Abstract
Flammulina velutipes, (Curt. ex Fr.) Sing, a popularly edible fungus, has been widely used both as a restorative drug and a tonic food in China. In the current study, the effect of F. velutipes polysaccharides was evaluated with a constipated rat model induced by loperamide hydrochloride. The rats were divided into six groups: normal group, model group, positive control group, F. velutipes polysaccharides high, moderate and low dose groups. Rats were given 2 mL of Loperamide hydrochloride (3 mg·kg·d), by intragastric administration 2 times per day for 10 days. F. velutipes polysaccharides at the doses of 600, 400 and 200 mg/kg (1 mL/100g weight) were administered to treat rats with constipation for 7 days. The gastrointestinal hormones, including motilin (MTL), gastrin (GAS), substance P (SP), somatostatin (SS), and intestinal propulsive rate and feces weight at 24 hours after treatment were used as the indexes to evaluate the effects of F. velutipes polysaccharides on constipation. The levels of MTL, GAS and SP in serum significantly increased and the levels of SS in serum of rats significantly decreased after the treatment of rats with F. velutipes polysaccharides as compared with those of rats in the model group.
1 Introduction
Flammulina velutipes (Curt. ex Fr.) Sing (Figure 1), belonging to Tricholomataceae, is a fruiting body [1], and one of the most popular edible fungi [2]. As a culinary and medicinal mushroom, F. velutipes also named golden needle mushroom (China) and enokitake (Japan) has been widely used as a restorative drug and as a tonic food in China [3]. It is a highly nutritious food rich in protein, vitamins, carbohydrates and crude fiber. One of its main groups of active substances are the polysaccharides, which have been reported to possess a wide spectrum of biological functions including anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, anti-virus, anti-fatigue activities and improvement of memory [4]. Using the DEAE Cellulose-52, high gel filtration chromatography (HPGFC) and PMP-HPLC, Li et al. analyzed the composition of the polysaccharides, molecular weight and monosaccharide constituents. Their results showed that the F. velutipes polysaccharides might be mainly composed of glucan, which was mixed with some other fractions, such as galactose glycan, mannan, xylan and fucosan [5].

Flammulina velutipes.
Constipation is a common bowel complaint, which is mainly characterized by difficulty in defecation, prolonged defecation time, dry stools and disorders of intestine physiological function [6-7]. Constipation has a significant negative impact on the quality of life of patients and can even seriously threaten their lives [8-9]. The pathogenesis of constipation is very complicated. Disorders of gastrointestinal (GI) metabolism, smooth muscle lesions, and disorders of the enteric nervous system are the main causes. GI hormones are one type of hormone discharged by dozens of endocrine cells, which live in the mucous membrane of the GI region. GI hormones are regular peptides and their physiological effects comprise regulating digestive gland secretion, the movements of the digestive tract [8,9,10] and cholecystokinin (CCK). Motilin (MTL), gastrin (GAS), cholecystokinin (CCK), somatostatin (SS) and Substance P are a group of the GI hormones and can be used as a constipation index.
Studies on the utilization of polysaccharides prepared from other plants in the treatment of patients with constipation have been reported. For instance, Chuncai polysaccharides showed therapeutic effects on treating constipation patients [11]. Plantago crude polysaccharides were evaluated for the treatment of constipation patients, and they presented a better therapeutic effect [12]. However, to date, no studies on the utilization of F. velutipes polysaccharides in treating constipation have been reported. Therefore, in this study, we firstly established a constipation model with loperamide hydrochloride and then evaluated the therapeutic effect of F. velutipes polysaccharides in the treatment of constipation with this model, aiming to evaluate the therapeutic effect of F. velutipes polysaccharides in the treatment of constipation.
2 Materials and Methods
2.1 Drugs and chemicals
F. velutipes powders (Figure 2) were provided by Henan LongFeng Industrial Co., Ltd. Loperamide hydrochloride (batch number: 170421860) was obtained from Xian Janssen Pharmaceutical Ltd. (Xian, Shaanxi, China). Arabian gum powder (batch number: 20170203) was purchased from Tianjin KeMiou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Rat Substance P (SP), Rat Motilin (MTL), Rat Somatostatin (SS), Rat Gastrin (Gas) (Batch numbers: 2017Z0060711, 2017Z060401, 2017Z060702, 2017Z060305, respectively) were obtained from Shenzhen Ziker Biological Technology Co. Ltd. (Shenzhen, Guangdong, China).

Flammulina velutipes powders.
2.2 Animals
Male Sprague-Dawley/specific pathogen free (SD/SPF) rats weighting 150-170 g were purchased from the Henan Animal Experiment Center (with a License key of SCXK 2015-0004) (Zhengzhou, Henan, China).
2.3 Extraction and isolation of polysaccharides from F. velutipes powders
F. velutipes powders were extracted three times with petroleum ether and 70% ethanol for 24 h each time. The extracts were then filtered and dried. The dried powder was extracted with distilled water of 1:20 (w/v), at 90°C every 3 h three times, then the filtrate was filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure and then precipitated with 95% ethanol (the final concentration was 70%) overnight. The insoluble precipitate was centrifuged after 24 h. The protein present was removed by the Sevage method. Then the refined polysaccharides were dialyzed using a dialysis bag for 24 h against distilled water and another 12 h against ultra-pure water. Finally, the dialyzed polysaccharides solution was dehydrated by freeze-drying to obtain the polysaccharides.
2.4 Acute toxicity test
The maximum dosage test was carried out according to the methods described previously [13,14,15,16,17,18]. The result showed that after administrating the rats, no excitement, scurry, listlessness, convulsions and other phenomena were observed and no change in skin and respiration, no death and no significant change in weight were found after 4 days of observation. The rats were sacrificed and their hearts, livers and spleens were excised, and no change was observed with the naked eye observation. However, the rats in the drug administrated-group developed flatulence. Therefore, F. velutipes caused no visible toxicity.
