Abstract
Due to the enormous of fossil fuels and the ensuing increase in automobiles, an unprecedented scenario has arisen with pollution levels that are out of human control. In this study, a fuzzy logic model is developed to predict how well a spark-ignition engine running on gasoline and ethanol mixes would operate. A test engine was operated on pure gasoline and gasoline–ethanol fuel mixtures in a range of ratios at varying engine speeds. In order to estimate outputs such as brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC), brake thermal efficiency, nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbon emissions, and carbon monoxide, a fuzzy logic model, a sort of logic model application, has been developed using experimental data. The developed fuzzy logic model’s output was compared to the results of the trials to see how well it performed. The output parameters were indicated, including braking power, thermal, volumetric, and mechanical efficiency. The input parameters were engine speed and ethanol mixes. Regression coefficients were nearly equal for training and testing data. According to the study, a superior method for accurately forecasting engine performance is the fuzzy logic model. To eliminate proportionality signs from equations, regression analysis is used. It is accurate to develop mathematical relations based on dimensional analysis. Based on the root mean square errors, BSFC is a minimum of 6.12 and brake power is a maximum of 8.16; lower than 2% of errors occur on average.
1 Introduction
Agro waste is a significant issue that many developing nations with an agricultural economy must deal with. Due to environmental harm and resource shortages, especially those in transportation and the cold chain, agro waste has increased. Municipal officials are likewise quite concerned about how to dispose of agro waste. In this situation, producing ethanol from agricultural waste may be an effective solution. Because ethanol-based biofuels are environmentally friendly, they have gained popularity recently [1]. When combined with gasoline, ethanol, an alternative fuel, improves the torque, power, and thermal efficiency of the engine. The addition of ethanol to gasoline improves combustion properties and engine performance in terms of braking force, brake thermal efficiency (BTE), and specific fuel consumption. [2]. A fuel blend’s octane rating is raised by adding ethanol to gasoline, which also lowers the engine’s hazardous emissions. Additionally, ethanol is added to diesel fuel, which is then used as a fuel blend to replace traditional fuels. Physical engine testing is required to determine engine performance for each fuel percentage and under various operating conditions. Creating a mathematical model for predicting engine performance is advantageous since it will save time and money [3]. Because of the world’s rising urbanization and industrialization, humanity has been obliged to explore alternatives to petroleum fuels, which are ecologically harmful and run out quickly. Environmental harm is caused by the waste products of fossil fuel combustion [4]. Several experiments have been performed to analyse the engine parameters. Some studies used experimental work to measure performance metrics, while others measured exhaust emissions and others concentrated on both. Spark ignition (SI) and compression ignition engines were employed in these trials, and both traditional and biofuels may be used in them. Biofuel trials, however, may be more beneficial since they meet the requirements of lowering pollution and protecting the fossil fuel supply. The majority of research [5] concentrates on modelling acceptable outcomes using experimental data and conventional fuzzy logic. Thermodynamic modelling is a highly helpful technique for predicting the behaviour of internal combustion engines and determining the trends for various fuels across a wide range of design and operational factors. Thermodynamics, fluid flow, heat transfer, burning rate, combustion, kinetics, and their effective characteristics are all described by many models. In various research studies, power cycle modelling has also been used to forecast engine operating parameters. Recent reviews of the multizone thermodynamic models for SI engines have been published by Liu et al. [6]. Researchers have looked at several ethanol–gasoline blends’ SI engine performance at various compression ratios and found a correlation between increased engine power and greater specific fuel consumption. The findings demonstrate that pomegranate waste may be utilized to generate ethanol and that ethanol blends can be used to gauge how well gasoline engines perform. A fuzzy logic model is used to forecast the performance of an engine [5]. Recently, artificial neural network (ANN), which has gained popularity in recent years, has been used to predict engine performance characteristics. Additionally, it is becoming increasingly common to apply fuzzy logic to predict engine performance. In comparison to experimental values, researchers found that fuzzy predictions can be 90–98% accurate [7]. The engine is currently operated effectively by optimizing the intended output and operating parameters using response surface methodology (RSM) approaches. RSM-based optimization techniques have gained widespread recognition due to their relevance in the context of modern engineering challenges. The competence and accuracy of RSM techniques have been thoroughly examined in an earlier study [8], which aims to improve the performance and emission outputs of a gasoline engine. An ANN was used in this study to evaluate the SI engine’s performance. Exploration uncovered a low brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) with greater volumetric efficiency and brake thermal efficiency (BTE) values. While CO2 and NOx emissions rose, CO and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions were determined to be lower. Validation was done for 14% of the experimental outcomes. The final 14% of the input saw an increase in network generalization results after 70% was used for training. Each performance component’s correlation coefficient was different; however, the exhaust emissions showed respectable R values [9].
It is unclear how SI engines that run on ethanol/gasoline mixtures operate. Since ethanol is a renewable alternative fuel made from agricultural waste, research on its application as an alternative fuel is crucial. Especially in COVID-like environments, the automobile sector has to rely less on experimentation. Fuzzy logic models have raised in popularity in recent years due to their high accuracy and quick prediction timeframes [10]. In this work, a fuzzy logic model is used to forecast the performance of the SI engine for a variety of fuel mixes and engine speeds. The data acquired from testing using ethanol and gasoline were used to build a fuzzy logic model for predicting engine performance.
2 Materials and methods
Natural fuel ethanol (C2H5OH) is produced using renewable energy sources. It is a liquid hydrocarbon with a strong, burning flavour and odour that is colourless, transparent, neutral, volatile, flammable, and oxygenated. Among the many fuel characteristics that set ethanol apart from gasoline are its higher-octane rating, heating value, latent heat of vaporization, FLSOM velocity, specific gravity, and Reid vapour pressure. Understanding how these elements impact the performance traits of SI engines becomes crucial as a result [11]. This is where the fuzzy logic system’s decision-making rules and membership functions are contained. It also includes the IF-THEN statements that are used to programme circumstances and operate the system. The fuzzy sets continue to the control system for additional processing. The output is subsequently generated as a fuzzy result by applying these rules to the supplied data. The last phase of a fuzzy logic system is defuzzification. The fuzzy logic model architecture is shown in Figure 1.

Fuzzy logic model architecture.
Generally speaking, bioethanol and ethanol are more reactive than gasoline. Because hydroxyl radicals, which are ethanol’s fundamental constituents, are polar and carbon chains, which are non-polar, ethanol may readily dissolve in both non-polar (like gasoline) and polar substances (like water). The ecological and regenerative qualities of ethanol make it a popular alternative fuel. The use of gasoline containing 5–15 vol% bioethanol is advised in various parts of the world. The fuel properties are shown in Table 1.
