Abstract
A composite of high-density polyethylene/ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (HDPE/UHMWPE) was synthesized via a high-temperature melting process. We specifically examined the effects of annealing on the morphological and rheological properties of the composite. Using scanning electron microscopy and advanced rotational rheometry, we determined that annealing notably alters the composite’s microstructure, with a reduction in pronounced features post-treatment. Rheologically, UHMWPE content significantly enhanced mechanical properties, particularly in storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), and complex viscosity (|η*|), which aligned with scaling law principles. Our findings highlight a distinct improvement in mechanical properties post-annealing, underscoring the potential of UHMWPE in enhancing polymer composite performance. The scaling laws relating G′, G″, and |η*| with UHMWPE were identified as follows: (1) pre-c e: G′ ∼ c 0.2, g″ ∼ c 0.07, |η*| ~ c0.07 and (2) post-c e: G′ ∼ c 1.20, g″ ∼ c 0.6, |η*| ∼ c 0.64, with a forward shift in c e noted after annealing. The addition of UHMWPE significantly enhanced the system’s properties, particularly after annealing. This study offers crucial insights into optimizing HDPE plastic films for enhanced durability and sustainability, ideally suiting them for eco-friendly agricultural uses.
1 Introduction
Polyethylene (PE) plastic film, a crucial polymer material, has emerged as a cornerstone in modern agricultural production. The widespread adoption of plastic film mulching technology has significantly propelled agricultural productivity in China [1]. In the year 2014 alone, the national consumption of plastic film astonishingly reached 1.425 million tons, covering nearly 300 million mu of agricultural land. This technique, primarily employed for its ability to elevate soil temperature and retain moisture, has proven to be instrumental in boosting crop yields by an impressive 20–50%. Such an increase is vital for bolstering Chinas food security. However, the extensive application of this technology has not been without its drawbacks, particularly leading to the adverse environmental impact known as “white pollution” due to film residues.
At the current stage, the primary strategy to combat this issue lies in the recycling and reusing of residual films. The challenge of recycling pollution predominantly stems from the quality and characteristics of the films used. Presently, the standards governing domestic film production are relatively low, coupled with insufficient management across the film’s lifecycle – from manufacturing and processing to usage and recycling. Consequently, the market is inundated with films that are ultra-thin, lack adequate strength, are prone to rapid aging, and have a short lifespan. This results in a proliferation of film fragments and residues in agricultural fields, presenting significant challenges in recovery and recycling. To address this, research and development focused on producing high-strength, high-quality, and cost-effective recyclable plastic films from the source is imperative. This approach is seen as a key solution for the prevention and control of residual film pollution [2]. Furthermore, current strategies for film PE materials emphasize enhancing recycling rates and material performance improvement [3,4]. Research exploring the recycling potential of waste high-density polyethylene (HDPE) films combined with natural fibers for creating decorative tiles revealed significant mechanical property enhancements [3]. Another study demonstrated molecular weight adjustment of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) through ultra-high-speed extrusion to facilitate injection molding recycling, showing substantial energy savings and CO2 emission reduction [5]. Additionally, industrial-scale plastic pyrolysis research identified the impact of operational conditions on HDPE degradation mechanisms, proposing a simplified kinetic mechanism for primary product formation pathways. These studies indicate that technological innovations enable effective recycling of film-grade PE materials, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional materials with environmental and economic benefits. HDPE/UHMWPE films showcase significant advantages in agricultural film application and recycling, enhancing durability and reducing fragmentation. Their high recyclability allows for conversion into new plastic products, easing environmental impacts and cutting waste management costs. This promotes resource recycling, environmental stewardship in farming, and advances sustainable agriculture.
In the realm of engineering plastics, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) stands out for its exceptional wear and impact resistance, self-lubrication, low water absorption, chemical corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties [6]. However, UHMWPE’s large molecular weight, extensive molecular chains, and numerous entanglement points [7–9] contribute to its significantly high melt viscosity [10,11]. HDPE, another crucial material in mulching applications, is known for its good heat and cold resistance, chemical stability, and excellent rigidity and toughness. Yet, it falls short in aspects such as aging resistance and environmental stress cracking resistance. The incorporation of UHMWPE long-chain molecules into HDPE can effectively ameliorate these drawbacks [12,13], facilitating the development of agricultural film materials that are both high in strength and easily recoverable.
Annealing treatment plays a pivotal role in altering the structural properties of polymers. It serves to alleviate internal stresses incurred during processing, heighten crystallinity, and enhance crystallization, thereby improving the polymer’s mechanical properties [14]. Research by Medel has demonstrated that the annealing process can refine the morphology and structure of PE, thus bolstering its tensile strength and fracture toughness [15]. Zhu’s study on the effect of annealing temperature on polymer structure reveals that below 110°C, the crystalline morphology of PE remains largely unchanged, while above 138°C, the crystal thickness experiences a significant increase [16]. Gaining insights into the impact of annealing mechanisms on the structure and properties of polymers is of considerable importance for polymer processing. In this study, HDPE and UHMWPE with varying concentrations were melt-blended to examine the influence of annealing treatment on their rheological and morphological properties. The scaling relationship between these parameters and the concentration was explored using scaling theory.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and instruments
Main raw materials: HDPE, grade 8008; melt flow rate: 15 g per 10 min, sourced from China Petroleum and Chemical Corporation. UHMWPE, molecular weight (M w) = 3 million, obtained from Beijing No. 2 Auxiliary Plant. The virgin resins without pretreatment were used. Antioxidant 1010 [17] procured from Guangdong Dongguan Huichen Chemical Co., Ltd, China.
Experimental instruments: Torque Rheometer (Model XSS-300, Shanghai Light Machinery Mould Factory, China). Flat vulcanizer (Model T-35, Henan Exploration Company, China). Scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Model JSM-6610LV, Japan Electronics Co., Ltd, Japan). Rheometer (Model HAAKE rs300, Thermo Scientific, USA).
Tensile testing: The UTM6502 Electronic Universal Testing Machine, provided by Sansi Zongheng Technology (referred to as the testing machine henceforth), is employed to assess the mechanical properties of all mulching films, focusing on longitudinal tensile strength and transverse tensile strength. The tensile test for films conforms to the National Standard GB/T1040.3-2006, “Determination of Tensile Properties of Plastics – Part 3: Test Conditions for Films and Sheets,” with a tensile rate set at 50 mm·min−1.
2.2 Experimental process
2.2.1 Preparation of blends
HDPE/UHMWPE blends were prepared by melt blending method. Weigh 15 g of evenly stirred HDPE/UHMWPE mixture, add antioxidant 1010 to prevent material oxidation [17], then add it to the torque rheometer with a volume of 20 mL, adjust the temperature of zones I, II, and III to 160°C, rotate at 60 rpm, and take out the material after internal mixing for 5 min. Refer Table 1 for the specific proportion of blends.
Composition ratios of the HDPE/UHMWPE blend system
| Samples (%) | HDPE (phw*) | UHMWPE (phw*) | Antioxidant 1010 (phw*) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 0.5 | 100 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 1 | 100 | 1 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 100 | 3 | 0.5 |
| 5 | 100 | 5 | 0.5 |
| 7 | 100 | 7 | 0.5 |
2.2.2 Rheological sample preparation
The prepared blend sample was put into a disc mold with a diameter of 200 mm and a thickness of 1.5 mm, and was formed by using a flat curing press, controlling the temperature of the upper and lower templates at 160℃, pressure at 20 MPa, and melting molding for 5 min.
2.2.3 Annealing treatment
The blend samples were put into an oven with nitrogen, and the oven was controlled at 160℃ for 5 h for thermal annealing. After annealing, they were cooled in a rheological mold for shaping.
2.3 Testing and characterization
2.3.1 Characterization of morphology and structure
The samples were brittle broken in liquid nitrogen, and the cross-section samples were dried and sprayed with gold in vacuum. The cross-section morphology was observed by scanning electron microscope.
2.3.2 Characterization of rheological properties
Advanced rotary rheometer, parallel plate mode, parallel plate diameter 20 mm, test temperature 160℃, dynamic frequency scanning, fixed strain value 1.0%, scanning frequency range 102–10−2 rad·s−1. The whole test process is protected by nitrogen to prevent sample aging.
2.3.3 Exposure test
The mulching film exposure test is an experimental method designed to assess the durability and performance of mulching films under sunlight exposure. Samples of mulching films listed in Tables 1 and Table 2 are measured for their weight-average molecular weight (M w) and number-average molecular weight (M n) both before exposure and after 60 days of exposure. The method for calculating the polydispersity index (PDI) is as follows:
Here, M w refers to the weight-average molecular weight and M n denotes the number-average molecular weight.
All data points depicted in the figures represent the average values derived from systematic experimental observations. Double-logarithmic plots can be used to identify how properties such as G′, G″, and |η*| change with UHMWPE concentration in HDPE/UHMWPE composites. These figures have been created using the ggplot2 package in R.
Changes in molecular weight of HDPE/UHMWPE blends after field exposure
| Samples (%) | Change in weight average molecular weight (M w) | Number average molecular weight (M n) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 0 | 50,475 | 124,996 | 2.48 |
| 0.5 | 50,763 | 125,646 | 2.48 | |
| 1 | 50,641 | 124,851 | 2.47 | |
| 3 | 50,543 | 125,467 | 2.48 | |
| 5 | 51,132 | 125,672 | 2.46 | |
| 7 | 50,488 | 124,953 | 2.47 | |
| After field exposure | 0 | 36,544 | 101,622 | 2.78 |
| 0.5 | 36,905 | 102,904 | 2.79 | |
| 1 | 37,272 | 103,501 | 2.78 | |
| 3 | 38,211 | 106,020 | 2.77 | |
| 5 | 40,241 | 110,214 | 2.74 | |
| 7 | 41,097 | 111,833 | 2.72 |
3 Results
3.1 Morphological characterization of HDPE/UHMWPE blends pre- and post-annealing
HDPE and UHMWPE, sharing identical basic units, exhibit excellent compatibility, resulting in a homogeneous blend system. Figure 1(a)–(d) depicts the cross-sectional morphology of UHMWPE/HDPE blends with varying UHMWPE mass fractions of 0%, 0.5%, 1%, and 5%, respectively. Observation from the micrographs reveals that the incorporation of UHMWPE into the matrix induces a distinct filamentous structure within the cross-section of the blend. In contrast, pure HDPE samples devoid of UHMWPE exhibit only a folded block distribution, lacking any filamentary features. As the concentration of UHMWPE increases, the filamentous structure becomes increasingly pronounced. The fundamental particle morphology of commercially synthesized UHMWPE is often described as a highly entangled spherical configuration [18]. The emergence of the filamentous structure aligns with the formation of a “shish-kebab” microstructure [19–21], attributed to the elongation of UHMWPE molecular coils, resonating with the filamentous appearance depicted in the figures. Studies by Hsiao et al. have also demonstrated that blending UHMWPE with low molecular weight PE facilitates the orientation of long-chain, highly entangled molecules to form a “shish-kebab” microstructure [13,22–24].
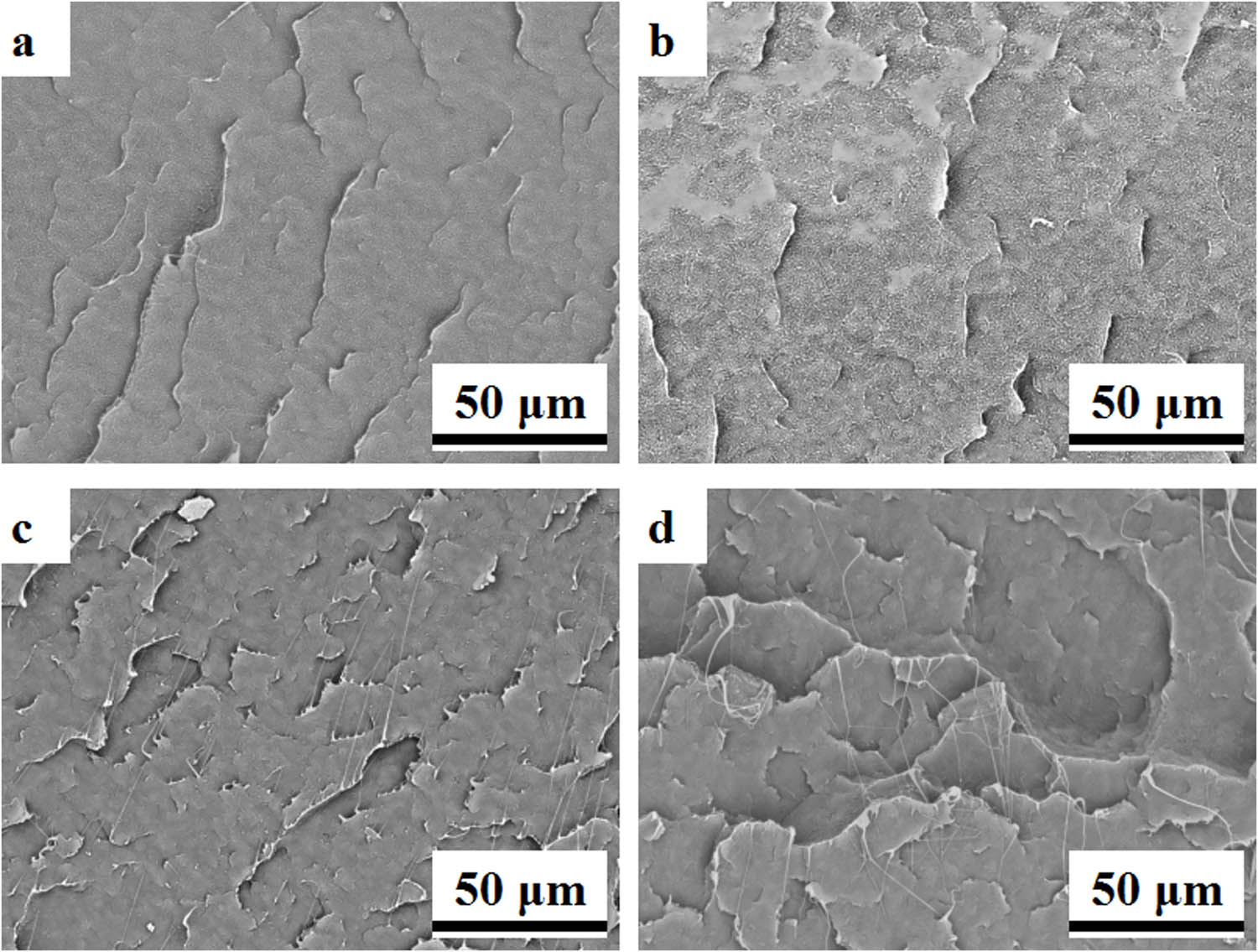
SEM images of fractured surfaces in HDPE/UHMWPE composite samples with varied UHMWPE content: (a) 0%, (b) 0.5%, (c) 1%, and (d) 5%.
The annealing process facilitates the mobility of molecular segments, promoting a more thorough fusion within the blend. Figure 2(a)–(d) illustrates the cross-sectional morphology of the blend system, pre- and post-annealing, with UHMWPE concentrations of 1%, 1% (post-annealing), 5%, and 5% (post-annealing), respectively. It is distinctly evident from the images that the filamentous structure diminishes following annealing. During this process, the osmotic pressure exerted by the low molecular weight HDPE enables the long chains of UHMWPE molecules to diffuse within the HDPE melt. This diffusion mitigates the high degree of entanglement typically observed in UHMWPE primary particles. Consequently, UHMWPE molecular coils and HDPE molecular chains achieve a more homogeneous state, impeding the tensile transformation of UHMWPE molecules that is necessary for the formation of the filamentous entanglement structure.
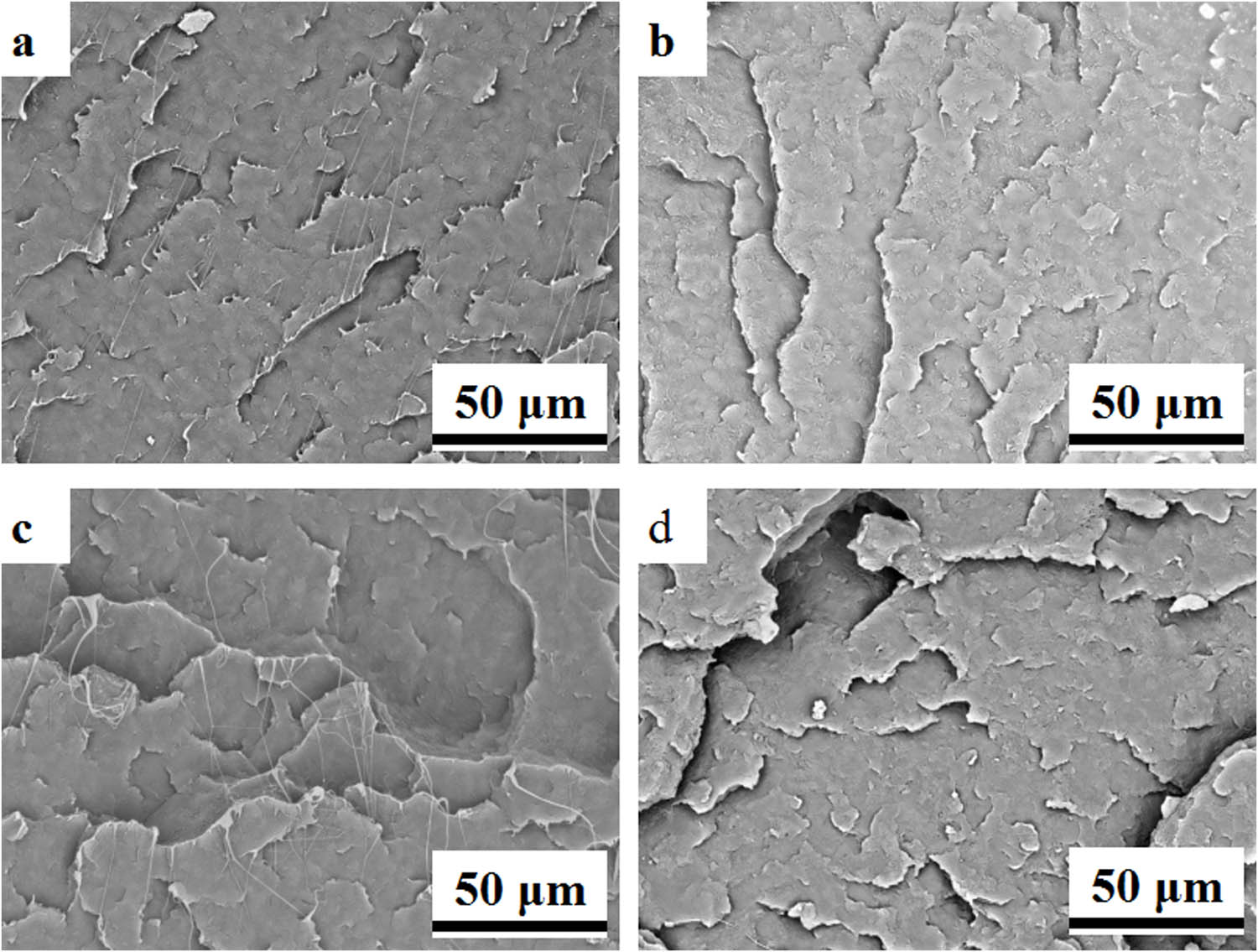
SEM images of fractured surfaces in HDPE/UHMWPE composites, pre- and post-annealing: (a) 1% UHMWPE, (b) 1% UHMWPE post-annealing, (c) 5% UHMWPE, and (d) 5% UHMWPE post-annealing.
3.2 Rheological characterization of HDPE/UHMWPE blends pre- and post-annealing
Figures 3–5 display the storage modulus, loss modulus, and complex viscosity of HDPE/UHMWPE blends with varying UHMWPE concentrations, both before and after annealing, across different scanning frequencies. As depicted in these figures, the storage modulus (G′), loss modulus (G″), and complex viscosity (|η*|) exhibit a marked growth trend with the increase in UHMWPE concentration. This is attributable to the long molecular chains of UHMWPE, which impart a reinforcing effect on the system. Post-annealing, there is a slight increase in the modulus and viscosity of each component. The pure HDPE sample also demonstrates a modest enhancement in mechanical properties following annealing, owing to the more orderly arrangement of HDPE molecular segments and improved crystallinity, resulting in enhanced mechanical performance [25].
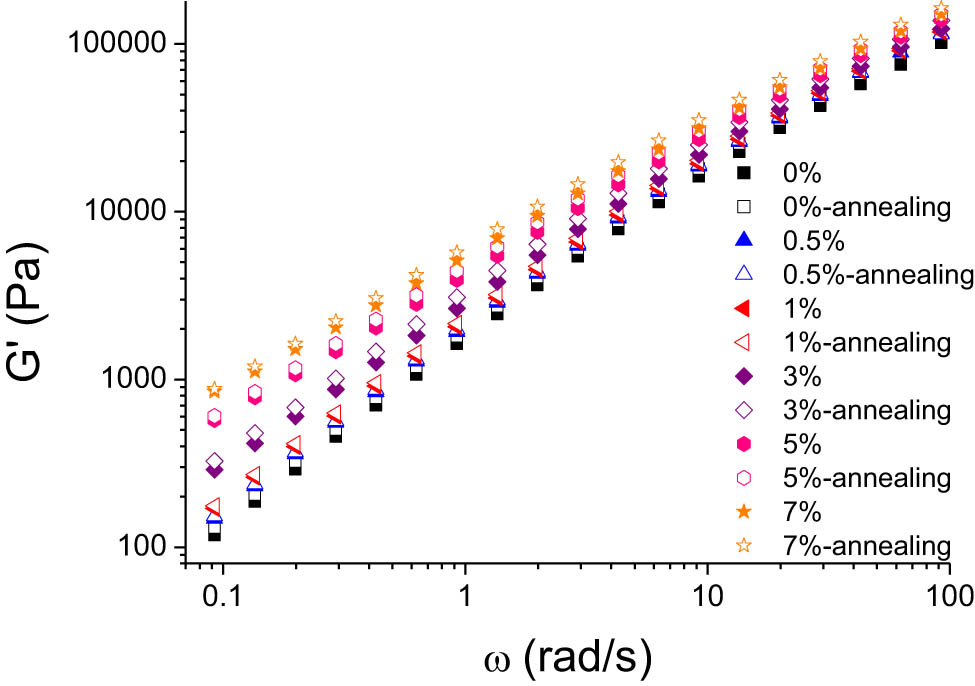
Variations in the storage modulus (G′) as a function of frequency for HDPE/UHMWPE composites, pre- and post-annealing, across different UHMWPE concentrations.
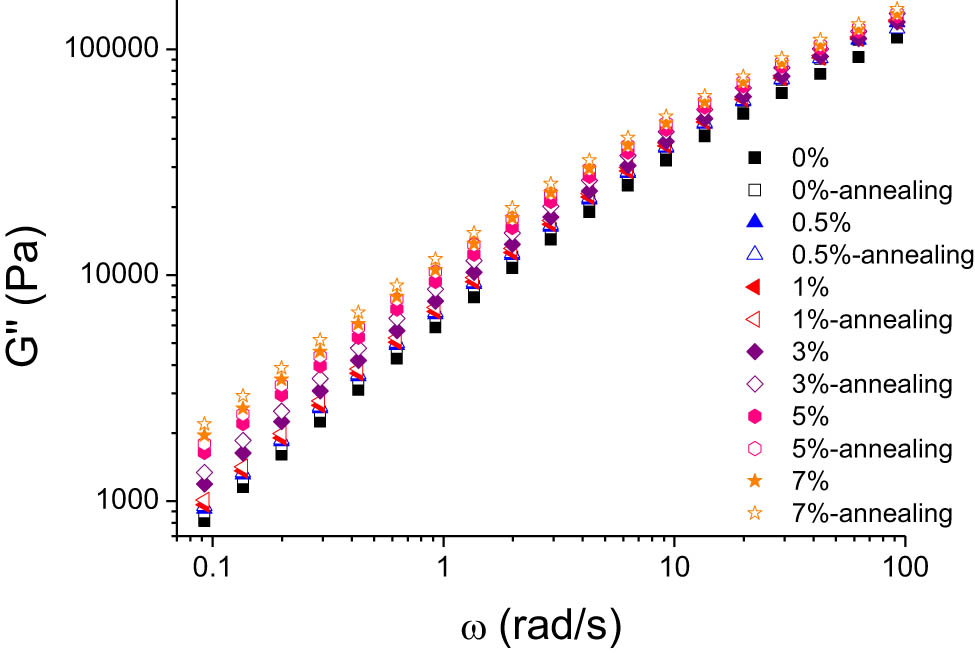
Alterations in loss modulus (G″) as a function of frequency in HDPE/UHMWPE composites, prior to and following annealing, at various UHMWPE concentrations.
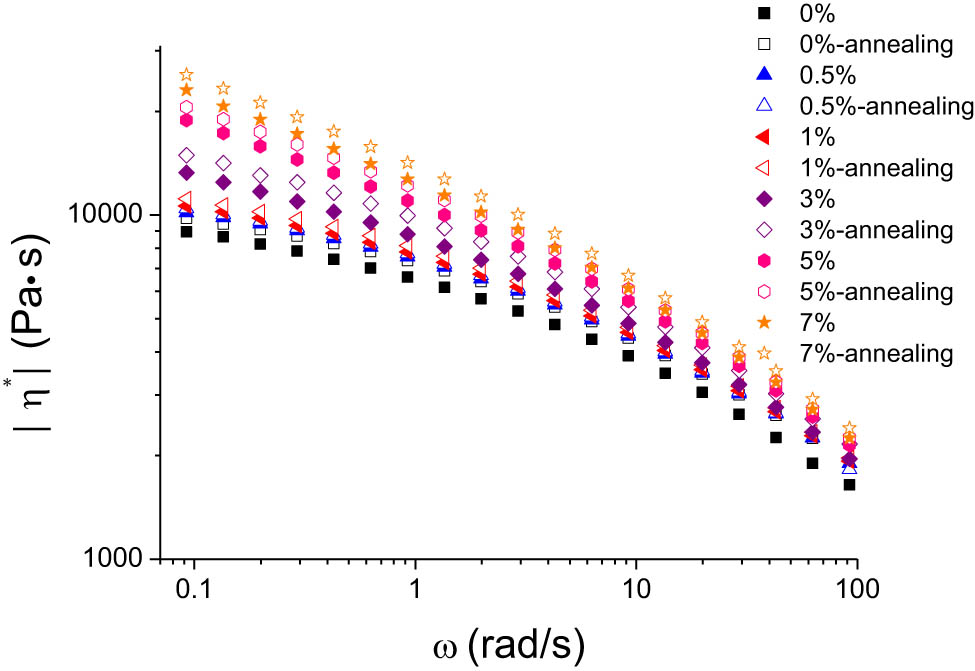
Variations in complex viscosity (|η*|) as a function of frequency for HDPE/UHMWPE composites, before and after annealing, across diverse UHMWPE concentrations.
When correlated with the morphological characterization results, the annealing process appears to facilitate a more regular arrangement of HDPE molecules, a more comprehensive intermingling of UHMWPE molecular chains with HDPE molecular chains, and a tendency toward a more uniform and complete network structure within the system, thereby improving its mechanical properties.
Figure 6 illustrates the loss tangent (tan δ = G″/G′) of HDPE/UHMWPE blends with different UHMWPE concentrations, both pre- and post-annealing, against scanning frequency. At the rheological working temperature of 160°C, the pure HDPE sample is in a viscous flow state, with G″ > G′, leading to a high tan δ value. Annealing of the pure samples results in increased crystallinity of HDPE post-cooling and more regular molecular arrangements, thus increasing G′ and slightly decreasing the tan δ value. UHMWPE primary particles, characterized by their high entanglement, behave as rigid entities with G′ significantly exceeding G″, resulting in a very small tan δ value. As the blend is increasingly supplemented with UHMWPE particles, the system’s tan δ value progressively decreases. However, post-annealing, the tan δ value conversely increases due to the annealing process causing UHMWPE molecular chains to extend and their degree of entanglement to decrease, leading to a reduction in UHMWPE particles’ G′ and a more pronounced increase in tan δ with rising UHMWPE content. The state change of UHMWPE particles plays a crucial role in the mechanical property alterations observed in the blends.
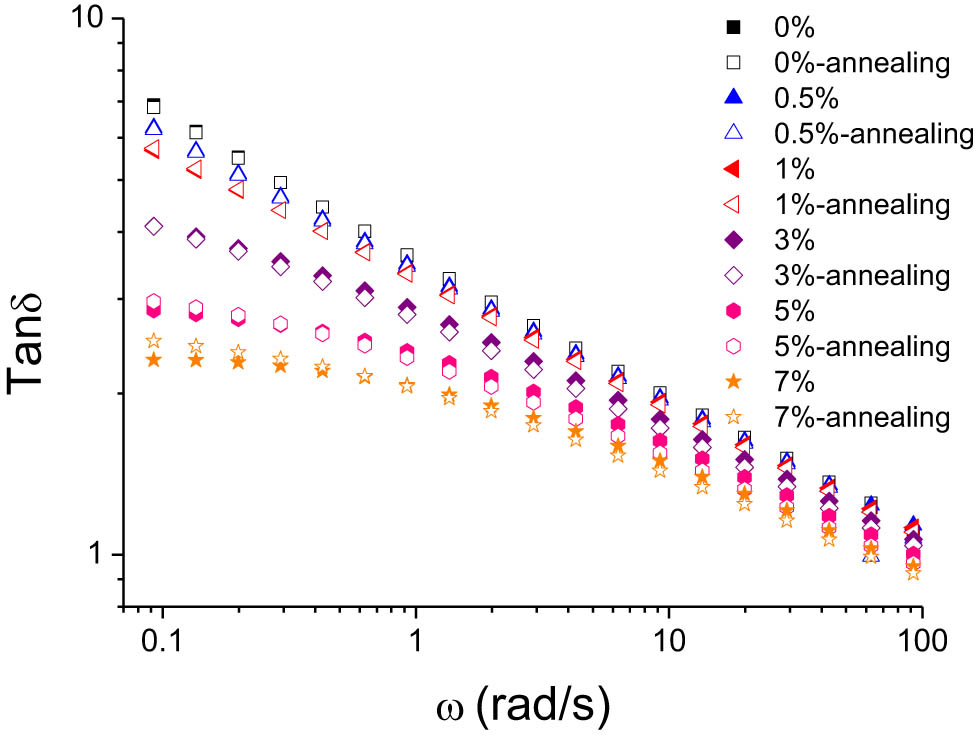
Alterations in loss factor (tan δ) as a function of frequency for HDPE/UHMWPE composites, pre- and post-annealing, at various UHMWPE concentrations.
3.3 Scaling relationships in HDPE/UHMWPE blends pre- and post-annealing
Scaling theory, a framework for studying the critical transition phenomena in matter, establishes the relationship between critical exponents and scaling. This theory, with its universal applicability, is significantly important for understanding the rheological behavior of polymers [26]. Figures 7–9 illustrate the low-frequency (ω = 0.92 rad·s−1) logarithmic relationships of log G″, log G′, and log |η*| against log (C UHMWPE%) in a double-logarithmic plot to derive the scaling relationships of G′, G″, and |η*| with UHMWPE concentration. Notably, the mechanical properties of the blends exhibited only marginal improvement post-annealing, thus the scaling relationships showed no substantial alteration before and after the annealing process.
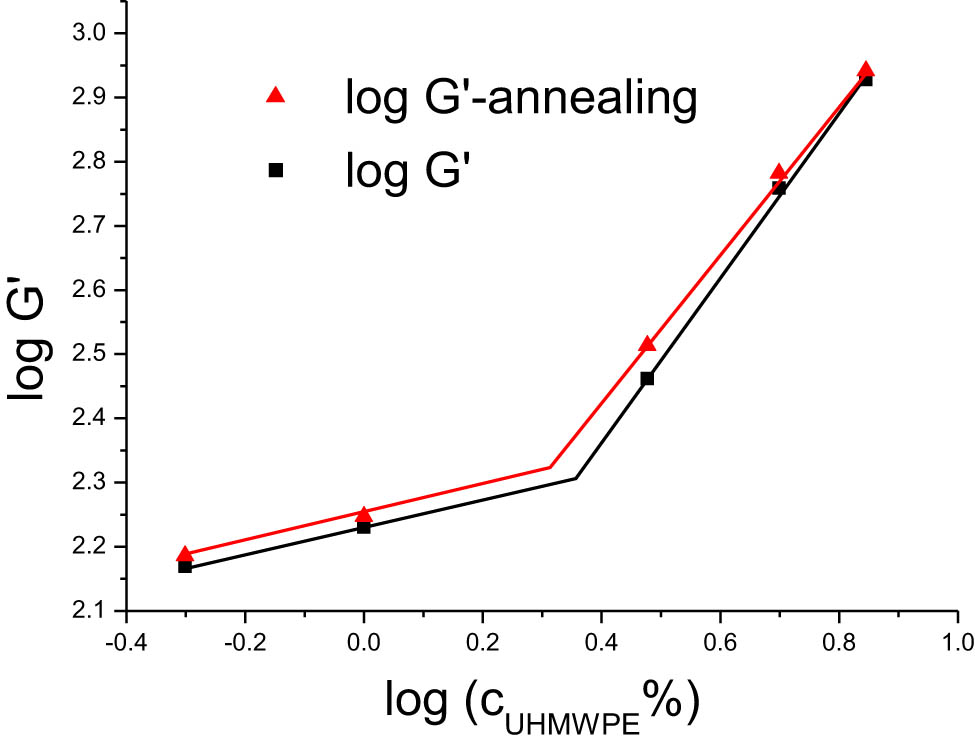
Scaling relationships of storage modulus relative to UHMWPE concentration in HDPE/UHMWPE composites pre- and post-annealing.
