Abstract
Introduction
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs) are rare and heterogeneous diseases characterized by excessive eosinophilic infiltration of the digestive system. D-dimer levels and its possible association with disease course were not reported.
Case series
We reported a series of three EGID cases presenting with high levels of D-dimer. No evidence for potential venous thromboembolism was found through computed tomography pulmonary angiogram and vascular ultrasounds. Moreover, D-dimer levels decreased after short-time systemic prednisolone administration, accompanied by remission of clinical symptoms and decrease of peripheral eosinophil counts and IgE levels.
Conclusion
Elevation of D-dimer in EGID may not represent thrombotic events but is possibly associated with disease severity. More population-based studies are needed to delineate the potential relationship among D-dimer, thrombosis, and inflammation in EGID.
1 Introduction
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs) are characterized by excessive infiltration of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract, ranging from the esophagus to the rectum, which includes eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), eosinophilic gastritis (EoG), eosinophilic enteritis, eosinophilic colitis (EoC), etc. [1]. Patients suffer from different types of symptoms depending on the involved segments, including nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc. [2]. Most patients are obliged to corticosteroid therapy accompanied by various side effects, such as metabolic disorders [3]. Moreover, more than half of the patients suffer persistent disease activity or a relapsing and remitting course.
Laboratory results in EGID are mostly unspecific, including eosinophilia [4], iron-deficiency anemia [5], elevation of serum IgE [6], etc. However, abnormalities of coagulation parameters are not reported in previous cases. In the coagulation process, D-dimer is derived from fibrin degradation products (FDPs) when plasmin cleaves insoluble fibrin monomers [7]. It has been widely used in the identification, evaluation, and treatment effects of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and various artery diseases [8]. However, role of D-dimer in EGID and its possible association with VTE are not reported. Thus, we report a case series of EGID with an uncommon presentation of D-dimer elevation in the absence of VTE.
2 Case series
2.1 Case 1
A 26-year-old Chinese man, with no significant past medical history, presented to the clinic with 3-day history of abdominal pain localized to the epigastrium. He denied any recent travel, sick contact, or drug administration prior to the onset of symptoms. The physical examination findings were unremarkable.
