Abstract
This article presents a developed lightweight data encryption algorithm called LBC-3. Its essential difference from the known algorithms is the R1 function and the procedure for generating round keys. The main characteristics of this lightweight algorithm and all the transformations used in the encryption and decryption processes are described. The process of generating the round keys of the algorithm is also considered. The results of the study of the cryptographic properties of the algorithm using the “avalanche effect” and statistical tests are presented. The avalanche property was tested for each round with each bit of the source text changing. Based on the work carried out, it was found that the proposed encryption algorithm is effective in providing a good avalanche effect, and the binary sequence obtained after encryption is close to random. The research revealed good cryptographic properties of this algorithm.
1 Introduction
The main directions of the development of cryptography are largely associated with the development of communications, information technology, and computing hardware. It is the progress in these areas that has made possible the widespread use of compact devices with low computing power that have access to the Internet and implement the concept of the “Internet of Things.” The Internet of Things is a wireless self-configuring network between objects such as household appliances, vehicles, various sensors, and detectors, as well as RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) tags. Severe restrictions on the internal computing resources of such devices make it difficult or impossible to use classical cryptographic algorithms. This led to the emergence of a new section of cryptography – lightweight cryptography – aimed at creating strong cryptographic algorithms and protocols with acceptable strength in the context of limited resources [1,2].
Along with the effective implementation of known block cipher algorithms, work on the creation of new block ciphers focused on optimal implementation at the microprogram or hardware level for specialized applications is topical. Most of the research work (R&D) on the development of lightweight cryptoalgorithms has been carried out in the field of block cipher algorithms. Recently, many lightweight solutions have been proposed [3].
The National Institute of Standards and Technology has initiated a public standardization process to select one or more data-associated authentication encryption and hashing schemes suitable for resource-constrained devices.
In February 2019, 57 candidates were submitted to NIST for consideration. Of those, 56 were accepted as candidates in the first round in April 2019. Four months later, NIST selected 32 candidates for a second round. In March 2021, NIST announced 10 finalists who will advance to the final round of the selection process.
As a result, the following algorithms made it to the final: ASCON, Elephant, GIFT-COFB, Grain-128AEAD, ISAP, PHOTON-Beetle, Romulus, SPARKLE, TinyJAMBU, and Xoodyak.
In Kazakhstan, in the field of information security, foreign hardware and software are mainly used, which are transparent to their developers. Therefore, the development of domestic cryptographic information protection facilities (CIPFs), including home-grown lightweight encryption algorithms based on previously developed encryption algorithms, is currently a pressing issue.
The Laboratory of Information Security of the Institute of Information and Computational Technologies (IICT) of the Committee of Science (CS) of the Ministry of Education and Science (MES) of the Republic of Kazakhstan (RK) conducts research scientific work on the development and analysis of new encryption systems, electronic digital signature, generation of cryptographic keys, and authentication, as well as the creation of software CIPFs based on them. This article presents the results of creating a domestic lightweight encryption algorithm and studying its cryptographic properties.
2 Description of the algorithm
The developed LBC-3 algorithm is structurally different from existing lightweight algorithms such as PRESENT, although the architecture is similar. The proposed LBC-3 algorithm has its own substitution table (S-Box), and the R1 function has been added to improve diffusion, due to which high “avalanche effect” rates are achieved. It should also be noted that, unlike PRESENT, in LBC-3, round keys are generated in five rounds using the R2 function.
The LBC-3 algorithm is a symmetric block algorithm and has the following main characteristics:
Block length is 64 bits,
Master key length is 80 bits,
Round key length is 64 bits, and
Number of rounds is 20.
The structure of the algorithm is shown in Figure 1.

General scheme of the LBC-3 algorithm.
The encryption process consists of several rounds, each of which includes the following transformations:
S transformation,
R1 transformation,
L transformation, and
X transformation.
2.1 S Transformation
Every modern encryption algorithm uses a non-linear transformation in the form of a substitution table. It has been proven to be a strong cryptographic primitive against linear and differential cryptanalysis [4]. Lightweight block algorithms for non-linear transformations also use tabular substitutions – S-boxes. However, due to the requirement for lightweight algorithms, S-boxes should not take up a large amount of memory (ROM and RAM). To store a table that replaces 8-bit data fragments, 256 bytes are needed, and to store a 4-bit S-box, only 16 bytes are required [5]. Hence, 4-bit S-boxes are mainly used in lightweight cryptography. These include algorithms such as PRESENT and SERPENT. For the non-linear transformation of the LBC-3 algorithm, the 4-bit form of the substitution table was chosen. This S-box was constructed using a pseudo-random sequence generator (Table 1) and used to create a lightweight algorithm.
S-Box
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2 | 7 | E | C | 6 | F | 1 | 0 | B | 5 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 8 | D |
The non-linear transformation of the LBC-3 algorithm uses operations on half-bytes (4 bits). For each half-byte, a non-linear bijective substitution is applied, given by a one-dimensional array of 16 elements (4-bit S-box).
A 16-bit subblock is fed to the input of the transformation S and is divided into four groups of 4 bits. Each half-byte of the input block is an index of the value in the substitution table (Table 1). Thus, at the output of the transformation S, a set of half-bytes will be obtained, located at the corresponding indices in the given substitution table:
where a is 16 input bits and a i are half-bytes of the subblock.
2.2 R1 transformation
The linear transformation of the LBC-3 algorithm is a cyclic shift of bits and sub-blocks to a certain position. The input block of bits is divided into four subblocks of 16 bits each. The linear transformation at the subblock level is performed using the R1 function, which is applied only to the first subblock (Figure 1). The result of the R1 function is added to the second block modulo 2 (XOR operation). The function R1 has the following form:
where “≪” is the operator of circular shifting the bits of the subblock to the left.
2.3 L Transformation (cyclic shift of subblocks)
This linear transformation is performed on the whole block. Here, the subblocks are rotated to the left by one position; i.e., the second subblock moves to the first position, the third subblock replaces the second block, the fourth subblock replaces the third one, and the first subblock moves to the fourth position (Figure 1).