Properties of a fuel
| Fuel property | Gasoline | Ethanol |
| Chemical formula | C5–C12 | C2H2OH |
| Molecular weight (kg·kmol−1) | 112.4 | 45.7 |
| Octane rating | ∼91 RON | |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 740 | 785 |
| Autoignition temperature (vol%) | 245 | 416 |
| Latent of vaporization (kJ·kg−1) | 390 | 910 |
| Flash point (°C) | −37 | 14 |
| Calorific value (kJ·kg−1) | 44,000 | 55 |
2.1 Performance criteria
Multiple factors are assessed in order to gauge the forecasting process’s dependability. The metrics employed in this analysis include accuracy, mean relative error, root mean square error (RMSE), and correlation coefficient (R). According to Dey et al. [12], the coefficient of correlation (R), which determines the degree of connection between experimental findings and expected outcomes, is calculated as follows:
where the correlation between sets a and p is shown by the variable COV(a,p). The expected output set is denoted by p, whereas the actual output set is denoted by a. The RSME is computed as follows:
where the collection’s total number of data points is n. The mean ratio between the experimental values and the errors, or MRE, is calculated as follows:
The quality of predictions is simply described as accuracy, which is quantified as follows:
3 Experimental set-up
This study makes use of the two-cylinder SI engine, as shown in Figure 2. Out of two cylinders, one is a functioning cylinder termed the thermodynamic cylinder in which combustion occurs continually, and the other cylinder is an optically accessible cylinder in which combustion occurs as needed. Since the combustion process cannot be optically diagnosed in this investigation, the optical access cylinder is shut off throughout the experiment. The engine has two overhead camshafts that operate four intake valves and four exhaust valves.

SI engine.
The airflow to the engine is managed by a throttle body that is electrically regulated. It is fixed to the inflow manifold ahead of the PFI injector locations. Using an air box instrument, the pressure drop across the orifice is used to calculate the airflow rate when air from a large volume box is forced through the plate. The electronic control unit (ECU) uses this pressure drop signal to determine the precise air flow rate. An automated volumetric fuel flow metre measures the fuel flow rate. It comprises two sensors that are located at the top and bottom of a 100 mL measuring burette. This burette is used to process the gasoline, and the ECU receives data on how long it takes to empty the burette. Based on the density of the manually fed gasoline, the ECU then determines the mass flow of fuel. Specifications of the engine are given in Table 2.
Specifications of the research engine
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| No. of running cylinders | 1 out of 2 |
| Bore (mm) | 94 |
| Stroke (mm) | 100 |
| Compression ratio | 10:1 |
| Connecting rod length (mm) | 235 |
| Inlet open (°) | 5 ATDC |
| Inlet close (°) | 21 ABDC |
| Exhaust open (°) | 25 BBDC |
| Exhaust close (°) | 9 BTDC |
| Injection pressure (bar) | 3 |
| Injection timing (°) | −90 before start of the intake stroke |
| Ignition system | Ignition coil system |
| Spark plug | TVS |
A piezoelectric pressure transducer is used to measure the pressure within the cylinder. It is attached to the cylinder head and is connected to the combustion chamber via a passageway that has been bored into the cylinder head. To apply and quantify the load on the engine, an eddy current dynamometer is directly connected to the crankshaft. It can support loads between 0 and 10 kg. The acquisition software is made by Legion Brother. This technology enables the real-time display of recorded parameters, such as in-cylinder pressure, exhaust gas temperature, cooling water temperature for the engine, and calorimeter temperature, on the screen. Additionally, it shows computed values for parameters like volumetric efficiency and BTE, air–fuel ratio, and more. Pressure measurements are taken at each test location for 400 consecutive cycles and then averaged. Each cycle’s characteristics, such as the IMEP and peak pressure, are determined before being averaged.
3.1 Uncertainty analysis
All assessment tools have a certain amount of inaccuracy that might result from a variety of working circumstances, inspection, standardization, trial planning, and environmental factors. As a result, all of the studies were conducted in such a way that the values were projected from the mean of all arithmetic values in order to discover an equal value [13]. The overall degree of uncertainty is determined using the following relationship:
The values lie in the acceptable range of the experiments.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 BTE
The test engine’s brake thermal performance at 2,500 rpm is affected by the ethanol–gasoline mixture, as shown in Figure 3a. The thermal performance of the brakes increased steadily in each case to an optimal level before decreasing with a further increase in the load. At 2,500 rpm, E20 had the best thermal efficiency. The lower heat content of the mixed fuels, as compared to diesel, is responsible for their improved thermal efficiency.

The effects of engine load and fuel type on the gasoline engine’s performance and emission characteristics, including (a) BTE, (b) BSFC, (c) CO, (d) HC, (e) NO x , and (f) CO2.
4.2 BSFC
Figure 3b shows the variation in BSFC values for all fuel samples in relation to the various engine loads at 2,500 rpm. The graph shows that when ethanol was added, BSFC showed higher values than gasoline. But as the loads were increased, the BSFC decreased.
4.3 CO emission
The outcome demonstrates that adding ethanol to mixtures lowers CO emissions. Ethanol contains more oxygen than gasoline, which helps it burn completely. CO emissions increase as the external load on the engine increases, as shown in Figure 3c. High engine loads lead to decreased combustion efficiency, which is the source of this.
4.4 HC emission
Figure 3d illustrates how ethanol–petrol mixtures affect the emission of HC for various external engine loads at 2,500 rpm. It is evident that HC emissions first reached a high before starting to decrease as the ethanol content of the mixture increased. This is because ethanol fuel has a larger oxygen content, which encourages full combustion and lowers HC emissions when the fuel’s ethanol content is increased.
4.5 NO x emission
Figure 3e illustrates the effect of ethanol–gasoline mixtures on NO x emission for various engine external loads at 2,500 rpm. The engine’s combustion is boosted, and NO x emissions are reduced when ethanol, which includes oxygen, is combined with gasoline. As the proportion of ethanol in the fuel combination increased, lower NO x emission levels were observed.
4.6 Carbon dioxide emissions
In Figure 3f, carbon dioxide emissions with ethanol–gasoline are illustrated. There is a difference between the mean CO2 emissions for E0, E5, E10, E15, and E20, which ranges from 0.54, 0.40, 0.45, 0.45, 0.45, 0.45, 0.45, 0.48, and 0.42 g·kW−1·h−1, respectively. Increasing the ethanol proportion in the blend results in an increase in CO2 emissions because esters have a higher oxygen content, which makes them burn more efficiently than neat diesel, resulting in CO2 emissions.
5 Development of a fuzzy logic model for the prediction of the SI engine performance and emission
Fuzzy logic was created by Prof. Zadeh to address uncertainty and imprecision in decision-making for practical applications [14]. Fuzzy logic systems have a faster and simpler design and development process, cheaper costs, and easier maintenance. A mathematical model is not necessary for fuzzy logic. Studies have been conducted by developing a fuzzy logic model to simulate the operation of different ethanol mixes in a gasoline engine. By using a fuzzy logic model, the performance of a four-stroke SI engine was studied using the experimental research techniques E0, E5, E10, E15, and E20. The engine’s power and torque output were on the higher side, according to the experiment results using ethanol–gasoline blended fuels, as shown in Figure 4. The link between braking power, torque, BSFC, and BTE was imagined using an ANN model with a range of gasoline–ethanol blends and speeds as input data. The study demonstrated that a fuzzy logic approach may be used to forecast spark-ignition engine performance with high accuracy.

