Abstract
The development of safe desalination plants with low environmental impact is as important an issue as the supply of drinking water. The desalination plant in Jeddah (Saudi Arabia, Red Sea coast) produces freshwater from seawater by multi-stage flash distillation (MSFD) and reverse osmosis (RO). The process produces brine as by-product, which is dumped into the sea. The aim of this study was to assess the impact of Jeddah desalination plant on the coastal water in the nearby of the plant. Total concentrations of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients in several locations around the plant were analyzed by cathodic stripping voltammetry. The average levels of dissolved Cu, Ni, and Zn on surface in the sampling locations were 15.02, 11.02, and 68.03 nM respectively, whereas the levels at the seafloor near the discharging point were much higher. Distribution of temperature, salinity, nutrients and dissolved oxygen were quite normal both on surface and in depth.
1 Introduction
Water is a vital and irreplaceable resource for drinking, farming and other human activities. The total water reserve on earth amounts to ~1.4 billion km3. The scarcity of fresh water resource is a major threat to many arid regions of the world and will be increasingly important in the future. According to the survey of the United Nations (UN), Environment program lighted up that one-third of the world’s population lives in countries with inadequate freshwater to uphold the population [1]. Out of the ~1.4 billion km3 of the total global water reserves, approximately 97.5% is present in the Ocean [2] and most interestingly, of this around 0.014% is the available quantity of human beings and other organisms [3]. The range of salinity in sea water is 35000-45000 ppm [4, 5, 6, 7], however, the permissible level of salinity in the drinking water is 500 ppm and for special case up to 1000 ppm [8]. This makes the importance of desalination plant in the present era. Drinking water can be produced from seawater by desalination, i.e., by removing salts and minerals. By desalination, the seawater salinity level (35000–45000 ppm) is lowered to a level acceptable for drinking water (500–1000 ppm) [5].
Due to the improvements in membrane technology [9, 10, 11, 12], the production cost of desalination water has been considerably decreased and is expected to decrease even further [13, 14]. The methods used in many arid countries are desalination from sea water. In the case of the Kingdome of Saudi Arabia, it is a relevant matter. It has scarcely of sufficient portable water resources. Therefore, Saudi Arabia depends entirely on desalination of sea water to supply potable water. In fact, more than 20 years’ desalination technology has assisted freshwater scarcity in the Middle East [15, 16]. Moreover, it appears to be saviors for lack of rainfall in such countries as Australia [17]. The countries in the Middle East, Central Asia, and North Africa primarily depend on desalination for their drinking water needs [18, 19]. Desalination could be superior options to cope with water scarcities for the countries close to coastal lands which represent 97% of the global water [20].
In fact, the desalination has become a globally useful method for delivering potable water [21]. The United States, Europe, China and Australia have a larger number of expanding desalination capacities [22], while Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Kuwait have almost half of the world’s desalination water produced [21]. It is important to point out that urgent need for potable water has meant that historically environmental issues with desalination plants have been considered secondary importance [23].
However, a vital concern of desalination plants is the effects of the high saline water, which may contain residual chemicals and heavy metals. Hence, it is widely recommended that desalination plants have clear evidence of harmfull effect on physical, chemical and biological attributes of receiving marine environment [24, 25, 26]. Hence the environmental concerns are important to investigate before desalination option is undertaken [27]. In order to develop a safe and clean marine environment, desalination activities should be controlled by proper management, that need to be estimate the adverse effect of desalination process and to reduce those contrary impacts as much as possible[22]. In fact, desalination of seawater has a range of advantages including, human’s daily needs, socio-economic and providing of good quality drinking water, maintain agricultural productions and helping restrict saline intrusion into coastal zone aquifers [22, 28]. Even though, many negative effects have been recorded [28]. The provision of potable water for Jeddah city was the most pressing issue for both its rulers and residents throughout its long history. Located on the shore of the Red Sea, the city of Jeddah grew and developed on a barren stretch of land which is not just devoid of rivers and springs, but also lack any forms of drinkable water, not to mention it’s salty soil, high temperature and scarcity and even lack of rain. So the development of desalination plant without much alteration in the environment and ecosystem is much important.
The technology which is used in desalination is a highly-advanced system, but it may have severe impacts on the marine environment should be managed and investigated [22]. Two common desalination methods are multi-stage flash distillation (MSFD) and reverse osmosis (RO) [2, 3, 4, 9, 13, 14, 15, 18]. MSFD is a series of flash evaporations in which each flash process uses the energy released from the condensation of the water vapor in the previous step. RO uses pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane against salt concentration gradient.
Jeddah is a city on the eastern coast of the Red Sea, in the Central-West part of Saudi Arabia. With a population of about 4 million people [29], Jeddah is the second largest city in Saudi Arabia after the capital Riyadh; it is also the largest sea port on the Red Sea and Saudi Arabia’s commercial capital. The provision of potable water is the most pressing issue for the city, which has no rivers, springs, and hardly any rain (average rainfall = 53.5 mm/ year). Therefore, an assessment of the environmental impact of Jeddah desalination plant would be important to a large number of people.
In this research, we investigated the distribution pattern of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and some nutrients in the coastal waters along Jeddah desalination plant. We also studied the distribution of four physico-chemical parameters: salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen and pH.
2 Materials and methods
The study area is shown in Figure 1. Samples were collected in a ‘net format’ from stations approximately 250 meters away from each other. The discharge point is located 33 meters below sea level. Vertical profiling was only done along the coast near to the dumping point (Figure 1, stations 1-4). Surface monitoring was performed for all the sampling locations (stations 1-14). Samples were collected using a Niskin sampler previously washed with nitric acid. Hydrographic parameters were measured using a YSI multi-parameter Sonde device (USA). The concentration of dissolved metals was measured by cathodic stripping voltammetry using a Metrohm 797 VA Computrace system. The level of nutrients was determined by UV-vis spectrophotometry using a Shimadzu UV-2450 spectrophotometer. Salinity samples were standardized by an MS-310 micro-salinometer, whereas pH samples were standardized using a pH meter. Dissolved oxygen (DO) samples were collected and analyzed on the same day using Winkler’s method.
