Abstract
Aim
With unknown etiology and limited treatment options, unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss (URPL) remains a thorny problem. Ferroptosis, a newly identified type of cell death, has been shown to be crucial in the development in reproductive disorders. This study aims to explore the specific mechanism of ferroptosis in URPL and to uncover whether alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) can inhibit ferroptosis, and then exert a protective effect in URPL.
Method
The decidua tissues of URPL and control patients who actively terminated pregnancy were collected. The CBA/J × DBA/2 murine models of URPL were established, and were randomly treated with peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ) agonists (Rosiglitazone) and ALA. The CBA/J × BALB/c murine models of normal pregnancy were intraperitoneally injected with PPARγ inhibitors (T0070907). Here, we used reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH)/GSSG, and FeRhoNox-1 analysis to detect the level of ferroptosis. We used quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis to evaluate the mRNA level of PPARγ. Besides, western blot and immunofluorescence were utilized to test the expression profile of PPARγ/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4).
Results
In this study, we found that iron deposition was increased in the decidual tissue of patients with URPL. Additionally, the changes in cell morphology, the level of ROS, MDA, GSH, and the expression of ferroptosis marker proteins NRF2/GPX4 confirmed activated ferroptosis in URPL. Besides, bioinformatics analysis combined with experiments confirmed that PPARγ was critical in triggering NRF2/GPX4 pathway in URPL. Furthermore, URPL mouse models were established, and the results showed that PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis was also significantly increased, which could be mitigated by ALA treatment.
Conclusion
Overall, these findings suggest that ferroptosis may play an important role in URPL, and ALA might be a promising therapeutic drug for improving pregnancy outcomes in URPL via targeting the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 pathway.
1 Introduction
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is usually defined as two or more miscarriages before 20 weeks of gestation [1], which affects approximately 1–2% of reproductive women trying to conceive [2]. Multiple pathogenic mechanisms complicated in RPL have been verified, including uterine abnormalities, endocrinological disorders, genetic anomalies, thrombophilia, and immunological factors [2]. Unfortunately, the causes of half cases, also known as unexplained RPL (URPL), remain poorly understood [3]. Ferroptosis, a newly emerged form of regulated necrotic cell death, is featured as the iron-dependent activation of lipoxygenase and the consequential cell death induced by excessive lipid peroxidation [4]. It has been confirmed that ferroptosis is triggered in a number of diseases and is closely associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes [5,6]. The latest research based on bioinformatics analysis revealed that multiple ferroptosis-related genes were differentially expressed in the decidual tissue of URPL [7]. However, there are still few studies to confirm the role of ferroptosis in the regulation of the pathological mechanism of URPL.
Previous research has identified that almost all genes associated with ferroptosis are mediated by nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) transcription, including, but not restricted to, glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) [4,8]. NRF2 is a highly sensitive transcription factor to oxidative stress, which can not only facilitate regulation of cellular redox stability but also protect cells from ferroptosis by targeting gene expression involving glutathione (GSH) synthesis and iron metabolism [9]. It has been confirmed that various proteins and enzymes are expressed under the mediation of Nrf2 to prevent lipid peroxidation and subsequent ferroptosis [10]. Of note, GPX4, one of the main downstream target gene of NRF2, is the main inhibitor of ferroptosis by acting as a repair enzyme to catalyze the reduction of lipids and other peroxides [4,11]. So far, research has elucidated that activating the NRF2–GPX4 axis exerts a significant role in preventing lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis [12]. Some evidence to date suggests that ferroptosis may play an important role in UPRL. For instance, serum malondialdehyde (MDA), the oxidation product of polyunsaturated fatty acids, is significantly increased in URPL [13]. However, the NRF2–GPX4 axis has not been discussed in URPL.
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), also named as 1,2-dithiolane-3-pentanoic acid, is a biological thiol widely existing in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells [14,15]. It has been demonstrated to exert several positive effects on human health, such as acting as a biological antioxidant, metal chelator, and detoxifying agent [16]. Besides, ALA also exhibits remarkable anti-inflammatory activities and is supposed to be a possible treatment for a number of inflammatory conditions that disrupt female reproduction [15,17]. To date, various studies have investigated that ALA exerts an evidence-based protective role in RPL [18]. However, the specific mechanisms of ALA by which it protects from early pregnancy loss remain poorly understood. Recently, various studies have investigated that ALA can attenuate ferroptosis via multiple molecular signaling pathways [19]. A study by Zhao et al. confirmed that ALA could alleviate fluoride-induced hepatocyte injury by preventing ferroptosis through the system Xc-/GPX4 axis, lipid peroxidation axis, and iron metabolism axis [20]. Additionally, ALA has been unraveled to alleviate ferroptosis in the MPP(+)-induced PC12 cells via activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway [21]. Moreover, ferroptosis-related signaling proteins targeted by ALA also play an important role in RPL. But whether ALA’s protection against URPL is related to its intervention in ferroptosis has not been studied.
Hence, the present study aimed to investigate the regulatory mechanisms of NRF2/GPX4-induced ferroptosis in URPL, and to explore whether ALA could effectively alleviate ferroptosis and restore impaired reproductive function in URPL.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents and antibodies
ALA (T5625) was purchased from Sigma. T0070907 (HY-13202) and rosiglitazone (HY-17386) was purchased from MedChemExpress. GSH and GSSG assay kit (S0053) and MDA assay kit (S0131S) were purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology. FeRhoNox-1 (Fe2+ indicator, MX4558) was purchased from Maokangbio. Tissue reactive oxygen species (ROS) test kit was obtained from BestBio (BB-470537). Western blot experiments were performed using the following antibodies: anti-β-actin (4970, 1:1,000) was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Anti-peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ (PPARγ; sc-7273, 1:1,000), anti-NRF2 (sc-365949, 1:1,000), and anti-GPX4 (sc-166570, 1:1,000) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Goat anti-rabbit IgG (H&L) (926-32211, 1:5,000) and goat anti-mouse IgG (H&L) (926-68070, 1:5,000) were purchased from LI-COR. Immunofluorescence experiments were performed using the following antibodies: anti-PPARγ (sc-7273, 1:200), anti-NRF2 (sc-365949, 1:200), and anti-GPX4 (sc-166570, 1:200). Goat anti-mouse IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150113, 1:200) was purchased from Abcam. TRIzol reagent (15596026) was purchased from Invitrogen. HiFiScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (CW2569M) was purchased from CWBIO. SYBR Green Pro Taq HS (AG11701) was purchased from AgBio.
