Abstract
This article a synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit. Accumulated industrial waste heavily pollutes the environment and has a direct impact on all living things. The accumulation of waste in landfills increases the pollution level of the atmosphere, soil, groundwater, and surface water, destroys the functioning of ecosystems, and damages agriculture and construction. A sieve analysis was carried out to study the fine fractions of coal waste, and a scanning electron microscope analysis was performed to study the mineralogical, structural state and X-ray chemical phase composition. The chemical composition of coal waste was studied using differential thermal analysis during heat treatment. The optimal parameters of the process for obtaining humic acids are established, and the results of experimental work are presented. The results are confirmed by mathematical planning of the experiment using the method of orthogonal plan of the second order. The mathematical planning results were tested according to the Student and Fischer criteria. Based on the conducted studies, it was identified that the degree of extraction of humic acid reaches up to 95.90% in terms of the organic phase, and the concentration of humic acid is 49.13%. From the humic acids obtained using potassium hydroxide, potassium humate was synthesized. The potassium humate obtained in its composition has fertilizer properties. Therefore, the obtained potassium humate will be used for the production of humic fertilizers to improve soil fertility and crop yields. The synthesis of humic acids with the production of potassium humate is aimed at reducing the accumulated industrial waste, which in turn allows you to regulate and improve the ecological situation and green ecology in the region.
1 Introduction
At the present development stage of science and technology, one of the most important problems is the processing of natural and industrial waste. Coal is mined all over the world, as coal is an energy carrier. Coal production leaves behind many tons of waste, which in turn pollute the environment. As a result of coal mining in Kazakhstan, more than 6 million tons of waste were generated, and the Lenger deposit of brown coal is located in south Kazakhstan. According to the data, the reserve balance part is 33,956 thousand tons, and the off-balance part is 3,244 thousand tons. The use of the balance part is currently economically feasible, whereas the processing of the off-balance part at the given level of technology and technology development is not economically feasible but can be later transferred to the balance [1,2].
The deposit [3] is named after a German miner of the Lenger developer. The Lenger coal deposit has been known since the nineteenth century. The Lenger coal deposit is located 35 km east of the city of Shymkent, 1 km north of the village of Lenger, and contains mostly brown coal (grade B3) with a heat release of up to 7.3 thousand kcal·kg−1.
Coal mining waste from the Lenger deposit is a promising and valuable source of organic and mineral raw materials that contain a wide variety of trace elements and organic substances with fertilizing properties, and in this regard, it is a valuable secondary raw material suitable for processing into humic acid [4].
The coal waste of the Lenger deposit consists of organic matter and mineral impurities. The main elements included in the organic mass of coal are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and organic sulfur. They have various forms of connection with the organic and mineral parts of coal and differ from each other in the content and nature of their active groups. Coals also contain chemical compounds of some metals – calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, etc. [5,6]. The location and view of the coal waste in the Lenger deposit are shown in Figure 1.
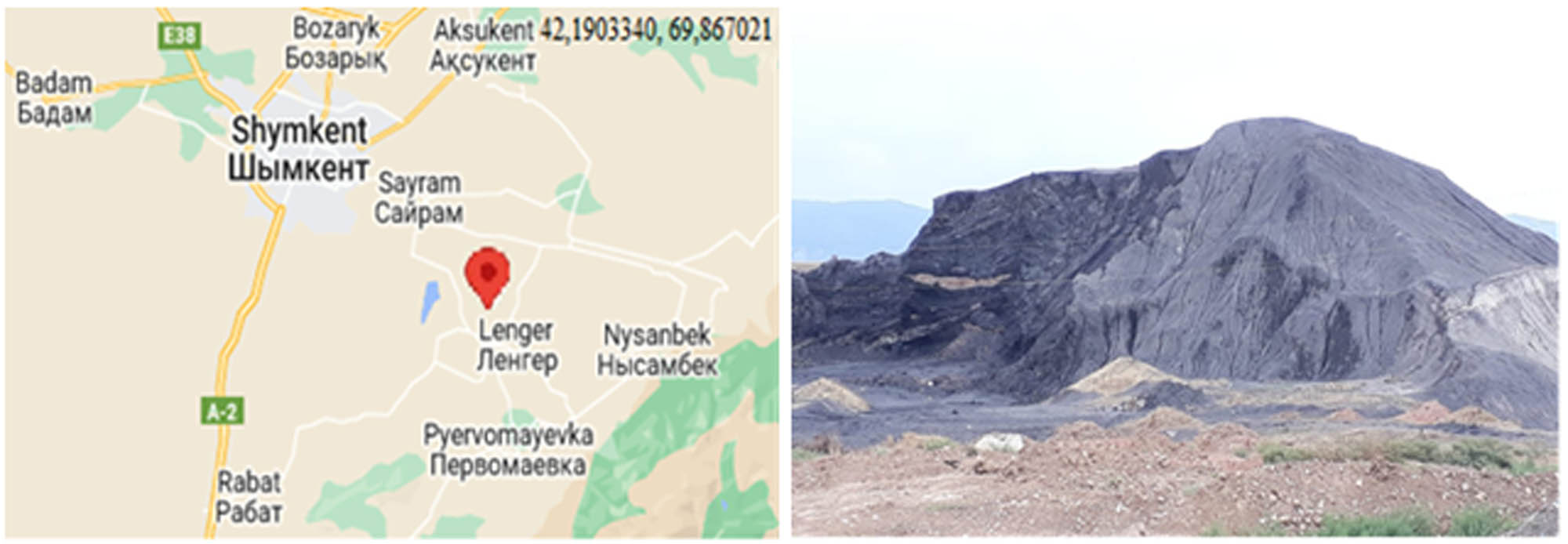

Location and view of the Lenger deposit, the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The relevance of scientific work lies in the fact that the accumulation of coal waste creates serious environmental problems in the regions. The accumulation of coal waste increases the pollution level of the atmosphere, soil, ground, and surface waters, destroys the functioning of ecosystems, damages agriculture, and has a negative impact on climate change. Environmental pollution from industrial waste is a global environmental problem of our time. This research has implications beyond chemical technology and environmental impact. It is also aimed at reducing and recycling accumulated coal waste [7].
In the work of the authors, the possibility of synthesis of humic acid from coal waste and the study of their composition and radioactivity are investigated. Humic acid is considered for practical use in the production of organic and mineral fertilizers and feed additives. In this work, the authors show the yield of humic acid with a description of the obtained elemental analysis [8,9].
Humates are natural organic mineral fertilizers that stimulate growth; humates are potassium salts obtained from humic acid. Potassium humate is most widely used in pre-sowing seed treatment and foliar feeding of plants during the growing season. Potassium humate – an organic and mineral fertilizer with a stimulating effect and fungicidal activity, is a product of high-tech processing of low-lying peat, coal, and coal waste.
The authors in their work indicate the scientific novelty of the work on the use of technogenic resources in the form of coal mining waste for the extraction of organic and mineral raw materials. The novelty of the scientific work lies in the decomposition of coal waste using 50% hydrochloric acid (HCl), followed by the release of humic acid by 95.9% in terms of organic mass and the determination of optimal technological parameters of the process. The purpose of the scientific work is to synthesize humic acid based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, followed by the production of humate-containing fertilizers with a high content of useful components and trace elements for crop yields [10,11].
