Abstract
Bromate–thiourea coordinated leaching of gold sulfide ore for gold sulfide ore as leaching object. The effects of leaching reagent, stirring speed, and leaching time on gold leaching were investigated in this article. The results showed that the optimum leaching conditions were potassium bromate 0.1 M, thiourea 0.6 g·L−1, hydrochloric acid 0.2 M, agitation speed 250 rpm, ratio of liquid to solid 4, and leaching time 10 min. Under these conditions, high efficiency and rapid leaching of gold can be achieved, and reagent consumption is reduced. The research results have theoretical and practical significance for expanding new green gold extraction technology.
1 Introduction
It is difficult to extract gold from refractory sulfur-bearing gold ore by cyanidation. At the same time, the highly toxic cyanide will cause serious environmental pollution and ecological damage, some countries have banned the use of cyanide gold extraction [1,2]. Therefore, it is urgent to find a non-cyanide leaching method that can deal with this kind of gold ore effectively. The exposure of gold in sulfide ore should be considered first. The direct leaching of sulfide ore is usually in the range of acidity, and the gold can be directly leached by a suitable oxidant. As a strong oxidant, bromate is more Standard electrode potential than most oxidants under acidic conditions. Due to the oxidizing property of bromate, it can completely satisfy the dissolution of gold. After the leaching of gold, the bromate reduction product is a bromide, which is usually non-toxic. Therefore, the method is also a green gold extraction method [3,4,5].
Thiourea process is a non-cyanide technology that can be applied in the future because of its quick leaching kinetics and non-toxicity [6]. In the thiourea process, the iron ion is usually used as an oxidant, but this method has the problems of difficult leaching and a slow leaching rate. In addition to iron, bromic acid as a strong oxidant can also be used for gold leaching. The potential at the initial stage of gold leaching is greater than 1.131 V, which satisfies the reduction potential of oxidant required for the bromination leaching system. Therefore, it is feasible to extract gold from raw ore by this method. However, due to the preservation of bromic acid, potassium bromate is usually acidified to form bromic acid which acts as an oxidant, in the leaching system, thiourea was used as a coordination agent for gold leaching [7]. The chemical reaction of the method is as follows:
Pre-leaching stage:
Later stage of leaching:
From the above chemical equations, it can be seen that the system has good gold-dissolving ability in both the early and late stages of leaching. It not only overcomes the weakness of traditional thiourea for gold dissolution of sulfide ores, but also reduces the excessive reagent consumption of the Bromic acid-thiourea system. In this article, the bromate–thiourea synergistic leaching of gold from refractory gold sulfide ore was studied. The effects of leaching reagent, stirring speed, and leaching time on gold leaching were investigated, and the experimental results have theoretical and practical significance for extending the new green gold extraction technology [8].
2 Experiment
2.1 Reagent
Potassium bromate, hydrochloric acid, thiourea, ferric chloride, and other reagents are analytical pure, experimental water for distilled water. The research object is a gold ore in Yunnan province. From Figure 1, it can be seen that the main minerals in the ore are quartz, dolomite, calcite, pyrite, chalcocite, etc. As can be seen from Table 1, the main recoverable valuable element in the ore is gold with a grade of 2.66 g·t−1. Among other elements, the content of S and As is higher. Due to the high content of S and As, the ore is refractory to leaching, and the gold grade is relatively low, but it still has a certain economic value.
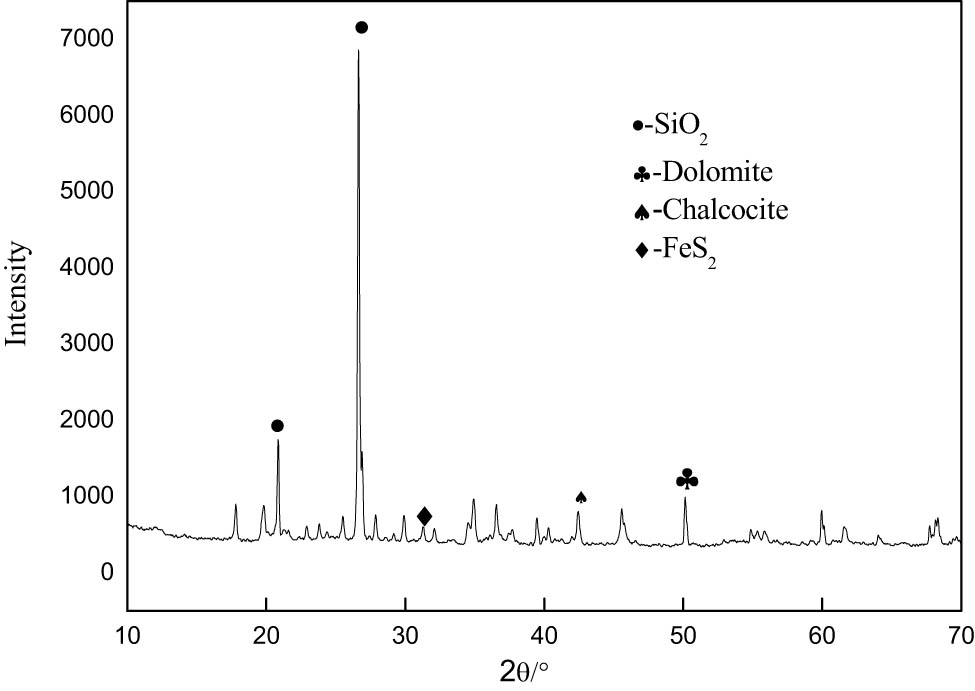
XRD diagram of raw ore.
Elemental analysis of raw gold ore
| Element | Au (g·t−1) | Cu | Fe | S | As | C | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 2.66 | 0.15 | 2.62 | 1.88 | 0.29 | 6.76 | 1.51 | 9.50 | 3.45 | 4.57 | 67.57 |
2.2 Equipment
TAS-990 atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Beijing Puxi); PHS-3C acidity meter (Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.).
