Abstract
Melanoma is a rare, fatal type of skin tumor. Although EPH receptor A3 (EphA3) is deregulated in melanoma, its detailed role remained uncharacterized. Using real time quantitative PCR analysis and western blotting, EphA3 was identified to be upregulated in melanoma tissues and cells, while miR-3666 showed an opposite expression trend. Cell counting kit-8, scratch wound, and in vivo assays proved that EphA3 silence inhibited the melanoma cell proliferation and migration and retarded tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, western blotting results displayed that EphA3 silence resulted in a low expression of p38-MAPK and p-ERK1/2. Mechanically, miR-3666 was proved to target EphA3 3′UTR by the luciferase reporter assay. Furthermore, miR-3666 mimic compromised the driven melanoma cell proliferation and migration by EphA3 overexpression. In addition, induction of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways offset the positive effect of EphA3 overexpression on melanoma cells. In conclusion, miR-3666 downregulated EphA3 expression and retarded melanoma malignancy via inactivating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways. Hence, miR-3666/EphA3 axis may represent a druggable target against melanoma progression.
1 Introduction
Melanoma is a kind of fatal cutaneous malignancy characterized by exceptional aggressiveness and metastasis. Global Cancer Statistics 2020 estimated about 324,635 new cases and 57,043 new death in 2021 [1]. Ultraviolet ray radiation, advanced age, and genetic predisposition caused the exacerbation burden of melanoma [2]. Though great strides in melanoma treatment have achieved in high-risk resectable melanoma, the overall prognosis remains inferior [3]. This consequence might be linked with the lack of prompt diagnosis and intervention due to silent and clinical presentation of melanoma. Therefore, understanding the mechanism behind melanoma progression might promote the diagnosis and treatment of melanoma.
EPH receptor A3 (EphA3) is one member of the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Hitherto, its role in cancers gains attention from scientists due to its tumor-promoting and tumor-suppressive role in different cancers. For example, loss of EphA3 expression is detected in colorectal cancer and verified as a tight linkage with advanced pathological feature of patients [4]. Overexpressing of EphA3 represses the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell growth in vitro [5]. On the contrary, upregulation of EphA3 activates AKT signaling pathway and then facilitates glioblastoma progression [6]. The bispecific antibody against EphA3 lessens the tumorigenesis of recurrent glioblastoma by downregulating ERK signaling pathway [7]. Therefore, the role of EPHA3 in cancers presents context dependence. In melanoma, a genomic investigation about melanoma by Timar et al. suggests that EphA3 is a marker gene of melanoma [8]. However, its role and associated mechanism remained elusive.
microRNA (miRNA) belongs to the non-coding transcripts, characterizing a size of 20 nt. Compelling evidence has shown that it could reshape the cellular protein expression by interacting with its targeted mRNA and stepwise influence different cell process [9]. Activities of miRNAs are also pinpointed in different cancers, including melanoma. For instance, miR-137 targeting solute carrier family 1 member 5 regulates ferroptosis in melanoma and exerts tumor-promotion effect [10]. MiR-204-5p actively participates vemurafenib resistance in melanoma by activating ERK1/2 signaling pathway [11]. As for miR-3666, its tumor-suppressive function has been elucidated in different cancers, such as ovarian carcinoma, glioblastoma, and thyroid carcinoma [12,13,14]. And yet, its role in melanoma remains under investigation. By the bioinformatics analysis, we found the potential interaction between miR-3666 and EphA3. More importantly, miR-3666 inactivated ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways to suppress colorectal cancer [15]. Therefore, we speculated that miR-3666/EphA3 might have inhibitory roles in melanoma cells by regulating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.
Together with literature review and bioinformatics analysis, we hypothesize that miR-3666 is downregulated in melanoma and inhibits melanoma development by targeting EphA3. Herein, our aim is to explore how EphA3 impacts melanoma in vitro and in vivo and identify the interaction of miR-3666 and EphA3 on melanoma cells. Our findings might offer novel insight for melanoma progression.
2 Methods
2.1 Clinical samples
A total of 45 paired melanoma tissues and corresponding normal tissues were surgically obtained from melanoma patients first diagnosed in Wuhan Asia General Hospital. The clinical samples were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in −80°C for the next gene quantification.
2.2 Cell cultivation, transfection, and treatment
Human melanoma cells (A375, A875, and A2058) and human immortalized epidermal HaCAT cells were purchased from BeNa culture collection (BNCC, China). HaCAT cells (T25 medium, ThermoFisher, USA), A375 (RPMI-1640, ThermoFisher), and A875 and A2058 (CM1-1 medium, ThermoFisher) were cultivated with 10% fetal bovine serum (ThermoFisher) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in the 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C.
Si-EphA3 and si-NC, pcDNA-EphA3 (EphA3-OE) and the empty vector, miR-3666 mimic and mimic NC were obtained from Gema (Shanghai, China). These vectors were introduced into A375 and A875 cells with Lipo 3000 reagent (ThermoFisher). The transfection efficiency was determined by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) after 48 h post-transfection.
ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) and p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) purchased from Cell Signaling Technologies (USA) were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), respectively. A375 and A875 cells were pretreated with 10 μM SB203580 or 30 μM PD98059 for 2 h before EphA3-OE stimulation. The control group was treated with equivalent DMSO [16].
Lentivirus-Sh-EphA3 and Lentivirus-sh-NC were purchased from Gema (China). After amplification in 293T cells by calcium phosphate transfection (ThermoFisher), the filtered lentiviral particles were infected to A375 cells with Lipo 3000 reagent (ThermoFisher). Forty-eight hours later, the cells carrying viral particles were subjected to puromycin (P8833; Sigma-Aldrich) selection for 14 days. The survivals were amplified and collected for RT-qPCR verification.
2.3 RT-qPCR
Total RNAs were extracted using a RNA isolation kit (MEFx Translational Medicine Co., Ltd, China). Construction of cDNA was implemented via SuperScript IV CellsDirect cDNA synthesis kit (ThemoFisher) or One-Step microRNA cDNA Synthesis Kit (Beijing Baiao Lai Bo Technology Co., Ltd, China). RT-qPCR analysis was performed on AB7500 fast platform (Applied Biosystems, USA) using 2× SYBR Green Mix (ThermoFisher). The data were normalized to GAPDH (for mRNA) or U6 (for miRNA) using the Delta-Delta CT method [17]. The primers are listed in Table 1.
Real-time PCR primer synthesis list
| Gene | Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| EphA3 | Forward | 5′-CCCGCCTCACAGTTCTACTC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-ATCTTTTGCAAGATCCCTGCC-3′ | |
| miR-3666 | Forward | 5′-AATGAGACCCAGTGCAAGTGT-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-GACAGAGACCAGGCAGTGTG-3′ | |
| U6 | Forward | 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′ | |
| GAPDH | Forward | 5′-AGAAAAACCTGCCAAATATGATGAC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-TGGGTGTCGCTGTTGAAGTC-3′ | |
2.4 Western blot
Protein samples were obtained from A375 and A875 cells exposed to RIPA lysis buffer (Solarbio, China). BCA assay kit (Abcam, USA) was adopted to assess the protein concentration. Proteins (20 μg per lane) were resolved in 12% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and detected on poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes after which was blocked by 5% skim milk powder at room temperature for 2 h. Protein detection on membranes was detected with anti-p38MAPK (FNab06077, 1:1,000, FineTest, Biological Technology Co., Ltd, China), anti-p-p38MAPK (44-684G, 1:1,000, ThermoFisher), anti-p-ERK1/2 (44-680G, 1:1,000, ThermoFisher), anti-ERK1/2 (13-6200, 1:1,000,ThermoFisher), anti-EphA3 (310438-T08, 1:1,000, SinoBiological, China), and anti-GAPDH (100242-T08, 1:1,000, SinoBiological) at 4°C for 24 h. Next, horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (A32731, 1:1,000, ThermoFisher) were added and incubated with these membranes at room temperature for 1 h. Immune blots were developed with enhanced chemiluminescence (GE Healthcare, USA) and counted quantitatively by ImageJ.
2.5 Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay
A375 and A875 cells (2.5 × 105 cells/well) received CCK-8 reagent (10 μL, ThermoFisher) treatments for 4 h after both cells on 96-well plates underwent cultivation for 0, 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively. The optical density values of 450 nm were read using a microplate (Bio-Rad, USA).
2.6 Scratch wound assay
A375 and A875 cells (2.5 × 104 cells/well) were seeded on six-well culture plates. When both cells were 100% confluence, wound gaps were scratched using a P200 pipette tip. Cells were washed thrice with 1× phosphate-buffered saline and photographed. After additional 24 h culture, the wound areas were captured and analyzed using ImageJ software (NIH, USA).
2.7 Tumorigenic assessment in vivo
BALB/c nude mice (4–5 weeks old, about 20 g) were purchased from the Wuhan University Center for Animal Experiment/Animal Biosafety Level III laboratory (ABSL-III lab) of Wuhan University (Wuhan, Hubei, China). All mice were supplied with autoclaved food and water with 12-h dark and 12-h light. The mice received a subcutaneous injection of A375 cells (107 cells/mouser) stably with sh-EphA3 or sh-NC in their flanks. Every 4 days, tumor size was measured and tumor volume was calculated as: (tumor volume = length × width2/2). At post-injection of 28 days, these mice were asphyxiated with CO2. The tumors were removed and measured. All the animal procedure in this research was conducted with the approval of Wuhan Asia General Hospital.
2.8 Luciferase reporter assay
The target site of miR-3666 to EphA3 3′UTR was named wild-type (WT) EphA3 3′UTR. The corresponding mutant (MUT) EphA3 3′UTR were obtained using the QuikChange Mutagenesis Kit (Stratagene, USA). The EphA3 3′UTR-WT and EphA3 3′UTR-MUT sequences were amplified and fused into pGL3 Luciferase Reporter Vectors (Promega, USA). The resulted pGL3-EphA3 3′UTR-MUT vectors or EphA3 3′UTR-WT vectors were co-transfected with miR-3666 mimic or mimic NC into A375 and A875 cells. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, the luciferase activities were quantified by luciferase reporter system (Promega).
2.9 Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Prism Software, USA) was employed to analyze the outcome expressed mean ± SD. Student’s t-test was utilized to compare the findings from two groups. One-way analysis of variance was implemented for multiple groups comparison accompanied with Dunnet’s tests. Pearson’s analysis was used to analyze the correlation of miR-3666 and EphA3 in melanoma tissues. Results were considered significant if P < 0.05.
-
Ethics approval: This research has been approved by the Ethics Committee of the Wuhan Asia General Hospital (Wuhan, China). The processing of clinical samples is in strict compliance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. All patients provided their written informed consent. The procedures executed in the animal study were approved by Wuhan Asia General Hospital. All animal experiments comply with the ARRIVE guidelines.
-
Consent to participate: All patients signed a written informed consent.
3 Results
3.1 Upregulation of EphA3 in melanoma tissues and cells
To confirm the previous findings that the EphA3 is associated with melanoma malignancy [18], we measured its expression in melanoma tissues and cells. Undeniably, highly expressed EphA3 was measured in melanoma tissues (Figure 1a). Similarly, in the three melanoma cells (A375, A875, and A2058), the high expression of EphA3 was confirmed compared to HaCAT cells (Figure 1b). Especially the A375 and A875 cells exhibited an approximate two-fold increment of EphA3 mRNA levels. Consequently, we chose both melanoma cells for following cell functional verification. Subsequently, we successfully knocked down EphA3 expression in A375 and A875 cells with sh-EphA3 (Figure 1c and d). Therefore, EphA3 expression was abundant in melanoma.

Upregulation of EphA3 in melanoma tissues and cells. (a) EphA3 mRNA levels were detected in melanoma tissues and normal tissues by RT-qPCR analysis. (b) EphA3 mRNA levels were detected in a pan of melanoma cells (A375, A875, and A2058) and HaCAT cells by RT-qPCR analysis. *P < 0.01 vs HaCAT. (c) Si-EphA3 or si-NC was transfected into A375 and A875 cells. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, phA3 mRNA levels were detected in these transfected cells using RT-qPCR analysis. **P < 0.01 vs si-NC. (d) Si-EphA3 or si-NC was transfected into A375 and A875 cells. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, EphA3 proteins were detected in these transfected cells using western blot analysis. **P < 0.01 vs si-NC.
3.2 EphA3 silencing curbs the melanoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro by the impairment of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
Based on above results, upon EphA3 silence, evident impairments in cell proliferation were detected in both melanoma cells (Figure 2a). A parallel decrement in cellular migration was also manifested in A375 and A875 cells transfected with si-EphA3 compared to si-NC (Figure 2b). To mine the behind mechanism of EphA3-driven melanoma progression, we tested whether EphA3 silence impacts the ERK signaling cascade since anti-EphA3 antibodies could retard glioblastoma progression by modifying ERK1/2 signaling pathway [7]. Unsurprisingly, a compelling decrement of p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 MAPK protein levels was detected in A375 and A875 cells when EphA3 silence (Figure 2c). Therefore, the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways plays an important role in EphA3-driven melanoma cell proliferation and migration.

EphA3 silencing curbs the melanoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro by the impairment of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Si-EphA3 or si-NC was transfected into A375 and A875 cells. Forty-eight hours post-transfection. (a) Cell proliferation was assessed by CCK-8 assays. (b) Scratch wound assays were adopted to determine the melanoma cell migration. (c) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, p38MAPK, and p-p38MAPK in these transfected cells. **P < 0.01 vs si-NC.
3.3 EphA3 silencing attenuates the tumorigenic potential in melanoma in vivo
Having verified the function of EphA3 in vitro, we next examined if EphA3 is necessary for melanoma malignancy in vivo. To address this question, we subcutaneously injected A375 cells stably transfected with sh-EphA3 or sh-NC into nude mice. As shown in Figure 3a–c, the tumor weight and size were strongly arrested upon EphA3 silence. Therefore, EphA3 silence decelerated the cancerogenic potential of melanoma in vivo.

EphA3 silencing attenuates the tumorigenic potential in melanoma in vivo. A375 cells (107 cells/mouser) carrying sh-EphA3 or sh-NC were subjected to subcutaneous flank injection to mouse (n = 5). (a) Representative pictures of tumor growth. (b) Tumor weight was tested every 4 days. (c) At 28 h post-injection, the tumors were resected and weight. **P < 0.01 vs sh-NC.
3.4 EphA3 is a target gene of miR-3666
Considering miRNA-mediated gene silencing, we next interrogated the upstream miRNAs controlling EphA3 expression and stepwise control cellular processes. Target prediction by starBase analysis showed that miR-3666 recognized the 3′UTR sequence of EphA3 (Figure 4a). To further clarify the base pairing between miR-3666 and EphA3 3′UTR, we constructed EphA3 3′UTR-WT and EphA3 3′UTR-MUT luciferase reporter vectors and then co-introduced them into A375 and A875 cells with miR-3666 mimic or mimic NC. This target recognition was further evidenced by that miR-3666 mimic diminished the EphA3 3′UTR-WT-derived luciferase activity while showed no impact on the EphA3 3′UTR-WT derived (Figure 4b). Furthermore, the low expression of miR-3666 was tested in melanoma tissues (Figure 4c) and cells (Figure 4d). In addition, the negative correlation between miR-3666 expression and EphA3 in clinical samples (Figure 4e) was further corroborated this miRNA-mRNA interaction. Taken together, miR-3666 directly targeted EphA3 and negatively regulated its expression.

EphA3 is targeted by miR-3666. (a) The base pairing between EphA3 3′UTR and miR-3666 was predicted by starBase analysis. (b) Luciferase activity of EphA3 3′UTR-WT or EphA3 3′UTR-MUT driven was assessed by luciferase system in A375 and A875 cells’ co-transfection with miR-3666 mimic or mimic NC. **P < 0.01 vs miR-NC. (c) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-3666 expression in melanoma tissues and normal tissues. (d) RT-qPCR analysis of miR-3666 expression in melanoma cells (A375 and A875) and HaCAT cells. **P < 0.01 vs HaCAT. (e) Pearson analysis of the correlation between EphA3 and miR-3666.
3.5 MiR-3666 overexpression abrogates the EphA3-driven proliferation and migration in melanoma cells through ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways
To verify the functional relevance of miR-3666 with EphA3, we delivered EphA3-OE vectors and miR-3666 mimic into A375 and A875 cells. As shown in Figure 5a, transfection of miR-3666 mimic diminished the EphA3 expression resulted from the transfection of EphA3-OE vectors. Functionally, EphA3 overexpression strengthened the proliferation and migration of A375 and A875 cells; on the contrary, miR-3666 mimic weakened two malignant behaviors of melanoma cells; more importantly, the promotion of EphA3 overexpression on melanoma cell growth was blockaded by miR-3666 mimic (Figure 5b and c). Western blot analysis further showed that the EphA3-induced upregulation of p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 MAPK was abrogated by miR-3666 mimic in melanoma cells (Figure 5d). Therefore, miR-3666 could sponge EphA3 to exert its inhibitory effect on melanoma malignancy.

MiR-3666 overexpression abrogates the EphA3-driven proliferation and migration in melanoma cells through MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Empty vectors, EphA3 overexpressing vectors (EphA3-OE), miR-3666 mimic (mimic), mimic NC, and EphA3-OE+ mimic were introduced into A375 and A875 cells. After 48 h transfection, (a) Western blot analysis of EphA3 expression in these above transfected cells. (b) Proliferation in these above transfected cells was determined by CCK-8 assay. (c) Migration in these above transfected cells was assessed by scratch wound assays. (d) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, p38MAPK, and p-p38MAPK expressions in these above transfected cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs empty vector; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 vs mimic NC; & P < 0.05, && P < 0.01 vs OE + mimic. OE + mimic: EphA3-OE + mimic.
3.6 The inactivation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways reverses the EphA3-driven proliferation and migration in melanoma cells
Next, we verified the functional correlation between EphA3 and ERK1/2 or P38 MAPK signaling pathways. As shown in Figure 6a, PD98059 (ERK1/2 inhibitor) and SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) treatment inhibited p-ERK1/2 and p-p38 MAPK protein levels induced by EphA3 overexpression, respectively. In addition, PD98059 and SB203580 could partially attenuate the enhanced effects of EphA3 overexpression on the proliferation and migration of A375 and A875 cells, respectively, and PD98059 combined with SB203580 could further inhibit the effect of EphA3 overexpression (Figure 6b and c). Therefore, the carcinogenesis of EphA3 on melanoma may be mediated through the activation of ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK signaling pathways.