The total white blood cell count was 10,840/µL (3,500–9,500/µL, reference range in our hospital), and eosinophil count was 5,130/µL (20–520/µL). The fecal occult blood test was weakly positive. The level of immunoglobin (Ig) E was 220 IU/mL (≤100 IU/mL) and the patient was weakly allergic to peanut and soya bean. D-dimer level was three times more than the normal range: 1.57 µg/mL (0–0.5 µg/mL). Liver and renal function, serum tumor markers, lipid levels, thyroid function, as well as immunity and inflammation-related markers, such as IgG, IgG4 isotype, IgA, IgM, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, antinuclear antibodies, and C-reactive protein were within the normal range.
A contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest and abdomen showed diffuse circumferential thickening of the esophagus and gastric antrum. The lung, liver, gall bladder, bile duct, spleen, and pancreas showed no abnormalities and there was no lymph node enlargement. Upper endoscopy revealed scattered flat hyperemia and erosion of the gastric antrum and duodenum (Figure 1). Colonoscopy showed scattered punctate erosion of the terminal ileum (Figure 2). Histological analysis showed moderately active gastritis and duodenitis, with more than 30 eosinophils per high-power field (HPF) in the gastric antrum (Figure 3). Differential diagnosis was also made according to current examinations. The patient reported no travel history. Stool tests for hookworm, whipworm, ascaris, and amoeba were negative. No evidence of parasitic infection was found. 13C-urea breath test and pathology analysis for Helicobacter pylori were negative. The patient also denied a history of medications, including mycophenolate and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The diagnosis of EoG was validated.

Representative images of upper endoscopy indicating scattered flat hyperemia and erosion of the gastric antrum and duodenum. (a) Esophagus, (b) gastric fundus, (c) gastric antrum, and (d) duodenum.
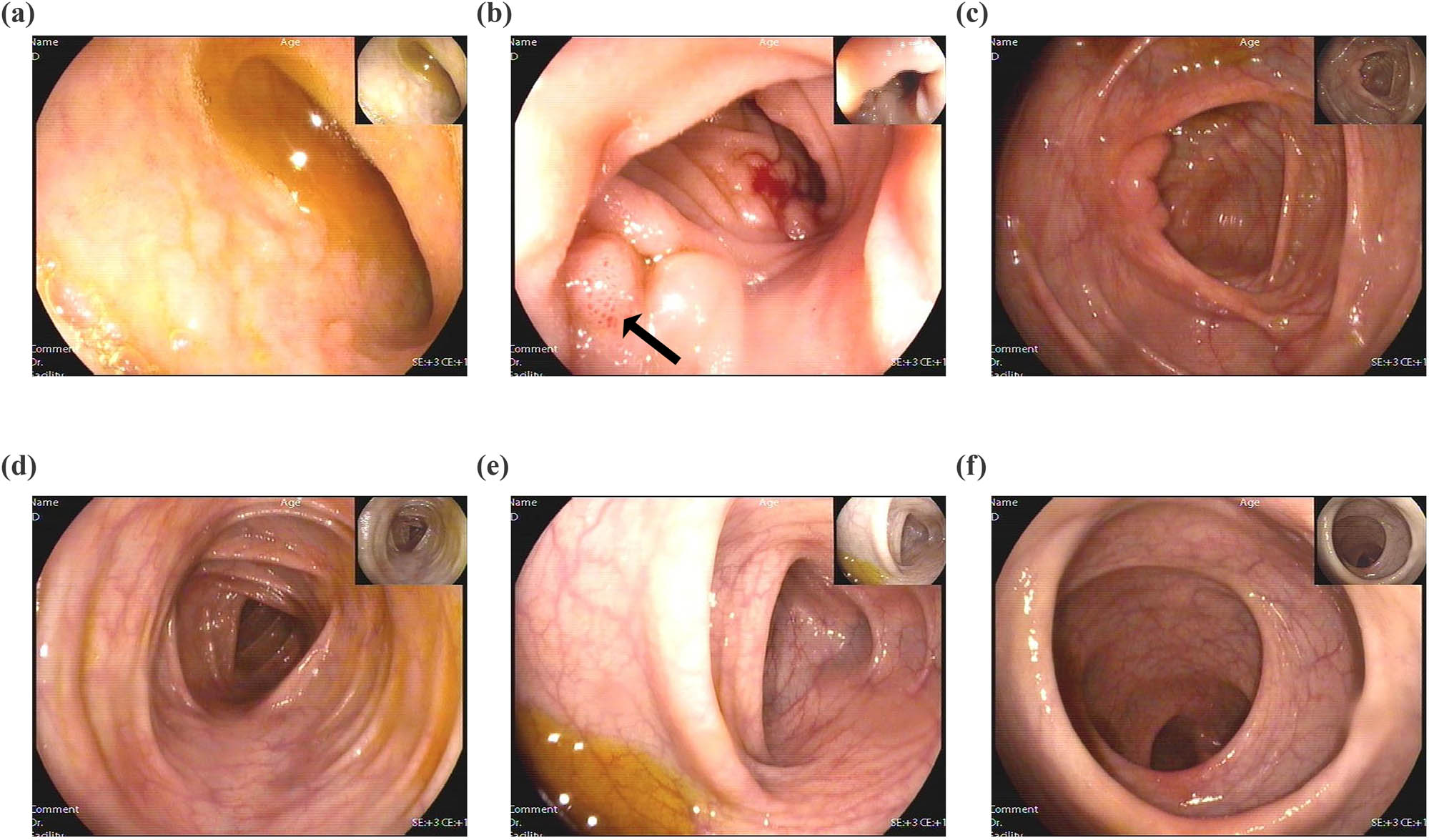
Representative images of colonoscopy indicating scattered punctate erosion of the terminal ileum. (a) Terminal ileum, (b) terminal ileum, (c) ileocecal region, (d) transverse colon, (e) descending colon, and (f) rectum.
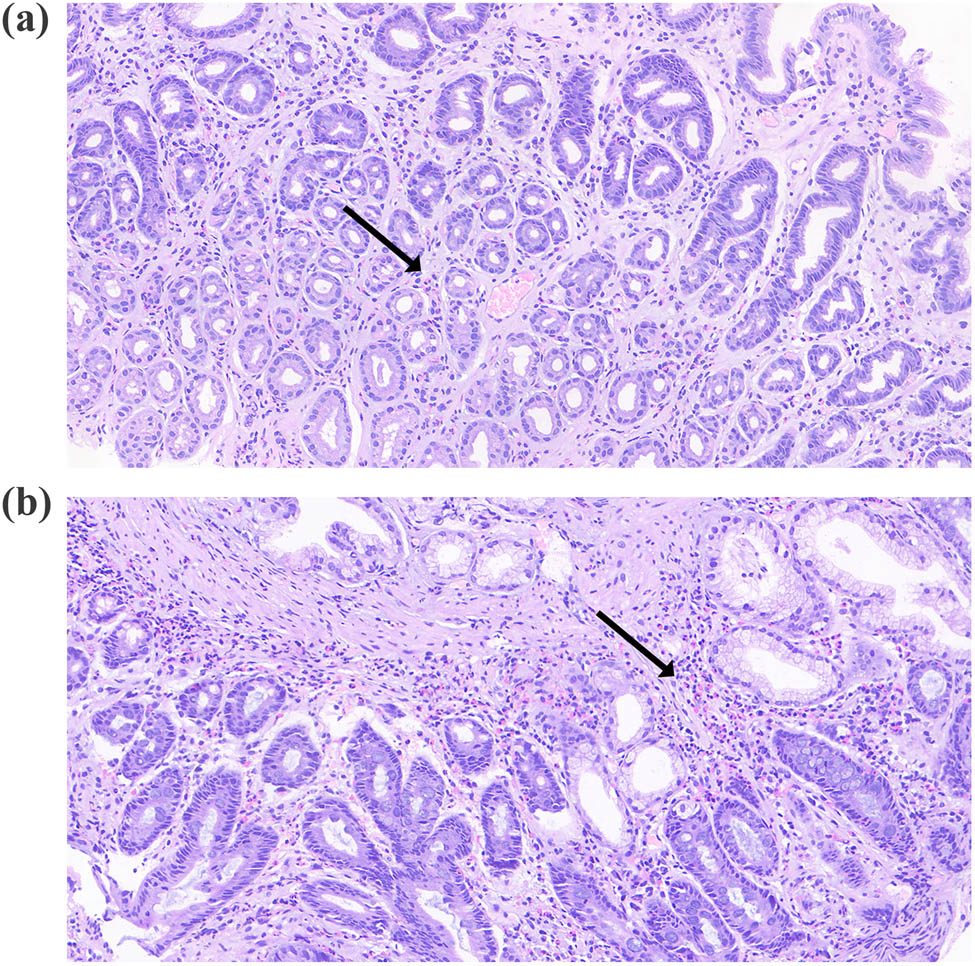
Histological images of the gastric antrum showing infiltration of eosinophils. (a) and (b) gastric antrum.
We wondered whether D-dimer elevation was a hint for venous thrombosis. However, computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA, Figure 4), vascular ultrasound for lower extremity, and mesenteric vessels were negative for possible thrombosis. Upon diagnosis, the patient was administered systemic steroid therapy (prednisolone 40 mg/day) followed by rapid symptomatic improvement. Five days after steroid administration, the eosinophil count was rapidly decreased to 590/µL and the D-dimer level was also within the normal range: 0.22 µg/mL. IgE was also downregulated to 180 IU/mL. The patient was discharged for further monitoring and follow-up.