2 Materials and methods
For the processing of coal mining waste under experimental conditions, test methods were selected using a Jeol JSM-6490l V scanning electron microscope (SEM), a multiparametric portable cyber scanner (PCS 650 Eutech), an IR Fourier spectrometer (Zhimadzu IR Prestige-21), a MicroXRF Analysis Report, an incident beam monochromator D878-PC75-17.0, and a Q-1500 derivatograph.
Experimental scientific work has been carried out on the obtaining of humic acids as a raw material, plant litter is used, which is pre-crushed to a fraction with a diameter of not more than 1 mm and are treated in heat at t = 145–150°C. Next, extraction is carried out, followed by filtering of the extract and precipitation of humic acids from the solution by adding HCl, then the deposition is separated from the solution [12].
2.1 Sieve analysis to determine the particle size distribution of raw materials
In the study of coal waste from the Lenger deposit, it was identified that its density is −0.67 kg·dm−3, and its specific gravity is −0.57 kg·dm−3. To determine the particle size distribution, a sieve analysis was carried out, and the results are shown in Figure 2.
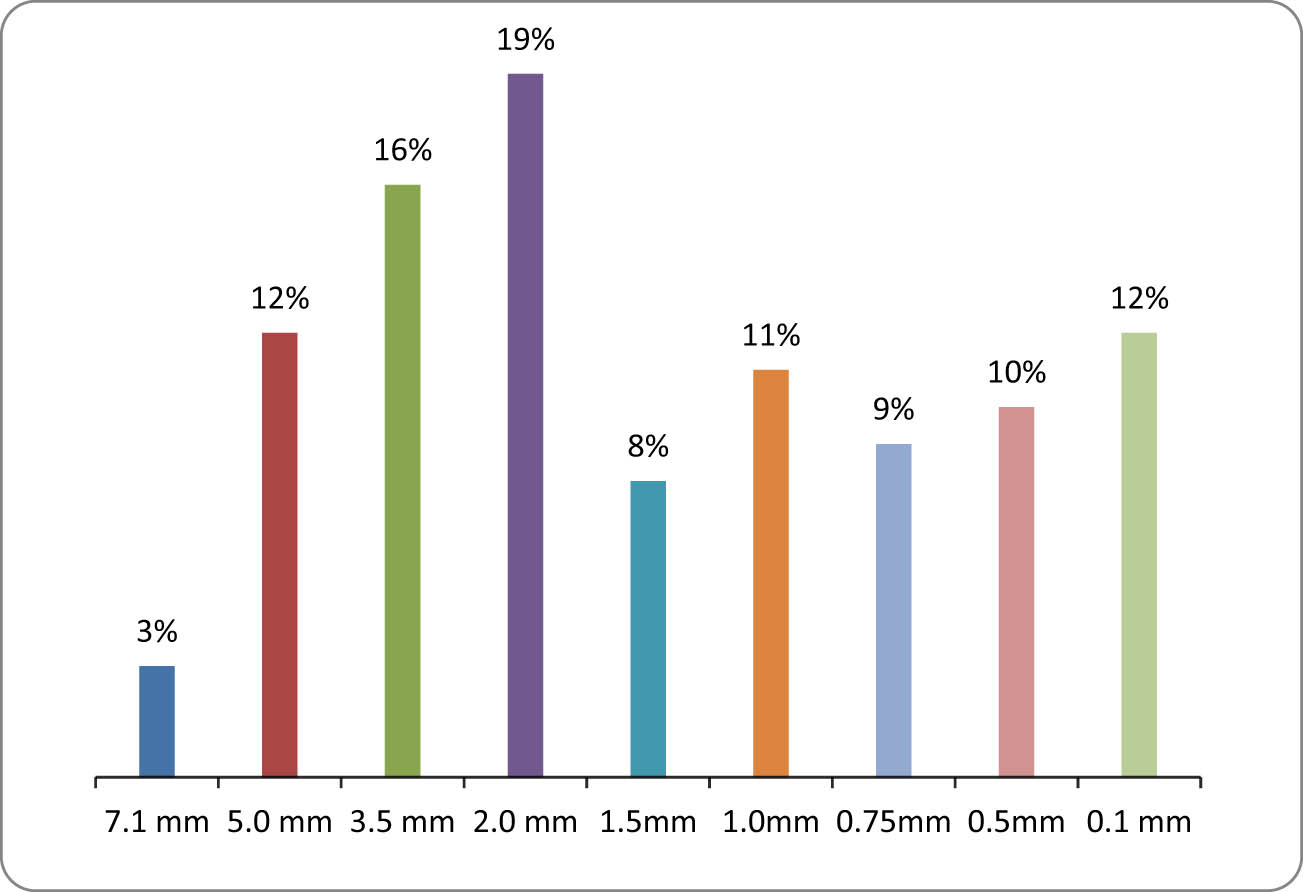
The sieve analysis of coal waste from the Lenger deposit.
On the basis of sieve analysis (Figure 2), it was identified that in the total mass of the waste, about 15% are large fractions with sizes of more than 7.10–5.0 mm. About 35% of coal waste falls on the share of the middle fraction with a particle size of 3.50–2.00 mm. Small particles account for about 50%. The coal waste from the Lenger deposit is made up of fractions with the following sizes: 2.00–1.50, 1.50–1.00, and 1.00–0.75 [13].
2.2 Differential thermal analysis of raw materials
To study the chemical composition of the coal under study during heat treatment, a differential thermal analysis was carried out in the derivatograph Q-1500D (DEMO). The derivatogram of coal waste is shown in Figure 3.