Experimental findings and fuzzy logic predictions of (a) BTE, (b) BSFC, (c) CO, (d) HC, and (e) NO x for different test patterns are compared.
Figure 5 displays an analysis of the data for the BSFC and BTE that were estimated and measured. In each case, R 2 values were found to be 0.955, 0.981, and 0.952. The results from the fuzzy logic model show that using fuzzy logic to estimate BSFC and BTE has sufficient accuracy. MRE values are 3.127% and 5.423% of BTE and BSFC, respectively, whereas RMSEs for BTE and BSFC are 6.12 kPa, 0.413%, and 11.572 g·kW−1·h−1. For NO x , CO, and HC, the experimental results are compared to predictions for each in Figure 5. R 2 values of 0.9645, 0.9941, and 0.9743 were observed for each case. The outcomes of the fuzzy logic model show that calculating BSFC and BTE using fuzzy logic gives accurate results. The RMSE values for NO x , CO, and HC are 49.573 ppm, 0.0247%, and 3.478 ppm, while their MRE values are 8.1754%, 3.2597%, and 4.6349% (Table 3).
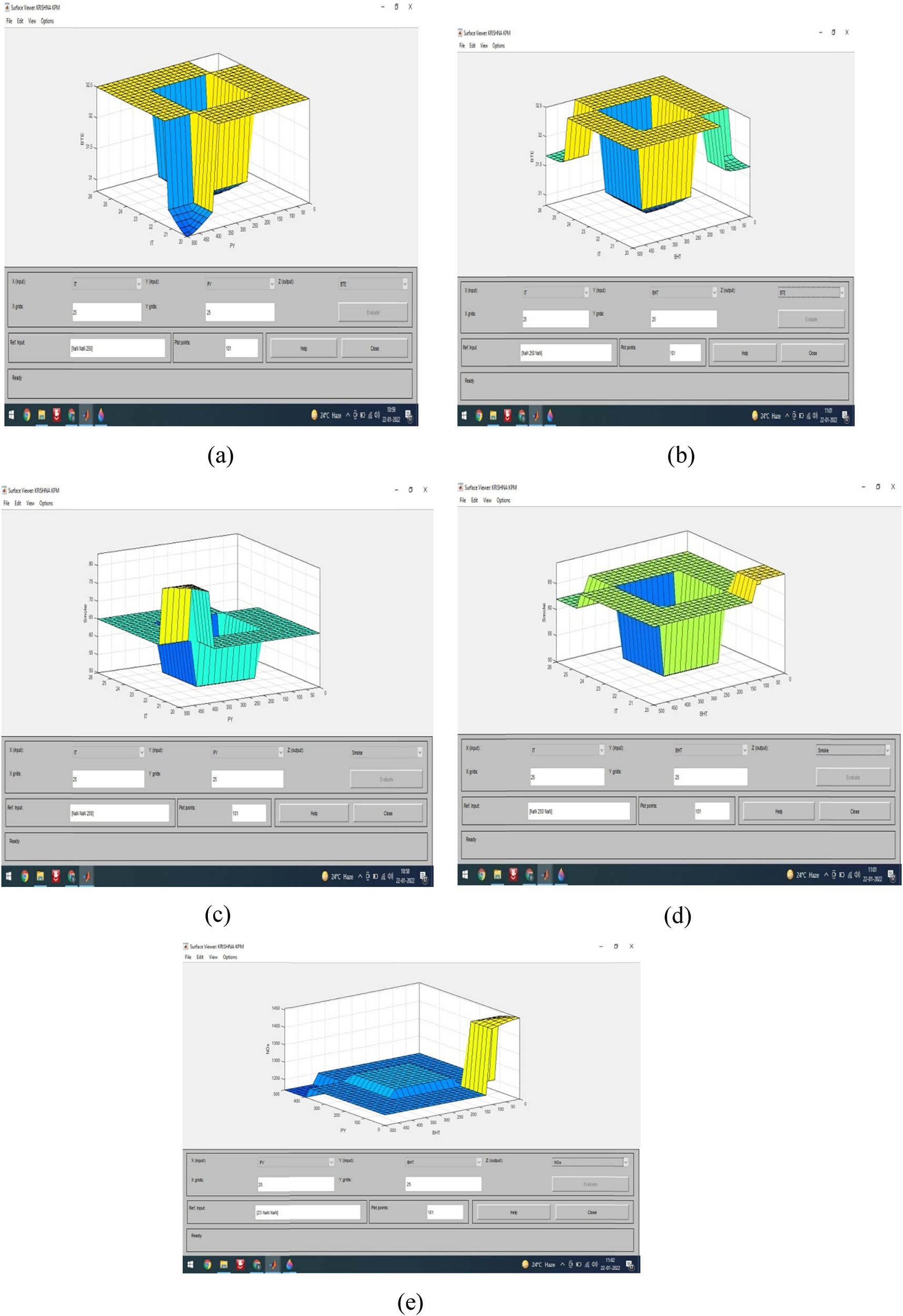
All performance and emission metrics are surface plotted using three factors: load, mix, and one output: (a) BTE, (b) BSFC, (c) CO, (d) HC, and (e) NO x .
Evaluated uncertainties associated with various parameters
| Measured variable | Uncertainty (%) |
|---|---|
| BTE | ±1.5 |
| Airflow rate | ±1.2 |
| Mechanical efficiency | ±1.3 |
| Engine speed | ±1.4 |
| Braking power | ±1.2 |
| Fuel flow rate | ±0.2 |
| Cooling water flow rate | ±1.0 |
| Volumetric efficiency | ±1.6 |
| In-cylinder pressure | ±1.4 |
5.1 Fuzzification
The fuzzy logic model is created in the MATLAB environment using the Fuzzy Logic Toolbox. Figure 6 depicts the created fuzzy logic model for predicting engine performance and emission characteristics. NO x , smoke, BTE, HC, CO, EGT, and MRPR are the inputs, and NOx, smoke, BTE, HC, CO, EGT, and MRPR are the outputs. To enhance performance, output values are normalized. For each injection time (23°bTDC), the load is represented by six fuzzy sets, whereas blends are expressed by five fuzzy sets (lowest, medium, centroid, high, and highest) [15].

Fuzzy logic model.
The surface plots for BTE and BSFC are shown in Figure 5a and b. The surface plots for CO, HC, and NO x pollutants are shown in Figure 5c–e, respectively. Eleven data sets were included for assessing the model. The intended model’s projected outcomes were in great agreement with the outcomes of the engine test, according to the statistical significance. The efficiency of the fuzzy logic model is significantly influenced by the type and quantity of membership functions. The triangle membership function (TMF) had the best performance after being compared to other membership functions for this investigation. For this research project, triangular membership functions were chosen because they require less computational work, are more cost-effective, and are better suited for real-time applications. The membership function and the quantity of training epochs have a big impact on how well a fuzzy logic model works. As the number of training periods increased to 200, the fuzzy logic model’s performance improved but there was no improvement after that. The ideal values for the training epoch and membership function are then 200 and 7, respectively.