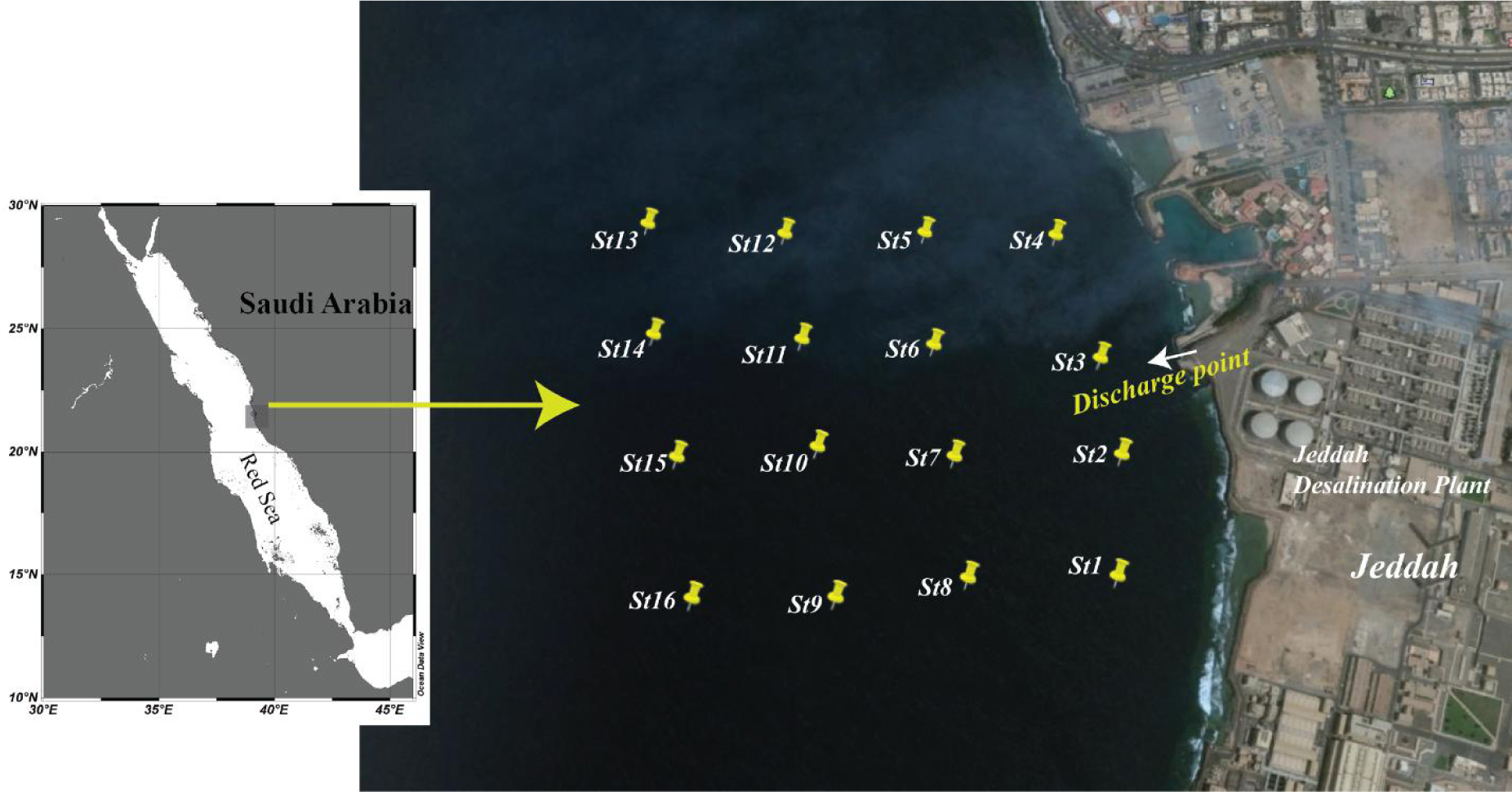
Sampling location in the coastal waters near Jeddah desalination plant.
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animals use.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Salinity and temperature
The salinity pattern in cross-section and in surface is shown in Figures 2b and 2d, respectively. Salinity was higher near the bottom of the effluent plumes than on surface. This result can be easily explained considering that waste brine from desalination plants is almost twice as dense as intake seawater [17, 30, 31, 32]; consequently, brine tends to stratify along the sea floor rather than on surface [33, 34, 35, 36, 38]. The highest values of salinity (38.90 psu) were found not in front of the plant (stations 2 and 3) but further north (station 4), probably due to the effect of deep sea currents.
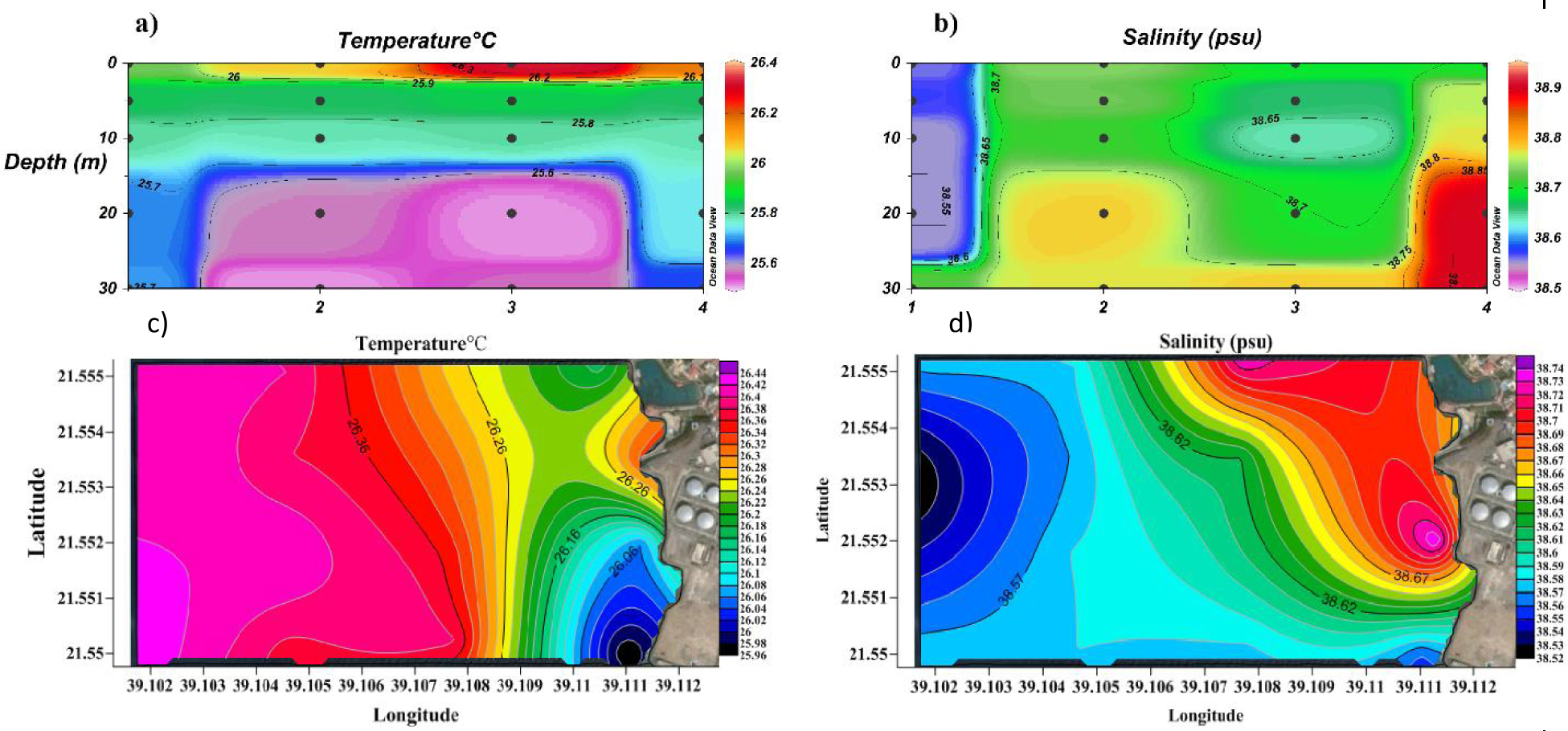
Cross-section profile of a) temperature and b) salinity; surface distribution pattern of c) temperature and d) salinity.
On surface (Figure 2d), salinity remains 0.1 ppt higher than background value (38.62 psu) over an area of about 350 m alongshore × 100–400 m offshore (depending on latitude). Specifically, high salinity extends offshore more on the north side than on the south side of the plant, probably due to the effect of sea currents and tidal cycles [37, 39]. Therefore, the coastal fringe is likely the most vulnerable to the harmful effects of desalination brine. Overall, the alteration in salinity observed in proximity of this desalination plant is lower than that measured for other plants (0.5–2.6 ppt, Table 1) [21].
Extent and intensity of brine plumes in receiving waters surrounding desalination plant Discharge outlets.
| Reference | Capacity (ML/d) | Discharge(ML/d) | Brine salinity (ppt) | Location | Habitat | Plume extension and intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdul-wahab, 2007 [49] | 92.4 | NR | 37.3 | Muscat, Oman | Soft sediments | Returned to background levels within approximately 100 m of outlet. |
| Abdul-Wahab, 2007 [49] | 191 | NR | 40.11 | Muscat, Oman | Soft sediments | Return to background levels within 980 m from outlet. |
| Altayaran and Madany, 1992 [50] | 106 | 288 | 51 | Sitra Island, Bahrain | Soft sediments | Salinity of receiving water was 51 ppt relative to reference area (45 ppt); plume extended at least 160 m from discharge. Temperature also affected: discharged water at 10–15 °C above ambient, receiving water up to 7 °C above ambient. |
| Chesher, 1971 [33] | 9.1 | 22 | 40-55 | Florida, USA Artificial | hard and soft sediments | 0.5 ppt above background levels within 10-20 m of outlet. Slight elevation maintained for 600 m within the harbour basin. |
| Talavera and Ruiz, 2001 [51] | 25 | 17 | 75.2 | Canary Islands, Spain | Sub-tidal rocky reef | 2 ppt above background on the seabed and 1 ppt above background on the surface within the 20 m of the outlet; background levels measured at 100 m. |
| Einav et al., 2003 [52] | NR | NR | NR | Dhkelia, Cyprus | Not reported | Above background 100e200 m from outlet, occasionally as high as 60 ppt. |
| Fernandez Torquemada et al., 2005 [53] | 50 | 75 | 68 | Alicante, Spain | Seagrass and soft sediments | 0.5 ppt above ambient for up to 4 km from outlet along the seafloor. |
| Malfeito et al., 2005 [54] | 28 | NR | 44 | Javea, Spain | Seagrass and | Slightly above background up to 300 m from the outlet. |
| Raventos et al., 2006 [44] | 60 | 33 | 60* | Blanes, Spain | Seagrass and soft sediments | Background levels reached within 10 m of outlet. No measurement or analysis of salinity. |
| Ruso et al., 2007 [55] | 50 | 65 | 68 | Alicante, Spain | Soft sediments | 2.6 ppt above ambient within 300 m of outlet; 1 ppt within 600 m; similar to background at 1300 m. |
| Safrai and Zask, 2008 [23] | 274 | 600 | 42 | Ashkelon, Israel | Not reported | Approximately 2 ppt above ambient within 400 m of outlet |
Desalination processes can increase the temperature of waste brine 10–15°C above seawater ambient temperature [22, 40, 42]. This happens because distillation plants heat the feedwater and this heat is largely retained in the waste brine. Such a temperature increase can play a significant effect on the marine ecosystem equilibrium [25, 41]. Therefore, we analyzed the temperature distribution around the desalination plant. In cross-section, temperature raised quickly to background levels within 20 meters of outfall (Figure 2a). In the entire surface sampling area, temperature ranged between 25.5 and 26.4°C, very close to the Red Sea average temperature in that area (Figure 2c). Overall, the thermal effects associated to the desalination plant dissipate quickly to background levels [24].
3.2 Dissolved oxygen, pH and nutrients
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important indicator of water quality, because a reduction in DO may have a negative impact on marine life [17, 22]. DO levels in proximity of dumping site, 30 m below sea level, are very low (<6.9 mg·L−1 at stations 2, 3 and 4; Figure 3b). Low DO levels are likely due to a combined effect of high temperature, which reduces the gas solubility in waste water, and the addition of oxygen-consuming chemicals (mostly sodium bisulfite) during the desalination process [22]. Most desalination plants that work by distillation actually produce brine with reduced DO levels [38, 43]. DO concentration in surface water is sensibly higher (7.0–7.3 mg·L–1) and close to background values, indicating that the effluent plume gets diluted with natural water on moving away from the dumping site (Figure 3d).
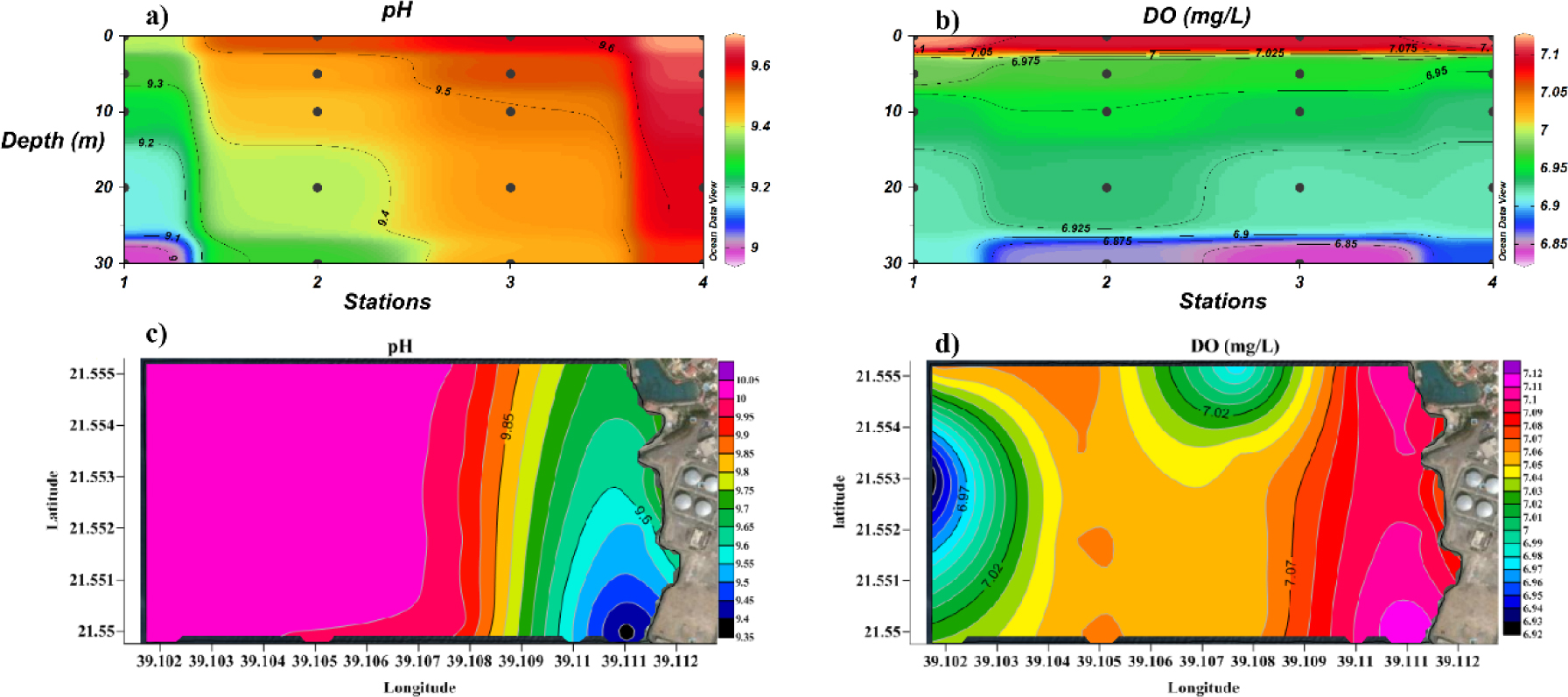
Surface distribution pattern of a) DO and b) pH; cross-section profile of c) pH and d) DO.
pH of deep and surface water along the sampling locations varies over a range of 9–10 (Figures 3a and 3c, respectively). These values are higher than the normal oceanic range (8.1–8.3), probably due to basic hydrolysis of bisulfite ions. The lowest pH values (9.0–9.3), both in deep and surface water, were measured at 21.55 N and 39.111 E, near station 1. This point is located far from the discharge point of the desalination plant, with pH gradually increasing to background levels on moving towards the discharge point. Therefore, the observed pH alterations do not seem caused by the desalination plant. The point at 21.55 N and 39.111 E shows pH (9.35) and temperature (25.96°C) values much lower than background values, as well as DO levels (7.11 mg·L–1) higher than background values. This observation suggests the presence of a dumping site of different nature (possibly of oxygen-rich chemicals) on the coast near that point.
Nitrogen and phosphorus also can negatively impact drinking water quality. The concentration of four nutrient ions (nitrite [NO2–], nitrate [NO3–], ammonium [NH4+], and phosphate [PO43–]) was measured along the sampling locations in both the cross-section and surface. Crosssection concentration of nitrite (0.1–0.4 μM) fell within background levels except at station 4, where a concentration of 0.8 μM, four times higher than background level, was measured 20 m below sea level (Figure 4a). Similarly, cross-section concentration of phosphate was normal [45] except at station 2, where a concentration of 0.6 μM, six times higher than background values, was measured 10 m below sea level (Figure 4c). Nitrate and ammonia seemed to follow an irregular vertical distribution pattern (Figures 4b and 4d, respectively). The surface concentrations of nitrite (0.02–0.42 μM), nitrate (0.1–0.3 μM), ammonium (0.9–1.2 μM) and phosphate (0.1–0.8 μM) were all in the safe range. Particularly, the concentration of ammonium (0.9–1.2 μM) was much lower than that reported for Al–Arbaeen lagoon in central Jeddah city (30–50 μM) [46]. Along seashore (stations 1–4), nitrate and phosphate showed background levels on surface, whereas ammonia and nitrite exceeded background levels, especially at stations 1 and 2 (Figures 5a and 5c, respectively).
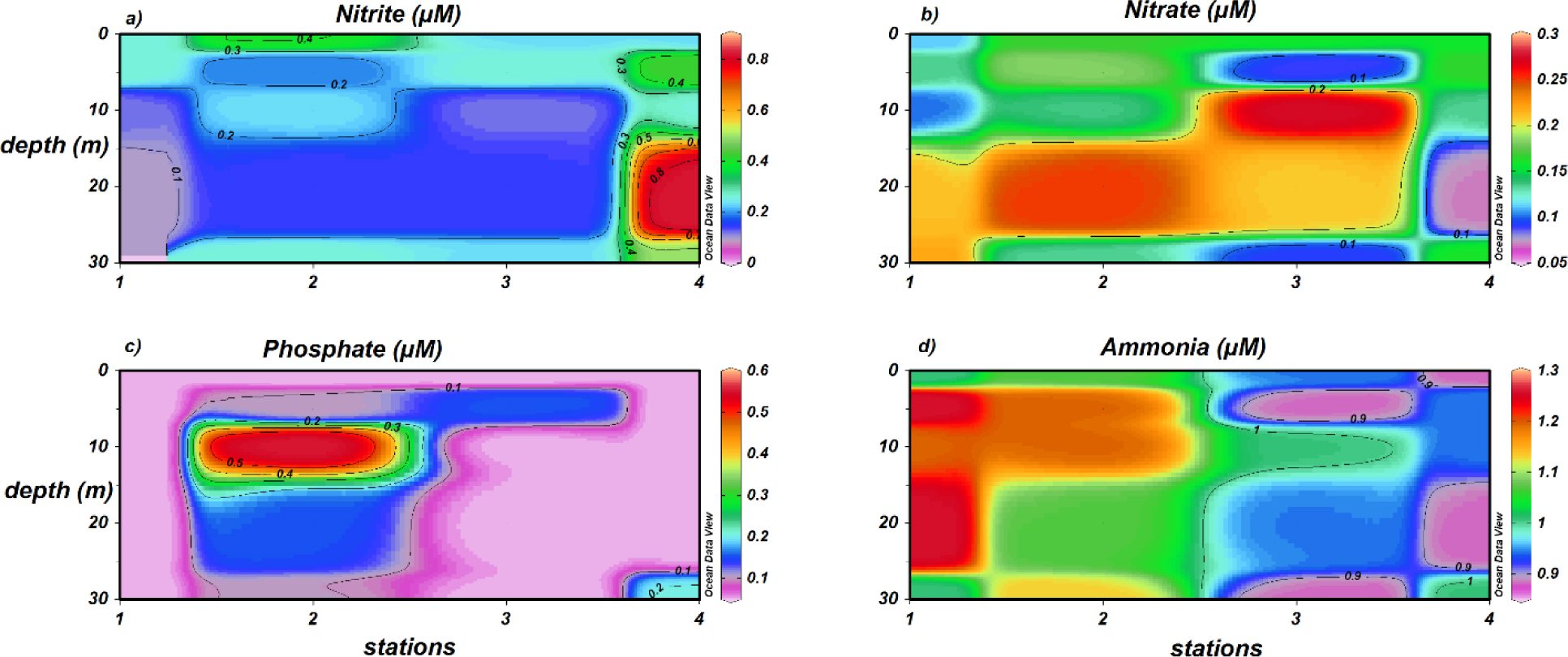
Cross-section profile of a) nitrite, b) nitrate, c) phosphate, and d) ammonia.
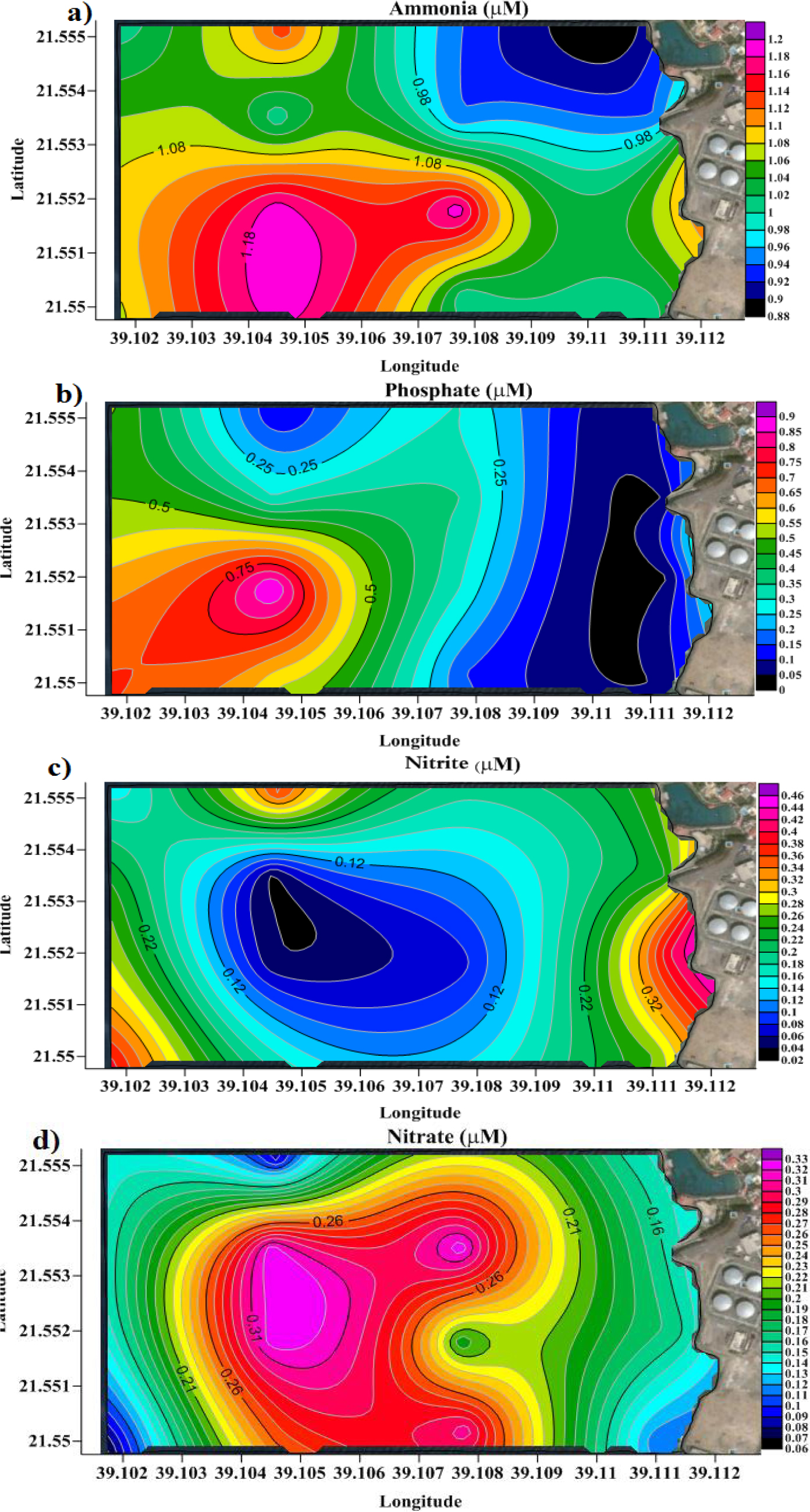
Surface distribution pattern of a) ammonia, b) phosphate, c) nitrite, and d) nitrate.
3.3 Distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni and Zn
The presence of heavy metals in discharge water of desalination plants is mainly due to the high temperature of distillation technique which enhances corrosion of metal alloys containing Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo, Fe and Zn [17, 22]. Desalination plants operating by reverse osmosis are less likely to release heavy metals as a result of corrosion because they do not use heating; the only heavy metals released by RO plants are those already present in seawater and concentrated during the osmosis process [38].
The distribution of Cu levels near the desalination plant is shown in Figures 6a (cross-section) and 6b (surface distribution). The United States Environmental Protecting Agency (US EPA) recommends a maximum Cu concentration in seawater of 75.94 nM for long-term exposure and 49.05 nM for short-term exposure. This value is exceeded not only close to the discharge location (station 3, 30 m below sea level, 800 nM), but also on surface at all stations (55-155 nM). The average surface value (15.02 nM) of dissolved Cu along the study area falls within safety limits but is sensibly higher than that reported for coastal Red Sea water (2.96±1.03 nM) [47].
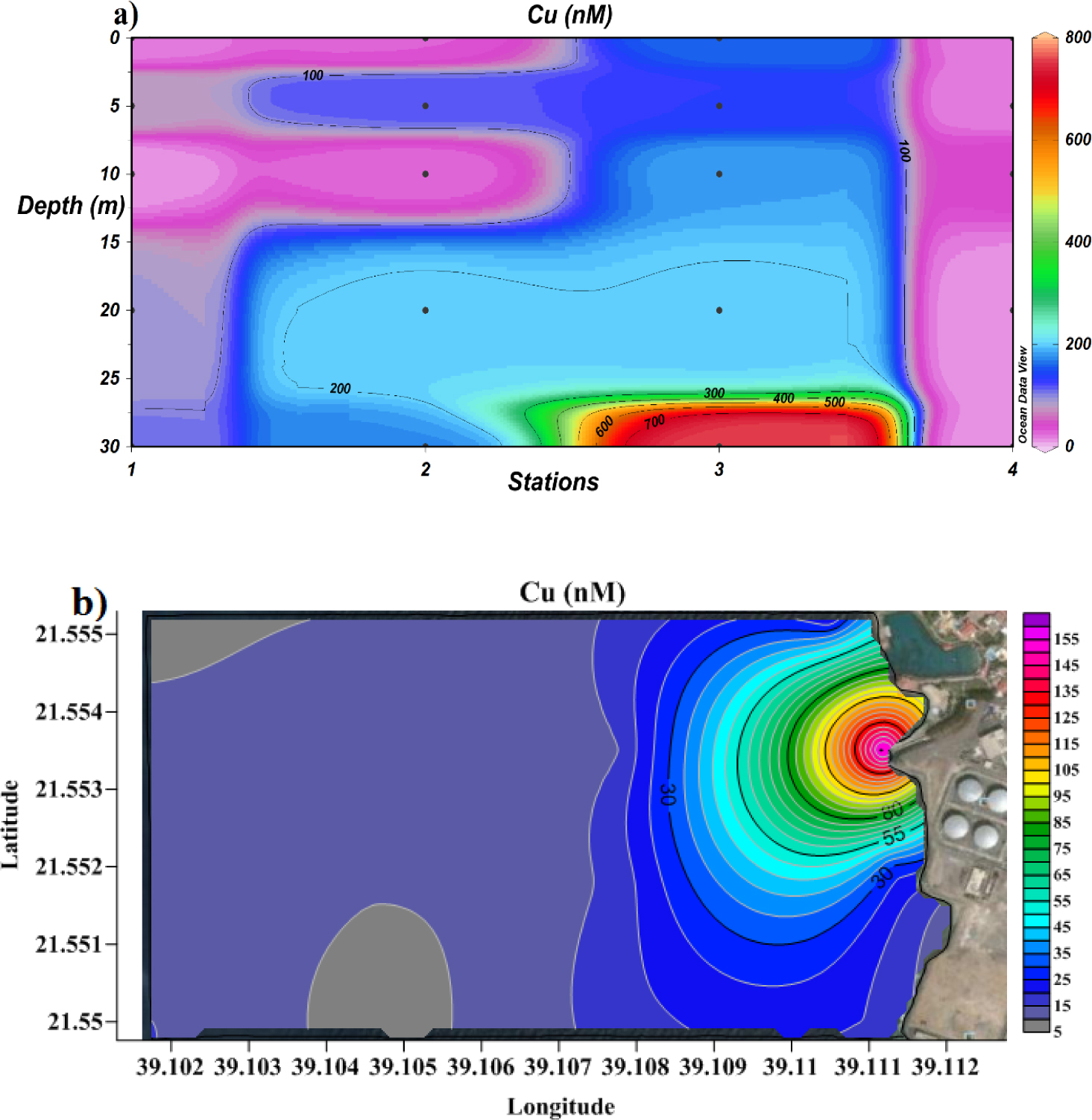
Cross-section profile (a) and surface distribution (b) of dissolved Cu.
The distribution pattern of Ni followed the same trend as that for Cu (Figures 7a and 7b). The highest Ni concentrations (25.6 nM) were measured at the discharging site (station 3) as well as at station 1 20 meters below sea level. The average value of dissolved Ni was 11.02 nM, far lower than the maximum value (1260.86 nM) recommended by US EPA.
