Abstract
This study systematically examines the behavior of multi-stacked long Josephson junctions (multi-sLJJs) under various magnetic inductances and a variety of drives. To investigate the localized modes in the multi-sLJJs, the tripled sine-Gordon equation (sGE) with a phase shift formation recognized as 0-
1 Introduction
The Josephson effect is a fundamental concept in superconductivity, which Josephson confirmed both theoretically and experimentally in 1964 [1]. The Josephson junction, which involves two weakly interacting superconductors separated by a thin insulator, explains this phenomenon. This phenomenon reveals that a current can be induced even in the absence of any voltage change due to the phase variation of the wave functions of the two superconductors: the dc Josephson relation, which is proportional to the sinusoidal function of the phase difference between the electrodes, and the ac Josephson relation. It relates the time derivative of the phase difference to the voltage across the barrier, which have been demonstrated by Josephson [1]. The Josephson junctions (JJs) have promising applications, such as in the development of superconducting meta-materials and quantum information technologies [2–6].
The stacked long Josephson junctions (sLJJs) are currently generating significant interest where one junction is positioned directly above the other with a sufficiently thin isolating layer linked to the London penetration depth [7]. It is important to note that the coupling between junctions is uniform in the system. Each junction has one outermost terminal and an additional terminal that connects to another junction. However, it has been observed that such uniformity is disrupted in the case of substantial stacks [8]. Experimental evidence has shown that the most effective way to couple sLJJs is by stacking them vertically. The Josephson vortices moving in adjacent junctions interact with each other through their screening currents flowing in a thin superconducting layer between the junctions. These interactions can be observed in the current–voltage characteristics [9]. Furthermore, two dynamic regimes characterized by different soliton propagation velocities have been found in twofold stacks [10].
Multi-sLJJs represent a fascinating physical system where the nonlinearity and the interaction between junctions play a crucial role and reveal interesting features in the field of superconductivity. Compared to single JJs, multi-sLJJs have the potential to produce larger output results with a relatively compact width depending on the extent of combined junctions observed during experiments [10]. They also offer an opportunity to investigate physical outcomes that do not arise in single LJJs [11]. Coupling the junctions has been shown to improve the performance of superconducting machines, particularly for the storage and communication of data [12]. Moreover, it has been observed that numerous properties of the LJJs cannot be determined without considering the stack configuration, which includes the investigation of certain dynamical changes such as the quantum and classical dynamics, as well as the chaotic behavior of solitons [13–16].
Multi-sLJJs hold great promise for a wide range of applications in various fields, such as superconducting electronics, quantum computing, spin current control, and high-sensitivity terahertz electromagnetic wave detection. These applications have been demonstrated in various studies, e.g., [17–21]. Moreover, multi-sLJJs exhibit non-trivial properties in both low-
2 The governing model
Several models have been employed to examine multi-stacked junctions experimentally using various models [26]. For example, Mineev et al. [27] first explored the fluxon dynamics in inductively sLJJs with multiple layers theoretically. In addition, double junctions have been utilized in single stacks to fabricate high-
In Eq. (1),
The investigation of integrating the sGE complexity has a comprehensive variety of physical and mathematical utilizations in LJJs [2,29], e.g., an ultra-short vibration transmission in a resonant medium, dynamics in weak ferromagnets [30], the dynamics of solitons and electro-acoustic interconnections in ferroelectric crystals [31], and quantum field theory of solitons [32]. Furthermore, the sGE also has very remarkable applications in many areas, in particular, the transport of information, the impact of solitary waves in the damped driven sG system [33], and continuous breather excitations, phase-pulling, and space-time complexity in an AC-driven sGE [34]. Similarly, coupled sGEs have been widely studied previously for different couplings to study a variety of physical phenomena [35], in particular, for investigations of non-equilibrium phenomena in superconductors, including voltage as well as phase-locking, and for demonstrations of superconducting devices in sLJJs [36].
The phase shift considered in Eq. (1)
was first proposed by Bulaevskii et al. [37] where a non-trivial ground state was realized by an unconfined fractional fluxon generation. It was also proposed that phase shift
where
The structure of the article is as follows: Section 3 presents the computation of the nonlinear amplitude equations for investigating defect modes in multi-layered LJJs analytically. This section involves the analytical solution of the tripled sGE under small-scale integration with parametric AC drives. Furthermore, we examine coupling without drives by utilizing an asymptotic expansion combined with multiple scale analysis. In Section 4, we apply a similar analytical approach as in Section 3, but focusing on strong coupling. Section 5 compares the derived approximate amplitude equations with the corresponding numerical simulations of Eq. (1). Finally, Section 6 provides a summary and conclusion of our study with a future work.
3 Weakly coupled multi-sLJJs
This section employs analytical techniques to investigate multi-layered LJJs using Eq. (1) under the influence of magnetic inductance with a phase shift. We restrict our analysis to the state where the system’s natural frequency is nearly identical to the driving frequency, i.e.,
3.1 Undriven multi-sLJJs
When
Introducing the asymptotic expansions
For simplicity, we consider
Linearizing the above equation by
where
where
It has been demonstrated that the system becomes unstable for
In order to perform the stability analysis of the model under consideration subject to the additional phase shift given in Eq. (2), one needs to consider the static version of the sGE. It is straightforward to show that the given model admits two static solutions, namely
To proceed further, we insert the stability ansatz
A uniform solution
For the uniform
Using the known functions
In order to obtain bounded solutions for
From Eq. (13), one can see that the left hand side is the second order differential operator which is self-orthogonal. The Fredholm theorem states that the necessary and sufficient conditions for Eq. (13) to have a bounded solution if the right-hand side be orthogonal to the complete system of linearly independent solutions of the corresponding homogeneous equation. Hence, we conclude that the above system has a bounded solution if and only if
Applying the above condition, we obtain
It should be noted that our focus is to find the localized modes for the amplitude
Using the known values of
where
The relationships mentioned above comprise two subharmonics. We obtain equations for the first harmonics by separating components for each harmonic
The solvability condition for the above equation is
where
For high harmonic oscillations, we consider the conditions
which gives the solvability condition as follows:
Equations (19) and (20) give same result as obtained at
We consider the relations for
where the values of
By combining and rescaling each of the solvability conditions, we obtain the amplitude equations as follows:
The synchronized oscillations can be observed in the tripled amplitude equations of multi-sLJJs with weak coupling. The gradual decrease in the amplitudes of oscillations in Eq. (23) without drives is caused by the numerical value
3.2 AC-driven multi-sLJJs
In this section, we focus on Eq. (1) with a direct AC drive where
The ground state for the aforementioned equations can be calculated using methods similar to those used in the Section 3.1 and is comparable to that found at Section 3.1. For simplicity and brevity, we limit our analysis to the solvability conditions derived from the hierarchy of equations at different order of
wherein the numerical section contains the numerical values indicated in the aforementioned solvability conditions.
Combining Eqs. (25)–(27), we obtain
In the occurrence of a direct AC drive, the amplitude equations (Eq. (28)) indicate that the applied drive with an amplitude of
3.3 Parametrically driven multi-sLJJs
Here, we examine multi-sLJJs with parametric driven. Applying the previous scaling to the considered model, we obtain
We restrict our analysis to the solvability conditions derived from the series of equations, without investigating into the details of the calculations. It is important to note that the conclusions drawn in Section 3.1 remain unchanged till
The numerical values can be found in the corresponding section dedicated to numerical analysis.
Combining Eqs. (30)–(32), we obtain
In the case of applying a parametric drive, the effect of driving in Eq. (33) is relatively smaller, as the term
4 Strongly coupled multi-sLJJs
In this part, we examine the dynamics of multi-sLJJs when
4.1 Undriven multi-sLJJs
Here, we consider multi-sLJJs governed by Eq. (1) without drives as when
As stated in Section 3.1, we establish a similar conclusion at
To normalize the above equation, we assume that
and
The above two assumptions (Eqs. (36) and (37)) have the same physical behavior. For simplicity and exactness, we consider Eq. (36) for odd and even parity and obtain
Consider ansatz
with
Express the solutions for the ground state by assuming either an odd or even parity as follows:
where
with
The equations can be written as
By applying the condition stated in Eq. (14) to obtain solution of
By Eq. (48), we find results similar to that as
Here, we obtain the solvability condition for even parity as
and for odd parity, we have
The numerical values are presented in Section 5.
For continuous spectrum, we take
Using assumption considered in Eq. (36), it becomes
Equation (53) gives solvability condition as follows:
Substituting the above values in Eq. (53), we can infer that
The solvability condition with respect to even parity is
The solvability condition with respect to odd parity is
Combining Eqs. (50) and (56) for the even parity, we obtain
Similarly, combining Eqs. (51) and (57) for the odd parity, we obtain
We assumed both odd and even parity to analyze the multi-sLJJs in the presence of strong coupling. In order to calculate the derived amplitude equations for both parities, it is assumed that all of the aforementioned situations will exhibit the similar physical behavior and synchronized oscillations. It is important to highlight that because of its dynamical behavior, we will only focus on the amplitudes obtained for even parity in the Section 5. When there are no drives, the resulting amplitude (Eq. (58)) provides the synchronized oscillation for multi-sLJJs that experience exponential decay due to the inherent damping effect in the system.
4.2 AC-driven multi-sLJJs
In this section, we examine multi-sLJJs using Eq. (1) when
For even parity,
Likewise, for odd parity,
Combining the Eqs. (61)–(63) for the even parity and using the original scaling, we obtain the amplitude equation as follows:
For odd parity, we combine Eqs. (64)–(66) and obtain
When a direct AC drive is applied, the nonlinear amplitudes experience fast oscillations because of the driving effect. It is anticipated that in multi-sLJJs, an external drive will cause oscillations in the breathing mode, with the phase shift being determined by Eq. (67).
4.3 Multi-sLJJs subjected to parametric driving
In this section, we examine multi-sLJJs using Eq. (1) with parametric drive and strong coupling. Applying the same scaling as considered in Section 4.2, Eq. (1) becomes
Similar to previous section, the amplitude equations for even parity are
Amplitude equations for odd parity are
By combining Eqs. (70)–(72) for the even parity and employing the initial scaling, we derive
Similarly, for odd parity, combining Eqs. (73)–(75), we define
For small driving amplitudes, the resulting oscillation amplitudes decay exponentially in response to parametric driving. As the driving amplitude in Eq. (76) is
5 Numerical simulations and Discussion
Here, we solve the governing tripled sGE (1) with phase shift Eq. (2) for multi-sLJJs numerically and compare derived analytical results for weak and strong magnetic inductance. The Laplace differential operator was used to estimate the partial derivatives through finite difference method, and central difference formula was applied to integrate the sGE from Eq. (1). To discretize, we set
Consider different values of
as the initial conditions where the approximation is formerly obtained by
The value of
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By resolving Eq. (44), we derived the driving frequencies for facet lengths of
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The numerical results for computations performed analytically under the condition of strong coupling with odd parity are likewise presented in the following table:
|
|
|
|
|
|
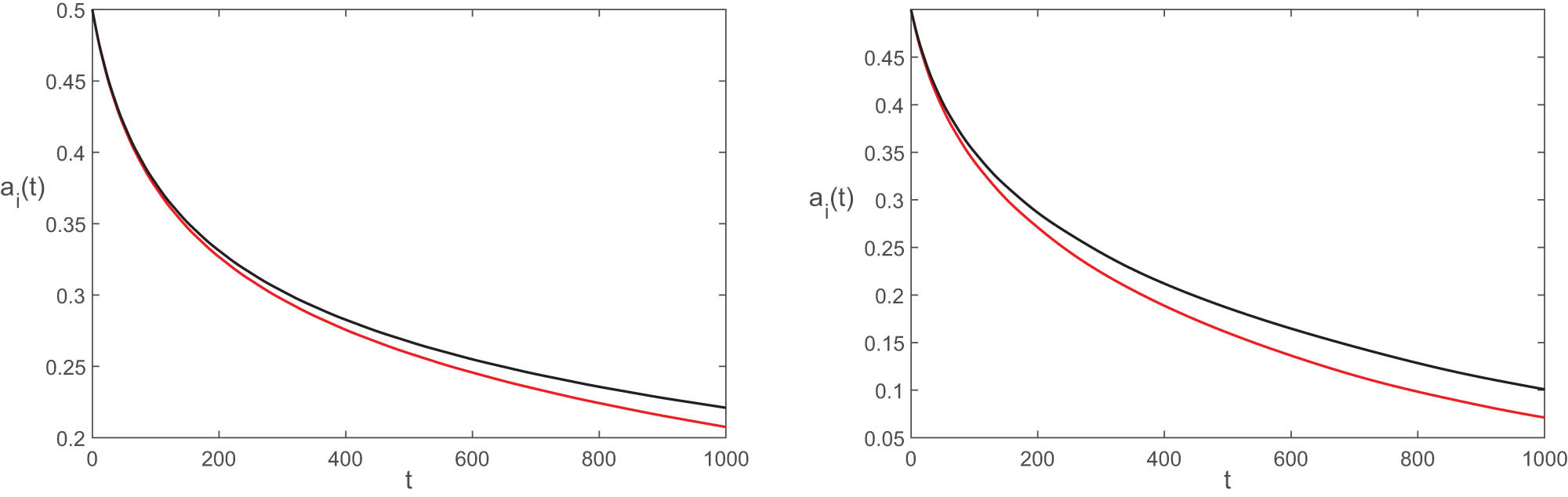
The numerical results and the systematically computed approximations in the form of amplitude are shown in Figures 1 and 2. The left panel of Figure 1 displays circles and stars that were formed under weak coupling conditions, while the black curve was generated using Eq. (23). It is evident that the obtained amplitudes are synchronized and decay exponentially over a period of time. In both panels of Figure 2 and the right panel of Figure 1, we exhibit

Profile for the two sLJJs that are weakly connected in the absence of drives. The synchronized oscillation of Eq. (23) is displayed in the left panel. The red curve in the right panel displays the numerical outcomes of Eq. (4), while the black curve in the panel represents the approximation derived in Eq. (23).

Profile for the two sLJJs that are strongly connected in the absence of drives. The synchronized oscillation of Eq. (58) is displayed in the left panel. The red curve in the right panel displays the results of numerical simulations of the governing system Eq. (34), while the black curve shows the approximation derived in Eq. (58).
Figures 3 and 4 demonstrate the numerical results derived from Eqs. (24) and (62), respectively, with red curves. Meanwhile, the black curves signify the amplitude solutions provided in Eqs. (28) and (67) for the weakly and strongly tripled multi-sLJJs with phase shift under direct drives. The driving amplitudes used in the two figures with phase shift were considered as
Figures 5 and 6 illustrate the numerical simulations derived from Eqs. (29) and (69), respectively with red curves. The approximate solutions are shown as black curves obtained in Eqs. (33) and (76) in the existence of parametric drives for both strong and weakly multi-sLJJs with phase shift. In comparison to direct AC drives, it is observed that the parametric drive has no influence on the governing system. The amplitude decreases exponentially more quickly over time to attain synchronized oscillation. In the left panel of Figure 5, we can deduce that the system oscillates for a while when the driving amplitude is large but ultimately tends to a constant state after some time.
Figure 7 illustrates the numerical simulation of the system in the existence of parametric drives (when

Profile for the strongly coupled multi-sLJJs with parametric drives with magnetic inductance
6 Conclusion
We investigated the behavior of a tripled sGE with various drives forming multi-sLJJs with a 0-
It has been shown that the coupled-mode amplitudes derived from the occurrence of AC-drive multi-sLJJs decrease over time, indicating that the stack goes through damping, which principally occurs because the breathing modes produce radiation as the assumed high excitations are analytical approximated at different orders in the system together with a coupling. It has also been discussed that the radiative annihilation in tripled sGE arises from exponential decay in the dynamics of breather, which may be suitable to attain super-radiant emission of radiations in the form of energy from coupled oscillators [43].
Furthermore, we explored the impact of parametric drives on the coupling effect in multi-sLJJs. Our findings indicate that when the driving amplitude is small enough, the oscillation is not affected by parametric drives. However, in the case of high driving amplitude with strong magnetic inductance, the system oscillates but eventually reaches a stable state due to the driving effect, as illustrated in the numerical section. Similar findings have been reported for single LJJs under external drives [44]. Therefore, it is determined that the parametric drive has no impact on the synchronization of the system when the applied drive is sufficiently small. On the other hand, we speculate that due to the existence of applied drives, the system can cause localized mode oscillations in multi-sLJJs with high dynamic amplitude as observed in the case of direct AC drive.
Coherent super-radiant emission has been previously discussed in coupled systems, with experimental studies actively exploring terahertz emission from stacked intrinsic JJs in cuprate superconductors under zero applied magnetic fields [45–47]. In this work, we conducted an analytical and numerical investigation of a triple system, leading to the observation of synchronized oscillation. It would be of interest to extend the present study to
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R447), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
-
Funding information: Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R447), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Josephson BD. Coupled superconductors. Rev Modern Phys. 1964;36(1):216. 10.1103/RevModPhys.36.216Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Cuevas-Maraver J, Kevrekidis PG, Williams F. The sine-Gordon model and its applications. Nonlinear Syst Complexity. 2014;10. 10.1007/978-3-319-06722-3Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Crotty P, Schult D, Segall K. Josephson junction simulation of neurons. Phys Rev E. 2010;82(1):011914. 10.1103/PhysRevE.82.011914Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Ezzat MA, El-Karamany AS, El-Bary AA, Fayik MA. Fractional calculus in one-dimensional isotropic thermo-viscoelasticity. Comptes Rendus Mécanique. 2013;341(7):553–66. 10.1016/j.crme.2013.04.001Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Ezzat MA, El-Karamany AS, El-Bary AA. On thermo-viscoelasticity with variable thermal conductivity and fractional-order heat transfer. International Journal of Thermophysics. 2015;36:1684–97. 10.1007/s10765-015-1873-8Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Mahdy AM, Lotfy K, El-Bary A, Sarhan HH. Effect of rotation and magnetic field on a numerical-refined heat conduction in a semiconductor medium during photo-excitation processes. Eur Phys J Plus. 2021;136:1–7. 10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01552-3Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Katterwe SO, Rydh A, Motzkau H, Kulakov AB, Krasnov VM. Superluminal geometrical resonances observed in Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x intrinsic Josephson junctions. Phys Rev B. 2010;82(2):024517. 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.024517Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Kleiner R. Two-dimensional resonant modes in stacked Josephson junctions. Phys Rev B. 1994;50(10):6919. 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.6919Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Wang P, Xie W, Hu L, Liu X, Ji L, He M, et al. Current-voltage characteristics of voltage-biased Tl2Ba2CaCu2O8 intrinsic Josephson junctions. Sci China Phys Mechanics Astron. 2014 Dec;57:2242–5. 10.1007/s11433-014-5438-9Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Ustinov AV. Experiments with solitons in coupled Josephson transmission lines. In Fluctuation phenomena: disorder and nonlinearity. Madrid, Spain: World Scientific; 1995. p. 197–203. 10.1142/9789814503877_0031Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Goldobin E, Ustinov AV. Current locking in magnetically coupled long Josephson junctions. Phys Rev B. 1999;59(17):11532. 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.11532Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Benz SP, Reintsema CD, Ono RH, Eckstein JN, Bozovic I, Virshup GF. Step-edge and stacked-heterostructure high-T/sub c/Josephson junctions for voltage-standard arrays. IEEE Trans Appl Superconductivity. 1995;5(2):2915–8. 10.1109/77.403202Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Mahdy AM, Lotfy K, El-Bary A, Tayel IM. Variable thermal conductivity and hyperbolic two-temperature theory during magneto-photothermal theory of semiconductor induced by laser pulses. Eur Phys J Plus. 2021;136:1–21. 10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01633-3Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Yasein MD, Mabrouk N, Lotfy K, El-Bary AA. The influence of variable thermal conductivity of semiconductor elastic medium during photothermal excitation subjected to thermal ramp type. Results Phys. 2019;15:102766. 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102766Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Ezzat MA, El-Bary AA. Effects of variable thermal conductivity on Stokes’ flow of a thermoelectric fluid with fractional order of heat transfer. Int J Thermal Sci. 2016;100:305–15. 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2015.10.008Suche in Google Scholar
[16] El-Bary A. Hyperbolic two-temperature generalized thermoelasticity with fractional order strain of solid cylinder. J Eng Thermal Sci. 2021;1(2):30–42. 10.21595/jets.2021.21969Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Cassidy MC, Bruno A, Rubbert S, Irfan M, Kammhuber J, Schouten RN, et al. Demonstration of an ac Josephson junction laser. Science. 2017;355(6328):939–42. 10.1126/science.aah6640Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Macklin C, O’brien K, Hover D, Schwartz ME, Bolkhovsky V, Zhang X, et al. A near-quantum-limited Josephson traveling-wave parametric amplifier. Science. 2015;350(6258):307–10. 10.1126/science.aaa8525Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] O’Brien K, Macklin C, Siddiqi I, Zhang X. Resonant phase matching of Josephson junction traveling wave parametric amplifiers. Phys Rev Lett. 2014;113(15):157001. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.157001Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Shimakage H, Tamura Y. Chaotic oscillations in Josephson junctions for random number generation. IEEE Tran Appl Superconductivity. 2014;25(3):1–4. 10.1109/TASC.2014.2377240Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Holdengreber E, Moshe AG, Mizrahi M, Khavkin V, Schacham SE, Farber E. High sensitivity high Tc superconducting Josephson junction antenna for 200 GHz detection. J Electromagnetic Waves Appl. 2019;33(2):193–203. 10.1080/09205071.2018.1535333Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Goldobin E, Wallraff A, Thyssen N, Ustinov AV. Cherenkov radiation in coupled long Josephson junctions. Phys Rev B. 1998;57(1):130. 10.1103/PhysRevB.57.130Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Rekhviashvili S, Pskhu A, Agarwal P, Jain S. Application of the fractional oscillator model to describe damped vibrations. Turkish J Phys. 2019;43(3):236–42. 10.3906/fiz-1811-16Suche in Google Scholar
[24] El-Sayed AA, Agarwal P. Spectral treatment for the fractional-order wave equation using shifted Chebyshev orthogonal polynomials. J Comput Appl Math. 2023;424:114933. 10.1016/j.cam.2022.114933Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Irkıl N, Pişkin E, Agarwal P. Global existence and decay of solutions for a system of viscoelastic wave equations of Kirchhoff type with logarithmic nonlinearity. Math Methods Appl Sci. 2022;45(5):2921–48. 10.1002/mma.7964Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Schulze H, Behr R, Kohlmann J, Müller F, Niemeyer J. Design and fabrication of 10 V SINIS Josephson arrays for programmable voltage standards. Superconductor Sci Technol. 2000;13(9):1293. 10.1088/0953-2048/13/9/301Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Mineev MB, Mkrtchyan GS, Schmidt VV. On some effects in a system of two interacting Josephson junctions. J Low Temp Phys. 1981;45:497–505. 10.1007/BF00654496Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Khan WA, Ali A, Huang WH, Din A, Liu P. Dynamics of coupled sine-Gordon equations: Inductively stacked long Josephson junctions with heterogeneous drives. Results Phys. 2021;31:104989. 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104989Suche in Google Scholar
[29] Braun OM, Kivshar YS. The Frenkel-Kontorova model: concepts, methods, and applications. Berlin: Springer; 2004. 10.1007/978-3-662-10331-9Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Bar’yakhtar VG, Ivanov BA, Chetkin MV. Dynamics of domain boundaries in weak ferromagnets.[Rare earth compounds: thulium, ytterbium, erbium, dysprosium, terbium, holmium]. Usp. Fiz. Nauk; (USSR). 1985;146(3):417–58. 10.3367/UFNr.0146.198507b.0417Suche in Google Scholar
[31] Pouget J, Maugin GA. Solitons and electroacoustic interactions in ferroelectric crystals. II. Interactions of solitons and radiations. Phys Rev B. 1985;31(7):4633. 10.1103/PhysRevB.31.4633Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Faddeev LD, Korepin VE. Quantum theory of solitons. Phys Reports. 1978;42(1):1–87. 10.1016/0370-1573(78)90058-3Suche in Google Scholar
[33] Abdalla E, Maroufi B, Melgar BC, Sedra MB. Information transport by sine-Gordon solitons in microtubules. Phys A Stat Mech Appl. 2001;301(1–4):169–73. 10.1016/S0378-4371(01)00399-5Suche in Google Scholar
[34] Lomdahl PS, Samuelsen MR. Persistent breather excitations in an ac-driven sine-Gordon system with loss. Phys Rev A. 1986;34(1):664. 10.1103/PhysRevA.34.664Suche in Google Scholar
[35] Grønbech-Jensen N, Samuelsen MR, Lomdahl PS, Blackburn JA. Bunched soliton states in weakly coupled sine-Gordon systems. Phys Rev B. 1990;42(7):3976. 10.1103/PhysRevB.42.3976Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Goldobin E, Kohlstedt H, Ustinov AV. Tunable phase locking of stacked Josephson flux-flow oscillators. Appl Phys Lett. 1996;68(2):250–2. 10.1063/1.115652Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Bulaevskii LN, Kuzii VV, Sobyanin AA. On possibility of the spontaneous magnetic flux in a Josephson junction containing magnetic impurities. Solid State Commun. 1978;25(12):1053–7. 10.1016/0038-1098(78)90906-7Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Hilgenkamp H. Pi-phase shift Josephson structures. Superconductor Sci Technol. 2008;21(3):034011. 10.1088/0953-2048/21/3/034011Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Gürlich C, Goldobin E, Straub R, Doenitz D, Smilde HJ, Hilgenkamp H, et al. Imaging of order parameter induced π phase shifts in cuprate superconductors by low-temperature scanning electron microscopy. Phys Rev Lett. 2009;103(6):067011. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.067011Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Khan WA, Ali A, Gul Z, Ahmad S, Ullah A. Localized modes in PT-symmetric sine-Gordon couplers with phase shift. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020;139:110290. 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110290Suche in Google Scholar
[41] Ahmad S. Semifluxons in 0-π-0 infinitely long Josephson junctions. Phys Lett A. 2015;379(38):2362–9. 10.1016/j.physleta.2015.05.003Suche in Google Scholar
[42] Ali A, Susanto H, Wattis JA. Breathing modes of long Josephson junctions with phase shifts. SIAM J Appl Math. 2011;71(1):242–69. 10.1137/090777360Suche in Google Scholar
[43] Krasnov VM. Radiative annihilation of a soliton and an antisoliton in the coupled sine-Gordon equation. Phys Rev B. 2012;85(13):134525. 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.134525Suche in Google Scholar
[44] Gul Z, Ali A. Localized modes in a variety of driven long Josephson junctions with phase shifts. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018;94:229–47. 10.1007/s11071-018-4355-2Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Ozyuzer L, Koshelev AE, Kurter C, Gopalsami N, Li Q, Tachiki M, et al. Emission of coherent THz radiation from superconductors. Science. 2007;318(5854):1291–3. 10.1126/science.1149802Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[46] Hu X, Lin SZ. Phase dynamics in a stack of inductively coupled intrinsic Josephson junctions and terahertz electromagnetic radiation. Superconductor Sci Technol. 2010;23(5):053001. 10.1088/0953-2048/23/5/053001Suche in Google Scholar
[47] Krasnov VM. Coherent flux-flow emission from stacked Josephson junctions: nonlocal radiative boundary conditions and the role of geometrical resonances. Phys Rev B. 2010;82(13):134524. 10.1103/PhysRevB.82.134524Suche in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Dynamic properties of the attachment oscillator arising in the nanophysics
- Parametric simulation of stagnation point flow of motile microorganism hybrid nanofluid across a circular cylinder with sinusoidal radius
- Fractal-fractional advection–diffusion–reaction equations by Ritz approximation approach
- Behaviour and onset of low-dimensional chaos with a periodically varying loss in single-mode homogeneously broadened laser
- Ammonia gas-sensing behavior of uniform nanostructured PPy film prepared by simple-straightforward in situ chemical vapor oxidation
- Analysis of the working mechanism and detection sensitivity of a flash detector
- Flat and bent branes with inner structure in two-field mimetic gravity
- Heat transfer analysis of the MHD stagnation-point flow of third-grade fluid over a porous sheet with thermal radiation effect: An algorithmic approach
- Weighted survival functional entropy and its properties
- Bioconvection effect in the Carreau nanofluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux using stagnation point flow in the entropy generation: Micromachines level study
- Study on the impulse mechanism of optical films formed by laser plasma shock waves
- Analysis of sweeping jet and film composite cooling using the decoupled model
- Research on the influence of trapezoidal magnetization of bonded magnetic ring on cogging torque
- Tripartite entanglement and entanglement transfer in a hybrid cavity magnomechanical system
- Compounded Bell-G class of statistical models with applications to COVID-19 and actuarial data
- Degradation of Vibrio cholerae from drinking water by the underwater capillary discharge
- Multiple Lie symmetry solutions for effects of viscous on magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer in non-Newtonian thin film
- Thermal characterization of heat source (sink) on hybridized (Cu–Ag/EG) nanofluid flow via solid stretchable sheet
- Optimizing condition monitoring of ball bearings: An integrated approach using decision tree and extreme learning machine for effective decision-making
- Study on the inter-porosity transfer rate and producing degree of matrix in fractured-porous gas reservoirs
- Interstellar radiation as a Maxwell field: Improved numerical scheme and application to the spectral energy density
- Numerical study of hybridized Williamson nanofluid flow with TC4 and Nichrome over an extending surface
- Controlling the physical field using the shape function technique
- Significance of heat and mass transport in peristaltic flow of Jeffrey material subject to chemical reaction and radiation phenomenon through a tapered channel
- Complex dynamics of a sub-quadratic Lorenz-like system
- Stability control in a helicoidal spin–orbit-coupled open Bose–Bose mixture
- Research on WPD and DBSCAN-L-ISOMAP for circuit fault feature extraction
- Simulation for formation process of atomic orbitals by the finite difference time domain method based on the eight-element Dirac equation
- A modified power-law model: Properties, estimation, and applications
- Bayesian and non-Bayesian estimation of dynamic cumulative residual Tsallis entropy for moment exponential distribution under progressive censored type II
- Computational analysis and biomechanical study of Oldroyd-B fluid with homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions through a vertical non-uniform channel
- Predictability of machine learning framework in cross-section data
- Chaotic characteristics and mixing performance of pseudoplastic fluids in a stirred tank
- Isomorphic shut form valuation for quantum field theory and biological population models
- Vibration sensitivity minimization of an ultra-stable optical reference cavity based on orthogonal experimental design
- Effect of dysprosium on the radiation-shielding features of SiO2–PbO–B2O3 glasses
- Asymptotic formulations of anti-plane problems in pre-stressed compressible elastic laminates
- A study on soliton, lump solutions to a generalized (3+1)-dimensional Hirota--Satsuma--Ito equation
- Tangential electrostatic field at metal surfaces
- Bioconvective gyrotactic microorganisms in third-grade nanofluid flow over a Riga surface with stratification: An approach to entropy minimization
- Infrared spectroscopy for ageing assessment of insulating oils via dielectric loss factor and interfacial tension
- Influence of cationic surfactants on the growth of gypsum crystals
- Study on instability mechanism of KCl/PHPA drilling waste fluid
- Analytical solutions of the extended Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation in nonlinear media
- A novel compact highly sensitive non-invasive microwave antenna sensor for blood glucose monitoring
- Inspection of Couette and pressure-driven Poiseuille entropy-optimized dissipated flow in a suction/injection horizontal channel: Analytical solutions
- Conserved vectors and solutions of the two-dimensional potential KP equation
- The reciprocal linear effect, a new optical effect of the Sagnac type
- Optimal interatomic potentials using modified method of least squares: Optimal form of interatomic potentials
- The soliton solutions for stochastic Calogero–Bogoyavlenskii Schiff equation in plasma physics/fluid mechanics
- Research on absolute ranging technology of resampling phase comparison method based on FMCW
- Analysis of Cu and Zn contents in aluminum alloys by femtosecond laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy
- Nonsequential double ionization channels control of CO2 molecules with counter-rotating two-color circularly polarized laser field by laser wavelength
- Fractional-order modeling: Analysis of foam drainage and Fisher's equations
- Thermo-solutal Marangoni convective Darcy-Forchheimer bio-hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable disk with activation energy: Analysis of interfacial nanolayer thickness
- Investigation on topology-optimized compressor piston by metal additive manufacturing technique: Analytical and numeric computational modeling using finite element analysis in ANSYS
- Breast cancer segmentation using a hybrid AttendSeg architecture combined with a gravitational clustering optimization algorithm using mathematical modelling
- On the localized and periodic solutions to the time-fractional Klein-Gordan equations: Optimal additive function method and new iterative method
- 3D thin-film nanofluid flow with heat transfer on an inclined disc by using HWCM
- Numerical study of static pressure on the sonochemistry characteristics of the gas bubble under acoustic excitation
- Optimal auxiliary function method for analyzing nonlinear system of coupled Schrödinger–KdV equation with Caputo operator
- Analysis of magnetized micropolar fluid subjected to generalized heat-mass transfer theories
- Does the Mott problem extend to Geiger counters?
- Stability analysis, phase plane analysis, and isolated soliton solution to the LGH equation in mathematical physics
- Effects of Joule heating and reaction mechanisms on couple stress fluid flow with peristalsis in the presence of a porous material through an inclined channel
- Bayesian and E-Bayesian estimation based on constant-stress partially accelerated life testing for inverted Topp–Leone distribution
- Dynamical and physical characteristics of soliton solutions to the (2+1)-dimensional Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky system
- Study of fractional variable order COVID-19 environmental transformation model
- Sisko nanofluid flow through exponential stretching sheet with swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms: An application to nanoengineering
- Influence of the regularization scheme in the QCD phase diagram in the PNJL model
- Fixed-point theory and numerical analysis of an epidemic model with fractional calculus: Exploring dynamical behavior
- Computational analysis of reconstructing current and sag of three-phase overhead line based on the TMR sensor array
- Investigation of tripled sine-Gordon equation: Localized modes in multi-stacked long Josephson junctions
- High-sensitivity on-chip temperature sensor based on cascaded microring resonators
- Pathological study on uncertain numbers and proposed solutions for discrete fuzzy fractional order calculus
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solution of stochastic coupled Konno–Oono equation with multiplicative noise in the Stratonovich sense
- Thermal radiation and heat generation on three-dimensional Casson fluid motion via porous stretching surface with variable thermal conductivity
- Numerical simulation and analysis of Airy's-type equation
- A homotopy perturbation method with Elzaki transformation for solving the fractional Biswas–Milovic model
- Heat transfer performance of magnetohydrodynamic multiphase nanofluid flow of Cu–Al2O3/H2O over a stretching cylinder
- ΛCDM and the principle of equivalence
- Axisymmetric stagnation-point flow of non-Newtonian nanomaterial and heat transport over a lubricated surface: Hybrid homotopy analysis method simulations
- HAM simulation for bioconvective magnetohydrodynamic flow of Walters-B fluid containing nanoparticles and microorganisms past a stretching sheet with velocity slip and convective conditions
- Coupled heat and mass transfer mathematical study for lubricated non-Newtonian nanomaterial conveying oblique stagnation point flow: A comparison of viscous and viscoelastic nanofluid model
- Power Topp–Leone exponential negative family of distributions with numerical illustrations to engineering and biological data
- Extracting solitary solutions of the nonlinear Kaup–Kupershmidt (KK) equation by analytical method
- A case study on the environmental and economic impact of photovoltaic systems in wastewater treatment plants
- Application of IoT network for marine wildlife surveillance
- Non-similar modeling and numerical simulations of microploar hybrid nanofluid adjacent to isothermal sphere
- Joint optimization of two-dimensional warranty period and maintenance strategy considering availability and cost constraints
- Numerical investigation of the flow characteristics involving dissipation and slip effects in a convectively nanofluid within a porous medium
- Spectral uncertainty analysis of grassland and its camouflage materials based on land-based hyperspectral images
- Application of low-altitude wind shear recognition algorithm and laser wind radar in aviation meteorological services
- Investigation of different structures of screw extruders on the flow in direct ink writing SiC slurry based on LBM
- Harmonic current suppression method of virtual DC motor based on fuzzy sliding mode
- Micropolar flow and heat transfer within a permeable channel using the successive linearization method
- Different lump k-soliton solutions to (2+1)-dimensional KdV system using Hirota binary Bell polynomials
- Investigation of nanomaterials in flow of non-Newtonian liquid toward a stretchable surface
- Weak beat frequency extraction method for photon Doppler signal with low signal-to-noise ratio
- Electrokinetic energy conversion of nanofluids in porous microtubes with Green’s function
- Examining the role of activation energy and convective boundary conditions in nanofluid behavior of Couette-Poiseuille flow
- Review Article
- Effects of stretching on phase transformation of PVDF and its copolymers: A review
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part IV
- Prediction and monitoring model for farmland environmental system using soil sensor and neural network algorithm
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part III
- Some standard and nonstandard finite difference schemes for a reaction–diffusion–chemotaxis model
- Special Issue on Advanced Energy Materials - Part II
- Rapid productivity prediction method for frac hits affected wells based on gas reservoir numerical simulation and probability method
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part III
- Adomian decomposition method for solution of fourteenth order boundary value problems
- New soliton solutions of modified (3+1)-D Wazwaz–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and (2+1)-D cubic Klein–Gordon equations using first integral method
- On traveling wave solutions to Manakov model with variable coefficients
- Rational approximation for solving Fredholm integro-differential equations by new algorithm
- Special Issue on Predicting pattern alterations in nature - Part I
- Modeling the monkeypox infection using the Mittag–Leffler kernel
- Spectral analysis of variable-order multi-terms fractional differential equations
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part I
- Heat treatment and tensile test of 3D-printed parts manufactured at different build orientations
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Dynamic properties of the attachment oscillator arising in the nanophysics
- Parametric simulation of stagnation point flow of motile microorganism hybrid nanofluid across a circular cylinder with sinusoidal radius
- Fractal-fractional advection–diffusion–reaction equations by Ritz approximation approach
- Behaviour and onset of low-dimensional chaos with a periodically varying loss in single-mode homogeneously broadened laser
- Ammonia gas-sensing behavior of uniform nanostructured PPy film prepared by simple-straightforward in situ chemical vapor oxidation
- Analysis of the working mechanism and detection sensitivity of a flash detector
- Flat and bent branes with inner structure in two-field mimetic gravity
- Heat transfer analysis of the MHD stagnation-point flow of third-grade fluid over a porous sheet with thermal radiation effect: An algorithmic approach
- Weighted survival functional entropy and its properties
- Bioconvection effect in the Carreau nanofluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux using stagnation point flow in the entropy generation: Micromachines level study
- Study on the impulse mechanism of optical films formed by laser plasma shock waves
- Analysis of sweeping jet and film composite cooling using the decoupled model
- Research on the influence of trapezoidal magnetization of bonded magnetic ring on cogging torque
- Tripartite entanglement and entanglement transfer in a hybrid cavity magnomechanical system
- Compounded Bell-G class of statistical models with applications to COVID-19 and actuarial data
- Degradation of Vibrio cholerae from drinking water by the underwater capillary discharge
- Multiple Lie symmetry solutions for effects of viscous on magnetohydrodynamic flow and heat transfer in non-Newtonian thin film
- Thermal characterization of heat source (sink) on hybridized (Cu–Ag/EG) nanofluid flow via solid stretchable sheet
- Optimizing condition monitoring of ball bearings: An integrated approach using decision tree and extreme learning machine for effective decision-making
- Study on the inter-porosity transfer rate and producing degree of matrix in fractured-porous gas reservoirs
- Interstellar radiation as a Maxwell field: Improved numerical scheme and application to the spectral energy density
- Numerical study of hybridized Williamson nanofluid flow with TC4 and Nichrome over an extending surface
- Controlling the physical field using the shape function technique
- Significance of heat and mass transport in peristaltic flow of Jeffrey material subject to chemical reaction and radiation phenomenon through a tapered channel
- Complex dynamics of a sub-quadratic Lorenz-like system
- Stability control in a helicoidal spin–orbit-coupled open Bose–Bose mixture
- Research on WPD and DBSCAN-L-ISOMAP for circuit fault feature extraction
- Simulation for formation process of atomic orbitals by the finite difference time domain method based on the eight-element Dirac equation
- A modified power-law model: Properties, estimation, and applications
- Bayesian and non-Bayesian estimation of dynamic cumulative residual Tsallis entropy for moment exponential distribution under progressive censored type II
- Computational analysis and biomechanical study of Oldroyd-B fluid with homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions through a vertical non-uniform channel
- Predictability of machine learning framework in cross-section data
- Chaotic characteristics and mixing performance of pseudoplastic fluids in a stirred tank
- Isomorphic shut form valuation for quantum field theory and biological population models
- Vibration sensitivity minimization of an ultra-stable optical reference cavity based on orthogonal experimental design
- Effect of dysprosium on the radiation-shielding features of SiO2–PbO–B2O3 glasses
- Asymptotic formulations of anti-plane problems in pre-stressed compressible elastic laminates
- A study on soliton, lump solutions to a generalized (3+1)-dimensional Hirota--Satsuma--Ito equation
- Tangential electrostatic field at metal surfaces
- Bioconvective gyrotactic microorganisms in third-grade nanofluid flow over a Riga surface with stratification: An approach to entropy minimization
- Infrared spectroscopy for ageing assessment of insulating oils via dielectric loss factor and interfacial tension
- Influence of cationic surfactants on the growth of gypsum crystals
- Study on instability mechanism of KCl/PHPA drilling waste fluid
- Analytical solutions of the extended Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation in nonlinear media
- A novel compact highly sensitive non-invasive microwave antenna sensor for blood glucose monitoring
- Inspection of Couette and pressure-driven Poiseuille entropy-optimized dissipated flow in a suction/injection horizontal channel: Analytical solutions
- Conserved vectors and solutions of the two-dimensional potential KP equation
- The reciprocal linear effect, a new optical effect of the Sagnac type
- Optimal interatomic potentials using modified method of least squares: Optimal form of interatomic potentials
- The soliton solutions for stochastic Calogero–Bogoyavlenskii Schiff equation in plasma physics/fluid mechanics
- Research on absolute ranging technology of resampling phase comparison method based on FMCW
- Analysis of Cu and Zn contents in aluminum alloys by femtosecond laser-ablation spark-induced breakdown spectroscopy
- Nonsequential double ionization channels control of CO2 molecules with counter-rotating two-color circularly polarized laser field by laser wavelength
- Fractional-order modeling: Analysis of foam drainage and Fisher's equations
- Thermo-solutal Marangoni convective Darcy-Forchheimer bio-hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable disk with activation energy: Analysis of interfacial nanolayer thickness
- Investigation on topology-optimized compressor piston by metal additive manufacturing technique: Analytical and numeric computational modeling using finite element analysis in ANSYS
- Breast cancer segmentation using a hybrid AttendSeg architecture combined with a gravitational clustering optimization algorithm using mathematical modelling
- On the localized and periodic solutions to the time-fractional Klein-Gordan equations: Optimal additive function method and new iterative method
- 3D thin-film nanofluid flow with heat transfer on an inclined disc by using HWCM
- Numerical study of static pressure on the sonochemistry characteristics of the gas bubble under acoustic excitation
- Optimal auxiliary function method for analyzing nonlinear system of coupled Schrödinger–KdV equation with Caputo operator
- Analysis of magnetized micropolar fluid subjected to generalized heat-mass transfer theories
- Does the Mott problem extend to Geiger counters?
- Stability analysis, phase plane analysis, and isolated soliton solution to the LGH equation in mathematical physics
- Effects of Joule heating and reaction mechanisms on couple stress fluid flow with peristalsis in the presence of a porous material through an inclined channel
- Bayesian and E-Bayesian estimation based on constant-stress partially accelerated life testing for inverted Topp–Leone distribution
- Dynamical and physical characteristics of soliton solutions to the (2+1)-dimensional Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky system
- Study of fractional variable order COVID-19 environmental transformation model
- Sisko nanofluid flow through exponential stretching sheet with swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms: An application to nanoengineering
- Influence of the regularization scheme in the QCD phase diagram in the PNJL model
- Fixed-point theory and numerical analysis of an epidemic model with fractional calculus: Exploring dynamical behavior
- Computational analysis of reconstructing current and sag of three-phase overhead line based on the TMR sensor array
- Investigation of tripled sine-Gordon equation: Localized modes in multi-stacked long Josephson junctions
- High-sensitivity on-chip temperature sensor based on cascaded microring resonators
- Pathological study on uncertain numbers and proposed solutions for discrete fuzzy fractional order calculus
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solution of stochastic coupled Konno–Oono equation with multiplicative noise in the Stratonovich sense
- Thermal radiation and heat generation on three-dimensional Casson fluid motion via porous stretching surface with variable thermal conductivity
- Numerical simulation and analysis of Airy's-type equation
- A homotopy perturbation method with Elzaki transformation for solving the fractional Biswas–Milovic model
- Heat transfer performance of magnetohydrodynamic multiphase nanofluid flow of Cu–Al2O3/H2O over a stretching cylinder
- ΛCDM and the principle of equivalence
- Axisymmetric stagnation-point flow of non-Newtonian nanomaterial and heat transport over a lubricated surface: Hybrid homotopy analysis method simulations
- HAM simulation for bioconvective magnetohydrodynamic flow of Walters-B fluid containing nanoparticles and microorganisms past a stretching sheet with velocity slip and convective conditions
- Coupled heat and mass transfer mathematical study for lubricated non-Newtonian nanomaterial conveying oblique stagnation point flow: A comparison of viscous and viscoelastic nanofluid model
- Power Topp–Leone exponential negative family of distributions with numerical illustrations to engineering and biological data
- Extracting solitary solutions of the nonlinear Kaup–Kupershmidt (KK) equation by analytical method
- A case study on the environmental and economic impact of photovoltaic systems in wastewater treatment plants
- Application of IoT network for marine wildlife surveillance
- Non-similar modeling and numerical simulations of microploar hybrid nanofluid adjacent to isothermal sphere
- Joint optimization of two-dimensional warranty period and maintenance strategy considering availability and cost constraints
- Numerical investigation of the flow characteristics involving dissipation and slip effects in a convectively nanofluid within a porous medium
- Spectral uncertainty analysis of grassland and its camouflage materials based on land-based hyperspectral images
- Application of low-altitude wind shear recognition algorithm and laser wind radar in aviation meteorological services
- Investigation of different structures of screw extruders on the flow in direct ink writing SiC slurry based on LBM
- Harmonic current suppression method of virtual DC motor based on fuzzy sliding mode
- Micropolar flow and heat transfer within a permeable channel using the successive linearization method
- Different lump k-soliton solutions to (2+1)-dimensional KdV system using Hirota binary Bell polynomials
- Investigation of nanomaterials in flow of non-Newtonian liquid toward a stretchable surface
- Weak beat frequency extraction method for photon Doppler signal with low signal-to-noise ratio
- Electrokinetic energy conversion of nanofluids in porous microtubes with Green’s function
- Examining the role of activation energy and convective boundary conditions in nanofluid behavior of Couette-Poiseuille flow
- Review Article
- Effects of stretching on phase transformation of PVDF and its copolymers: A review
- Special Issue on Transport phenomena and thermal analysis in micro/nano-scale structure surfaces - Part IV
- Prediction and monitoring model for farmland environmental system using soil sensor and neural network algorithm
- Special Issue on Advanced Topics on the Modelling and Assessment of Complicated Physical Phenomena - Part III
- Some standard and nonstandard finite difference schemes for a reaction–diffusion–chemotaxis model
- Special Issue on Advanced Energy Materials - Part II
- Rapid productivity prediction method for frac hits affected wells based on gas reservoir numerical simulation and probability method
- Special Issue on Novel Numerical and Analytical Techniques for Fractional Nonlinear Schrodinger Type - Part III
- Adomian decomposition method for solution of fourteenth order boundary value problems
- New soliton solutions of modified (3+1)-D Wazwaz–Benjamin–Bona–Mahony and (2+1)-D cubic Klein–Gordon equations using first integral method
- On traveling wave solutions to Manakov model with variable coefficients
- Rational approximation for solving Fredholm integro-differential equations by new algorithm
- Special Issue on Predicting pattern alterations in nature - Part I
- Modeling the monkeypox infection using the Mittag–Leffler kernel
- Spectral analysis of variable-order multi-terms fractional differential equations
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part I
- Heat treatment and tensile test of 3D-printed parts manufactured at different build orientations