Abstract
N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) is widely used in chemical industries because of its excellent solvent properties. Poisoning accidents caused by DMF have been frequently reported, particularly hepatotoxicity; however, the hepatic pathological changes have rarely been described. This study aimed to summarise the pathological characteristics of the hepatotoxicity associated with DMF in clinical cases and to verify in animal models. Liver pathologies of two patients with liver failure due to DMF were retrospectively analysed. Thirty-six rats were categorised into the DMF group (intraperitoneally injected with 4 g/kg DMF once a week), carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) group (intraperitoneally injected with 0.5 g/kg CCl4 twice a week) and control group (intraperitoneally injected with normal saline once a week). The general condition and changes in hepatic pathology at 48 h and 8 weeks were observed. Liver tissues of patients exhibited multiple unevenly distributed inflammatory and fibrotic lesions. The DMF-induced liver injury animal model was successfully established. Inflammation and fibrosis were heterogeneously observed throughout the liver in the DMF group, contrast to entirely homogeneous lesions in the CCl4 group. Specific hepatic pathological findings (heterogeneous lesions) caused by DMF detected for the first time in humans and animal model, may be significant in the clinical diagnosis of DMF poisoning.
1 Introduction
N,N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) is a broad-spectrum chemical compound and an excellent solvent, primarily used in industries involved in organic synthesis, inorganic chemical industry, and the production of synthetic fibre and artificial leather. Because DMF is a colourless, amine-flavoured, and volatile liquid, it can be absorbed into the body through the skin and respiratory tract in the workplace [1]. Toxic effects of DMF were reported [2,3,4,5] to harm the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, respiratory system, reproductive system, immune system, and nervous system. The injury mechanism involves lipid peroxidation [6], mitochondrial damage [7], calcium homeostasis disorder [8], as well as cell apoptosis [9,10], proliferation, and differentiation [11]. A cross-sectional study [12] showed that the levels of blood urea nitrogen, platelets, hemoglobin and triglyceride were higher in the DMF exposure group (elderly residents living near synthetic leather factories) than in the control group (permanent residents living far away from leather factories). Mice models showed cardiac toxicity of DMF characterised by increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase and creatine kinase-MB partly owing to lipid peroxidation [13]. Zhang et al. [14] found that an alteration of gut microbial community after DMF exposure may cause encephalopathy. The toxic effect on the liver is particularly severe and may cause liver failure, with a high fatality rate [15,16,17]. Although poisoning accidents owing to occupational exposure to DMF have been reported, pathological changes in the liver of these patients have rarely been described. In our centre, a few patients with acute liver failure caused by occupational DMF exposure were successfully treated in recent years and we found that they exhibited specific pathological changes associated with hepatotoxicity. The purpose of the present study was to describe the clinicopathological characteristics of DMF-induced liver toxicity and compare it with a rat liver injury model resulting from intraperitoneal injections of DMF. If representative, such a model can be used to unravel the pathogenesis and test novel treatments.
2 Methods
2.1 Clinical data collection
Two patients were diagnosed with occupational acute liver failure due to DMF and underwent liver biopsy in 900th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force between 2015 and 2018. Details such as general information, occupational exposure history, clinical manifestations, laboratory results, imaging findings, and liver histological examination findings were collected and analysed.
2.2 Toxicological model of DMF-induced liver injury
The animal studies were conducted in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals according to the regulation in the People’s Republic of China. The protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of 900th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force. All animals were sacrificed by peritoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital.
Thirty-six sterile Sprague-Dawley rats aged 6–7 weeks and weighing 200 ± 20 g were purchased from the Zhejiang Provincial Laboratory Animal Centre (Licence Number: SCXK (Zhejiang) 20140001). The animals were kept in the Animal Experimental Centre of the 900th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force. After adaptive feeding for 1 week, they were randomly categorised into 3 groups.
2.2.1 DMF group
Twelve rats were injected with DMF (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, 81007718) intraperitoneally at a dose of 10 mL/kg as a 40% saline solution (final dose 4 g/kg) once a week. At 48 h and 8 weeks, 6 animals in each treatment were euthanised and liver tissue samples were collected.
2.2.2 CCl4 group
Twelve rats were intraperitoneally injected with CCl4 (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, cat. no. 10006464) at a dose of 1 mL/kg as a 50% olive oil solution twice a week. At 48 h and 8 weeks, 6 animals in each treatment were euthanised and liver tissue samples were collected.
2.2.3 Control group
Twelve rats were intraperitoneally injected with normal saline at a dose of 10 mL/kg once a week. Euthanasia was conducted after 48 h and 8 weeks.
3 Histological processing
The liver tissues including patient and rat samples were fixed in 10% formaldehyde solution overnight and embedded in paraffin before 3 µm thick sections were cut from the tissue blocks. The staining methods and reagents that haematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, reticular fibre staining, and Masson staining need were conducted according to the standard protocols established by pathology department of 900th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force. The staining results were examined independently by two pathologists.
-
Ethics approval: Informed consent for the collection of clinical information was obtained in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and this study was approved by the ethics committee of 900th Hospital of Joint Logistics Support Force (2020-044). The written informed consent was obtained from these two patients. Patients and the public were not involved in the design and conduct of our research.
4 Results
4.1 Clinical cases of hepatic failure exposed to DMF
Case 1: A 36-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with chief complaints of abdominal distention, fatigue, and jaundice that persisted for 2 weeks. The patient had a history of exposure to DMF owing to his job at a leather factory 2.5 months before admission (the first 2 months of drying operation and the next 0.5 month of stirring operation). The patient experienced somnolence and was found to be positive for asterixis. The whole-body skin and sclera had turned severely yellow, with petechiae and ecchymosis noted in both lower limbs. The abdominal shifting dullness was positive. The biochemical analysis revealed: alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 589 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 559 U/L, total bilirubin (TBIL) 411 µmol/L, direct bilirubin (DBIL) 273.6 µmol/L, prothrombin activity (PTA) 23%, and fibrinogen 0.83 g/L. Results of serological tests for hepatitis virus, cytomegalovirus, and EB virus were negative. Autoimmune antibodies, ceruloplasmin, and anti-hepatic antigens were not detected. No complications of other organ damage were found. Thus, there were indications of acute severe dimethylformamide poisoning, acute liver failure, and hepatic encephalopathy (phase A2). After admission, the patient received anti-hepatic encephalopathy, infusion of albumin and plasma, prothrombin complex, plasma exchange, and other therapies, and after 2 weeks, he gained consciousness. After 123 days of treatment, liver and coagulation functions returned to normal at discharge (the tendency chart can be seen in Figure A1). On the 78th day of admission, according to the enhancement CT, multiple intrahepatic nodules were significantly enlarged, evenly enhanced in the arterial phase (Figure 1a), and isopycnic with peripheral liver tissues in the portal and delayed phases. Malignant lesions could not be excluded [18]; therefore, a percutaneous liver biopsy was conducted on the 83rd day after obtaining informed consent.