2.2 Human samples
The decidual tissues were collected after obtaining written informed consent from 15 patients diagnosed with URPL and 15 normal pregnant women at the first affiliated hospital of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine. This project met with the declaration of Helsinki in clinical research and was granted by the human research ethics committee of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine (HZYLLBA2021014). There was no difference in age, gestational period, and menstrual cycle between the two groups of patients. The baseline data of clinical samples are shown in Table A1.
2.3 Animals and grouping
A total of 42 CBA/J female mice (6–8 weeks), four 9 BALB/c mice and 12 male DBA/2 mice were obtained from the Beijing HFK Bioscience CO., LTD and housed in a standardized laboratory environment: temperature 22°C, 50–60% humidity, and 12:12 h light–dark cycle with free access to water and food. After 1 week of adaptive feeding, the CBA/J female mice during the proestrus period were randomly divided into two groups, in which the CBA/J × BALB/c combination demonstrated normal pregnancy, whereas the CBA/J × DBA/2 mouse combination exhibited pregnancy loss as an acknowledged model of URPL, which was first proposed by Clark et al. [22]. The mice cohabited at 16:00 each afternoon, and the females were examined at 8:00–8:30 the next day, and finding a vaginal plug under the microscope was regarded as the first day of pregnancy (D1). On D14, mice were anesthetized and sacrificed, and endometrial tissue was collected for subsequent experiments. All of the experimental procedures were supervised by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine (Ethics number: 2023042804), and the research was performed in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines 2.0.
To address the role of PPARγ in NRF2/GPX4 pathway in URPL, PPARγ inhibitors (T0070907) and agonists (Rosiglitazone) were utilized, and the mice were divided into the following groups: Control, Control + T0070907, URPL, and URPL + Rosiglitazone group. To address the role of ALA in PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 pathway in URPL, the mice were divided into the following groups: Control, URPL, and URPL + ALA group. T0070907 was administered once daily by intraperitoneal injection at 5 mg/kg, and rosiglitazone was administered once daily by intraperitoneal injection at 0.1 mg/kg. Moreover, mice in the URPL + ALA group received treatment once daily with ALA (50 mg/kg) by oral administration according to the previous studies [23]. Mice in the control and URPL group were received saline.
2.4 GSH/GSSG, MDA, and ROS assays
Decidua GSH content was measured using a GSH and GSSG assay kit (Beyotime, S0053) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The GSH content of the test samples was calculated as: total GSH–GSSG × 2. Decidua MDA content was measured using a lipid peroxidation MDA assay kit (Beyotime, S0131S) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Moreover, ROS levels in the tissues were detected with tissue ROS detection kit obtained from BestBio Company.
2.5 Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Trypsinase-digested decidual tissue was quickly fixed for 24 h in 2.5% glutaraldehyde solution, washed with PBS, and then transferred to 1% osmium and 1.5% K3[Fe(CN)3] for 1 h. The decidual tissues were soaked in a dioxy solution of 2% acetic acid at 4℃ overnight, and then dehydrated in a graded ethanol solution and immersed in varying proportions of pure acetone and embedding agent. The samples were thinly sectioned after being polymerized at 60℃. Then the sections were stained using uranyl acetate and lead citrate (3%) solutions. The formation of mitochondria was observed under an electron microscope (Hitachi, Japan).
2.6 Fe2+ content
The decidual tissues were removed and fixed overnight in 4% paraformaldehyde. Dehydrated with 20–30% sucrose the next day and wait for complete dehydration. The completely dehydrated tissues were prepared into 12 μm frozen sections for immunofluorescence staining. FeRhoNox-1 was placed on the frozen sections and incubated for 60 min at 37°C in a dark chamber. Thereafter, the specimen was counterstained with 4′,6-diaminido-2-phenylindole, dihydrochloride (DAPI) and photographed under a fluorescence microscope (OLYPUMS, Japan).
2.7 Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR)
q-PCR analysis was conducted following previously described protocols. Total RNA from cells was extracted using TRIzol reagent, and reverse transcription was performed using the HiFiScript cDNA Synthesis Kit. The resulting cDNA was subjected to q-PCR using the SYBR Green Pro Taq HS. The relative mRNA expression level was calculated using the comparative 2−ΔΔCt method based on the threshold cycle (Ct). The primer sequences used for real-time PCR are as follows: PPARγ Forward primer (5′–3′): TCTGGCCCACCAACTTTGGG, PPARγ Reverse primer (5′–3′): CTTCACAAGCATGAACTCCA; GAPDH Forward primer (5′–3′): CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT, GAPDH Reverse primer (5′–3′): GAAGGCTGGG GCTCATTT.
2.8 Western blot
Total proteins were extracted with RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, P0013B) and protease inhibitors, and the protein concentrations were detected with BCA Protein Assay Kit (Beyotime, P0011). SDS-PAGE was used to separate the proteins that were transferred afterward onto nitrocellulose membranes by wet transfer at 280 mA. The membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk for 1 h at room temperature and incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies. Then, the membranes were followed by incubations with secondary antibodies. After the membranes were scanned in Odyssey fluorescence imaging system, quantitative analysis was performed by Image J software.
2.9 Immunofluorescence
The frozen sections were blocked with BSA (BSA 5 g, 30%Triton X-100 0.5 mL, sodium azide 0.05 g, 1× PBS) at room temperature for 2 h. Afterward, tissue sections were incubated with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight: anti-PPARγ (sc-7273, 1:200), anti-NRF2 (sc-365949, 1:200), and anti-GPX4 (sc-166570, 1:200), followed by incubation with the secondary antibody: goat anti-mouse IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150113, 1:200) in the dark for 2 h. Besides, cell nuclei were stained with DAPI. Finally, images of tissue sections were photographed under a fluorescence microscope (OLYPUMS, Japan). The mean immunofluorescence intensity of PPARγ, NRF2, and GPX4 were performed by Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Three to five different high magnification (×200) fields of the tissue were randomly selected from each section for the statistics of the average optical density value, and the average value was taken as the average optical density value of the section.
2.10 Searching and screening microarray data
The microarray datasets were systematically extracted from the gene expression omnibus (GEO) database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) [24] with the keywords of “recurrent pregnancy loss,” “recurrent miscarriage,” “unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion,” and “unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion.” The screening conditions were as follows: (1) Homo sapiens, (2) expression profiling by array, and (3) all samples were taken from the endometrial tissue during the mid-secretory phase of menstruation. Finally, two datasets were included (GSE26787 and GSE165004).