2.4 X Transformation (adding round keys)
After rotating the subblocks, round keys modulo 2 are added. The round key, consisting of 64 bits, is divided into four subkeys of 16 bits each and added to the corresponding data subblocks.
2.5 Encryption process
Encryption by the LBC-3 algorithm begins with “whitening” the source text; that is, “zero keys” are added to the source text before the round transformation. The initial 64 bits of the master key are taken as “zero keys.” Next, round transformations are performed.
If we designate the round encryption process as E, we get:
where
2.6 Decryption process
The decryption process is performed in reverse order. Here, instead of the transformations S and L, the inverse transformations S −1 and L −1 are used, and the transformations R1 and X remain the same as in the encryption process (Table 2):
where
Reverse S-box
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 7 | 1 | B | D | A | 5 | 2 | E | C | 0 | 9 | 4 | F | 3 | 6 |
2.7 Round key generation
The LBC-3 algorithm has a master key of 80 bits. From this sequence of bits, the round keys of the algorithm are generated. The key generation process consists of several transformations. The scheme for generating round keys is shown in Figure 2.
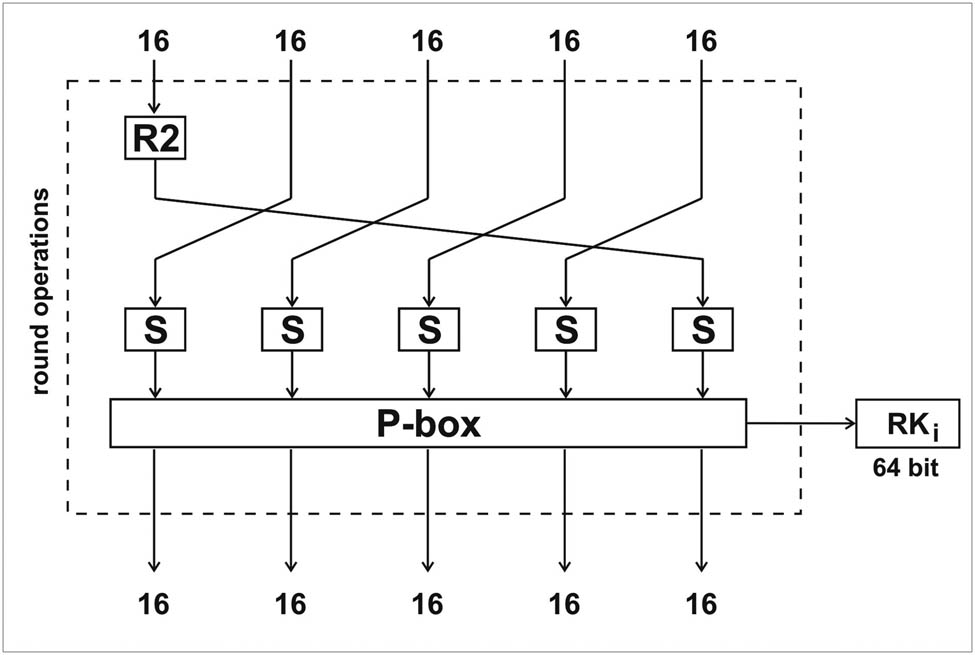
Scheme for generating round keys of the LBC-3 algorithm.
The master key of 80 bits is divided into five subblocks of 16 bits each. The key generation process itself has internal transformation rounds. The R2 function is applied to the first subblock and has the following form:
where “≪” is the subblock left-shift bit operator. Then, the sub-blocks are rotated to the left by one position (Figure 2). Each subblock is then replaced via a 4-bit S-box with new values. Here, the S-box from the main encryption algorithm is used (Table 1). The resulting new bit values are combined into one sequence, forming 80 bits. These bits are grouped by 4 bits, forming 20 groups. These groups of bits are permutated according to Table 3 (P-Box).
P-Box
| A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 5 | 12 | 18 | 16 | 10 | 13 | 20 | 2 | 15 | 4 | 17 | 7 | 19 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 1 | 8 | 11 | 14 |
In the table, row A is the initial position of 4-bit groups, row B is the new position of these bits in the sequence. Thus, the earlier transformations (function R2, rotation, S-box, P-box) are repeated 5 times (rounds). After five rounds of 80 bits, the initial 64 bits (on the left side of the sequence) are taken and used as round encryption (decryption) keys. The 80 bits obtained from the previous transformations will be used as the basis for the next round of keys. This process continues until all round encryption keys are obtained.
3 Study of the cryptographic properties of the algorithm
First, such a cryptographic property of the LBC-3 algorithm as the “avalanche effect” was investigated. To check for a good avalanche effect in a particular algorithm, an avalanche criterion is used. A cryptographic algorithm satisfies the avalanche criterion if a change in one bit of the input sequence changes, on average, half of the output bits.
Using the developed computer program that implements the avalanche criterion, the LBC-3 algorithm was investigated for the presence of the avalanche effect.
To characterize the degree of the avalanche effect in the transformation, an avalanche parameter is determined and used – the numerical value of the deviation of the probability of changing bits in the output sequence when bits in the input sequence change from the required probability value equal to 0.5.
For the avalanche criterion, the value of the avalanche parameter is determined by the formula
where i is the number of the bit to be changed at the input and k i is the probability of changing half of the bits in the output sequence when the ith bit in the input sequence is changed.
The values of the specified avalanche parameter are in the range from 0 to 1 inclusive. In this case, the smaller the value of the avalanche parameter, the stronger the avalanche effect in the transformation [6].
The results of the study are shown in Tables 4–6.
Results of the study of the avalanche effect
| Round number | Number of bits changed | Avalanche effect | Avalanche parameter value ɛ i ≈ | Round number | Number of bits changed | Avalanche effect | Avalanche parameter value ɛ i ≈ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0.1563 | 0.6874 | 11 | 32 | 0.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 19 | 0.2969 | 0.4062 | 12 | 34 | 0.5313 | 0.0626 |
| 3 | 30 | 0.4688 | 0.0624 | 13 | 26 | 0.4063 | 0.1874 |
| 4 | 29 | 0.4531 | 0.0938 | 14 | 35 | 0.5469 | 0.0938 |
| 5 | 34 | 0.5313 | 0.0626 | 15 | 36 | 0.5625 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 29 | 0.4531 | 0.0938 | 16 | 30 | 0.4688 | 0.0624 |
| 7 | 40 | 0.625 | 0.25 | 17 | 35 | 0.5469 | 0.0938 |
| 8 | 33 | 0.5156 | 0.0312 | 18 | 31 | 0.4844 | 0.0312 |
| 9 | 34 | 0.5313 | 0.0626 | 19 | 34 | 0.5313 | 0.0626 |
| 10 | 34 | 0.5313 | 0.0626 | 20 | 33 | 0.5156 | 0.0312 |
Results of the study of the avalanche effect by rounds
| Rounds | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average value of the avalanche parameter | 0.8837 | 0.7671 | 0.5805 | 0.3877 | 0.2031 | 0.1479 | 0.0952 | 0.0849 | 0.0947 | 0.0991 |
| Rounds | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average value of the avalanche parameter | 0.1147 | 0.0879 | 0.0928 | 0.0937 | 0.103 | 0.0879 | 0.0845 | 0.0869 | 0.0962 | 0.083 |
Results of the avalanche effect
| Source text | Ciphertext | Avalanche effect |
|---|---|---|
| 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 | E3 0D DC 82 CB 19 35 B0 | 0.4375 (28) |
| 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 10 | EC CF 52 D1 D8 0A 5B F2 | |
| 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 | 0B 16 94 70 8A E4 0D 56 | 0.4063 (26) |
| 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 87 | 49 44 89 00 42 61 DB 67 | |
| 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | 07 77 C8 DD 8F FD 55 A6 | 0.4844 (31) |
| 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 | B2 96 C8 6F 78 93 FD E5 |
The following table shows the number of output bits changed in each round, given that the first bit of the source text is changed.
During the study of the “avalanche effect” property, all values of the avalanche parameter were calculated when changing each bit of the source text for each round. The calculation results are shown in Table 5.
According to the results of the study, the best indicator of the avalanche effect is achieved after the sixth round of encryption (Figure 3). Based on this result, it can be assumed that 20-round encryption will provide high security of the ciphertext.
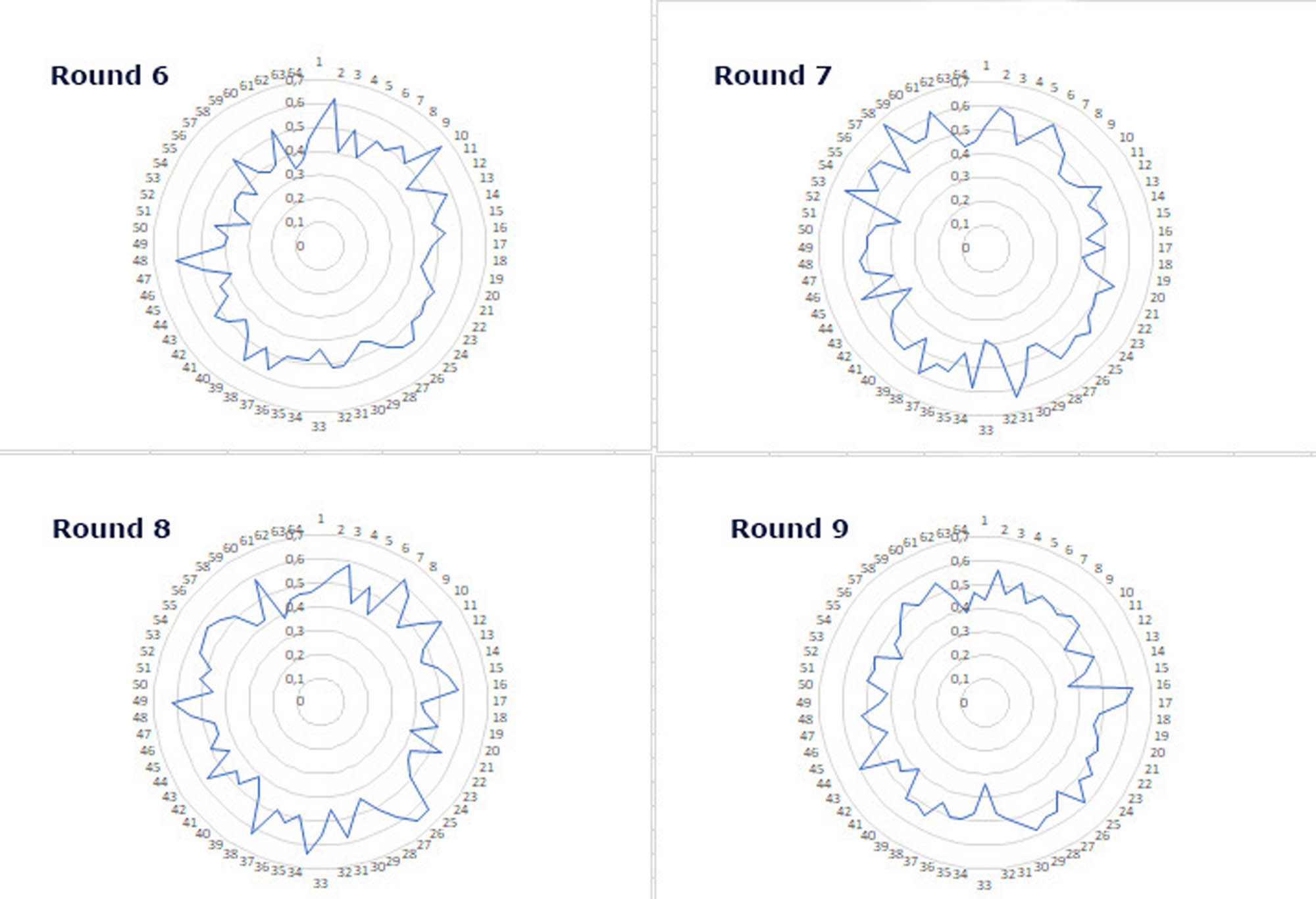
Histogram of avalanche parameter values in rounds 6–9.
Test examples of the avalanche effect of the algorithm are listed in Table 6.
4 Statistical analysis of the algorithm
For statistical analysis, 20 files of various types and sizes were selected, containing from 20 to 1,000 kb of information. Data on the selected files are presented in Table 7. Testing was carried out using the software package “Automated system for the selection of statistical tests by D. Knuth and graphic tests,” which implements a set of statistical tests.
Plaintext files used in testing the LBC-3 algorithm
| File number | File type | File format |
|---|---|---|
| 1–5 | *.docx | Microsoft Word document |
| 6–10 | *.xls | Microsoft Excel document |
| 11–15 | *.pptx | Microsoft PowerPoint document |
| 16–20 | Cross-platform open format | |
| 21–25 | *.rar | Archived RAR document |
| 26–30 | *.zip | Archived ZIP document |
| 31–35 | *.jpg | Graphic document in raster format |
| 36–40 | *.png | Graphic document in raster format |
| 41–45 | *.txt | Text file |
| 46–50 | *.gif | Graphic document in raster format |
| 51–55 | *.html | Web document |
| 56–60 | *.cat | System file for merging files |
| 61–65 | *.mp4 | Audio file |
| 66–70 | *.wmz | Vector Image Media file |
| 71–75 | *.dll | Dynamic Link Library file |
| 76–80 | *.log | Event log file |
| 80–85 | *.lex | Adobe Linguistic Library Data File |
| 86–90 | *.djvu | Graphic and text format document |
| 91–95 | *.xml | Web document |
| 96–100 | *.mp3 | Audio file |
After converting each file using five different keys, the corresponding encrypted files were obtained. The resulting 100 files were subjected to graphical and evaluation statistical tests. In graphical tests, the statistical properties of ciphertexts are displayed in the form of graphical dependencies, and in evaluation tests, the statistical properties are determined by numerical characteristics. As a result, according to the relevant data, a conclusion is made about the success of the passed test. Figures 4 and 5 show data on the number of files that successfully passed the graphical and evaluation tests.
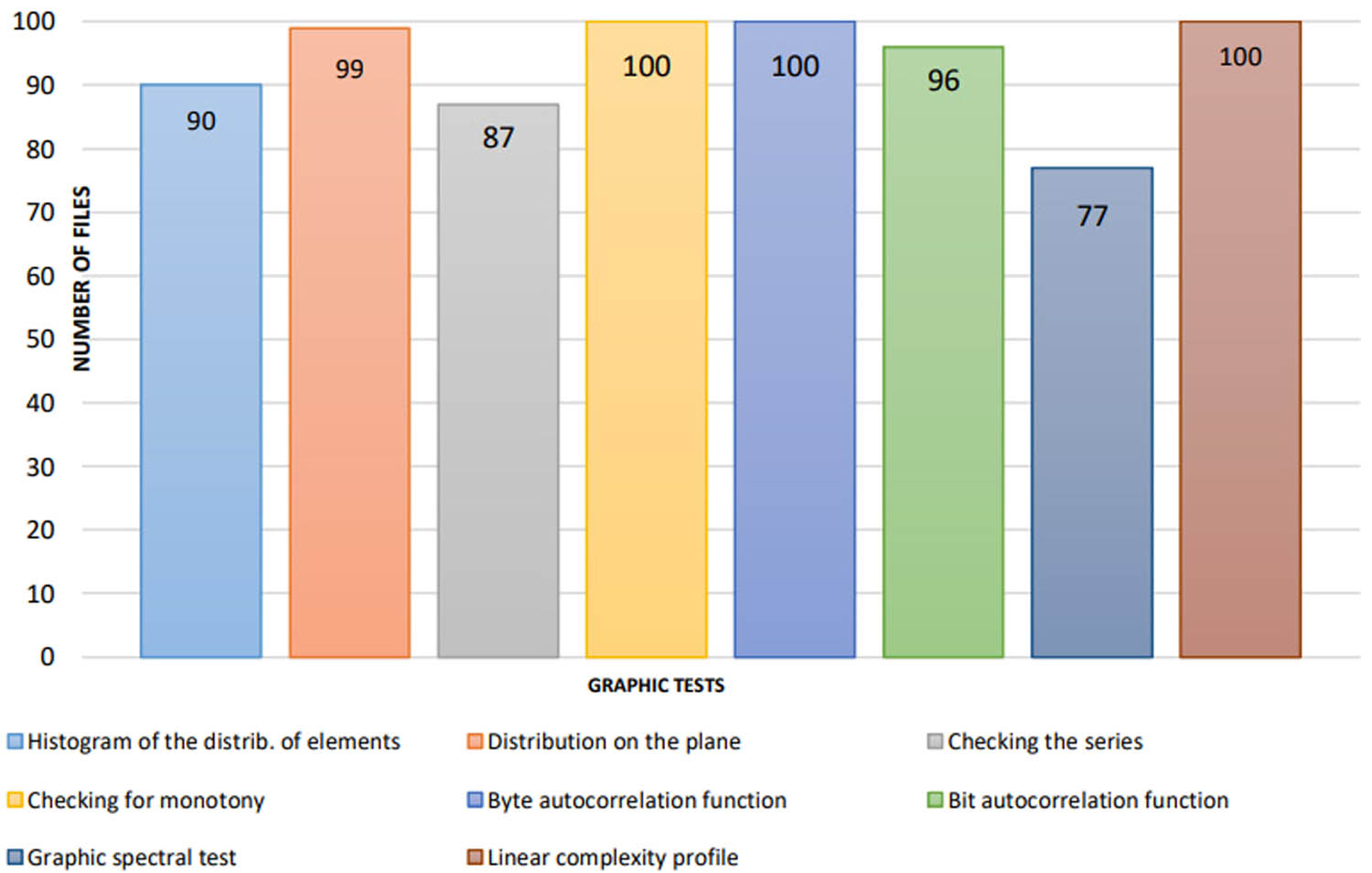
Graphical test results.
