Abstract
Gene expression profiling studies have shown the pathogenetic role of oncogenic pathways in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (ENKL). In this study, we aimed to identify the microRNAs (miRNAs) playing potential roles in ENKL, and to evaluate the genes and biological pathways associated to them. Gene expression profiles of ENKL patients were acquired from the gene expression omnibus (GEO) database. Most differentially expressed (DE)-miRNAs were identified in ENKL patients using limma package. Gene targets of the DE-miRNAs were collected from online databases (miRDB, miRWalk, miRDIP, and TargetScan), and used in Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analyses on Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery database, and then used in protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis on STRING database. Hub genes of the PPI network were identified in cytoHubba, and were evaluated in Biological networks gene ontology. According to the series GSE31377 and GSE43958 from GEO database, four DE-miRNAs were screened out: hsa-miR-363-3p, hsa-miR-296-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p, and hsa-miR-221-3p. Totally 164 gene targets were collected from the online databases, and used in the GO and KEGG pathway analyses and PPI network analysis. Ten hub genes of the PPI network were identified: AURKA, TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CCNB1, PLK1, CUL1, ESR1, CDC20, and PIK3CA. Those hub genes, as well as their correlative pathways, may be of diagnostic or therapeutic potential for ENKL, but further clinical evidence is still expected.
1 Introduction
Natural killer (NK) cell tumors are categorized as extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKL), aggressive NK-cell leukemia, chronic NK-cell lymphoproliferative disorders, etc., according to the 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) classification [1,2]. Among them, ENKL is relatively more common, which include both nasal and extra-nasal ENKL categories of disease in the current 2016 WHO classification [3]. ENKL is rarely diagnosed in Western countries, but relatively more common in East Asian countries [2]. ENKL is associated with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) because EBV can infect T and NK cells and lead to EBV-associated T/NK cell lymphoproliferative disorders [1], according to observations of EBV molecules in tumor tissue and the correlations between EBV load and disease diagnosis and prognosis [4]. ENKL is a unique clinical entity characterized by an aggressive clinical course, and the prognosis is poor [5].
The pathogenesis of this tumor is poorly understood, but in recent years gene expression profiling studies have demonstrated the pathogenetic role of several oncogenic pathways in ENKL, such as AKT, STAT3, NF-KB, Notch-1, and Aurora kinase A [6,7]. In this sense, an important task is to find novel molecular and biological candidates for diagnostic, predictive, and prognostic potential in ENKL, including microRNAs (miRNAs).
miRNAs are small non-coding RNAs, which can regulate the gene expression in many cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and tumor genesis [8]. Since the discovery of miRNAs in circulation, a large amount of miRNA-related biological studies have confirmed that each miRNA can affect numerous target mRNAs [9] and each mRNA can be targeted by multiple miRNAs, enabling wide regulatory complexity of gene expression adjustment [10]. Furthermore, quantification of miRNAs can have potential diagnostic and prognostic utility in lymphoma [11,12,13]. miRNAs are easily detectable, relatively stable, and tissue specific, making them attractive candidate biomarkers [14]. Enhancing our understanding of the relationships between miRNAs and gene targets can help reveal detailed mechanisms and identify novel biomarkers for lymphoma.
In this study, we aimed to identify the miRNAs playing potential roles in the ENKL patients, which might further help provide valuable advice in clinical treatment. To that end, we acquired typical gene expression profiles of ENKL patients from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, and identified four miRNAs that are most differentially expressed (DE) in those ENKL patients using limma package in R. After that, gene targets of these four DE-miRNAs were collected by employing online databases, and then in terms of those gene targets, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were performed on the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID), protein–protein interaction (PPI) were performed on STRING, and finally hub genes of the PPI network were identified in cytoHubba and evaluated in Biological Networks Gene Ontology (BiNGO) tool, in Cytoscape. Hope our study is helpful for revealing the mechanisms of ENKL pathogenesis, and for identifying the diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers of ENKL.
2 Methods
2.1 Data source
The expression profiles of ENKL patients were collected from the GEO database. We searched the GEO for series about the expressions of miRNAs in ENKL patients which must contain both the tumor and normal samples, and only two series GSE31377 [15] and GSE43958 [16] were regarded suitable for this study. In GSE31377, we regarded the samples of ENKL patients’ tissues and NK tumor cell-lines as “ENKL” group, and those of normal NK cells from healthy individuals’ blood and ENKL patients’ normal tissues as “normal” group, while in GSE43958, we took the NK tumor cell-line samples as “ENKL” group, and those of normal NK cells from healthy individuals’ blood as “normal” group (Table 1). Differential expression analysis was performed between “ENKL” and “normal” groups in both series, separately.
Sample grouping of GSE31377 and GSE43958 for DE-miRNA identification
| Series | Groups | Sources of samples |
|---|---|---|
| GSE31377 | ENKL | ENKL patients’ tissues and NK tumor cell-lines |
| Normal | Normal NK cells from healthy individuals’ blood and ENKL patients’ normal tissues | |
| GSE43958 | ENKL | NK tumor cell-lines |
| Normal | Normal NK cells from healthy individuals’ blood |
2.2 Identification of DE-miRNAs
The limma R package v3.12 was applied and served as the processor. An R GUI application v1.77 with R v4.0.4 was installed via home-brew 3.0 with –cask option on Mac OS Catalina. The limma package was installed in the package installer tool of this application. DE-miRNAs of the normal and ENKL groups were screened out according to the criteria adjusted p < 0.05 and absolute log fold change |log2 FC| >1, where the FDR method was used to adjust the p, with an option adjust=“BH” for the toptable( ) function of limma. As both series GSE31377 and GSE43958 gave DE-miRNA lists, the common DE-miRNAs appearing in both lists were collected for subsequent analysis.
2.3 miRNA-target interactions
Investigating the gene targets of miRNAs is crucial for identifying the regulatory mechanisms and functions of miRNAs. Herein we predicted the gene target of the DE-miRNAs by employing four miRNA-target prediction tools: miRDIP, miRWalk, miRDB, and TargetScan. The gene targets were determined by overlapping results from the four websites: first, for each miRNA, gene targets from the four websites were overlapped and common ones were picked up as a candidate list; and second the candidate lists of the four miRNAs were merged. After the miRNA targets were determined, the interactions of them would be visualized in Cytoscape.
2.4 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of gene targets
GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the determined gene targets were performed using the DAVID, which revealed gene enrichments associated with biological processes (BPs), cellular components (CCs), molecular functions (MFs), and KEGG pathways associated with the gene targets. Number of the gene targets enriched in each of those items would be listed.
2.5 PPI network and biological analysis of hub genes
To gain insights into the interactions between gene targets, a PPI network was constructed using the STRING tool to reveal the molecular mechanisms of ENKL. The STRING was able to give a complex full PPI network, and usually the interactions between the hub genes were more interesting. The full network from the STRING was imported into the cytoHubba plugin of the Cytoscape to identify the hub genes. For biological analysis of hub genes, another plugin of Cytoscape BiNGO was employed. BiNGO has the capability to evaluate and visualize the pathways of enriched BPs, CCs, and MFs. We only performed the analysis on enriched BPs of the ten hub genes in this study.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was used only for the identification of DE-miRNAs. Specifically, when applying the limma package, first, a linear model lmfit( ) would be fit for the expression data to estimate the expression levels of genes in each group, and then contrast fit contrasts.fit( ) was performed to estimate the expression differences of genes between ENKL group and control group. After that, empirical Bayes statistics ebayes( ) was employed for t-statistics, moderated F-statistics, and log-odds of differential expression, and finally top DE-miRNAs were exported via toptable( ) of limma, where p values of the t-statistics were adjusted using FDR method with the option adjust=“BH”. The significant DE-miRNAs of each series that we were interested in were selected according to the criterion adjusted p < 0.05, and |log2 FC| > 1.
-
Statement of ethics: Ethical approval was not required in this study because all the data were collected from public papers and databases.
3 Results
3.1 DE-miRNAs: hsa-miR-363-3p, hsa-miR-296-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p, and hsa-miR-221-3p
According to GSE31377, 229 DE-miRNAs (including 59 downregulated and 170 upregulated) were screened out, while for GSE43958, 49 DE-miRNAs (including 47 upregulated and 2 downregulated) were found (Figure 1 and Table 2). The common four appearing in both the DE-miRNA lists were finally selected for further analysis: hsa-miR-363-3p (down), hsa-miR-296-5p (up), hsa-miR-155-5p (up), and hsa-miR-221-3p (up in GSE43958 but down in GSE31377) (Table 3).
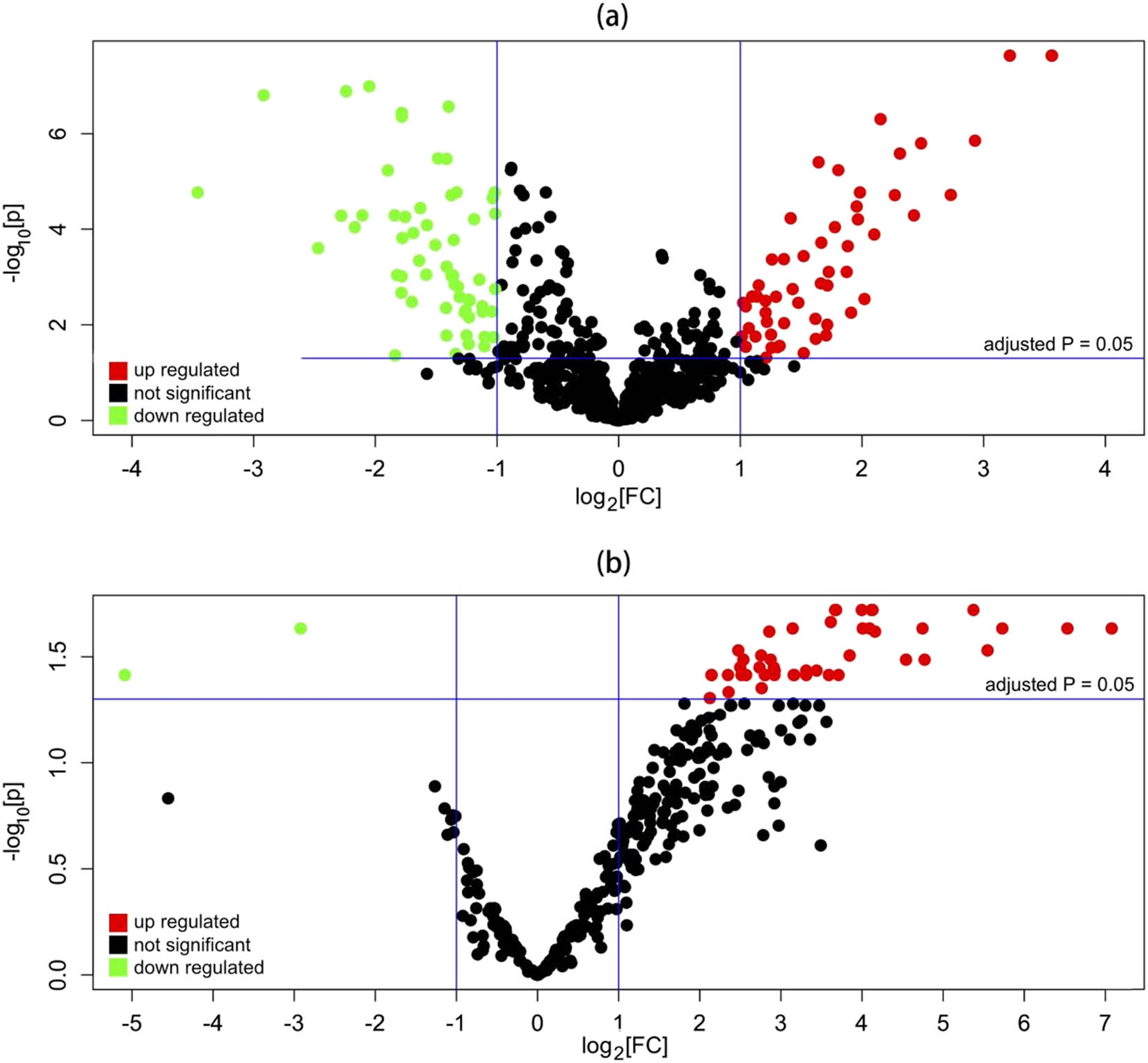
Volcano plots of the expressions of miRNAs for (a) GSE31377, and (b) GSE43958.
Upregulated and downregulated miRNAs for series GSE31377 and GSE43958
| GSE31377 | Upregulated | hsa-miR-218-1*, hsa-miR-486-3p, hsa-miR-499-3p, hsa-miR-520a-5p, hsa-miR-633, hsa-miR-582-3p, hsa-miR-411*, hsa-miR-1233, hsa-miR-635, hsa-miR-541, hsa-miR-138-1*, hsa-miR-758, hsa-miR-637, hcmv-miR-UL148D, ebv-miR-BART20-5p, hsa-miR-1236, hsa-miR-196a*, hsa-miR-661, hsa-miR-501-3p, hsa-miR-625*, kshv-miR-K12-9*, hsa-miR-518b, hcmv-miR-UL112, ebv-miR-BART10*, hsa-miR-133a, hsa-miR-200a*, hsa-miR-486-5p, ebv-miR-BART13*, ebv-miR-BHRF1-1, hsa-miR-602, hsa-miR-596, ebv-miR-BART7*, hsa-miR-18b*, ebv-miR-BART20-3p, hsa-miR-583, hsa-miR-765, hsa-miR-493, hsa-miR-518c*, ebv-miR-BART2-5p, ebv-miR-BART9*, kshv-miR-K12-8, hsa-miR-566, hsa-miR-648, hsa-miR-483-5p, hsa-miR-1228, hsa-miR-639, hsa-miR-130b, hsa-miR-622, hsa-miR-155, hsa-miR-296-5p, hsa-miR-542-5p, kshv-miR-K12-3, hsa-miR-424*, ebv-miR-BART2-3p, ebv-miR-BART12, hsa-miR-630, hsa-miR-188-5p, hsa-miR-940, hsa-miR-345, hsa-miR-150*, ebv-miR-BART14*, kshv-miR-K12-10a, hsa-miR-572, hsa-miR-431, ebv-miR-BART18-3p, hsa-miR-135a*, ebv-miR-BART16, hsa-miR-575, hsv1-miR-LAT, ebv-miR-BART11-5p, hsa-miR-1224-5p, hcmv-miR-UL70-3p, hsa-miR-10b*, ebv-miR-BART11-3p, ebv-miR-BART13, ebv-miR-BART19-5p, hsa-miR-638, hsa-miR-614, hiv1-miR-H1, ebv-miR-BART19-3p, hsa-miR-801, ebv-miR-BART5, hsa-miR-663, ebv-miR-BART18-5p, hsa-miR-494, ebv-miR-BART4, ebv-miR-BART6-5p, ebv-miR-BART1-5p, hsa-miR-923, ebv-miR-BART8, ebv-miR-BART17-3p, ebv-miR-BART6-3p, ebv-miR-BART17-5p, ebv-miR-BART10, ebv-miR-BART8*, ebv-miR-BART1-3p, ebv-miR-BART3, ebv-miR-BART7, ebv-miR-BART9, and ebv-miR-BART14 |
| Downregulated | hsa-miR-150, hsa-miR-363, hsa-miR-26b, hsa-miR-101, hsa-miR-338-3p, hsa-miR-374a, hsa-miR-30b, hsa-miR-873, hsa-miR-28-5p, hsa-miR-140-5p, hsa-miR-142-5p, hsa-miR-768-3p, hsa-miR-29c, hsa-miR-30e, hsa-miR-152, hsa-miR-181a-2*, hsa-miR-374b, hsa-miR-186, hsa-miR-194, hsa-miR-340, hsa-miR-30c, hsa-miR-342-5p, hsa-miR-32, hsa-miR-361-3p, hsa-miR-148b, hsa-miR-10a, hsa-miR-22, hsa-miR-876-3p, hsa-miR-26a, hsa-miR-33a, hsa-miR-598, hsa-miR-876-5p, hsa-miR-148a, hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-590-5p, hsa-miR-30e*, hur_5, hsa-miR-744, hsa-miR-181c, hsa-miR-192, hsa-miR-22*, hsa-let-7c, hsa-miR-23a, hsa-miR-141, hsa-miR-27a, hsa-miR-98, hsa-miR-23b, hsa-miR-361-5p, hsa-miR-195, hsa-miR-215, hsa-miR-221, hsa-miR-185, hsa-miR-425, hsa-miR-151-5p, hsa-miR-95, hsa-miR-7-1*, hsa-miR-339-5p, hsa-miR-362-3p, hsa-miR-29c*, hsa-miR-200b, hsa-miR-132, hsa-miR-221*, hsa-miR-27b, hsa-let-7d, hsa-let-7b, hsa-miR-101*, hsa-miR-106a*, hsa-miR-138-2*, hsa-miR-191, hsa-miR-32*, hsa-miR-497, hsa-miR-505, hsa-miR-627, hsa-miR-122, hsa-miR-31, hsa-miR-30a, hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-660, hsa-miR-505*, hsa-miR-454, hsa-miR-539, hsa-miR-324-5p, hsa-miR-885-3p, hsa-miR-331-3p, hsa-miR-532-3p, hsa-miR-545, hsa-miR-30d, hsa-miR-625, hsa-let-7i*, hsa-miR-26b*, hcmv-miR-US25-2-5p, hsa-miR-196b, hsa-miR-190b, dmr_285, hsa-miR-132*, hsa-miR-29b-2*, hsa-miR-29a*, hsa-miR-513a-3p, hsa-miR-335, hsa-miR-340*, hsa-miR-769-5p, hsa-miR-499-5p, hsa-miR-595, hsa-miR-30d*, hsa-miR-624*, hsa-miR-339-3p, hiv1-miR-N367, hsa-miR-146b-3p, hsa-miR-197, hsa-miR-297, hsa-miR-374b*, hsa-miR-642, hsa-miR-326, hsa-let-7g*, hsa-miR-548c-5p, hsa-miR-148b*, hsa-miR-520f, hsa-miR-190, hsa-miR-449b, hsa-miR-186*, hsa-miR-188-3p, hsa-miR-185*, hsa-miR-590-3p, hsa-miR-593, hsa-miR-200c*, hsa-miR-24-1*, hsa-miR-519a, hsa-miR-374a*, hsa-miR-577, hsa-miR-592, hsa-miR-578, hsa-miR-363*, and hsa-miR-573 | |
| GSE43958 | Upregulated | hsa-miR-20a-5p, hsa-miR-17-5p, hsa-miR-19b-3p, hsa-miR-106a-5p, hsa-miR-20b-5p, hsa-miR-1275, hsa-miR-1973, hsa-miR-1246, hsa-miR-19a-3p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-29b-3p, hsa-miR-210-3p, hsa-miR-3648, hsa-miR-3197, hsa-miR-4284, hsa-miR-711, hsa-miR-4294, hsa-miR-3154, hsa-miR-221-3p, hsa-miR-3679-5p, hsa-miR-29a-3p, hsa-miR-642b-3p, hsa-miR-3687, hsa-miR-3175, hsa-miR-370-3p, hsa-miR-1281, hsa-miR-1825, hsa-miR-3141, hsa-miR-4279, hsa-miR-3651, hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-92a-3p, hsa-miR-1908-5p, hsa-miR-1976, hsa-miR-4299, hsa-miR-1913, hsa-miR-301a-3p, hsa-miR-1274a, hsa-let-7f-5p, hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-296-5p, hsa-miR-92b-3p, hsa-miR-320a-3p, hsa-miR-4327, hsa-miR-1236-3p, hsa-miR-1229-3p, and hsa-miR-4323 |
| Downregulated | hsa-miR-363-3p and hsa-miR-150-5p |
The four common DE-miRNAs of GSE31377 and GSE43958 series
| GSE31377 | GSE43958 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log2 FC | Adjusted p | log2 FC | Adjusted p | |
| hsa-miR-363-3p | −2.92 | 1.57 × 10−7 | −2.92 | 0.023 |
| hsa-miR-155-5p | 1.04 | 0.004 | 7.08 | 0.023 |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | −1.12 | 0.005 | 2.76 | 0.031 |
| hsa-miR-296-5p | 1.07 | 0.012 | 2.80 | 0.039 |
3.2 164 gene targets and interactions were identified for DE-miRNAs
After searching the four online databases, finally 164 genes associated with the four DE-miRNAs were determined as the ones playing potential roles in ENKL pathogenesis (Table 4). The bridge genes between hsa-miR-363-3p and hsa-miR-221-3p are FNIP2 and ANKIB1, and the other bridge gene between hsa-miR-221-3p and hsa-miR-155-5p is ZNF652, while the genes associated with hsa-miR-296-5p appear isolated from others.
miRNA-target interactions of hsa-miR-363-3p, hsa-miR-296-5p, hsa-miR-221-3p, and hsa-miR-155-5p according to miRDIP, miRWalk, miRDB, and TargetScan
| miRNA | Gene targets |
|---|---|
| hsa-miR-363-3p | ZDHHC5, ZDHHC3, XRN1, USP28, TTC28, TRAF3, TNRC6B, TMEM50B, TEF, SYT1, SYNJ1, SYNDIG1, SOX11, SLC25A36, SETD5, SEL1L3, RRN3, RGS3, RBPMS2, RASSF3, RAP1B, RAB23, PRKCE, POLK, PITPNM2, PIP4K2C, PIK3R3, PHLPP2, PAPOLA, OTUD3, NUFIP2, NSMAF, NFIX, NF2, MYO5A, MMP16, MBNL3, MAN2A1, LUZP1, LPP, LHFPL2, KIF5B, KCNC4, KAT2B, ITGAV, HOXD10, HAS3, GPR180, GPR158, FNIP2, FNIP1, FNDC3B, FAR1, FAM160B1, FAM133B, FAM126B, ELOVL6, DYRK2, DUS2, DCP1A, DACT1, DAB2IP, CPEB2, CD69, C21ORF91, C20ORF194, AURKA, APPL1, ANKRD44, ANKIB1, and ADAM19 |
| hsa-miR-296-5p | TMEM135, TEAD3, NUAK2, NSD1, MACF1, KCTD15, GPC2, GAB2, FGFR1, FAM53B, EPN1, ECHDC1, DYNLL2, CMTM4, and BAHD1 |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | ZNF652, UBN2, TNRC6C, TFG, TCF12, SYT10, SLC4A4, SLC25A37, SEMA6D, SBK1, PTBP3, POGZ, PLEKHA2, PCDHAC1, PCDHA3, PANK3, NRG1, NIPAL4, NFATC3, NDST3, NDFIP1, MIER3, MIDN, KPNA1, KMT2A, KLF7, KDR, KCNK2, IGF2BP2, HIPK1, GBX2, GABRA1, FRY, FNIP2, FAM214A, ETV3, ESR1, ERBB4, EML6, DYRK1A, DPP8, DLG2, DCUN1D4, DCUN1D1, DCAF7, CRKL, CPNE8, CDON, CACNB4, C6ORF120, C3ORF70, BRWD1, BMF, BEND4, BCL2L11, ATXN1, ATAD2B, ARID1A, ARHGEF7, ANKIB1, ANGPTL2, AKAP5, and ADAM22 |
| hsa-miR-155-5p | ZNF652, XKR4, VAV3, TSPAN14, TRIM32, TM9SF3, SOX10, MYLK, KDM5B, KANSL1, HNRNPA3, FBXO11, DUSP14, CKAP5, C6ORF89, BNC2, ATXN1L, and AAK1 |
3.3 Enrichment of 164 gene targets in BPs, CCs, MFs, and KEGG pathways
Using the 164 gene targets, the DAVID listed the top 10 enriched gene counts of 61 BPs, 15 CCs, 18 MFs, and 10 KEGG pathways (Figure 2). The significantly enriched entries of BPs include positive and negative regulations of transcription from RNA polymerase II, and protein phosphorylation; the majority of the enriched CCs include nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cytosol, and nucleoplasm; and the most enriched MFs is protein binding. The enriched entries of KEGG pathways include regulation of actin cytoskeleton, FcγR-mediated phagocytosis, proteoglycans in cancer, focal adhesion, ErbB signaling pathway, thyroid hormone signaling pathway, sphingolipid signaling pathway, microRNAs in cancer, rap1 signaling pathway, and pathways in cancer.
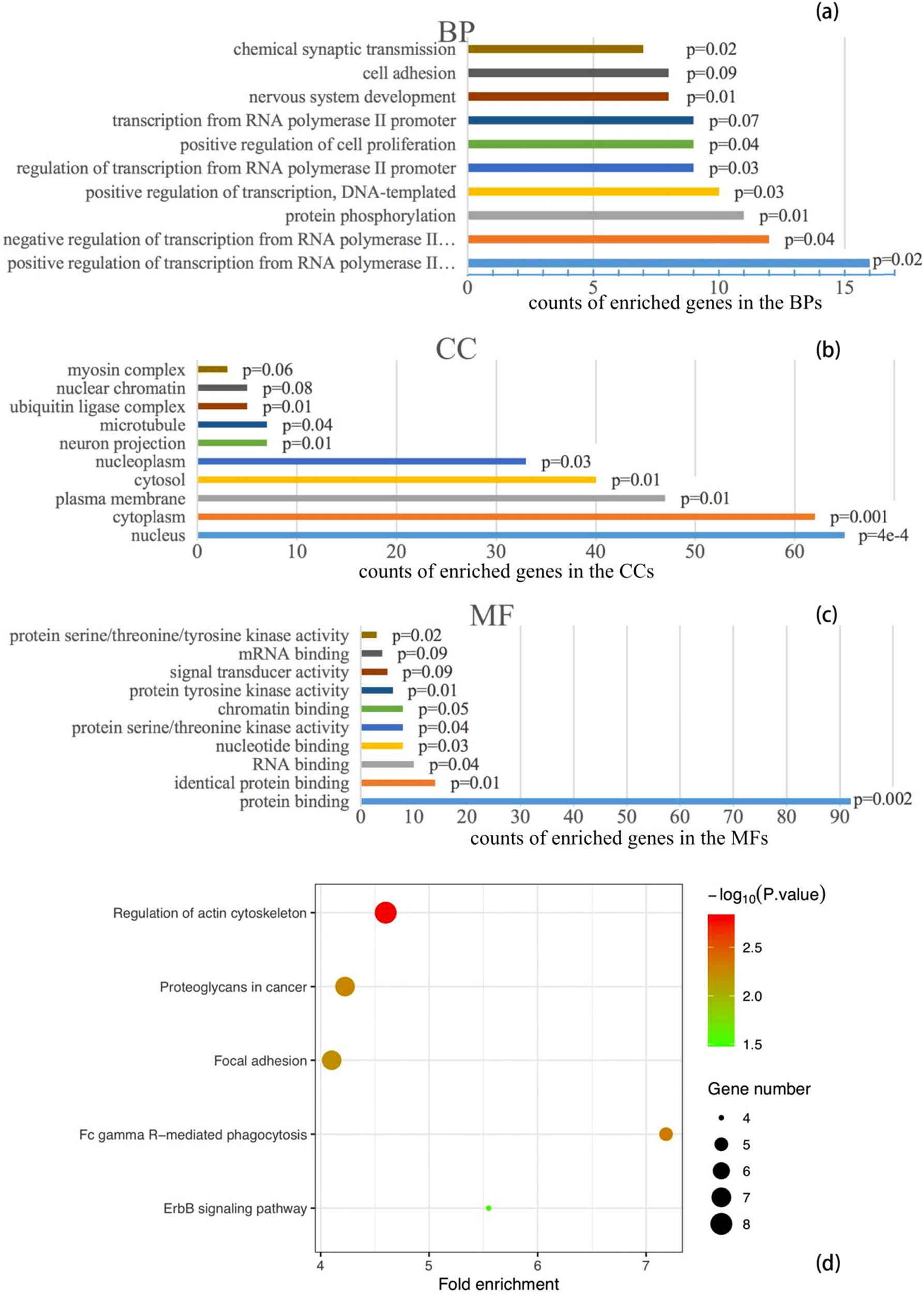
Top 10 gene counts of enrichment in BPs (a), CCs (b), and MFs (c), and KEGG pathways (d). Note: bar colors in (a), (b), and (c) only represent intuitive distinguishing of entries, not any scale of values.
3.4 Hub genes of 164 gene targets: AURKA, TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CCNB1, PLK1, CUL1, ESR1, CDC20, and PIK3CA
According to the 164 gene targets, STRING gave a complex network with 1,638 lines and 253 nodes. A reduced graph of this network is shown in Figure 3, in which only the top 100 scored nodes are kept, and the node color represents the connection degree of node, evaluated in cytoHubba. Hub genes, playing essential potential roles in the network, were distinguished in terms of the connection degree. We selected the top 10 hub genes for further analysis: AURKA, TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CCNB1, PLK1, CUL1, ESR1, CDC20, and PIK3CA (Figure 4). Figure 5 is the biological pathways of enriched BPs of hub genes, where the nodes with associated gene count less than five have been removed for a more clear network. This biological process pathway network involves 64 nodes and 91 edges.
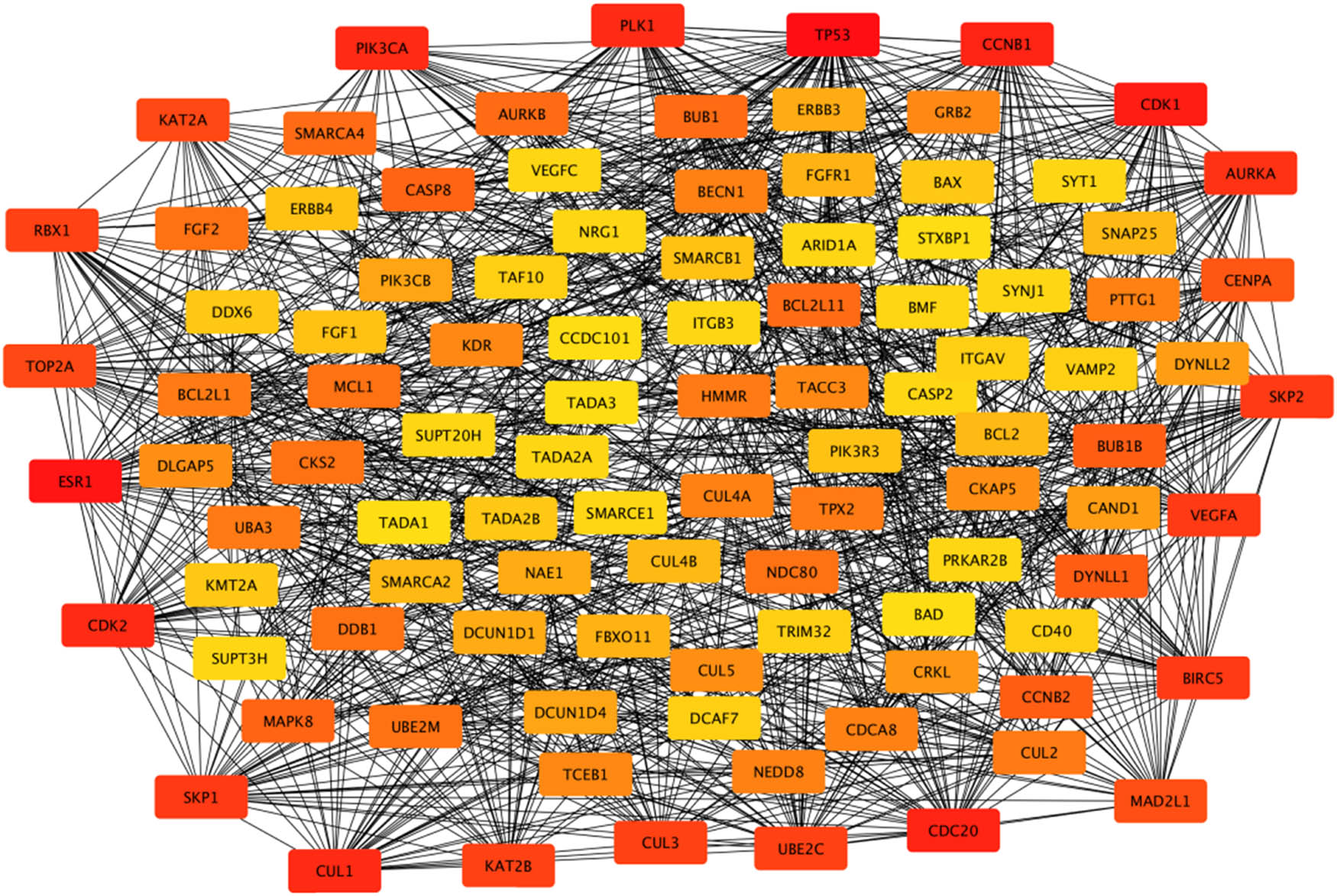
The PPI network associated with the 164 gene targets. Note: Box colors only represent relative comparison of connection counts of boxes in the network. Deeper red represents more connections.
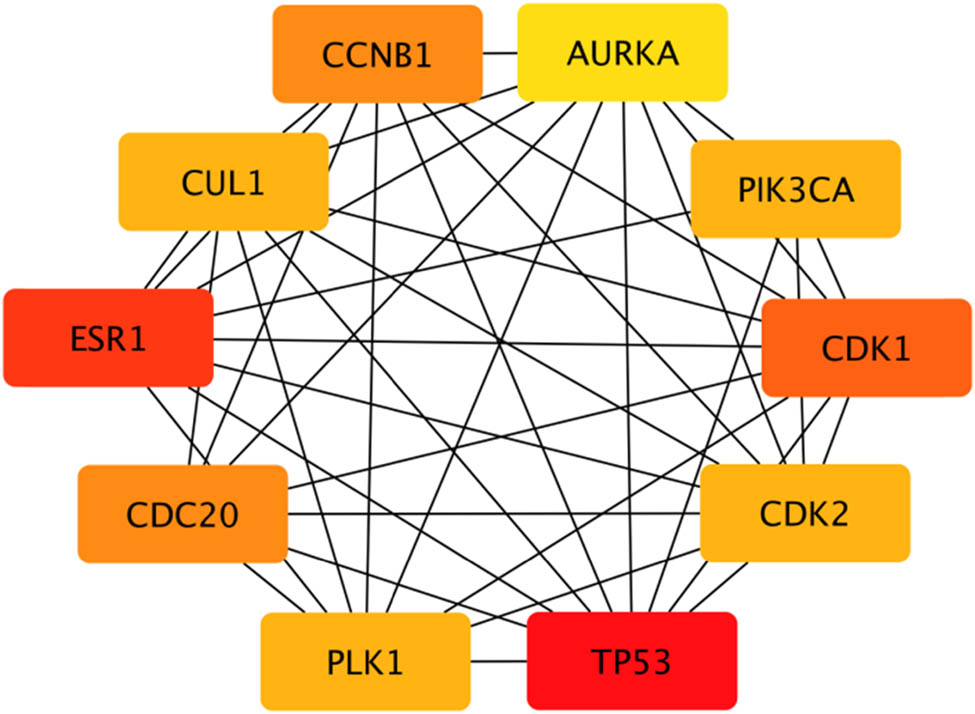
Top hub genes and their interactions of the PPI network. Note: Box colors only represent relative comparison of connection counts of boxes in Figure 3. Deeper red represents more connections.
