Abstract
During the last two decades, number of peoples suffering from diabetes has increased from 30-230 million globally. Today, seven out of the ten top countries are suffering from diabetes, are emergent countries. Due to alarming situations of diabetes, chemists and pharmacist are continuously searching and synthesizing new potent therapeutics to treat this disease. Now a days, considerable attention is being paid to the chemistry of the metal-drug interactions. Metals and their organic based complexes are being used clinically for various ailments. In this review, a comprehensive discussion about synthesis and diabetic evaluation of zinc and vanadium complex is summarized.
1 Introduction
1.1 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus (DM), complex, multi-valued endocrine ailment in which the body does not deliver (type 1) or notice the insulin (hormone required for theentry of glucose from plasma to cells) in right way (type 2) [1]. Oral therapeutics can often be used to control the insulin for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Now a days sulphonylureas (1), biguanides (2) and thiazolidenemoieties (3) are being used as the hypoglycemic drugs for the cure of diabetes [2]. Due to aftereffects of diabetes mellitus i.e. population aging, lifestyle manner and urbanization, it is becoming the global health problem [3]. In all countries, one of the central public health question is diabetes mellitus as due to increased number of people suffering it [4] and predictable to boost to 439 million in 2030 [5]. Tentative and clinical studies proposed that chronic hyperglycemia which evoked oxidative stress is one of the main cause of growthand evolution of diabetes [6].
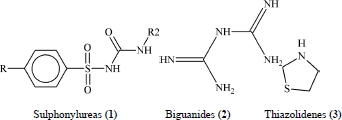
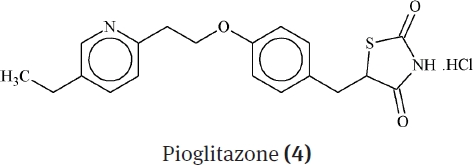
Now a days, a strong antidiabetic drug, Sulphonylurea (1) is going to stop due to its adverse effects on the bone marrow. An oral antidiabetic agent i.e. Pioglitazone hydrochloride (4) is used for curing of type 2 diabetes. It clearances the insulin dependent glucose by lowering insulin resistance in the periphery and liver by reducing the hepatic glucose output [7].
1.2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metal Complexes
Metal ions are necessary for many important operationin humans and some diseases are caused due to deficiency of metal ions [8] iron deficiency mightresult in pernicious anemia. Zinc deficiency causes growth retardation, copper deficiency leads to heart disease in infants. A fundamental aspect of medicinal bioinorganic chemistry is to notice and interpret at the level of molecular of the diseases, initiated by unsatisfactory in function metal-ion [9]. In 1980 Coulson and Dandona primitively examined that similar to the action of insulin, ZnCl2 also activate lipogenesis in rat adipocytes. In last thirty years, large number of scientists reported insulin-mimetic activity along inhibition of sugar related enzymes with metal complexes [10].
Number of selective transition metal ions i.e. V(IV) [11, 12, 13], Zn (II) [14, 15, 16, 17, 18] and Cr (III) [19, 20, 21] are known to reduce the glucose in blood both in-vivocally as well as in-vitrocally. Metal based insulin derivatives have developed the pharmaceutical interest. Anderson summarized different effects of chromium additives on animals and humans, and considered that active form of chromium increases insulin signaling by pushing the activity of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase which direct the glucose uptake [20, 21, 22, 23, 24].
1.2.1 Zinc Complex as Antidiabetic Agents
Peculiarly, Zinc containing compounds have got fewer notice for the advancement of potential antidiabetic molecules. However, advance studies conducted by models (animal) and clinical reports sustain the idea that Zinc additives will regulate the diabetes while its deficiency causes the diabetes [25, 26]. Zinc enhances the insulin activity as well contributes structural roles in case of many proteins and enzymes [27]. Among the Zn compounds which were prepared, mononuclear Zn coordination compounds exhibited remarkable antidiabetic activity [28, 29, 30]. Salil et al. studied and synthesized the complex of zinc containing sulpha drugs [31]. Iqbal and co-workers [32, 33] claimed that the antidiabetic activity of zinc complex is greater than the parent drug [7]. Coulston and Dandona stated that almost the action of insulin was similar to zinc ions which activate in-vitro rat adipocyte lipogenesis [27] and was recognized that in the synthesis, storage and discharge of insulin, Zn imparts a greatrole [34]. Increase loss of Zinc by urinary and reduced level of Zinc in the body is due to chronic hyperglycemia [35, 36]. Vijay and coworker prepared a novel Zn complex of flavanol and checked thier anti-diabetic potential in rats [37]. Zinc mixed ligand (metformin-3-hydroxyflavone) was prepared by Koothappan et al. in their laboratory and their structure were characterized through latest techniques. The synthesized molecules were evaluated against rat for antidiabetic properties [38].
1.2.2 Vanadium Complex as Antidiabetic Agents
Vanadiumis an important trace element found in animals, humans and also in plant cells. Insulin-mimetic and antidiabetic activities were showed by vanadium derivatives in animal as well as in human [39, 40, 41, 42]. Vanadium has vast utility due to its coordination chemistry and used for alteration of medical characteristics [43]. Antidiabetic activities of mostly complexes of vanadium was examined which showed that complexes were weakly effected in in-organic and needed higher quantity which ultimately results in undesirable side effects. Different organo-complex of vanadium have been prepared and checked their antidiabetic activities to avoid the toxicity [44].
2 Literature Review
2.1 Synthesis of Vanadium Complex
A novel vanadium complex of 3-hydroxy flavones was prepared and spectrally characterized by Pillai et al. They also measured its stability constant and antidiabetic activities in streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats and observed that high glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetic rats was remarkably decreased. The lower level of plasma insulin was remarkably increased by treating the diabetic rats with thiscomplex [2].
Vanadate and oxovanadium (IV) complexes are the key genus, survive in physiological situation. The physiological belongings are in a lot of gear a result of the superior performance of the complex of VO2+ ion with ligand, allow to rivet in a complex and after that unconstrained in the bloodstream to be stopped by biological ligands [45] such as transfer in to cells. Vanadium has been concerned in doing numerous working of insulin such as retardation of gluconeogenesis and lipolysis along motivating lipogenesis/cellular glucose uptake. Thus, such agents are subjected to as insulin mimetics [46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51].
Scientists have paid attention to the biological activation of complexes of V(V) and V(IV) with main blood serum proteins (albumin, immunoglobulins, and transferring) [52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61] and the attachment of V complexes with blood [62, 63, 64, 65], or RBC only [66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73]. The potential roles of Vas carriers to peripheral organs have recently noted [74]. Dixithas measured the insulin mimetic activity of vanadium complexes such as bis(α-furancarboxylato) oxovanadium (IV), bis(pyridine-2-carboxylato), oxovanadium (IV) [VO(pic)2], bis(α-furancarboxylato) oxovanadium (IV), vanadyl complexes with maltol(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone) and kojic acid and used for clinical purpose in humans due to less toxicity [75, 76, 77].
Authors worked on the metal complexes of kojato and benzoic acid moieties together by adjusting the lipo/hydrophilicity and finally synthesized BBOV (bis(5-hydroxy-4-oxo-4-hpyran-2-yl) methylbenzoatato). Antidiabetic activity of this compound demonstrated that it reduced hyperglycemia and impaired glucose tolerance activity is improved and giving BBOV and BMOV shifted blood glucose level to near normal level [78].