2.11 Data preprocessing, normalizing, and screening of differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
The background calibration, data normalization, and log2 transformation were conducted on the included data sets using affy in R software (version 4.1.2) [25]. When multiple probes corresponded to one specific gene, their average expression level was considered [26]. Moreover, we used the surrogate variable analysis in Bioconductor to reduce batch effects and other variables [27]. The principal component analysis before and after the batch correction was conducted. At last, the “limma” packages in R software was used to identify the DEGs of RPL with the criteria of adjusted P-value <0.05 and |log2 fold change (FC)| > 0.05. DEGs screened from the integrated dataset were shown by heat map and volcano plots.
2.12 Acquisition of genes associated with ferroptosis
We obtained the ferroptosis-related genes from the FerrDB database (http://www.zhounan. org/ferrdb)[28], GSEA database (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/) [29], and Genecards (https://www.genecards.org/) [30] (screening genes with relevance score ≥1.5), the acquired genes will be combined, and ferroptosis-related genes will be found after removing duplicate genes.
2.13 Acquisition and protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis of URPL-related ferroptosis genes
Intersection genes of URPL DEGs and ferroptosis-related genes were obtained by Venn diagram. Then, we constructed a PPI network of URPL-related ferroptosis genes using the STRING (https://cn.string-db.org/) [31] online website, and the cytoHubba plug-in in Cytoscape software (3.8.1) was used to identify the top ten maximum margin criterion proteins.
2.14 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) functional enrichment analysis of URPL-related ferroptosis genes
In this study, we used the clusterProfiler package for KEGG functional enrichment analysis of URPL-related ferroptosis genes.
2.15 Screening the transcription factor of NRF2 in URPL
We performed the PROMO database (https://alggen.lsi.upc.es/cgi-bin/promo_v3/promo/promoinit.cgi? dirDB = TF_8.3) (set the factors predicted within a dissimilarity margin less or equal than 15%) [32] and TRRUST database (https://www.grnpedia.org/trrust/) [33] to find corresponding transcription factor NRF2. The obtained NRF2 transcription factors were intersected with URPL-related ferroptosis genes to identify transcription factors that might regulate NRF2 in URPL.
2.16 Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. All the performed statistical analyses were described in each figure legend. Statistical P-values were obtained by application of the appropriate statistical tests using the GraphPad Prism 9. For all tests, P < 0.05 was considered significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).
-
Ethical approval: This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki in clinical research and was approved by the human research ethics committee of Heilongjiang University of traditional Chinese medicine (HZYLLBA2021014). Written informed consent was obtained from individual or guardian participants. All of the animal experimental procedures were supervised by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine (Ethics number: 2023042804), and the research was performed in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines 2.0.
3 Results
3.1 Increased ferroptosis in decidual tissue in URPL patients
First, we observed Fe2+ content in URPL patients and health controls. The RhoNox-1 staining results showed that Fe2+ content was increased in the URPL group when compared with the control group (Figure 1a). Moreover, TEM showed that there was a decrease in mitochondrial volume and an increase in cavitation in the URPL group, as compared with the results in the control group (Figure 1b). Next, the relative values of ROS, MDA, and GSH were assessed. Results showed that the ROS and MDA levels were significantly increased, and GSH was significantly decreased in the URPL group (Figure 1c–e).

Increased ferroptosis in decidual tissue in URPL patients. (a) Fe2+ content was assessed by RhoNox-1 staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. (b) Ferroptosis in decidua was observed by TEM. The red arrow shows a decrease in mitochondrial volume and an increase in cavitation. Scale bar: 2 μm (left), 500 nm (right). (c)–(e). ROS, MDA, and GSH levels were observed by GSH/GSSG, MDA, and ROS assays. *P < 0.05 compared with the control group.
3.2 Expression of NRF2/GPX4 was decreased in URPL
GPX4 is a phospholipid hydroperoxidase that protects cells against membrane lipid peroxidation. NRF2 can protect cells from ferroptosis by targeting gene expression involving GSH synthesis such as GPX4. The western blot and immunofluorescence showed that the expression levels of the NRF2 and GPX4 significantly decreased in the URPL group, as compared with the results in the control group (Figure 2a–c).

Expression of NRF2/GPX4 in decidual tissue of URPL patients decreased. (a) and (b) NRF2 and GPX4 were assessed by immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 50 μm. (c) NRF2 and GPX4 were assessed by western blot. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the control group.
3.3 PPARγ-mediated ferroptosis in URPL through NRF2/GPX4
Next, we sought to study which regulated NRF2/GPX4 ferroptosis in URPL via bioinformatics analysis. The results displayed that there were 721 DEGs in URPL. Then 483 ferroptosis-related genes were obtained from FerrDB database, 64 were from the GSEA database and 918 were from Genecards. Subsequently, a total of 1,314 ferroptosis-related genes were obtained by removal of duplicate genes from the three databases. After that, 21 intersection genes of URPL DEGs and ferroptosis-related genes were obtained, namely URPL ferroptosis-related DEGs (Figure 3a). Then, PPI was conducted to reveal inter-molecular interactions during ferroptosis in UPRL. And the results showed that PPARG and HMOX1 were hub genes, and these two proteins were closely correlated with CYBB, DPP4, SREBF2, and SLC40A1 (Figure 3b). Besides, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis displayed that URPL ferroptosis-related DEGs were mainly enriched in ferroptosis, PPAR signaling pathway, fatty acid biosynthesis, and so on. Besides, PPARG was one of the core genes in PPAR signaling pathway (Figure 3c). Furthermore, PPARγ was a key transcription factor of NRF2 associated with ferroptosis in URPL according to the transcription factor analysis based on PROMO and TRRUST databases (Figure 3d). In addition, immunofluorescence revealed that the immunofluorescence intensity of PPARγ was significantly decreased in the decidua of URPL (Figure 4a). Uniformly, the mRNA level of PPARγ was also significantly decreased in the decidua of URPL detected by qRT-PCR (Figure 4b). Thus, PPARG may play an important role in ferroptosis in URPL.