2.5 Establishment of Constipation Model with loperamide hydrochloride
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD)/SPF rats were kept for a week and offered a standard diet and tap water at 25±2°C and 40-45% relative humidity. According to body weight, all the rats were randomly divided into six groups: normal group, model group, positive control group, F. velutipes polysaccharides high dose group, moderate dose group and low dose group, respectively. Expect for the normal group, other groups were modeled with loperamide hydrochloride (3 mg·kg·d·2 mL) according to weight for 10 days [18-19]. During the establishment of the constipation model, the 24 h-feces were collected on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 10.
2.6 Treatment of Rats with F. velutipes Polysaccharides
After successful establishment of the constipation model, the rats in normal group and model group received saline (1 mL/100 g weight). Rats in the positive control group received Maren boluses (3 g/kg, 1 mL/100 g weight). Rats in F. velutipes polysaccharides high, moderate and low dose groups received 600, 400, and 100 (mg/kg), 1 mL/100 g weight of F. velutipes polysaccharides, respectively. Medication was given consecutively for 7 days.
During the experiment, the feces weight of 6 hours was collected daily. The body weight of the rats was recorded daily.
On the last day of the experiment, all the rats were left with no food for 12 hours. All the rats were given activated carbon suspension by intragastric administration. The rats were sacrificed and their intestinal tissue samples were dissected out and measured. The concentrations of MTL, GAS, SS and substance P were measured by abdominal aorta blood collection according to the methods described previously [10,20-21].
Statistical analysis of experimental results: the results were expressed as the arithmetic mean plus or minus standard deviation. Numerical statistics were performed using SPSS 19.0 software with single factor analysis of variance (ANOVA One-Way) to determine the significant differences.
Ethics
We declare that the ethical background to this study was approved by the National Ethical Committee.
3 Results
During the course of establishing the model, the diet, activity and feces of rats were observed daily. The rats in the normal groups showed no significant difference. But the rats in model group, positive control group, F. velutipers polysaccharides high, moderate and low dose group all took less diet. Their activities and feces weights were lower than those of rats in normal group. The data in all the tables is also shown in Figure 3.
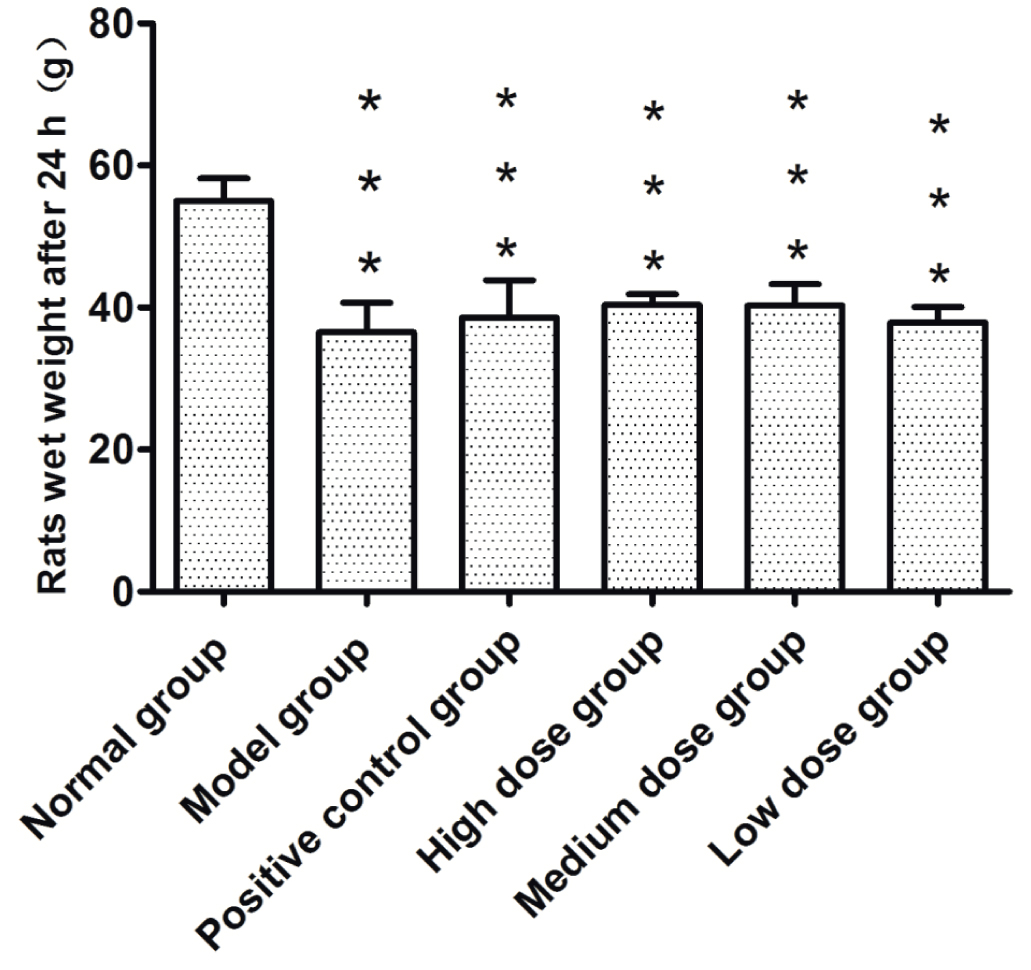
The body weight of rats for 24 h.
As shown in Table 1 and Figure 3, at 24 h, the feces weights of rats of the model group, positive control group, F. velutipes polysaccharides high, moderate and low dose groups significantly decreased compared with that of the normal group (P<0.001), indicating the successfully establishment of constipation model.