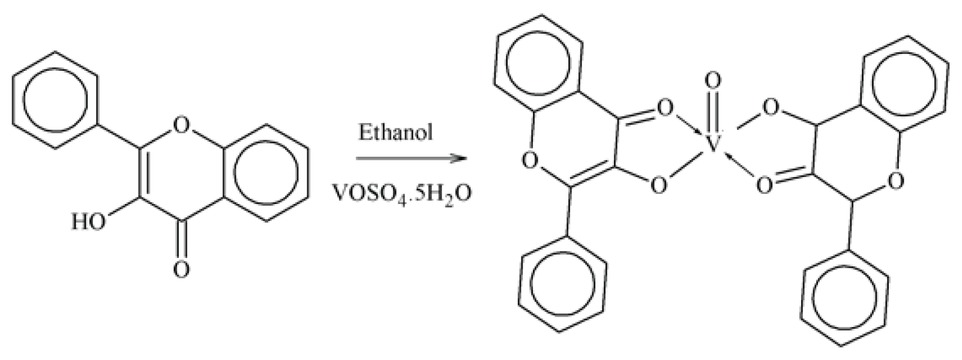
Vanadium-3-hydroxy flavone (V3HF) Complex
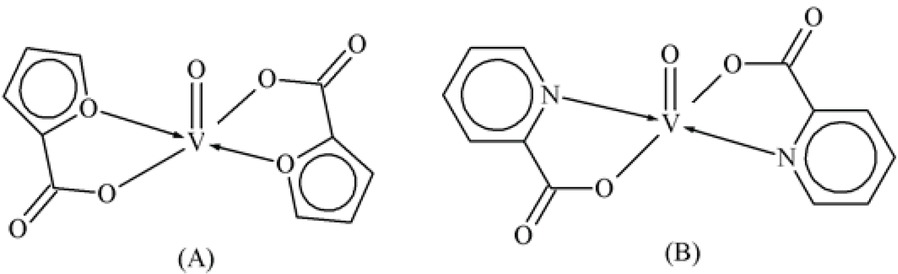
Bis-(α-furancarboxylato)oxovanadium (IV).
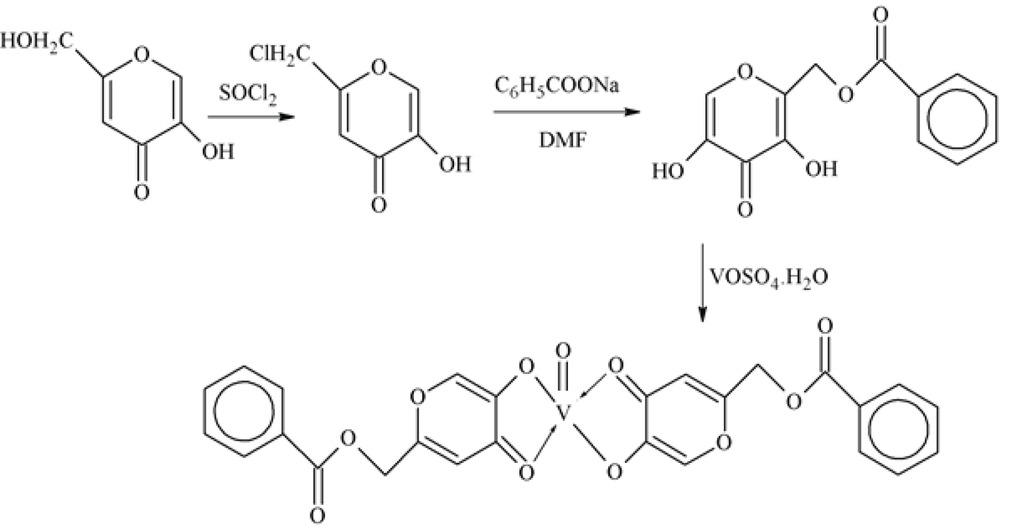
Bis((5-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)methylbenzoatato)oxovanadium(IV)(BBOV).
Pharmacologists and chemists showed interest in the diabetic activity of vanadium (IV) complexes of oxygen, nitrogen and oxygen, oxygen donor ligands and their complexes which was characterized. Among them bis-maltolatooxidovanadium (IV) complex and maltol which is monoprotic bidentate O,O chelating ligand showed best activity. Recent research involves the synthesis of few oxovanadium (IV) complexes of the type [M2(H2O)n] [VO(mal)2(H2O)] with malonic acid and their structural characterization, spectroscopic studiesand antidiabetic activities were also checked. Insulin mimetic activity of the complexes, blood sugar level and lipid profile of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats were checked. Results showed that drug [Na2(H2O)][VO(mal)2(H2O)] protected the damage of liver and other organs by diabetes and contributes highest hypoglycemic effect. It was concluded that the synthesized complexes are best antidiabetic agents [79].
Synthesis of BPOV.
Xie et al. synthesized complex (BPOV) which showed insulin-enhancing and antidiabetic activity. Their structures were confirmed with latest techniques.V(IV) atom has five-coordinated atomsand surrounded by distorted square-pyramidal. In-vivo study, by giving BPOV to STZ-diabetic rats for four weeks andblood glucose levels were decreased [80].
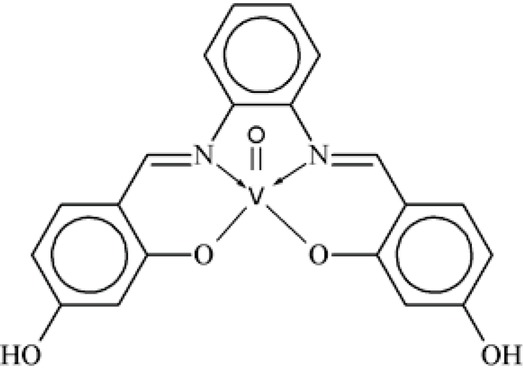
Xie along his team synthesized the two novel vanadium complexes by using Schiff bases of substituted salicylaldehyde and 2-hydroxyethylenediamine. IR were described paramountcally as a dinuclear complexes of six centers coordinated vanadium bridged by O-O atoms of the homocitrate with a V2O2 diamondcore. In-vivo tests showed that complex has no antidiabetic activity, while other complex showed remarkable antidiabetic activity by lowering the glucose level in blood and also improved impaired glucose patience in diabetic rats. This result demonstrated that the ligand with a halogenatom was initiate to boost antidiabetic characteristics of vanadium complexes with Schiff base [81].
Vanadium complexes by usingsalicylaldehyde2-hydroxyethylenediamine.
![Scheme 6 Structure of [VO(Vit-E)2(H2O)2]2H2O complex.](/document/doi/10.1515/chem-2018-0118/asset/graphic/j_chem-2018-0118_fig_006.jpg)
Structure of [VO(Vit-E)2(H2O)2]2H2O complex.
A number of vanadyl complexes with vitamin E were synthesized and characterized. The antimicrobial activity of vanadyl (II) complex was considerable as compared to the ligands. Results showed that the blood glucose level remarkably reduced from 442.87 to 294.87 mg/dl with vanadyl (II) sulfate at a dose100mg. Hence indicated that synthesized vanadyl complex [VO(Vit-E)2(H2O)2]2H2O complex is good enough to treat a type I diabetic experimental animal [82].
Researchers tested hypoglycemic effect of ‘glycosylated flavonoids’ (free) and complex of V (IV) and VO (IV) with flavonoid on rats. Antidiabetic activities of complexes) were checked by different routes on wistar rats. Potentiometric study was used to measure the equilibrium constants and two group of complex were projected at working pH, VOH2L2 (kaempferitrin) and VOHL (kaempferol-3-neohesperidoside). The second one showed diabetic potential throughout starting from 50-100 mg/kg while first one decreased from 0 to 6 hour and serum glucose level is lowered by the administration of the VO (IV) complexes (0.0146 mmol/kg). Results indicated that kaempferol-3-neohesperidoside-VO(IV) (56.0%) was 2.5 times more helpful than VO(IV) (16.8%), double effective as compare to free compound and thrice than kaempferitrin VO (IV) (17.8%) [83].
In 2005, Xie along his co-workers synthesized a potent oral active bis-(α-furancarboxylato)oxovanadium (IV) complex used for treatment of diabetes mellitus in experimental animals. The complex showed antidiabetic activity by normalizing the glucose and lipids values without any effect on insulin level after 4-week treatment. The results indicated that complex has an antidiabetic activity by increasing the sensitivity of insulin-receptor inperiphery and biological efficacy of insulin [84].