2.3 Leaching of gold
The ore is leached directly without roasting. The gold leaching test of the ore is carried out at room temperature by weighing a certain amount of ore sample and placing it in a conical flask. The leaching solution was prepared by mixing corresponding leaching reagent with deionized water. Adjust the pH of the pulp with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid. During the leaching process, the pulp is stirred at a constant rate. At the end of the leaching test, the ore slurry is separated by solid and liquid to get the leached slag, and the leached slag is washed several times with deionized water, dried, and crushed, and then the gold content in the leached slag is analyzed, the leaching rate of gold was calculated. The formula for the gold leaching rate is as follows:
Here, α is the gold content in the sample (g·t−1), β is the gold content in the leach residue (g·t−1), m is the weight of the sample (g), and m 1 is the weight of the leach residue (g).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effect of bromate concentration
In order to study the effect of the concentration of potassium bromate on gold leaching rate, the effect of different concentrations of potassium bromate on gold extraction was investigated. The other test conditions were: Hydrochloric acid 0.2 M, thiourea 0.6 g·L−1, the leaching time was 30 min and the stirring speed was 250 rpm. The results are shown in Figure 2. With the increase in the concentration of potassium bromate, the leaching rate of gold increased significantly. When the concentration of potassium bromate is 0.1 M, the leaching rate of gold is 90.5%. At the same time, when the concentration of potassium bromate is more than 0.1 M, the leaching rate of gold has little relation with the concentration of potassium bromate. Therefore, 0.1 M was chosen as the optimum concentration of potassium bromate.
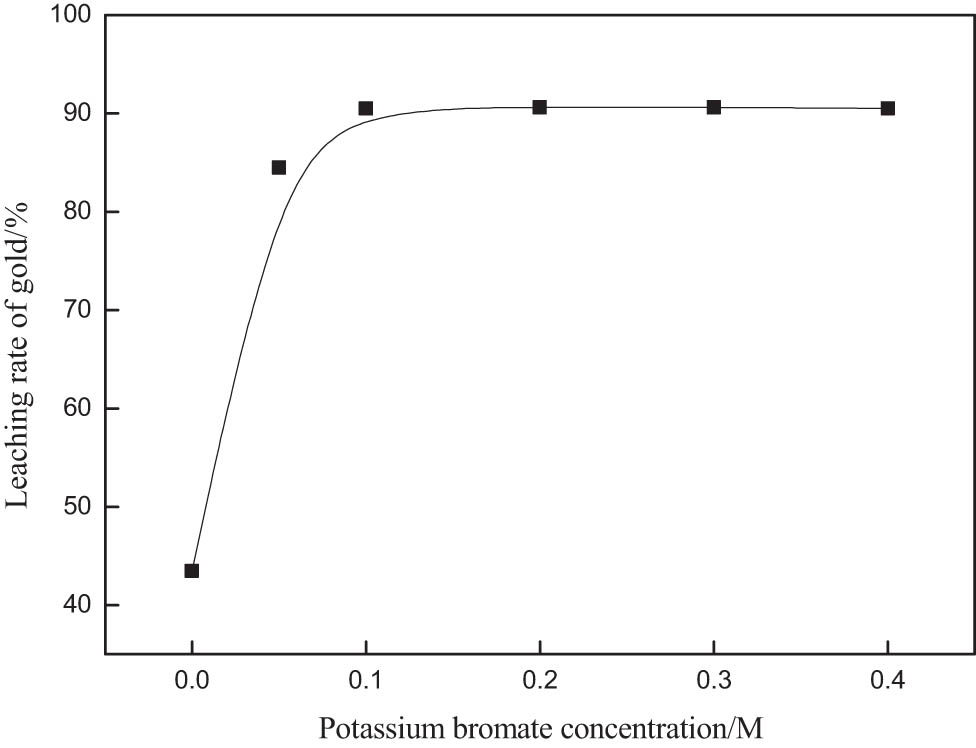
Effect of potassium bromate concentration on gold extraction rate.
3.2 Effect of thiourea concentration
When only potassium bromate is used as an oxidant, its consumption is larger [7]. In order to reduce the consumption of potassium bromate, thiourea was used as a leaching aid to oxidize sulfide ore. The design of the experiment is as follows: thiourea has the characteristics of a fast gold leaching rate and good selectivity. However, potassium bromate as an oxidant has a strong oxidation ability and can oxidize thiourea [9]. Therefore, it is necessary to control the concentration of thiourea. The effect of thiourea concentration on gold leaching from raw ore was studied at room temperature. The other test conditions were potassium bromate 0.1 M, hydrochloric acid 0.2 M, liquid–solid ratio of 4, reaction time of 30 min, and agitation speed of 250 rpm; the test results are shown in Figure 3. It was found that the leaching rate of gold reached 91.7% when the concentration of thiourea was 0.6 g·L−1. When the concentration of thiourea exceeds 0.6 g·L−1, the leaching rate of gold no longer increases. Therefore, 0.6 g·L−1 is the optimum concentration of thiourea for leaching of raw ore.
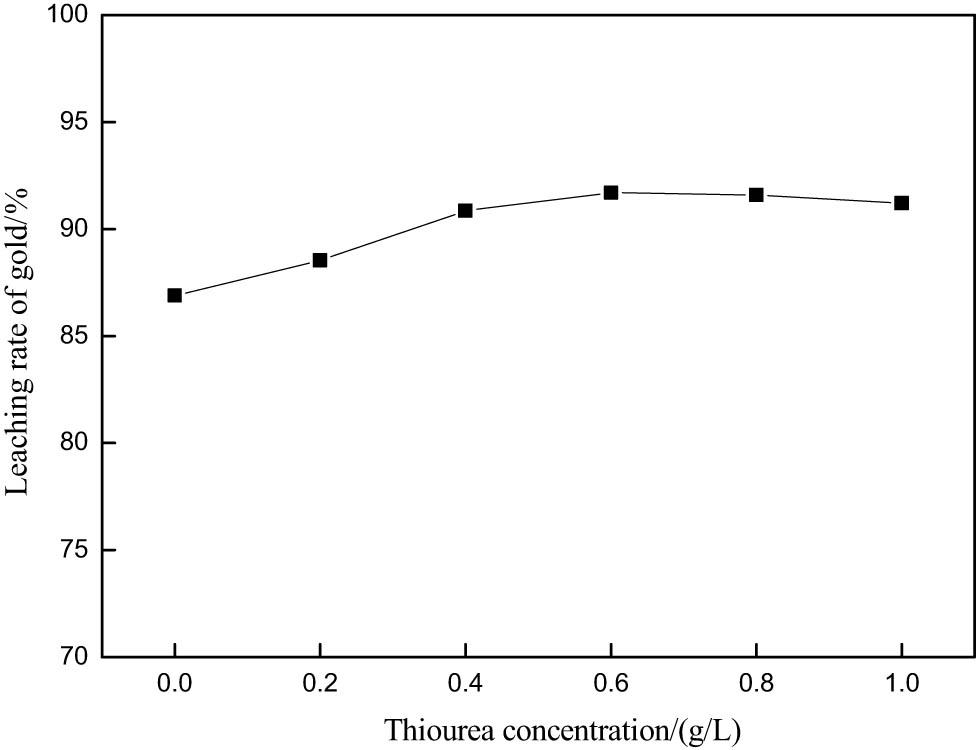
The effect of thiourea concentration on gold extraction rate.
3.3 Effect of hydrochloric acid concentration
Thiourea is relatively stable in the acidic range, but potassium bromate has strong oxidation under acidic conditions. In order to reduce the over-oxidation of thiourea, it is necessary to keep suitable acidic conditions in the leaching system. In the leaching test, hydrochloric acid provided hydrogen ions, thus creating suitable acidic conditions and promoting the reaction. In order to investigate the influence of hydrochloric acid concentration on gold dissolution, the experimental conditions were set as follows: potassium bromate, 0.1 M; thiourea, 0.6 g·L−1; liquid–solid ratio, 4; leaching time, 30 min; agitation speed, 250 rpm; the result is shown in Figure 4. The leaching rate of gold increases rapidly with the increase in the concentration of hydrochloric acid, but when the concentration of hydrochloric acid is more than 0.2 M, the leaching rate of gold does not change significantly, so the optimum concentration of hydrochloric acid is 0.2 M.
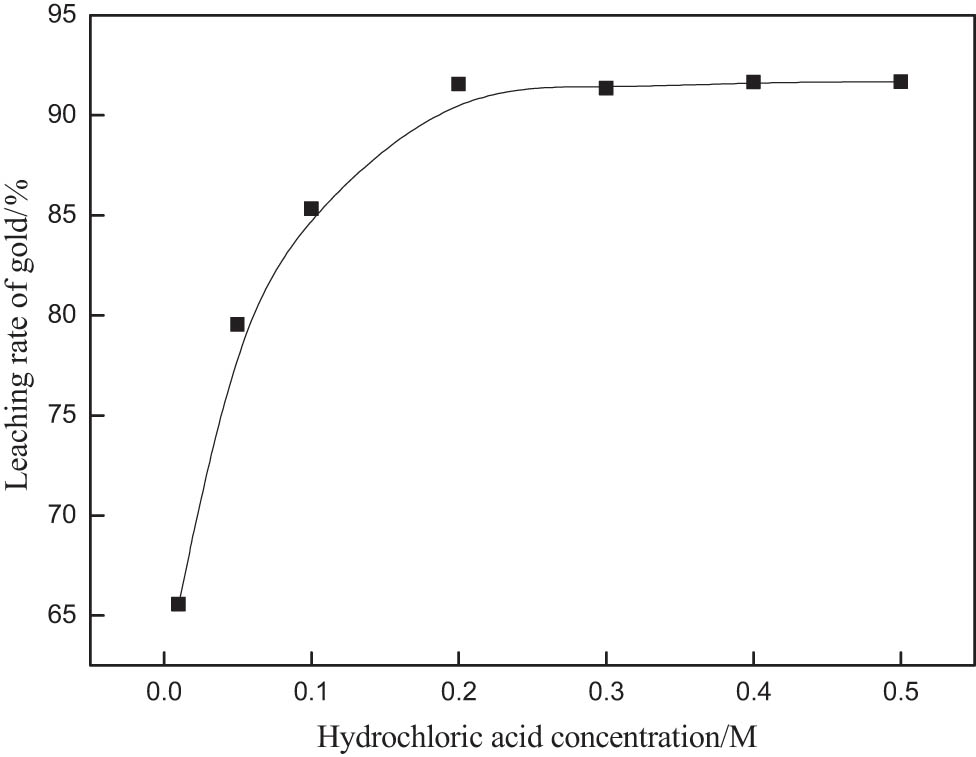
The effect of hydrochloric acid concentration on gold extraction rate.
3.4 The effect of liquid–solid ratio
In the process of gold leaching, the liquid–solid ratio has an important effect on the gold leaching rate [10]. The immobilization conditions were as follows: potassium bromate 0.1 M; thiourea, 0.6 g·L−1; hydrochloric acid, 0.2 M; leaching time, 30 min; and agitation speed, 250 rpm. Higher liquid–solid ratio is beneficial to the continuous improvement of the gold leaching rate. But the increase in liquid–solid ratio will lead to an increase in equipment cost. As can be seen from Figure 5, the leaching rate of gold does not increase when the liquid–solid ratio is greater than 4. Therefore, the optimal liquid–solid ratio is 4.
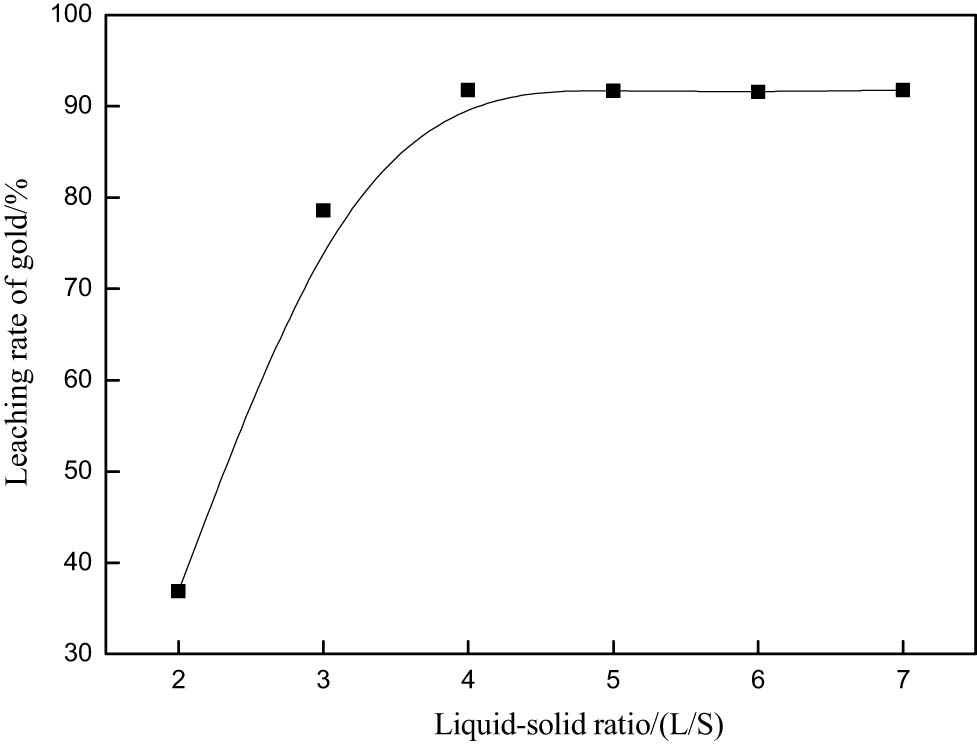
Effect of L/S on gold extraction rate.
3.5 The influence of stirring speed
Generally speaking, the agitation speed has a great influence on gold leaching, by increasing the agitation speed and increasing the mass transfer rate [11]. Therefore, moderately increasing the stirring speed can promote the contact between the leaching solution and the solid particles, thus improving the gold leaching rate. The effect of stirring speed on gold leaching rate was studied. The reaction was carried out under the conditions of 0.1 M, fixed potassium bromate, 0.6 g·L−1 thiourea, 0.2 M hydrochloric acid, 30 min of reaction time, and 4 liquid–solid ratio. As shown in Figure 6, the gold leaching rate reaches its maximum at 250 rpm with the increase in stirring speed. When the stirring speed was further increased, the gold leaching rate did not change. The results show that the leaching effect of gold ore is best when the stirring speed is 250 rpm under the conditions.
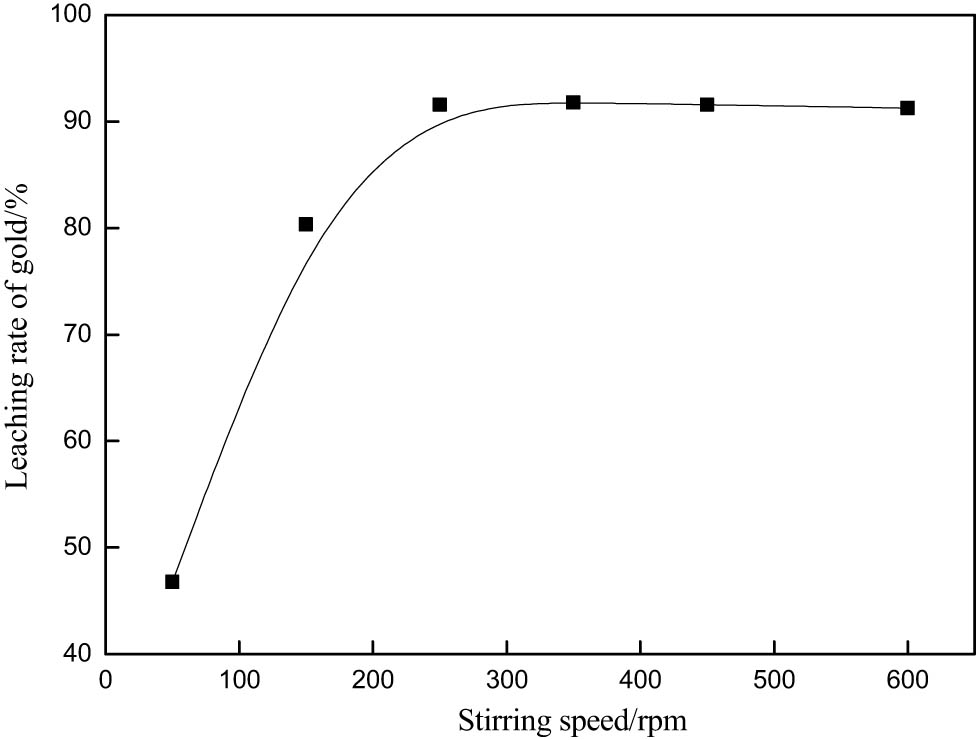
Effect of stirring speed on gold extraction rate.
3.6 Effect of leaching time
The leaching rate of gold increases with the prolongation of leaching time. But prolonged leaching time will lead to increased capital and reagent costs after a certain time [12]. Therefore, the selection of appropriate leaching time is the key to guarantee the efficient leaching of gold. The experimental conditions were as follows: potassium bromate, 0.1 M; thiourea, 0.6 g·L−1; hydrochloric acid, 0.2 M; agitation speed, 250 rpm; and liquid–solid ratio, 4. As can be seen from Figure 7, the leaching rate of the system is very fast, and the gold extraction rate can reach 92.3% in 10 min. Fast leaching rate is the biggest advantage of the bromate–thiourea synergistic leaching of gold sulfide ore. Secondly, compared with the literature [13,14,15], it can be found that this method reduces reagent consumption. But the reagent consumption is still large. Further optimization is needed.
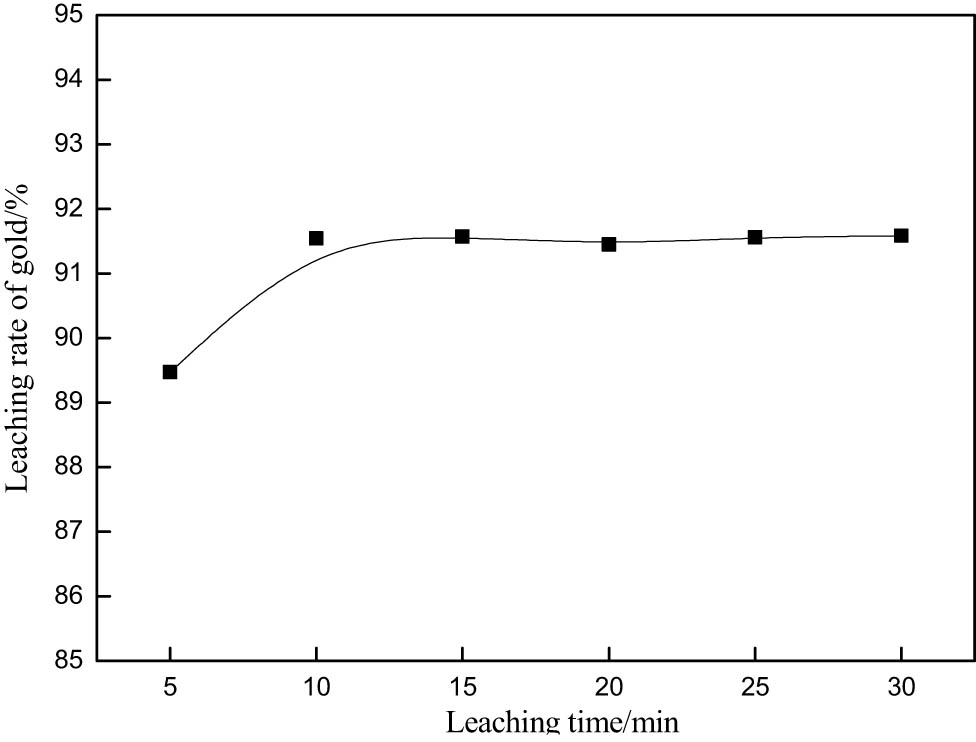
Effect of leaching time on gold extraction rate.
3.7 Compared with thiourea methods
The test conditions of thiourea method are as follows [10,16]: thiosulfate concentration is 0.1 M, copper ion concentration is 0.05 M, ammonia concentration is 0.4 M, agitation speed is 250 rpm, liquid–solid ratio is 4, leaching time is 12 h, and pH is 2. The leaching rate of the same gold sample is 33.4%. The experimental conditions of the thiourea method were as follows: reaction temperature, 30°C; thiourea concentration, 1.5 g·L−1; iron ion concentration, 1.5 g·L−1, pH 1.5; leaching process with air, ratio of liquid to solid 4, leaching time 6 h, and the leaching rate of gold was only 43.1%. Due to the high content of S and As, the two methods did not achieve good leaching results. The reason is that the oxidizing agent has weak oxidizing ability and cannot fully oxidize sulfides in gold ore.
3.8 Characterization of gold ore before and after leaching
From the comparison of the surface of gold ore before and after leaching (Figure 8), the surface of gold ore becomes smooth and rough after leaching, and there are many pores. This shows that the surface of the gold ore was strongly corroded. Gold is leached by contact with the leaching solution of gold after the surface of the ore is corroded.
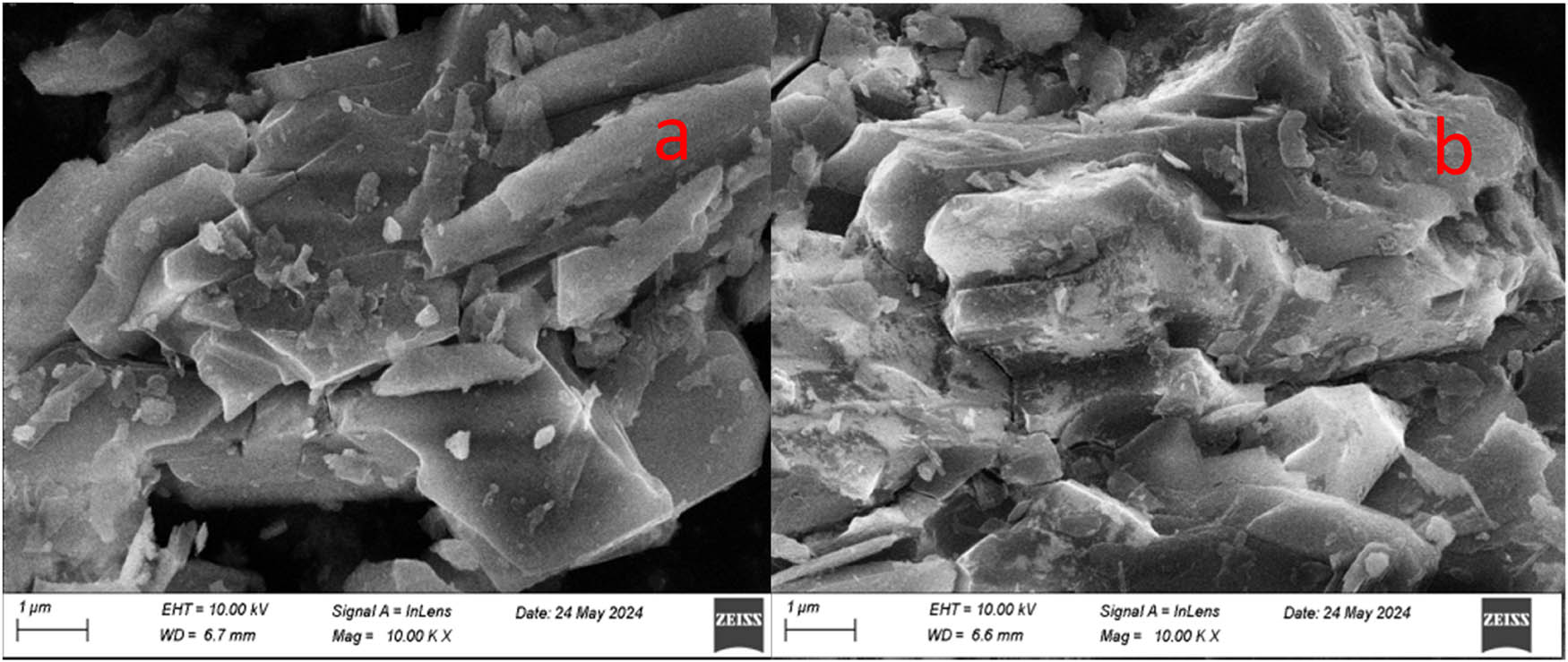
Characterization of gold ore before and after leaching (a) before leaching, (b) after leaching.
3.9 Comparison of thiourea consumption
The consumption of reagents is an important content in the leaching process. Thiourea concentration is the most important reagent in this method, and the amount of thiourea determines whether gold can be further leached. The consumption of two kinds of process reagents was compared. The two processes are potassium bromate, 0.1 M, thiourea, 0.6 g·L−1; hydrochloric acid, 0.2 M; agitation speed, 250 rpm; ratio of liquid to solid, 4; and leaching time, 10 min; thiourea concentration, 1.5 g·L−1, iron ion concentration, 1.5 g·L−1, pH 1.5; leaching process with air: ratio of liquid to solid, 4; leaching time, 6 h. The consumption of thiourea was investigated after leaching under the optimum experimental conditions. The results are shown in the Table 2.
Comparison of leaching results and thiourea consumption by two different methods
| System | Leaching rate of gold (%) | Leaching time | Thiourea consumption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bromate–thiourea | 92.3 | 10 min | 88.7 |
| Fe3+–thiourea | 43.1 | 6 h | 53.1 |
The results show that thiourea is consumed more than other methods, but this method still has a high leaching rate and short leaching time. Although the leaching time is very short, the oxidation of bromic acid is so strong that thiourea is oxidized quickly.
From the results of previous tests, the gold leaching rate is very high; the reason is that bromic acid can leach gold even at a low concentration of thiourea. The chemical reaction of the method is as follows:
Compared with the bromic acid method, the concentration of potassium bromate used in this method is relatively less, so it is more environmentally friendly. But it is undeniable that the composition of the leaching solution is more complex, which will bring trouble for the next step of gold recovery.
4 Conclusion
In this article, bromate–thiourea synergistic leaching of gold sulfide ore has been studied. This method reduces the consumption of reagents, and the leaching time is greatly reduced compared with other gold extraction methods such as cyanidation and thiosulfate. The gold leaching effect is satisfactory. Through the experiment, the conditions of bromate–thiourea synergistic leaching of gold sulfide ore are as follows: the concentration of potassium bromate is 0.1 M, the concentration of thiourea is 0.6 g·L−1, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is 0.2 M, the agitation speed is 250 rpm, the ratio of liquid to solid is 4, and the leaching time was 10 min. Although the reagent consumption of this method is large, the leaching rate is high, and the leaching time is short; compared with the cyanide method, this method is still a green gold extraction method.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Rare and Precious Metals Extraction and Mine Ecological Management Team Foundation(22YNOUTD02).
-
Author contributions: Zhang Qiang: resources, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing; Duan Jing-ze: project administration and funding acquisition; Peng-Zhi Xiang: methodology and formal analysis.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Aylmore MG, Muir DM. Thiosulfate leaching of gold – A review. Min Eng. 2001;14(2):135–74.10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00172-2Search in Google Scholar
[2] Jeffrey MI, Breuer PL, Choo WL. A kinetic study that compares the leaching of gold in the cyanide, thiosulfate and chloride system. Metall Mater Trans B. 2001;32(6):979–86.10.1007/s11663-001-0086-7Search in Google Scholar
[3] Hong S, Deng S, Yao X, Wang B, Wang Y, Huang J, et al. Bromate removal from water by polypyrrole tailored activated carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;467:10–6.10.1016/j.jcis.2016.01.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Han P, Xia Y. Thiol-functionalized metal-organic framework for highly efficient removal of bromate from water. J Environ Chem Eng. 2018;6(2):3384–91.10.1016/j.jece.2018.03.045Search in Google Scholar
[5] Chiu YT, Lee PY, Wi-Afedzi T, Lee J, Lin KY. Elimination of bromate from water using aluminum beverage cans via catalytic reduction and adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;532:416–25.10.1016/j.jcis.2018.07.112Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Tao Y, Xiang P, Zhou X. Study on electrochemical behavior of thiourea leaching of gold. Precious Met. 2021;42(1):22–7.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Wang Q, Hu X, Zi F, Qin X, Nie Y, Zhang Y. Extraction of gold from refractory gold ore using bromate and ferric chloride solution. Min Eng. 2019;136:89–98.10.1016/j.mineng.2019.02.037Search in Google Scholar
[8] Jia Y, Wang X, Cheng W, Ma SH. Progress in non-cyanide leaching of refractory gold ores. J Eng Sci. 2019;41(3):307–15.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Ubaldini S, Fornari P, Massidda R, Abbruzzese C. An innovative thiourea gold leaching process. Hydrometallurgy. 1998;48(1):113–24.10.1016/S0304-386X(97)00076-5Search in Google Scholar
[10] Lin Y, Hu X, Zi F. Synergistical thiourea and thiosulfate leaching gold from a gold concentrate calcine with copper-ammonia catalysis. Sep Purif Technol. 2023;327:327–9.10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124928Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sasaki K, Suyama I, Aoki Y, Konadu KT, Chuaicham C, Miki H, et al. Significance of Fe contents on the surface of the gold ores in gold leaching by thiourea and ethylene thiourea. Min Eng. 2023;191:1–10.10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107957Search in Google Scholar
[12] Barani K, Kogani Y, Nazarian F. Leaching of complex gold ore using a cyanide-glycine solution. Min Eng. 2022;180:107475.10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107475Search in Google Scholar
[13] Li Q, Yue H, Zhang Y. Research progress and prospect of non-cyanide gold leaching agent. Chin J Nonferrous Met. 2024;34(7):2356–82.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Wang Q. Non-cyanide extraction of gold from fine-grained carbonaceous gold ore. Doctoral dissertation. Kunming University of Science and Technology; 2020.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Li G, Zhang J. Experimental study on metallurgical separation from a high-grade gold ore. Hydrometallurgy. 2022;41(6):493–7.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Ray DA, Baniasadi M, Graves JE, Greenwood A, Farnaud S. Thiourea leaching: An update on a sustainable approach for gold recovery from E-waste. J Sustain Metall. 2022;8(2):597–612.10.1007/s40831-022-00499-8Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Green polymer electrolyte and activated charcoal-based supercapacitor for energy harvesting application: Electrochemical characteristics
- Research on the adsorption of Co2+ ions using halloysite clay and the ability to recover them by electrodeposition method
- Simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen, caffeine, and paracetamol in commercial products using a green reverse-phase HPTLC method
- Isolation, screening and optimization of alkaliphilic cellulolytic fungi for production of cellulase
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles coated with bacterial alginate and their antibacterial and anticancer activities
- Comparative analysis of bio-based amino acid surfactants obtained via Diels–Alder reaction of cyclic anhydrides
- Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles on yellow phosphorus slag and its application in organic coatings
- Exploring antioxidant potential and phenolic compound extraction from Vitis vinifera L. using ultrasound-assisted extraction
- Manganese and copper-coated nickel oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Carica papaya leaf extract induce antimicrobial activity and breast cancer cell death by triggering mitochondrial caspases and p53
- Insight into heating method and Mozafari method as green processing techniques for the synthesis of micro- and nano-drug carriers
- Silicotungstic acid supported on Bi-based MOF-derived metal oxide for photodegradation of organic dyes
- Synthesis and characterization of capsaicin nanoparticles: An attempt to enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological actions
- Synthesis of Lawsonia inermis-encased silver–copper bimetallic nanoparticles with antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activity
- Facile, polyherbal drug-mediated green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their potent biological applications
- Zinc oxide-manganese oxide/carboxymethyl cellulose-folic acid-sesamol hybrid nanomaterials: A molecularly targeted strategy for advanced triple-negative breast cancer therapy
- Exploring the antimicrobial potential of biogenically synthesized graphene oxide nanoparticles against targeted bacterial and fungal pathogens
- Biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Uncaria tomentosa L.: Insight into characterization, antibacterial activities combined with antibiotics, and effect on Triticum aestivum germination
- Membrane distillation of synthetic urine for use in space structural habitat systems
- Investigation on mechanical properties of the green synthesis bamboo fiber/eggshell/coconut shell powder-based hybrid biocomposites under NaOH conditions
- Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungal strain to improve the growth, metabolic activities, yield traits, and phenolic compounds content of Nigella sativa L.
- Estimation of greenhouse gas emissions from rice and annual upland crops in Red River Delta of Vietnam using the denitrification–decomposition model
- Synthesis of humic acid with the obtaining of potassium humate based on coal waste from the Lenger deposit, Kazakhstan
- Ascorbic acid-mediated selenium nanoparticles as potential antihyperuricemic, antioxidant, anticoagulant, and thrombolytic agents
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Illicium verum extract: Optimization and characterization for biomedical applications
- Antibacterial and dynamical behaviour of silicon nanoparticles influenced sustainable waste flax fibre-reinforced epoxy composite for biomedical application
- Optimising coagulation/flocculation using response surface methodology and application of floc in biofertilisation
- Green synthesis and multifaceted characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles derived from Senna bicapsularis for enhanced in vitro and in vivo biological investigation
- Potent antibacterial nanocomposites from okra mucilage/chitosan/silver nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium eradication
- Trachyspermum copticum aqueous seed extract-derived silver nanoparticles: Exploration of their structural characterization and comparative antibacterial performance against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
- Microwave-assisted ultrafine silver nanoparticle synthesis using Mitragyna speciosa for antimalarial applications
- Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical structure Ag/Fe2O3/TiO2 nanocomposite using acacia in the presence of neem and tulsi oils
- Green quantitative methods for linagliptin and empagliflozin in dosage forms
- Enhancement efficacy of omeprazole by conjugation with silver nanoparticles as a urease inhibitor
- Residual, sequential extraction, and ecological risk assessment of some metals in ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Vietnam
- Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.) leaf extract: Comparative preliminary in vitro antibacterial study
- Simultaneous determination of lesinurad and febuxostat in commercial fixed-dose combinations using a greener normal-phase HPTLC method
- A greener RP-HPLC method for quaternary estimation of caffeine, paracetamol, levocetirizine, and phenylephrine acquiring AQbD with stability studies
- Optimization of biomass durian peel as a heterogeneous catalyst in biodiesel production using microwave irradiation
- Thermal treatment impact on the evolution of active phases in layered double hydroxide-based ZnCr photocatalysts: Photodegradation and antibacterial performance
- Preparation of silymarin-loaded zein polysaccharide core–shell nanostructures and evaluation of their biological potentials
- Preparation and characterization of composite-modified PA6 fiber for spectral heating and heat storage applications
- Preparation and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution of bimetallic phosphates (NiFe)2P/NF
- Rod-shaped Mo(vi) trichalcogenide–Mo(vi) oxide decorated on poly(1-H pyrrole) as a promising nanocomposite photoelectrode for green hydrogen generation from sewage water with high efficiency
- Green synthesis and studies on citrus medica leaf extract-mediated Au–ZnO nanocomposites: A sustainable approach for efficient photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B dye in aqueous media
- Cellulosic materials for the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous environments
- The analytical assessment of metal contamination in industrial soils of Saudi Arabia using the inductively coupled plasma technology
- The effect of modified oily sludge on the slurry ability and combustion performance of coal water slurry
- Eggshell waste transformation to calcium chloride anhydride as food-grade additive and eggshell membranes as enzyme immobilization carrier
- Synthesis of EPAN and applications in the encapsulation of potassium humate
- Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential
- Enhancing mechanical and rheological properties of HDPE films through annealing for eco-friendly agricultural applications
- Immobilisation of catalase purified from mushroom (Hydnum repandum) onto glutaraldehyde-activated chitosan and characterisation: Its application for the removal of hydrogen peroxide from artificial wastewater
- Sodium titanium oxide/zinc oxide (STO/ZnO) photocomposites for efficient dye degradation applications
- Effect of ex situ, eco-friendly ZnONPs incorporating green synthesised Moringa oleifera leaf extract in enhancing biochemical and molecular aspects of Vicia faba L. under salt stress
- Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium and silver nanoparticles using Trichoderma viride filtrate and their impact on Culex pipiens
- Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)
- Assessment of antiproliferative activity of green-synthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles against glioblastoma cells using Terminalia chebula
- Chlorine-free synthesis of phosphinic derivatives by change in the P-function
- Anticancer, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of nanoemulsions based on water-in-olive oil and loaded on biogenic silver nanoparticles
- Study and mechanism of formation of phosphorus production waste in Kazakhstan
- Synthesis and stabilization of anatase form of biomimetic TiO2 nanoparticles for enhancing anti-tumor potential
- Microwave-supported one-pot reaction for the synthesis of 5-alkyl/arylidene-2-(morpholin/thiomorpholin-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4(5H)-one derivatives over MgO solid base
- Screening the phytochemicals in Perilla leaves and phytosynthesis of bioactive silver nanoparticles for potential antioxidant and wound-healing application
- Graphene oxide/chitosan/manganese/folic acid-brucine functionalized nanocomposites show anticancer activity against liver cancer cells
- Nature of serpentinite interactions with low-concentration sulfuric acid solutions
- Multi-objective statistical optimisation utilising response surface methodology to predict engine performance using biofuels from waste plastic oil in CRDi engines
- Microwave-assisted extraction of acetosolv lignin from sugarcane bagasse and electrospinning of lignin/PEO nanofibres for carbon fibre production
- Biosynthesis, characterization, and investigation of cytotoxic activities of selenium nanoparticles utilizing Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- Highly photocatalytic materials based on the decoration of poly(O-chloroaniline) with molybdenum trichalcogenide oxide for green hydrogen generation from Red Sea water
- Highly efficient oil–water separation using superhydrophobic cellulose aerogels derived from corn straw
- Beta-cyclodextrin–Phyllanthus emblica emulsion for zinc oxide nanoparticles: Characteristics and photocatalysis
- Assessment of antimicrobial activity and methyl orange dye removal by Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated silver nanoparticles