The feces weight of rats at 24 h after treatment.
| The feces weight (g) | |
|---|---|
| Normal group | 55.00±3.19 |
| Model group | 36.50±4.20[***] |
| Positive control group | 38.56±5.29[***] |
| High dose group | 40.40±1.50[***] |
| Moderate dose group | 40.26±3.00[***] |
| Low dose group | 37.86±2.23[***] |
(n=8) 0.001<**P<0.01, *P<0.05
It can be seen from Table 2, Figures 4a and 4b that the intestinal propulsive rate and the feces weight of rats in the model group significantly decreased as compared with those of the normal group (P<0.001). The intestinal propulsive rate significantly increased in the rats in the positive control group (P<0.001), F. velutipes polysaccharides high, moderate and low dose groups (P<0.001 and P<0.01), compared with that of the model group. The intestinal propulsive rate of F. velutipes polysaccharides moderate dose group was relatively similar to that of the positive control group.
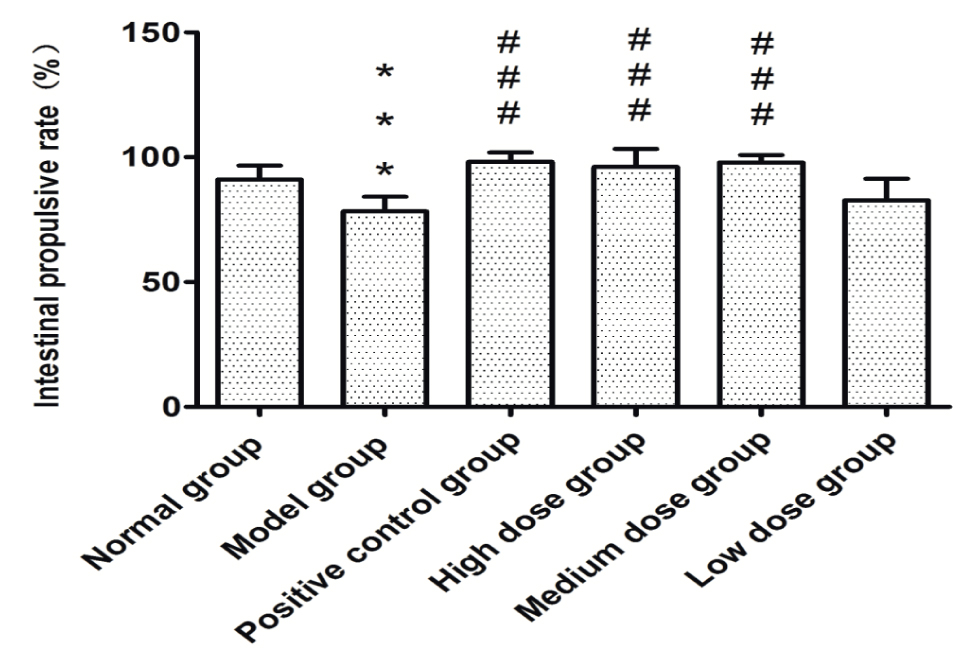
Intestinal propulsive rate.
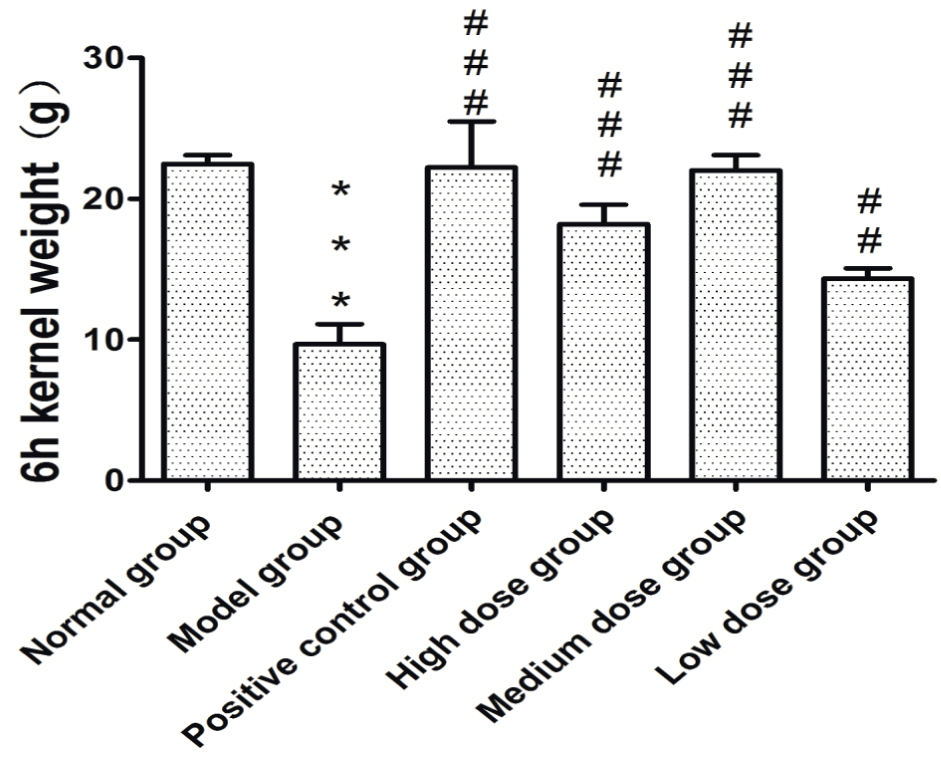
The body weight of rats for 6 h.