Regression coefficients observed in training, testing, validation, and all other situations are higher than the critical specified value (Figure 7). Following network training, the MSE and MAPE values of each anticipated response are also computed. BTE, BSEC, and NO x prediction MSE and MAPE values were measured at 0.000214389, 0.000358127, and 0.000417895 and 4.12%, 5.36%, and 5.12%, respectively. These exceptionally low MSE and MAPE values are only made feasible by the model’s built-in sensitivity and a high degree of accuracy. Correlation coefficients of 0.99965, 0.99951, and 0.99962 have been reported for BTE, BSEC, and NO x , respectively, which is very close to 1, from this fuzzy logic model. This correlation coefficient of the ANN models is found to be greater than the values noted by Yang et al. [16] (0.979–0.997) and Singh et al. [17] (0.99124–0.99421). The MSE, MAPE, and R values are still insufficient to say how well the anticipated and actual data match each other.

The fuzzy logic model’s overall correlation coefficient.
6 Conclusion
This study indicates that considerable advancements have been made in improving the performance characteristics of SI engines using gasoline–ethanol blends, gasoline with all other alcohol derivatives, and subsequently alternative fuels. The primary findings are as follows:
When ethanol–gasoline was employed as a fuel, BTE was only slightly on the higher side. The highest BTE for E5, E10, E15, and E20, respectively, was determined to be 3.5%, 2.5%, 5.2%, and 6%.
For larger volumes of ethanol content, it was found that BSFC increased. Using E5, E10, E15, and E20, the specific gasoline consumption for brakes increased by 5.17%, 10%, 20%, 37%, and 56%, respectively.
As a result of lean combustion, the CO emission decreased, indicating that the combustion cycle was complete. Ethanol was also added, which reduced the CO output. Due to the reduced oxygen level in the mixture, HC emission decreased when ethanol was combined with gasoline. The emission of NO x increased as the flame temperature increased.
The findings of fuzzy logic models are quite strong, with R values very close to 1 and RMSE values being negligible for all factors that play a big role in determining how well an engine behaves.
As a result, it was feasible to compare and simulate engine characteristics using fuzzy logic models. The example illustration shows that fuzzy logic modelling is a reliable modelling approach that may predict a SI engine’s performance and emission characteristics even in complex, non-linear scenarios. The degree to which the predicted and experimental findings agree may be used to determine how accurate the created model is. This is in favour of simulating the harmful emissions and performance characteristics of spark-ignition engines utilizing RBMTF technology.
In future investigations, it is better to adapt the heat transfer model and incorporate the chemical equilibrium/kinetic model.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Mr. Elangovan and the Anna University laboratory for supplying the experimental data.
-
Funding information: The authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Manikandan Kaliyaperumal: investigation and fuel preparation; Ramabalan Sundaresan: supervision; Balu Pandian: design and fabrication and methodology; Silambarasan Rajendran: writing – original draft and fuel property analysis.
-
Conflict of interest: One of the authors (Silambarasan Rajendran) is a member of the Editorial Board of Green Processing and Synthesis.
References
[1] Manochio C, Andrade BR, Rodriguez RP, Moraes BS. Ethanol from biomass: A comparative overview. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;80:743–55. 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.063.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Nagenderan S, Rajamamundi P, Chandran M, Gopinath KP. Bioethanol from moringa olefira and pithecellobium dulce leafs: Production and characterization. Energy Sources Part A Recov Util Environ Eff. 2020;42(1):66–72. 10.1080/15567036.2019.1587055.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Huang Q, Liu J, Ulishney C, Dumitrescu CE. On the use of artificial neural networks to model the performance and emissions of a heavy-duty natural gas spark-ignition engine. Int J Engine Res. 2021;23:1879–98. 10.1177/14680874211034409.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Thakur AK, Mer KKS, Kaviti A. An artificial neural network approach to predict the performance and exhaust emissions of a gasoline engine using ethanol-gasoline blended fuels. Biofuels. 2018;9(3):379–93.10.1080/17597269.2016.1271630Search in Google Scholar
[5] Liu Z, Zuo Q, Wu G, Li Y. An artificial neural network developed for predicting of performance and emissions of a spark-ignition engine fueled with butanol–gasoline blends. Adv Mech Eng. 2018;10(1):1687814017748438. 10.1177/1687814017748438.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Liu J, Huang Q, Ulishney C, Dumitrescu CE. Comparison of random forest and neural network in modeling the performance and emissions of a natural gas spark ignition engine. J Energy Resour Technol. 2022;144:032310.10.1115/1.4053301Search in Google Scholar
[7] Tekin M, Saridemir S. Prediction of engine performance and exhaust emissions with different proportions of ethanol-gasoline blends using artificial neural networks. Int J Ambient Energy. 2019;40(5):470–6.10.1080/01430750.2017.1410225Search in Google Scholar
[8] Efemwenkiekie UK, Oyedepo SO, Idiku UD, Uguru-Okorie DC, Kuhe A. Comparative analysis of a four stroke spark ignition engine performance using local ethanol and gasoline blends. Procedia Manuf. 2019;35:1079–86.10.1016/j.promfg.2019.06.060Search in Google Scholar
[9] Gul M, Shah AN, Aziz U, Husnain N, Mujtaba MA, Kousar T, et al. Grey-Taguchi and ANN based optimization of a better performing low-emission diesel engine fueled with biodiesel. Energy Sources, Part A: Recov Util Environ Eff. 2019;44(1):1019–32. 10.1080/15567036.2019.1638995.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Ghadikolaei MA, Cheung CS, Yung KF. Study of combustion, performance and emissions of diesel engine fueled with diesel/biodiesel/alcohol blends having the same oxygen concentration. Energy. 2018;157:258–69. 10.1016/j.energy.2018.05.164.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Ileri E, Karaoglan AD, Atmanli A. Response surface methodology based prediction of engine performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with canola oil methyl ester. J Renew Sustain Energy. 2013;5:033132. 10.1063/1.4811801.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Dey S, Reang NM, Das PK, Deb M. Comparative study using RSM and ANN modelling for performance-emission prediction of CI engine fuelled with bio-diesohol blends: A fuzzy optimization approach. Fuel. 15 May 2021;292:120356. 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120356.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Uslu S, Celik MB. Performance and exhaust emission prediction of a SI engine fueled with iamyl alcohol-gasoline blends: An ANN coupled RSM based optimization. Fuel. 2020;265:116922. 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116922.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Thakur AK, Kaviti AK, Mehra R, Mer KKS. Performance analysis of ethanol–gasoline blends on a spark ignition engine: A review. Biofuels. 2016;8(1):91–112. 10.1080/17597269.2016.1204586.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Ji C, Wang H, Shi C, Wang S, Yang J. Multi-objective optimization of operating parameters for a gasoline wankel rotary engine by hydrogen enrichment. Energy Convers Manag. 2020;229:113732.10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113732Search in Google Scholar
[16] Yang R, Yan Y, Sun X, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Fu J, et al. An artificial neural network model to predict efficiency and emissions of a gasoline engine. Processes. 2022;10:204.10.3390/pr10020204Search in Google Scholar
[17] Singh Y, Sharma A, Tiwari S, Singla A. Optimization of diesel engine performance and emission parameters employing cassia tora methyl esters-response surface methodology approach. Energy. 2019;168:909–18.10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.013Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Value-added utilization of coal fly ash and recycled polyvinyl chloride in door or window sub-frame composites
- High removal efficiency of volatile phenol from coking wastewater using coal gasification slag via optimized adsorption and multi-grade batch process
- Evolution of surface morphology and properties of diamond films by hydrogen plasma etching
- Removal efficiency of dibenzofuran using CuZn-zeolitic imidazole frameworks as a catalyst and adsorbent
- Rapid and efficient microwave-assisted extraction of Caesalpinia sappan Linn. heartwood and subsequent synthesis of gold nanoparticles
- The catalytic characteristics of 2-methylnaphthalene acylation with AlCl3 immobilized on Hβ as Lewis acid catalyst
- Biodegradation of synthetic PVP biofilms using natural materials and nanoparticles
- Rutin-loaded selenium nanoparticles modulated the redox status, inflammatory, and apoptotic pathways associated with pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in mice
- Optimization of apigenin nanoparticles prepared by planetary ball milling: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Origanum onites leaves: Cytotoxic, apoptotic, and necrotic effects on Capan-1, L929, and Caco-2 cell lines
- Exergy analysis of a conceptual CO2 capture process with an amine-based DES
- Construction of fluorescence system of felodipine–tetracyanovinyl–2,2′-bipyridine complex
- Excellent photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B over Bi2O3 supported on Zn-MOF nanocomposites under visible light
- Optimization-based control strategy for a large-scale polyhydroxyalkanoates production in a fed-batch bioreactor using a coupled PDE–ODE system
- Effectiveness of pH and amount of Artemia urumiana extract on physical, chemical, and biological attributes of UV-fabricated biogold nanoparticles
- Geranium leaf-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their transcriptomic effects on Candida albicans
- Synthesis, characterization, anticancer, anti-inflammatory activities, and docking studies of 3,5-disubstituted thiadiazine-2-thiones
- Synthesis and stability of phospholipid-encapsulated nano-selenium
- Putative anti-proliferative effect of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) seed and its nano-formulation
- Enrichment of low-grade phosphorites by the selective leaching method
- Electrochemical analysis of the dissolution of gold in a copper–ethylenediamine–thiosulfate system
- Characterisation of carbonate lake sediments as a potential filler for polymer composites
- Evaluation of nano-selenium biofortification characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)
- Quality of oil extracted by cold press from Nigella sativa seeds incorporated with rosemary extracts and pretreated by microwaves
- Heteropolyacid-loaded MOF-derived mesoporous zirconia catalyst for chemical degradation of rhodamine B
- Recovery of critical metals from carbonatite-type mineral wastes: Geochemical modeling investigation of (bio)hydrometallurgical leaching of REEs
- Photocatalytic properties of ZnFe-mixed oxides synthesized via a simple route for water remediation
- Attenuation of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate-induced hepatic and renal toxicity by naringin nanoparticles in a rat model
- Novel in situ synthesis of quaternary core–shell metallic sulfide nanocomposites for degradation of organic dyes and hydrogen production
- Microfluidic steam-based synthesis of luminescent carbon quantum dots as sensing probes for nitrite detection
- Transformation of eggshell waste to egg white protein solution, calcium chloride dihydrate, and eggshell membrane powder
- Preparation of Zr-MOFs for the adsorption of doxycycline hydrochloride from wastewater
- Green nanoarchitectonics of the silver nanocrystal potential for treating malaria and their cytotoxic effects on the kidney Vero cell line
- Carbon emissions analysis of producing modified asphalt with natural asphalt
- An efficient and green synthesis of 2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-ones via t-BuONa-mediated oxidative condensation of 2-aminobenzamides and benzyl alcohols under solvent- and transition metal-free conditions
- Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with mesosulfuron methyl and mesosulfuron methyl + florasulam + MCPA isooctyl to manage weeds of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Synergism between lignite and high-sulfur petroleum coke in CO2 gasification
- Facile aqueous synthesis of ZnCuInS/ZnS–ZnS QDs with enhanced photoluminescence lifetime for selective detection of Cu(ii) ions
- Rapid synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Nepeta cataria leaves: An eco-friendly management of disease-causing vectors and bacterial pathogens
- Study on the photoelectrocatalytic activity of reduced TiO2 nanotube films for removal of methyl orange
- Development of a fuzzy logic model for the prediction of spark-ignition engine performance and emission for gasoline–ethanol blends
- Micro-impact-induced mechano-chemical synthesis of organic precursors from FeC/FeN and carbonates/nitrates in water and its extension to nucleobases
- Green synthesis of strontium-doped tin dioxide (SrSnO2) nanoparticles using the Mahonia bealei leaf extract and evaluation of their anticancer and antimicrobial activities
- A study on the larvicidal and adulticidal potential of Cladostepus spongiosus macroalgae and green-fabricated silver nanoparticles against mosquito vectors
- Catalysts based on nickel salt heteropolytungstates for selective oxidation of diphenyl sulfide
- Powerful antibacterial nanocomposites from Corallina officinalis-mediated nanometals and chitosan nanoparticles against fish-borne pathogens
- Removal behavior of Zn and alkalis from blast furnace dust in pre-reduction sinter process
- Environmentally friendly synthesis and computational studies of novel class of acridinedione integrated spirothiopyrrolizidines/indolizidines
- The mechanisms of inhibition and lubrication of clean fracturing flowback fluids in water-based drilling fluids
- Adsorption/desorption performance of cellulose membrane for Pb(ii)
- A one-pot, multicomponent tandem synthesis of fused polycyclic pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinolinone/pyrrolizino[2,3-c]quinolinone hybrid heterocycles via environmentally benign solid state melt reaction
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using durian rind extract and optical characteristics of surface plasmon resonance-based optical sensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide
- Electrochemical analysis of copper-EDTA-ammonia-gold thiosulfate dissolution system
- Characterization of bio-oil production by microwave pyrolysis from cashew nut shells and Cassia fistula pods
- Green synthesis methods and characterization of bacterial cellulose/silver nanoparticle composites
- Photocatalytic research performance of zinc oxide/graphite phase carbon nitride catalyst and its application in environment
- Effect of phytogenic iron nanoparticles on the bio-fortification of wheat varieties
- In vitro anti-cancer and antimicrobial effects of manganese oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the Glycyrrhiza uralensis leaf extract on breast cancer cell lines
- Preparation of Pd/Ce(F)-MCM-48 catalysts and their catalytic performance of n-heptane isomerization
- Green “one-pot” fluorescent bis-indolizine synthesis with whole-cell plant biocatalysis
- Silica-titania mesoporous silicas of MCM-41 type as effective catalysts and photocatalysts for selective oxidation of diphenyl sulfide by H2O2
- Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from molted feathers of Pavo cristatus and their antibiofilm and anticancer activities
- Clean preparation of rutile from Ti-containing mixed molten slag by CO2 oxidation