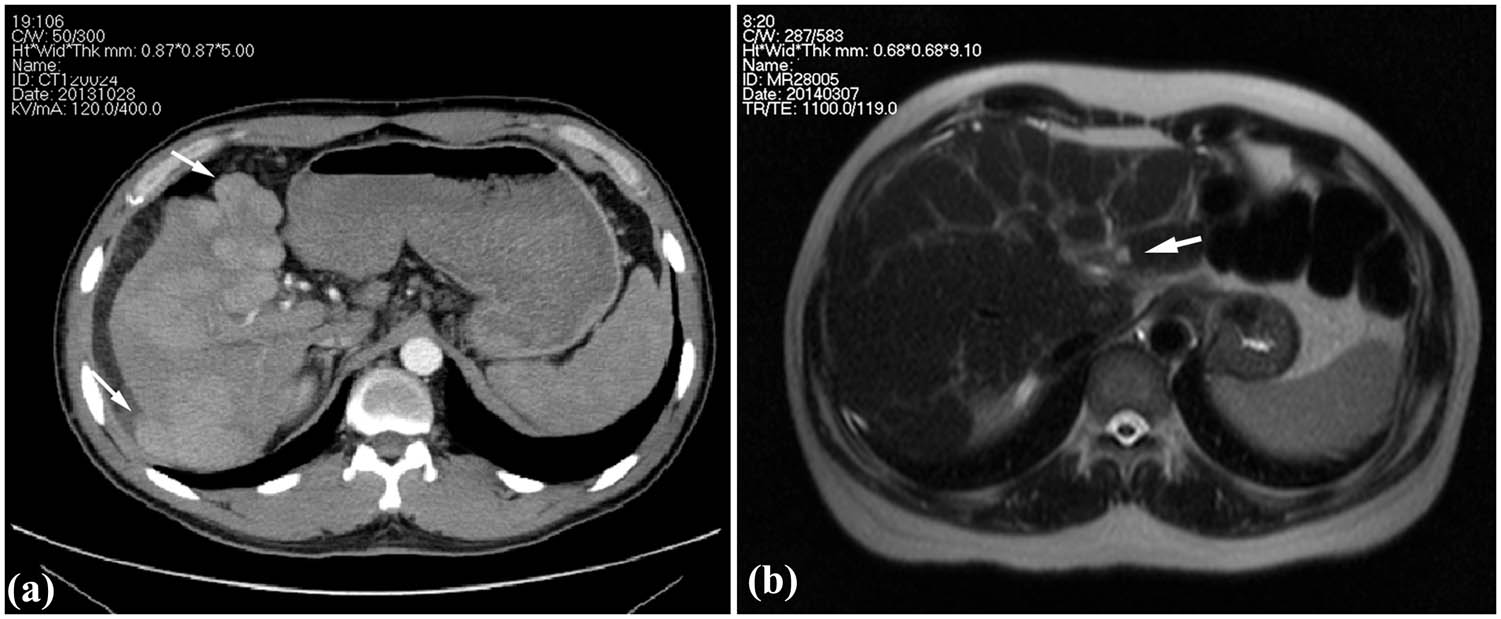
Images of clinical cases. (a) Enhancement CT showing the multiple intrahepatic nodules protruded from the liver surface (arrow) in Case 1 and (b) T2WI of MR showing heterogeneous fibrosis and a nodule in the left inner lobe (arrow) in Case 2.
Case 2: A 50-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with chief complaints of abdominal distention, abdominal pain, and poor appetite with yellowing of the skin and sclera that persisted for 1 week. The patient was employed at the local leather factory 5 months before the onset (the first 4 months of drying operation and the next 1 month of coating process). He had a history of exposure to DMF and no alcohol abuse. The shifting dullness was positive. Serological tests for hepatitis virus, cytomegalovirus, and EB virus, autoimmune antibodies and ceruloplasmin were all negative. Biochemical investigations revealed: ALT 321.2 U/L, AST 304.5 U/L, TBIL 231.8 µmol/L, DBIL 127.3 µmol/L, PTA 27%, and fibrinogen 1.06 g/L. The patient was diagnosed with acute severe dimethylformamide poisoning and acute liver failure. Liver protection drugs, infusion of plasma and albumin, and plasma exchange were administered after admission. The symptoms improved, and jaundice faded away, with the PTA gradually recovering. The patient was discharged from the hospital 33 days after admission, returning for re-examination 40 days after discharge. Liver function and coagulation function were normal (the tendency chart can be seen in Supplement Figure 2). Hepatic MR enhancement scan showed reduced liver volume, wavy edge, and an imbalanced proportion of the liver lobe with heterogeneous fibrosis (Figure 1b). Multiple intrahepatic patchy signals, with long T1 signals and slightly long T2 signals, showed enhanced signals after enhanced scan; hence, a percutaneous liver aspiration biopsy was conducted 73 days after the onset.

Pathological characteristics of liver tissue in patients. (a) Liver cells with diffuse oedema, balloon-like degeneration, dotted/focal necrosis (*), and local bridging necrosis (arrow) in Case 2 (HE 40× and HE 200×). (b) Hepatic lobules were replaced by proliferative fibrous tissues with hepatocyte regeneration (arrow) in Case 2 (HE 40× and HE 200×). Uneven fibrosis of liver tissues and clusters of regenerative cells (arrow) surrounded by reticulum fibres in Case 1 (c, Reticulum 20×) and Case 2 (d, Reticulum 40×). C: central veins, V: hepatic vein, P: portal vein.
Clinicopathological changes in the livers of both patients were mainly characterised by multiple unevenly distributed lesions of inflammation and fibrosis. Some liver tissues exhibited features of moderate chronic hepatitis (Figure 2a), accompanied by partial balloon-like degeneration, focal necrosis, local bridging necrosis, or different sizes of steatosis on HE staining. In other parts of the liver tissue, the pathological presentation was dominated by fibrosis, in which the hepatic lobules were replaced by significantly proliferative fibrous tissues (Figure 2b). Further, reticulum fibre staining showed local fibrosis and clusters of regenerative cells with clear cytoplasm surrounded by reticular fibres in two cases (Figure 2c and d).