Rat granules and intestinal propulsive rate at 6 h after treatment.
| The feces weight (g) | intestinal propulsive rate | |
|---|---|---|
| Normal group | 22.48±0.61 | 90.99±5.70 |
| Model group | 9.68±1.42[***] | 78.31±5.88[***] |
| Positive control group | 22.23±3.26[###] | 98.19±3.69[###] |
| High dose group | 18.20±1.38[###][&&] | 96.12±7.26[###] |
| Moderate dose group | 22.03±1.07[###] | 97.84±3.01[###] |
| Low dose group | 14.33±0.74[##][&&&] | 82.77±8.60 |
The feces weight of rats in the moderate dose group at 6 hours was similar to that of rats in the positive control group. Therefore, F. velutipes polysaccharides at moderate level can have better therapeutic effect.
In Table 3 and Figure 5, compared with those in the normal group, the amounts of the GAS (P<0.001), MTL (P<0.001) and substance P (P<0.001) significantly decreased in the rats of the model group while the amount of SS (P<0.001) significantly increased. Compared with that of the model group, the amounts of GAS, MTL, and SP (P<0.001) in rats of the positive control group and F. velutipes polysaccharides moderate dose group significantly increased where as the amount of SS was significantly decreased (P<0.001). The levels of MTL and SP in the rats of the high dose group increased but the level of SS was decreased. Thus, F. velutipes polysaccharides at high and moderate dose groups can have good therapeutic effect, but the effect of the moderate dose was much better.
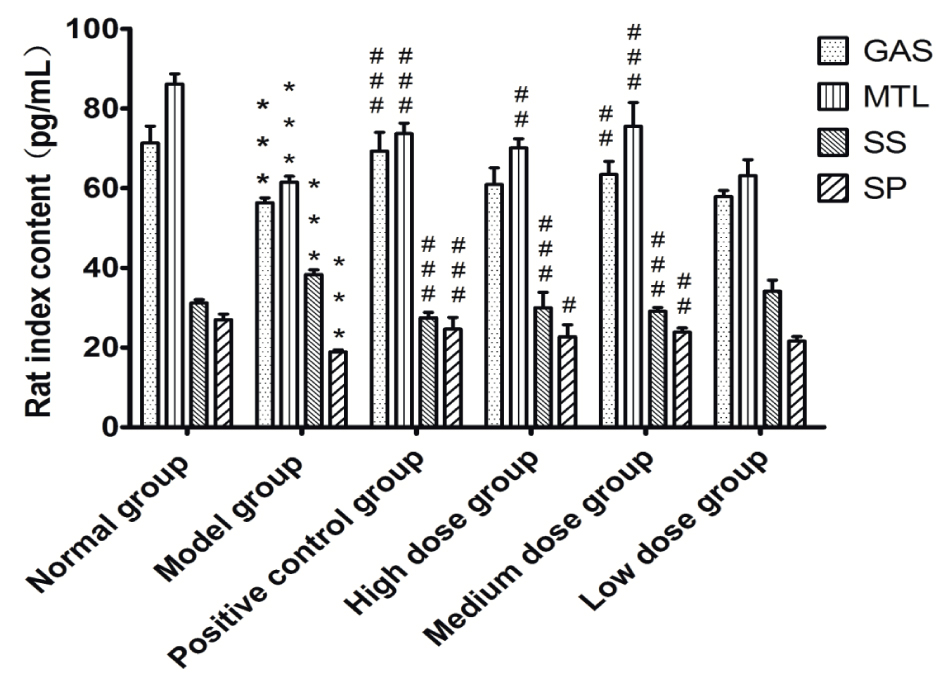
Contents of MTL, GAS, and SS of rats.
Contents of MTL, GAS, and SS of rats.
| GAS | MTL | SS | SP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal group | 71.31±4.25 | 86.15±2.57 | 31.18±0.86 | 27.00±1.37 |
| Model group | 56.36±1.20[***] | 61.54±1.44[***] | 38.33±1.18[***] | 18.90±0.47[***] |
| Positive control group | 69.32±4.71[###] | 73.68±2.64[###] | 27.46±1.36[###] | 24.60±2.96[###] |
| High dose group | 60.90±4.22 | 70.08±2.34## | 30.00±3.87[###] | 22.69±3.00# |
| Moderate dose group | 63.47±3.23## | 75.54±5.94[###] | 29.09±0.93[###] | 23.89±1.01## |
| Low dose group | 57.88±1.59 | 63.13±3.99 | 34.16±2.77 | 21.63±1.13 |
(n=8)0.001<##P<0.01, *P<0.05
The levels of MTL, GAS and SP in rats were lower than those in healthy rats. However, the level of SS was higher than that of healthy rats. From the changes in MTL, GAS, SP and SS, we can clearly observe the changes in the intestinal peristalsis. These results showed that F. velutipes polysaccharides at either high or moderate doses could improve intestinal peristalsis and contraction of the intestinal smooth muscle with a moderate dose exhibiting a better therapeutic effect.
4 Histological observations
Colon samples were collected, washed with saline, fixed in 4% para formaldehyde for 24 h, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin, made into 5 μm small sections and stained with hematoxylin-eosin.
According to the cross section shown in Figure 6a, the cells of the normal group were very complete and well organized in great order. As shown in Figure 6b, after being molded, pathological changes in the colon tissue were found, and the colon cells of the model group began to break, and the stroma increased and its shape went irregular. Figure 6c and Figure 6d showed that after being treated, the cells in the positive control group and the moderate dose group began to recover, and the cell membrane and the nucleus also returned to normal without breakage, and the cells were well-organized. As illustrated in Figure 6e, cells in the high dose group, when compared with the model group, showed remarkable improvement, but when compared with the positive control group, the cells showed less obvious improvement and some cells were still damaged. As illustrated in Figure 6f, cells in the low dose group, when compared with the model group, showed no obvious change, had excessive stroma, were arranged disorderly, and some cells were damaged.