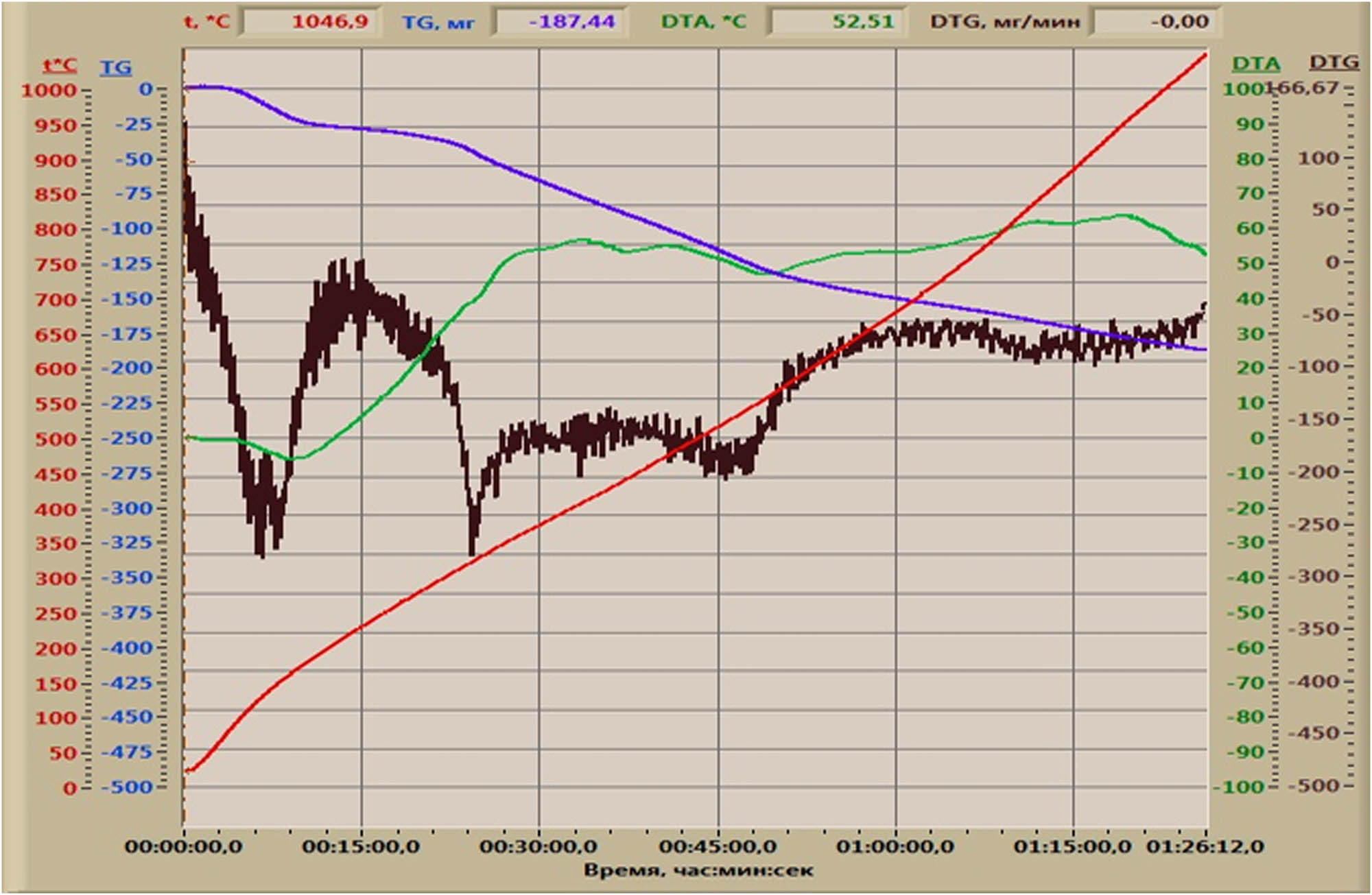
Derivatogram of coal waste from the Lenger deposit.
The curves of differential thermal analysis in Figure 3 are characterized by three endoeffects at 150°C, 330°C, 530°C, and 830°C. The first one at 150°C characterizes the removal of crystallohydrate moisture. The other three endoeffects characterize the decomposition of carbonate compounds of iron 330°C and magnesium 530°C, as well as 830°C calcium carbonates. Exoeffects at 130°C, 200°C, 470°C, and 750°C. They are characteristic of burnout reactions of sulfur compounds of iron and sulfate impurity metals.
2.3 Spectral analysis of raw materials
The infrared spectral analysis of the coal waste (Figure 4) was carried out using an IR Fourier spectrometer, Shimadzu IR Prestige-21, with a frustrated total internal reflection device, Miracle (Pike Technologies Kyoto, Japan). The IR Prestige-21 uses a bright ceramic light source, a high-sensitivity DLATGS detector, and high-throughput optical elements. Optimization of optical/electronics/signal systems minimizes noise and maximizes the S/N ratio (40,000:1 and better).
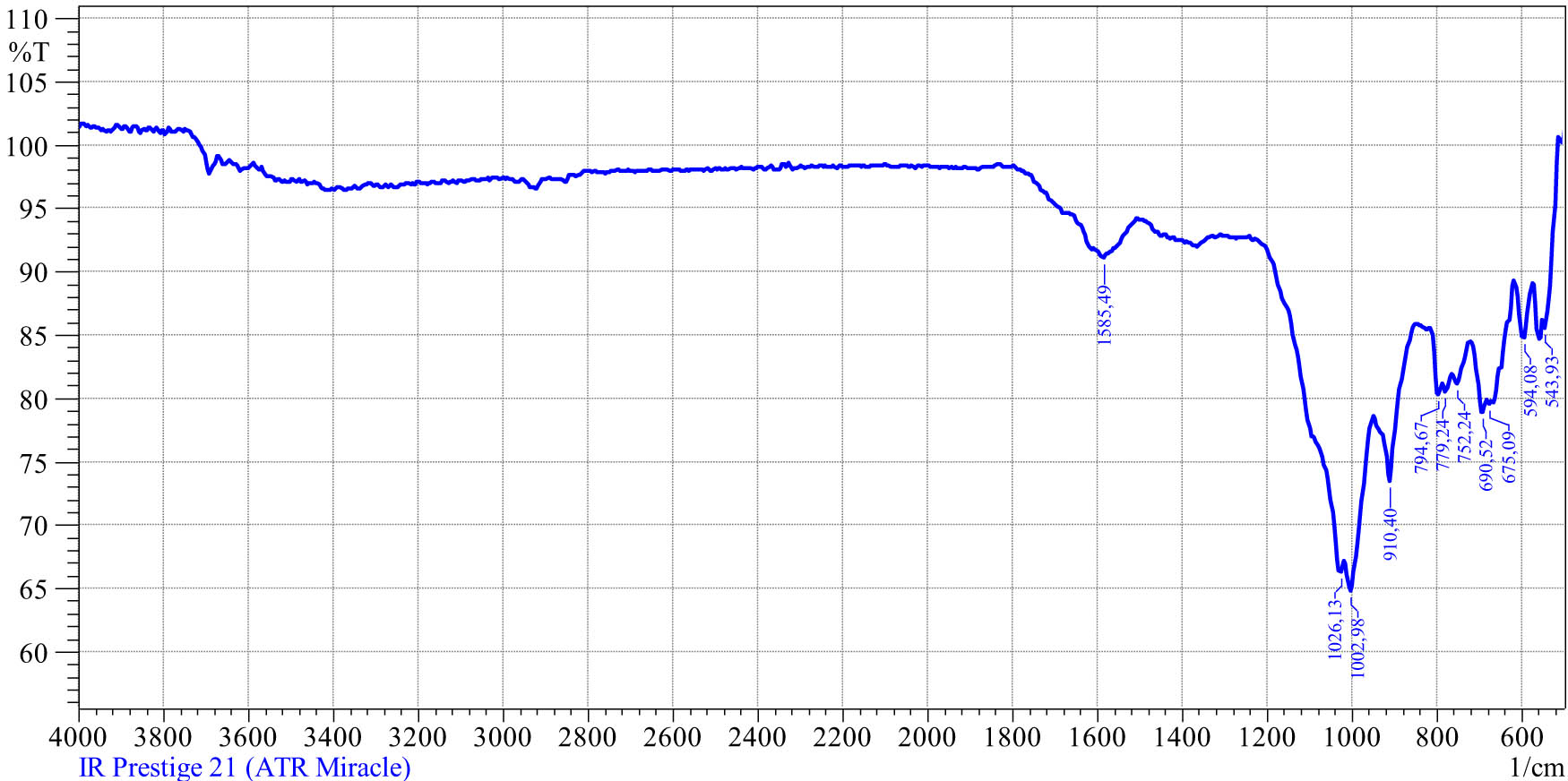
The IR spectrum of the coal waste from the Lenger deposit.
The infrared spectrum of the coal waste, represented in Figure 4, shows that
less intensive absorption spectra at 1,585.5 cm−1 are characteristic for sodium-containing carboxyl groups – C–O–K,
absorption spectra with wavelengths of 1,090–1,020 (1,033.8) cm−1 show the presence of silicates with valency bonds Si–O–Si and Si–O–C; in addition, they are characteristic for oxygen-containing ether groups,
intensive fluctuations in the range of 910.4 cm−1 inorganic metal (Mg, Al, Fe, and Ca) compounds,
absorption spectra in the interval of 794.6–752.2 cm−1 characterize organic functional groups.
2.4 Elemental analysis of raw materials
The elemental composition and micrograph of coal waste (Table 1, Figure 5) were determined using scanning microscopy (JSM-6490lV, Jeol, Tokyo, Japan).
Elemental composition of coal waste from the Lenger deposit
| Element | Weight % | Element | Weight % | Element | Weight % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 51.23 | Al | 4.43 | K | 0.41 |
| O | 33.98 | Si | 4.09 | Ca | 1.08 |
| Mg | 0.55 | S | 1.85 | Fe | 2.38 |
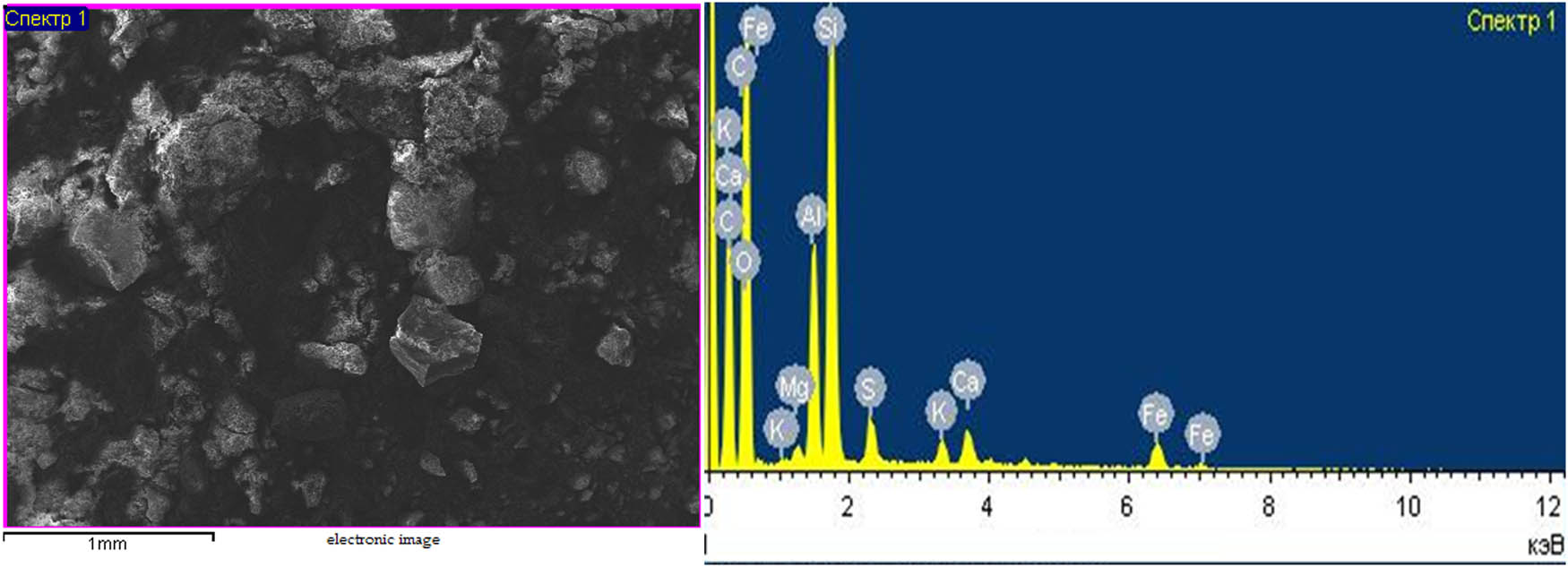
The micrograph of coal waste from the Lenger deposit.
The micrograph of the coal waste (Figure 5) is characterized by the indistinct dense congestion of irregular-shaped crystals. The irregular hexahedral single minerals are evidence of the presence of calcium aluminates. The dark aggregates around the fine-crystalline aluminate minerals are characteristic of calcium and silicon ferrites. The sample contains quartz minerals (as confirmed by fine chain aggregates), silicon aluminates, and iron-containing minerals [14].
From the analysis of Table 1, it follows that in the elemental composition of coal waste, the content of the main useful component is (C) carbon – 51.23%. This carbon content is sufficient for humic acids [15].
2.5 X-ray phase analysis of raw materials
To determine the structural state and chemical phase composition of coal waste, X-ray phase analysis using an incident beam monochromator D878-PC75-17.0 (London, England) was carried out, and the results are shown in Figure 6.
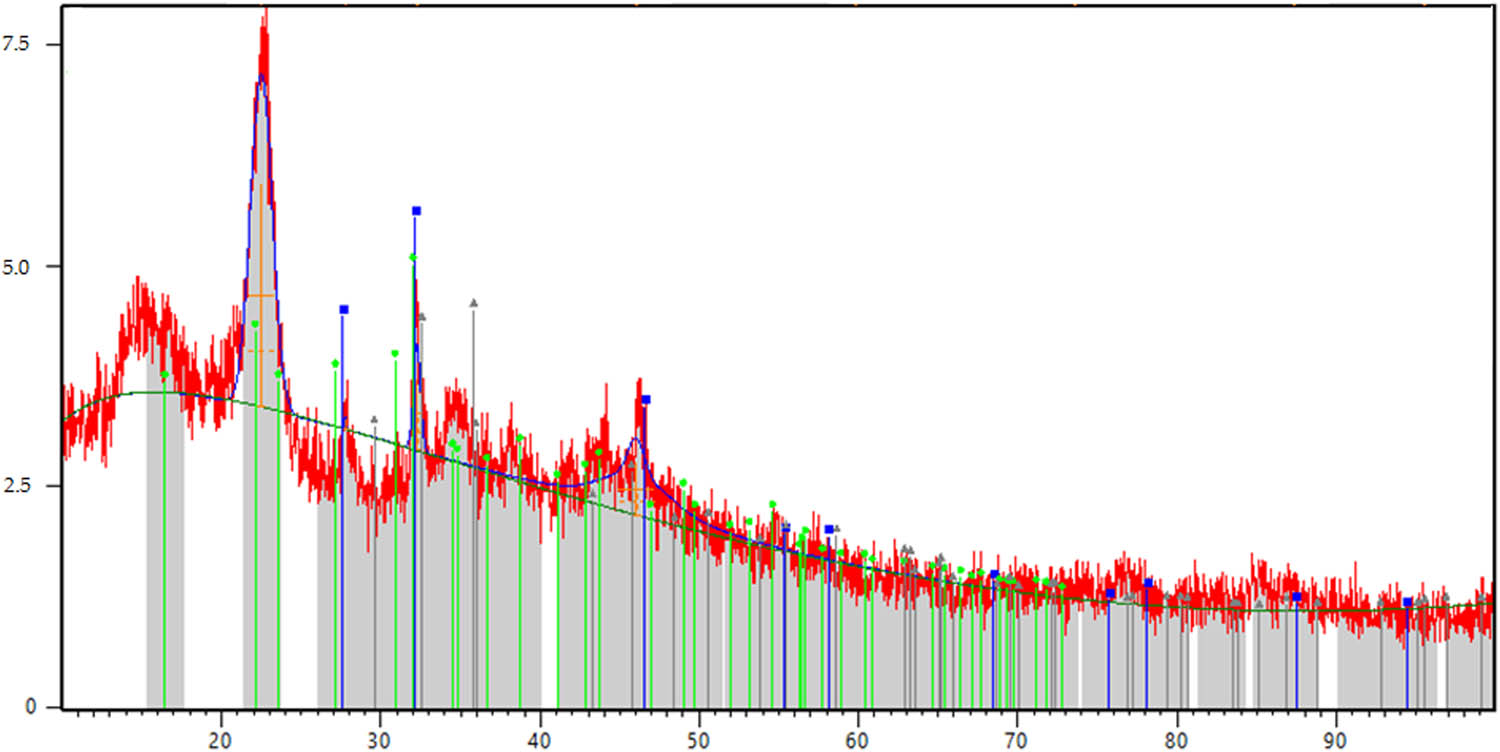
The X-ray image of coal waste from the Lenger deposit.
From Figure 6, it follows that the analysis of the X-ray pattern shows that the structure of the test sample is amorphous. Diffraction peaks with values of interplanar distances A 0 = 4.24–3.84–2.45–2.28–1.81–1.53 indicate the presence of quartzite – SiO2 – in the crystal structure of the sample, which is the main component. The composition of the test sample contains in significant quantities: iron oxide – Fe2O3, with diffraction maxima A 0 = 2.77–2.56–2.21–2.08–1.66–1.48, and gypsum – CaSO4·2H2O, for which the diffraction maxima A 0 = 7.14–3.34–3.02–2.70–2.12–1.66, are characteristic. The presence of coal impurities is evidenced by diffraction peaks with low intensity A 0 = 3.12–2.08–1.63–1.48 [16].
In order to increase the yield of humic acids in this coal, the process of coal oxidation with the use of HCl has been studied. The oxidation process was carried out at a concentration of HCl of 40–50% at a temperature of 30–60°C for a duration of 10–60 min, with a weight ratio of coal:HCl from 1:0.5 to 1:2. Moreover, the ratio of coal:acid meant the ratio of the organic part of coal to HCl [17].
Experimental work was carried out in a glass cylindrical reactor equipped with a thermostatic jacket and a screw-type stirrer. Acid was poured into the reactor, a set temperature was set, a stirrer was turned on, and coal was loaded. At the end of the process, the reaction mass was divided into liquid and solid phases. The solid phase was washed with distilled water from HCl to a neutral reaction, then dried to an air-dry state, and ash content, humidity, organic substances, and humic acid yield were determined in it by a known method.
Humic acid was synthesized from coal waste from the Lenger deposit using sodium hydroxide (NaOH – 10%), with a concentration yield of 27.8% in terms of organic mass. The synthesis of humic acid was also carried out using NaOH and ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) with a concentration yield of 22.5% and 18.3%. Synthesis of humic acid based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit using nitric acid (HNO3 – 50%), with a concentration yield of 45.2% in terms of organic mass [18,19,20,21,22]. The experimental work carried out on the synthesis of humic acids based on coal waste using HCl (50%) is a new method.
3 Results and discussion
During the research, it was determined that the coal waste of the Lenger deposit had the following composition (wt%) after drying to an air-dry state: moisture 17.26, determined by GOST 9516-92; ash 31.51, determined by GOST 11022-95, ISO 1171-97; organic matter 51.23. Microscopic examination revealed that the structure of coal has a microcellular composition, and the cells are rounded or slightly lenticular and are not large (0.0001–0.0002 mm). This structure is due to the high porosity and moisture capacity of coal. Under experimental conditions, it was identified that the degree of decomposition of coal waste is 95.9% with a solution of HCl concentration of 50% at a temperature of 30–60°C. The scientific novelty of this work is the yield of humic acid by 95.9% in terms of organic mass and the yield of acid by 49.13% (GOST 9517-94, ISO 5073-85).
It follows from Table 2 that when coal is decomposed with 50% HCl in the ratio T:W, equal to 1:2,0 and the degree of extraction of humic acid reaches up to 95.90% in terms of the organic phase, and the concentration of humic acid is 49.13%. Chemism of this process can be described as follows:
where CW denotes coal waste and (R–OH), (R–COH), and (R–COOH)– are functional groups in humic acid. According to the chemical characteristics of humic acids isolated according to GOST 9517-94, they contain approximately 8.40 mg-eq·g−1 (COOH – 4.97, OH – 2.49, and CO – 0.94) of the sum of functional groups.
The dependence of the yield of humic acid on temperature and acid concentration
| Name of products | Temperature (°C) | Concentration HCl (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 20% | 30% | 40% | 50% | ||
| Yield of humic acid from total organic mass (%) | 30 | 83.61 | 84.18 | 88.04 | 92.14 | 94.16 |
| 40 | 84.74 | 84.89 | 88.27 | 93.67 | 94.15 | |
| 50 | 84.78 | 84.96 | 88.93 | 94.14 | 95.22 | |
| 60 | 85.61 | 85.98 | 89.49 | 94.05 | 95.90 | |
The synthesis of humic acid was analyzed using an IR spectrometer (Shimadzu IRPrestige-21), and the results of the studies are shown in Figure 7.
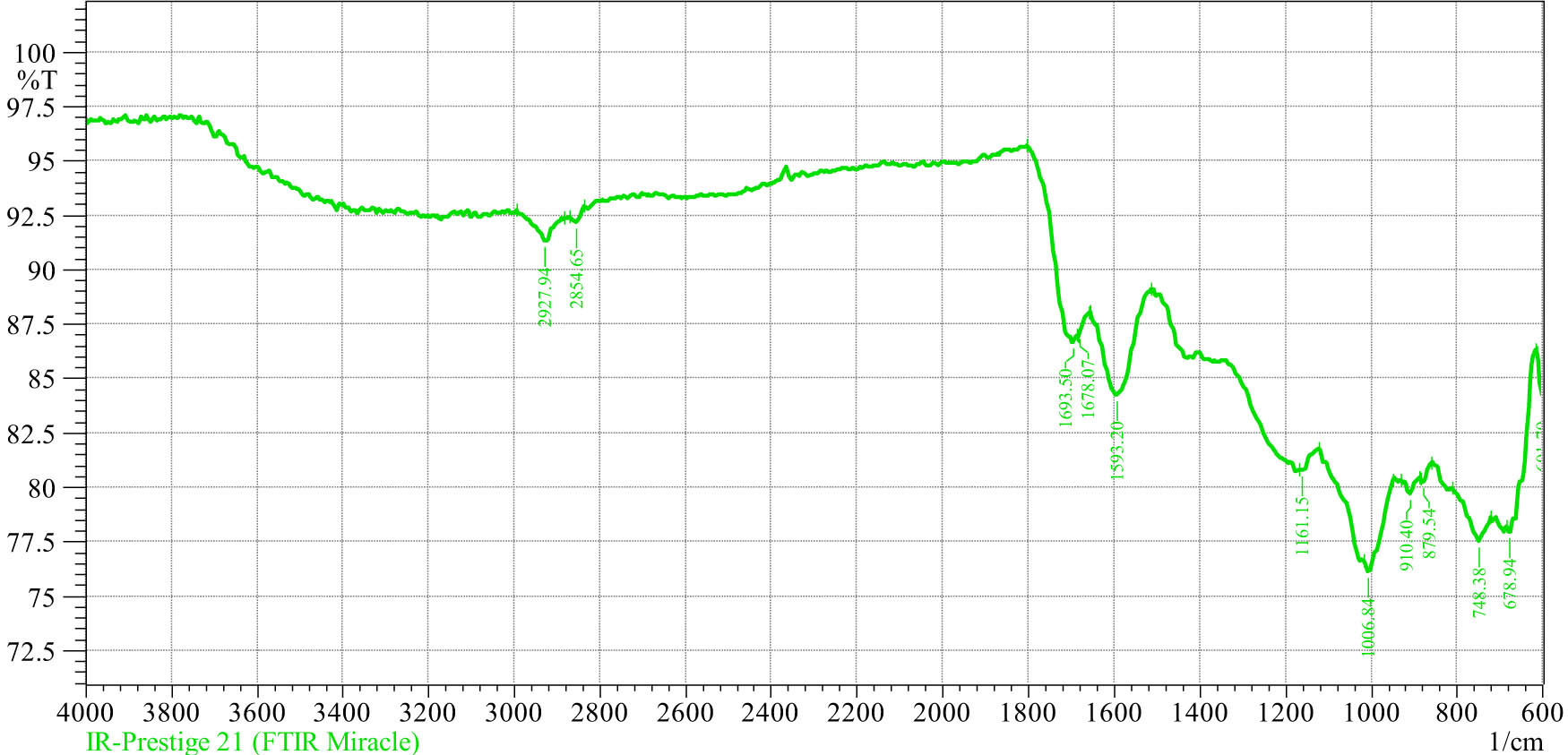
IR spectrum of humic acid.
As can be seen from the data in Figure 7, there are the following IR spectra and functional groups in humic acid:
spectra 3,000–2,800 cm−1 (2,927.91–2,854.65) cm−1 determine compounds between carboxylic acids with –OH-groups and methyl groups;
spectra 1,700–1,500 cm−1 (1,693.5–1,678.07–1,593.2) cm−1 determines compounds of carbonyl aromatic hydrocarbons;
spectra 1,161.15 cm−1, characteristic of aromatic aldehyde hydrocarbon compounds forming a C–O–C oxygen bridge;
spectra 910.40–879.54 cm−1 correspond to organic thiophene compounds;
spectra 748.38–678.94 cm−1 correspond to organic methylene compounds.
For the reliability of the experimental data obtained, mathematical methods of processing the process were carried out. For processing, the methods of mathematical planning of the experiment according to the orthogonal plan of the second order for k = 3 were used. The results of studies on the oxidation of brown coals were used as initial data. At the same time, the concentration of HCl varied from 10% to 50%, the temperature regime of the process varied from 30°C to 60°C, and the duration of the oxidation process varied from 10 to 60 min. As a result of the studies carried out to optimize the HCl oxidation process of brown coals, the reproducibility variances for the criteria y coefficients of regression equations were determined as an evaluation criterion. The plan and results of the experiment are shown in Table 3.
Experimental plan and research results on optimizing the HCl process of coal oxidation
| No. | Z 1 | Z 2 | Z 3 | y1 | No. | Z 1 | Z 2 | Z 3 | y1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 54.88 | 32.61 | 52.68 | 94.05 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 40 | 88.04 |
| 2 | 30.12 | 32.61 | 52.68 | 94.14 | 11 | 60 | 50 | 60 | 95.90 |
| 3 | 54.88 | 14.39 | 52.68 | 85.98 | 12 | 42.5 | 30 | 10 | 88.93 |
| 4 | 30.12 | 14.39 | 52.68 | 87.67 | 13 | 42.5 | 40 | 10 | 94.40 |
| 5 | 54.88 | 35.61 | 17.32 | 93.27 | 14 | 42.5 | 30 | 20 | 89.11 |
| 6 | 30.12 | 14.39 | 17.32 | 89.69 | 15 | 42.5 | 30 | 40 | 89.28 |
| 7 | 54.88 | 14.39 | 17.32 | 89.17 | 16 | 42.5 | 50 | 40 | 89.88 |
| 8 | 30.12 | 14.39 | 17.32 | 89.17 | 17 | 42.5 | 50 | 20 | 88.28 |
| 9 | 60 | 30 | 50 | 89.49 | 18 | 42.5 | 40 | 20 | 88.22 |
The dependences of the following criteria were investigated: Y is the yield of humic substances, %; Z 1 is the temperature (25–60°C); Z 2 is the HCl concentration (10–50%); and Z 3 is the oxidation time (10–60 min).
Using formulas 2–4, the results of four experiments in the center of the plan were calculated using reproducibility variances for the criterion y – yield of humic substances.
Based on the results of the experiments, the coefficients of the regression equations were calculated according to formulas 5 and 6. The calculation results are shown in Table 4.
Coefficients of regression equations
| Coefficients | y1 | Coefficients | y1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| b 0 | 95.90 | b 13 | 0.061 |
| b 1 | 0.476 | b 23 | 0.536 |
| b 2 | 2.657 | b 11 | 0.837 |
| b 3 | 0.128 | b 22 | 0.771 |
| b 12 | −0.184 | b 33 | 0.035 |
The significance of the regression equation coefficients was verified (7) by the Student’s criterion, and the adequacy of the regression equation to the experiment was verified (8) by the Fisher criterion. After excluding insignificant coefficients of regression equations, the regression equations adequate to the experiment have the following form:
where x 1 = z 1 − 42.5/12.38, x 2 = z 2 − 25/14.14, and x 3 = z 3 − 40/17.68.
The regression Eq. 9 allows us to calculate the values of the selected criterion for any study factors’ combination in the studied range, analyze the intensity of the influence of individual factors on the process indicators, and determine the optimal conditions for the oxidation of coal fines. According to the results of mathematical planning of the process, the optimal conditions ensuring the maximum yield of humic acids (up to 95.90%) during the HCl oxidation process of coal fines are as follows: HCl concentration – 50%, process temperature – 60°C, and oxidation duration – 60 min. The results of humic acid yield are shown (Figure 8) by 3D modeling [23].