- Synthesis and characterization of Pluronic F-127-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles synthesized from extracts of Atractylodes macrocephala leaf for antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties
- Effect of pretreatment with alkali on the anaerobic digestion characteristics of kitchen waste and analysis of microbial diversity
- Ameliorated antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties by Plectranthus vettiveroides root extract-mediated green synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles
- Microwave-accelerated pretreatment technique in green extraction of oil and bioactive compounds from camelina seeds: Effectiveness and characterization
- Studies on the extraction performance of phorate by aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in plasma samples
- Investigation of structural properties and antibacterial activity of AgO nanoparticle extract from Solanum nigrum/Mentha leaf extracts by green synthesis method
- Green fabrication of chitosan from marine crustaceans and mushroom waste: Toward sustainable resource utilization
- Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of nanoparticles of clodinofop propargyl and fenoxaprop-P-ethyl on weed control, growth, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- The enhanced adsorption properties of phosphorus from aqueous solutions using lanthanum modified synthetic zeolites
- Separation of graphene oxides of different sizes by multi-layer dialysis and anti-friction and lubrication performance
- Visible-light-assisted base-catalyzed, one-pot synthesis of highly functionalized cinnolines
- The experimental study on the air oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid with Co–Mn–Br system
- Highly efficient removal of tetracycline and methyl violet 2B from aqueous solution using the bimetallic FeZn-ZIFs catalyst
- A thermo-tolerant cellulase enzyme produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M7, an insight into synthesis, optimization, characterization, and bio-polishing activity
- Exploration of ketone derivatives of succinimide for their antidiabetic potential: In vitro and in vivo approaches
- Ultrasound-assisted green synthesis and in silico study of 6-(4-(butylamino)-6-(diethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)oxypyridazine derivatives
- A study of the anticancer potential of Pluronic F-127 encapsulated Fe2O3 nanoparticles derived from Berberis vulgaris extract
- Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Consolida orientalis flowers: Identification, catalytic degradation, and biological effect
- Initial assessment of the presence of plastic waste in some coastal mangrove forests in Vietnam
- Adsorption synergy electrocatalytic degradation of phenol by active oxygen-containing species generated in Co-coal based cathode and graphite anode
- Antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and cytotoxicity activities of the aqueous extract of Syzygium aromaticum-mediated synthesized novel silver nanoparticles
- Synthesis of a silica matrix with ZnO nanoparticles for the fabrication of a recyclable photodegradation system to eliminate methylene blue dye
- Natural polymer fillers instead of dye and pigments: Pumice and scoria in PDMS fluid and elastomer composites
- Study on the preparation of glycerylphosphorylcholine by transesterification under supported sodium methoxide
- Wireless network handheld terminal-based green ecological sustainable design evaluation system: Improved data communication and reduced packet loss rate
- The optimization of hydrogel strength from cassava starch using oxidized sucrose as a crosslinking agent
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharum officinarum leaf extract for antiviral paint
- Study on the reliability of nano-silver-coated tin solder joints for flip chips
- Environmentally sustainable analytical quality by design aided RP-HPLC method for the estimation of brilliant blue in commercial food samples employing a green-ultrasound-assisted extraction technique
- Anticancer and antimicrobial potential of zinc/sodium alginate/polyethylene glycol/d-pinitol nanocomposites against osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
- Nanoporous carbon@CoFe2O4 nanocomposite as a green absorbent for the adsorptive removal of Hg(ii) from aqueous solutions
- Characterization of silver sulfide nanoparticles from actinobacterial strain (M10A62) and its toxicity against lepidopteran and dipterans insect species
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Withania somnifera: Investigating antioxidant potential
- Effect of e-waste nanofillers on the mechanical, thermal, and wear properties of epoxy-blend sisal woven fiber-reinforced composites
- Magnesium nanohydroxide (2D brucite) as a host matrix for thymol and carvacrol: Synthesis, characterization, and inhibition of foodborne pathogens
- Synergistic inhibitive effect of a hybrid zinc oxide-benzalkonium chloride composite on the corrosion of carbon steel in a sulfuric acidic solution
- Review Articles
- Role and the importance of green approach in biosynthesis of nanopropolis and effectiveness of propolis in the treatment of COVID-19 pandemic
- Gum tragacanth-mediated synthesis of metal nanoparticles, characterization, and their applications as a bactericide, catalyst, antioxidant, and peroxidase mimic
- Green-processed nano-biocomposite (ZnO–TiO2): Potential candidates for biomedical applications
- Reaction mechanisms in microwave-assisted lignin depolymerisation in hydrogen-donating solvents
- Recent progress on non-noble metal catalysts for the deoxydehydration of biomass-derived oxygenates
- Rapid Communication
- Phosphorus removal by iron–carbon microelectrolysis: A new way to achieve phosphorus recovery
- Special Issue: Biomolecules-derived synthesis of nanomaterials for environmental and biological applications (Guest Editors: Arpita Roy and Fernanda Maria Policarpo Tonelli)
- Biomolecules-derived synthesis of nanomaterials for environmental and biological applications
- Nano-encapsulated tanshinone IIA in PLGA-PEG-COOH inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
- Green fabrication of silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach ripened fruit extract, their characterization, and biological properties
- Green-synthesized nanoparticles and their therapeutic applications: A review
- Antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxicity potential of synthesized silver nanoparticles from the Cassia alata leaf aqueous extract
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Callisia fragrans leaf extract and its anticancer activity against MCF-7, HepG2, KB, LU-1, and MKN-7 cell lines
- Algae-based green AgNPs, AuNPs, and FeNPs as potential nanoremediators
- Green synthesis of Kickxia elatine-induced silver nanoparticles and their role as anti-acetylcholinesterase in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
- Phytocrystallization of silver nanoparticles using Cassia alata flower extract for effective control of fungal skin pathogens
- Antibacterial wound dressing with hydrogel from chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol from the red cabbage extract loaded with silver nanoparticles
- Leveraging of mycogenic copper oxide nanostructures for disease management of Alternaria blight of Brassica juncea
- Nanoscale molecular reactions in microbiological medicines in modern medical applications
- Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/β-cyclodextrin/nicotinic acid nanocomposite and its biological and environmental application
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via Taxus wallichiana Zucc. plant-derived Taxol: Novel utilization as anticancer, antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and antiurolithic potential
- Recyclability and catalytic characteristics of copper oxide nanoparticles derived from bougainvillea plant flower extract for biomedical application
- Phytofabrication, characterization, and evaluation of novel bioinspired selenium–iron (Se–Fe) nanocomposites using Allium sativum extract for bio-potential applications