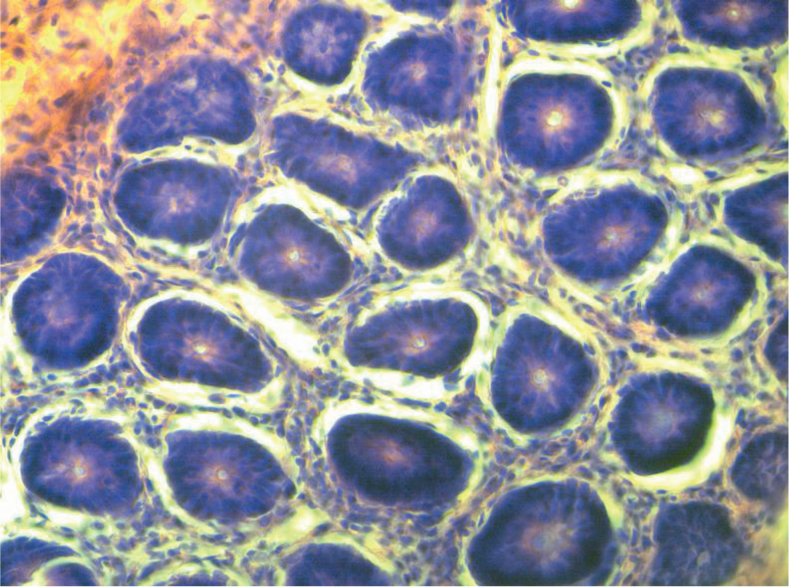
Normal group.
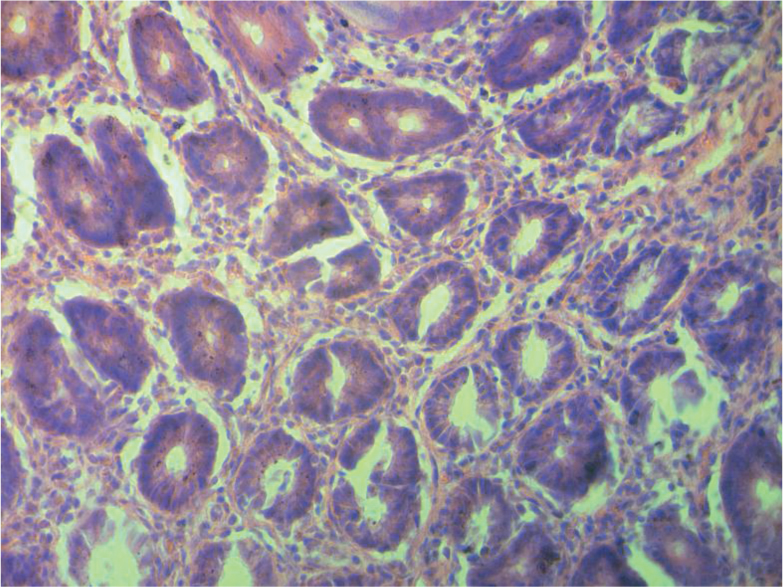
Model group.
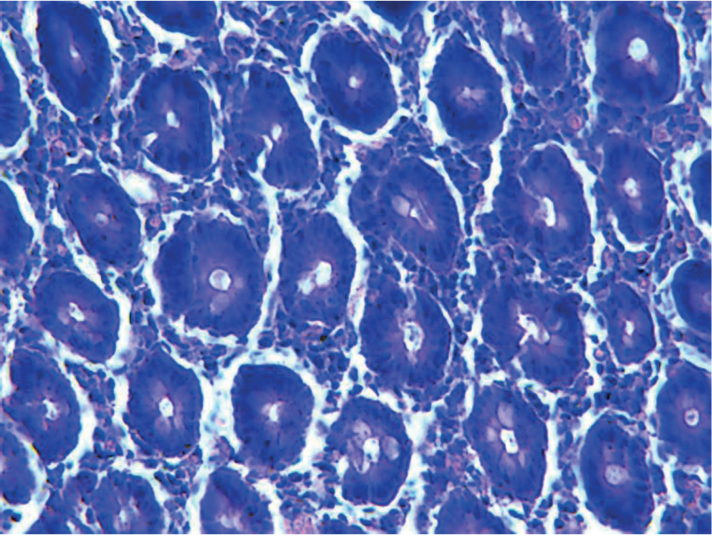
Positive control group.
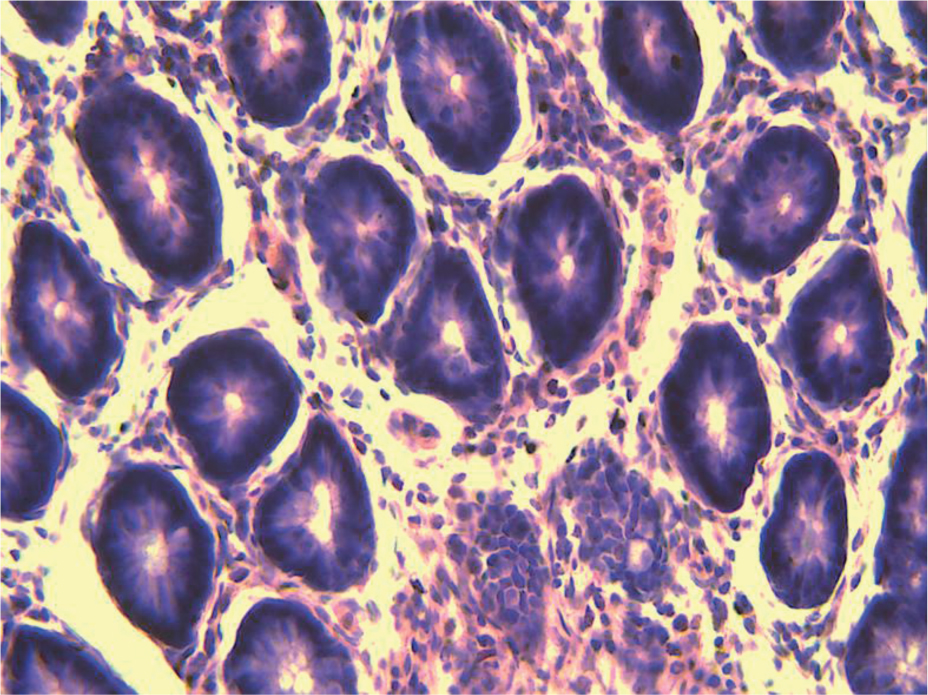
Moderate dose group.
