Abstract
In this study, we investigate the production of hypolipidemic agents in the form of Acipimox sustained-release tablets, using a wet pelleting process. The purpose of this research is to reduce the total intake time for patients and to lower the initial dose in such that the adverse reactions could be reduced. This study adopts the single-factor method and orthogonal experiments by using hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC K15M) as the main sustained-release prescription composition. The final prescription is Acipimox 20%, HPMC K15M 26.67%, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose 30%, polyethylene glycol (PEG 6000) 1%, ethyl cellulose 16.6%, lactose 4.67% and magnesium stearate 1%. The dissolution of tablets reached 85.88% in 8 h. The difference in the weight, hardness and friability of the tables met the requirements in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia; to test the stability, a temperature and illumination accelerated test method was used, the results indicate that the Acipimox sustained-release tablets should be sealed and stored in a dark, cool area. A preliminary study on the tablets’ releasing mechanism showed that their release curve fitted the Higuchi model (the formula is Mt/M∞ = 31.137 t1/2–3.605 (R2 = 0.9903)). The Acipimox tablets’ release principle is dominated by the diffusion mechanism.
1 Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is a blood lipid metabolic disorder which can lead to atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, pancreatitis, and other severe complications [1,2]. Acipimox is a derivative of niacin, 4-oxo-5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid, which is a hypolipidemic drug [3,4,5]. Acipimox mainly reduces the generations of triglycerides (TG), very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL) [6,7] by inhibiting the release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue. This drug also has the capacity to increase high density lipoprotein (HDL) generation by inhibiting hepatic lipase and reducing triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) levels in plasma. This plays a role in lowering blood lipids. Acipimox is also capable of reducing the incidence of coronary heart disease by decreasing lipoprotein (a) [LP(a)] level [8,9].
Acipimox was developed by Pfizer Inc. in the United States. In Italy, Acipimox capsules first appeared in the market in 1985 [10]. Currently, there are five registered Acipimox-breed drugs in the Chinese market. These are all tablets or capsules, and none of them are sustained-release formulations.
There are two problems that need to be considered when preparing Acipimox release tablets. Firstly, the elimination half-life of Acipimox is 12 hours, so patients need to take it 2–3 times a day [11,12]. As hypolipidemic agent is frequently used as a long-term or lifelong medication, this high frequency of doses is inconvenient for patients. Therefore, our goal is to reduce the number of doses and improve patient compliance. Secondly, sustained-release tablets can reduce the strong impact (causing side effects like facial flushing) of the first dose and improve the initial patient tolerance [13,14].
In this study, we used sustained-release formulation technology. A single dose was administered once a day, and so it was designed to enable a smooth release of the drug in the gastrointestinal tract and maintain a stable blood concentration.
2 Experimental Procedure
This study investigated the effect of different hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose viscosities on the quality and stability of the tablet, while searching for an excellent prescription process. We found that using the matrix hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) enabled us to prepare an Acipimox sustained-release tablet that can be completely released in 8 hours. Moreover, the tablet’s in vitro level meets FDA (United States Food and Drug Administration) regulations.
Acipimox (Renpu Suzhou Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.); hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC; Weifang Teli Reagent Factory); polyethylene glycol (PEG6000; Jiangsu Province MSC oil chemical plant); carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC; Tianjin Fu Chen Chemical Reagent Factory); ethyl cellulose ethoce (EC; Huainan City Cody Chemical Technology Co.); ethanol (Beijing Jijiyuan Chemical Plant); pharmaceutical-grade lactose (Tianjin Fucheng Chemical Reagent Factory); pharmaceutical-grade magnesium stearate (Tianjin Guangfu Fine Chemical Research Institute); distilled water.
UVmini-1240 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan); T-214 electronic scale (Sartorius (Shanghai) Trading Co. Ltd); GZX-DH202-4-BS-II electrothermal constant temperature drying oven (Shanghai Wan Rui laboratory equipment factory); DP12 Rotary tablet press machine (Shandong Tianqi pharmacy press factory); RC-14DF intelligent dissolution instrument (Tianjin Chuangxing Electronic); GTSONIC-T3 Ultrasonic clean instrument (Jinan Cole Ultrasonic Equipment Co., Ltd.); YD-2 Hardness instrument (Tianjin Chuangxing electronic); CS-2B tablet friability & hardness tester (Tianjin Chuangxing Electronic); SHH-150SD Drug stability test chamber (Chongqing Yongsheng Experimental Instrument Factory ).
2.1 Sustained-release Acipimox tablets preparation method
Each component of the prescription was crushed and sieved (through a #80 mesh sieve).
Each component of the prescription was weighed proportionately, then mixed.
Ethanol (85%) solution was used to moisturize the mix materials, then the wetted material was divided into small particles by a #20 mesh sieve.
The wet particles were dried at 50–60°C for 2 hours.
The particles were sieved again (#18 mesh sieve).
Magnesium stearate 1% was added to the particles and tableting was done following thorough mixing (Figure 1).