Bioinformatics analysis revealed PPARγ-mediated ferroptosis in URPL through NRF2/GPX4. (a) Venn diagram shows URPL ferroptosis-related genes. (b) PPI analysis of the URPL ferroptosis-related genes. (c) KEGG of URPL ferroptosis-related genes. (d) Venn diagram shows the intersection gene between URPL ferroptosis-related genes and the transcription factor of NRF2.

Expression of PPARγ in decidual tissue of URPL patients decreased. (a) PPARγ was assessed by immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 50 μm. (b) mRNA level of PPARγ was assessed by qRT-PCR. *P < 0.05 compared with the control group.
3.4 PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in URPL
To address the role of PPARγ in the NRF2/GPX4 pathway in URPL, we investigated the mechanism of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in URPL by using PPARγ inhibitors (T0070907) and agonists (Rosiglitazone) in mouse models. First, the immunofluorescence intensity of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 were significantly decreased in the control + T0070907 and the URPL group, as compared with the control group. Then the immunofluorescence intensity of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 were significantly increased in URPL + Rosiglitazone group when compared with the URPL group (Figure 5a). Next, the relative values of ROS, MDA, and GSH were assessed. Results showed that the level of ROS and MDA was significantly increased, and GSH was significantly decreased in the control + T0070907 and the URPL group when compared with the control group. Besides, the level of ROS and MDA was significantly decreased, and GSH was significantly increased in the URPL + Rosiglitazone group when compared with URPL group (Figure 5b–d). Next, we found that inhibition of PPARγ increased embryonic absorption in mice, while activation of PPARγ decreased it (Figure 5e–f).

PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in URPL. (a) Fe2+ content was assessed by RhoNox-1 staining; the PPARγ, NRF2, and GPX4 were assessed by immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 50 μm. (b)–(d) ROS, MDA, and GSH levels were observed by ROS, MDA, and GSH assays. (e) and (f) Absorption of mouse embryos. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the control group, #P < 0.05 compared with the URPL group.
3.5 ALA improved ferroptosis in URPL by activating the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 pathway
ALA is a widespread organosulfur component with multiple properties. Among them, the strong antioxidant potential makes it a potential drug for patients with threatened miscarriage [18]. First, the Fe2+ content was assessed, and the RhoNox-1 staining results showed that the Fe2+ content of the URPL group was increased when compared with the control group, and the Fe2+ content of the URPL + ALA group was decreased when compared with the URPL group (Figure 6a). Next, the immunofluorescence and western blot showed that the expression levels of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 significantly decreased in URPL group, as compared with the results in control group, and the expression levels of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 significantly increased in the URPL + ALA group when compared with URPL group (Figure 6a and b). Next, the relative values of ROS, MDA, and GSH were assessed. Results showed that the level of ROS and MDA was significantly increased, and GSH was significantly decreased in URPL group when compared with the control group. The levels of ROS and MDA were significantly decreased, and GSH was significantly increased in the URPL + ALA group when compared with the URPL group (Figure 6c–e). Next, we found that ALA decreased the embryonic absorption in mice (Figure 6f and g).
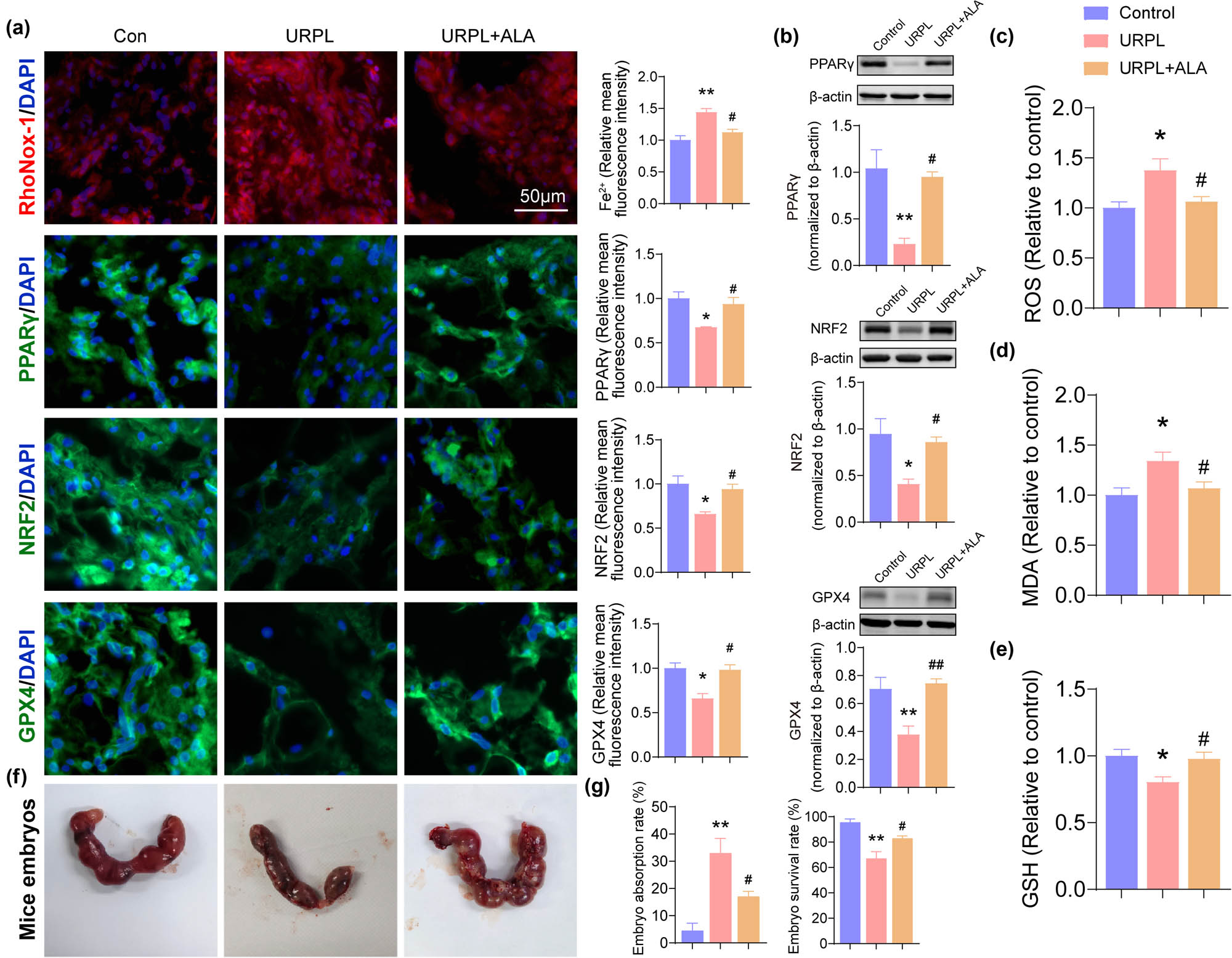
ALA improves ferroptosis in URPL by activating the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 pathway. (a) Fe2+ content was assessed by RhoNox-1 staining; the PPARγ, NRF2, and GPX4 were assessed by immunofluorescence. Scale bar: 50 μm. (b) PPARγ, NRF2, and GPX4 were assessed by western blot. (c)–(e) ROS, MDA, and GSH levels were observed by ROS, MDA, and GSH assays. (f) and (g) Absorption of mouse embryos. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the control group, #P < 0.05 compared with the URPL group, ##P < 0.01 compared with the URPL group.
4 Discussion
During pregnancy, the endometrium undergoes significant modifications and evolves into decidua, a newly formed tissue that plays an important part in successful embryo implantation and fetal growth regulation. During this transfer, the endometrium is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress attack for its high oxygen consumption, active redox-based metabolism, and rich changes in cell fate. Interestingly, oxidative stress has been suggested as a potential mechanism for the occurrence and development of URPL [34]. In this study, we also identified that ROS and MDA levels were significantly increased, and GSH was significantly decreased in the decidual tissue of the URPL group. MDA is one of the products formed by the reaction of lipids with oxygen free radicals, and their content represents the degree of lipid peroxidation. Furthermore, lipid peroxidation caused by oxidative stress is a marker of ferroptosis, which directly damages the integrity of cell membranes and contributes to ferroptotic cell death [35]. Recent studies identify that ferroptosis is closely associated with endometrial-related reproductive disorders. According to Ni et al., iron-rich follicular fluid enhanced the likelihood of endometriosis-related infertility [36]. Besides, Hu et al. discovered a link between uterine and placental ferroptosis and fetal loss caused by oxidative stress [37]. Furthermore, iron deposition and ferroptosis in the decidua have been verified to induce pregnancy loss. And the ferroptosis inhibitor could effectively reverse theembryo loss in the abortion model [38]. In this study, we found that iron deposition was increased in URPL. Data have confirmed that iron overload can facilitate ferroptosis by creating ROS via the Fenton chemistry [39]. Accordingly, we found that ferroptosis was significantly increased in decidual tissues of patients with URPL, characterized by classic ferroptosis changes in cell morphology and cell compositions. Physiologically, decidual tissue is not only to provide a physical anchorage but also to provide a conducive biochemical microenvironment for embryo implantation and development at the early stage, such as immune regulation, vascular recasting embryo implantation, and placentation, thus orchestrating the homeostatic balance between the mother and fetus [40,41]. While, excessive ferroptosis not only causes functional decline or loss but also emphasizes inflammatory signals and promotes embryo rejection [9]. Compelling evidence indicates that ferroptosis holds great potential for initiating inflammation or at least has proinflammatory effects [4]. Inhibiting ferroptosis can prevent the ensuing immune cell invasion and inflammatory reaction, thus contributing to the improvement of various inflammatory diseases [42,43]. Previous advances in immunologic studies have confirmed the overactive inflammation in decidual tissue of URPL, accompanied by high level of proinflammatory cytokines and inflammasome [44]. Besides, there is some preliminary evidence showing that ferroptosis could be important in inducing cell death by immune cells [45]. Similarly, a bioinformatic study has shown that ferroptosis is also associated with immune landscape disorders in the decidual tissue of the URPL [7]. Collectively, ferroptosis and the biological processes secondary to ferroptosis are closely related to the recognition and tolerance of the decidual tissue to the embryo in URPL. However, the specific molecular network responsible for ferroptosis regulation remains to be explored, which may provide potential targets for future treatment.
Previous research has shown that NRF2/GPX4 controls nearly all ferroptosis-related genes. NRF2 exerts significant roles in establishing a cellular antioxidative defense system via regulating iron metabolism, GSH regulation, NADPH regeneration, which is pivotal for GPX4 activity [46,47]. GPX4 is one of numerous members of the GPX family, and it is crucial to ferroptosis development. If GPX4 activity declines, lipid peroxides cannot be broken down by the GPX4-catalyzed reduction process. Additionally, Fe2+ oxidizes lipids in a Fenton-like way, producing numerous ROS in the process that encourages ferroptosis. Yang et al. confirmed that cells with downregulated GPX4 expression were more sensitive to ferroptosis, while cells with upregulated GPX4 expression could avoid ferroptosis [48]. So far, studies have shown that the inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 that fails to suppress ferroptosis may be a critical pathomechanism for triggering pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia [49]. However, it is still unclear how NRF2/GPX4 contributes to URPL. In this study, we found that the NRF2/GPX4 signal axis was significantly suppressed in UPRL. Of note, this is the first time that NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis has been discovered in decidua samples of UPRL. Activating this signal axis may provide a possibility for improving decidual tissue function in URPL.
Despite the fact that NRF2/GPX4 is largely important for preventing ferroptosis, little is known about how cells control their anti-ferroptotic potential in both physiological and pathological conditions. In this study, we confirmed that PPARγ was significantly reduced in the decidua of URPL based on bioinformatics analysis and animal experiments, which may be account of the disregulation of NRF2/GPX4-dependent ferroptosis in URPL. PPARγ belongs to the transcription factor family, and has been demonstrated to orchestrate lipid and glucose metabolism pathways, including lipogenesis, steroidogenesis, and glucose transporters [50]. Previous studies have confirmed that PPARγ can regulate sequences of many genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and cell differentiation by binding with retinoid X receptor as a heterodimeric partner to specific DNA sequences, termed PPAR response elements [51]. In addition, PPARγ is highly expressed in the maternal–fetal interface during pregnancy and supposed to represent a critical link between energy metabolism and reproduction [52]. Substantial studies have confirmed that PPARγ can affect trophoblast proliferation, differentiation, and migration via regulating cellular metabolism [53,54]. Similarly, a study by Duan et al. confirmed that the lack of PPARγ could lead to embryonic lethality due to implantation defects [55]. Furthermore, due to its crucial role in antioxidant defense and redox balance [56], recent research begins to highlight the tight link between PPARγ and ferroptosis. A study conducted by Chen et al. displayed that PPARγ stimulated the NRF2/ARE axis to neutralize oxidative stress and ferroptosis [57]. Thus, moving from evidence to practice, our study focused on the modulation between PPARγ and NRF2–GPX4 axis. The result uncovered that PPARγ activation significantly induced NRF2/GPX4 signal, and the level of ferroptosis and the embryo absorption rate in URPL mice were significantly reduced. On the contrary, PPARγ inhibition significantly suppressed NRF2/GPX4 axis and increased ferroptosis and embryo absorption in normal mice. These results suggested that PPAR played a crucial role in NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in UPRL. Thus, we presume that PPARγ is a potential target in URPL on account of its ability to attenuate oxidative stress and ferroptosis. Of note, exploring the protective role of PPARγ agonists in URPL is a very promising area. Consistent with our ideas, Rosiglitazone, an agonist of PPAR, has been verified to improve the endometrial receptivity via restraining endometrial angiogenesis during decidualization, while decidualization deficiency is a critical pathomechanism in URPL [58,59]. Besides, in our study, we confirmed that Rosiglitazone significantly ameliorated oxidative stress and upregulated the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signaling axis, which in turn amplified ferroptosis and reduced embryo absorption in mice. However, the safety and efficacy of Rosiglitazone in URPL remains to be validated by clinical data.
Now it has been discovered that iron chelators (Deferoxamine) and lipid peroxidation inhibitors (Ferrostatin-1) can prevent ferroptosis [60]. However, their safety for use in pregnant women has not been confirmed. Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore safe and effective drugs to intervene in ferroptosis in URPL. ALA has been described as an ideal or universal antioxidant in various diseases. Recently, ALA has been suggested as a possible therapeutic approach for several oxidative stress disorders that affect pregnancy outcomes [61]. Its supplementation has been recently proposed in some clinical trials to identify the efficacy in RPL. For instance, a clinical trial studying the effects of ALA supplementation for male partners of couples with RPL showed that ALA mitigates sperm DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in the male partner of couples with PRL [62]. In addition, existing studies have shown that ALA not only has no adverse effects on female and male reproductive function, but also protects oocytes and sperm from toxic substances [63]. In particular, ALA has a protective effect on embryos in adverse environments [64]. Thus, in terms of efficacy and safety, ALA exhibits remarkable potential in the treatment of URPL.
At present, the role of ALA in women with URPL mainly focuses on its anti-inflammatory activity, especially its inhibition of NF-κB. It has been confirmed that ALA can target NF-κB by regulating upstream kinases such as MAPK to prevent IkB degradation, or through regenerating vitamin E and thus inhibiting protein kinase C, which can phosphorylate IkB [15]. Besides, Di Nicuolo et al. showed that ALA supplementation for 3 months significantly reduced the endometrial inflammasome NALP-3 expression and the consequent pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-18 and Il-1β) secretion in women with RPL [18]. In addition to that, recent studies have proved that ALA could inhibit ferroptosis-like cell death [14,65]. The mechanism study identified that ALA could prevent ferroptosis through the system Xc-/GPX4 axis, lipid peroxidation axis, and iron metabolism axis [21]. Nevertheless, few studies have discussed whether ALA attenuates ferroptosis in URPL. In combination with the latest frontiers, we found for the first time in this study that ALA could improve ferroptosis by acting on PPARγ–NRF2–GPX4 in decidual tissue and significantly reduce abortion in URPL mice. In line with our results, recent investigations indicate that ALA can activate PPAR-γ, modulate PPAR-regulated genes, and upregulate the expression of PPARγ mRNA and protein [66]. Taken together, these findings imply that PPARγ activation by ALA plays a crucial protective role in URPL via targeting ferroptosis.
5 Conclusion
In summary, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first time we have identified the role of PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in the pathology of URPL, and it is also the first time we have demonstrated that ALA plays a protective role in URPL by regulating ferroptosis via targeting PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4. Taken together, our study throw new mechanistic insights into ferroptosis caused by PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 in URPL, as well as the experimental and theoretical basis for the treatment of URPL by ALA treatment.
Abbreviations
- ALA
-
alpha-lipoic acid
- DEGs
-
differentially expressed genes
- GSH
-
glutathione
- GPX4
-
glutathione peroxidase 4
- KEGG
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- MDA
-
malondialdehyde
- NRF2
-
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- PPARγ
-
peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ
- PPI
-
protein–protein interaction
- RPL
-
recurrent pregnancy loss
- ROS
-
reactive oxygen species
- TEM
-
transmission electron microscope
- URPL
-
unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all patients for their participation.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the Project on Traditional Chinese Medicine in Heilongjiang Province (No. ZHY2023-219), Scientific Research project of Heilongjiang Provincial Health Commission (No. 20210505010346), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 82174421, 81973894).
-
Author contributions: Y.Z. designed the experiments, conducted the experiments, and prepared the manuscript. X.-X.Z. conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. X.-L.F. critically reviewed the manuscript and study initiation. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Appendix
The baseline data of clinical samples
| Control group (n = 15) | URPL group (n = 15) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.60 ± 3.11 | 31.00 ± 2.95 | 0.592 |
| The gestation period (days) | 58.67 ± 2.69 | 58.53 ± 3.14 | 0.901 |
| The menstrual cycle (days) | 29.13 ± 2.23 | 29.00 ± 2.24 | 0.871 |
References
[1] Carp H. Immunotherapy for recurrent pregnancy loss. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2019;60:77–86. 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2019.07.005.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Dimitriadis E, Menkhorst E, Saito S, Kutteh WH, Brosens JJ. Recurrent pregnancy loss. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020;6(1):98. 10.1038/s41572-020-00228-z.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Cornish EF, Mcdonnell T, Williams DJ. Chronic inflammatory placental disorders associated with recurrent adverse pregnancy outcome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:825075. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.825075.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107–25. 10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Beharier O, Kajiwara K, Sadovsky Y. Ferroptosis, trophoblast lipotoxic damage, and adverse pregnancy outcome. Placenta. 2021;108:32–8. 10.1016/j.placenta.2021.03.007.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shen X, Obore N, Wang Y, Yu T, Yu H. The role of ferroptosis in placental-related diseases. Reprod Sci. 2023;30(7):2079–86. 10.1007/s43032-023-01193-0.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Nong B, Liang Y, Fang D, Pan Z, Li W, Yang C, et al. Investigation of hub ferroptosis-related genes and the immune landscape in recurrent pregnancy loss and unexplained infertility using bioinformatics analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2023;11(5):209. 10.21037/atm-23-97.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266–82. 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med. 2021;218(6):e20210518. 10.1084/jem.20210518.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Dai X, Yan X, Wintergerst KA, Cai L, Keller BB, Tan Y. Nrf2: redox and metabolic regulator of stem cell state and function. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(2):185–200. 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.09.007.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Babaei-Abraki S, Karamali F, Nasr-Esfahani MH. Ferroptosis: the functions of nrf2 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Signal. 2023;106:110654. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110654.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Wang Y, Yan S, Liu X, Deng F, Wang P, Yang L, et al. Prmt4 promotes ferroptosis to aggravate doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via inhibition of the nrf2/gpx4 pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(10):1982–95. 10.1038/s41418-022-00990-5.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Baban RS. Oxidative stress in recurrent pregnancy loss women. Saudi Med J. 2010;31(7):759–63.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Salehi B, Berkay YY, Antika G, Boyunegmez TT, Fawzi MM, Lobine D, et al. Insights on the use of α-lipoic acid for therapeutic purposes. Biomolecules. 2019;9(8):356. 10.3390/biom9080356.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Di Nicuolo F, Castellani R, Ticconi C, Scambia G, Pontecorvi A, Di Simone N. A-lipoic acid and its role on female reproduction. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(11):767–74. 10.2174/1389203722666211029102417.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Najafi N, Mehri S, Ghasemzadeh RM, Hosseinzadeh H. Effects of alpha lipoic acid on metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 2022;36(6):2300–23. 10.1002/ptr.7406.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Di Tucci C, Galati G, Mattei G, Bonanni V, Capri O, D’Amelio R, et al. The role of alpha lipoic acid in female and male infertility: a systematic review. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2021;37(6):497–505. 10.1080/09513590.2020.1843619.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Di Nicuolo F, D’Ippolito S, Castellani R, Rossi ED, Masciullo V, Specchia M, et al. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid and myoinositol on endometrial inflammasome from recurrent pregnancy loss women. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2019;82(3):e13153. 10.1111/aji.13153.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Li X, Zou Y, Fu YY, Xing J, Wang KY, Wan PZ, et al. A-lipoic acid alleviates folic acid-induced renal damage through inhibition of ferroptosis. Front Physiol. 2021;12:680544. 10.3389/fphys.2021.680544.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Zhao Y, Liu X, Liang C, Pei T, Guo M, Wang J, et al. A-lipoic acid alleviated fluoride-induced hepatocyte injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(50):15962–71. 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07484.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Liu L, Yang S, Wang H. A-lipoic acid alleviates ferroptosis in the mpp(+)-induced pc12 cells via activating the pi3k/akt/nrf2 pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(2):422–31. 10.1002/cbin.11505.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Clark DA, Coulam CB, Daya S, Chaouat G. Unexplained sporadic and recurrent miscarrage in the new millennium: a critical analysis of immune mechanisms and treatments. Hum Reprod Update. 2001;7(5):501–11. 10.1093/humupd/7.5.501.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Van Nguyen T, Piao CH, Fan YJ, Shin DU, Kim SY, Song HJ, et al. Anti-allergic rhinitis activity of α-lipoic acid via balancing th17/treg expression and enhancing nrf2/ho-1 pathway signaling. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12528. 10.1038/s41598-020-69234-1.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, et al. Ncbi geo: archive for functional genomics data sets – update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D991–5. 10.1093/nar/gks1193.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F, Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U, et al. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 2003;4(2):249–64. 10.1093/biostatistics/4.2.249.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Cao Z, Zeng Z, Wang B, Liu C, Liu C, Wang Z, et al. Identification of potential bioactive compounds and mechanisms of gegenqinlian decoction on improving insulin resistance in adipose, liver, and muscle tissue by integrating system pharmacology and bioinformatics analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;264:113289. 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113289.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(6):882–3. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Zhou N, Yuan X, Du Q, Zhang Z, Shi X, Bao J, et al. Ferrdb v2: update of the manually curated database of ferroptosis regulators and ferroptosis-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D571–82. 10.1093/nar/gkac935.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(43):15545–50. 10.1073/pnas.0506580102.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Safran M, Rosen N, Twik M, Barshir R, Stein TI, Dahary D, et al. The genecards suite. In: Abugessaisa I, Kasukawa T, editors. Practical guide to life science databases. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore; 2021. p. 27–56.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Szklarczyk D, Kirsch R, Koutrouli M, Nastou K, Mehryary F, Hachilif R, et al. The string database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D638–46. 10.1093/nar/gkac1000.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Farré D, Roset R, Huerta M, Adsuara JE, Roselló L, Albà MM, et al. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the alggen server: promo and malgen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(13):3651–3. 10.1093/nar/gkg605.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Han H, Cho JW, Lee S, Yun A, Kim H, Bae D, et al. Trrust v2: an expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D380–6. 10.1093/nar/gkx1013.Search in Google Scholar
[34] Goutami L, Jena SR, Swain A, Samanta L. Pathological role of reactive oxygen species on female reproduction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1391:201–20. 10.1007/978-3-031-12966-7_12.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(2):88. 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Ni Z, Li Y, Song D, Ding J, Mei S, Sun S, et al. Iron-overloaded follicular fluid increases the risk of endometriosis-related infertility by triggering granulosa cell ferroptosis and oocyte dysmaturity. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):579. 10.1038/s41419-022-05037-8.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Hu M, Zhang Y, Ma S, Li J, Wang X, Liang M, et al. Suppression of uterine and placental ferroptosis by n-acetylcysteine in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Hum Reprod. 2021;27(12):gaab067. 10.1093/molehr/gaab067.Search in Google Scholar
[38] Sun F, Cui L, Qian J, Li M, Chen L, Chen C, et al. Decidual stromal cell ferroptosis associated with abnormal iron metabolism is implicated in the pathogenesis of recurrent pregnancy loss. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7836. 10.3390/ijms24097836.Search in Google Scholar
[39] Poprac P, Jomova K, Simunkova M, Kollar V, Rhodes CJ, Valko M. Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(7):592–607. 10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.005.Search in Google Scholar
[40] Ng SW, Norwitz GA, Pavlicev M, Tilburgs T, Simón C, Norwitz ER. Endometrial decidualization: the primary driver of pregnancy health. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):4092. 10.3390/ijms21114092.Search in Google Scholar
[41] Zhang X, Wei H. Role of decidual natural killer cells in human pregnancy and related pregnancy complications. Front Immunol. 2021;12:728291. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.728291.Search in Google Scholar
[42] Sun Y, Chen P, Zhai B, Zhang M, Xiang Y, Fang J, et al. The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110108. 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110108.Search in Google Scholar
[43] Zhou Z, Ye TJ, Decaro E, Buehler B, Stahl Z, Bonavita G, et al. Intestinal sirt1 deficiency protects mice from ethanol-induced liver injury by mitigating ferroptosis. Am J Pathol. 2020;190(1):82–92. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.09.012.Search in Google Scholar
[44] Pei CZ, Kim YJ, Baek KH. Pathogenetic factors involved in recurrent pregnancy loss from multiple aspects. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2019;62(4):212–23. 10.5468/ogs.2019.62.4.212.Search in Google Scholar
[45] Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijón M, Kennedy PD, Johnson JK, et al. Cd8( +) t cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;569(7755):270–4. 10.1038/s41586-019-1170-y.Search in Google Scholar
[46] Thiruvengadam R, Venkidasamy B, Samynathan R, Govindasamy R, Thiruvengadam M, Kim JH. Association of nanoparticles and nrf2 with various oxidative stress-mediated diseases. Chem Biol Interact. 2023;380:110535. 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110535.Search in Google Scholar
[47] Shakya A, Mckee NW, Dodson M, Chapman E, Zhang DD. Anti-ferroptotic effects of nrf2: beyond the antioxidant response. Mol Cells. 2023;46(3):165–75. 10.14348/molcells.2023.0005.Search in Google Scholar
[48] Yang WS, Sriramaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by gpx4. Cell. 2014;156(1–2):317–31. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010.Search in Google Scholar
[49] Liao T, Xu X, Ye X, Yan J. Dj-1 upregulates the nrf2/gpx4 signal pathway to inhibit trophoblast ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):2934. 10.1038/s41598-022-07065-y.Search in Google Scholar
[50] Marion-Letellier R, Savoye G, Ghosh S. Fatty acids, eicosanoids and ppar gamma. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;785:44–9. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.11.004.Search in Google Scholar
[51] Wójtowicz S, Strosznajder AK, Jeżyna M, Strosznajder JB. The novel role of ppar alpha in the brain: promising target in therapy of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(5):972–88. 10.1007/s11064-020-02993-5.Search in Google Scholar
[52] Vitti M, Di Emidio G, Di Carlo M, Carta G, Antonosante A, Artini PG, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in female reproduction and fertility. Ppar Res. 2016;2016:4612306. 10.1155/2016/4612306.Search in Google Scholar
[53] Lendvai Á, Deutsch MJ, Plösch T, Ensenauer R. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors under epigenetic control in placental metabolism and fetal development. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;310(10):E797–810. 10.1152/ajpendo.00372.2015.Search in Google Scholar
[54] Peng L, Yang H, Ye Y, Ma Z, Kuhn C, Rahmeh M, et al. Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (ppars) in trophoblast functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(1):433. 10.3390/ijms22010433.Search in Google Scholar
[55] Duan SZ, Ivashchenko CY, Whitesall SE, D’Alecy LG, Duquaine DC, Brosius FR, et al. Hypotension, lipodystrophy, and insulin resistance in generalized ppargamma-deficient mice rescued from embryonic lethality. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(3):812–22. 10.1172/JCI28859.Search in Google Scholar
[56] Tseng V, Sutliff RL, Hart CM. Redox biology of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in pulmonary hypertension. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019;31(12):874–97. 10.1089/ars.2018.7695.Search in Google Scholar
[57] Chen J, Wang Y, Li M, Zhu X, Liu Z, Chen Q, et al. Netrin-1 alleviates early brain injury by regulating ferroptosis via the pparγ/nrf2/gpx4 signaling pathway following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 2023;15(1):219–37. 10.1007/s12975-022-01122-4.Search in Google Scholar
[58] Li M, Hu J, Yao L, Gao M. Decreased angptl4 impairs endometrial angiogenesis during peri-implantation period in patients with recurrent implantation failure. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(18):10730–43. 10.1111/jcmm.15696.Search in Google Scholar
[59] Ewington LJ, Tewary S, Brosens JJ. New insights into the mechanisms underlying recurrent pregnancy loss. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019;45(2):258–65. 10.1111/jog.13837.Search in Google Scholar
[60] Liu P, Feng Y, Li H, Chen X, Wang G, Xu S, et al. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020;25:10. 10.1186/s11658-020-00205-0.Search in Google Scholar
[61] Monastra G, De Grazia S, Cilaker MS, Goker A, Unfer V. Immunomodulatory activities of alpha lipoic acid with a special focus on its efficacy in preventing miscarriage. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(12):1695–708. 10.1080/17425247.2016.1200556.Search in Google Scholar
[62] Habibi M, Abbasi B, Fakhari ZZ, Esmaeili V, Shaverdi A, Sadighi GM, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid ameliorates sperm dna damage and chromatin integrity in men with high dna damage: a triple blind randomized clinical trial. Cell J. 2022;24(10):603–11. 10.22074/cellj.2022.8273.Search in Google Scholar
[63] Prathima P, Pavani R, Sukeerthi S, Sainath SB. A-lipoic acid inhibits testicular and epididymal oxidative damage and improves fertility efficacy in arsenic-intoxicated rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2018;32(2):e22016. 10.1002/jbt.22016.Search in Google Scholar
[64] Mokhtari S, Mahdavi AH, Hajian M, Kowsar R, Varnosfaderani SR, Nasr-Esfahani MH. The attenuation of the toxic effects of lps on mouse pre-implantation development by alpha-lipoic acid. Theriogenology. 2020;143:139–47. 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.12.008.Search in Google Scholar
[65] Peng W, Zhu Z, Yang Y, Hou J, Lu J, Chen C, et al. N2l, a novel lipoic acid-niacin dimer, attenuates ferroptosis and decreases lipid peroxidation in ht22 cells. Brain Res Bull. 2021;174:250–9. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.06.014.Search in Google Scholar
[66] Pershadsingh HA. Alpha-lipoic acid: physiologic mechanisms and indications for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16(3):291–302. 10.1517/13543784.16.3.291.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis