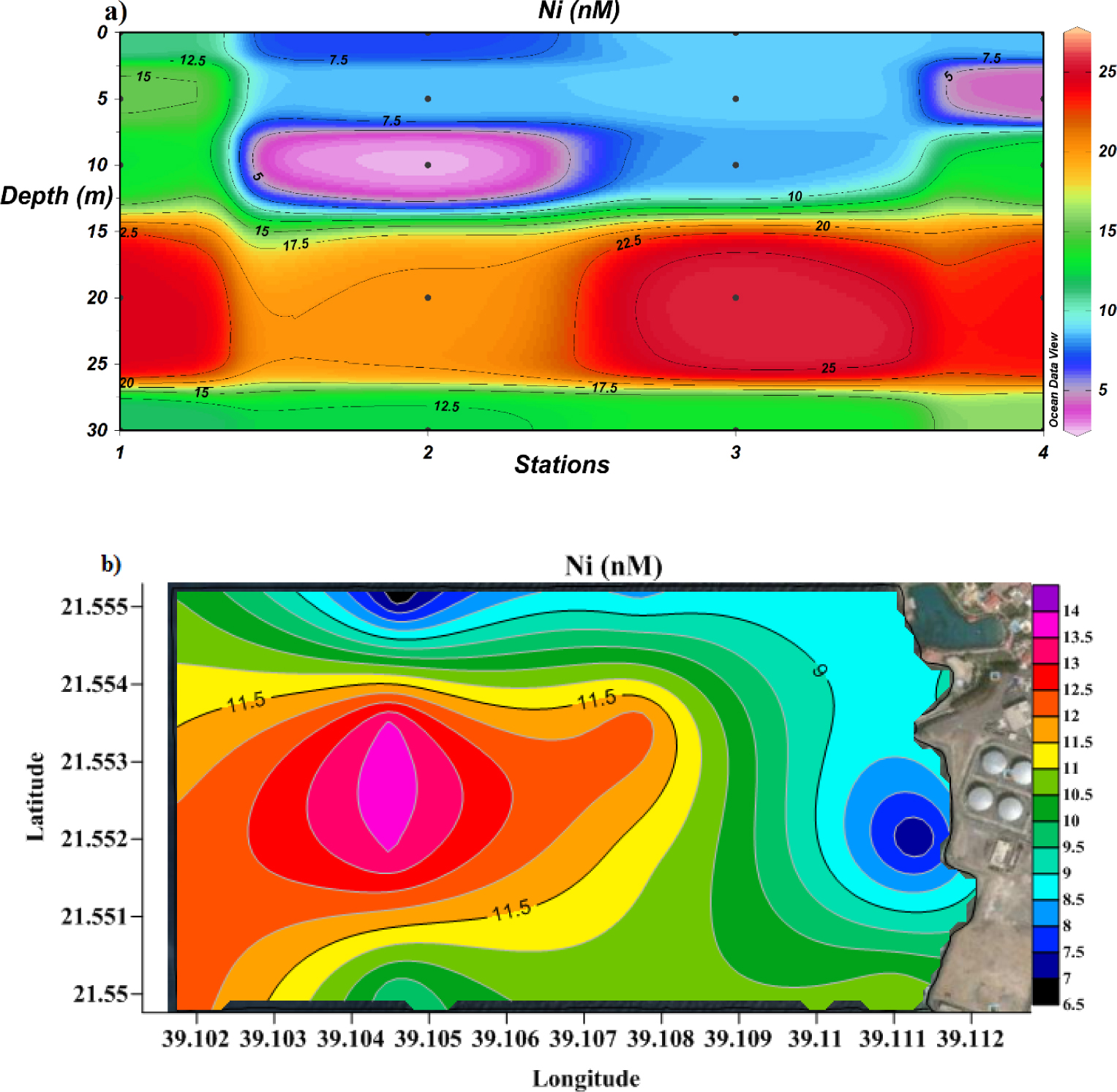
Cross-section profile (a) and surface distribution (b) of dissolved Ni.
Similarly to copper, the highest zinc concentration (143.81 nM) was found at the effluent site (station 3) 20 meters below sea level (Figure 8a). The average Zn level (68.03 nM) measured in the study area was lower than the US EPA-recommended maximum value (1376.56 nM) but higher than that reported for other regions of coastal Red Sea [47, 48].
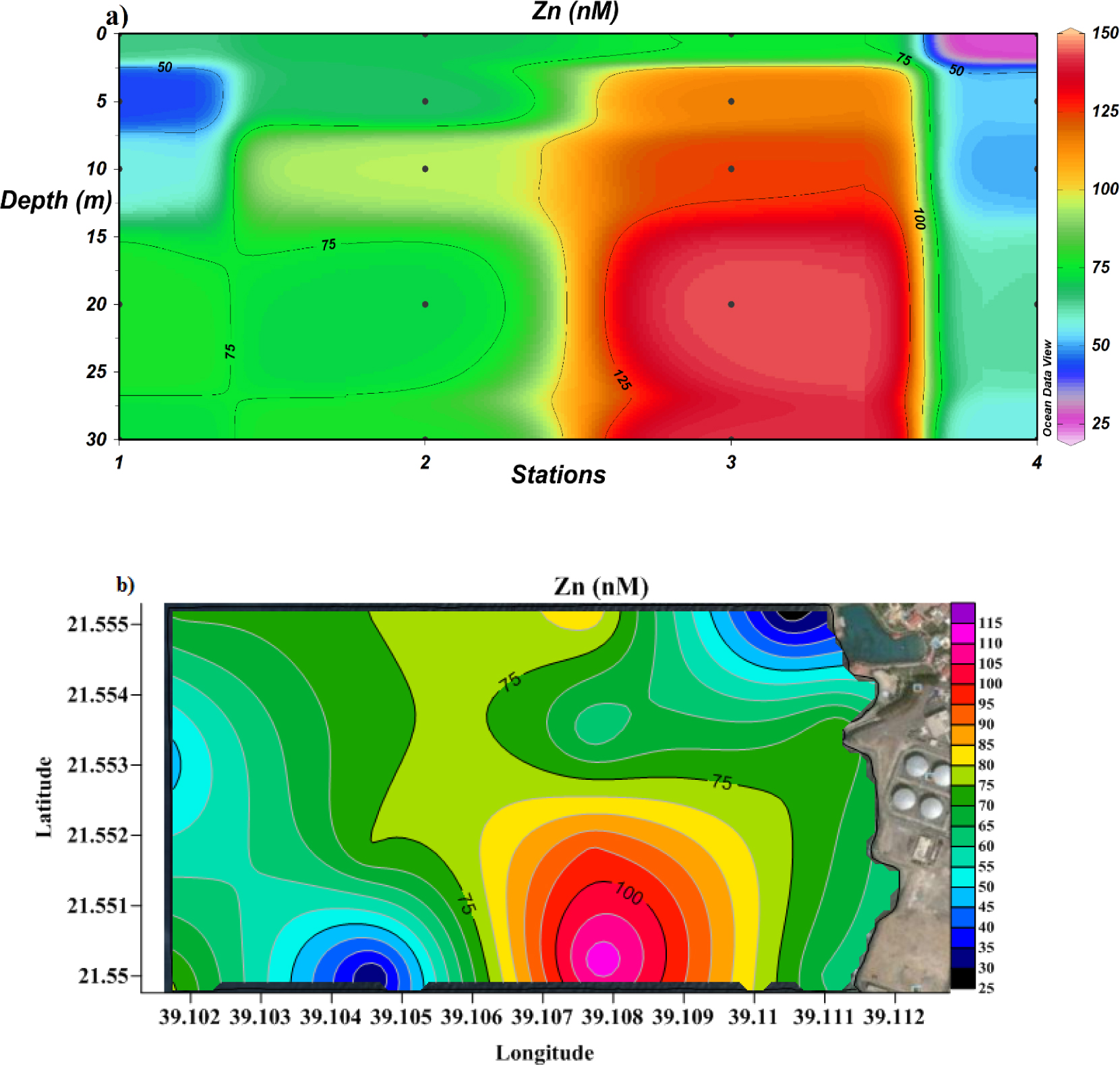
Cross-section profile (a) and surface distribution (b) of dissolved Zn.
Overall, the levels of dissolved Cu, Ni and Zn measured in this study are in agreement with those reported in a recent work by Farawati et al. [47]. As a comparison, the distribution of Cu, Ni, and Zn along the world ocean is shown in Table 2.
Comparative study of average Cu, Ni, and Zn levels in the surface water of world oceans.
| Study Area | Cu (nM) | Ni (nM) | Zn (nM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Sea | 3.6 | 2.74 | 21.20 | Al Farawti et al, 2011[47] |
| Arabian Gulf-Kuwait coast (after Gulf war oil spill) | 9.1 | 21.8 | 55.52 | Olayan et al, 1998 [58] |
| Indian Ocean | 2.22 | 2.63 | 0.96 | Saager et al, 1992 [62] |
| South China Sea | 2.9 | 1.38 | 1.59 | Norisuye et al, 2007 [61] |
| South Japan coast | 9.4 | 20.45 | 27.5 | Chester and Stoner, 1974 [59] |
| South African coast | 4.72 | 10.22 | 15.29 | Chester and Stoner, 1974 [59] |
| North-eastern Atlantic coast | 4.72 | 18.74 | 12.23 | Chester and Stoner, 1974 [59] |
| Pacific Ocean | 0.5 | 2.1 | 0.07 | Bruland et al, 1980 [57] |
| Southern Ocean | 5.1-6.52 | 1.44-5.99 | 1.14 | Abbolino et al, 2004 [54] |
| California coastal waters, USA | 7.2 | 0.35-1.02 | 1.64-1.74 | Geen and Luoma,1993 [63]; Flegel et al, 1991 [60] |
| Massachusetts Bay, USA | 3.47 | 18.45 | 2.56-7.48 | Flegel et al, 1991 [60] |
| Jeddah coast, Saudi Arabia | 24.12 | 10.35 | 68.03 | Present study, 2017 |
4 Conclusions
The variations in dissolved Cu, Ni and Zn levels in the seawater around Jeddah desalination plant were evident, both horizontally and vertically. Concentrations were maximum at the discharging site, indicating the erosion of Cu, Ni and Zn from metal alloys of desalination plant. The surface concentration of Cu exceeded the recommended US-EPA values in all stations, highlighting the need for a more efficient purification of waste waters. The levels of Ni and Zn were in the safe range. The detailed monitoring of the hydrographic parameters and dissolved heavy metals both temporally and spatially will shed light on the tidal effects and currents around the desalination plant.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Jeddah Desalination Plant for granting the permission to carry out sampling. Special thanks are extended to P. R. Shanas for his technical support. Mohammad M. Fallatah, Yasar N. Kavil and Ahmed S. A. Ibrahim are grateful to the Deanship of Graduate Studies (King Abdulaziz University) for providing a PhD fellowship.
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] United Nations Environment Programme. http://www.unep.org/themes/freshwater.html (10 April 2008).Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Shatat M., Riffat, S. B., Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources, International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, cts025, 2012.10.1093/ijlct/cts025Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Al-Kharabsheh S., Theoretical and experimental analysis of water desalination system using low grade solar heat (Doctoral dissertation, University of Florida), 2003.10.1115/ISEC2003-44009Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Tiwari G. N., Singh H. N., Tripathi, R., Present status of solar distillation, Sol. Energy, 2003, 75(5), 367-373.10.1016/j.solener.2003.07.005Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Li C., Goswami Y., Stefanakos E., Solar assisted sea water desalination: A review, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2013, 19, 136-163.10.1016/j.rser.2012.04.059Suche in Google Scholar
[6] von Medeazza G.M., Moreau V., Modelling of water–energy systems. The case of desalination, Energy, 2007, 32(6), 1024-1031.10.1016/j.energy.2006.10.006Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Wang Y., Lior N., Proposal and analysis of a high-efficiency combined desalination and refrigeration system based on the LiBr–H2O absorption cycle—Part 2: Thermal performance analysis and discussions, Energy conversion and management, 2011, 52(1), 228-235.10.1016/j.enconman.2010.06.064Suche in Google Scholar
[8] WHO/EU drinking water standards comparative table, Water treatment & Air purification and other supporting information. http://www.lenntech.Com/WHO-EU-water-standards.html (26 October 2007).Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Elimelech M., Phillip W.A., The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science, 2011, 333(6043), 712-717.10.1126/science.1200488Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Greenlee L.F., Lawler D.F., Freeman B.D., Marrot B., Moulin P., Reverse osmosis desalination: water sources, technology, and today’s challenges, Water research, 2009, 43(9), 2317-2348.10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.010Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Yip N.Y., Tiraferri A., Phillip W.A., Schiffman J.D., Elimelech M., High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane, Environmental science & technology, 2010, 44(10), 3812-3818.10.1021/es1002555Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Cohen-Tanugi D., McGovern R.K., Dave S.H., Lienhard J.H., Grossman J.C., Quantifying the potential of ultra-permeable membranes for water desalination, Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(3), 1134-1141.10.1039/C3EE43221ASuche in Google Scholar
[13] Shannon M. A., Bohn P. W., Elimelech M., Georgiadis J. G., Marinas B. J., Mayes A. M., Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades, Nature, 2008, 452(7185), 301-310.10.1142/9789814287005_0035Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Li D., Wang, H., Recent developments in reverse osmosis desalination membranes, Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010 20(22), 4551-4566.10.1039/b924553gSuche in Google Scholar
[15] Fkirin M. A., Al-Madhari A. F., Prediction of time-varying dynamic processes, International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, 1997, 14(5), 505-511.10.1108/02656719710170729Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Semiat R., Present and future, Water International, 2000, 25(1), 54-65.10.1080/02508060008686797Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Tularam G. A., Ilahee, M., Environmental concerns of desalinating seawater using reverse osmosis, J Environ Monit, 2007, 9(8), 805-813.10.1039/b708455mSuche in Google Scholar
[18] El-Dessouky H. T., Ettouney H. M., Fundamentals of salt water desalination. Elsevier, 2002.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Gleick P. H., The world’s water 1998-1999: the biennial report on freshwater resources. Island Press, 1998.Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Oki T., Kanae S., Global hydrological cycles and world water resources, science, 2006, 313(5790), 1068-1072.10.1126/science.1128845Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Roberts D. A., Johnston E. L., Knott N. A., Impacts of desalination plant discharges on the marine environment: A critical review of published studies, Water Res, 2010, 44(18), 5117-5128.10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.036Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Lattemann S., Höpner T., Environmental impact and impact assessment of seawater desalination, Desalination, 2008, 220(1), 1-15.10.1016/j.desal.2007.03.009Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Safrai I., Zask A., Reverse osmosis desalination plants—marine environmentalist regulator point of view, Desalination, 2008, 220(1-3), 72-84.10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.023Suche in Google Scholar
[24] Winter H., Isquith I. R., Bakish, R., Influence of desalination effluents on marine ecosystems, Desalination, 1979 30(1), 403-410.10.1016/S0011-9164(00)88470-2Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Miri R., Chouikhi A., Ecotoxicological marine impacts from seawater desalination plants, Desalination, 2005, 182(1), 403-410.10.1016/j.desal.2005.02.034Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Riley M.R., Gerba C.P., Elimelech, M., Biological approaches for addressing the grand challenge of providing access to clean drinking water, Journal of biological engineering, 2011, 5(1), 2.10.1186/1754-1611-5-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Busch M., Chu R., Rosenberg S., Novel trends in dual membrane systems for seawater desalination: minimum primary pretreatment and low environmental impact treatment schemes, IDA Journal of Desalination and Water Reuse, 2010 2(1), 56-71.10.1179/ida.2010.2.1.56Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Schiffler M., Perspectives and challenges for desalination in the 21st century, Desalination, 2004, 165, 1-9.10.1016/j.desal.2004.06.001Suche in Google Scholar
[29] https://www.economist.com/news/middle-east-and-africa/21728686-rapprochement-iran-may-be-pushing-it-saudis-may-be-stretching-out.Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Kalogirou S.A., Seawater desalination using renewable energy sources, Progress in energy and combustion science, 2005, 31(3), 242-281.10.1016/j.pecs.2005.03.001Suche in Google Scholar
[31] El-Fadel M., Alameddine I., Desalination in arid regions: Merits and concerns, Journal of water supply: research and technology-Aqua, 2005, 54(7), 449-461.10.2166/aqua.2005.0042Suche in Google Scholar
[32] Berktay A., Environmental approach and influence of red tide to desalination process in the Middle East region, International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2011, 2(3).Suche in Google Scholar
[33] Chesher R. H., Biological impact of a large-scale desalination plant at Key West. Copy Available From GPO SUP DOC AS EPA 18080 GBX 12/71 FOR$ 1. 25, 1971.Suche in Google Scholar
[34] Cintron G., Maddux W., Burkholder P., Some consequences of brine pollution in the Bahi’a Fosforescente, Puerto Rico, Limnol Oceanogr, 1970, 15 (2), 246-249.10.4319/lo.1970.15.2.0246Suche in Google Scholar
[35] Gacia E., Invers O., Manzanera M., Ballesteros E., Romero J., Impact of the brine from a desalination plant on a shallow seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) meadow, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 2007, 72(4), 579-590.10.1016/j.ecss.2006.11.021Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Purnama A., Al-Barwani H. H., Smith R., Calculating the environmental cost of seawater desalination in the Arabian marginal seas, Desalination, 2005, 185(1), 79-86.10.1016/j.desal.2005.03.072Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Shao D., Law A. W. K., Salinity build-up due to brine discharges into shallow coastal waters, Mod Phys Lett B, 2009, 23(03), 541-544.10.1142/S0217984909018850Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Hashim A., Hajjaj M., Impact of desalination plants fluid effluents on the integrity of seawater, with the Arabian Gulf in perspective, Desalination, 2005, 182(1), 373-393.10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.020Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Purnama A., Al-Barwani H. H., Spreading of brine waste discharges into the Gulf of Oman, Desalination, 2006, 195(1), 26-31.10.1016/j.desal.2005.09.036Suche in Google Scholar
[40] Dawoud M.A., Environmental impacts of seawater desalination: Arabian Gulf case study, International Journal of Environment and Sustainability, 2012, 1(3).10.24102/ijes.v1i3.96Suche in Google Scholar
[41] Mabrook B., Environmental impact of waste brine disposal of desalination plants, Red Sea, Egypt, Desalination, 1994, 97(1), 453-465.10.1016/0011-9164(94)00108-1Suche in Google Scholar
[42] Hoepner T., A procedure for environmental impact assessments (EIA) for seawater desalination plants, Desalination, 1999, 124(1), 1-12.10.1016/S0011-9164(99)00083-1Suche in Google Scholar
[43] Bleninger T., Jirka G.H., Lattemann, S., Environmental planning, prediction and management of brine discharges from desalination plants, Middle East Desalination Research Center (MEDRC): Muscat, Sultanate of Oman, 2010.Suche in Google Scholar
[44] Raventós N., Macpherson E., García-Rubies A., Effect of brine discharge from a desalination plant on macrobenthic communities in the NW Mediterranean, Mar Environ Res., 2006, 62(1), 1-14.10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.02.002Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Al-Farawati R., Environmental conditions of the coastal waters of Southern Corinche, Jeddah, Eastern red sea: Physicochemical approach, Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci., 2010, 4(8), 3324-3337.10.1007/s12517-010-0137-ySuche in Google Scholar
[46] Orif M.I., Kavil Y.N., Kelassanthodi R., Al-Farawati R., Zobidi, M.I.A., Dissolved methane and oxygen depletion in the two coastal lagoons, Red Sea. Indian J. Mar. Sci., 2017, 46(7), 1287-1297.Suche in Google Scholar
[47] Al-Farawati R.K., Gazzaz M.O., El Sayed M.A., El-Maradny A., Temporal and spatial distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni and Zn in the coastal waters of Jeddah, eastern Red Sea, Arab. J. Geo. Sc., 2011, 4(7-8), 1229-1238.10.1007/s12517-010-0137-ySuche in Google Scholar
[48] Turki A.J., El Sayed M.A., Basaham A.S., Al-Farawati R., Study on the distribution, dispersion and mode association of some organic and inorganic pollutants in a coastal lagoon receiving sewage disposal. Research project. King Abdulaziz University Scientific Research Council, Jeddah, 2002.Suche in Google Scholar
[49] Abdul-Wahab S.A., Characterization of water discharges from two thermal power/desalination plants in Oman. Environ. Eng. Sci., 2007, 24(3), 321-337.10.1089/ees.2005.0126Suche in Google Scholar
[50] Altayaran A.M., Madany I.M., Impact of a desalination plant on the physical and chemical properties of seawater, Bahrain. Water Research, 1992 26(4), 435-441.10.1016/0043-1354(92)90043-4Suche in Google Scholar
[51] Talavera J.P., Ruiz J.Q., Identification of the mixing processes in brine discharges carried out in Barranco del Toro Beach, south of Gran Canaria (Canary Islands). Desalination, 2001, 139(1), 277-286.10.1016/S0011-9164(01)00320-4Suche in Google Scholar
[52] Einav R., Harussi K., Perry D., The footprint of the desalination processes on the environment. Desalination, 2003, 152(1-3), 141-154.10.1016/S0011-9164(02)01057-3Suche in Google Scholar
[53] Fernández-Torquemada Y., Sánchez-Lizaso J.L., González-Correa J.M., Preliminary results of the monitoring of the brine discharge produced by the SWRO desalination plant of Alicante (SE Spain). Desalination, 2005, 182(1-3), 395-402.10.1016/j.desal.2005.03.023Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Malfeito J.J., Díaz-Caneja J., Farinas M., Fernandez-Torrequemada Y., Gonzalez-Correa, J.M., Carratala-Gimenez, A., Sanchez-Lizaso, J.L., Brine discharge from the Javea desalination plant. Desalination, 2005, 185(1), 87-94.10.1016/j.desal.2005.05.010Suche in Google Scholar
[55] Ruso Y.D.P., De la Ossa Carretero J.A., Casalduero F.G., Lizaso J.S., Spatial and temporal changes in infaunal communities inhabiting soft-bottoms affected by brine discharge. Mar. Envir. Res., 2007, 64(4), 492-503.10.1016/j.marenvres.2007.04.003Suche in Google Scholar
[56] Abbolino O., Aceto M., Malandrino M., Mentasi E., Sarzanini C., Petrella F., Heavy metal in agricultural soils from Piedomant, Italy. Distribution, speciation and chemometric data treatment, Chemosphere, 2002, 49, 545-557.10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00352-1Suche in Google Scholar
[57] Bruland K.W., Oceanographic distributions of cadmium, zinc, nickel, and copper in the North Pacific, Earth Planet. Sci Lett., 1980, 47(2), 176-198.10.1016/0012-821X(80)90035-7Suche in Google Scholar
[58] Bu-Olayan A.H., Subrahmanyam M.N.V., Al-Sarawi M., Thomas B. V., Effects of the Gulf War oil spill in relation to trace metals in water, particulate matter, and PAHs from the Kuwait Coast, Environt Int., 1998, 24(7), 789-797.10.1016/S0160-4120(98)00056-7Suche in Google Scholar
[59] Chester R., Stoner J.H., The distribution of zinc, nickel, manganese, cadmium, copper, and iron in some surface waters from the world ocean, Mar Chem., 1974, 2(1), 17-32.10.1016/0304-4203(74)90003-6Suche in Google Scholar
[60] Flegal A.R., Smith G.J., Gill G.A., Sanudo-Wilhelmy S., Anderson L.C.D., Dissolved trace element cycles in the San Francisco Bay estuary, Mar Chem., 1991, 36(1-4), 329-363.10.1016/S0304-4203(09)90070-6Suche in Google Scholar
[61] Norisuye K., Ezoe M., Nakatsuka S., Umetani S., Sohrin Y., Distribution of bioactive trace metals (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and Cd) in the Sulu Sea and its adjacent seas, Deep-Sea Res PT I, 2007, 54(1), 14-37.10.1016/j.dsr2.2006.04.019Suche in Google Scholar
[62] Saager P.M., De Baar H.J., Howland R.J., Cd, Zn, Ni and Cu in the Indian Ocean, Deep-Sea Res PT A, 1992, 39(1), 9-35.10.1016/0198-0149(92)90017-NSuche in Google Scholar
[63] Van Geen A., Luoma S.N., Trace metals (Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn) and nutrients in coastal waters adjacent to San Francisco Bay, California., Estuaries, 1993, 16(3), 559-566.10.2307/1352603Suche in Google Scholar
© 2018 Mohammad M. Fallatah et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution