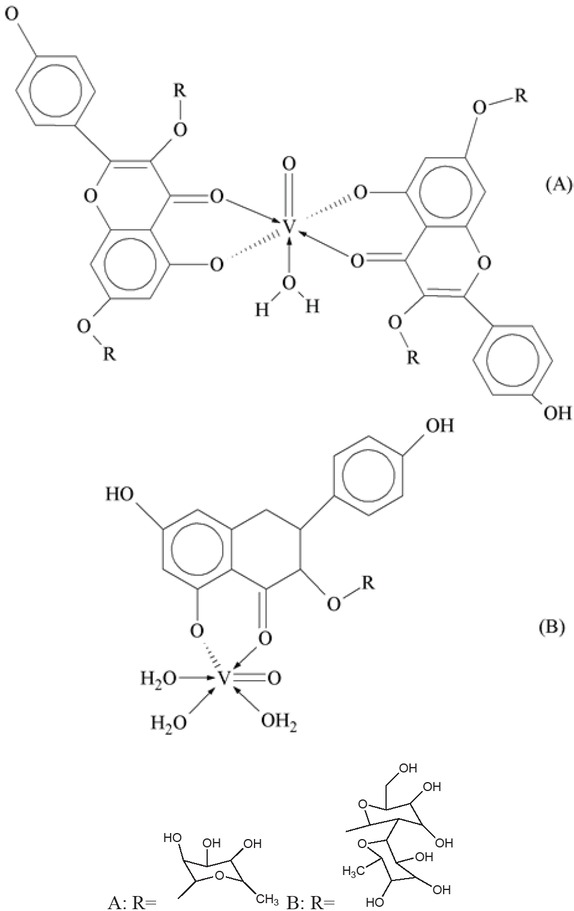
Glycosylated flavonoids complexes (A) = M: L (1:2) & (B) = M: L (1:1).
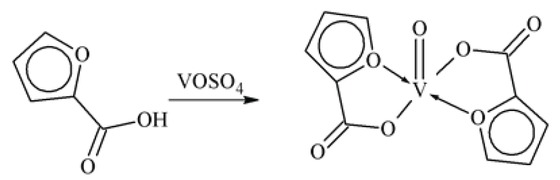
Bis-(α-furancarboxylato)oxovanadium (IV) complex.
2.2 Synthesis of Zinc Complexes
Zinc-diosmin complex were evaluated in rats by inducing experimental type 2 diabetes. Zn- diosmin complex was prepared and characterization was done by various spectral studies. Rats were treated orally with complex at 20 mg/ kg for 30 days. Treatment notably enhanced the glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in diabetic rats. The findings suggested that this compound is nontoxic and has praising prospective to extend as an anti-hyperglycemic molecule for the cure of mellitus [35].
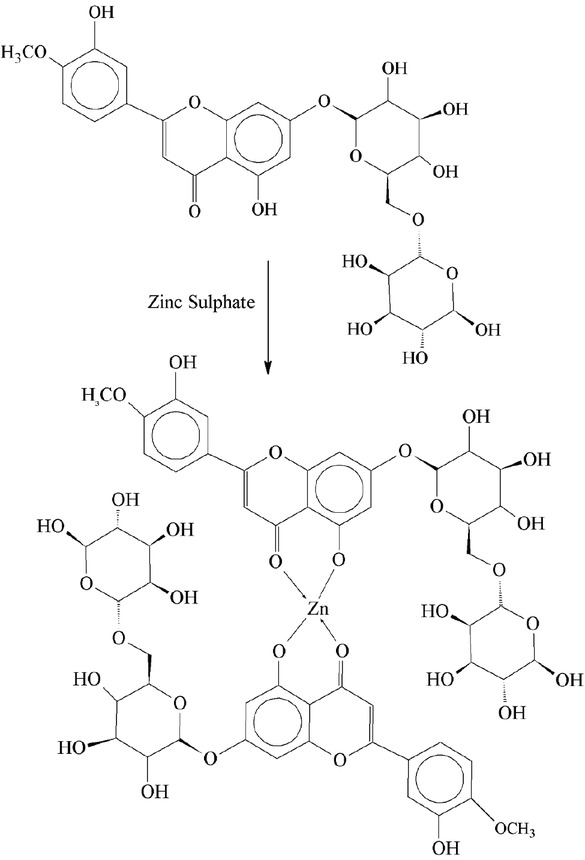
Zinc-diosmin complex.
Solutions of PLZ and metallic salt were stirred, refluxed for 3-4h at 70°C and solid product was yielded on cooling. Fe (II) and Zn (II) complexes were evaluated as hypoglycemic agents. The geometry of the complexes were octahedral and tetrahedral on the basis of elemental and structural data. Hypoglycemic effect of pioglitazone zinc complexes on alloxan induced diabetic rats ranges from 27 to 33% from 0 to 8 hours [7].
Rakesh and Vaidya synthesized metal complex by mixing to butamide equal molar solution of metal chloride and ligand were refluxed for one hour in EtOH which resulted solid product. Zn complex was given to albino rats. It was confirmed that this complex may be used as antidiabetic agent by decreasing blood glucose from 220-82 after 14 hours [85].
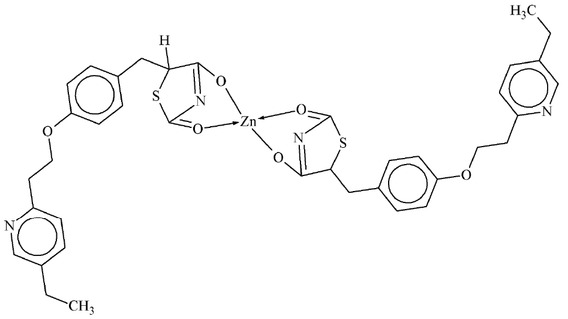
PLZ-Zn Complex.
Glipizide, commonly known sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agent and complexed with the metals. FTIR analysis recommended the coordination of ‘N’ and carbonyl oxygen atom of –SO2NHCONH- moiety of glipizide with the under investigated metals. Complexes have been characterized using AAS and this technique was also useful for the indirect grit of glipizide in the form of dosage for first time [86].
2.3 Mechanism of Action of Zn and Its Complexes Against Diabetes Mellitus
Various animal models were used to check the activity of zinc for the treatment of diabetes.
Zinc is a known antioxidant in the immune system [87]. Different tests were performed to prevent the type 1 DM by enhancing the zinc level in diet, which is due to blockage of NF-κB activity in pancreas [88]. The experiments performed on alloxan and STZ induces diabetic animal models revealed that risk factors of type 1 diabetes is significantly minimized by increasing the zinc intake. In genetic type 2 diabetes of mouse model insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity was regulated by zinc in skeletal muscle. The β-subunit of the insulin receptor produces less tyrosine phosphorylation as compared to insulin in the presence of zinc as well as insulin receptor substrate (IRS) does not increase the glucose uptake on stimulation of zinc [89]. This model presented the activation of P13K without the participation of IRS; in epididymal cells the production of H2O2 may stimulated by zinc, which than stimulates focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and at the end FAK, triggers the P13K-Akt pathway. Furthermore, zinc activates Akt in preadipocytes and enhance the phosphorylation of serine residues which leads the stimulation of Akt in preadipocytes and adipocytes, thereby increasing GLUT translocation [89]. Ezaki also revealed glucose uptake is increased by tissue cells by stimulation of zinc which transfer GLUT to the plasma membrane [90].
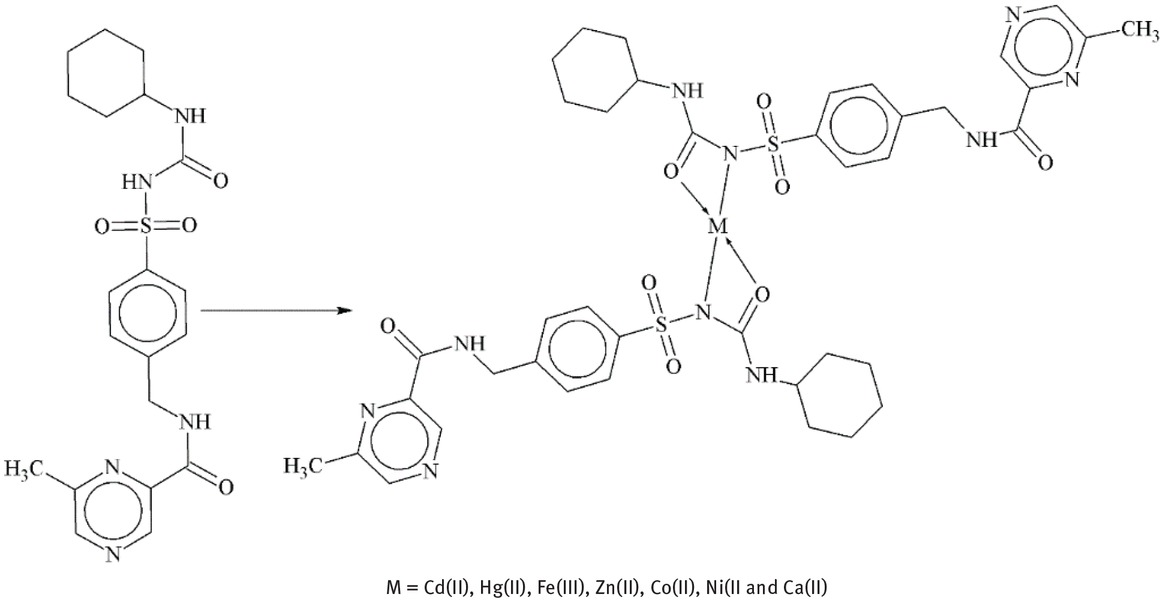
Glipizidemetal complexes.