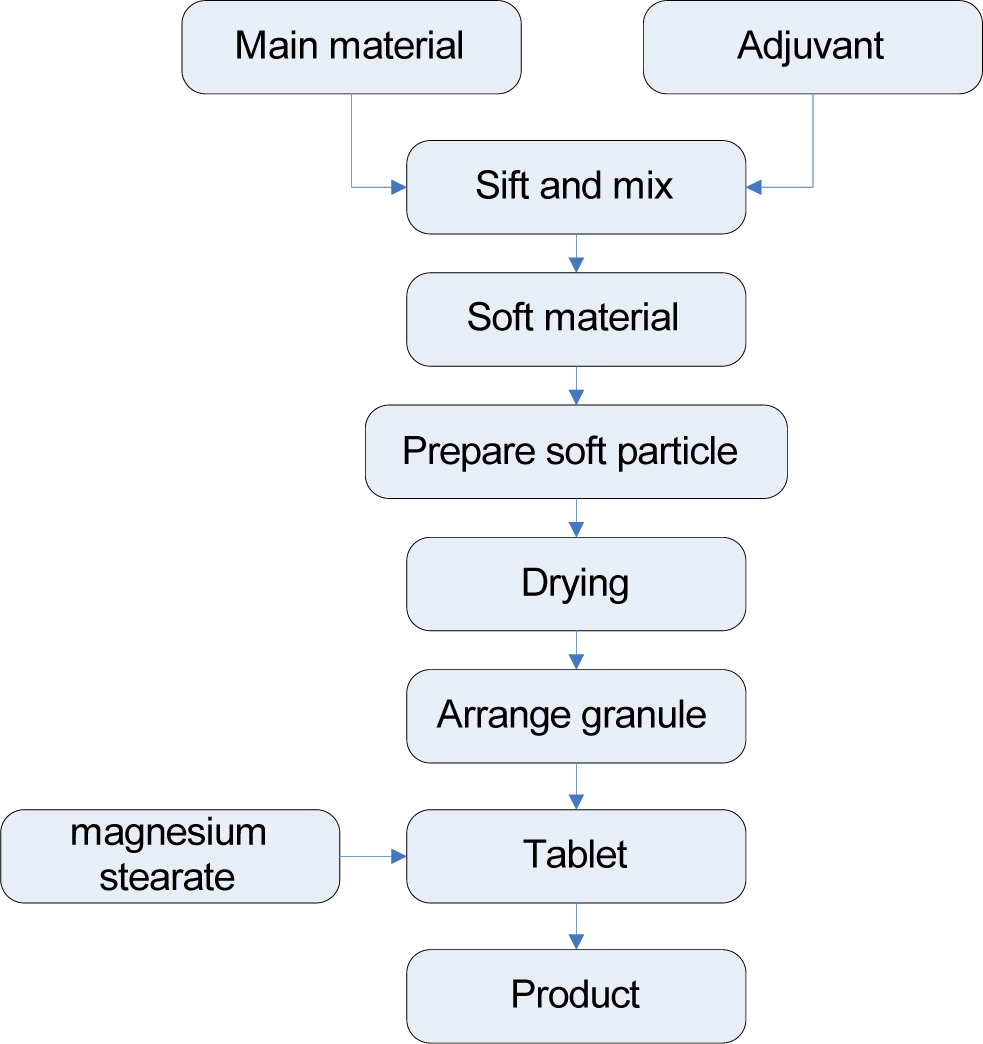
Manufacturing process of Acipimox sustained-release tablets.
2.2 Analytical method
To determine the content of Acipimox, ultraviolet (UV) analysis was applied. 2.1 mg Acipimox was dissolved in 10 mL water; the mother liquid was diluted 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 and 0.6 mL to 10mL by water, the working calibration curve based on Acipimox standard solutions demonstrated strong linearity over the range of 2.1 μg/mL < C < 12.6 μg/ mL. The regression line was represented by y = 11.657x–0.58 (R2 = 0.9996), where y is the concentration of Acipimox (μg/mL) and x is the absorbance at 264 nm.
2.3 Determination of the rate of release
A drug sample was taken in accordance with Chinese Pharmacopoeia for determination of the release rate (Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010, edition two, appendix XC) [15]. The paddle device of the dissolution test method was used. Nine hundred milliliters of water were released at a speed of 100 r/min. According to the second method, 10 mL of solution were taken and filtered at intervals of 1, 2, 4, 8 and 10 hours; then the same volume of water at the same temperature was added at once. The filtrate was diluted and then the concentration (C) was measured by UV spectrophotometry. According to Acipimox’s standard curve, the main ingredients per tablet are 0.03 g with a rate of release of 900×C×10–6/ 0.03. The release was evaluated at 1, 2, 4, 8 and 10 h. Usually, there are at least three dissolution time intervals. Generally, the first interval of the sampling time was 0.5 to 2 hours; at this time, we examined whether the drug had been released in a burst. The second interval was the cumulative release of about 50%; it is indicative of the drug’s characteristics and whether it has been released smoothly. The final interval was the cumulative release of at least 80%.
2.4 Process research
Process research included repeatability tests, Acipimox sustained-release tablet weight variation detection, the hardness test and the friability test.
2.5 Friability test
According to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, if the weight of each tablet is 0.65 g or less, samples should take several tables to reach the total weight of approximately 6.5 g. We used a hair dryer to blow off the powder, weighted the tablets, and placed them in the friability tester. The samples were rotated 100 times at a speed of 25 r/min. The tablets were then taken out. Remaining powder were removed using the same method. After weighting again, the weight loss should not exceed 1%. Broken, cracked and/or crushed tablets should not be detected [15].
2.6 Stability study
The stability study included illumination experiments, heat-resistance test and air tests.
2.7 Data analysis
Data are mean values from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., USA).
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animals use.
3 Results
3.1 Formulation optimization of sustained release Acipimox tablets using orthogonal experiment
In the Acipimox sustained-release tablet formulation, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC K15M) is used as the sustained release matrix; EC, PEG 6000 and CMC are used as the binders. In order to meet the release requirements for sustained-release tablets, the amount of each ingredient in the prescription needs to be studied further. An orthogonal experimental offers a way to qualitatively analyze the correlations between relevant variables at different levels; we can achieve this by designing an orthogonal table and performing statistical analysis. As shown in Table 1, we designed the orthogonal table according to four factors and three levels. The four factors were HPMC K15, EC, PEG 6000 and CMC. We then processed the data of the release rates at 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 8 h and 10 h (Table 2). Finally, K is calculated, which is the average of one certain level with a certain factor; R is the extremum, which is the largest K minus the smallest K (Table 3).
Factors and levels of orthogonal experimental design.
| Level | HPMC(K15) (g) | EC (g) | PEG(6000) (g) | CMC (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.015 | 0.23 |
| 2 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.34 |
| 3 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.075 | 0.45 |
Results and calculations of L9(3)4.
| Test | Release rate(%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPMC (K15)(g) | EC(g) | PEG-6000(g) | CMC(g) | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 8 h | 10 h | |
| 1 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.015 | 0.23 | 27.93 | 46.55 | 83.10 | 87.23 | 88.05 |
| 2 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.34 | 24.95 | 43.41 | 81.71 | 88.13 | 90.15 |
| 3 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.075 | 0.45 | 22.53 | 37.62 | 71.25 | 92.14 | 95.22 |
| 4 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.045 | 0.45 | 28.19 | 49.01 | 78.61 | 87.10 | 90.05 |
| 5 | 0.40 | 0.25 | 0.075 | 0.23 | 23.50 | 44.50 | 80.12 | 86.82 | 87.12 |
| 6 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.015 | 0.34 | 23.48 | 39.89 | 72.82 | 84.74 | 85.62 |
| 7 | 0.50 | 0.16 | 0.075 | 0.34 | 23.68 | 43.99 | 85.14 | 89.13 | 90.05 |
| 8 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.45 | 23.78 | 48.14 | 85.61 | 88.44 | 91.08 |
| 9 | 0.50 | 0.34 | 0.015 | 0.23 | 21.66 | 42.06 | 75.43 | 88.17 | 88.74 |
Results from orthogonal design for the release rate.
| Release time (h) | Level of factor | HPMC(K15) A | EC B | PEG6000 C | CMC D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | K1 | 25.14 | 26.60 | 24.36 | 24.36 |
| K2 | 25.06 | 24.08 | 25.64 | 24.04 | |
| K3 | 23.04 | 22.56 | 23.24 | 24.83 | |
| R | 2.096 | 4.043 | 2.403 | 0.7966 | |
| 2 | K1 | 42.53 | 46.52 | 42.83 | 44.37 |
| K2 | 44.47 | 45.35 | 46.85 | 42.43 | |
| K3 | 44.73 | 39.86 | 42.04 | 44.92 | |
| R | 2.203 | 6.660 | 4.816 | 2.493 | |
| 4 | K1 | 78.69 | 82.28 | 77.12 | 79.55 |
| K2 | 77.18 | 82.48 | 81.98 | 79.89 | |
| K3 | 82.06 | 73.17 | 78.84 | 78.49 | |
| R | 4.876 | 9.313 | 4.860 | 1.400 | |
| 8 | K1 | 89.17 | 87.82 | 86.71 | 87.41 |
| K2 | 86.22 | 87.80 | 87.89 | 87.33 | |
| K3 | 88.58 | 88.35 | 89.36 | 89.23 | |
| R | 2.946 | 0.5533 | 2.650 | 1.893 | |
| 10 | K1 | 91.14 | 89.38 | 87.47 | 87.97 |
| K2 | 87.60 | 89.45 | 90.43 | 88.61 | |
| K3 | 89.96 | 89.86 | 90.80 | 92.12 | |
| R | 3.543 | 0.4766 | 3.326 | 4.147 |
On the basis of univariate analysis, orthogonal experiment design was performed to further optimize the formulation, the results showed that, up to 4 h, B (EC) and C (PEG 6000) had the maximum effect on the release; after 4 hours, the effect of A (HPMC K15) and D (CMC) on the release rate began to grow. In general, for the commercial formulation of Acipimox, the peak of plasma concentration occurs within 2 hours, and the half-life is about 2 hours as well. On the basis of release rate result analysis, the sequence of effects on composite grade to evaluate the release process was: A >D > B > C. The optimum composition was A1D3B2C1, which means HPMC 0.3g, CMC 0.45g, EC 0.25g, PEG 0.015g.
3.2 Effect of different fillers on the rate of release
Based on the results from the orthogonal experimental design, the final optimum formulation when lactose or starch fillers are used can be summarized as follow: Acipimox 20%, HPMC 26.67%, CMC 30%, EC 16.6%, PEG (6000) 1%, fillers 4.67% and magnesium stearate 1%. The test results presented in Figure 2 show that the type of filler used has a significant effect on the release rate of Acipimox. For instance, the release rate is higher with lactose than with starch. However, considering smooth finish, fluidity and hardness, lactose appears to be superior to starch. Nonetheless, at this point of our experiment, the lactose release has not yet reached the requirements for sustained release.
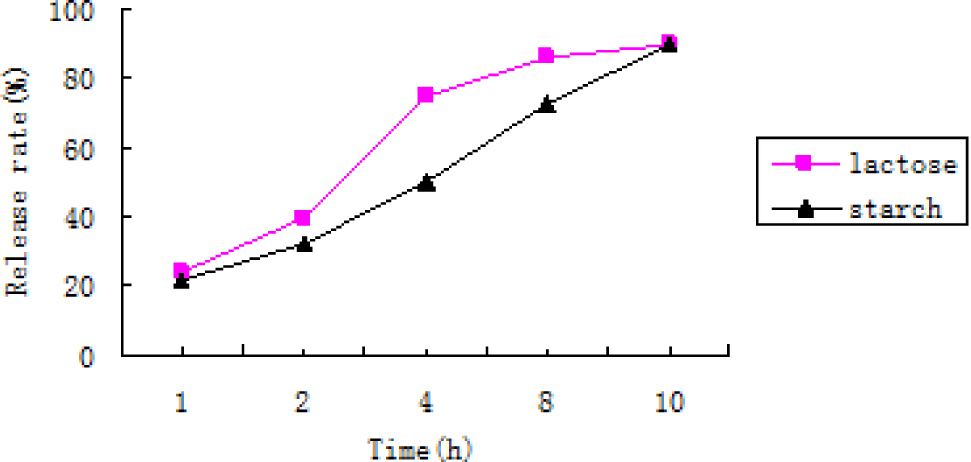
Effect of different fillers on the releasing rate.
3.3 Analysis and inspection of sustained-release Acipimox tablets
3.3.1 Repeatability detection
In the preparation of 1000 sustained-release Acipimox tablets, the prescription composition was as follows: Acipimox, 30g; CMC, 45g; HPMC K15, 40g; PEG 6000, 1.5 g; EC, 24.9 g; magnesium stearate, 1.5 g; lactose, 7.0 g.
Following the above formulation, we prepared three small batches of sustained-release Acipimox tablets and measured the release rates respectively (Figure 3). The release curve clearly tended to be consistent. Therefore, the release effect could meet the design requirements, indicating that the quality of the sustained-release tablets was stable and the process was reproducible.