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of nanoparticles of clodinofop propargyl and fenoxaprop-P-ethyl on weed control, growth, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)”
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Value-added utilization of coal fly ash and recycled polyvinyl chloride in door or window sub-frame composites
- High removal efficiency of volatile phenol from coking wastewater using coal gasification slag via optimized adsorption and multi-grade batch process
- Evolution of surface morphology and properties of diamond films by hydrogen plasma etching
- Removal efficiency of dibenzofuran using CuZn-zeolitic imidazole frameworks as a catalyst and adsorbent
- Rapid and efficient microwave-assisted extraction of Caesalpinia sappan Linn. heartwood and subsequent synthesis of gold nanoparticles
- The catalytic characteristics of 2-methylnaphthalene acylation with AlCl3 immobilized on Hβ as Lewis acid catalyst
- Biodegradation of synthetic PVP biofilms using natural materials and nanoparticles
- Rutin-loaded selenium nanoparticles modulated the redox status, inflammatory, and apoptotic pathways associated with pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in mice
- Optimization of apigenin nanoparticles prepared by planetary ball milling: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Origanum onites leaves: Cytotoxic, apoptotic, and necrotic effects on Capan-1, L929, and Caco-2 cell lines
- Exergy analysis of a conceptual CO2 capture process with an amine-based DES
- Construction of fluorescence system of felodipine–tetracyanovinyl–2,2′-bipyridine complex
- Excellent photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B over Bi2O3 supported on Zn-MOF nanocomposites under visible light
- Optimization-based control strategy for a large-scale polyhydroxyalkanoates production in a fed-batch bioreactor using a coupled PDE–ODE system
- Effectiveness of pH and amount of Artemia urumiana extract on physical, chemical, and biological attributes of UV-fabricated biogold nanoparticles
- Geranium leaf-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their transcriptomic effects on Candida albicans
- Synthesis, characterization, anticancer, anti-inflammatory activities, and docking studies of 3,5-disubstituted thiadiazine-2-thiones
- Synthesis and stability of phospholipid-encapsulated nano-selenium
- Putative anti-proliferative effect of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) seed and its nano-formulation
- Enrichment of low-grade phosphorites by the selective leaching method
- Electrochemical analysis of the dissolution of gold in a copper–ethylenediamine–thiosulfate system
- Characterisation of carbonate lake sediments as a potential filler for polymer composites
- Evaluation of nano-selenium biofortification characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)
- Quality of oil extracted by cold press from Nigella sativa seeds incorporated with rosemary extracts and pretreated by microwaves
- Heteropolyacid-loaded MOF-derived mesoporous zirconia catalyst for chemical degradation of rhodamine B
- Recovery of critical metals from carbonatite-type mineral wastes: Geochemical modeling investigation of (bio)hydrometallurgical leaching of REEs
- Photocatalytic properties of ZnFe-mixed oxides synthesized via a simple route for water remediation
- Attenuation of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate-induced hepatic and renal toxicity by naringin nanoparticles in a rat model
- Novel in situ synthesis of quaternary core–shell metallic sulfide nanocomposites for degradation of organic dyes and hydrogen production
- Microfluidic steam-based synthesis of luminescent carbon quantum dots as sensing probes for nitrite detection
- Transformation of eggshell waste to egg white protein solution, calcium chloride dihydrate, and eggshell membrane powder
- Preparation of Zr-MOFs for the adsorption of doxycycline hydrochloride from wastewater
- Green nanoarchitectonics of the silver nanocrystal potential for treating malaria and their cytotoxic effects on the kidney Vero cell line
- Carbon emissions analysis of producing modified asphalt with natural asphalt
- An efficient and green synthesis of 2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-ones via t-BuONa-mediated oxidative condensation of 2-aminobenzamides and benzyl alcohols under solvent- and transition metal-free conditions
- Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with mesosulfuron methyl and mesosulfuron methyl + florasulam + MCPA isooctyl to manage weeds of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Synergism between lignite and high-sulfur petroleum coke in CO2 gasification
- Facile aqueous synthesis of ZnCuInS/ZnS–ZnS QDs with enhanced photoluminescence lifetime for selective detection of Cu(ii) ions
- Rapid synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Nepeta cataria leaves: An eco-friendly management of disease-causing vectors and bacterial pathogens
- Study on the photoelectrocatalytic activity of reduced TiO2 nanotube films for removal of methyl orange
- Development of a fuzzy logic model for the prediction of spark-ignition engine performance and emission for gasoline–ethanol blends
- Micro-impact-induced mechano-chemical synthesis of organic precursors from FeC/FeN and carbonates/nitrates in water and its extension to nucleobases
- Green synthesis of strontium-doped tin dioxide (SrSnO2) nanoparticles using the Mahonia bealei leaf extract and evaluation of their anticancer and antimicrobial activities
- A study on the larvicidal and adulticidal potential of Cladostepus spongiosus macroalgae and green-fabricated silver nanoparticles against mosquito vectors
- Catalysts based on nickel salt heteropolytungstates for selective oxidation of diphenyl sulfide
- Powerful antibacterial nanocomposites from Corallina officinalis-mediated nanometals and chitosan nanoparticles against fish-borne pathogens
- Removal behavior of Zn and alkalis from blast furnace dust in pre-reduction sinter process
- Environmentally friendly synthesis and computational studies of novel class of acridinedione integrated spirothiopyrrolizidines/indolizidines
- The mechanisms of inhibition and lubrication of clean fracturing flowback fluids in water-based drilling fluids
- Adsorption/desorption performance of cellulose membrane for Pb(ii)
- A one-pot, multicomponent tandem synthesis of fused polycyclic pyrrolo[3,2-c]quinolinone/pyrrolizino[2,3-c]quinolinone hybrid heterocycles via environmentally benign solid state melt reaction
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using durian rind extract and optical characteristics of surface plasmon resonance-based optical sensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide
- Electrochemical analysis of copper-EDTA-ammonia-gold thiosulfate dissolution system
- Characterization of bio-oil production by microwave pyrolysis from cashew nut shells and Cassia fistula pods
- Green synthesis methods and characterization of bacterial cellulose/silver nanoparticle composites
- Photocatalytic research performance of zinc oxide/graphite phase carbon nitride catalyst and its application in environment
- Effect of phytogenic iron nanoparticles on the bio-fortification of wheat varieties
- In vitro anti-cancer and antimicrobial effects of manganese oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the Glycyrrhiza uralensis leaf extract on breast cancer cell lines
- Preparation of Pd/Ce(F)-MCM-48 catalysts and their catalytic performance of n-heptane isomerization
- Green “one-pot” fluorescent bis-indolizine synthesis with whole-cell plant biocatalysis
- Silica-titania mesoporous silicas of MCM-41 type as effective catalysts and photocatalysts for selective oxidation of diphenyl sulfide by H2O2
- Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from molted feathers of Pavo cristatus and their antibiofilm and anticancer activities
- Clean preparation of rutile from Ti-containing mixed molten slag by CO2 oxidation
- Synthesis and characterization of Pluronic F-127-coated titanium dioxide nanoparticles synthesized from extracts of Atractylodes macrocephala leaf for antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer properties
- Effect of pretreatment with alkali on the anaerobic digestion characteristics of kitchen waste and analysis of microbial diversity
- Ameliorated antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties by Plectranthus vettiveroides root extract-mediated green synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles
- Microwave-accelerated pretreatment technique in green extraction of oil and bioactive compounds from camelina seeds: Effectiveness and characterization
- Studies on the extraction performance of phorate by aptamer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in plasma samples
- Investigation of structural properties and antibacterial activity of AgO nanoparticle extract from Solanum nigrum/Mentha leaf extracts by green synthesis method
- Green fabrication of chitosan from marine crustaceans and mushroom waste: Toward sustainable resource utilization
- Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of nanoparticles of clodinofop propargyl and fenoxaprop-P-ethyl on weed control, growth, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- The enhanced adsorption properties of phosphorus from aqueous solutions using lanthanum modified synthetic zeolites
- Separation of graphene oxides of different sizes by multi-layer dialysis and anti-friction and lubrication performance
- Visible-light-assisted base-catalyzed, one-pot synthesis of highly functionalized cinnolines
- The experimental study on the air oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid with Co–Mn–Br system
- Highly efficient removal of tetracycline and methyl violet 2B from aqueous solution using the bimetallic FeZn-ZIFs catalyst
- A thermo-tolerant cellulase enzyme produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M7, an insight into synthesis, optimization, characterization, and bio-polishing activity
- Exploration of ketone derivatives of succinimide for their antidiabetic potential: In vitro and in vivo approaches
- Ultrasound-assisted green synthesis and in silico study of 6-(4-(butylamino)-6-(diethylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)oxypyridazine derivatives
- A study of the anticancer potential of Pluronic F-127 encapsulated Fe2O3 nanoparticles derived from Berberis vulgaris extract
- Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Consolida orientalis flowers: Identification, catalytic degradation, and biological effect
- Initial assessment of the presence of plastic waste in some coastal mangrove forests in Vietnam
- Adsorption synergy electrocatalytic degradation of phenol by active oxygen-containing species generated in Co-coal based cathode and graphite anode
- Antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant, and cytotoxicity activities of the aqueous extract of Syzygium aromaticum-mediated synthesized novel silver nanoparticles
- Synthesis of a silica matrix with ZnO nanoparticles for the fabrication of a recyclable photodegradation system to eliminate methylene blue dye
- Natural polymer fillers instead of dye and pigments: Pumice and scoria in PDMS fluid and elastomer composites
- Study on the preparation of glycerylphosphorylcholine by transesterification under supported sodium methoxide
- Wireless network handheld terminal-based green ecological sustainable design evaluation system: Improved data communication and reduced packet loss rate
- The optimization of hydrogel strength from cassava starch using oxidized sucrose as a crosslinking agent
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharum officinarum leaf extract for antiviral paint
- Study on the reliability of nano-silver-coated tin solder joints for flip chips
- Environmentally sustainable analytical quality by design aided RP-HPLC method for the estimation of brilliant blue in commercial food samples employing a green-ultrasound-assisted extraction technique
- Anticancer and antimicrobial potential of zinc/sodium alginate/polyethylene glycol/d-pinitol nanocomposites against osteosarcoma MG-63 cells
- Nanoporous carbon@CoFe2O4 nanocomposite as a green absorbent for the adsorptive removal of Hg(ii) from aqueous solutions
- Characterization of silver sulfide nanoparticles from actinobacterial strain (M10A62) and its toxicity against lepidopteran and dipterans insect species
- Phyto-fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Withania somnifera: Investigating antioxidant potential
- Effect of e-waste nanofillers on the mechanical, thermal, and wear properties of epoxy-blend sisal woven fiber-reinforced composites
- Magnesium nanohydroxide (2D brucite) as a host matrix for thymol and carvacrol: Synthesis, characterization, and inhibition of foodborne pathogens
- Synergistic inhibitive effect of a hybrid zinc oxide-benzalkonium chloride composite on the corrosion of carbon steel in a sulfuric acidic solution
- Review Articles
- Role and the importance of green approach in biosynthesis of nanopropolis and effectiveness of propolis in the treatment of COVID-19 pandemic
- Gum tragacanth-mediated synthesis of metal nanoparticles, characterization, and their applications as a bactericide, catalyst, antioxidant, and peroxidase mimic
- Green-processed nano-biocomposite (ZnO–TiO2): Potential candidates for biomedical applications
- Reaction mechanisms in microwave-assisted lignin depolymerisation in hydrogen-donating solvents
- Recent progress on non-noble metal catalysts for the deoxydehydration of biomass-derived oxygenates
- Rapid Communication
- Phosphorus removal by iron–carbon microelectrolysis: A new way to achieve phosphorus recovery
- Special Issue: Biomolecules-derived synthesis of nanomaterials for environmental and biological applications (Guest Editors: Arpita Roy and Fernanda Maria Policarpo Tonelli)
- Biomolecules-derived synthesis of nanomaterials for environmental and biological applications
- Nano-encapsulated tanshinone IIA in PLGA-PEG-COOH inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
- Green fabrication of silver nanoparticles using Melia azedarach ripened fruit extract, their characterization, and biological properties
- Green-synthesized nanoparticles and their therapeutic applications: A review
- Antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytotoxicity potential of synthesized silver nanoparticles from the Cassia alata leaf aqueous extract
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Callisia fragrans leaf extract and its anticancer activity against MCF-7, HepG2, KB, LU-1, and MKN-7 cell lines
- Algae-based green AgNPs, AuNPs, and FeNPs as potential nanoremediators
- Green synthesis of Kickxia elatine-induced silver nanoparticles and their role as anti-acetylcholinesterase in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
- Phytocrystallization of silver nanoparticles using Cassia alata flower extract for effective control of fungal skin pathogens
- Antibacterial wound dressing with hydrogel from chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol from the red cabbage extract loaded with silver nanoparticles
- Leveraging of mycogenic copper oxide nanostructures for disease management of Alternaria blight of Brassica juncea
- Nanoscale molecular reactions in microbiological medicines in modern medical applications
- Synthesis and characterization of ZnO/β-cyclodextrin/nicotinic acid nanocomposite and its biological and environmental application
- Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via Taxus wallichiana Zucc. plant-derived Taxol: Novel utilization as anticancer, antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and antiurolithic potential
- Recyclability and catalytic characteristics of copper oxide nanoparticles derived from bougainvillea plant flower extract for biomedical application
- Phytofabrication, characterization, and evaluation of novel bioinspired selenium–iron (Se–Fe) nanocomposites using Allium sativum extract for bio-potential applications
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of nanoparticles of clodinofop propargyl and fenoxaprop-P-ethyl on weed control, growth, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)”