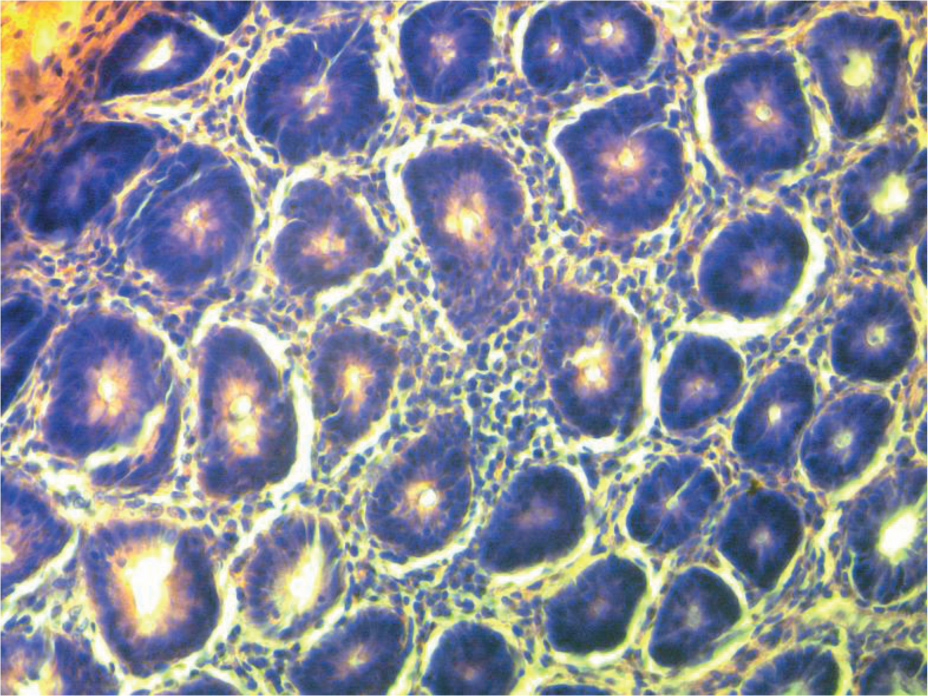
High dose group.
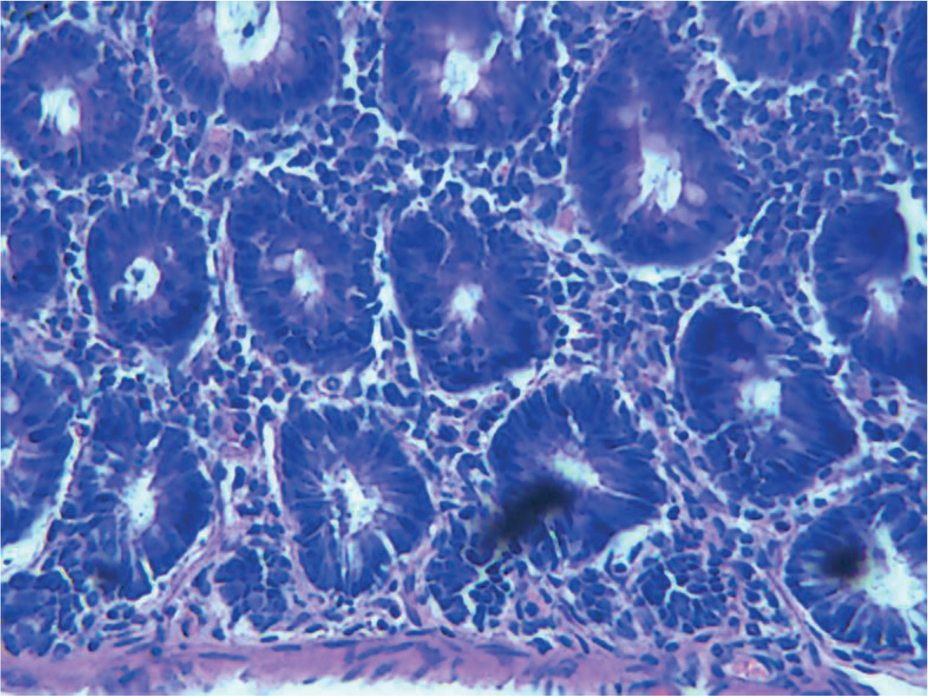
Low dose group.
5 Discussion
In the current study, the effect of F. velutipes polysaccharides on the improvement of constipation was evaluated through measuring the contents of MTL, GAS, SS and Substance P [20-21].
It has been demonstrated that MTL, GAS, SS and SP can be evaluated as the indexes for constipation. They are all GI hormones and can regulate the movements and secretions of the alimentary tract. MTL can improve intestinal peristalsis and contraction of the intestinal smooth muscle. Thus, it can be used as an indicator of constipation. GAS has the effect of promoting intestinal peristalsis and intestinal smooth muscle contraction. Thus, it can improve the contraction of the pyloric sphincter. SS can inhibit the secretion of pepsin and reduce the contraction of smooth muscle, and slow down peristalsis. Therefore, the increased content of SS can increase the constipation in rats. Substance P is a type of GI hormone that inhibits the secretion of gastrointestinal mucosa and promotes intestinal peristalsis. Thus, it is one of the main indexes used for evaluation of constipation [10,22-23].
As a kind of edible fungus, F. velutipes is rich in nutrients, protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and crude fiber [4]. One of the main active substances of F. velutipes is polysaccharides, which has been reported to play important roles in controlling a wide spectrum of biological roles, including anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, anti-virus, anti-fatigue activities and memory-improving function [24,25,26,27,28,29]. Polysaccharides represent a structurally diverse class of macromolecules and have a variety of biological functions, especially immune-enhancing activity. Studies by Chen et al. proved that the F. velutipes polysaccharides stimulate a macrophage whose supernatant has good inhibition on B16F10 and L919 proliferation, most likely through stimulating macrophages to produce cytokines that lead to the apoptosis of tumor cells [30]. Pan et al. used the F. velutipes polysaccharides at a dose of 1.5 mg/ mL to gavage for 20 days, and then conducted the behavior training for 7 days. When the training was over, according to the original mode of administration, administration was continued for 32 d. The results showed the F. velutipes polysaccharides had a positive effect on learning and memory [19]. After F. velutipes polysaccharides were separated using various methods, including DEAE52-cellulose ion-exchange column chromatography and Sephadex S-200 gel column chromatography, its antioxidant activity was detected. The results showed that F. velutipes polysaccharides did possessed antioxidant activity [31]. At the present, while there have been many reports on the effects of F. velutipes polysaccharides such as anti-virus and anti-oxidation, there are no reports about the use of F. velutipes polysaccharides to treat constipation [4]. In the current study, experimental results showed that the F. velutipes polysaccharides at a moderate dose could significantly improve the contents of MTL, GAS and SP in the constipation of rats and significantly reduce the content of SS, indicating that the F. velutipes polysaccharides at a moderate dose can have a beneficial effect.
The F. velutipes polysaccharides might be mainly composed of glucan, which is mixed by some fractions, such as galactose glycan, mannan, xylan and fucosan. Galactomannan is composed of mannose and galactose and can promote the proliferation of intestinal bacteria, improving the constipation effect [32]. Schoeni et al. used the manna oligosaccharides to feed small broilers, and found a decrease in Staphylococcus aureus in the intestinal tract [33]. The method of PCR-DGGE and with the object of weaned piglets was used to study galactomannan. Galactomannan promotes the propagation of probiotics such as lactobacillus, bifidobacterium and inhibits the growth of S. aureus [34]. Yao et al. learned that galactomannan significantly improved intestinal motility, regulated intestinal function and improved constipation [35]. F. velutipes polysaccharides can be used to treat constipation. This function is due to the reason that polysaccharides in the composition of intestinal bifidobacteria and other probiotics improve the intestinal microflora, bifidobacteria and other probiotics proliferation of lactic acid, acetic acid and other short-chain fatty acids, stimulate peristalsis, increase stool moisture, improve intestinal motility, and improve constipation [35].
The F. velutipes polysaccharides at a moderate dose can improve the GI function and strengthen the GI peristalsis of patients with constipation, thus alleviating constipation and improving patients’ living quality. Therefore, the F. velutipes polysaccharides at a moderate dose group can have the beneficial function of relaxing the bowel with few toxic side effects.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Henan Province University Science and Technology Innovation Team (16IRTSTHN019).
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no potential conflicts interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
References
[1] Editor Committee of National Chinese Medical Manage Bureau “Chinese Herb”, Traditional Chinese Medicine Volume 10. Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1999, 1, 570-571.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Zhang Z.F., Lv G.Y., He W.Q., Shi L.G., Pan H.J., Fan L.F., Effects of extraction methods on the antioxidant activities of polysaccharides obtained from Flammulina velutipes, Carbohyd. Polym., 2013, 98, 1524-1531.10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.07.052Search in Google Scholar
[3] Yang W.J., Pei F., Shi Y., Zhao L.Y., Fang Y., Hu Q.H., Purification, characterization and anti-proliferation activity of polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes, Carbohyd. Polym., 2012, 88(2), 474-480.10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.018Search in Google Scholar
[4] Zhang L.X., Zhao L.J., Study on antioxidant activity of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide, Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 1, 240-243.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Li W.X., Fan M.C., Zhang S.J., Hu X. L., Sun Y.N., Chen X.Y., Discussion and Analysis on Flammulina velutipes Polysaccharides Compositions, Edible Fungi of China, 2015, 34(2), 60-65.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shimotoyodome A., Meguro S., Hase T., Tokimitsu I., Sakata T., Sulfated polysaccharides, but not cellulose, increase colonic mucus in rats with loperamide-induced constipation, Digest Dis Sci, 2001, 46, 1482-1489.10.1023/A:1010644021888Search in Google Scholar
[7] Fernández-Bañares F., Nutritional care of the patient with constipation, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2006, 20, 575-587.10.1016/j.bpg.2005.11.002Search in Google Scholar
[8] Sui N., Tian Z.G., Effect of Zhu yang tong bian decoction on 5-HT and VIP and expression in intestinal tissue of mouse slow transit constipation model, Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 5, 32-36.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Liu Y.J., Cheng X.Y., Zhao G.S., Zhao H.B., Zhang X.Y., Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine for oral treatment of constipation, Asia-Pacific Tradit. Med., 2009, 2, 128-129.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Ning Y.J., Zhang W., Relationship between gastrointestinal hormones and functional constipation, Int. J. Intern. Med., 2009, 7, 399-404.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Yu Q.Y., Liu C.L., Xue L.Q., Jiang W.N., Zhang S.H., Observation by chuncai polysaccharide protein nutrient solution for the treatment of constipation, Journal of Shenyang Medical College, 1996, 1, 38-42.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Li H., Zhang M.L., Zhang Z.F., Ou X.M., Zhou Y., Clinical observation on 45 cases of functional constipation treated by polysaccharide capsule of plantain seed, Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007, 9, 74-75.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Gao X.M., Han W.D., Yu Z.J., Acute toxicity test and mutagenicity evaluation of Avicennia marina aqueous extract, J. Forest. Eng., 2008, 4, 98-99.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Xin L.G., Acute toxicity of fengshigubi oral liquid, China Pharmaceuticals, 2014, 23, 29-30.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Liang Y.J., Xie T.T., Chen L.Y., Sun W.C., Yuan S.G., The stanch bleeding function and the acute toxicity experiment research of the conyzoides produced in Minnan, Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2011, 3(11), 37-38.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Guo J., Zhang X.S., Acute toxicity of Fengdaining capsule mice by intragastric administration, Shaanxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012, 33(9), 1251-1252.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Liang L.L., Xu Y.T., Zhang Y., Cai Y.W., Study on acute toxicity test of Tiaoqixiaoji decoction, Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009, 11(10), 162-163.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Lin Y.L., Chen D., Zeng H.P., Guo K., Liao S.B., Acute toxicity test of lily flakes, Fujian Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 47(1), 24-25.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Wu D.Z., Wang X.H., Zhou J.Y., Yuan J.Y., Cui B., An R., Hu Z.B., Traditional Chinese formula, lubricating gut pill, improves loperamide-induced rat constipation involved in enhance of Cl-secretion across distal colonic epithelium, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2010, 130, 347-353.10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.018Search in Google Scholar
[20] Qian Y., Suo H.Y., Du M.Y., Zhao X., Li J., Li G.J., et al., Preventive effect of Lactobacillus fermentum Lee on activated carbon-induced constipation in mice, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 2015, 9, 272-278.10.3892/etm.2014.2064Search in Google Scholar
[21] Zhao S.P., Gui L., Bian H.L., Zhang Y., Chen Q., Zhang F., A study on the changes and reducibility of substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in the intestinal wall of constipation model rats, Chinese Journal of Difficult and Complicated Cases, 2008, 3, 158-160.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Wang Q., Sun P., Li G.J., Zhu K., Wang C., Zhao X., Inhibitory effects of Dendrobium candidum Wall ex Lindl. on azoxymethane- and dextran sulfate sodium-induced colon carcinogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Oncol. Lett., 2014, 7, 493-498.10.3892/ol.2013.1728Search in Google Scholar
[23] Wang R., Sun P., Zhou Y., Zhao X., Preventive effect of Dendrobium candidum Wall. ex Lindl. on activated carbon-induced constipation in mice, Exp. Ther. Med., 2015, 9, 563-568.10.3892/etm.2014.2119Search in Google Scholar
[24] Pan H.H., Yu X.T., Huang J.G., Xie Y.Z., Research on improving learning memory of Flammulina velutiper polysaccharides in mice, Edible Fungi of China, 2014, 5, 40-42.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Fu M.H., Hong M.D., Study on anti-oxidant activity of the polysaccharide from the fruit body of Flammulina velutipes, Food Research and Development, 2011, 12, 20-22.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Zhang S.J., Wang W.L., Shi X.Q., Gong Z.Q., Cheng A.W., Chen X.Y., Bioactivity and functional food development of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharides, Food and Nutrition in China, 2013, 10, 62-64.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Huang Q., Huang X.M., Zhang P., Ding L., Antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes, Food Research and Development, 2014, 35, 66-69.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Liu, X.Y., Chen L.L., Qiu J.Y., Sun X., Wang W.M., Zhou Q.X., et al., Research progress of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharides, Food and Nutrition in China, 2012, 18, 63-67.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Li W.X., Fan M.C., Zhang S.J., Hu X.L., Sun Y.N., Chen X.Y., Discussion and analysis on Flammulina velutipes polysaccharides compositions, Edible Fungi of China, 2015, 34, 60-65.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Chen G.T., Fu Y.X., Yang W.J., Hu Q.H., Zhao L.Y., Effects of polysaccharides from the base of Flammulina velutipes stipe on growth of murine RAW264.7, B16F10 and L929 cells, Int. J. Biol. Macromo., 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.09010.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.090Search in Google Scholar
[31] Shimotoyodome A., Meguro S., Hase T., Tokimitsu I., Sakata T., et al., Decreased colonic mucus in rats with loperamide-induced constipation, Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part A, 2000, 126, 203-212.10.1016/S1095-6433(00)00194-XSearch in Google Scholar
[32] Hou D.H., Liu Y.G., Zhang L., Li Y.Y., Gu Y.H., Liu L.X., Research Progress in physiological function of Galacto mannan-oligo scessharides, Farm Products Processing, 2016, 10, 67-69.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Schoeni J.L., Wong A.C.L., Inhibition of Campylobacter jejuni colonization in chicks by defined CE bacteria, Appl. Environ. Microbil., 1994, 60, 1191-1197.10.1128/aem.60.4.1191-1197.1994Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Hou Z.P., Zhang P., Zhang J., Li T.J., Huang R.L., Yin Y.L., et al, Effect of galactomannan oligosaccharides on intestinal microglora and bacterial community in weaning pigs, J. Grad. Sch. Chinese Acad. Sci., 2008, 25(3), 413-418.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Yao P.N., Zhao X.F., Wei Y.A., Physiological function test of galactooligosaccharide oligosaccharide on the effect of small intestinal motility in mice, National exchange for the production and application of functional biological products, 2008, 88-90.Search in Google Scholar
© 2018 Xin Xin et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution