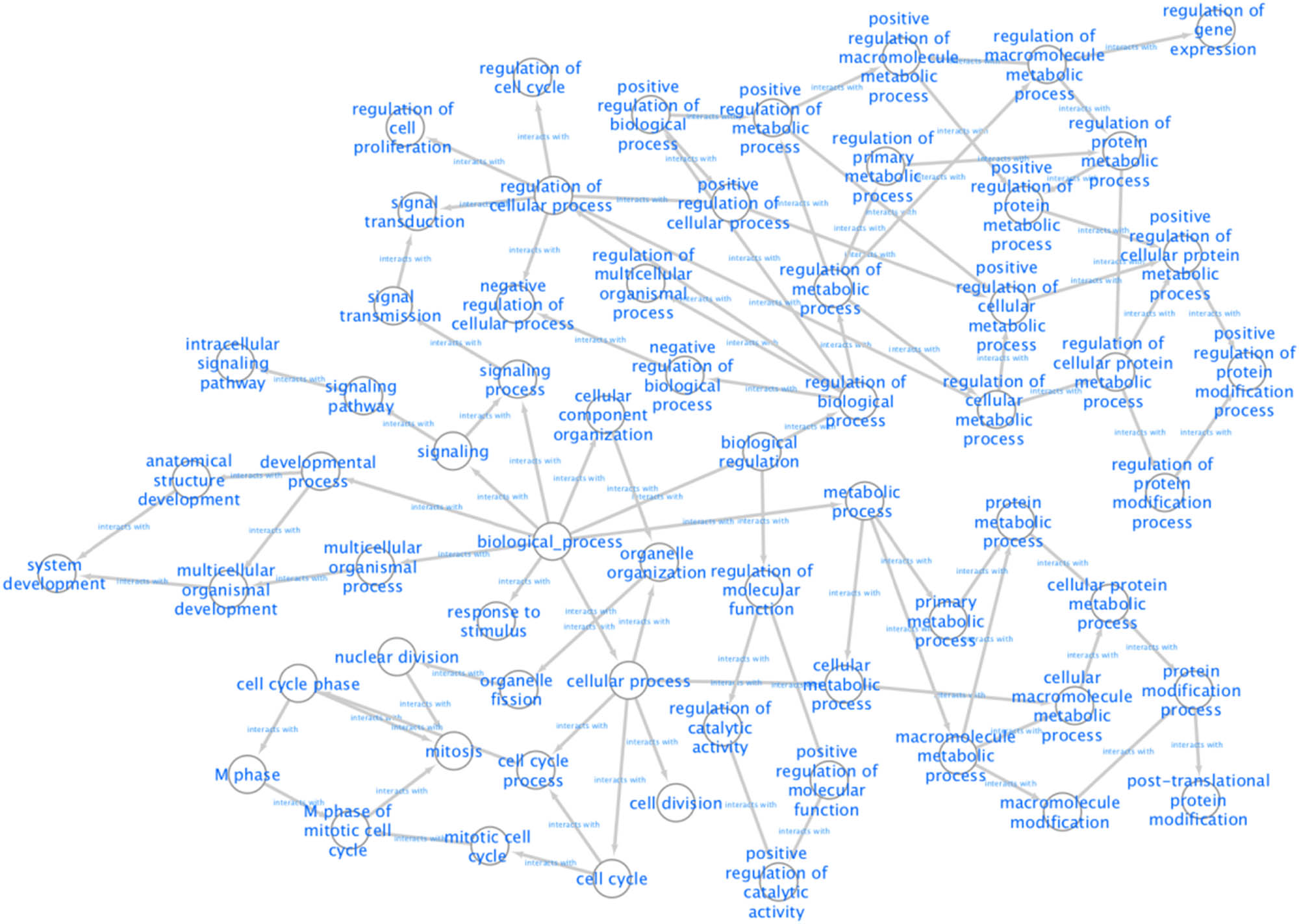
Pathways of enriched BPs according to results of the BiNGO.
4 Discussion
ENKL is a highly aggressive tumor, and a better understanding about the molecular abnormalities could provide important insights into the biology of this disease, as well as potential new therapeutic choice. Numerous trials have indicated that miRNAs may play key roles in the development of ENKL. Accordingly, strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of ENKL might be furnished via analysis of correlative data in GEO database and construction of ENKL-associated miRNA-target interactions regulatory network.
In this study, we screened out four common DE-miRNAs from GEO series GSE31377 and GSE43958. Among the four DE-miRNAs, miR-155 has been reported in several hematologic malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia [17,18], acute and chronic lymphoblastic leukemia [19,20], myelodysplastic syndrome [21], diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [22], follicular lymphoma [22], Hodgkin’s lymphoma [23], and ENKL [24].
miRNA-155 is highly expressed in ENKL and NK tumor cell-lines where it activates the AKT signaling pathway to down-regulate tumor suppressor genes, leading to tumor cell proliferation [25]. As ENKLs are closely associated with EBV, miR-155 plays an important role in the regulating immune responses and the development of viral infections, indicating that this miRNA can promote the development of tumors by regulating the expression of inflammatory factors and changing the microenvironment [24,26,27]. Furthermore, inhibition of miR-155 expression could improve the sensitivity of ENKL to doxorubicin, even reverse the drug resistance [24,28]. Therefore, miR-155 is a key factor in the emergence and development of ENKL, making it a potential clinical indicator to evaluate the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of patients with ENKL.
Likewise, as for miR-363, several studies have revealed the possible regulatory functions of miR-363 in diverse BPs. The miR-363 was found downregulated in the Burkitt’s lymphoma than in normal tissue [29], and the downregulation of miR-363 could precisely differentiate the high-grade lymphomas into ABC or GCB subtypes [30]. Evidence has shown that the expression of miR-363 is correlated with clinical outcomes [30]. Moreover, the down-regulation of miR-363 has been shown to be associated with drug-resistance [31] and poor prognosis [32]. Its downregulation has also been detected in many solid tumors such as ovarian cancer, and in human papillomavirus-transfected keratinocyte HaCaT cells [33]. In this study, as the downregulation of miR-363-3p was only shown in bioinformatics, more information is needed for larger scale clinical verification.
The miR-221-3p in this study was found upregulated in GSE43958 but downregulated in GSE31377. In fact such difference has been noticed in clinical practice by Guo et al. [34]. Plasma miR-221 of 79 ENKL patients were measured in that study, and were found upregulated or downregulated differently. The authors compared the upregulated and downregulated groups, and found significant differences with respect to gender (p = 0.003) and ECOG performance status (p = 0.023), but insignificant with respect to their response rate and complete remission rates. They also found the upregulation of miR-221 associated with shorter overall survival. So it is indicated that miR-221 may either be upregulated or downregulated in ENKL patients, but upregulated miR-221 may be associated with poorer prognosis. We must note, however, that as the discrepancy of regulations of hsa-miR-221-3p exists in GSE43958 and GSE31377, the role of hsa-miR-221-3p in ENKL needs still further investigation.
miR-296 is located in chromosomal region 20q13.32. It has a high degree of sequence conservation among species and plays important roles in many BPs [35]. miR-296 is upregulated in various types of cancers, such as DLBCL, gastric cancer, etc. [36]. It functions as an oncogene by targeting important tumor suppressors, such as CDX1, STAT5A, SOCS2, ICAM1, CASP8, NGFR, NF2, and HGS, and thereby regulates important cancer-related processes, such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration, blood vessel development, and chemoresistance [36]. In this study, bioinformatics show that miRNA-296-5p was upregulated, and the TMEM135, TEAD3, NUAK2, NSD1, MACF1, KCTD15, GPC2, GAB2, FGFR1, FAM53B, EPN1, ECHDC1, DYNLL2, CMTM4, and BAHD1 are potential target genes of miRNA-296-5p, but no definitive evidence has yet been reported in literature. Our findings indicate that miR-296-5p might play roles in inflammatory and malignant tumors, but further clinical evidence is still expected.
Thus, more detailed research is needed to explore the potential functions of the identified DE-miRNAs in ENKL. We found that several hub genes, such as AURKA, TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CCNB1, PLK1, CUL1, ESR1, CDC20, and PIK3CA, and correlative pathways, including regulation of actin cytoskeleton, FcγR-mediated phagocytosis, proteoglycans in cancer, focal adhesion, and ErbB signaling pathway, may be of diagnostic or therapeutic potential for ENKL.
A wide range of diseases, including cancer, result from malfunctioning of actin cytoskeletal proteins [37] and proteoglycans [38]. So further studies and more clinical samples are underway to determine whether an actin cytoskeleton or proteoglycan panel targeted antibody could be useful in the classification and better characterization of ENKL. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a promising target for the treatment of solid tumors because its expression has been linked to tumor progression, invasion, and drug resistance [39]. Several FAK inhibitors have been developed and tested for efficacy in treating advanced cancers [39]. As lymphoma’s biological behavior is more inclined to solid tumor [40], and we found focal adhesion to play an important role in ENKL, so FAK may serve as an effective therapeutic target to ENKL. Two important types of ErbB inhibitor are in clinical use: humanized antibodies directed against the extracellular domain of EGFR or ErbB2, and small-molecule tyrosine-kinase inhibitors that compete with ATP in the tyrosine-kinase domain of the receptor [41]. As we lack experience of ErbB inhibitor used for ENKL, so a larger scale verification for it is still needed. Hope in the future, further factors that underlie clinical response to signaling pathway targeted therapeutics could be uncovered by continuing the combination of fundamental and clinical studies. We also hope that the network of biological process pathways will contribute not only to the development of novel therapeutics, but also in allowing us to optimally use those already in the clinic.
5 Limitations
There are several limitations to our present study. (1) The number of samples we obtained from GSE31377 and GSE43958 is relatively small, and the data from the two series were not comprehensive enough, especially the amount of data in GSE43958 were very limited, even with plenty of blanks, which partially limits the result of this study. However, other series in GEO either contain fewer samples, or lack healthy samples as control group; (2) in GSE31377, the “ENKL” group contains samples of both ENKL tissue and NK tumor cell-lines, while in GSE43958, the “ENKL” group contains samples of only NK tumor cell-lines, thus uncertainties might be introduced because the miRNA and genes in NK tumor cell-lines may be different from those in ENKL tissues; (3) the normal NK cells were collected from healthy individuals’ blood, while ENKL tissue samples were from tissues. This difference in their sources may also affect the results. Thus, more samples are needed for validation with quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in further research. In addition, the functions and molecular mechanisms of genes are very complicated, thus predictions based only on bioinformatics need cellular and animal experiments for verification.
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, by employing the GEO series GSE31377 and GSE43958 and bioinformatic analysis, we not only found four DE-miRNAs in ENKL: hsa-miR-363-3p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-221-3p, and hsa-miR-296-5p but also determined ten hub genes that may serve as potential biomarkers of ENKL: AURKA, TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CCNB1, PLK1, CUL1, ESR1, CDC20, and PIK3CA. Our findings might help improve the understanding of the pathogenesis of ENKL, help provide reliable biomarkers for precise diagnosis and individualized treatment of ENKL, and help discover novel therapeutics of ENKL in the future.
Abbreviations
- BiNGO
-
Biological networks gene ontology
- BP
-
biological processes
- CC
-
cellular components
- DAVID
-
database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery
- DE
-
differentially expressed
- DLBCL
-
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- EBV
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- ENKL
-
extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- FAK
-
focal adhesion kinase
- GEO
-
gene expression omnibus
- GO
-
gene ontology
- KEGG
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- MF
-
molecular functions
- miRNA
-
microRNA
- PPI
-
protein–protein interaction
- WHO
-
World Health Organization
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the editors of this journal for their nice help during the manuscript preparation.
-
Funding information: No financial funding was available for this study.
-
Conflict of interest: All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
-
Data availability statement: Original data of this study are from public databases. The R script as well as its output could be provided upon request.
References
[1] Montes-Mojarro IA, Kim WY, Fend F, Quintanilla-Martinez L. Epstein-Barr virus positive T and NK-cell lymphoproliferations: Morphological features and differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2020;37(1):32–46.10.1053/j.semdp.2019.12.004Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Peng YY, Xiong YY, Zhang LX, Wang J, Zhang HB, Xiao Q, et al. Allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation in extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma. Turk J Haematol. 2021;38(2):126–37.10.4274/tjh.galenos.2021.2020.0438Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, et al. A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(3):389–400.10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00533-1Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Peng RJ, Han BW, Cai QQ, Zuo XY, Xia T, Chen JR, et al. Genomic and transcriptomic landscapes of Epstein-Barr virus in extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2019;33(6):1451–62.10.1038/s41375-018-0324-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Allen PB, Lechowicz MJ. Management of NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15(10):513–20.10.1200/JOP.18.00719Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, Chowdhury A, Tsai MY, Srivastava G, Greiner TC, et al. Natural killer cell lymphoma shares strikingly similar molecular features with a group of non-hepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphoma and is highly sensitive to a novel aurora kinase A inhibitor in vitro. Leukemia. 2011;25(2):348–58.10.1038/leu.2010.255Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Huang Y, de Reyniès A, de Leval L, Ghazi B, Martin-Garcia N, Travert M, et al. Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood. 2010;115(6):1226–37.10.1182/blood-2009-05-221275Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Zeng K, Li HY, Peng YY. Gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance imaging of microRNA-155 using a functional nucleic acid-based amplification machine. Microchimica Acta. 2017;184(8):2637–44.10.1007/s00604-017-2276-2Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–33.10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Forrest AR, Kanamori-Katayama M, Tomaru Y, Lassmann T, Ninomiya N, Takahashi Y, et al. Induction of microRNAs, mir-155, mir-222, mir-424 and mir-503, promotes monocytic differentiation through combinatorial regulation. Leukemia. 2010;24(2):460–6.10.1038/leu.2009.246Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Bryant A, Lutherborrow M, Ma D. The clinicopathological relevance of microRNA in normal and malignant haematopoiesis. Pathology. 2009;41(3):204–13.10.1080/00313020902756287Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T. miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 2011;223(2):102–15.10.1002/path.2806Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Di Lisio L, Gómez-López G, Sánchez-Beato M, Gómez-Abad C, Rodríguez ME, Villuendas R, et al. Mantle cell lymphoma: transcriptional regulation by microRNAs. Leukemia. 2010;24(7):1335–42.10.1038/leu.2010.91Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Wang Q, Liu B, Wang Y, Bai B, Yu T, Chu XM. The biomarkers of key miRNAs and target genes associated with acute myocardial infarction. Peer J. 2020;8:e9129.10.7717/peerj.9129Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Ng SB, Yan J, Huang G, Selvarajan V, Tay JL, Lin B, et al. Dysregulated microRNAs affect pathways and targets of biologic relevance in nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2011;118(18):4919–29.10.1182/blood-2011-07-364224Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Komabayashi Y, Kishibe K, Nagato T, Ueda S, Takahara M, Harabuchi Y. Downregulation of miR-15a due to LMP1 promotes cell proliferation and predicts poor prognosis in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(1):25–33.10.1002/ajh.23570Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Ramamurthy R, Hughes M, Morris V, Bolouri H, Gerbing RB, Wang YC, et al. MiR-155 expression and correlation with clinical outcome in pediatric AML: a report from Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63:2096–103.10.1002/pbc.26157Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Narayan N, Bracken CP, Ekert PG. MicroRNA-155 expression and function in AML: an evolving paradigm. Exp Hematol. 2018;62:1–6.10.1016/j.exphem.2018.03.007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Zhou G, Cao Y, Dong W, Lin Y, Wang Q, Wu W, et al. The clinical characteristics and prognostic significance of AID, miR-181b, and miR-155 expression in adult patients with de novo B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017;58(9):1–9.10.1080/10428194.2017.1283028Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Stolyar MA, Gorbenko AS, Bakhtina VI, Martynova EV, Moskov VI, Mikhalev MA, et al. Investigation of miR-155 level in the blood of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. Klin Lab Diagn. 2020;65(4):258–64.10.18821/0869-2084-2020-65-4-258-264Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Choi Y, Hur EH, Moon JH, Goo BK, Choi DR, Lee JH. Expression and prognostic significance of microR-NAs in Korean patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Korean J Intern Med. 2019;34(2):390–400.10.3904/kjim.2016.239Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Bedewy AML, Elmaghraby SM, Shehata AA, Kandil NS. Prognostic value of miRNA-155 expression in B-cell Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Turk J Haematol. 2017;34:207–12.10.4274/tjh.2016.0286Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Paydas S, Acikalin A, Ergin M, Celik H, Yavuz B, Tanriverdi K. Micro-RNA (miRNA) profile in Hodgkin lymphoma: association between clinical and pathological variables. Med Oncol. 2016;33(4):34.10.1007/s12032-016-0749-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Zhang X, Ji W, Huang R, Li L, Wang X, Li L, et al. MicroRNA-155 is a potential molecular marker of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(33):53808–19.10.18632/oncotarget.10780Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Yamanaka Y, Tagawa H, Takahashi N, Watanabe A, Guo YM, Iwamoto K, et al. Aberrant overexpression of microRNAs activate AKT signaling via downregulation of tumor suppressors in natural killer-cell lymphoma/leukemia. Blood. 2009;114:3265–75.10.1182/blood-2009-06-222794Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Jiang S, Zhang HW, Lu MH, He XH, Li Y, Gu H, et al. MicroRNA-155 functions as an OncomiR in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3119–27.10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4250Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Cheng CJ, Bahal R, Babar IA, Pincus Z, Barrera F, Liu C, et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature. 2015;518:107–10.10.1038/nature13905Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nuckeic Acids Res. 2005;33(20):e179.10.1093/nar/gni178Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Hafsi S, Candido S, Maestro R, Falzone L, Soua Z, Bonavida B, et al. Correlation between the overexpression of Yin Yang 1 and the expression levels of miRNAs in Burkitt’s lymphoma: A computational study. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(2):1021–5.10.3892/ol.2015.4031Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Sandhu SK, Croce CM, Garzon R. Micro-RNA expression and function in lymphomas. Adv Hematol. 2011;2011:347137.10.1155/2011/347137Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Zou J, Yin F, Wang Q, Zhang W, Li L. Analysis of microarray-identified genes and microRNAs associated with drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):6847–58.Suche in Google Scholar
[32] Jamali Z, Asl Aminabadi N, Attaran R, Pournagiazar F, Ghertasi Oskouei S, Ahmadpour F. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015;51(4):321–31.10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.01.008Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Dreher A, Rossing M, Kaczkowski B, Andersen DK, Larsen TJ, Christophersen MK, et al. Differential expression of cellular microRNAs in HPV 11, -16, and -45 transfected cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412(1):20–5.10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.011Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Guo HQ, Huang GL, Guo CC, Pu XX, Lin TY. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-221 for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Dis Markers. 2010;29(5):251–8.10.1155/2010/474692Suche in Google Scholar
[35] Li H, Ouyang XP, Jiang T, Zheng XL, He PP, Zhao GJ. MicroRNA-296: a promising target in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis? Mol Med. 2018;24(1):12.10.1186/s10020-018-0012-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Zhu L, Deng H, Hu J, Huang S, Xiong J, Deng J. The promising role of miR-296 in human cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(12):1915–22.10.1016/j.prp.2018.09.026Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Lee SH, Dominguez R. Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics in Cells. Mol Cells. 2010;29(4):311–25.10.1007/s10059-010-0053-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Spyridaki I, Krasanakis T, Tsatsakis A, Tzanakakis GN. Proteoglycans-biomarkers and targets in cancer therapy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:69.10.3389/fendo.2018.00069Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Mohanty A, Pharaon RR, Nam A, Salgia S, Kulkarni P, Massarelli E. FAK-targeted and combination therapies for the treatment of cancer: an overview of phase I and II clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020;29(4):399–409.10.1080/13543784.2020.1740680Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Araf S, Wang J, Korfi K, Pangault C, Kotsiou E, Rio-Machin A, et al. Genomic profiling reveals spatial intra-tumor heterogeneity in folicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2018;32:1261–5.10.1038/s41375-018-0043-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(5):341–54.10.1038/nrc1609Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2022 Yin-yin Peng et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy


