-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Hamada M, Shino K, Horibe S, Mitsuoka T, Toritsuka Y, Nakamura N. Changes in cross-sectional area of hamstring anterior cruciate ligament grafts as a function of time following transplantation. Arthrosc: J Arthrosc Relat Surg: Off Publ Arthrosc Assoc North Am Int Arthrosc Assoc. 2005;21(8):917–22.10.1016/j.arthro.2005.05.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Muneta T, Takakuda K, Yamamoto H. Intercondylar notch width and its relation to the configuration and cross-sectional area of the anterior cruciate ligament. A cadaveric knee study. Am J Sports Med. 1997;25(1):69–72.10.1177/036354659702500113Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Harner CD, Xerogeanes JW, Livesay GA, Carlin GJ, Smith BA, Kusayama T, et al. The human posterior cruciate ligament complex: an interdisciplinary study. Ligament morphology and biomechanical evaluation. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(6):736–45.10.1177/036354659502300617Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Harner CD, Baek GH, Vogrin TM, Carlin GJ, Kashiwaguchi S, Woo SL. Quantitative analysis of human cruciate ligament insertions. Arthrosc: J Arthrosc Relat Surg: Off Publ Arthrosc Assoc North Am Int Arthrosc Assoc. 1999;15(7):741–9.10.1016/S0749-8063(99)70006-XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Romanini E, D’Angelo F, De Masi S, Adriani E, Magaletti M, Lacorte E, et al. Graft selection in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Traumatol: Off J Ital Soc Orthop Traumatol. 2010;11(4):211–9.10.1007/s10195-010-0124-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Frank RM, Hamamoto JT, Bernardoni E, Cvetanovich G, Bach Jr BR, Verma NN, et al. ACL reconstruction basics: quadruple (4-strand) hamstring autograft harvest. Arthrosc Tech. 2017;6(4):e1309–13.10.1016/j.eats.2017.05.024Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Jeong WS, Yoo YS, Kim DY, Shetty NS, Smolinski P, Logishetty K, et al. An analysis of the posterior cruciate ligament isometric position using an in vivo 3-dimensional computed tomography-based knee joint model. Arthrosc: J Arthrosc Relat Surg: Off Publ Arthrosc Assoc North Am Int Arthrosc Assoc. 2010;26(10):1333–9.10.1016/j.arthro.2010.02.016Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Fules PJ, Madhav RT, Goddard RK, Newman-Sanders A, Mowbray MA. Evaluation of tibial bone tunnel enlargement using MRI scan cross-sectional area measurement after autologous hamstring tendon ACL replacement. Knee. 2003;10(1):87–91.10.1016/S0968-0160(02)00086-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Dataset F. https://fastmri.med.nyu.edu/[Z]; 2020.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Gentili A, Seeger LL, Yao L, Do HM. Anterior cruciate ligament tear: indirect signs at MR imaging. Radiology. 1994;193(3):835–40.10.1148/radiology.193.3.7972834Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Brandser EA, Riley MA, Berbaum KS, El-Khoury GY, Bennett DL. MR imaging of anterior cruciate ligament injury: independent value of primary and secondary signs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(1):121–6.10.2214/ajr.167.1.8659355Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Chen WT, Shih TT, Tu HY, Chen RC, Shau WY. Partial and complete tear of the anterior cruciate ligament. Acta Radiol (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987). 2002;43(5):511–6.10.1258/rsmacta.43.5.511Search in Google Scholar
[16] Strauss MJ, Varatojo R, Boutefnouchet T, Condello V, Samuelsson K, Gelber PE, et al. The use of allograft tissue in posterior cruciate, collateral and multi-ligament knee reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumato Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA. 2019;27(6):1791–809.10.1007/s00167-019-05426-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Sutton KM, Bullock JM. Anterior cruciate ligament rupture: differences between males and females. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(1):41–50.10.5435/JAAOS-21-01-41Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Davis TJ, Shelbourne KD, Klootwyk TE. Correlation of the intercondylar notch width of the femur to the width of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. Knee Surg Sports Traumato Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA. 1999;7(4):209–14.10.1007/s001670050150Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Harner CD, Livesay GA, Kashiwaguchi S, Fujie H, Choi NY, Woo SL. Comparative study of the size and shape of human anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments. J Orthop Res: Off Publ Orthop Res Soc. 1995;13(3):429–34.10.1002/jor.1100130317Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Offerhaus C, Albers M, Nagai K, Arner JW, Höher J, Musahl V, et al. Individualized anterior cruciate ligament graft matching: in vivo comparison of cross-sectional areas of hamstring, patellar, and quadriceps tendon grafts and ACL insertion area. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(11):2646–52.10.1177/0363546518786032Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Park SY, Nam HS, Ho JPY, Tu NT, Lee YS. Association between tunnel position, tunnel angle, graft signal intensity, and graft thickness in the reconstructed posterior cruciate ligament. Orthop J Sports Med. 2023;11(7):23259671231168893.10.1177/23259671231168893Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Śmigielski R, Zdanowicz U, Drwięga M, Ciszek B, Williams A. The anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament and its relevance to the technique of reconstruction. Bone Jt J. 2016;98-b(8):1020–6.10.1302/0301-620X.98B8.37117Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Gögele C, Hahn J, Schulze-Tanzil G. Anatomical tissue engineering of the anterior cruciate ligament entheses. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):7.10.3390/ijms24119745Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Winkler PW, Zsidai B, Wagala NN, Hughes JD, Horvath A, Senorski EH, et al. Evolving evidence in the treatment of primary and recurrent posterior cruciate ligament injuries, part 1: anatomy, biomechanics and diagnostics. Knee Surg Sports Traumato Arthrosc: Off J ESSKA. 2021;29(3):672–81.10.1007/s00167-020-06357-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Fanelli GC. Posterior cruciate ligament. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2020;28(1):1.10.1097/JSA.0000000000000280Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Fujimaki Y, Thorhauer E, Sasaki Y, Smolinski P, Tashman S, Fu FH. Quantitative in situ analysis of the anterior cruciate ligament: length, midsubstance cross-sectional area, and insertion site areas. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(1):118–25.10.1177/0363546515611641Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Lee BH, Seo DY, Bansal S, Kim JH, Ahn JH, Wang JH. Comparative magnetic resonance imaging study of cross-sectional area of anatomic double bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction grafts and the contralateral uninjured knee. Arthrosc: J Arthrosc Relat Surg: Off Publ Arthrosc Assoc North Am Int Arthrosc Assoc. 2016;32(2):321–9.e1.10.1016/j.arthro.2015.08.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Sadoghi P, Röggla V, Beiglböck H, Schett B, Reschl M, Fischerauer S, et al. Prediction of individual graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using anthropometric data. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(6):3219–27.10.1007/s00402-022-04682-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis