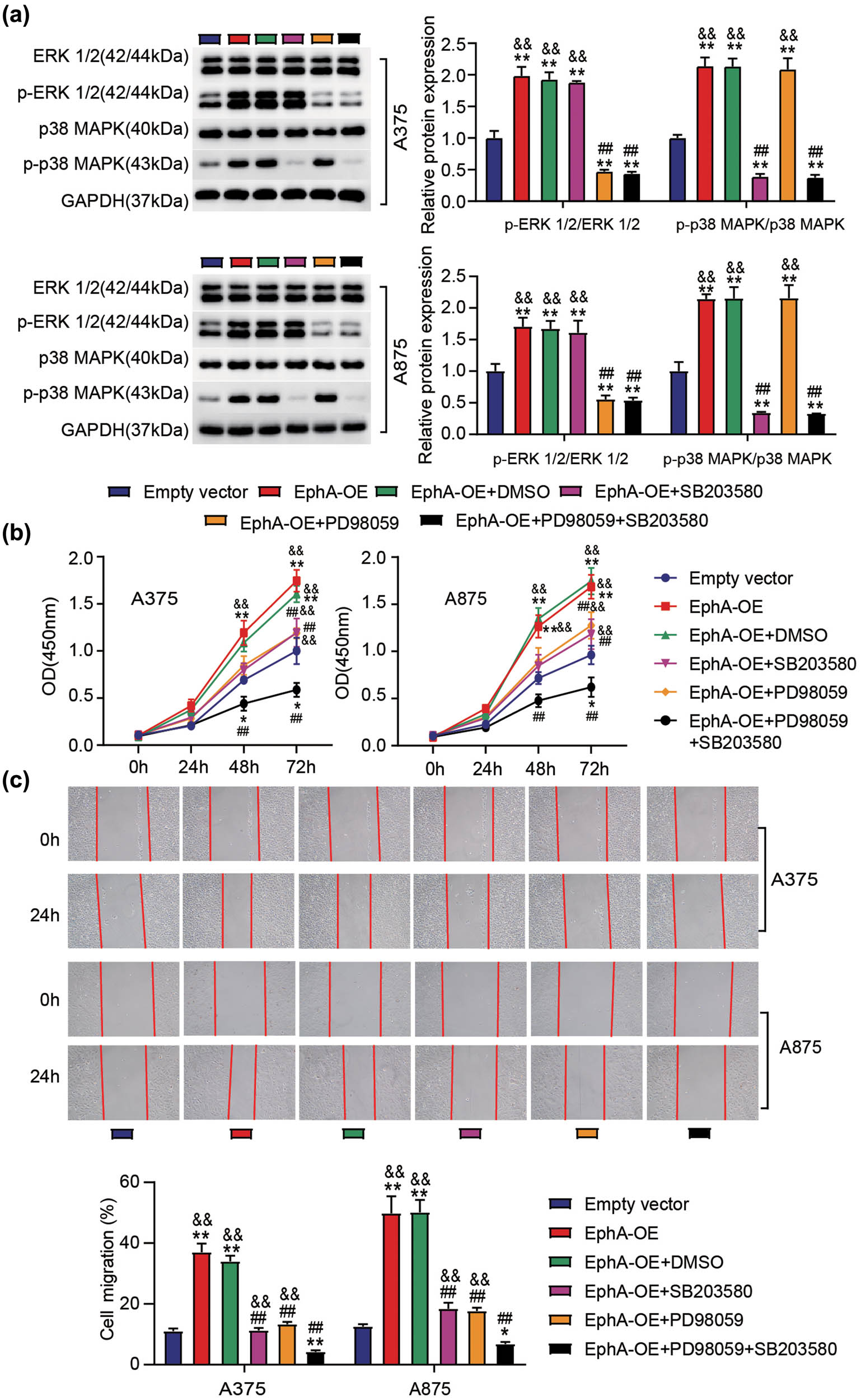
The inactivation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways’ reverses the EphA3-driven proliferation and migration in melanoma cells. A375 and A875 cells transfected with empty vectors or EphA3 overexpressing vectors (EphA3-OE) were pretreated with D98059 (ERK1/2 inhibitor) or SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor). After 48 h transfection, (a) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, p38MAPK, and p-p38MAPK expressions in these above transfected cells. (b) Proliferation in these above treated cells was determined by CCK-8 assay. (c) Migration in these above treated cells was assessed by scratch wound assays. P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs empty vector; ## P < 0.01 vs EphA-OE; && P < 0.01 vs EphA-OE + PD98059 + SB203580.
4 Discussion
In our present work, we found that EphA3 silence inhibited melanoma cells’ proliferation and migration by inactivating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. The tumor suppression of EphA3 silence in melanoma in vitro was further validated by in vivo. Mechanically, miR-3666 could abrogate the pro-proliferation and pro-migration effect of EphA3 overexpression on melanoma cell growth by inactivating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Collectively, EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways.
Previous investigations have showed that EphA3 has different roles in different cancers [19]. For example, EphA3 upregulation stimulates angiogenesis in multiple myeloma and attenuates cancer progression [20]. And yet, the downregulation of EphA3 protein is detected in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma and negatively associated with tumor diameter and advanced stage of patients [21]. In melanoma progression, somatic and germline mutations of EphA3 have been detected [22]. Furthermore, irradiation treatment could lessen malignant behaviors of human melanoma cells in parallel with the downregulation of EphA3 [23]. However, its detailed role in melanoma is still unknown. Our data showed that EphA3 was highly expressed in melanoma tissues and cells, and EphA3 silence mitigated the tumorigenic potential of melanoma in vitro and in vivo. And EphA3 overexpression boosted melanoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro. In glioma stem cells, EphA3 is responsible for sustained ERK1/2 activation and promotes its differentiation [24]. Hence, we test the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in melanoma cell when EphA3 silence. The outcome showed that EphA3 silence disrupted sustained ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. In a word, EphA3 promoted the malignant phenotypes of melanoma through driving ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways.
miRNA regulation plays an important role in shaping the cellular protein landscape by targeting mRNA 3′UTR [25]. Subsequent prediction showed that miR-3666 target EphA3 3′UTR, which is validated by luciferase reporter assays. Previously, miR-3666 performs its tumor-suppressive action in different cancers. For example, miR‑3666 suppressed the uncontrolling proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells [26]. The well-known oncoprotein of STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) is downregulated by miR‑3666, resulting in the retention of ovarian carcinoma progression [12]. Consistently, for the first time, we also found tumor suppression in miR‑3666 overexpressing melanoma cells, evidenced by the reduction of cell proliferation and migration along with the transfection of miR-3666 transfection. Notably, miR-3666 is reportedly responsible for the disruption of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in colorectal cancer [15]. Congruently, miR-3666 transfection blunted the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Therefore, miR-3666 might inactivate ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways to retard the melanoma progression. As its interaction with EphA3, miR-3666 mimic abrogated the increased proliferation and migration of melanoma cells driven by EphA3 overexpression through ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Therefore, miR-3666 downregulates EphA3 expression and suppresses melanoma malignancy via suppressing ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways.
5 Conclusion
In summary, our results showed that miR-3666 targeting EphA3 downregulated EphA3 expression and thereby suppressed the melanoma cell proliferation and migration through disruption of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Our findings suggest that miR-3666/EphA3 axis might be an effective target for melanoma intervention. However, this study is limited as the small sample size. Furthermore, EphA3’s function might be regulated by different miRNAs because of different base pairs. Therefore, more detailed mechanism of EphA3 driven should be explored in the future.
Acknowledgments
None.
-
Funding information: Funding information is not available.
-
Author contributions: DM and JJM performed the experiments and the analysis of the data. JJM designed and devised the study. DM obtained the data. DM and JJM processed and interpreted the data. The article has been read and approved by all authors.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets that have been used and/or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49.10.3322/caac.21660Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Rastrelli M, Tropea S, Rossi CR, Alaibac M. Melanoma: epidemiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and classification. In Vivo (Athens, Greece). 2014;28(6):1005–11.Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Lee AY, Brady MS. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy for melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 2021;123(3):782–8.10.1002/jso.26229Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Wang Y, Xuan Z, Wang B, Zhang D, Zhang C, Wang J, et al. EphA3 downregulation by hypermethylation associated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage in colorectal cancer. Digestive Dis Sci. 2019;64(6):1514–22.10.1007/s10620-018-5421-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Chen X, Lu B, Ma Q, Ji CD, Li JZ. EphA3 inhibits migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by activating the mesenchymal‑epithelial transition process. Int J Oncol. 2019;54(2):722–32.10.3892/ijo.2018.4639Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Toyama M, Hamaoka Y, Katoh H. EphA3 is up-regulated by epidermal growth factor and promotes formation of glioblastoma cell aggregates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(3):715–21.10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Qazi MA, Vora P, Venugopal C, Adams J, Singh M, Hu A, et al. Cotargeting ephrin receptor tyrosine kinases A2 and A3 in cancer stem cells reduces growth of recurrent glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78(17):5023–37.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0267Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Tímár J, Mészáros L, Ladányi A, Puskás LG, Rásó E. Melanoma genomics reveals signatures of sensitivity to bio- and targeted therapies. Cell Immunol. 2006;244(2):154–7.10.1016/j.cellimm.2006.12.009Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(4):1202–7.10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Luo M, Wu L, Zhang K, Wang H, Zhang T, Gutierrez L, et al. miR-137 regulates ferroptosis by targeting glutamine transporter SLC1A5 in melanoma. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(8):1457–72.10.1038/s41418-017-0053-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Díaz-Martínez M, Benito-Jardón L, Alonso L, Koetz-Ploch L, Hernando E, Teixidó J. miR-204-5p and miR-211-5p Contribute to BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78(4):1017–30.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1318Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Tan H, Wu C, Huang B, Jin L, Jiang X. MiR-3666 serves as a tumor suppressor in ovarian carcinoma by down-regulating AK4 via targeting STAT3. Cancer Biomarkers: Sect A Dismarkers. 2021;30(4):355–63.10.3233/CBM-190538Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Shou T, Yang H, Lv J, Liu D, Sun X. MicroRNA‑3666 suppresses the growth and migration of glioblastoma cells by targeting KDM2A. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(2):1049–55.10.3892/mmr.2018.9698Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Wang G, Cai C, Chen L. MicroRNA-3666 regulates thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation via MET. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;38(3):1030–9.10.1159/000443054Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Liu W, Song Y, Zhang C, Gao P, Huang B, Yang J. The protective role of all-transretinoic acid (ATRA) against colorectal cancer development is achieved via increasing miR-3666 expression and decreasing E2F7 expression. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:94–101.10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.015Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Weng J, Tu M, Wang P, Zhou X, Wang C, Wan X, et al. Amiodarone induces cell proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation via ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling in fibroblasts. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;115:108889.10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108889Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods (San Diego, Calif). 2001;25(4):402–8.10.1006/meth.2001.1262Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Chiari R, Hames G, Stroobant V, Texier C, Maillère B, Boon T, et al. Identification of a tumor-specific shared antigen derived from an Eph receptor and presented to CD4 T cells on HLA class II molecules. Cancer Res. 2000;60(17):4855–63.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] London M, Gallo E. Critical role of EphA3 in cancer and current state of EphA3 drug therapeutics. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(7):5523–33.10.1007/s11033-020-05571-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Caivano A, La Rocca F, Laurenzana I, Annese T, Tamma R, Famigliari U, et al. Epha3 acts as proangiogenic factor in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(21):34298–309.10.18632/oncotarget.16100Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Wang X, Xu H, Cao G, Wu Z, Wang J. Loss of EphA3 protein expression is associated with advanced TNM stage in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15(2):e169–73.10.1016/j.clgc.2016.07.028Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Balakrishnan A, Bleeker FE, Lamba S, Rodolfo M, Daniotti M, Scarpa A, et al. Novel somatic and germline mutations in cancer candidate genes in glioblastoma, melanoma, and pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007;67(8):3545–50.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0065Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Mosch B, Pietzsch D, Pietzsch J. Irradiation affects cellular properties and Eph receptor expression in human melanoma cells. Cell Adhes Migr. 2012;6(2):113–25.10.4161/cam.20655Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Day BW, Lathia JD, Bruce ZC, D’Souza RCJ, Baumgartner U, Ensbey KS, et al. The dystroglycan receptor maintains glioma stem cells in the vascular niche. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138(6):1033–52.10.1007/s00401-019-02069-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Thomson DW, Dinger ME. Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(5):272–83.10.1038/nrg.2016.20Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Yang D, Li R, Xia J, Li W, Zhou H. miR‑3666 suppresses cellular proliferation and invasion in colorectal cancer by targeting SATB2. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(6):4847–54.10.3892/mmr.2018.9540Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy