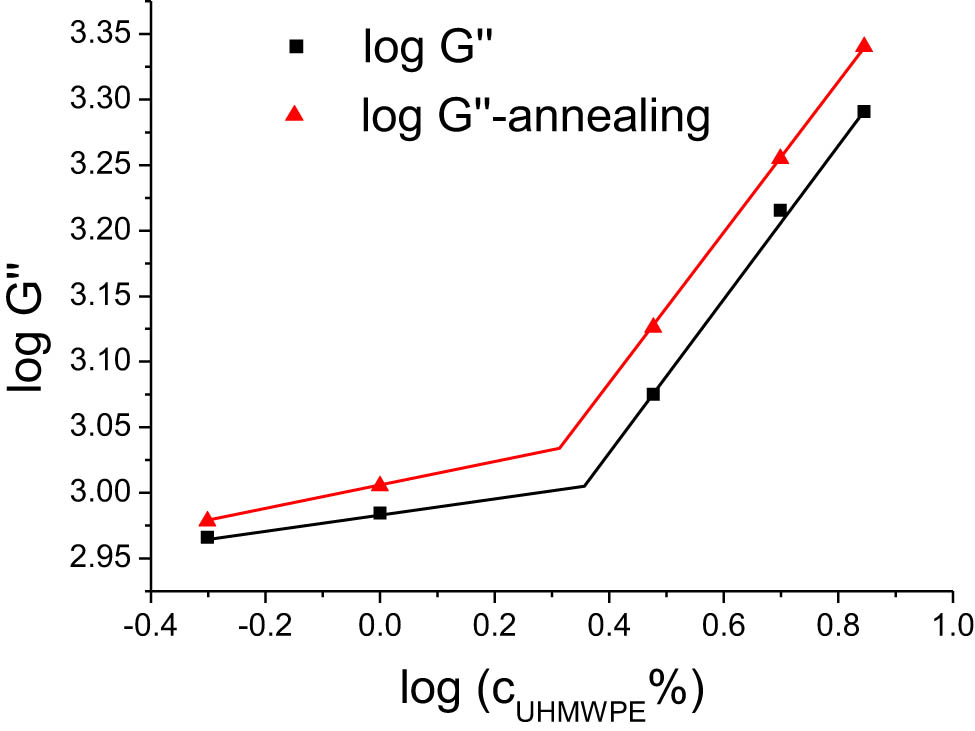
Scaling laws of loss modulus in relation to UHMWPE concentration in HDPE/UHMWPE composites, analyzed pre- and post-annealing.
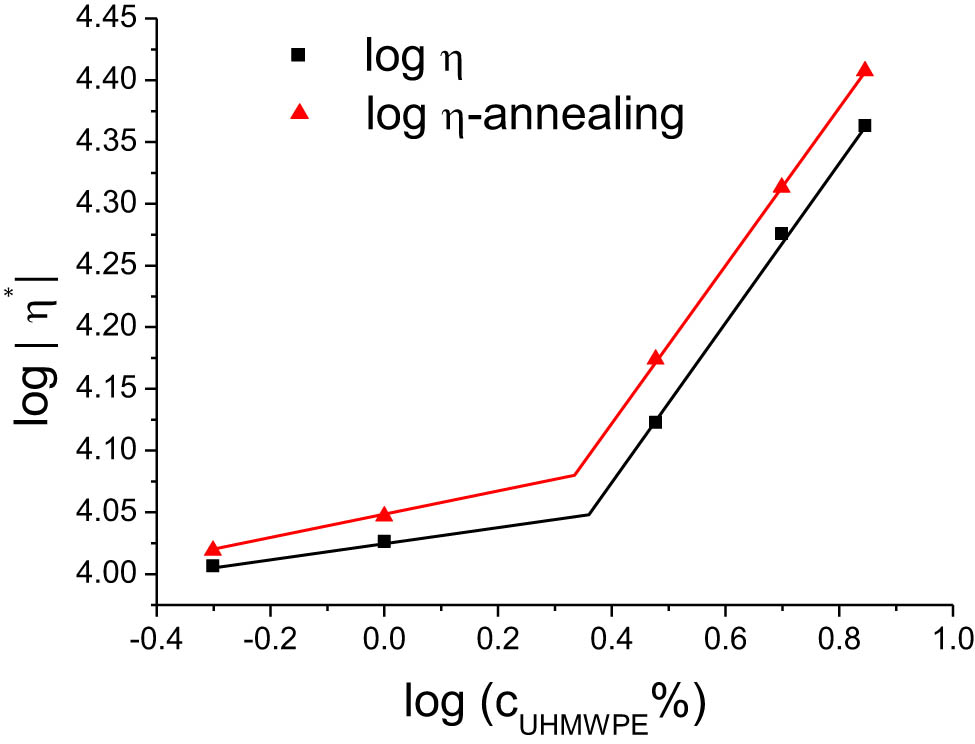
Scaling relationships of complex viscosity relative to UHMWPE concentration in HDPE/UHMWPE composites, evaluated pre- and post-annealing.
Double-logarithmic plots can be utilized to identify how properties such as G′, G″, and |η *| vary with UHMWPE concentration in HDPE/UHMWPE composites. Significant shifts in data point trends and abrupt changes in the slope of trend lines signal a transformation in material properties. As depicted in Figures 7–9, all three graphs demonstrate that the relationships of G′, G″, and |η*| undergo noticeable changes in slope both before and after the critical concentration, pre- and post-annealing. From these double-logarithmic plots, the corresponding scaling relationships can be deduced as follows: (1) before the critical point: G′ ∼ c 0.2, G″ ∼ c 0.07, |η*| ∼ c 0.07 and (2) after the critical point: G′ ∼ c 1.20, G″ ∼ c 0.6, |η*| ∼ c 0.64. This scaling relationship indicates that the scaling values post-critical point are substantially higher than those pre-critical point. The variation in scaling relationships around the critical point is associated with the critical entanglement phenomenon of polymer chains [27,28]. As the concentration of UHMWPE increases, the proportion of long UHMWPE molecular chains in the system rises, reaching the critical entanglement concentration (c e) of UHMWPE. This leads to mutual entanglement among long chains, significantly increasing the modulus and viscosity of the blend.
The c e of UHMWPE experienced a shift pre- and post-annealing, with c e being 2.3% before annealing and 2.1% after, advancing the transition point post-annealing. This is because the UHMWPE molecular chains, originally highly entangled, become more extended post-annealing. These elongated chains then form mutual entanglements between UHMWPE particles, enabling the establishment of an entanglement network at a lower concentration post-annealing and enhancing the mechanical properties of the blends. The scaling relationships of G′, G″, and |η*| with UHMWPE concentration and the alteration in the critical entanglement concentration are profoundly significant for further exploring the motion of UHMWPE molecular chains during the annealing process.
3.4 Exposure testing for molecular weight alterations in HDPE/UHMWPE blends
Initially, the HDPE/UHMWPE blends showed uniform molecular weights (M w, M n) and PDI. Post-exposure, significant changes were observed: both weight-average (M w) and number-average (M n) molecular weights increased with higher UHMWPE content, while PDI decreased. This indicates enhanced molecular stability and more uniform weight distribution in blends with increased UHMWPE, suggesting improved environmental resilience and consistent performance. These results highlight the significant impact of real-world conditions on the molecular integrity of polymer composites.
4 Discussion
The exploration of HDPE/UHMWPE blends offers compelling insights into the impact of UHMWPE concentration and annealing on the material’s characteristics. Notably, the observed morphological transformations, particularly the development and eventual diminishment of filamentous structures upon annealing, resonate with existing literature findings. This study, delving into the synthesized HDPE/UHMWPE composite, emphasizes the effects of annealing, alongside the morphological and rheological properties, and evaluates the environmental stress cracking resistance.
Yin et al. [29] underscores the morphological evolution of UHMWPE from primary to swollen particles, which significantly influences HDPE’s crystallization. This aligns with our observations of microstructural changes post-annealing, where an increased UHMWPE concentration led to notable morphological alterations, as verified by SEM imaging. This transformation suggests that annealing modifies UHMWPE morphology, consequently enhancing the composite’s mechanical strength. Different UHMWPE morphologies have marked effects on HDPE’s crystallization, and our study corroborates this, demonstrating improved mechanical properties and modulus following annealing. The annealing process likely induces changes in UHMWPE morphology, thereby impacting the crystallization and mechanical traits of the blend.
Li et al.’s [30] examination of the influence of HDPE’s melting flow rate (MFR) on the UHMWPE/HDPE blend’s attributes complements our rheological analysis. The finding that neither excessively high nor low MFR of HDPE is beneficial for the blend’s properties aligns with our results. Enhancements in mechanical properties were observed upon optimizing UHMWPE concentration and conducting post-annealing treatment. The significance of chain entanglement and its effect on blend properties is pertinent. Our study’s scaling laws, particularly for storage and loss modulus post-annealing, suggest that annealing alters UHMWPE’s molecular interactions within HDPE, leading to modifications in mechanical properties.
In comparison with Chen et al.’s findings [31], the superior stress cracking resistance of the LDPE/UHMWPE blend relative to the HDPE/UHMWPE blend offers insights into the varying impacts of polymer matrices on composite properties. The established correlation between morphological characteristics and blend composition aligns with our study. Our post-annealing morphological analysis and the consequent improvements in mechanical properties demonstrate a similar correlation, where the annealing-induced altered microstructure plays a pivotal role in enhancing the composite’s mechanical performance.
Annealing emerges as a crucial factor in modulating these properties, heralding potential advancements in the development of high-strength, sustainable HDPE films for diverse applications, including eco-friendly agricultural practices. This integrated approach provides a comprehensive perspective on the material’s behavior, paving the way for further research and application in the realm of sustainable material development. Additionally, they highlighted that blends with better-distributed molecular weights exhibit enhanced resistance to thermal and UV degradation, a critical aspect for applications in challenging environmental conditions.
5 Conclusions
The HDPE/UHMWPE blend, prepared via melt blending, exhibited a filamentous structure in its cross-section, becoming more pronounced with increased UHMWPE content. Post-annealing, this structure dissipated, resulting in a more uniform blend, thereby enhancing the system’s mechanical properties. Rheological analysis revealed that UHMWPE addition improved the blend’s mechanical characteristics. Annealing led to a more cohesive network structure within the system, aligning mechanical properties with morphological changes. The scaling relationship analysis of rheological data revealed that before the critical entanglement concentration: G′ ∼ c 0.2, g″ ∼ c 0.07, |η*|∼ c 0.07 and post-critical concentration: G′ ∼ c 1.20, g″ ∼ c 0.6|η*|∼ c 0.64. Post-annealing, the system’s critical entanglement concentration decreased, suggesting that UHMWPE forms a filamentous entanglement structures at a lower concentration, thus enhancing the blends’ mechanical properties. This scaling relation and the shift in critical concentration are crucial for understanding UHMWPE chain mobility in the melt. The samples displayed consistent M w, M n, and PDI values. Following exposure testing, changes in these parameters were observed, with both weight-average and number-average molecular weights increasing and PDI decreasing with higher UHMWPE content. This trend highlights the blend’s enhanced molecular stability and uniformity, crucial for creating plastic films that are both strong and sustainable, suitable for eco-friendly agricultural applications.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the reviewers, editors, and the editor-in-chief for their comments and suggestions on the revision and publication of the article. We also appreciate the assistance provided by the No. 2 Plastic Color Printing Factory in Fuxin, Liaoning Province, China, for this research work.
-
Funding information: This study received generous support from the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant Nos. 2023YFD1500904-04, 2023YFD2202104, and 2021YFD1700700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32071551 and 31501269), the Liaoning Province Applied Basic Research Program Project (Grant No. 2022022020371-JH2/1013), the Shenyang Science and Technology Plan (Grant Nos. 22-317-2-04 and 23-409-2-06), and Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation General Project (2022-MS-055).
-
Author contributions: Ning Yang: writing – original draft, formal analysis, analysis visualization, and project administration; Ying Li: methodology, project administration, and writing – review; Liangshan Feng: writing – review; Qi Liu: writing – original draft and formal analysis; Qing Luo: writing – formal analysis visualization; Jialei Liu: writing – review, editing, and project administration.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wang XF, Shen MX. Plastic agricultural films: the hope and dawn of china’s agricultural development. Department of Rural Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing; 1998.Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Möller K, Gevert T, Holmström A. Examination of a low density polyethylene (LDPE) film after 15 years of service as an air and water vapour barrier. Polym Degrad Stab. 2001;73(1):69–74.10.1016/S0141-3910(01)00067-2Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Periyasamy D, Manoharan B, Arockiasamy FS, Aravind D, Senthilkumar K, Rajini N, et al. Exploring the recycling potential of HDPE films reinforced with flax fiber for making sustainable decorative tiles. J Mater Res Technol. 2023;25:2049–60.10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.06.067Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Abbas-Abadi MS, Zayoud A, Kusenberg M, Roosen M, Vermeire F, Yazdani P, et al. Thermochemical recycling of end-of-life and virgin HDPE: a pilot-scale study. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2022;166:105614.10.1016/j.jaap.2022.105614Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Gao P, Krantz J, Ferki O, Nieduzak Z, Perry S, Sobkowicz MJ, et al. Thermo-mechanical recycling via ultrahigh-speed extrusion of film-grade recycled LDPE and injection molding. Sustain Mater Technol. 2023;38:e00719.10.1016/j.susmat.2023.e00719Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Des Cloizeaux J. Double reptation vs. simple reptation in polymer melts. Europhys Lett. 1988;5(5):437–42.10.1209/0295-5075/5/5/010Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Smith P, Lemstra PJ. Ultra-high-strength polyethylene filaments by solution spinning/drawing. J Mater Sci. 1980;15(2):505–14.10.1007/BF02396802Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Smith P, Lemstra P, Kalb B, Pennings A. Ultrahigh-strength polyethylene filaments by solution spinning and hot drawing. Polym Bull. 1979;1(11):733–6.10.1007/BF00256272Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Smith P, Lemstra PJ. Ultrahigh-strength polyethylene filaments by solution spinning/drawing, 2. Influence of solvent on the drawability. Die Makromolekulare Chem. 1979;180(12):2983–6.10.1002/macp.1979.021801220Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Liu C, Wang J, He J. Rheological and thermal properties of m-LLDPE blends with m-HDPE and LDPE. Polymer. 2002;43(13):3811–8.10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00201-XSuche in Google Scholar
[11] Delgado‐Rangel JA, Addiego F, Eddoumy F, Ahzi S, Patlazhan S, Toniazzo V, et al. Impact of microextrusion and addition of graphite nanoplatelets on bulk and surface mechanical properties of UHMWPE. J Appl Polym Sci. 2012;125(6):4316–25.10.1002/app.36594Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Lucas AA, Ambrósio JD, Otaguro H, Costa LC., Agnelli JAM. Abrasive wear of HDPE/UHMWPE blends. Wear. 2011;270(9):576–83.10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.011Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Keum JK, Zuo F, Hsiao BS. Formation and stability of shear-induced shish-kebab structure in highly entangled melts of UHMWPE/HDPE blends. Macromolecules. 2008;41(13):4766–76.10.1021/ma800063eSuche in Google Scholar
[14] Yuan Y, Jing X, Jiang B. Annealing effect in polyethylene single crystals. Chin J Appl Chem. 1997;3:24–8.10.3724/j.issn.1000-0518.1997.3.24Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Medel FJ, Peña P, Cegoñino J, Gómez-Barrena E, Puértolas JA. Comparative fatigue behavior and toughness of remelted and annealed highly crosslinked polyethylenes. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater. 2007;83(2):380–90.10.1002/jbm.b.30807Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Zhu QR, Hong KL, Ji LQ, Qi RR, Zhou GE, Song MS, et al. Morphological changes in annealed ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) gel-films. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys. 1995;33(5):739–44.10.1002/polb.1995.090330501Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Aguilar M, Martín S, Vega JF, Muñoz‐Escalona A., Martínez‐Salazar J. Processability of a metallocene-catalyzed linear PE improved by blending with a small amount of UHMWPE. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys. 2005;43(21):2963–71.10.1002/polb.20581Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Jauffrès D, Lame O, Vigier G, Doré F. Microstructural origin of physical and mechanical properties of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene processed by high velocity compaction. Polymer. 2007;48(21):6374–83.10.1016/j.polymer.2007.07.058Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Kimata S, Sakurai T, Nozue Y, Kasahara T, Yamaguchi N, Karino T, et al. Molecular basis of the shish-kebab morphology in polymer crystallization. Science. 2007;316(5827):1014–7.10.1126/science.1140132Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Yan TZ, Zhao BJ, Cong YH, Fang YY, Chen SW, Li LB, et al. Critical strain for shish-kebab formation. Macromolecules. 2009;43(2):602–5.10.1021/ma9020642Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Keller A, Kolnaar HWH. Flow-induced orientation and structure formation. Mater Sci Technol. 1997;187–268.Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Rastogi S, Lippits DR, Peters GWM, Graf R, Yao YF, Spiess HW. Heterogeneity in polymer melts from melting of polymer crystals. Nat Mater. 2005;4(8):635–41.10.1038/nmat1437Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Ronca S, Forte G, Ailianou A, Kornfield JA., Rastogi S. Direct route to colloidal UHMWPE by including LLDPE in solution during homogeneous polymerization of ethylene. ACS Macro Lett. 2012;1(9):1116–20.10.1021/mz300369xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Somani RH, Yang L, Zhu L, Hsiao BS. Flow-induced shish-kebab precursor structures in entangled polymer melts. Polymer. 2005;46(20):8587–623.10.1016/j.polymer.2005.06.034Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Lee SY, Park SY, Song HS. Effects of melt-extension and annealing on row-nucleated lamellar crystalline structure of HDPE films. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;103(5):3326–33.10.1002/app.25495Suche in Google Scholar
[26] De Gennes PG. Scaling concepts in polymer physics. Ithaca and London: Cornell University Press; 1979.Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Graessley WW. The entanglement concept in polymer rheology. In The Entanglement Concept in Polymer Rheology. Advances in Polymer Science. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1974. p. 1–179.10.1007/BFb0031037Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Shenoy SL, Bates WD, Frisch HL, Gary EW. Role of chain entanglements on fiber formation during electrospinning of polymer solutions: good solvent, non-specific polymer-polymer interaction limit. Polymer. 2005;46(10):3372–84.10.1016/j.polymer.2005.03.011Suche in Google Scholar
[29] Yin W, Shen HW, Lin ZT, Tan HS, Xie BH. Influence of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene morphology on the crystallization behavior of high-density polyethylene. Polym Mater Sci Eng. 2020;36(12):76–81 (in Chinese).Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Li BH, Chen Y, Duan KS, Chen CQ, Liu M. Fluidity and mechanical properties of UHMWPE/HDPE Blends. Plastic Ind. 2003;31(9):9–12.Suche in Google Scholar
[31] Chen Y, Nie X, Zhou S, Huawei Z, Mei L, Pengbo L. Investigations of environmental stress cracking resistance of HDPE/UHMWPE and LDPE/UHMWPE blends. J Polym Res. 2013;20:141. 10.1007/s10965-013-0141-5.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”