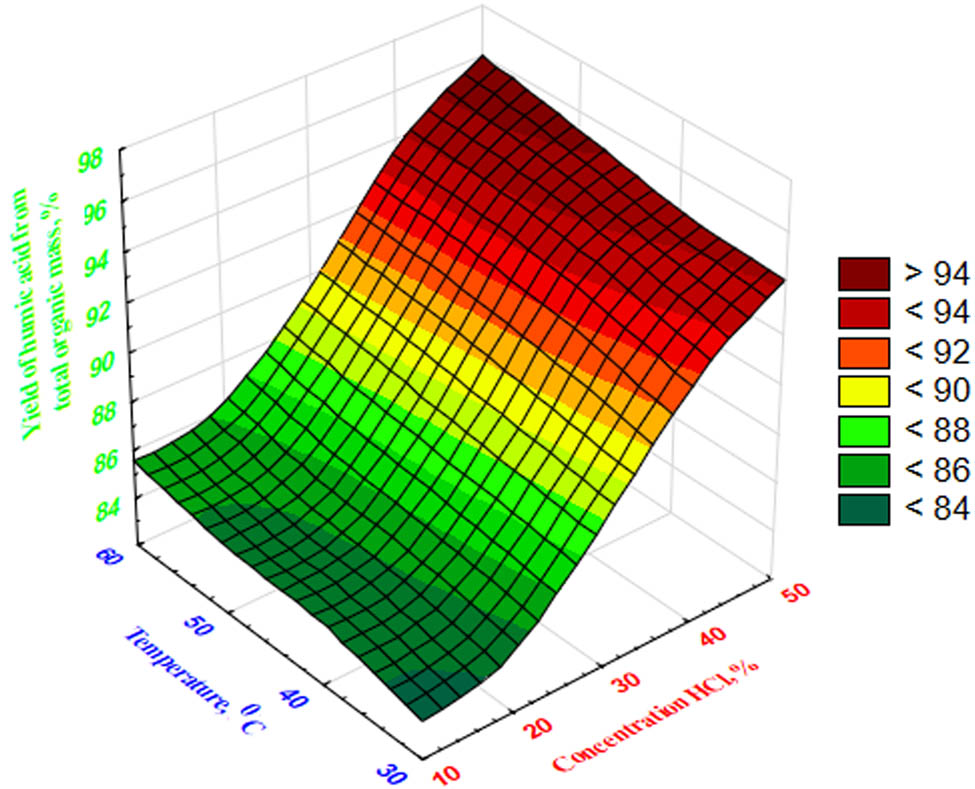
Dependence of humic acid yield on HCl concentration and temperature.
Based on the data in Figure 8, an increase in the yield of humic acid under the influence of HCl concentration and temperature during the decomposition of coal waste is characterized by a change in the square appearance of the plane from green to saturated red.
Many scientific research works have been carried out for the synthesis of humic acids. These studies were carried out to establish the regime conditions for the synthesis and output parameters for the production of humic acids. For the synthesis of humic acids, various inorganic alkalis and acids were used, among them are commonly used alkalis such as sodium, potassium, and NH4OH, as well as HNO3s [23].
Due to an increase in the concentration of alkali used in the production of potassium humate, the yield of the resulting potassium humate increases. Chemism of this process can be described in the following way:
The elemental composition of the resulting potassium humate was determined by an instrumental method using scanning microscopy (JSM-6490lV, Jeol, Tokyo, Japan). The results of the experimental work are shown in Figure 9.
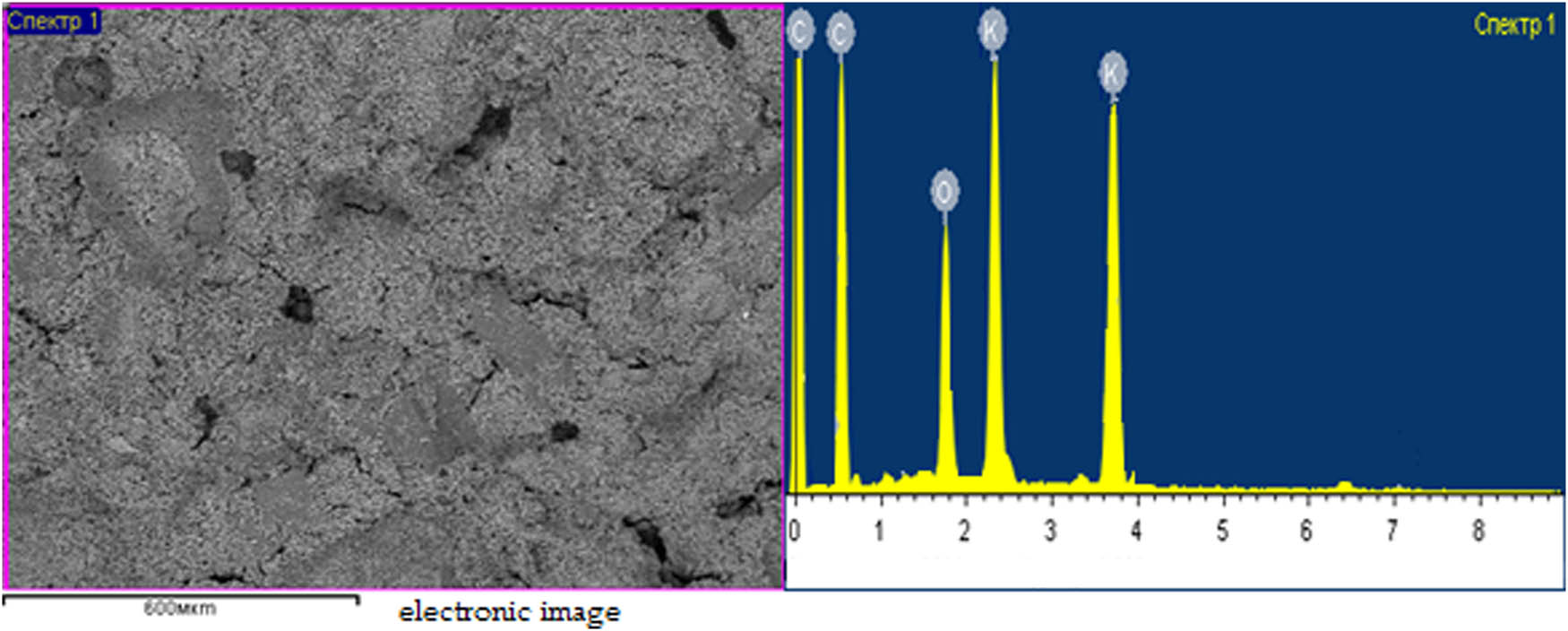
Microscopic image of potassium humate.
From Figure 9, it can be seen that the results of microscopic studies of potassium humate carried out using a SEM JSM-6490l using the energy-dispersive method are shown in the form of yellow spectra. These yellow spectra, respectively, indicate the elements that are present in a given sample and their mass fraction in ratios, %. Based on these data, the elemental composition of the test sample is determined and converted to the oxide form (Table 5).
Elemental composition of potassium humate
| Element | Weight % | Oxides | In terms of oxides (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 58.2 | — | — |
| O | 22.4 | — | — |
| K | 19.4 | К2O | 23.4 |
From Table 5, it follows that the carbon content is 58.2% and potassium is 19.4%. Such a content of useful components of potassium humate is enough to use it as a humate-containing fertilizer to increase crop yields.
4 Conclusions
A synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit using inorganic solutions was studied. The synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate is aimed at reducing accumulated industrial waste, which in turn allows regulating and improving the environmental situation in the region [5,24,25].
The elemental and mineralogical composition of coal waste has been studied, as well as the yield and structural–functional composition of humic acid. The chemical composition of coal waste was studied using differential thermal analysis during heat treatment. A sieve analysis was carried out to study fine fractions of coal waste, and an X-ray phase analysis was carried out to study the mineralogical, structural state, and chemical phase composition of coal waste from the Lenger deposit [26].
Based on the results of experimental work, the optimal parameters of the process of obtaining humic acids were determined and established. Also, the results were confirmed by the mathematical planning of the experiment using the method of the orthogonal plan of the second order. The mathematical planning results were tested according to the Student and Fisher criteria. Based on the conducted studies, it was identified that the degree of extraction of humic acid reaches up to 95.90% in terms of the organic phase, and the concentration of humic acid is 49.13%. Potassium humate is involved in the formation of soil structure and the accumulation of nutrients and microelements in a form available to plants and helps regulate the content of metals in water and soil ecosystems.
Based on the synthesized humic acids, potassium humate was obtained using potassium hydroxide. Based on the results of experimental work, the optimal technological parameters for the process of obtaining potassium humate and the elemental mineralogical composition were determined. The resulting potassium humate, in its composition, has fertilizer properties. Therefore, the resulting potassium humate will be used for the production of humic fertilizers to improve soil fertility and crop yields.
-
Funding information: This research was funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Grant No. AP14972664.
-
Author contributions: Bakyt Smailov: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data writing – original draft preparation, writing – review and editing, visualization, project administration, and funding acquisition. Usha Aravind: software, validation, resources, and supervision.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Akhunbaev A. Status and prospects of the coal industry in Kazakhstan. Min Metall Ind. 2017;8(8):25–31.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Beisenbayev OK, Issa AB, Kovaleva E. Research of polyacrylonitrile saponification heterophase process mechanism in different conditions. Orient J Chem. 2015;31(4):2369. 10.13005/ojc/310466.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Lenger coal deposit//Kazakhstan. National Encyclopedia. – Almaty: Kazakh encyclopedias, 2005. - T. III. — ISBN 9965-9746-4-0. (CC BY SA 3.0).Search in Google Scholar
[4] Smailov BM, Tleuov AS, Beisenbayev OK, Tleuova ST, Yeskendirova MM, Userbaeva BA. Multifunctional sorbents based on refractory clays for chemical industry wastewater treatment. Rasayan J Chem. 2022;15(2):1085–90. 10.31788/RJC.2022.1526806.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Smailov BM, Beisenbayev OK, Tleuov AS, Kadirbaeva AA, Zakirov BS, Mirzoyev B. Production of chelate polymer-containing microfertilizers based on humic acid and ammophos. Rasayan J Chem. 2020;13(3):1372–8. 10.31788/RJC.2020.1335726.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Gong G, Xu L, Zhang Y, Liu W, Wang M, Zhao Y, et al. Extraction of fulvic acid from lignite and characterization of its functional groups. Am Chem Soc Omega. 2020;5(43):27953–61. 10.1021/acsomega.0c03388.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Beysenbayev OК, Tleuov AS, Smailov BM, Zakirov BS. Obtaining and research of physical and chemical properties of chelated polymer-containing microfertilizers on the basis of technogenic waste for rice seed biofortification. News Natl Acad Sci Repub Kazakhstan. 2019;438:80–9. 10.32014/2019.2518-170X.10.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Huang Z, Liaquat R, Ahmad B, Ali Haider R, Shoukat M. Extraction and chemical characterization of humic acid from nitric acid treated lignite and bituminous coal samples. Sustainability. 2021;13:8969–75.10.3390/su13168969Search in Google Scholar
[9] Vjalykh EA. Humic acid synthesis method. Government Agency Higher Professional Education “Perm State University” (RU). Patent No. 2010105598/21. 2022.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Nazarbek U. Development of technologies for the processing of phosphorus sludge into target fertilizer products: dis …. doc. philosophy PhD. SKU M. Auezov. - Shymkent, 2017. p. 89–93.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Temirov US, Namazov SS, Usanbayev NK. Intensive technology for processing bird litter in organic and mineral fertilizers. ChemTech. 2020;63(12):85–94. 10.6060/ivkkt.20206312.6210.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Smailov BM. Development of technology for obtaining chelated microfertilizers based on coal and phosphorus waste: dis …. doc. philosophy PhD. SKU M.Auezov. – Shymkent, 2020. p. 45–55.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Jing J, Zhang S, Yuan L, Li Y, Lin Z, Xiong Q, et al. Combining humic acid with phosphate fertilizer affects humic acid structure and its stimulating efficacy on the growth and nutrient uptake of maize seedlings. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17502. 10.1038/s41598-020-74349-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Smailov BM, Kydyralyeva ASh, Beisenbayev OK, Issabayev NN, Azimov AM, Issa AB, et al. Study of modification of sodium montmorillonite from the Darbazinsk deposit. Rasayan J Chem. 2022;15(3):1787–91. 10.31788/RJC.2022.1536934.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Havlin JL, Beaton JD, Tisdale SL, Nelson WL. Soil fertility and fertilizers: An introduction to nutrient management. 7th edn. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education; 2025. p. 148–52. https://novapublishers.com/.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Smailov BM, Zakirov BS, Beisenbayev OK, Tleuov AS, Issa AB, Azimov AM. Thermodynamic-kinetic research and mathematical planning on the obtaining of phosphorus-containing components based on cottrel dust from phosphorus production waste. Rasayan J Chem. 2022;15(4):2274–9. 10.31788/RJC.2022.1547022.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Ismailov B, Zakirov B, Kadirbayeva A, Koshkarbayeva Sh, Smailov B, Azimov A, et al. Methods for obtaining phosphorus-containing fertilizers based on industrial waste. Inorganics. 2023;11:224. 10.3390/inorganics11060224.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Karataev SS, Kholoshenko LK, Batkaev LV, Beisenbayev OK Method of obtaining organic and mineral fertilizer. Committee on Intellectual Property Rights of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Patent No. 30648. 2015.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Nazarbek U, Abdurazova P, Raiymbekov Y. Extraction and characterization of humic acid based on coal mining waste. Chem Eng Technol. 2022;45(6):1133–40. 10.1002/ceat.202200038.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Kambatyrov M, Nazarbek U, Abdurazova P, Nazarbekova S, Raiymbekov Y. Humates from coal mining waste: Synthesis, study of composition and radioactivity. Rasayan J Chem. 2020;13:1308–12. 10.31788/RJC.2020.1335729.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Nazarbek U, Abdurazova P, Nazarbekova S, Assylbekova D, Kambatyrov M, Raiymbekov Y. Alkaline extraction of organic and mineral potassium humate from coal mining waste. Appl Sci. 2022;12(7):3658. 10.3390/app12073658.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Myrzakhmetova BB. Development of technology for the production of complex organic and mineral fertilizer based on humates of local origin: dis …. doc. philosophy PhD. SKU. M.Auezov. – Shymkent, 2012. p. 152.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Roine A. Outokumpu HSC chemistry for windows. Chemical reaction and equilibrium software with extensive thermochemical database. Pori: Outokumpu Research; 2016.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Raiymbekov Y, Abdurazova P, Nazarbek U. Enrichment of low-grade phosphorites by the selective leaching method. Green Process Synth. 2023;12:20228150. 10.1515/gps-2022-8150.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Beysenbayev OK, Ahmedov UK, Issa AB, Smailov BM, Esirkepova MM, Artykova ZhK. Receiving and research of the mechanism of capsulation of superphosphate and double superphosphate for giving of strength properties. News Natl Acad Sci Repub Kazakhstan. 2019;6:36–45. 10.32014/2019.2518-170X.153.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Smailov BM, Aravind UK, Zakirov BS, Azimov AM, Tleuov AS, Beisenbayev OK, et al. Technology for obtaining chelated organic and mineral micro-fertilizers based on humate-containing components. Rasayan J Chem. 2023;16(1):428–33. 10.31788/RJC.2023.1618007.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”