- Influential eradication of resistant Salmonella Typhimurium using bioactive nanocomposites from chitosan and radish seed-synthesized nanoselenium
- Antimicrobial activities and neuroprotective potential for Alzheimer’s disease of pure, Mn, Co, and Al-doped ZnO ultra-small nanoparticles
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Bauhinia variegata and their biological applications
- Synthesis and optimization of long-chain fatty acids via the oxidation of long-chain fatty alcohols
- Eminent Red Sea water hydrogen generation via a Pb(ii)-iodide/poly(1H-pyrrole) nanocomposite photocathode
- Green synthesis and effective genistein production by fungal β-glucosidase immobilized on Al2O3 nanocrystals synthesized in Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) leaf extracts
- Green stability-indicating RP-HPTLC technique for determining croconazole hydrochloride
- Green synthesis of La2O3–LaPO4 nanocomposites using Charybdis natator for DNA binding, cytotoxic, catalytic, and luminescence applications
- Eco-friendly drugs induce cellular changes in colistin-resistant bacteria
- Tangerine fruit peel extract mediated biogenic synthesized silver nanoparticles and their potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic assessments
- Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil
- A highly sensitive β-AKBA-Ag-based fluorescent “turn off” chemosensor for rapid detection of abamectin in tomatoes
- Green synthesis and physical characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) derived from the methanol extract of Euphorbia dracunculoides Lam. (Euphorbiaceae) with enhanced biosafe applications
- Detection of morphine and data processing using surface plasmon resonance imaging sensor
- Effects of nanoparticles on the anaerobic digestion properties of sulfamethoxazole-containing chicken manure and analysis of bio-enzymes
- Bromic acid-thiourea synergistic leaching of sulfide gold ore
- Green chemistry approach to synthesize titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Fagonia Cretica extract, novel strategy for developing antimicrobial and antidiabetic therapies
- Green synthesis and effective utilization of biogenic Al2O3-nanocoupled fungal lipase in the resolution of active homochiral 2-octanol and its immobilization via aluminium oxide nanoparticles
- Eco-friendly RP-HPLC approach for simultaneously estimating the promising combination of pentoxifylline and simvastatin in therapeutic potential for breast cancer: Appraisal of greenness, whiteness, and Box–Behnken design
- Use of a humidity adsorbent derived from cockleshell waste in Thai fried fish crackers (Keropok)
- One-pot green synthesis, biological evaluation, and in silico study of pyrazole derivatives obtained from chalcones
- Bio-sorption of methylene blue and production of biofuel by brown alga Cystoseira sp. collected from Neom region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
- Synthesis of motexafin gadolinium: A promising radiosensitizer and imaging agent for cancer therapy
- The impact of varying sizes of silver nanoparticles on the induction of cellular damage in Klebsiella pneumoniae involving diverse mechanisms
- Microwave-assisted green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles obtained from lemon peel extract
- Rhus microphylla-mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy
- Harnessing trichalcogenide–molybdenum(vi) sulfide and molybdenum(vi) oxide within poly(1-amino-2-mercaptobenzene) frameworks as a photocathode for sustainable green hydrogen production from seawater without sacrificial agents
- Magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@SiO2 supported phosphonium ionic liquids for efficient and sustainable transformation of CO2 into oxazolidinones
- A comparative study of Fagonia arabica fabricated silver sulfide nanoparticles (Ag2S) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with distinct antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant properties
- Visible light photocatalytic degradation and biological activities of Aegle marmelos-mediated cerium oxide nanoparticles
- Physical intrinsic characteristics of spheroidal particles in coal gasification fine slag
- Exploring the effect of tea dust magnetic biochar on agricultural crops grown in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil
- Crosslinked chitosan-modified ultrafiltration membranes for efficient surface water treatment and enhanced anti-fouling performances
- Study on adsorption characteristics of biochars and their modified biochars for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution
- Zein polymer nanocarrier for Ocimum basilicum var. purpurascens extract: Potential biomedical use
- Green synthesis, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo biological screening of iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4) generated with hydroalcoholic extract of aerial parts of Euphorbia milii
- Novel microwave-based green approach for the synthesis of dual-loaded cyclodextrin nanosponges: Characterization, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics evaluation
- Bi2O3–BiOCl/poly-m-methyl aniline nanocomposite thin film for broad-spectrum light-sensing
- Green synthesis and characterization of CuO/ZnO nanocomposite using Musa acuminata leaf extract for cytotoxic studies on colorectal cancer cells (HCC2998)
- Review Articles
- Materials-based drug delivery approaches: Recent advances and future perspectives
- A review of thermal treatment for bamboo and its composites
- An overview of the role of nanoherbicides in tackling challenges of weed management in wheat: A novel approach
- An updated review on carbon nanomaterials: Types, synthesis, functionalization and applications, degradation and toxicity
- Special Issue: Emerging green nanomaterials for sustainable waste management and biomedical applications
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mature-pseudostem extracts of Alpinia nigra and their bioactivities
- Special Issue: New insights into nanopythotechnology: current trends and future prospects
- Green synthesis of FeO nanoparticles from coffee and its application for antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-oxidation activity
- Dye degradation activity of biogenically synthesized Cu/Fe/Ag trimetallic nanoparticles
- Special Issue: Composites and green composites
- Recent trends and advancements in the utilization of green composites and polymeric nanocarriers for enhancing food quality and sustainable processing
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Cedrela toona leaf extracts: An exploration into their antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant potential”
- Retraction of “Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and biological potentials of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the polar extract of Cyperus scariosus R.Br. (Cyperaceae)”
- Retraction to “Green synthesis on performance characteristics of a direct injection diesel engine using sandbox seed oil”