4.2 Hepatic injury induced by DMF in animal models
To further observe and verify this specific pathological feature, we successfully created an animal model of DMF-induced liver injury. Meanwhile, as a positive control, CCl4 treatment was used to induce the classic model of liver fibrosis.
Compared with the CCl4 group, the rats in the DMF group were more depressed, hypoactive, and insensitive to external stimuli. None of the above symptoms were found in the negative control group. Probably because of drug toxicity, one rat each in the DMF group died after 36 h and 7 weeks, respectively, and two rats died in the CCl4 group in the seventh week. No rats died in the negative control group.
In the acute phase, liver inflammation in the DMF group was less severe than that in the CCl4 group. At 48 h, 6 rats were euthanised and liver tissues were stained using HE. DMF group exhibited occasional focal-point-like necrosis and slight swelling of central lobular hepatocytes, with partial inflammatory cells infiltrating the portal area and surrounding central veins (Figure 3a). In the CCl4 group, diffuse hepatocyte degeneration was observed, including balloon-like degeneration and steatosis, spot-like necrosis, and partial apoptosis of hepatocytes around the central vein in area 3, accompanied by some inflammatory cell infiltration. Furthermore, there were a small number of inflammatory cells infiltrating the portal area (Figure 3b).

Pathological changes in the liver after administration of for 48 h. (a) The lobules were intact with inflammatory cells infiltrating (arrow) in central veins (DMF group, HE 100×). (b) Balloon-like degeneration and steatosis (arrow), spot-like necrosis (*), and partial apoptosis (triangle) of hepatocytes around the central vein, accompanied by some inflammatory cell infiltration (CCl4 group, HE 100×). (c) Normal hepatocytes and hepatic lobular structure (Control group, HE 100×). C: central veins.
By the eighth week, rats were sacrificed to assess chronic liver injury after modelling. The liver surface showed a round and blunt edge, and the liver lobe proportion was unbalanced in both DMF and CCl4 groups (Figure 4a and b). The liver capsule in the DMF group was attached to the flatulent intestinal tract, whereas the intraperitoneal adhesions and flatulence in the CCl4 group were light. Furthermore, a portion of the liver tissue protruded from the surface in the DMF group, whereas no such changes were observed in the CCL4 group.

Appearance of the rat liver. (a) Liver tissue protruded from the liver surface (arrow) at week 8 in the DMF group. (b) The liver surface was spotted with a round and blunt edge, and the liver lobe proportion was unbalanced at week 8 in the CCl4 group. (c) The livers in the control group were normal, smooth, and soft texture.
The liver tissues of the DMF group exhibited varying and heterogeneous extent of degeneration or necrosis and heterogeneous distribution of fibrosis (Figure 5a and b). The HE staining exhibited some structures of hepatic lobules that were intact with swollen and degenerated hepatocytes alone and some structures that were disordered with focal or lytic necrosis of hepatocytes around the central vein, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration (Figure 5a). Double staining of reticulum and Masson showed heterogeneous fibrosis: the intact nodules formed by the arcuate connection among the surrounding normal hepatic lobules, the bridging fibres formed in the adjacent portal area and absence of fibrous tissue hyperplasia in the portal area all appeared in the same pathological section (Figure 5b). In contrast, in the CCl4 group, liver tissues showed entirely homogeneous and significant inflammation and diffuse homogeneous distribution of micronodular cirrhosis (Figure 6a and b). The hepatic lobules were structurally disordered, with extensive degeneration of hepatocytes, patchy coagulation necrosis, interlobular fusion necrosis, and portal area-central vein bridging necrosis, accompanied by a large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration (Figure 6a). The diffuse proliferation of fibrous tissues between hepatic lobules was observed under reticulation-Masson staining, forming thick fibrous septum connecting portal vein and central vein, as well as segmenting the hepatic cell mass to form small nodular cirrhosis with round, square, or irregular shape being observed (Figure 6b). The structure of the liver tissue in the negative control group was normal, and no inflammation or fibrosis was observed (Figure A3).

Pathological changes in the liver after administration for 8 weeks in DMF group. (a) Uneven lesions with cell degeneration and narrowed hepatic sinuses in some areas, necrosis, and inflammation (arrow) in other areas (HE 40× and HE 100×). (b) Heterogeneous fibrosis was present in the same pathological section (Reticulum Masson 20×). C: central veins, V: hepatic vein, P: portal vein.

Pathological changes in the liver after administration for 8 weeks in CCl4 group. (a) Disordered lobules with extensive degeneration of hepatocytes, patchy coagulation necrosis (*), interlobular fusion necrosis (triangle), and portal area-central vein bridging necrosis (arrow), accompanied by a large amount of inflammatory cell infiltration (HE 40× and HE 100×). (b) Diffuse proliferation of fibrous tissues between hepatic lobules (Reticulum Masson 20×). C: central veins, P: portal vein.
5 Discussion
DMF is a known hepatotoxic chemical capable of volatilisation at room temperature, and it can be absorbed through the skin and respiratory tract even when wearing gloves and masks [19]. The occurrence of DMF poisoning is closely associated with the concentration of DMF in the working environment and personal protection measures, with a higher incidence of poisoning in high temperature and high humidity conditions [20]. Besides, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and chronic liver diseases, such as chronic HBV infection, have also been reported to have synergistic effects with DMF poisoning [21]. Additionally, there is an obvious individual difference in human beings with DMF exposure [22,23].
Although poisoning accidents involving occupational exposure to DMF have frequently been reported, pathological changes in the liver have rarely been described. A previous study reported severe liver injury in a patient exposed to DMF for 2 months. Liver biopsy revealed prominent post-necrotic fibrosis after massive hepatic necrosis, primarily in zone 3, and hepatocyte degeneration in the surrounding tissues, consistent with our study findings [24]. Trevisani et al. [25] also conducted a liver biopsy on a patient with liver failure on the 14th day caused by an overdose of T-61, an animal euthanasia drug with DMF as the solvent, in which DMF contributes to hepatotoxicity. Focal hepatocellular necrosis and early fibrosis were observed within a short time. Considering the cases in this report in combination with other reports, it was suggested that the typical morphological changes in liver fibrosis can occur within a short time of hepatic failure owing to severe DMF poisoning. These morphological changes coincide with regional sub-massive liver necrosis, a special pathological manifestation caused by chemicals [26].
In this study, uneven distribution of multiple inflammation and fibrosis sites was noted in DMF-induced liver injury. Under the microscope, polymorphic inflammation, such as hepatocyte degeneration, necrosis, apoptosis, or regeneration, as well as heterogeneous distribution of fibrosis, were noted simultaneously. This phenomenon was considered a specific liver pathology due to DMF poisoning. As is described above [24,25], patients exposed to large doses of DMF may show similar pathological changes in different time periods. In addition, short exposure and long exposure to DMF may lead to totally different hepatic pathological feature in workers with occupational poisoning [27]. According to Senoh et al. [28], rats were exposed by inhalation to different concentrations of DMF. Massive necrosis associated with centrilobular fibrosis was observed in the liver of 1,600 ppm (v/v) DMF-exposed (6 h/day × 5 days/week) rat 2 weeks later. Only hepatic fatty change and centrilobular necrosis were observed at low concentrations or with the increase in exposure duration. Therefore, we speculate that the specific pathological changes may not be related to the biopsy time point, but is closely related to the concentration and time of exposure to DMF.
In the present study, this specific liver pathology of DMF poisoning is an aid to diagnosis. Liver puncture is not a prerequisite for the diagnosis of DMF poisoning, which is clinically based on a short-term exposure history of a significant amount of DMF, clinical manifestation, laboratory examination of liver damage, and investigation of the work environment after excluding other possible causes of liver damage. For patients with unexplained liver injury, liver biopsy should be conducted as soon as possible if there is no contraindication. Hence, considering special pathological changes in hepatotoxicity in patients, a model of liver injury induced by DMF in rats was established to validate or evaluate liver histopathology.
The DMF concentration required for modelling through inhalation is high, and this cannot truly simulate occupational exposure to DMF. Additionally, subcutaneous administration of DMF is more irritating as it causes skin erosion and ulceration [29]. Therefore, this study was modelled by intraperitoneal injection, which simulates toxin-induced liver fibrosis. It has been found that the median lethal dose of DMF via intraperitoneal injection in rats was 3–7.17 g/kg [30]; meanwhile, previous studies found that a dosage ranging from 0.5 to 1.8 g/kg of DMF could cause liver injury in rats when injected intraperitoneally [30,31,32]. In this study, to induce liver damage for the activation of fibrogenesis without high mortality, we repeated the preliminary experiments by intraperitoneally increasing the dose and finally discovered that rats injected with DMF once a week at a dose of 4 g/kg can develop liver fibrosis at the eighth week. CCl4 is currently the most used standard drug for creating liver fibrosis animal models as it can be administered through various routes and has the advantages of simplicity and low cost [33]. Therefore, the administration of CCl4 was used as the positive control.
Although DMF and CCl4 are both chemical substances, the pathological characteristics of liver damage caused by these are different. In the present study, we found hepatocyte injury and inflammatory response were mild, while hepatocytes were extensively denatured, necrotic, and the inflammatory was prominent in the CCl4 group. Fibrosis distribution was not uniform and the fibrous cords were thin in the DMF group. In contrast, CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis was diffuse, with the formation of pseudolobules throughout the field of vision, and the fibre strands were thick.
The reason for the specific pathological changes may be attributed to the toxic effect of DMF [34,35,36]. Most scholars believe that methylisocyanate (MIC), a metabolite of DMF catalysed by CYP2E1 in hepatocytes, plays a potentially vital role in pathogenicity. It undergoes electrophilic activity and can covalently bind with proteins, nucleic acids, and other cellular macromolecules, thereby causing cell damage. Meanwhile, part of MIC can consume glutathione, which could weaken the antioxidant function in vivo and cause lipid peroxidation. After intraperitoneal injection of DMF, the drug enters the liver parenchyma through the portal vein. The uneven distribution of the drug and its metabolites in the structural unit of the hepatic acinar may lead to uneven liver injury. Because DMF is less toxic than CCl4, liver cells are mainly degenerative without prominent necrosis and inflammatory infiltration in the lobules and portal area is not obvious. Heterogeneous fibrosis was accompanied by uneven inflammation. Collagen fibres formed are thin and mainly distributed in the portal area. During the late stage, there was no fibrosis interval reconstruction of hepatic lobules after massive necrosis of liver cells. However, diffuse distribution of hepatic lobules of fibrous tissue can be observed around the large veins, owing to reduced blood supply, severe ischaemia and hypoxia in this area, which results in post-necrotic cirrhosis.
In conclusion, we first found that uneven distribution and polymorphism of liver inflammation and fibrosis were detected in both humans and animals exposed to DMF. When encountering liver damage of unknown aetiology, the specific pathological finding could be a useful clue for the clinical diagnosis of DMF poisoning. Moreover, to our knowledge, an animal model of DMF-induced liver fibrosis has been established for the first time. However, the mechanism remains unclear. Hence, further studies in clinical and animal experiments are required. Additionally, varying extent and distribution of liver fibrosis including no fibrosis, mild–severe fibrosis and cirrhosis in this model could occur simultaneously in the same individual, which can provide self-contrast advantages in liver fibrosis research on the pathogenetic and progression mechanism to avoid individual differences of animals.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the grants from Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (2021J011263) and 900th Hospital of the Joint Logistic Support Force Fund (Grant number: 2021JQ04).
-
Author contributions: Designed the study and carried out the experiments: H.C.W. and D.L.L.; drafting the manuscript: Y.X.S.; assisting with the experimentation: J.X.Z.; pathological examination: Y.Q.Y. and Z.Y.Z.; management of patients: X.L.Z. and X.M. All authors have read and approved the final text.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
-
Data availability statement: All relevant data and materials are presented in the manuscript. For more information, please contact the corresponding author.
Appendix

The level of ALT, TBIl and PTA of case 1 during hospitalization.

The level of ALT, TBIl and PTA of case 2 during hospitalization.

Liver pathology of the control group. The structure of the liver tissue was normal, with no fibrous tissue hyperplasia ((a) HE100×, (b) Reticulum Masson40×).
References
[1] Kennedy GL. Toxicology of dimethyl and monomethyl derivatives of acetamide and formamide: a second update. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2012;42(10):793–826.10.3109/10408444.2012.725028Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Lu L, Song XP, Ding K, Ding B. Investigation on the health status of workers exposed to dimethylformamid. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi. 2018;36(12):896–9.Search in Google Scholar
[3] He YY, Lv Y, Wang DW, Zhang BX. Case analysis of occupational DMF poisonings occurred in 1990 through 2007 in China. Industrial Health and Occupational. Diseases. 2009;35(3):184–9.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Yang S, Zhou BY, Jiang CQ, Liu WW, Xiang ZH, Yong HE, et al. Clinical experience of occupational acute dimethylformamide poisoning. Chin J Ind Med. 2000;13(4):212–4.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Chang HY, Shih TS, Guo YL, Tsai CY, Hsu PC. Sperm function in workers exposed to N,N-dimethylformamide in the synthetic leather industry. Fertil Steril. 2004;81(6):1589–94.10.1016/j.fertnstert.2003.10.033Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Jiang H, Li R, Zhang Z, Chang C, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRalpha)-mediated erythroid-2-related factor-2 (NRF2) inactivation contributes to N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF)-induced oxidative stress in HL-7702 and HuH6 cells. J Appl Toxicol: JAT. 2020;40(4):470–82.10.1002/jat.3919Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Ma L, Dong JX, Fu WR, Li XY, Chen J, Liu Y. Mitochondrial morphology and function impaired by dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethylformamide. J Bioenerg Biomembranes. 2018;50(4):297–305.10.1007/s10863-018-9759-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Wang J, Chen JQ, Wu W, Huang XM, Feng LF, Jia ZY, et al. Effect of N,N-dimethylformamide on calcium homeostasis and the calpain gene expression in human hepatocytes. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi. 2013;31(3):184–8.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Zhang Z, Zhu W, Liu Z, Liu Y, Chang C, Jiang H, et al. Aberrant expression of miRNA-192-5p contributes to N,N-dimethylformamide-induced hepatic apoptosis. J Appl Toxicol: JAT. 2020;40(12):1683–93.10.1002/jat.4028Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Li S, Wang C. Study on the potential way of hepatic cytotoxicity of N,N-dimethylformamide. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2018;32(9):e22190.10.1002/jbt.22190Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Twiner MJ, Hirst M, Valenciano A, Zacharewski TR, Dixon SJ. N,N-Dimethylformamide modulates acid extrusion from murine hepatoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacology. 1998;153(2):143–51.10.1006/taap.1998.8536Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Hu ZY, Chang J, Guo FF, Deng HY, Pan GT, Li BY, et al. The effects of dimethylformamide exposure on liver and kidney function in the elderly population: A cross-sectional study. Medicine. 2020;99(27):e20749.10.1097/MD.0000000000020749Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Rui D, Daojun C, Yongjian Y. Liver and heart toxicity due to 90-day oral exposure of ICR mice to N,N-dimethylformamide. Environ Toxicol Pharmacology. 2011;31(3):357–63.10.1016/j.etap.2011.01.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Zhang M, Zheng M, Wu Z, Guan M, Liu S, Zhao W, et al. Alteration of gut microbial community after N,N-Dimethylformamide exposure. J Toxicol Sci. 2017;42(2):241–50.10.2131/jts.42.241Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Li MJ, Zeng T. The deleterious effects of N,N-dimethylformamide on liver: A mini-review. Chem-Biol Interact. 2019;298:129–36.10.1016/j.cbi.2018.12.011Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Yang J, Chen W, Li J, Ning F, Zhang L. A retrospective occupational epidemiology survey of the cases of occupational exposure to N, N-Dimethylformamide (DMF) acute poisoning in recent years. Chinese. J Health Lab Technol. 2011;21:1284–7.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Zhang H, Liu Q, Duan Y, Dong H, Zhou Y. Chronic occupational N, N-dimethylformamide poisoning induced death: a case report. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2015;11(4):584–8.10.1007/s12024-015-9705-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Senoh H, Aiso S, Arito H, Nishizawa T, Nagano K, Yamamoto S, et al. Carcinogenicity and chronic toxicity after inhalation exposure of rats and mice to N,N-dimethylformamide. J Occup Health. 2004;46(6):429–39.10.1539/joh.46.429Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Wang SM, Shih TS, Huang YS, Chueh MR, Chou JS, Chang HY. Evaluation of the effectiveness of personal protective equipment against occupational exposure to N,N-dimethylformamide. J Hazard Mater. 2006;138(3):518–25.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.072Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Tsuda Y, Miyauchi H, Minozoe A, Tanaka S, Arito H, Tsukahara T, et al. Seasonal difference in percutaneous absorption of N,N-dimethylformamide as determined using two urinary metabolites. J Occup Health. 2014;56(4):252–9.10.1539/joh.13-0228-OASearch in Google Scholar
[21] Luo JC, Kuo HW, Cheng TJ, Chang MJ. Abnormal liver function associated with occupational exposure to dimethylformamide and hepatitis B virus. J Occup Environ Med. 2001;43(5):474–82.10.1097/00043764-200105000-00008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Nomiyama T, Haufroid V, Buchet JP, Miyauchi H, Tanaka S, Yamauchi T, et al. Insertion polymorphism of CYP2E1 and urinary N-methylformamide after N,N- dimethylformamide exposure in Japanese workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2001;74(7):519–22.10.1007/s004200100252Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Luo JC, Cheng TJ, Kuo HW, Chang MJ. Abnormal liver function associated with occupational exposure to dimethylformamide and glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms. Biomarkers: Biochem Indic Exposure Response Susceptibility Chem. 2005;10(6):464–74.10.1080/13547500500333648Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Hamada M, Abe M, Tokumoto Y, Miyake T, Murakami H, Hiasa Y, et al. Occupational liver injury due to N,N-dimethylformamide in the synthetics industry. Intern Med. 2009;48(18):1647–50.10.2169/internalmedicine.48.2332Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Trevisani F, Tamé MR, Bernardi M, Tovoli C, Gasbarrini A, Panarelli M, et al. Severe hepatic failure occurring with T61 ingestion in an attempted suicide. Early recovery with the use of intravenous infusion of reduced glutathione. Digestive Dis Sci. 1993;38(4):752–6.10.1007/BF01316810Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Watkins PB, Seeff LB. Drug-induced liver injury: summary of a single topic clinical research conference. Hepatology. 2006;43(3):618–31.10.1002/hep.21095Search in Google Scholar
[27] Redlich CA, West AB, Fleming L, True LD, Cullen MR, Riely CA. Clinical and pathological characteristics of hepatotoxicity associated with occupational exposure to dimethylformamide. Gastroenterology. 1990;99(3):748–57.10.1016/0016-5085(90)90964-3Search in Google Scholar
[28] Senoh H, Katagiri T, Arito H, Nishizawa T, Nagano K, Yamamoto S, et al. Toxicity due to 2- and 13-wk inhalation exposures of rats and mice to N, N-dimethylformamide. J Occup Health. 2003;45(6):365–75.10.1539/joh.45.365Search in Google Scholar
[29] Kennedy GL. Acute and subchronic toxicity of dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide following various routes of administration. Drug Chem Toxicol. 1986;9(2):147–70.10.3109/01480548608998272Search in Google Scholar
[30] Jyothi K, Kalyani D, Nachiappan V. Effect of acute exposure of N,N-dimethylformamide, an industrial solvent on lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in liver and kidney of rats. Indian J Biochem & Biophysics. 2012;49(4):279–84.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Roure MB, Lambert AM, Cour C, Bonnet P, Saillenfait AM. Hepatotoxicity of N, N-dimethylformamide in rats following intraperitoneal or inhalation routes of administration. J Appl Toxicol: JAT. 1996;16(3):265–7.10.1002/(SICI)1099-1263(199605)16:3<265::AID-JAT343>3.0.CO;2-ISearch in Google Scholar
[32] Kim KW, Chung YH. Hepatotoxicity in rats treated with dimethylformamide or toluene or both. Toxicol Res. 2013;29(3):187–93.10.5487/TR.2013.29.3.187Search in Google Scholar
[33] Duffield JS, Forbes SJ, Constandinou CM, Clay S, Partolina M, Vuthoori S, et al. Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct, opposing roles during liver injury and repair. J Clin Investigation. 2005;115(1):56–65.10.1172/JCI200522675Search in Google Scholar
[34] Gescher A. Metabolism of N,N-dimethylformamide: key to the understanding of its toxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993;6(3):245–51.10.1021/tx00033a001Search in Google Scholar
[35] Mutlib A, Jiang P, Atherton J, Obert L, Kostrubsky S, Madore S, et al. Identification of potential genomic biomarkers of hepatotoxicity caused by reactive metabolites of N-methylformamide: Application of stable isotope labeled compounds in toxicogenomic studies. Chem Res Toxicol. 2006;19(10):1270–83.10.1021/tx060093jSearch in Google Scholar
[36] Seitz M, Kilo S, Eckert E, Muller J, Drexler H, Goen T. Validity of different biomonitoring parameters for the assessment of occupational exposure to N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). Arch Toxicol. 2018;92(7):2183–93.10.1007/s00204-018-2219-7Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- AMBRA1 attenuates the proliferation of uveal melanoma cells
- A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Differences in complications between hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and alcohol-related cirrhosis
- Effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 stimulates the tumorigenic behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-363-3p to increase SOX4
- Promising novel biomarkers and candidate small-molecule drugs for lung adenocarcinoma: Evidence from bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data
- Plasmapheresis: Is it a potential alternative treatment for chronic urticaria?
- The biomarkers of key miRNAs and gene targets associated with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- Gene signature to predict prognostic survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Effects of miRNA-199a-5p on cell proliferation and apoptosis of uterine leiomyoma by targeting MED12
- Does diabetes affect paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in colorectal cancer?
- Is there any effect on imprinted genes H19, PEG3, and SNRPN during AOA?
- Leptin and PCSK9 concentrations are associated with vascular endothelial cytokines in patients with stable coronary heart disease
- Pericentric inversion of chromosome 6 and male fertility problems
- Staple line reinforcement with nebulized cyanoacrylate glue in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A propensity score-matched study
- Retrospective analysis of crescent score in clinical prognosis of IgA nephropathy
- Expression of DNM3 is associated with good outcome in colorectal cancer
- Activation of SphK2 contributes to adipocyte-induced EOC cell proliferation
- CRRT influences PICCO measurements in febrile critically ill patients
- SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis
- lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells
- circ_AKT3 knockdown suppresses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer
- Prognostic value of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase in human cancers: Evidence from a meta-analysis and database validation
- GPC2 deficiency inhibits cell growth and metastasis in colon adenocarcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of Holliday junction recognition protein in human tumors
- Radiation increases COL1A1, COL3A1, and COL1A2 expression in breast cancer
- Association between preventable risk factors and metabolic syndrome
- miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- Cardiac contractility modulation ameliorates myocardial metabolic remodeling in a rabbit model of chronic heart failure through activation of AMPK and PPAR-α pathway
- Quercitrin protects human bronchial epithelial cells from oxidative damage
- Smurf2 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via ubiquitin degradation of Smad2
- circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- Sonoclot’s usefulness in prediction of cardiopulmonary arrest prognosis: A proof of concept study
- Four drug metabolism-related subgroups of pancreatic adenocarcinoma in prognosis, immune infiltration, and gene mutation
- Decreased expression of miR-195 mediated by hypermethylation promotes osteosarcoma
- LMO3 promotes proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells by regulating LIMK1-mediated cofilin and the β-catenin pathway
- Cx43 upregulation in HUVECs under stretch via TGF-β1 and cytoskeletal network
- Evaluation of menstrual irregularities after COVID-19 vaccination: Results of the MECOVAC survey
- Histopathologic findings on removed stomach after sleeve gastrectomy. Do they influence the outcome?
- Analysis of the expression and prognostic value of MT1-MMP, β1-integrin and YAP1 in glioma
- Optimal diagnosis of the skin cancer using a hybrid deep neural network and grasshopper optimization algorithm
- miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells
- Clinical value of SIRT1 as a prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, a systematic meta-analysis
- circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8
- miR-22-5p regulates the self-renewal of spermatogonial stem cells by targeting EZH2
- hsa-miR-340-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition in endometriosis by targeting MAP3K2 and inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling
- circ_0085296 inhibits the biological functions of trophoblast cells to promote the progression of preeclampsia via the miR-942-5p/THBS2 network
- TCD hemodynamics findings in the subacute phase of anterior circulation stroke patients treated with mechanical thrombectomy
- Development of a risk-stratification scoring system for predicting risk of breast cancer based on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease, and uric acid
- Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway
- circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis
- Human amniotic fluid as a source of stem cells
- lncRNA NONRATT013819.2 promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced myofibroblastic transition of hepatic stellate cells by miR24-3p/lox
- NORAD modulates miR-30c-5p-LDHA to protect lung endothelial cells damage
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis telemedicine management during COVID-19 outbreak
- Risk factors for adverse drug reactions associated with clopidogrel therapy
- Serum zinc associated with immunity and inflammatory markers in Covid-19
- The relationship between night shift work and breast cancer incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- LncRNA expression in idiopathic achalasia: New insight and preliminary exploration into pathogenesis
- Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Moscatilin suppresses the inflammation from macrophages and T cells
- Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in coronary artery disease
- The effect evaluation of traditional vaginal surgery and transvaginal mesh surgery for severe pelvic organ prolapse: 5 years follow-up
- Repeated partial splenic artery embolization for hypersplenism improves platelet count
- Low expression of miR-27b in serum exosomes of non-small cell lung cancer facilitates its progression by affecting EGFR
- Exosomal hsa_circ_0000519 modulates the NSCLC cell growth and metastasis via miR-1258/RHOV axis
- miR-455-5p enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells by targeting PIK3R1 and DEPDC1
- The effect of tranexamic acid on the reduction of intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and thromboembolic risk in patients with hip fracture
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutation in cholangiocarcinoma impairs tumor progression by sensitizing cells to ferroptosis
- Artemisinin protects against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via inhibiting the NF-κB pathway
- A 16-gene signature associated with homologous recombination deficiency for prognosis prediction in patients with triple-negative breast cancer
- Lidocaine ameliorates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through regulating M1/M2 microglia polarization
- MicroRNA 322-5p reduced neuronal inflammation via the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis in a rat epilepsy model
- miR-1273h-5p suppresses CXCL12 expression and inhibits gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis
- Clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients of long course of illness infected with SARS-CoV-2
- circRNF20 aggravates the malignancy of retinoblastoma depending on the regulation of miR-132-3p/PAX6 axis
- Linezolid for resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections in children under 12 years: A meta-analysis
- Rack1 regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines by NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy
- Comprehensive analysis of molecular mechanism and a novel prognostic signature based on small nuclear RNA biomarkers in gastric cancer patients
- Smog and risk of maternal and fetal birth outcomes: A retrospective study in Baoding, China
- Let-7i-3p inhibits the cell cycle, proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells via downregulating CCND1
- β2-Adrenergic receptor expression in subchondral bone of patients with varus knee osteoarthritis
- Possible impact of COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown on suicide behavior among patients in Southeast Serbia
- In vitro antimicrobial activity of ozonated oil in liposome eyedrop against multidrug-resistant bacteria
- Potential biomarkers for inflammatory response in acute lung injury
- A low serum uric acid concentration predicts a poor prognosis in adult patients with candidemia
- Antitumor activity of recombinant oncolytic vaccinia virus with human IL2
- ALKBH5 inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HUVECs through Bcl-2 pathway
- Risk prediction of cardiovascular disease using machine learning classifiers
- Value of ultrasonography parameters in diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome
- Bioinformatics analysis reveals three key genes and four survival genes associated with youth-onset NSCLC
- Identification of autophagy-related biomarkers in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension based on bioinformatics analysis
- Protective effects of glaucocalyxin A on the airway of asthmatic mice
- Overexpression of miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via targeting FZD8
- Bioinformatics-based analysis of SUMOylation-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals a role of upregulated SAE1 in promoting cell proliferation
- Effectiveness and clinical benefits of new anti-diabetic drugs: A real life experience
- Identification of osteoporosis based on gene biomarkers using support vector machine
- Tanshinone IIA reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer through microRNA-30b-5p/AVEN axis
- miR-212-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by targeting METTL3
- Association of ST-T changes with all-cause mortality among patients with peripheral T-cell lymphomas
- LINC00665/miRNAs axis-mediated collagen type XI alpha 1 correlates with immune infiltration and malignant phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma
- The perinatal factors that influence the excretion of fecal calprotectin in premature-born children
- Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study
- Does the use of 3D-printed cones give a chance to postpone the use of megaprostheses in patients with large bone defects in the knee joint?
- lncRNA HAGLR modulates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in mice through regulating miR-133a-3p/MAPK1 axis
- Protective effect of ghrelin on intestinal I/R injury in rats
- In vivo knee kinematics of an innovative prosthesis design
- Relationship between the height of fibular head and the incidence and severity of knee osteoarthritis
- lncRNA WT1-AS attenuates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal injury during cerebral ischemic stroke via miR-186-5p/XIAP axis
- Correlation of cardiac troponin T and APACHE III score with all-cause in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients with acute pulmonary embolism
- LncRNA LINC01857 reduces metastasis and angiogenesis in breast cancer cells via regulating miR-2052/CENPQ axis
- Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) promoted by transcription factor SPI1 acts as an oncogene to modulate the malignant phenotype of endometrial cancer
- SELENBP1 inhibits progression of colorectal cancer by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
- Treatment and outcomes of mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction during the Covid-19 era: A comparison with the pre-Covid-19 period. A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neonatal stroke surveillance study protocol in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland
- Oncogenic role of TWF2 in human tumors: A pan-cancer analysis
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin predicts the length of hospital stay independent of severity classification in patients with acute pancreatitis
- Association of gallstone and polymorphisms of UGT1A1*27 and UGT1A1*28 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- TGF-β1 upregulates Sar1a expression and induces procollagen-I secretion in hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts
- Antisense lncRNA PCNA-AS1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the miR-2467-3p/PCNA axis
- NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin–angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes
- The effect of dilution with glucose and prolonged injection time on dexamethasone-induced perineal irritation – A randomized controlled trial
- miR-146-5p restrains calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing TRAF6
- Role of lncRNA MIAT/miR-361-3p/CCAR2 in prostate cancer cells
- lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2
- Noninvasive diagnosis of AIH/PBC overlap syndrome based on prediction models
- lncRNA FAM230B is highly expressed in colorectal cancer and suppresses the maturation of miR-1182 to increase cell proliferation
- circ-LIMK1 regulates cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-512-5p/HMGA1 axis
- LncRNA SNHG3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-151a-3p/PFN2 axis
- Risk perception and affective state on work exhaustion in obstetrics during the COVID-19 pandemic
- lncRNA-AC130710/miR-129-5p/mGluR1 axis promote migration and invasion by activating PKCα-MAPK signal pathway in melanoma
- SNRPB promotes cell cycle progression in thyroid carcinoma via inhibiting p53
- Xylooligosaccharides and aerobic training regulate metabolism and behavior in rats with streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes
- Serpin family A member 1 is an oncogene in glioma and its translation is enhanced by NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 through RNA-binding activity
- Silencing of CPSF7 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by blocking the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Ultrasound-guided lumbar plexus block versus transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia in children with hip dislocation: A double-blind, randomized trial
- Relationship of plasma MBP and 8-oxo-dG with brain damage in preterm
- Identification of a novel necroptosis-associated miRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Delayed femoral vein ligation reduces operative time and blood loss during hip disarticulation in patients with extremity tumors
- The expression of ASAP3 and NOTCH3 and the clinicopathological characteristics of adult glioma patients
- Longitudinal analysis of factors related to Helicobacter pylori infection in Chinese adults
- HOXA10 enhances cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in esophageal cancer via activating p38/ERK signaling pathway
- Meta-analysis of early-life antibiotic use and allergic rhinitis
- Marital status and its correlation with age, race, and gender in prognosis of tonsil squamous cell carcinomas
- HPV16 E6E7 up-regulates KIF2A expression by activating JNK/c-Jun signal, is beneficial to migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells
- Amino acid profiles in the tissue and serum of patients with liver cancer
- Pain in critically ill COVID-19 patients: An Italian retrospective study
- Immunohistochemical distribution of Bcl-2 and p53 apoptotic markers in acetamiprid-induced nephrotoxicity
- Estradiol pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol for IVF/ICSI treatment
- Long non-coding RNAs LINC00689 inhibits the apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via miR-3127-5p/ATG7 axis-mediated autophagy
- The relationship between oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and COVID-19 mortality
- Monitoring hypertensive disorders in pregnancy to prevent preeclampsia in pregnant women of advanced maternal age: Trial mimicking with retrospective data
- SETD1A promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway
- The role of Shunaoxin pills in the treatment of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion and its main pharmacodynamic components
- TET3 governs malignant behaviors and unfavorable prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway
- Associations between morphokinetic parameters of temporary-arrest embryos and the clinical prognosis in FET cycles
- Long noncoding RNA WT1-AS regulates trophoblast proliferation, migration, and invasion via the microRNA-186-5p/CADM2 axis
- The incidence of bronchiectasis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Integrated bioinformatics analysis shows integrin alpha 3 is a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer
- Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway
- Comparison of hospitalized patients with severe pneumonia caused by COVID-19 and influenza A (H7N9 and H1N1): A retrospective study from a designated hospital
- lncRNA ZFAS1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by upregulating AAK1
- Pathological characteristics of liver injury induced by N,N-dimethylformamide: From humans to animal models
- lncRNA ELFN1-AS1 enhances the progression of colon cancer by targeting miR-4270 to upregulate AURKB
- DARS-AS1 modulates cell proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating miR-330-3p/NAT10 axis
- Dezocine inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting CRABP2 in ovarian cancer
- MGST1 alleviates the oxidative stress of trophoblast cells induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 ameliorated the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice by changing ileum FXR-CYP7A1
- circRNA DENND1B inhibits tumorigenicity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via miR-122-5p/TIMP2 axis
- EphA3 targeted by miR-3666 contributes to melanoma malignancy via activating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways
- Pacemakers and methylprednisolone pulse therapy in immune-related myocarditis concomitant with complete heart block
- miRNA-130a-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to activate the microglial and astrocytes and to promote neural injury under the high glucose condition
- Review Articles
- Current management of cancer pain in Italy: Expert opinion paper
- Hearing loss and brain disorders: A review of multiple pathologies
- The rationale for using low-molecular weight heparin in the therapy of symptomatic COVID-19 patients
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and delayed onset muscle soreness in light of the impaired blink and stretch reflexes – watch out for Piezo2
- Interleukin-35 in autoimmune dermatoses: Current concepts
- Recent discoveries in microbiota dysbiosis, cholangiocytic factors, and models for studying the pathogenesis of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Advantages of ketamine in pediatric anesthesia
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Role of dentist in early diagnosis
- Migraine management: Non-pharmacological points for patients and health care professionals
- Atherogenic index of plasma and coronary artery disease: A systematic review
- Physiological and modulatory role of thioredoxins in the cellular function
- Case Reports
- Intrauterine Bakri balloon tamponade plus cervical cerclage for the prevention and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage in late pregnancy complicated with acute aortic dissection: Case series
- A case of successful pembrolizumab monotherapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: Use of multiple biomarkers in combination for clinical practice
- Unusual neurological manifestations of bilateral medial medullary infarction: A case report
- Atypical symptoms of malignant hyperthermia: A rare causative mutation in the RYR1 gene
- A case report of dermatomyositis with the missed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer and concurrence of pulmonary tuberculosis
- A rare case of endometrial polyp complicated with uterine inversion: A case report and clinical management
- Spontaneous rupturing of splenic artery aneurysm: Another reason for fatal syncope and shock (Case report and literature review)
- Fungal infection mimicking COVID-19 infection – A case report
- Concurrent aspergillosis and cystic pulmonary metastases in a patient with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Paraganglioma-induced inverted takotsubo-like cardiomyopathy leading to cardiogenic shock successfully treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
- Lineage switch from lymphoma to myeloid neoplasms: First case series from a single institution
- Trismus during tracheal extubation as a complication of general anaesthesia – A case report
- Simultaneous treatment of a pubovesical fistula and lymph node metastasis secondary to multimodal treatment for prostate cancer: Case report and review of the literature
- Two case reports of skin vasculitis following the COVID-19 immunization
- Ureteroiliac fistula after oncological surgery: Case report and review of the literature
- Synchronous triple primary malignant tumours in the bladder, prostate, and lung harbouring TP53 and MEK1 mutations accompanied with severe cardiovascular diseases: A case report
- Huge mucinous cystic neoplasms with adhesion to the left colon: A case report and literature review
- Commentary
- Commentary on “Clinicopathological features of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma”
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 fear, post-traumatic stress, growth, and the role of resilience
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway”
- Erratum to “Effect of femoral head necrosis cystic area on femoral head collapse and stress distribution in femoral head: A clinical and finite element study”
- Erratum to “lncRNA NORAD promotes lung cancer progression by competitively binding to miR-28-3p with E2F2”
- Retraction
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Retraction to “miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part II
- Usefulness of close surveillance for rectal cancer patients after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy