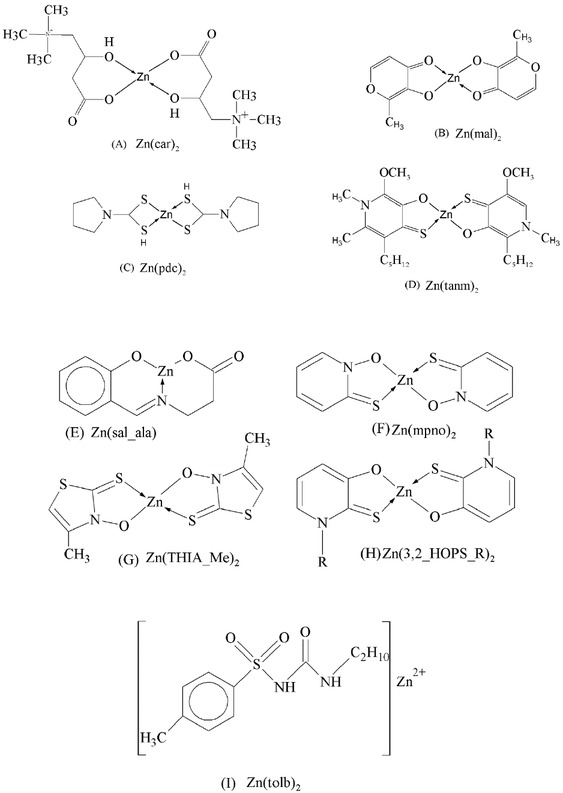
Anti-diabetic active zinc complexes.
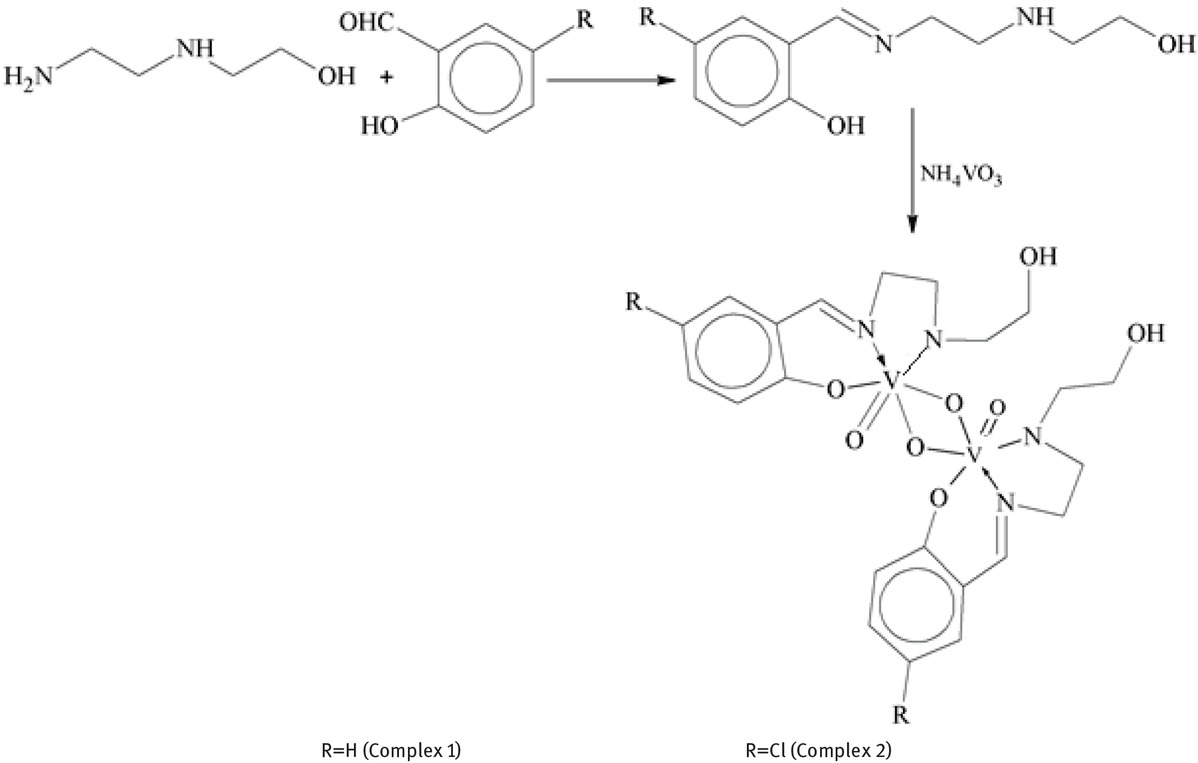
Since 2001, orally active anti-diabetic zinc complexes have been produced and evaluated. Various zinc complexes of different coordination compounds have recently been exposed which have impressive anti-diabetic activity. Zinc is considered as biologically active and react with several objective proteins connected to diabetes mellitus [90]. For the clinically useful metallopharmaceutics, zinc complexes are being evaluated for long-term toxicity (side effects) and clear-cut proof of marked agent for the in-vivo pharmacological application. The superior pharmacokinetic assets are important in the this as well as for past [91]. Kalavakunda synthesized Zn complex by reacting equal molar zinc aceteate and flavanol in ethanol at 80°C with stirring for 4 hours.
The synthesized zinc-3-hydroxy flavone and characterized with spectral techniques. It was concluded that toxicity and dosage fixation were depicted that it was non-toxic and by orally giving complex (5 mg/ kg b.w. (body weight)/rat/day) for 30 days to induced diabetic rats, blood glucose level and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), uric acid, urea, and creatinine were lowered indicating the non-toxic nature of the zinc-flavonol complex while the plasma insulin and C-peptide levels were improved. Further the Zn-flavonol complex depicted noteworthy anti-hyperglycemic potential in induced diabetic rats. The antidiabetic activity (142.83mg/dl) of the complex was comparable with gliclazide, a standard antidiabetic drug (127.66mg/dl) [36]. Glimepiride zinc complex was synthesized by mixing the metal salt solution with that of ligand in 1:2 molar ratios at pH 6.5–8 for 3 hours at 80°C [92].
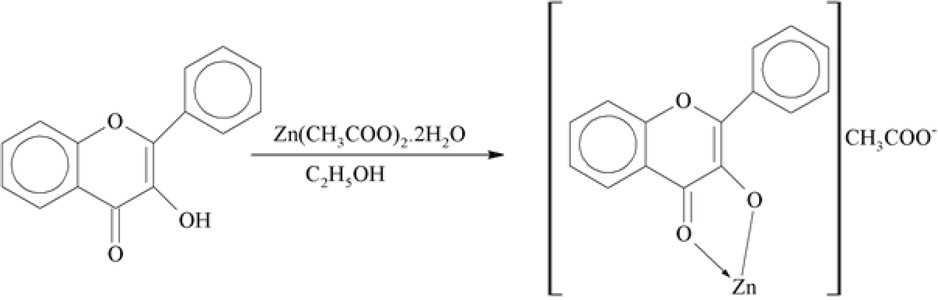
Synthesis of zinc-flavonol complex.