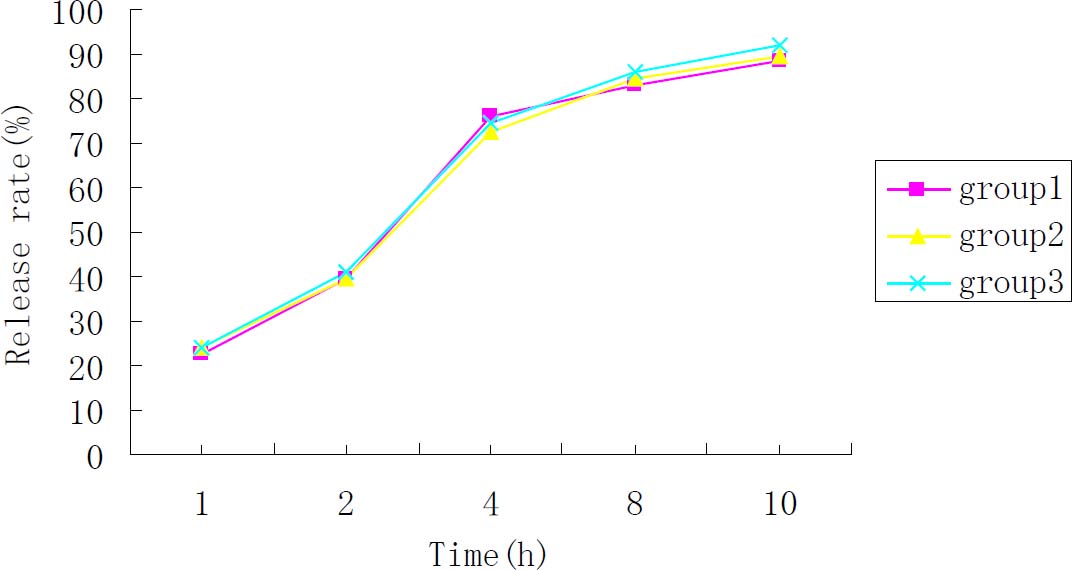
The release rate curve of three batches of Acipimox sustained-release tablets.
3.3.2 Weight variation detection of Acipimox sustained-release tablets
Twenty Acipimox tablets were accurately weighed and these measurements were used to calculate the tablets’ average weight. According to the Pharmacopoeia, when the tablets’ average weight is 0.30 g or less, the weight difference limit is ± 7.5% and the tablet weight variation range is between 0.1396 and 0.1622 g. In our experiment, the range of weight variation was 0.1396–0.1622 g, which is 0.1509 (1–7.5%)≤tablet≤0.1509 (1+7.5%). Only one sustained-release tablet had a weight of 0.1368 g, which is not within the range; the other 19 tablets had weight within the allowed range. Since the overweight tablet did not go beyond the weight of 0.1281–0.1735g, which is 0.1509 (1–2×7.5%)≤tablet≤0.1509 (1+2×75%), the weight difference was considered to comply with the pharmacopoeia.
3.3.3 Hardness test
Twenty Acipimox sustained-release tablets were fixed in the hardness instrument, and the clamping pressure was gradually increased until the sustained-release tablets were broken. The results showed that the hardness values of all 20 tablets met the requirement in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The average hardness is 4.57±0.29 kg.
3.3.4 Friability test
According to the Pharmacopeia [15], the friability test is generally done only once, but if the weight loss exceeds more than 1%, the test should be performed again. The average weight loss determined by three different tests should not exceed 1%, and there should not be any fractured, cracked or crushed tablets.
After blowing off any powder, we placed 44 Acipimox sustained-release tablets (weighing 6.5936 g) in the friability tester. They were turned 100 times and any powder was removed off the surface of the tablets with a hair dryer. At this point, the tablets weighed 6.5372 g. The weight loss, therefore, did not exceed 1%; moreover, there were no broken, cracked or crushed tablets.
3.4 Stability tests
3.4.1 Light-resistance test
We placed the Acipimox sustained-release tablets on a plate under 4500 Lx illumination for 10 days. We took samples on the first, third, fifth and tenth day, and tested their release rates within 10 hours. Our results showed that under 4500 Lx light intensity, the quality of the sample did not change essentially, but the release rate of Acipimox was slightly accelerated; the dissolution of Acipimox sustained-release tablets reached 87.09-87.63% in 8 h during 1-10 days. This indicates that the drug should be stored away from light.
3.4.2 Heat-resistance test
The sustained-release tablets were placed on a plate at 60°C and 80°C for 10 days. The release rate of sample tabletes on the first, third, fifth and tenth day was tested within 10 hours. Our results showed that although there was some increase in the release rate at 60°C, the dissolution of Acipimox sustained-release tablets reached 87.93-89.13% in 8 h during 1-10 days, there was no degradation of tablets, indicating that the tablet is still in compliance. At 80°C, however, the tablet surface turned yellow. Some of the tablets became loose and started breaking down. Thus, this drug should be stored in a relatively cool place.
3.4.3 Air tests
By analogy, we placed the sustained-release tablets on a plate at room temperature for 10 days, and took samples on the first, third, fifth and tenth day. When the release rate was evaluated within 10 hours, the results showed that it was slightly altered under these room temperature conditions. Nevertheless, the tablets still met the quality requirements and showed no degradation products; no significant change was observed in the properties of the sustained-release tablets. The drug should therefore be kept sealed.
3.5 Release mechanism of Acipimox sustained-release tablets
First, we fitted the release data of Acipimox sustained-release tablets (Table 4) using the zero-level model, primary-level model (Table 5) and Higuchi model (Figure 4). The tablets’ release curve in the zero-level and primary-level models did not fit very well, indicating that it does not follow these models.
Release kinetics of Acipimox sustained-release tablets.
| Time | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | 7 h | 8 h | 9 h | 10 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release rate (%) | 24.17 | 40.85 | 53.89 | 80.99 | 85.88 | 88.61 | 91.79 |
The release data are fitted using the zero level, primary level.
| Model categories | Regression equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-level model | C = 2.4047t + 8.4577 | 0.9563 |
| Primary level model | lnC = 0.1299t + 2.2641 | 0.8716 |
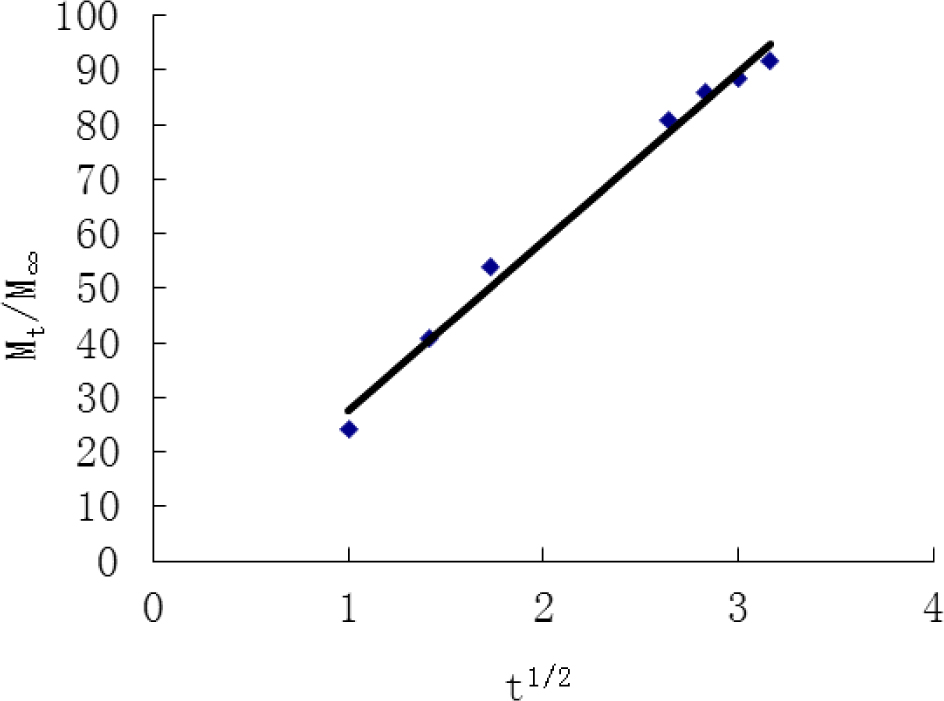
Release data Higuchi model fitting diagram.
The Higuchi model expression is: Mt/M∞=kt1/2
Where Mt is the amount of drug released at time t; M∞ is the maximum amount of drug released; t is the time and kis the release rate constant.
With the regression equation: Mt/M∞ = 31.137 t1/2–3.605 (R2 = 0.9903), the release profile of the Acipimox tablets showed a better fit to the Higuchi model, which is based mainly on a diffusion mechanism [16]. The data still needs to be fitted in order to determine if there are any corrosion mechanisms involved.
The Ritger-Peppas model expression is: Mt/M∞=ktn
With the regression equation: log(Mt/M∞) = 0.568log(t) + 1.4182 (R2 = 0.9863), the results did not fit the Ritger– Peppas model (Figure 5) as well as the Higuchi model.
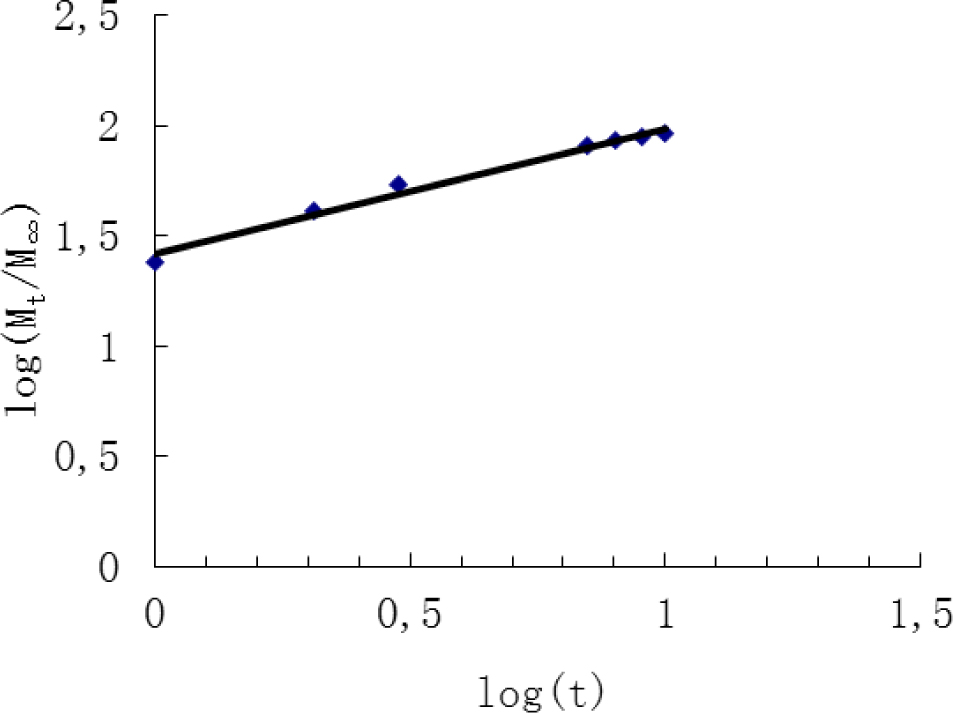
Release data Ritger-Peppas model fitting diagram.
The release principles of sustained-release tablets are basically diffusion mechanism, dissolution mechanism, and corroding mechanism. The releasing process data can fit the curves of different equations such as the zero-level model, primary-level model, and Higuchi model. The ingredients of the Acipimox sustained-release tablets are released at a non-constant speed over time, during which the amount of initial release is large and the amount released later is less. The “peak/valley” fluctuations are smaller; a relatively stable plasma concentration, which provides the best treatment, can be achieved. With the Higuchi model regression equation: Mt/M∞ = 31.137 t1/2–3.605 (R2=0.9903), the release profile of the Acipimox tablets has shown to fit better with the Higuchi model. We conclude that the release process of the Acipimox tablets is mainly dominated by the diffusion mechanism.
4 Conclusions
Using HPMC K15M as the sustained release matrix and EC, PEG 6000 and CMC as the binders, we are able to prepare Acipimox in the form of sustained-release tablets; its releasing process takes less than 10 hours. The tablet release curve has shown to fit better with the Higuchi model, which is based mainly on the diffusion mechanism. The tablet release behavior meets the design requirements; the drug delivery systems are theoretically and practically valuable. In this study, we have showed that producing Acipimox tablets via wet granulation is feasible, cost-effective and reproducible, and that the tablets meet the FDA standard.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China #1 under Grant number 11475020; the National Natural Science Foundation of China #2 under Grant number 8151114029; and Building virtual teaching and researching team to enhance teaching quality and project #3 under Grant number PXM2016_014209_000023. Chaoyang District collaborative innovation project # 4 under Grant number 2016-8.
Disclosure statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Eaton, Charles B., Hyperlipidemia, Primary Care, 2005, 32(4),1027–1055.10.1016/j.pop.2005.09.002Search in Google Scholar
[2] Hsu J. H., Chien I. C., Lin C. H., Increased risk of hyperlipidemia in patients with bipolar disorder: a population-based study, General Hospital Psychiatry, 2015, 37(4), 294–298.10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2015.04.003Search in Google Scholar
[3] Yan F. F., Tian L., Xiao Z., Li, S.Y., Fu, M.D., Tian H.M., Comparison of the efficacy of fenofibrate and acipimox on plasma lipoprotein subclasses distribution in the Chinese population with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertriglyceridemia, Clinical Lipidology, 2014, 9(2), 171–177.10.2217/clp.14.11Search in Google Scholar
[4] Xing J. N., Zhang Y. P., Han S. J., Li, B., Synthesis, crystal structures, and characterization of two new complexes constructed from Acipimox ligands: two three-dimensional networks formed via hydrogen bonding, Inorganic Metals - Synthesis and Reactions in Organic and Nano-Metals Chemistry, 2016, 46(3), 409–413.10.1080/15533174.2015.1031046Search in Google Scholar
[5] Nellemann B., Søndergaard E., Jensen J., Pedersen S. B., Jessen N., Nielsen S., Kinetics and utilization of lipid sources during acute exercise and acipimox, American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2014, 307(2), E199–208.10.1152/ajpendo.00043.2014Search in Google Scholar
[6] Seed M., O’Connorb B., Perombelonc N., O’Donnell M., Reaveley D., Knight BL., The effect of nicotinic acid and acipimox on lipoprotein(a) concentration and turnover, Atherosclerosis, 1993, 101, 61–68.10.1016/0021-9150(93)90102-ZSearch in Google Scholar
[7] Franceschini G., Bernini E., Michelagnoli S., Stefano B., Viola V., Remo F., Cesare R.S., Lipoprotein changes and increased affinity of LDL for their receptors after acipimox treatment in hypertriglyceridemia, Atherosclerosis, 1990, 81(1), 41-49.10.1016/0021-9150(90)90057-PSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Ball M.J., Vella M., Rechlass J.P.D., Acipimox in the treatment of patients with hyperlipidaemia: A double blind trial, European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1986, 31, 201-204.10.1007/BF00606659Search in Google Scholar
[9] Gianantonio S., Aldo G., Alfredo A., Gemfibrozil and mediterranean diet for patients with high plasma levels of lipoprotein [Lp(a)] and cholesterol—Pilot study, Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 1995, 9,347–350.10.1007/BF00878680Search in Google Scholar
[10] Jin L.R., Chen W.C., Hu W.G., Bao Y.Q., The lipid-lowering effect of acyclovir, Chinese Journal of New Drugs and Clinical Remedies, 1999, 12(5), 297–298.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Efthymiopoulos C., Strolin B. M., Poggesi I., Ruff F., Basileo G., Musatti L., Pharmacokinetics of acipimox and of its N-deoxy metabolite following single and repeated oral administration of a sustained release formulation to healthy volunteers, Therapie, 1993, 48 (1), 23-26.10.1016/0378-5173(93)90399-ZSearch in Google Scholar
[12] Yang X.G., Nie S.F., Bai H.J., Zhang G.J., Pan, W.S., The pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of acipimox sustained-release tablets after a single and multiple oral administration in healthy dogs, Acta pharmaceutica Sinica, 2005, 40(5), 457–461.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Efthymiopoulos C., Strolin B.M., Ruff F., Advenier C., Musatti L., Bioavailability of a sustained release formulation of acipimox, following a single dose in healthy volunteers in fasting and fed conditions, European Journal of Pharmacology, 1990, 183(2), 391–391.10.1016/0014-2999(90)93269-VSearch in Google Scholar
[14] Pontiroli A.E., Fattort B., Pozza G., Pianezzola E., Benedetti M. S., Musatti L., Acipimox-induced facial skin flush: Frequency, thermographic evaluation and relationship to plasma acipimox level, European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 1992, 43,145–148.10.1007/BF01740661Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] The Pharmacopeia Committee of China. Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2010 version appendix 201). Beijing (BJ): Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Zhang J.W., Zhong D.F., BI D.Z., The release-division method: a novel in vitro pharmacokinetic evaluation method for the sustained release dosage forms with a release profile characterized by the Higuchi equation, Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, 2001, 18(5), 324–326.Search in Google Scholar
© 2018 Wanying Liu et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- The effect of CuO modification for a TiO2 nanotube confined CeO2 catalyst on the catalytic combustion of butane
- The preparation and antibacterial activity of cellulose/ZnO composite: a review
- Linde Type A and nano magnetite/NaA zeolites: cytotoxicity and doxorubicin loading efficiency
- Performance and thermal decomposition analysis of foaming agent NPL-10 for use in heavy oil recovery by steam injection
- Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, UV, 1H and 13C NMR) insights, electronic profiling and DFT computations on ({(E)-[3-(1H-imidazol-1-yl)-1-phenylpropylidene] amino}oxy)(4-nitrophenyl)methanone, an imidazole-bearing anti-Candida agent
- A Simplistic Preliminary Assessment of Ginstling-Brounstein Model for Solid Spherical Particles in the Context of a Diffusion-Controlled Synthesis
- M-Polynomials And Topological Indices Of Zigzag And Rhombic Benzenoid Systems
- Photochemical Transformation of some 3-benzyloxy-2-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-4Hchromen-4-ones: A Remote Substituent Effect
- Dynamic Changes of Secondary Metabolites and Antioxidant Activity of Ligustrum lucidum During Fruit Growth
- Studies on the flammability of polypropylene/ammonium polyphosphate and montmorillonite by using the cone calorimeter test
- DSC, FT-IR, NIR, NIR-PCA and NIR-ANOVA for determination of chemical stability of diuretic drugs: impact of excipients
- Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effects of Methanolic Extracts of Zilla spinosa and Hammada elegans Against Carbon Tetrachlorideinduced Hepatotoxicity in Rats
- Prunus cerasifera Ehrh. fabricated ZnO nano falcates and its photocatalytic and dose dependent in vitro bio-activity
- Organic biocides hosted in layered double hydroxides: enhancing antimicrobial activity
- Experimental study on the regulation of the cholinergic pathway in renal macrophages by microRNA-132 to alleviate inflammatory response
- Synthesis, characterization, in-vitro antimicrobial properties, molecular docking and DFT studies of 3-{(E)-[(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)imino]methyl} naphthalen-2-ol and Heteroleptic Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) complexes
- M-Polynomials and Topological Indices of Dominating David Derived Networks
- Human Health Risk Assessment of Trace Metals in Surface Water Due to Leachate from the Municipal Dumpsite by Pollution Index: A Case Study from Ndawuse River, Abuja, Nigeria
- Analysis of Bowel Diseases from Blood Serum by Autofluorescence and Atomic Force Microscopy Techniques
- Hydrographic parameters and distribution of dissolved Cu, Ni, Zn and nutrients near Jeddah desalination plant
- Relationships between diatoms and environmental variables in industrial water biotopes of Trzuskawica S.A. (Poland)
- Optimum Conversion of Major Ginsenoside Rb1 to Minor Ginsenoside Rg3(S) by Pulsed Electric Field-Assisted Acid Hydrolysis Treatment
- Antioxidant, Anti-microbial Properties and Chemical Composition of Cumin Essential Oils Extracted by Three Methods
- Regulatory mechanism of ulinastatin on autophagy of macrophages and renal tubular epithelial cells
- Investigation of the sustained-release mechanism of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose skeleton type Acipimox tablets
- Bio-accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Grey Mangrove (Avicennia marina) along Arabian Gulf, Saudi Coast
- Dynamic Change of Secondary Metabolites and spectrum-effect relationship of Malus halliana Koehne flowers during blooming
- Lipids constituents from Gardenia aqualla Stapf & Hutch
- Effect of using microwaves for catalysts preparation on the catalytic acetalization of glycerol with furfural to obtain fuel additives
- Effect of Humic Acid on the Degradation of Methylene Blue by Peroxymonosulfate
- Serum containing drugs of Gua Lou Xie Bai decoction (GLXB-D) can inhibit TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in A549 Cells
- Antiulcer Activity of Different Extracts of Anvillea garcinii and Isolation of Two New Secondary Metabolites
- Analysis of Metabolites in Cabernet Sauvignon and Shiraz Dry Red Wines from Shanxi by 1H NMR Spectroscopy Combined with Pattern Recognition Analysis
- Can water temperature impact litter decomposition under pollution of copper and zinc mixture
- Released from ZrO2/SiO2 coating resveratrol inhibits senescence and oxidative stress of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASC)
- Validated thin-layer chromatographic method for alternative and simultaneous determination of two anti-gout agents in their fixed dose combinations
- Fast removal of pollutants from vehicle emissions during cold-start stage
- Review Article
- Catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts obtained by copolymerization of metal-containing 2-(acetoacetoxy)ethyl methacrylate
- Antibiotic Residue in the Aquatic Environment: Status in Africa
- Regular Articles
- Mercury fractionation in gypsum using temperature desorption and mass spectrometric detection
- Phytosynthetic Ag doped ZnO nanoparticles: Semiconducting green remediators
- Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by SMAD4 Activation in Invasive Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas
- Physicochemical properties of stabilized sewage sludge admixtures by modified steel slag
- In Vitro Cytotoxic and Antiproliferative Activity of Cydonia oblonga flower petals, leaf and fruit pellet ethanolic extracts. Docking simulation of the active flavonoids on anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2
- Synthesis and Characterization of Pd exchanged MMT Clay for Mizoroki-Heck Reaction
- A new selective, and sensitive method for the determination of lixivaptan, a vasopressin 2 (V2)-receptor antagonist, in mouse plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study
- Anti-EGFL7 antibodies inhibit rat prolactinoma MMQ cells proliferation and PRL secretion
- Density functional theory calculations, vibration spectral analysis and molecular docking of the antimicrobial agent 6-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethyl)-5-ethyl-2-{[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl] sulfanyl}pyrimidin-4(3H)-one
- Effect of Nano Zeolite on the Transformation of Cadmium Speciation and Its Uptake by Tobacco in Cadmium-contaminated Soil
- Effects and Mechanisms of Jinniu Capsule on Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- Calculating the Degree-based Topological Indices of Dendrimers
- Efficient optimization and mineralization of UV absorbers: A comparative investigation with Fenton and UV/H2O2
- Metabolites of Tryptophane and Phenylalanine as Markers of Small Bowel Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- Adsorption and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water through the aggregation of graphene oxide
- The role of NR2C2 in the prolactinomas
- Chromium removal from industrial wastewater using Phyllostachys pubescens biomass loaded Cu-S nanospheres
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Preparation of Calcium Fluoride using Phosphogypsum by Orthogonal Experiment
- The mechanism of antibacterial activity of corylifolinin against three clinical bacteria from Psoralen corylifolia L
- 2-formyl-3,6-bis(hydroxymethyl)phenyl benzoate in Electrochemical Dry Cell
- Electro-photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin using calcium titanate
- Effect of Malus halliana Koehne Polysaccharides on Functional Constipation
- Structural Properties and Nonlinear Optical Responses of Halogenated Compounds: A DFT Investigation on Molecular Modelling
- DMFDMA catalyzed synthesis of 2-((Dimethylamino)methylene)-3,4-dihydro-9-arylacridin-1(2H)-ones and their derivatives: in-vitro antifungal, antibacterial and antioxidant evaluations
- Production of Methanol as a Fuel Energy from CO2 Present in Polluted Seawater - A Photocatalytic Outlook
- Study of different extraction methods on finger print and fatty acid of raw beef fat using fourier transform infrared and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Determination of trace fluoroquinolones in water solutions and in medicinal preparations by conventional and synchronous fluorescence spectrometry
- Extraction and determination of flavonoids in Carthamus tinctorius
- Therapeutic Application of Zinc and Vanadium Complexes against Diabetes Mellitus a Coronary Disease: A review
- Study of calcined eggshell as potential catalyst for biodiesel formation using used cooking oil
- Manganese oxalates - structure-based Insights
- Topological Indices of H-Naphtalenic Nanosheet
- Long-Term Dissolution of Glass Fibers in Water Described by Dissolving Cylinder Zero-Order Kinetic Model: Mass Loss and Radius Reduction
- Topological study of the para-line graphs of certain pentacene via topological indices
- A brief insight into the prediction of water vapor transmissibility in highly impermeable hybrid nanocomposites based on bromobutyl/epichlorohydrin rubber blends
- Comparative sulfite assay by voltammetry using Pt electrodes, photometry and titrimetry: Application to cider, vinegar and sugar analysis
- MicroRNA delivery mediated by PEGylated polyethylenimine for prostate cancer therapy
- Reversible Fluorescent Turn-on Sensors for Fe3+ based on a Receptor Composed of Tri-oxygen Atoms of Amide Groups in Water
- Sonocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution using Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under mechanical agitation
- Hydrotalcite Anchored Ruthenium Catalyst for CO2 Hydrogenation Reaction
- Production and Analysis of Recycled Ammonium Perrhenate from CMSX-4 superalloys
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants
- Survey of content of cadmium, calcium, chromium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, manganese, mercury, sodium and zinc in chamomile and green tea leaves by electrothermal or flame atomizer atomic absorption spectrometry
- Biogas digestate – benefits and risks for soil fertility and crop quality – an evaluation of grain maize response
- A numerical analysis of heat transfer in a cross-current heat exchanger with controlled and newly designed air flows
- Freshwater green macroalgae as a biosorbent of Cr(III) ions
- The main influencing factors of soil mechanical characteristics of the gravity erosion environment in the dry-hot valley of Jinsha river
- Free amino acids in Viola tricolor in relation to different habitat conditions
- The influence of filler amount on selected properties of new experimental resin dental composite
- Effect of poultry wastewater irrigation on nitrogen, phosphorus and carbon contents in farmland soil
- Response of spring wheat to NPK and S fertilization. The content and uptake of macronutrients and the value of ionic ratios
- The Effect of Macroalgal Extracts and Near Infrared Radiation on Germination of Soybean Seedlings: Preliminary Research Results
- Content of Zn, Cd and Pb in purple moor-grass in soils heavily contaminated with heavy metals around a zinc and lead ore tailing landfill
- Topical Issue on Research for Natural Bioactive Products
- Synthesis of (±)-3,4-dimethoxybenzyl-4-methyloctanoate as a novel internal standard for capsinoid determination by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS(QTOF)
- Repellent activity of monoterpenoid esters with neurotransmitter amino acids against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti
- Effect of Flammulina velutipes (golden needle mushroom, eno-kitake) polysaccharides on constipation
- Bioassay-directed fractionation of a blood coagulation factor Xa inhibitor, betulinic acid from Lycopus lucidus
- Antifungal and repellent activities of the essential oils from three aromatic herbs from western Himalaya
- Chemical composition and microbiological evaluation of essential oil from Hyssopus officinalis L. with white and pink flowers
- Bioassay-guided isolation and identification of Aedes aegypti larvicidal and biting deterrent compounds from Veratrum lobelianum
- α-Terpineol, a natural monoterpene: A review of its biological properties
- Utility of essential oils for development of host-based lures for Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), vector of laurel wilt
- Phenolic composition and antioxidant potential of different organs of Kazakh Crataegus almaatensis Pojark: A comparison with the European Crataegus oxyacantha L. flowers
- Isolation of eudesmane type sesquiterpene ketone from Prangos heyniae H.Duman & M.F.Watson essential oil and mosquitocidal activity of the essential oils
- Comparative analysis of the polyphenols profiles and the antioxidant and cytotoxicity properties of various blue honeysuckle varieties
- Special Issue on ICCESEN 2017
- Modelling world energy security data from multinomial distribution by generalized linear model under different cumulative link functions
- Pine Cone and Boron Compounds Effect as Reinforcement on Mechanical and Flammability Properties of Polyester Composites
- Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Prediction of SNR Effected by Probe Properties on Ultrasonic Inspection of Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments
- Calculation and 3D analyses of ERR in the band crack front contained in a rectangular plate made of multilayered material
- Improvement of fuel properties of biodiesel with bioadditive ethyl levulinate
- Properties of AlSi9Cu3 metal matrix micro and nano composites produced via stir casting
- Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Ag Doped TiO2 Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning Process
- Modeling of Total Phenolic contents in Various Tea samples by Experimental Design Methods
- Nickel doping effect on the structural and optical properties of indium sulfide thin films by SILAR
- The effect mechanism of Ginnalin A as a homeopathic agent on various cancer cell lines
- Excitation functions of proton induced reactions of some radioisotopes used in medicine
- Oxide ionic conductivity and microstructures of Pr and Sm co-doped CeO2-based systems
- Rapid Synthesis of Metallic Reinforced in Situ Intermetallic Composites in Ti-Al-Nb System via Resistive Sintering
- Oxidation Behavior of NiCr/YSZ Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs)
- Clustering Analysis of Normal Strength Concretes Produced with Different Aggregate Types
- Magnetic Nano-Sized Solid Acid Catalyst Bearing Sulfonic Acid Groups for Biodiesel Synthesis
- The biological activities of Arabis alpina L. subsp. brevifolia (DC.) Cullen against food pathogens
- Humidity properties of Schiff base polymers
- Free Vibration Analysis of Fiber Metal Laminated Straight Beam
- Comparative study of in vitro antioxidant, acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) collected during different growth stages
- Isothermal Oxidation Behavior of Gadolinium Zirconate (Gd2Zr2O7) Thermal Barrier Coatings (TBCs) produced by Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition (EB-PVD) technique
- Optimization of Adsorption Parameters for Ultra-Fine Calcite Using a Box-Behnken Experimental Design
- The Microstructural Investigation of Vermiculite-Infiltrated Electron Beam Physical Vapor Deposition Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Modelling Porosity Permeability of Ceramic Tiles using Fuzzy Taguchi Method
- Experimental and theoretical study of a novel naphthoquinone Schiff base
- Physicochemical properties of heat treated sille stone for ceramic industry
- Sand Dune Characterization for Preparing Metallurgical Grade Silicon
- Catalytic Applications of Large Pore Sulfonic Acid-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica for Esterification
- One-photon Absorption Characterizations, Dipole Polarizabilities and Second Hyperpolarizabilities of Chlorophyll a and Crocin
- The Optical and Crystallite Characterization of Bilayer TiO2 Films Coated on Different ITO layers
- Topical Issue on Bond Activation
- Metal-mediated reactions towards the synthesis of a novel deaminolysed bisurea, dicarbamolyamine
- The structure of ortho-(trifluoromethyl)phenol in comparison to its homologues – A combined experimental and theoretical study
- Heterogeneous catalysis with encapsulated haem and other synthetic porphyrins: Harnessing the power of porphyrins for oxidation reactions
- Recent Advances on Mechanistic Studies on C–H Activation Catalyzed by Base Metals
- Reactions of the organoplatinum complex [Pt(cod) (neoSi)Cl] (neoSi = trimethylsilylmethyl) with the non-coordinating anions SbF6– and BPh4–
- Erratum
- Investigation on Two Compounds of O, O’-dithiophosphate Derivatives as Corrosion Inhibitors for Q235 Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Solution