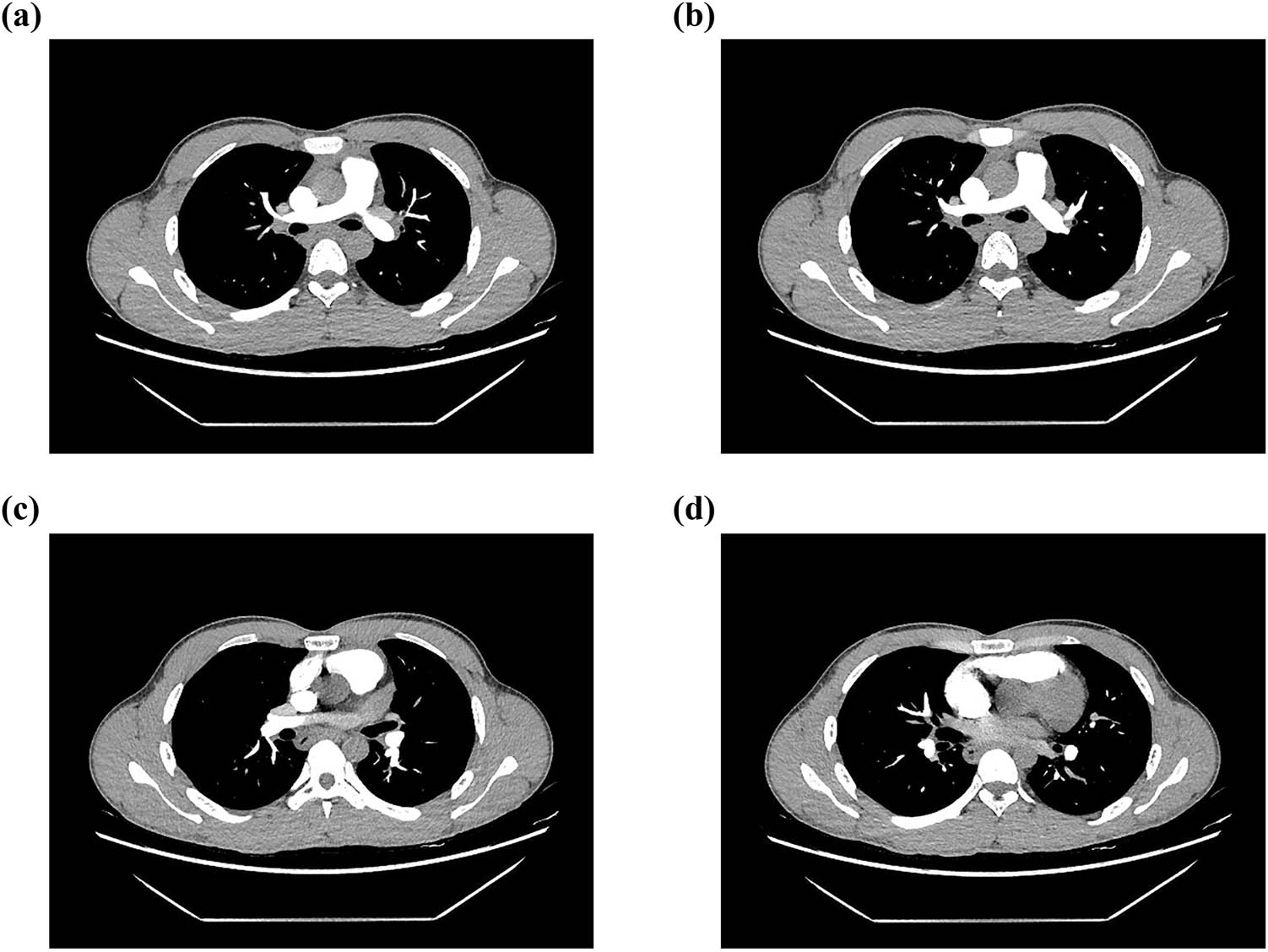
Representative images of CTPA showing no thrombosis. (a) to (d), different slices of CTPA.
2.2 Case 2
A 67-year-old female was referred to our department for abdominal pain over 10 days. She also had a distended abdomen and diarrhea. Her past medical history was significant for hypertension and her only surgical history was appendectomy due to appendicitis. She was taking valsartan to treat hypertension. Vital signs were stable and physical examination findings were not significant.
Labs were notable for a white cell count of 24,870/µL and an eosinophil count of 17,970/µL. The fecal occult blood test was also positive. The level of IgE was more than the upper limit 1,130 IU/mL and she was also weakly allergic to soybeans. Her lipid levels were abnormal with total triglyceride being 2.37 mmol/L and total cholesterol being 5.81 mmol/L. The D-dimer level was also more than the normal range: 0.8 µg/mL. Liver and renal function, serum tumor markers, and immunity-related markers were within normal range.
CTPA, vascular ultrasound for the lower extremity, and mesenteric vessels also showed no potential thrombosis. CT scan of the chest and abdomen showed cholecystitis and a small amount of pelvic effusion. Upper endoscopic findings indicated schistose erythema and erosion of the gastric antrum and duodenum. Histology of gastric antrum suggested massive infiltration of eosinophils (approximately 35 cells/HPF). Colonoscopy showed no abnormal findings. The patient also had no travel history. Stool tests were negative for parasitic infection. 13C-urea breath test and pathology analysis for H. pylori were negative. Apart from valsartan, the patient denied the current administration of medications. Diagnosis of EoG was verified.
She was administered with prednisolone 20 mg/day. Following the corticosteroid prescription, abdominal pain was soon relieved. Seven days after the prednisolone prescription, peripheral eosinophils were 2,460/µL. IgE level was decreased to 835 IU/mL. D-dimer concentration was 0.23 µg/mL.
2.3 Case 3
A 28-year-old Congolese male complained of symptoms of epigastric pain, abdominal distension, and acid reflux for 20 days, which were deteriorated after meals. No significant past medical history was reported and physical examination was unremarkable.
The peripheral blood profile showed a leukocytosis (11,540/µL) with 42.5% eosinophils (4,900/µL). IgE level was slightly high (156 IU/mL). Serum CA-125 was over normal range: 122.71U/ml. A high concentration of D-dimer (19.59 µg/mL) was also observed. Venous thrombosis was preliminarily excluded through CTPA and vascular ultrasound for mesenteric vessels and lower extremity. Chest and abdominal CT scans revealed diffuse thickening of the small intestine, ascites, and pleural effusion. No solid mass was observed. Upper endoscopy showed punctate erythema and erosion of the esophagus and gastric corpus, diffuse mucosal edema, and erosion of gastric angle and antrum. Histological analysis showed severely active gastritis and duodenitis with eosinophil infiltration more than 50/HPF in the gastric antrum and descending part of duodenum. He refused to undergo a colonoscopy.
The patient was prescribed prednisolone 30 mg/day to induce clinical remission. Shortly after corticosteroid administration, he reported significant alleviation of symptoms of abdominal pain, distension, and acid reflux. Five days after treatment, the peripheral eosinophil count was reduced to the normal range: 50/µL. D-dimer level was markedly decreased to 0.63 µg/mL. IgE level was within normal range. The peripheral eosinophil count, D-dimer, and IgE levels of all three cases before and after corticosteroid treatment are displayed in Table 1.
Peripheral eosinophil count, D-dimer, and IgE levels of all three cases before and after corticosteroid treatment
| At admission | After treatment (5–7 days) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral eosinophil count (cell/µL) | D-dimer level (µg/mL) | IgE level (IU/mL) | Peripheral eosinophil count (cell/µL) | D-dimer level (µg/mL) | IgE level (IU/mL) | |
| Case 1 | 5,130 | 1.57 | 220 | 590 | 0.22 | 180 |
| Case 2 | 17,970 | 5.81 | 1,130 | 2,460 | 0.23 | 835 |
| Case 3 | 4,900 | 19.59 | 156 | 50 | 0.63 | 74 |
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
3 Discussion
The overall prevalence of EoG and EoE is 5.1/100,000 persons, and the prevalence rate of EoC is 2.1/100,000 in the US [9], which makes EGID still a rare disease. No consensus has been reached concerning diagnostic criteria for EGID and patients showed various clinical symptoms and disease courses. In some cases, uncommon clinical presentations could be observed. Here, we reported a case series of EGID with elevation of D-dimer in the absence of VTE. D-dimer levels decreased after short-time prednisolone administration, with the remission of clinical symptoms and a decrease of peripheral eosinophil counts and IgE levels.
During coagulation progress, plasmin cleaves cross-linked insoluble fibrin monomers to yield by-products known as FDPs [10]. Among these products, the remnant composed of two adjacent bonded D-domains from cross-linked fibrils are what are now known as “D-dimers” [11]. Serum D-dimer levels correlate with various pathophysiological conditions. One of the critical roles is the diagnosis of VTE [12]. Increased D-dimer levels indicated highly possible active VTE, especially when D-dimer assays were performed shortly after symptom onset [13]. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of D-dimer concentration greater than 500 ng/mL for acute pulmonary emboli were 93.3, 25.0, and 30.4%, respectively [14]. To rule out possible thrombosis, all three cases underwent CTPA, as well as vascular ultrasound for mesenteric vessels and lower extremity. All results were negative, which indicated that thrombosis may not be the appropriate explanation for D-dimer elevation.
D-dimer was also associated with the onset and disease course of various cardiovascular diseases. In acute aortic dissection (AAD), D-dimer testing provided high sensitivity and a negative likelihood ratio. At a cut-off level of 0.9 and 0.1 µg/mL, negative predictive value (NPV) achieved 92% and 100%, respectively [15]. Similar results confirming the high NPV of D-dimer levels in AAD were also demonstrated by Cui et al. [16]. Plasma D-dimer was also strongly association with aortic aneurysm (AA) for cut-offs 400 and 900 ng/mL, respectively, and its high concentration (>900 ng/mL) correlated with a faster aneurysmal growth rate [17]. However, the role of D-dimers in the diagnosis and risk stratification of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients remains disputable. The potential hypothesis may be that the underlying coronary atherosclerotic activity may lead to fibrinolysis, and a subsequent increase in plasma D-dimer levels [18]. Its increase might precede the onset of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). In this case series, all three cases were excluded for AAD and AA based on symptoms, chest CT scan, and CTPA. Electrocardiogram and classic cardiac biomarkers such as troponin and creatine kinase MB also did not support ACS diagnosis. Moreover, the rapid decrease in D-dimer concentration after corticosteroid administration was not consistent with CAD or ACS disease course.
Inflammation has been recognized as a regulator of coagulation and fibrinolytic system [19,20]. Acute inflammation is known to shift the hemostatic balance toward a prothrombotic and antifibrinolytic state in which there is an increase in circulating levels of several key procoagulant and antifibrinolytic mediators. In HIV patients, D-dimer levels were markedly decreased in antiretroviral therapy (ART) compared to untreated patients [21]. Stopping ART in primary HIV patients leads to IL-6 and D-dimer significantly increase in pre-treatment concentrations [21]. Besides, in type 1 diabetic patients, serum D-dimer levels showed a significant positive correlation with TNF-α concentrations, indicating a possible interrelationship between inflammation and hypercoagulability status [22]. The potential explanation might be that proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-α, can stimulate the release of pro-coagulant molecules and inhibit the expression of anti-coagulant molecules by endothelial cells, resulting in a hypercoagulability state [23]. However, such studies were not reported in EGID and the correlation needed further validation in large-scale population studies.
In conclusion, we reported a case series of EGID with elevation of D-dimer in the absence of VTE. D-dimer levels decreased after short-time prednisolone administration, with a remission of clinical symptoms and a decrease in peripheral eosinophil counts and IgE levels. Further large-scale population-based studies are warranted to validate D-dimer levels in EGID.
-
Funding information: Supported by Qingdao Outstanding Health Professional Development Fund and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81800543).
-
Author contributions: Boyu Yang and Doudou Hu: patient diagnosis and management. Yang Song and Wanlei Ren: data collection and draft manuscript preparation. Doudou Hu: revising manuscript critically. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further requirements could be directed to the corresponding author.
References
[1] Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Abonia JP, Alexander JA, Arva NC, Atkins D, et al. International consensus recommendations for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disease nomenclature. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(11):2474–84.e3. 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.02.017.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Gonsalves N. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;57(2):272–85. 10.1007/s12016-019-08732-1.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Hua S, Cook D, Walker MM, Talley NJ. Pharmacological treatment of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9(9):1195–209. 10.1080/17512433.2016.1190268.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Lee J, Dierkhising R, Wu TT, Alexander J, Weiler C. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID) with peripheral eosinophilia: a retrospective review at Mayo Clinic. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(11):3254–61. 10.1007/s10620-011-1754-3.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Ekunno N, Munsayac K, Pelletier A, Wilkins T. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting with severe anemia and near syncope. J Am Board Fam Med. 2012;25(6):913–8. 10.3122/jabfm.2012.06.110269.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Votto M, De Filippo M, Caminiti L, Carella F, de Castro G, Landi M, et al. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders and allergen immunotherapy: Lights and shadows. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2021;32(5):814–23. 10.1111/pai.13458.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Johnson ED, Schell JC, Rodgers GM. The D-dimer assay. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(7):833–9. 10.1002/ajh.25482.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Weitz JI, Fredenburgh JC, Eikelboom JW. A test in context: D-dimer. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(19):2411–20. 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.09.024.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Mansoor E, Saleh MA, Cooper GS. Prevalence of eosinophilic gastroenteritis and colitis in a population-based study, from 2012 to 2017. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(11):1733–41. 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.05.050.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Gaffney PJ, Joe F. The lysis of crosslinked human fibrin by plasmin yields initially a single molecular complex, D dimer-E. Thromb Res. 1979;15(5–6):673–87. 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90177-4.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Gaffney PJ. Fibrin degradation products. A review of structures found in vitro and in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:594–610.10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03547.xSuche in Google Scholar
[12] Rodger MA, Le Gal G, Wells P, Baglin T, Aujesky D, Righini M, et al. Clinical decision rules and D-Dimer in venous thromboembolism: current controversies and future research priorities. Thromb Res. 2014;134(4):763–8. 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.07.031.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] de Bastos M, de Bastos MR, Bogutchi T, Carneiro-Proietti AB, Rezende SM. Duration of symptoms and D-dimer testing in the ruling-out of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(9):2079–80. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2006.02063.x.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Goldhaber SZ, Simons GR, Elliott CG, Haire WD, Toltzis R, Blacklow SC, et al. Quantitative plasma D-dimer levels among patients undergoing pulmonary angiography for suspected pulmonary embolism. JAMA. 1993;270(23):2819–22.10.1001/jama.270.23.2819Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Sodeck G, Domanovits H, Schillinger M, Ehrlich MP, Endler G, Herkner H, et al. D-dimer in ruling out acute aortic dissection: a systematic review and prospective cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(24):3067–75. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm484.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Cui JS, Jing ZP, Zhuang SJ, Qi SH, Li L, Zhou JW, et al. D-dimer as a biomarker for acute aortic dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltim). 2015;94(4):e471. 10.1097/MD.0000000000000471.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Golledge J, Muller R, Clancy P, McCann M, Norman PE. Evaluation of the diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma D-dimer for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(3):354–64. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq171.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Ridker PM, Vaughan DE, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Hennekens CH. Endogenous tissue-type plasminogen activator and risk of myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1993;341(8854):1165–8. 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90998-v.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Esmon CT. Coagulation and inflammation. J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9(3):192–8. 10.1179/096805103125001603.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Esmon CT. Crosstalk between inflammation and thrombosis. Maturitas. 2004;47(4):305–14. 10.1016/j.maturitas.2003.10.015.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Hamlyn E, Stohr W, Cooper DA, Fisher M, Tambussi G, Schechter M, et al. The effect of short-course antiretroviral therapy initiated in primary HIV-1 infection on interleukin-6 and D-dimer levels. AIDS. 2015;29(11):1355–61. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000675.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Domingueti CP, Foscolo RB, Reis JS, Campos FM, Dusse LM, Carvalho M, et al. Association of haemostatic and inflammatory biomarkers with nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:2315260. 10.1155/2016/2315260.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Margetic S. Inflammation and haemostasis. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012;22(1):49–62.10.11613/BM.2012.006Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- EDNRB inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells by activating the cGMP-PKG pathway
- STK11 (LKB1) mutation suppresses ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by facilitating monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis
- Association of SOX6 gene polymorphisms with Kashin-Beck disease risk in the Chinese Han population
- The pyroptosis-related signature predicts prognosis and influences the tumor immune microenvironment in dedifferentiated liposarcoma
- METTL3 attenuates ferroptosis sensitivity in lung cancer via modulating TFRC
- Identification and validation of molecular subtypes and prognostic signature for stage I and stage II gastric cancer based on neutrophil extracellular traps
- Novel lumbar plexus block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia and motor recovery after total knee arthroplasty
- Correlation between ABCB1 and OLIG2 polymorphisms and the severity and prognosis of patients with cerebral infarction
- Study on the radiotherapy effect and serum neutral granulocyte lymphocyte ratio and inflammatory factor expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Transcriptome analysis of effects of Tecrl deficiency on cardiometabolic and calcium regulation in cardiac tissue
- Aflatoxin B1 induces infertility, fetal deformities, and potential therapies
- Serum levels of HMW adiponectin and its receptors are associated with cytokine levels and clinical characteristics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- METTL3-mediated methylation of CYP2C19 mRNA may aggravate clopidogrel resistance in ischemic stroke patients
- Understand how machine learning impact lung cancer research from 2010 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis
- Pressure ulcers in German hospitals: Analysis of reimbursement and length of stay
- Metformin plus L-carnitine enhances brown/beige adipose tissue activity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling to reduce lipid accumulation and inflammation in murine obesity
- Downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in mouse xenograft nasopharyngeal carcinoma model via doxorubicin nanobubble combined with ultrasound
- Feasibility of 3-dimensional printed models in simulated training and teaching of transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- miR-335-3p improves type II diabetes mellitus by IGF-1 regulating macrophage polarization
- The analyses of human MCPH1 DNA repair machinery and genetic variations
- Activation of Piezo1 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer to hyperthermia therapy
- Comprehensive analysis based on the disulfidptosis-related genes identifies hub genes and immune infiltration for pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Changes of serum CA125 and PGE2 before and after high-intensity focused ultrasound combined with GnRH-a in treatment of patients with adenomyosis
- The clinical value of the hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with or without liver cirrhosis
- Development and validation of a novel model to predict pulmonary embolism in cardiology suspected patients: A 10-year retrospective analysis
- Downregulation of lncRNA XLOC_032768 in diabetic patients predicts the occurrence of diabetic nephropathy
- Circ_0051428 targeting miR-885-3p/MMP2 axis enhances the malignancy of cervical cancer
- Effectiveness of ginkgo diterpene lactone meglumine on cognitive function in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- The construction of a novel prognostic prediction model for glioma based on GWAS-identified prognostic-related risk loci
- Evaluating the impact of childhood BMI on the risk of coronavirus disease 2019: A Mendelian randomization study
- Lactate dehydrogenase to albumin ratio is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the MIMIC-III database
- CD36-mediated podocyte lipotoxicity promotes foot process effacement
- Efficacy of etonogestrel subcutaneous implants versus the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system in the conservative treatment of adenomyosis
- FLRT2 mediates chondrogenesis of nasal septal cartilage and mandibular condyle cartilage
- Challenges in treating primary immune thrombocytopenia patients undergoing COVID-19 vaccination: A retrospective study
- Let-7 family regulates HaCaT cell proliferation and apoptosis via the ΔNp63/PI3K/AKT pathway
- Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition
- Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients with colorectal cancer: A randomized controlled study comparing goal-directed and conventional fluid therapy
- Long-pulsed ultrasound-mediated microbubble thrombolysis in a rat model of microvascular obstruction
- High SEC61A1 expression predicts poor outcome of acute myeloid leukemia
- Comparison of polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing with conventional urine culture for the diagnosis of urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Secreted frizzled-related protein 5 protects against renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Pan-cancer and single-cell analysis of actin cytoskeleton genes related to disulfidptosis
- Overexpression of miR-532-5p restrains oxidative stress response of chondrocytes in nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting ABL1
- Autologous liver transplantation for unresectable hepatobiliary malignancies in enhanced recovery after surgery model
- Clinical analysis of incomplete rupture of the uterus secondary to previous cesarean section
- Abnormal sleep duration is associated with sarcopenia in older Chinese people: A large retrospective cross-sectional study
- No genetic causality between obesity and benign paroxysmal vertigo: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Identification and validation of autophagy-related genes in SSc
- Long non-coding RNA SRA1 suppresses radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating glycolytic reprogramming
- Evaluation of quality of life in patients with schizophrenia: An inpatient social welfare institution-based cross-sectional study
- The possible role of oxidative stress marker glutathione in the assessment of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis
- Compilation of a self-management assessment scale for postoperative patients with aortic dissection
- Left atrial appendage closure in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation: Effects on left atrial functioning in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
- Effect of anterior femoral cortical notch grade on postoperative function and complications during TKA surgery: A multicenter, retrospective study
- Clinical characteristics and assessment of risk factors in patients with influenza A-induced severe pneumonia after the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2
- Analgesia nociception index is an indicator of laparoscopic trocar insertion-induced transient nociceptive stimuli
- High STAT4 expression correlates with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and facilitates disease progression by upregulating VEGFA expression
- Factors influencing cardiovascular system-related post-COVID-19 sequelae: A single-center cohort study
- HOXD10 regulates intestinal permeability and inhibits inflammation of dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis through the inactivation of the Rho/ROCK/MMPs axis
- Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-26a induces ferroptosis, suppresses hepatic stellate cell activation, and ameliorates liver fibrosis by modulating SLC7A11
- Endovascular thrombectomy versus intravenous thrombolysis for primary distal, medium vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke
- ANO6 (TMEM16F) inhibits gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth and induces ferroptosis
- Prognostic value of EIF5A2 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis
- The role of enhanced expression of Cx43 in patients with ulcerative colitis
- Choosing a COVID-19 vaccination site might be driven by anxiety and body vigilance
- Role of ICAM-1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- Cost-effectiveness of ambroxol in the treatment of Gaucher disease type 2
- HLA-DRB5 promotes immune thrombocytopenia via activating CD8+ T cells
- Efficacy and factors of myofascial release therapy combined with electrical and magnetic stimulation in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Efficacy of tacrolimus monotherapy in primary membranous nephropathy
- Mechanisms of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F on treating rheumatoid arthritis explored by network pharmacology analysis and molecular docking
- FBXO45 levels regulated ferroptosis renal tubular epithelial cells in a model of diabetic nephropathy by PLK1
- Optimizing anesthesia strategies to NSCLC patients in VATS procedures: Insights from drug requirements and patient recovery patterns
- Alpha-lipoic acid upregulates the PPARγ/NRF2/GPX4 signal pathway to inhibit ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss
- Correlation between fat-soluble vitamin levels and inflammatory factors in paediatric community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective study
- CD1d affects the proliferation, migration, and apoptosis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma TPC-1 cells via regulating MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway
- miR-let-7a inhibits sympathetic nerve remodeling after myocardial infarction by downregulating the expression of nerve growth factor
- Immune response analysis of solid organ transplantation recipients inoculated with inactivated COVID-19 vaccine: A retrospective analysis
- The H2Valdien derivatives regulate the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatoma carcinoma cells through the Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Clinical efficacy of dexamethasone combined with isoniazid in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis and its effect on peripheral blood T cell subsets
- Comparison of short-segment and long-segment fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis
- Lycopene inhibits pyroptosis of endothelial progenitor cells induced by ox-LDL through the AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 pathway
- Methylation regulation for FUNDC1 stability in childhood leukemia was up-regulated and facilitates metastasis and reduces ferroptosis of leukemia through mitochondrial damage by FBXL2
- Correlation of single-fiber electromyography studies and functional status in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Risk factors of postoperative airway obstruction complications in children with oral floor mass
- Expression levels and clinical significance of serum miR-19a/CCL20 in patients with acute cerebral infarction
- Physical activity and mental health trends in Korean adolescents: Analyzing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from 2018 to 2022
- Evaluating anemia in HIV-infected patients using chest CT
- Ponticulus posticus and skeletal malocclusion: A pilot study in a Southern Italian pre-orthodontic court
- Causal association of circulating immune cells and lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study
- Assessment of the renal function and fibrosis indexes of conventional western medicine with Chinese medicine for dredging collaterals on treating renal fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comprehensive landscape of integrator complex subunits and their association with prognosis and tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer
- New target-HMGCR inhibitors for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: A drug Mendelian randomization study
- Population pharmacokinetics of meropenem in critically ill patients
- Comparison of the ability of newly inflammatory markers to predict complicated appendicitis
- Comparative morphology of the cruciate ligaments: A radiological study
- Immune landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: The central role of TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- Serum SIRT3 levels in epilepsy patients and its association with clinical outcomes and severity: A prospective observational study
- SHP-1 mediates cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transformation and inflammation in 16HBE cells
- Acute hyper-hypoxia accelerates the development of depression in mice via the IL-6/PGC1α/MFN2 signaling pathway
- The GJB3 correlates with the prognosis, immune cell infiltration, and therapeutic responses in lung adenocarcinoma
- Physical fitness and blood parameters outcomes of breast cancer survivor in a low-intensity circuit resistance exercise program
- Exploring anesthetic-induced gene expression changes and immune cell dynamics in atrial tissue post-coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism
- Analysis of the risk factors of the radiation-induced encephalopathy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study
- Reproductive outcomes in women with BRCA 1/2 germline mutations: A retrospective observational study and literature review
- Evaluation of upper airway ultrasonographic measurements in predicting difficult intubation: A cross-section of the Turkish population
- Prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating IGFBP2 in pancreatic cancer
- Postural stability after operative reconstruction of the AFTL in chronic ankle instability comparing three different surgical techniques
- Research trends related to emergence agitation in the post-anaesthesia care unit from 2001 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis
- Frequency and clinicopathological correlation of gastrointestinal polyps: A six-year single center experience
- ACSL4 mediates inflammatory bowel disease and contributes to LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell dysfunction by activating ferroptosis and inflammation
- Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts
- Effectiveness of nutritional support for clinical outcomes in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The relationship between IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-6 cytokines, and severity of the condition with serum zinc and Fe in children infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Paraquat disrupts the blood–brain barrier by increasing IL-6 expression and oxidative stress through the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Sleep quality associate with the increased prevalence of cognitive impairment in coronary artery disease patients: A retrospective case–control study
- Dioscin protects against chronic prostatitis through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- Association of polymorphisms in FBN1, MYH11, and TGF-β signaling-related genes with susceptibility of sporadic thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection in the Zhejiang Han population
- Application value of multi-parameter magnetic resonance image-transrectal ultrasound cognitive fusion in prostate biopsy
- Laboratory variables‐based artificial neural network models for predicting fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
- Decreased BIRC5-206 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through sponging miR-145-5p
- Sepsis induces the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction through activation of YAP1/Serpine1/caspase-3 pathway
- Assessment of iron metabolism and iron deficiency in incident patients on incident continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Tibial periosteum flap combined with autologous bone grafting in the treatment of Gustilo-IIIB/IIIC open tibial fractures
- The application of intravenous general anesthesia under nasopharyngeal airway assisted ventilation undergoing ureteroscopic holmium laser lithotripsy: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Long intergenic noncoding RNA for IGF2BP2 stability suppresses gastric cancer cell apoptosis by inhibiting the maturation of microRNA-34a
- Role of FOXM1 and AURKB in regulating keratinocyte function in psoriasis
- Parental control attitudes over their pre-school children’s diet
- The role of auto-HSCT in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma
- Significance of negative cervical cytology and positive HPV in the diagnosis of cervical lesions by colposcopy
- Echinacoside inhibits PASMCs calcium overload to prevent hypoxic pulmonary artery remodeling by regulating TRPC1/4/6 and calmodulin
- ADAR1 plays a protective role in proximal tubular cells under high glucose conditions by attenuating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The risk of cancer among insulin glargine users in Lithuania: A retrospective population-based study
- The unusual location of primary hydatid cyst: A case series study
- Intraoperative changes in electrophysiological monitoring can be used to predict clinical outcomes in patients with spinal cavernous malformation
- Obesity and risk of placenta accreta spectrum: A meta-analysis
- Shikonin alleviates asthma phenotypes in mice via an airway epithelial STAT3-dependent mechanism
- NSUN6 and HTR7 disturbed the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaques by regulating the immune responses of macrophages
- The effect of COVID-19 lockdown on admission rates in Maternity Hospital
- Temporal muscle thickness is not a prognostic predictor in patients with high-grade glioma, an experience at two centers in China
- Luteolin alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cell pyroptosis
- Therapeutic role of respiratory exercise in patients with tuberculous pleurisy
- Effects of CFTR-ENaC on spinal cord edema after spinal cord injury
- Irisin-regulated lncRNAs and their potential regulatory functions in chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
- DMD mutations in pediatric patients with phenotypes of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
- Combination of C-reactive protein and fibrinogen-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of all-cause mortality in heart failure patients
- Significant role and the underly mechanism of cullin-1 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Ferroptosis-related prognostic model of mantle cell lymphoma
- Observation of choking reaction and other related indexes in elderly painless fiberoptic bronchoscopy with transnasal high-flow humidification oxygen therapy
- A bibliometric analysis of Prader-Willi syndrome from 2002 to 2022
- The causal effects of childhood sunburn occasions on melanoma: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Oxidative stress regulates glycogen synthase kinase-3 in lymphocytes of diabetes mellitus patients complicated with cerebral infarction
- Role of COX6C and NDUFB3 in septic shock and stroke
- Trends in disease burden of type 2 diabetes, stroke, and hypertensive heart disease attributable to high BMI in China: 1990–2019
- Purinergic P2X7 receptor mediates hyperoxia-induced injury in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway
- Investigating the role of oviductal mucosa–endometrial co-culture in modulating factors relevant to embryo implantation
- Analgesic effect of external oblique intercostal block in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A retrospective study
- Elevated serum miR-142-5p correlates with ischemic lesions and both NSE and S100β in ischemic stroke patients
- Correlation between the mechanism of arteriopathy in IgA nephropathy and blood stasis syndrome: A cohort study
- Risk factors for progressive kyphosis after percutaneous kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- Predictive role of neuron-specific enolase and S100-β in early neurological deterioration and unfavorable prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke
- The potential risk factors of postoperative cognitive dysfunction for endovascular therapy in acute ischemic stroke with general anesthesia
- Fluoxetine inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in vitro
- Detection of serum FOXM1 and IGF2 in patients with ARDS and their correlation with disease and prognosis
- Rhein promotes skin wound healing by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- Differences in mortality risk by levels of physical activity among persons with disabilities in South Korea
- Review Articles
- Cutaneous signs of selected cardiovascular disorders: A narrative review
- XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis
- A narrative review on adverse drug reactions of COVID-19 treatments on the kidney
- Emerging role and function of SPDL1 in human health and diseases
- Adverse reactions of piperacillin: A literature review of case reports
- Molecular mechanism and intervention measures of microvascular complications in diabetes
- Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by autophagy
- Molecular landscape of borderline ovarian tumours: A systematic review
- Advances in synthetic lethality modalities for glioblastoma multiforme
- Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics
- Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment
- Sox9: A potential regulator of cancer stem cells in osteosarcoma
- Early detection of cardiovascular risk markers through non-invasive ultrasound methodologies in periodontitis patients
- Advanced neuroimaging and criminal interrogation in lie detection
- Maternal factors for neural tube defects in offspring: An umbrella review
- The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
- Progress in cytokine research for ARDS: A comprehensive review
- Utilizing reactive oxygen species-scavenging nanoparticles for targeting oxidative stress in the treatment of ischemic stroke: A review
- NRXN1-related disorders, attempt to better define clinical assessment
- Lidocaine infusion for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome: Case series and literature review
- Trends and future directions of autophagy in osteosarcoma: A bibliometric analysis
- Iron in ventricular remodeling and aneurysms post-myocardial infarction
- Case Reports
- Sirolimus potentiated angioedema: A case report and review of the literature
- Identification of mixed anaerobic infections after inguinal hernia repair based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Successful treatment with bortezomib in combination with dexamethasone in a middle-aged male with idiopathic multicentric Castleman’s disease: A case report
- Complete heart block associated with hepatitis A infection in a female child with fatal outcome
- Elevation of D-dimer in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in the absence of venous thrombosis: A case series and literature review
- Four years of natural progressive course: A rare case report of juvenile Xp11.2 translocations renal cell carcinoma with TFE3 gene fusion
- Advancing prenatal diagnosis: Echocardiographic detection of Scimitar syndrome in China – A case series
- Outcomes and complications of hemodialysis in patients with renal cancer following bilateral nephrectomy
- Anti-HMGCR myopathy mimicking facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Recurrent opportunistic infections in a HIV-negative patient with combined C6 and NFKB1 mutations: A case report, pedigree analysis, and literature review
- Letter to the Editor
- Letter to the Editor: Total parenteral nutrition-induced Wernicke’s encephalopathy after oncologic gastrointestinal surgery
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Bladder-embedded ectopic intrauterine device with calculus”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “XRCC1 and hOGG1 polymorphisms and endometrial carcinoma: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Investigating hormesis, aging, and neurodegeneration: From bench to clinics”
- Corrigendum to “Frankincense: A neuronutrient to approach Parkinson’s disease treatment”
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part II
- Machine-learning-based prediction of a diagnostic model using autophagy-related genes based on RNA sequencing for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Unlocking the future of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: A comprehensive analysis of disulfidptosis-related lncRNAs for prognosis and drug screening
- Elevated mRNA level indicates FSIP1 promotes EMT and gastric cancer progression by regulating fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part I
- Ultrasound-guided transperineal vs transrectal prostate biopsy: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy and complication rates
- Assessment of diagnostic value of unilateral systematic biopsy combined with targeted biopsy in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer
- SENP7 inhibits glioblastoma metastasis and invasion by dissociating SUMO2/3 binding to specific target proteins
- MARK1 suppress malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and improves sorafenib resistance through negatively regulating POTEE
- Analysis of postoperative complications in bladder cancer patients
- Carboplatin combined with arsenic trioxide versus carboplatin combined with docetaxel treatment for LACC: A randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part I
- Comprehensive pan-cancer investigation of carnosine dipeptidase 1 and its prospective prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Identification of signatures associated with microsatellite instability and immune characteristics to predict the prognostic risk of colon cancer
- Single-cell analysis identified key macrophage subpopulations associated with atherosclerosis