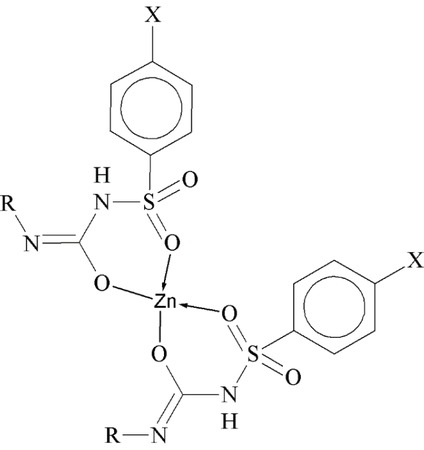
Structure of glimepiride zinc complex.
Tetrahedral structure was given to complex with spectral and X-ray studies that indicating the co-ordination of sulphonyl oxygen on one face and enolic oxygen fond of from other pose with the metal ion [91]. Solutions of Zn (II) chloride and 3-carboxy-pyrazole in water (30 mL) were stirred at normal condition and white crystals obtained. Lopez and coworker synthesized new Zinc complex (mononuclear) with 3-carboxy-pyrazole (ligand) showed a probable anti-diabetic activity can be regarded insignificant. Vijayaraghavan et al. [36] following cure with Zn-3HF (5–50 mg/kg) for 30 days failed glycemic glucose less than 150 mg/dl. Moniz et al. explained different Zn complexes specially with Zn (dmpp)2 at doses of 10 mg/kg intraperitoneally administered daily. They find good results of blood glucose which were comparable to standard administered orally. However, Zn (dmpp)2 produces a significant hyperglycemic effect. Zn sulfate tested by Moniz et al. is less active as hypoglycemic agent. The results showed that it has similar pharmacological characteristics to Zn (dmpp)2 [29].
Bytzek and coworker synthesized Zn (II) complexes in situ by reacting ZnCl2 solution and ligand in buffer (pH 7.4) at various ratios. When anti-diabetic Zn (II)-complexes are administered in animal DM type 2 models, the Zn (II) level was increased significantly to 100-200 mM. Zn (II) complex which are applied as insulin increasing agents in the cure of diabetes are under development. CZE-ICP-MS analysis on the interaction of Zn (II) maltolato [Zn(mal)2(H2O)2], 2-picolinato and [Zn(pic)2(H2O)2] and 2,6-dipicolinato complexes [Zn(dipic)2]2 with serum (human) proteins were studied [93].
Zn complexes were synthesized by added excess amounts of ZnSO4 (1 M) and 10 mL of ᵧ-pgaD, L-poly(ᵧ-glutamic acid) (1% w/v) solutions and stirred over night at room temperature.
The synthesized Zinc (II) complexes were characterized and checked in-vitro insulin-mimetic activity which was considerable better than that of ZnSO4 as well as in vivo antidiabetic activity in type-2 diabetic in KKAy mice. The Zn(ᵧ-pga) complex were given orally (0.15–0.31 mmol) for 30 days and the hyperglycemia in mice was normalized within 21 days. The impaired glucose tolerance and prominent HbA1c levels along metabolic syndromes were appreciably enhanced in Zn(ᵧ-pga)-treated mice as compared to those with saline and ZnSO4 [94].
2.4 Mechanisms of Action of Vanadyl and Zinc Complexes
Recently, action mechanisms for some oxovanadium (IV) and zinc (II) complexes were purposed in isolated rat adipocytes [95, 96, 97, 98, 99]. Both these complexes raised glucose uptake into the adipocytes without the addition of any hormones [99, 100] and inhibited epinephrine-induced free fatty acid (FFA) release [97, 98]. The results showed that the complexes have common insulin-mimetic activities. The inhibition of FFA release by vanadyl and zinc complexes was reversed by selective insulin receptor β-subunit (IRβ) inhibitor [HNMPA-(AM)3] [101].
![Scheme 20 [Zn(pic)2(H2O)2] and 2,6-dipicolinato complexes [Zn(dipic)2]2.](/document/doi/10.1515/chem-2018-0118/asset/graphic/j_chem-2018-0118_fig_015.jpg)
[Zn(pic)2(H2O)2] and 2,6-dipicolinato complexes [Zn(dipic)2]2.
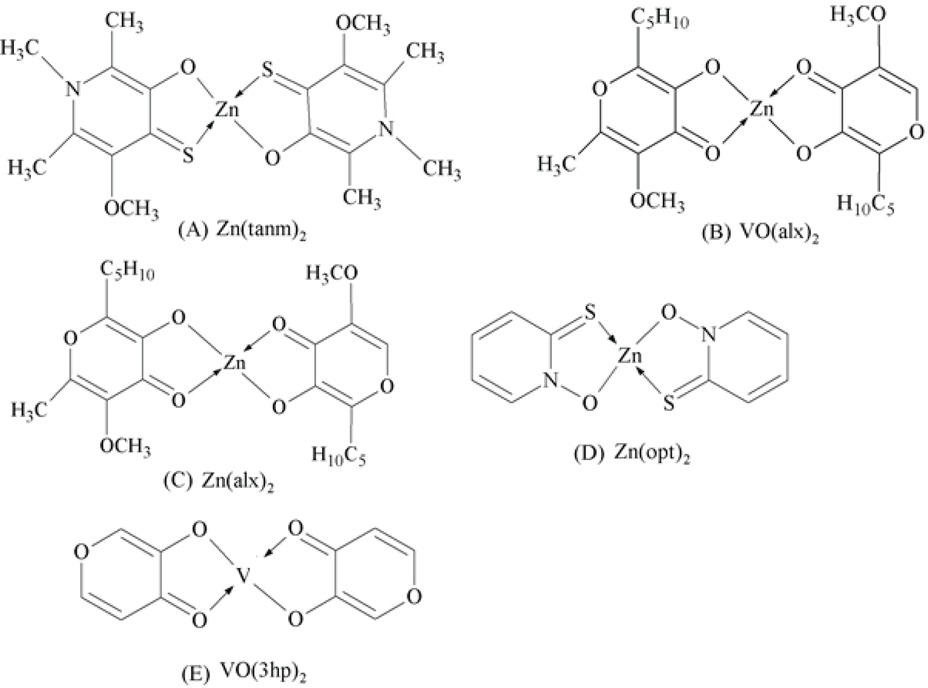
Oxovanadium (IV) and zinc (II) complexes.
To measure the insulin mimetic ability 10 vanadium and zinc ion containing organic complexes were synthesized by Cheol-Min Lee and Cheong-Soo Hwang to compare their PTP-1B inhibition activities. Complexes of Zn were depicted to reduce FFA (free fatty acid) release from adipocytes of rats, and to display in vivo lowering of blood glucose [101].
3 Conclusion
Metal complexes as therapeutic agents playing vital role inthe field of medicinal chemistry. A large numberof metal complexes are formed by the use of different metal ions and organic ligand ofinterest. Metal complexes like cis-platin have confirmed to be extremely efficient chemotherapeutic agents for cure of different disorder. The inhibition of PTP1B (protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B is a latent objective for healing of type 2 diabetes. The complexes of Vanadium and zinc metal have insulin increasing potencies, while vanadium complexes slow down the PTP1B, slight is recognized on the method of zinc compounds. Researchers designed a robotic PTP1B inhibition method for a rapid assessment of the PTP1B inhibition. It is the need of this era to synthesize new metal complexes with lease side effect to treat diabetes.
Conflict of interest: Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Reference
[1] Abegunde D.O., Mathers C.D., Adam T., Ortegon M., Strong K., The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low-income and middle-income countries, Lancet., 2007, 370, 1929-1938.10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61696-1Search in Google Scholar
[2] Pillai S.I., Subramanian S.P., Kandaswamy M.A, novel insulin mimetic vanadium-flavonol complex: synthesis, characterization and in vivo evaluation in STZ-induced rats, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2013, 63, 109-117.10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.02.002Search in Google Scholar
[3] Zimmet P., Alberti K.G., Shaw J., Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic, Nature., 2001, 414, 782-787.10.1038/414782aSearch in Google Scholar
[4] Danaei G., Finucane M.M., Lu Y., Singh G.M., Cowan M.J., Paciorek C.J., et al., National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants, Lancet., 2011, 378, 31-40.10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-XSearch in Google Scholar
[5] Shaw J.E., Sicree R.A., Zimmet P.Z., Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030, Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract., 2010, 87, 4–14.10.1016/j.diabres.2009.10.007Search in Google Scholar
[6] Folli F., Corradi D., Fanti P., Davalli A., Paez A., Giaccari A., et al., The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Micro- and Macrovascular Complications: Avenues for a Mechanistic-Based Therapeutic Approach, Curr Diabetes Rev., 2011, 7, 313-324.10.2174/157339911797415585Search in Google Scholar
[7] Prakash O., Iqbal S.A., Hypoglycemic Study of Fe(II) and Zn(II) Complexesof Pioglitazone Hydrochloride on Wistar Albino Rats using Alloxan Induced Method, Biomed. & Pharmacol. J., 2014, 7, 75-80.10.13005/bpj/454Search in Google Scholar
[8] Underwood E.J., Trace element in human and animal nutrition 3rd ed, Academic press, New York N.Y., 1971.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sharma B.K., Iqbal S.A., Prakash O., X-Ray Diffraction and structural studies of Cu(II) complex with Gliclazide(N-(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1H)-ylcarbamoyl)4-methylbenzenesulfonamide),and its hypoglycemic activity, Chem Mater Res., 2013, 9, 2224-3224.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Tripathi I.P., Kumar M.M., Arti K., Chinmayi M., Ruchita T., Kant S.L., et al., Synthesis, Characterization of some Antidiabetic Copper Complexes with Ethylenediamine, Res. J. Chem. Sci., 2013, 12, 54-59.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sakurai H., Kojima Y., Yoshikawa Y., Kawabe K., Yasui H., Antidiabetic vanadium(IV) and zinc(II) complexes, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2002, 226, 187-198.10.1016/S0010-8545(01)00447-7Search in Google Scholar
[12] Watanabe H., Nakai M., Komazawa K., Sakurai H., A new orally active insulin-mimetic vanadyl complex: bis(pyrrolidine-N-carbodithioato)oxovanadium(IV), J. Med. Chem., 1994, 37, 876-877.10.1021/jm00033a002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Sakurai H.A., New Concept: The Use of VanadiumComplexes in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus, Chem. Rec., 2002, 2, 237-248.10.1002/tcr.10029Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Sakurai H., Adachi Y., The pharmacology of the insulinomimetic effect of zinc complexes, Biometals., 2005, 18, 319-323.10.1007/s10534-005-3688-8Search in Google Scholar
[15] Adachi Y., Yoshida J., Kodera Y., Kato A., Yoshikawa Y., Kojima Y., et al., A new insulin-mimetic bis(allixinato)zinc(II) complex: structure–activity relationship of zinc(II) complexes, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2004, 9, 885-893.10.1007/s00775-004-0590-8Search in Google Scholar
[16] Yamaguchi M., Wakasugi K., Saito R., Adachi Y., Yoshikawa Y., Sakurai H., Syntheses of vanadyl and zinc(II) complexes of 1-hydroxy-4,5,6-substituted 2(1H)-pyrimidinones and their insulin-mimetic activities, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2006, 100, 260-269.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.11.010Search in Google Scholar
[17] Yoshikawa Y., Ueda E., Miyake H., Sakurai H., Kojima Y., Metallomics: Recent Analytical Techniques and Applications, Biochem. Biophys. Res.Commun., 2001, 281, 1190-1193.10.1006/bbrc.2001.4456Search in Google Scholar
[18] Yoshikawa Y., Ueda E., Kawabe K., Miyake H., Takino T., Sakurai H., et al., Development of new insulinomimetic zinc(II) picolinate complexes with a Zn(N2O2) coordination mode: structure characterization, in vitro, and in vivo studies, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2002, 7, 68-73.10.1007/s007750100266Search in Google Scholar
[19] Vincent J.B., Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II: From Biology to Nanotechnology, Polyhedron., 2001, 20, 1-26.10.1016/S0277-5387(00)00624-0Search in Google Scholar
[20] Anderson R.A., Chromium, glucose intolerance and diabetes, J. Am. Coll. Nutr., 1998, 17, 548-555.10.1080/07315724.1998.10718802Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Anderson R.A., Chromium in the prevention and control of diabetes, Diabetes Metab., 2000, 26, 22-27.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Davis C.M., Vincent J.B., Chromium oligopeptide activates insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity, Biochem., 1997, 36, 4382-4385.10.1021/bi963154tSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Wang H., Kruszewski A., Brautigan D.L., Cellular Chromium Enhances Activation of Insulin Receptor Kinase, Biochem., 2005, 44, 8167-8175.10.1021/bi0473152Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Yasarawan N., Thipyapong K., Sirichai S., Ruangpornvisuti V., Synthesis of chromium(III) complex with 1-hydroxy-2-pyridinone-6-carboxylic acid as insulin mimetic agent and its spectroscopic and computational studies, J. Mol. Struct., 2013, 1031, 144-151.10.1016/j.molstruc.2012.07.041Search in Google Scholar
[25] Jansen J., Karges W., Rink L., Zinc and diabetes--clinical links and molecular mechanisms, J. Nutr. Biochem., 2009, 20, 399-417.10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.01.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Song Y., Wang J., Li X.K., Cai L., Metallothioneins in Biochemistry and Pathology, Biometals., 2005, 18, 325-332.10.1007/s10534-005-3689-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Coulston L., Dandona P., Insulin-like effect of zinc on adipocytes, Diabetes., 1980, 29, 665-667.10.2337/diab.29.8.665Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Seale A.P., de Jesus L.A., Kim S.Y., Choi Y.H., Lim H.B., Hwang C.S., et al., Development of an automated protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibition assay and the screening of putative insulin-enhancing vanadium(IV) and zinc(II) complexes, Biotechnol. Lett., 2005, 221-225.10.1007/s10529-004-7855-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] López Fernández B., Hilfiker S., González C.S., González J.L., Calahorro A.J., Colacio E., et al., A. In vivo potential antidiabetic activity of a novel zinc coordination compound based on 3-carboxy-pyrazole, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2014, 131, 64-67.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2013.10.019Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Philip J.E., Shahid M., Kurup M.R.P., Velayudhan M.P., Metal based biologically active compounds: Design, synthesis, DNA binding and antidiabetic activity of 6-methyl-3-formyl chromone derived hydrazones and their metal (II) complexes, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biology., 2017, 175, 178-191.10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.09.003Search in Google Scholar
[31] Salil A.A., Hamdani A., Shaker S.A., Synthesis, Characterization, Structural Studies and Biological Activity of a New Schiff Base- Azo Ligand and its Complexation with Selected Metal Ions, Orient. J. Chem., 2011, 27, 835-845.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Iqbal S.A., Jose S., Jacob G., Synthesis, Characterisation and Spectral Studies of Metal Complexes of Glimepiride, An Oral Antidiabetic Drug, Orient. J. Chem., 2011, 27, 731-735.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Iqbal S.A., Zaafarny I., Synthesis, Physico-chemical and Spectral Studies of Mercury Complex of Glibenclamide, An Oral Antidiabetic Drug, Orient. J. Chem., 2012, 28, 613-618.10.13005/ojc/280183Search in Google Scholar
[34] Emdin S.O., Dodson G.G., Cutfield J.M., Cutfield S.M., Oncogenes and Human Cancer Blood Groups in Cancer Copper and Inflammation Human Insulin. Diabetologia., 1980, 19, 174-182.10.1007/BF00275265Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Ozcelik D., Nazıroglu M., Tunc M., Elik O.C., Ozturk, M., Arce M.F., Zinc Supplementation Attenuates Metallothionein and Oxidative Stress Changes in Kidney of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 2012, 150, 342-349.10.1007/s12011-012-9508-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[36] Gopalakrishnan V., Pillai S.I., Subramanian S.P., Synthesis, Spectral Characterization, and Biochemical Evaluation of Antidiabetic Properties of a New Zinc-Diosmin Complex Studied in High Fat Diet Fed-Low Dose Streptozotocin Induced Experimental Type 2 Diabetes in Rats, Biochem Res Int., 2015, 1–11.10.1155/2015/350829Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Vijayaraghavan, K., Pillai, S. I., Subramanian, S. P., Design, Synthesis and characterization of zinc-3 hydroxy flavone, a novel zinc metallo complex for the treatment of experimental diabetes in rats. Eur. J. Pharm. 2012, 680, 129.10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.01.022Search in Google Scholar
[38] Ramachandran B., Sekar D.S., Kandaswamy M., Narayanan V., Subramanian S., Hypoglycemic Effect of Macrocyclic Binuclear Oxovanadium (IV) Complex on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats, Exp. Diabesity Res., 2004, 5, 137-142.10.1080/15438600490277842Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Koothappan M., Vellai R.D., Subramanian P.L., Pillai I., Pillai S.S., Synthesis and evaluation of antidiabetic properties of a zinc mixed ligand complex in high-fat diet - low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Asian J. Pharma. Clin. Res., 2018, 11, 429-438.10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i5.24870Search in Google Scholar
[40] Ramachandran B., Kandaswamy M., Narayanan V., Subramanian S., Insulin mimetic effects of macrocyclic binuclear oxovanadium complexes on streptozotocin induced experimental diabetes in rats, Diabetes Obes. Metab., 2003, 5, 455-461.10.1046/j.1463-1326.2003.00302.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Ramachandran B., Ravi K., Narayanan V., Kandaswamy M., Subramanian S.,10.1016/j.cbi.2004.06.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Effect of macrocyclic binuclear oxovanadium complex on tissue defense system in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Clin. Chim. Acta., 2004, 345, 141-150.10.1016/j.cccn.2004.03.014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Ramachandran B., Ravi K., Narayanan V., Kandaswamy M., Subramanian S., Protective effect of macrocyclic binuclear oxovanadium complex on oxidative stress in pancreas of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats, Chem. Biol. Interact., 2004, 149, 9-21.10.1016/j.cbi.2004.06.007Search in Google Scholar
[44] Thompson H.K., Orvig C., Design of vanadium compounds as insulin enhancing agents, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans., 2000, 2881-2892.10.1039/b002753gSearch in Google Scholar
[45] Sakurai H., Sano H., Takino T., Yasui H., An orally active antidiabetic vanadyl complex, bis(1-oxy-2-pyridinethiolato) oxovanadium(IV), with VO(S2O2) coordination mode; in vitro and in vivo evaluations in rats, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2000, 80, 99-105.10.1016/S0162-0134(00)00045-3Search in Google Scholar
[46] Thompson K.H., McNeill J.H., Orvig C., Vanadium Compounds as Insulin Mimics, Chem. Rev., 1999, 99, 2561-2572.10.1021/cr980427cSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Sanna D., Micera G., Garribba E., New Developments in the Comprehension of the Biotransformation and Transport of Insulin-Enhancing Vanadium Compounds in the Blood Serum, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 174-187.10.1021/ic9017213Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Rehder D., Pessoa J., Geraldes C.F., Castro M.C., Kabanos T., Kiss T., et al., In vitro study of the insulin-mimetic behaviour of vanadium(IV, V) coordination compounds. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2002, 7, 384-396.10.1007/s00775-001-0311-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Passadouro M., Metelo A.M., Melão A.S., Pedro J.R., Faneca H., Carvalho E., et al., A.Study of the antidiabetic capacity of the VO(dmpp)2 complex, J. Inorg. Biochem. Chem., 2010, 104, 987-992.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2010.05.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Shukla R., Blonde R.R., Adipogenic action of vanadium: a new dimension in treating diabetes, Biometals., 2008, 21, 205-210.10.1007/s10534-007-9109-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Hiromura M., Adachi Y., Machida M., Hattori M., Sakurai H., Glucose lowering activity by oral administration of bis(allixinato)oxidovanadium(IV) complex in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and gene expression profiling in their skeletal muscles, Metallomics., 2009, 1, 92-100.10.1039/B815384CSearch in Google Scholar
[52] Gundhla I.Z., Walmsley R.S., Ugirinema V., Mnonopi N.O., Hosten E., Betz R., et al., effects of bis[(imidazolyl)carboxylato] oxidovanadium(IV) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem., 2014, 145, 11-18.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.12.019Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Jakusch T., Dean A., Oncsik T., Benyei A.C., Di Marco V., Kiss T., Binding, Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells, Dalton Trans., 2010, 39, 212-220.10.1039/B914849CSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[54] Costa Pessoa J., Tomaz I., Transport of therapeutic vanadium and ruthenium complexes by blood plasma components, Curr. Med. Chem., 2010, 17, 3701-3738.10.2174/092986710793213742Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Mehtab S., Gonçalves G., Roy S., Tomaz A., I.;Santos-Silva T., Santos M.F.A., et al., Interaction of vanadium(IV) with human serum apo-transferrin, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2013, 121, 187-195.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.12.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Costa Pessoa J., Gonçalves G., Roy S., Correia I., Mehtab S., Santos M.F.A., et al., New insights on vanadium binding to human serum transferrin, Inorg. Chim. Acta., 2014, 420, 60-68.10.1016/j.ica.2013.11.025Search in Google Scholar
[57] Sanna D., Micera G., Garribba E., New Developments in the Comprehension of the Biotransformation and Transport of Insulin-Enhancing Vanadium Compounds in the Blood Serum, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 174-187.10.1021/ic9017213Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Sanna D., Micera G., Garribba E., Interaction of VO2+ Ion and Some Insulin-Enhancing Compounds with Immunoglobulin G, Inorg. Chem., 2011, 50, 3717-3728.10.1021/ic200087pSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[59] Sanna D., Biro L., Buglyo P., Micera G., Garribba E., Transport of the anti-diabetic VO2+ complexes formed by pyrone derivatives in the blood serum, .J. Inorg. Biochem., 2012, 115, 87-99.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.04.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Sanna D., Micera G., Garribba E., Interaction of Insulin-Enhancing Vanadium Compounds with Human Serum holo-Transferrin, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 11975-11985.10.1021/ic401716xSearch in Google Scholar
[61] Makinen M.W., Salehitazangi M., The structural basis of action of vanadyl (VO2+ chelates in cells, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2014, 279, 1-22.10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.003Search in Google Scholar
[62] Crans D.C., Antidiabetic, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Organic Vanadates as Presumed Transition-State Inhibitors for Phosphatases, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 11899-11915.10.1021/acs.joc.5b02229Search in Google Scholar
[63] Harris W.R., Friedman S.B., Silberman D., Behavior of vanadate and vanadyl ion in canine blood, J. Inorg. Biochem., 1984, 20, 157-169.10.1016/0162-0134(84)80015-XSearch in Google Scholar
[64] Yasui H., Takechi K., Sakurai H., Metallokinetic analysis of disposition of vanadyl complexes as insulin-mimetics in rats using BCM-ESR method, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2000, 78, 185-196.10.1016/S0162-0134(00)00002-7Search in Google Scholar
[65] Yasui H., Tamura A., Takino T., Sakurai H., Structure-dependent metallokinetics of antidiabetic vanadyl-picolinate complexes in rats: studies on solution structure, insulinomimetic activity, and metallokinetics, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2002, 91, 327-338.10.1016/S0162-0134(02)00443-9Search in Google Scholar
[66] Yasui H., Adachi Y., Katoh A., Sakurai H., Metallokinetic characteristics of antidiabetic bis(allixinato) oxovanadium(IV)-related complexes in the blood of rat, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2007, 12, 843-853.10.1007/s00775-007-0239-5Search in Google Scholar
[67] Cantley L.C., Resh M.D., Guidotti G., Vanadate inhibits the red cell (Na+, K+) ATPase from the cytoplasmic side, Nature., 1978, 272, 552-554.10.1038/272552a0Search in Google Scholar
[68] Cantley L.C., Aisen P., The fate of cytoplasmic vanadium. Implications on (NA,K)-ATPase inhibition, J. Biol. Chem., 1979, 254, 1781-1784.10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37721-9Search in Google Scholar
[69] Heinz A., Rubinson K.A., Grantham J.J., The transport and accumulation of oxyvanadium compounds in human erythrocytes in vitro, J. Lab. Clin. Med., 1982, 100, 593-612.Search in Google Scholar
[70] Garner M., Reglinski J., Smith W.E., McMurray J., Abdullah I., Wilson R.A.,1H spin echo and51V NMR study of the interaction of vanadate with intact erythrocytes, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 1997, 2, 235-241.10.1007/s007750050129Search in Google Scholar
[71] Yang X., Wang K., Lu J., Crans D.C., Membrane transport of vanadium compounds and the interaction with the erythrocyte membrane, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2003, 237, 103-111.10.1016/S0010-8545(02)00247-3Search in Google Scholar
[72] Delgado T.C., Tomaz A.I., Correia I., Costa Pessoa J., Jones J.G., Geraldes C.F.G.C., et al., Uptake and metabolic effects of insulin mimetic oxovanadium compounds in human erythrocytes, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2005, 99, 2328-2339.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.08.014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[73] Sanna D., Serra M., Micera G., Garribba E., Interaction of Antidiabetic Vanadium Compounds with Hemoglobin and Red Blood Cells and Their Distribution between Plasma and Erythrocytes, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 1449-1464.10.1021/ic402366xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[74] Sanna D., Serra M., Micera G., Garribba E., Uptake of potential anti-diabetic VIVO compounds of picolinate ligands by red blood cells, Inorg. Chim. Act.,. 2014, 420, 75-84.10.1016/j.ica.2013.12.038Search in Google Scholar
[75] Levina A., McLeod A.I., Gasparini S.J., Nguyen A., Manori W.G., Aitken J.B., Reactivity and Speciation of Anti-Diabetic Vanadium Complexes in Whole Blood and Its Components: The Important Role of Red Blood Cells, Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54, 6707-6718.10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b00665Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] Bharti S.K., Singh S.K., Metal Based Drugs: Current Use and Future Potential, Pharm. Lett., 2009, 1, 39-51.Search in Google Scholar
[77] Xie M., Gao L., Li L., Liu W., Yan S., A new orally active antidiabetic vanadyl complex-bis(alpha-furancarboxylato) oxovanadium(IV), J. Inorg. Biochem., 2005, 99, 546-551.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.10.033Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[78] Dikanov S.A., Liboiron B.D., Orvig C., Two-Dimensional (2D) Pulsed Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Study of VO2+−Triphosphate Interactions: Evidence for Tridentate Triphosphate Coordination, and Relevance To Bone Uptake and Insulin Enhancement by Vanadium Pharmaceuticals, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 2969-2978.10.1021/ja011104sSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[79] Dixit R., Current Status on Metal Based Drugs, Quest, 2015, 3, 14-18.Search in Google Scholar
[80] Xie M., Li L., Yang X., Liu W., Yan S., Niu Y., et al., A new insulin-enhancing agent: [N,N′-bis(4-hydroxysalicylidene)-o-phenylene-diamine]oxovanadium(IV) and its permeability and cytotoxicity, Eur J Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 2327-2335.10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.02.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[81] Xie M., Niu Y., Yang X., Liu W., Li L., Gao L., et al., Effect of the chloro-substitution on lowering diabetic hyperglycemia of vanadium complexes with their permeability and cytotoxicity, Eur J Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 6077-6084.10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.10.013Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[82] Refat M., El-Shazly S., Identification of a new anti-diabetic agent by combining VOSO4 and vitamin E in a single molecule: Studies on its spectral, thermal and pharmacological properties, Eur J Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 3070-3079.10.1016/j.ejmech.2010.03.040Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[83] Cazarolli L.H., Zanatta L., Jorge A.P., Sousa E., Horst H., Woehl V.M., et al., Follow-up studies on glycosylated flavonoids and their complexes with vanadium: Their anti-hyperglycemic potential role in diabetes, Chem. Biol. Interact., 2006, 163, 177-191.10.1016/j.cbi.2006.07.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[84] Xie M., Gao L., Li L., Liu W., Yan S., A new orally active antidiabetic vanadyl complex--bis(alpha-furancarboxylato) oxovanadium(IV), J. Inorg. Biochem., 2005, 99, 546-551.10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.10.033Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[85] Choure R., Vaidya N., Polarograpy of Zn (II)-Tolbutamide complex and its Pharmacological Study, Elixir Appl. Chem., 2013, 57, 14467-14469.Search in Google Scholar
[86] Ali H.R.H., Saleh G.A., Hussein S.A., Hassan A.I., Preparation, characterization and atomic absorption spectroscopic determination of some metal complexes of glipizide, Der pharma Chem.., 2013, 5, 156-163.Search in Google Scholar
[87] Baum M.K., Shor-Posner G., Campa A., Zinc Status in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection, J. Nutr., 2000, 130, 1421-1423.10.1093/jn/130.5.1421SSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[88] Ho E., Quan H., Tsai Y.H., Lai W., Bray T.M., Dietary zinc supplementation inhibits NFκB activation and protects against chemically induced diabetes in CD1 mice, Exp. Biol. Med., 2001, 226, 103-111.10.1177/153537020122600207Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[89] Tang X.H., Shay N.F., Zinc Has an Insulin-Like Effect on Glucose Transport Mediated by Phosphoinositol-3-Kinase and Akt in 3T3-L1 Fibroblasts and Adipocytes, J. Nut., 2001, 131, 1414-1420.10.1093/jn/131.5.1414Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[90] Yoshikawa Y., Yasui H., Zinc Complexes Developed as Metallopharmaceutics for Treating Diabetes Mellitus based on the Bio-Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry, Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2012, 12, 210-218.10.2174/156802612799078874Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[91] Jacob G., Synthesis, Physico-chemical and Antidiabetic Studies of Zinc Complex of Glimepiride, An Oral Hypoglycemic Agent, Orient. J. Chem., 2013, 29, 1351-1358.10.13005/ojc/290410Search in Google Scholar
[92] Ohly P., Dohle C., Abel J., Seissler J., Gleichmann H., Zinc sulphate induces metallothionein in pancreatic islets of mice and protects against diabetes induced by multiple low doses of streptozotocin, Diabetologia., 2000, 43, 1020-1030.10.1007/s001250050009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[93] Bytzek A.K., Enyedy E.K., Kiss T., Keppler B.K., Hartinger C.G., Biodistribution of anti-diabetic Zn(II) complexes in human serum and in vitro protein-binding studies by means of CZE–ICP-MS, Electrophoresis., 2009, 30, 4075-4082.10.1002/elps.200900212Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[94] Karmaker S., Saha T.K., Yoshikawa Y., Sakurai H., A Zinc(II)/Poly(γ-glutamic acid) Complex as an Oral Therapeutic for the Treatment of Type2 Diabetic KKAyMice, Macromol. Biosci., 2009, 9, 279-286.10.1002/mabi.200800190Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[95] Sakurai H., Katoh A., Yoshikawa. Y., Chemistry and Biochemistry of Insulin-Mimetic Vanadium and Zinc Complexes. Trial for Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2006, 79, 1645-1664.10.1246/bcsj.79.1645Search in Google Scholar
[96] Sakurai H., Kojima Y., Yoshikawa Y., Kawabe K., Yashu H., Antidiabetic vanadium(IV) and zinc(II) complexes, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2002, 226, 187-198.10.1016/S0010-8545(01)00447-7Search in Google Scholar
[97] Kawabe K., Yoshikawa Y., Adachi Y., Sakurai H., Possible mode of action for insulinomimetic activity of vanadyl(IV) compounds in adipocytes, Life Sci., 2006, 78, 2860-2866.10.1016/j.lfs.2005.11.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[98] Yoshikawa Y., Ueda E., Kojima Y., Sakurai H., The action mechanism of zinc(II) complexes with insulinomimetic activity in rat adipocytes, Life Sci., 2004, 75, 741-751.10.1016/j.lfs.2004.02.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[99] Adachi Y., Sakurai H., Insulin-Mimetic Vanadyl(IV) Complexes as Evaluated by Both Glucose-Uptake and Inhibition of Free Fatty Acids (FFA)-Release in Isolated Rat Adipocytes, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 2004, 52, 428-433.10.1248/cpb.52.428Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[100] Yoshikawa Y., Adachi Y., Sakurai H., A new type of orally active anti-diabetic Zn(II)-dithiocarbamate complex, Life Sci., 2007, 80, 759-766.10.1016/j.lfs.2006.11.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[101] Hiromura M., Sakurai H., Action mechanism of metallo-allixin complexes as antidiabetic agents, Pure Appl. Chem., 2008, 80, 2727-2733.10.1351/pac200880122727Search in Google Scholar
[102] Lee C., Hwang C., Synthesis and characterization of insulin enhancing vanadium and zinc metal coordinated complexes, JNBT., 2005, 2, 80-84.Search in Google Scholar
© 2018 Aisha Azam et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution