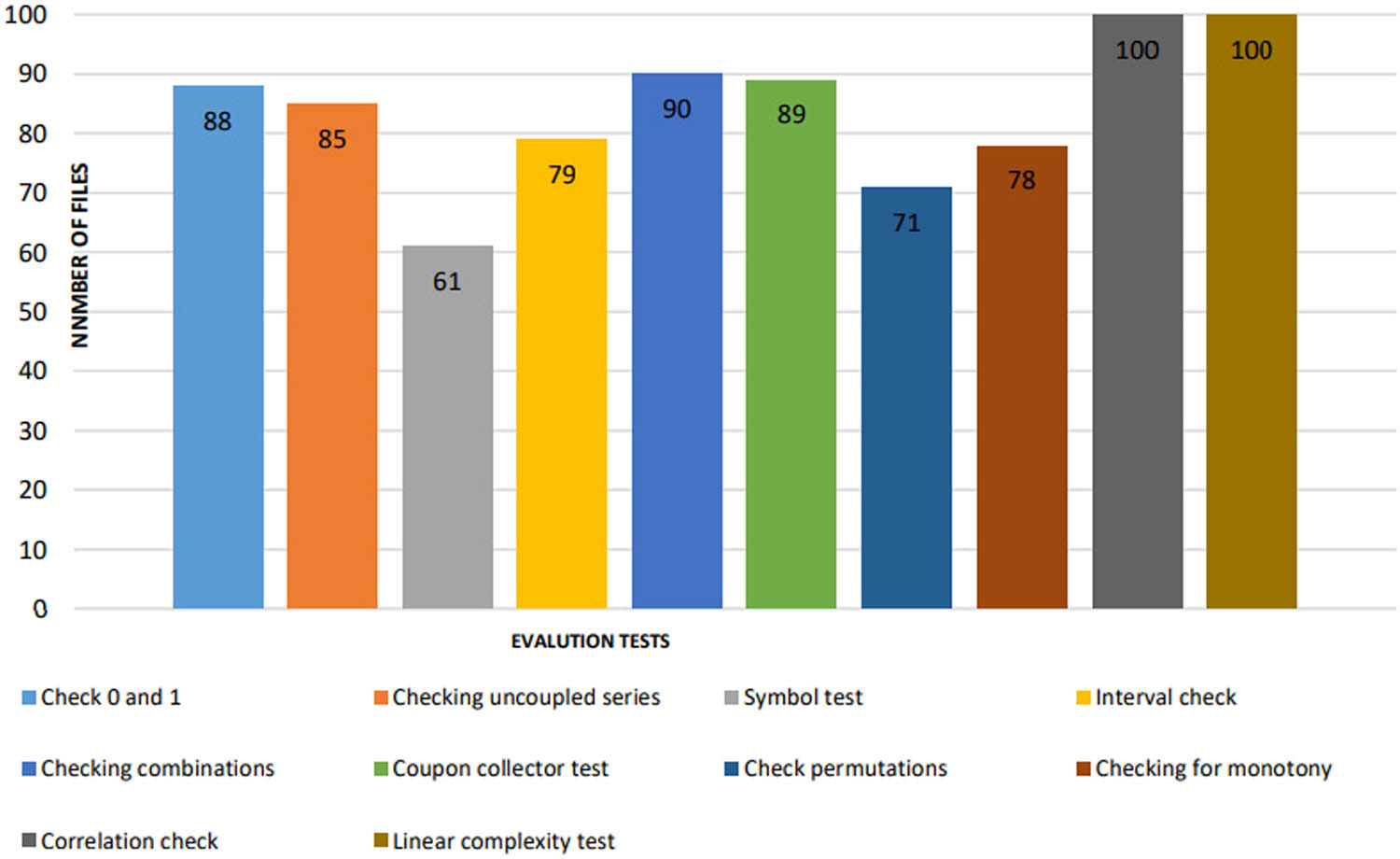
Evaluation test results.
In practice, the following approaches to testing lightweight encryption algorithms in software implementation are used:
Microcontroller Benchmarking by NIST LWC team (https://github.com/usnistgov/Lightweight-Cryptography-Benchmarking).
AVR/ARM Microcontroller Benchmarking by Rhys Weatherley (https://rweather.github.io/lightweight-crypto).
AVR/ARM/RISC-V Microcontroller Benchmarking by Sebastian Renner, Enrico Pozzobon, and Jürgen Mottok (https://lwc.las3.de).
RISC-V Benchmarking by Fabio Campos, Lars Jellema, Mauk Lemmen, Lars Müller, Daan Sprenkels, and Benoit Viguier (https://github.com/AsmOptC-RiscV/Assembly-Optimized-C-RiscV).
eBACS (ECRYPT Benchmarking of Cryptographic Systems): General-purpose Processor (Intel, AMD, ARM Cortex-A, Qualcomm) Benchmarking (http://bench.cr.yp.to).
Of all the approaches presented earlier, for testing the developed and other lightweight encryption algorithms, the second option was chosen, i.e., AVR/ARM Microcontroller Benchmarking by Rhys Weatherley.
The developed lightweight encryption algorithm was tested on the ArduinoUnoR3 board.
Main features of ArduinoUnoR3:
Microcontroller – ATmega328;
Clock frequency – 16 MHz;
Operating voltage – 5 V; and
Flash-memory – 32 MB.
The free software Arduino IDE version 2.0.0-rc3 was used as a software shell for compiling and uploading the source code of the developed encryption algorithm to the ArduinoUnoR3 board.
ISL_LBC was developed in the high-level C++ programming language, which allowed us to slightly modify the source code for use in the ArduinoIDE. All necessary source codes and sketches for the study were taken from the corresponding website [7].
Theoretical and experimental tests have shown that the algorithm fully complies with the basic cryptographic requirements. The study of the cryptographic strength of the encryption algorithm will be continued in subsequent works.
5 Conclusion
Based on the tests and studies carried out, it has been established that the proposed LBC-3 encryption algorithm provides a good avalanche effect. According to the results of randomness testing using statistical tests, it was found that the binary sequence obtained after encryption is close to random.
Further work is to investigate other cryptographic properties of this algorithm using various cryptanalysis methods. This lightweight cipher will be implemented in software on different platforms to analyze and evaluate its reliability. Recommendations and calculations for its hardware implementation will also be prepared.
Acknowledgment
The research work was carried out within the framework of the project AP09259570 “Development and study of a domestic lightweight encryption algorithm with limited resources” at the IICT of the RK MES CS.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Zhukov AE. Lightweight cryptography. Part 1. Cybersecurity issues, NPO Echelon, Moskow. Vol. 1, 2015. p. 26–43 (in Russian).10.21681/2311-3456-2015-1-26-43Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Zhukov AE. Lightweight cryptography. Part 2. Cybersecurity issues, NPO Echelon, Moskow. Vol. 2, 2015. p. 2–10 (in Russian).Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Kapalova NA, Haumen A, Suleimenov OT. Lightweight cryptographic information protection systems. Proceedings of the International Scientific-Practical Conference Actual Problems of Information Security in Kazakhstan. Almaty; 2021. p. 48–53 (in Russian).Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Kazlauskas K, Kazlauskas J. Key-dependent S-box generation in AES block cipher system. Informatica. 2009;20:23–34.10.15388/Informatica.2009.235Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Preneel B. Perspectives on lightweight cryptography. Inscript: Shanghai, China; October 2010. p. 20–4.Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Kapalova NA, Haumen A, Sakan K. Diffusion properties of linear transformations. Proceedings of the Scientific Conference RK MES IICT Modern Problems of Informatics and Computing Technologies. Almaty; 2020. p. 189–93 (in Russian).Suche in Google Scholar
[7] https://github.com/rweather/arduinolibs.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2022 Saule Nyssanbayeva et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Performance of a horizontal well in a bounded anisotropic reservoir: Part I: Mathematical analysis
- Key competences for Transport 4.0 – Educators’ and Practitioners’ opinions
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Constraint evaluation and effects on selected fracture parameters for single-edge notched beam under four-point bending
- Minimizing form errors in additive manufacturing with part build orientation: An optimization method for continuous solution spaces
- The method of selecting adaptive devices for the needs of drivers with disabilities
- Control logic algorithm to create gaps for mixed traffic: A comprehensive evaluation
- Numerical prediction of cavitation phenomena on marine vessel: Effect of the water environment profile on the propulsion performance
- Boundary element analysis of rotating functionally graded anisotropic fiber-reinforced magneto-thermoelastic composites
- Effect of heat-treatment processes and high temperature variation of acid-chloride media on the corrosion resistance of B265 (Ti–6Al–4V) titanium alloy in acid-chloride solution
- Influence of selected physical parameters on vibroinsulation of base-exited vibratory conveyors
- System and eco-material design based on slow-release ferrate(vi) combined with ultrasound for ballast water treatment
- Experimental investigations on transmission of whole body vibration to the wheelchair user's body
- Determination of accident scenarios via freely available accident databases
- Elastic–plastic analysis of the plane strain under combined thermal and pressure loads with a new technique in the finite element method
- Design and development of the application monitoring the use of server resources for server maintenance
- The LBC-3 lightweight encryption algorithm
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on road traffic accident forecasting in Poland and Slovakia
- Development and implementation of disaster recovery plan in stock exchange industry in Indonesia
- Pre-determination of prediction of yield-line pattern of slabs using Voronoi diagrams
- Urban air mobility and flying cars: Overview, examples, prospects, drawbacks, and solutions
- Stadiums based on curvilinear geometry: Approximation of the ellipsoid offset surface
- Driftwood blocking sensitivity on sluice gate flow
- Solar PV power forecasting at Yarmouk University using machine learning techniques
- 3D FE modeling of cable-stayed bridge according to ICE code
- Review Articles
- Partial discharge calibrator of a cavity inside high-voltage insulator
- Health issues using 5G frequencies from an engineering perspective: Current review
- Modern structures of military logistic bridges
- Retraction
- Retraction note: COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part II
- Solving transportation externalities, economic approaches, and their risks
- Demand forecast for parking spaces and parking areas in Olomouc
- Rescue of persons in traffic accidents on roads
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part II
- Switching transient analysis for low voltage distribution cable
- Frequency amelioration of an interconnected microgrid system
- Wireless power transfer topology analysis for inkjet-printed coil
- Analysis and control strategy of standalone PV system with various reference frames
- Special Issue: AESMT
- Study of emitted gases from incinerator of Al-Sadr hospital in Najaf city
- Experimentally investigating comparison between the behavior of fibrous concrete slabs with steel stiffeners and reinforced concrete slabs under dynamic–static loads
- ANN-based model to predict groundwater salinity: A case study of West Najaf–Kerbala region
- Future short-term estimation of flowrate of the Euphrates river catchment located in Al-Najaf Governorate, Iraq through using weather data and statistical downscaling model
- Utilization of ANN technique to estimate the discharge coefficient for trapezoidal weir-gate
- Experimental study to enhance the productivity of single-slope single-basin solar still
- An empirical formula development to predict suspended sediment load for Khour Al-Zubair port, South of Iraq
- A model for variation with time of flexiblepavement temperature
- Analytical and numerical investigation of free vibration for stepped beam with different materials
- Identifying the reasons for the prolongation of school construction projects in Najaf
- Spatial mixture modeling for analyzing a rainfall pattern: A case study in Ireland
- Flow parameters effect on water hammer stability in hydraulic system by using state-space method
- Experimental study of the behaviour and failure modes of tapered castellated steel beams
- Water hammer phenomenon in pumping stations: A stability investigation based on root locus
- Mechanical properties and freeze-thaw resistance of lightweight aggregate concrete using artificial clay aggregate
- Compatibility between delay functions and highway capacity manual on Iraqi highways
- The effect of expanded polystyrene beads (EPS) on the physical and mechanical properties of aerated concrete
- The effect of cutoff angle on the head pressure underneath dams constructed on soils having rectangular void
- An experimental study on vibration isolation by open and in-filled trenches
- Designing a 3D virtual test platform for evaluating prosthetic knee joint performance during the walking cycle
- Special Issue: AESMT-2 - Part I
- Optimization process of resistance spot welding for high-strength low-alloy steel using Taguchi method
- Cyclic performance of moment connections with reduced beam sections using different cut-flange profiles
- Time overruns in the construction projects in Iraq: Case study on investigating and analyzing the root causes
- Contribution of lift-to-drag ratio on power coefficient of HAWT blade for different cross-sections
- Geotechnical correlations of soil properties in Hilla City – Iraq
- Improve the performance of solar thermal collectors by varying the concentration and nanoparticles diameter of silicon dioxide
- Enhancement of evaporative cooling system in a green-house by geothermal energy
- Destructive and nondestructive tests formulation for concrete containing polyolefin fibers
- Quantify distribution of topsoil erodibility factor for watersheds that feed the Al-Shewicha trough – Iraq using GIS
- Seamless geospatial data methodology for topographic map: A case study on Baghdad
- Mechanical properties investigation of composite FGM fabricated from Al/Zn
- Causes of change orders in the cycle of construction project: A case study in Al-Najaf province
- Optimum hydraulic investigation of pipe aqueduct by MATLAB software and Newton–Raphson method
- Numerical analysis of high-strength reinforcing steel with conventional strength in reinforced concrete beams under monotonic loading
- Deriving rainfall intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves and testing the best distribution using EasyFit software 5.5 for Kut city, Iraq
- Designing of a dual-functional XOR block in QCA technology
- Producing low-cost self-consolidation concrete using sustainable material
- Performance of the anaerobic baffled reactor for primary treatment of rural domestic wastewater in Iraq
- Enhancement isolation antenna to multi-port for wireless communication
- A comparative study of different coagulants used in treatment of turbid water
- Field tests of grouted ground anchors in the sandy soil of Najaf, Iraq
- New methodology to reduce power by using smart street lighting system
- Optimization of the synergistic effect of micro silica and fly ash on the behavior of concrete using response surface method
- Ergodic capacity of correlated multiple-input–multiple-output channel with impact of transmitter impairments
- Numerical studies of the simultaneous development of forced convective laminar flow with heat transfer inside a microtube at a uniform temperature
- Enhancement of heat transfer from solar thermal collector using nanofluid
- Improvement of permeable asphalt pavement by adding crumb rubber waste
- Study the effect of adding zirconia particles to nickel–phosphorus electroless coatings as product innovation on stainless steel substrate
- Waste aggregate concrete properties using waste tiles as coarse aggregate and modified with PC superplasticizer
- CuO–Cu/water hybrid nonofluid potentials in impingement jet
- Satellite vibration effects on communication quality of OISN system
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part III
- Mechanical and thermal properties of recycled high-density polyethylene/bamboo with different fiber loadings
- Special Issue: Advanced Energy Storage
- Cu-foil modification for anode-free lithium-ion battery from electronic cable waste
- Review of various sulfide electrolyte types for solid-state lithium-ion batteries
- Optimization type of filler on electrochemical and thermal properties of gel polymer electrolytes membranes for safety lithium-ion batteries
- Pr-doped BiFeO3 thin films growth on quartz using chemical solution deposition
- An environmentally friendly hydrometallurgy process for the recovery and reuse of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries, using organic acid
- Production of nickel-rich LiNi0.89Co0.08Al0.03O2 cathode material for high capacity NCA/graphite secondary battery fabrication
- Special Issue: Sustainable Materials Production and Processes
- Corrosion polarization and passivation behavior of selected stainless steel alloys and Ti6Al4V titanium in elevated temperature acid-chloride electrolytes
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part II
- The modelling of railway subgrade strengthening foundation on weak soils
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part II
- Manufacturing operations as services by robots with skills
- Foundations and case studies on the scalable intelligence in AIoT domains
- Safety risk sources of autonomous mobile machines
- Special Issue: 49th KKBN - Part I
- Residual magnetic field as a source of information about steel wire rope technical condition
- Monitoring the boundary of an adhesive coating to a steel substrate with an ultrasonic Rayleigh wave
- Detection of early stage of ductile and fatigue damage presented in Inconel 718 alloy using instrumented indentation technique
- Identification and characterization of the grinding burns by eddy current method
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part II
- Selection of MR damper model suitable for SMC applied to semi-active suspension system by using similarity measures
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Performance of a horizontal well in a bounded anisotropic reservoir: Part I: Mathematical analysis
- Key competences for Transport 4.0 – Educators’ and Practitioners’ opinions
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Constraint evaluation and effects on selected fracture parameters for single-edge notched beam under four-point bending
- Minimizing form errors in additive manufacturing with part build orientation: An optimization method for continuous solution spaces
- The method of selecting adaptive devices for the needs of drivers with disabilities
- Control logic algorithm to create gaps for mixed traffic: A comprehensive evaluation
- Numerical prediction of cavitation phenomena on marine vessel: Effect of the water environment profile on the propulsion performance
- Boundary element analysis of rotating functionally graded anisotropic fiber-reinforced magneto-thermoelastic composites
- Effect of heat-treatment processes and high temperature variation of acid-chloride media on the corrosion resistance of B265 (Ti–6Al–4V) titanium alloy in acid-chloride solution
- Influence of selected physical parameters on vibroinsulation of base-exited vibratory conveyors
- System and eco-material design based on slow-release ferrate(vi) combined with ultrasound for ballast water treatment
- Experimental investigations on transmission of whole body vibration to the wheelchair user's body
- Determination of accident scenarios via freely available accident databases
- Elastic–plastic analysis of the plane strain under combined thermal and pressure loads with a new technique in the finite element method
- Design and development of the application monitoring the use of server resources for server maintenance
- The LBC-3 lightweight encryption algorithm
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on road traffic accident forecasting in Poland and Slovakia
- Development and implementation of disaster recovery plan in stock exchange industry in Indonesia
- Pre-determination of prediction of yield-line pattern of slabs using Voronoi diagrams
- Urban air mobility and flying cars: Overview, examples, prospects, drawbacks, and solutions
- Stadiums based on curvilinear geometry: Approximation of the ellipsoid offset surface
- Driftwood blocking sensitivity on sluice gate flow
- Solar PV power forecasting at Yarmouk University using machine learning techniques
- 3D FE modeling of cable-stayed bridge according to ICE code
- Review Articles
- Partial discharge calibrator of a cavity inside high-voltage insulator
- Health issues using 5G frequencies from an engineering perspective: Current review
- Modern structures of military logistic bridges
- Retraction
- Retraction note: COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part II
- Solving transportation externalities, economic approaches, and their risks
- Demand forecast for parking spaces and parking areas in Olomouc
- Rescue of persons in traffic accidents on roads
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part II
- Switching transient analysis for low voltage distribution cable
- Frequency amelioration of an interconnected microgrid system
- Wireless power transfer topology analysis for inkjet-printed coil
- Analysis and control strategy of standalone PV system with various reference frames
- Special Issue: AESMT
- Study of emitted gases from incinerator of Al-Sadr hospital in Najaf city
- Experimentally investigating comparison between the behavior of fibrous concrete slabs with steel stiffeners and reinforced concrete slabs under dynamic–static loads
- ANN-based model to predict groundwater salinity: A case study of West Najaf–Kerbala region
- Future short-term estimation of flowrate of the Euphrates river catchment located in Al-Najaf Governorate, Iraq through using weather data and statistical downscaling model
- Utilization of ANN technique to estimate the discharge coefficient for trapezoidal weir-gate
- Experimental study to enhance the productivity of single-slope single-basin solar still
- An empirical formula development to predict suspended sediment load for Khour Al-Zubair port, South of Iraq
- A model for variation with time of flexiblepavement temperature
- Analytical and numerical investigation of free vibration for stepped beam with different materials
- Identifying the reasons for the prolongation of school construction projects in Najaf
- Spatial mixture modeling for analyzing a rainfall pattern: A case study in Ireland
- Flow parameters effect on water hammer stability in hydraulic system by using state-space method
- Experimental study of the behaviour and failure modes of tapered castellated steel beams
- Water hammer phenomenon in pumping stations: A stability investigation based on root locus
- Mechanical properties and freeze-thaw resistance of lightweight aggregate concrete using artificial clay aggregate
- Compatibility between delay functions and highway capacity manual on Iraqi highways
- The effect of expanded polystyrene beads (EPS) on the physical and mechanical properties of aerated concrete
- The effect of cutoff angle on the head pressure underneath dams constructed on soils having rectangular void
- An experimental study on vibration isolation by open and in-filled trenches
- Designing a 3D virtual test platform for evaluating prosthetic knee joint performance during the walking cycle
- Special Issue: AESMT-2 - Part I
- Optimization process of resistance spot welding for high-strength low-alloy steel using Taguchi method
- Cyclic performance of moment connections with reduced beam sections using different cut-flange profiles
- Time overruns in the construction projects in Iraq: Case study on investigating and analyzing the root causes
- Contribution of lift-to-drag ratio on power coefficient of HAWT blade for different cross-sections
- Geotechnical correlations of soil properties in Hilla City – Iraq
- Improve the performance of solar thermal collectors by varying the concentration and nanoparticles diameter of silicon dioxide
- Enhancement of evaporative cooling system in a green-house by geothermal energy
- Destructive and nondestructive tests formulation for concrete containing polyolefin fibers
- Quantify distribution of topsoil erodibility factor for watersheds that feed the Al-Shewicha trough – Iraq using GIS
- Seamless geospatial data methodology for topographic map: A case study on Baghdad
- Mechanical properties investigation of composite FGM fabricated from Al/Zn
- Causes of change orders in the cycle of construction project: A case study in Al-Najaf province
- Optimum hydraulic investigation of pipe aqueduct by MATLAB software and Newton–Raphson method
- Numerical analysis of high-strength reinforcing steel with conventional strength in reinforced concrete beams under monotonic loading
- Deriving rainfall intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves and testing the best distribution using EasyFit software 5.5 for Kut city, Iraq
- Designing of a dual-functional XOR block in QCA technology
- Producing low-cost self-consolidation concrete using sustainable material
- Performance of the anaerobic baffled reactor for primary treatment of rural domestic wastewater in Iraq
- Enhancement isolation antenna to multi-port for wireless communication
- A comparative study of different coagulants used in treatment of turbid water
- Field tests of grouted ground anchors in the sandy soil of Najaf, Iraq
- New methodology to reduce power by using smart street lighting system
- Optimization of the synergistic effect of micro silica and fly ash on the behavior of concrete using response surface method
- Ergodic capacity of correlated multiple-input–multiple-output channel with impact of transmitter impairments
- Numerical studies of the simultaneous development of forced convective laminar flow with heat transfer inside a microtube at a uniform temperature
- Enhancement of heat transfer from solar thermal collector using nanofluid
- Improvement of permeable asphalt pavement by adding crumb rubber waste
- Study the effect of adding zirconia particles to nickel–phosphorus electroless coatings as product innovation on stainless steel substrate
- Waste aggregate concrete properties using waste tiles as coarse aggregate and modified with PC superplasticizer
- CuO–Cu/water hybrid nonofluid potentials in impingement jet
- Satellite vibration effects on communication quality of OISN system
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part III
- Mechanical and thermal properties of recycled high-density polyethylene/bamboo with different fiber loadings
- Special Issue: Advanced Energy Storage
- Cu-foil modification for anode-free lithium-ion battery from electronic cable waste
- Review of various sulfide electrolyte types for solid-state lithium-ion batteries
- Optimization type of filler on electrochemical and thermal properties of gel polymer electrolytes membranes for safety lithium-ion batteries
- Pr-doped BiFeO3 thin films growth on quartz using chemical solution deposition
- An environmentally friendly hydrometallurgy process for the recovery and reuse of metals from spent lithium-ion batteries, using organic acid
- Production of nickel-rich LiNi0.89Co0.08Al0.03O2 cathode material for high capacity NCA/graphite secondary battery fabrication
- Special Issue: Sustainable Materials Production and Processes
- Corrosion polarization and passivation behavior of selected stainless steel alloys and Ti6Al4V titanium in elevated temperature acid-chloride electrolytes
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part II
- The modelling of railway subgrade strengthening foundation on weak soils
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part II
- Manufacturing operations as services by robots with skills
- Foundations and case studies on the scalable intelligence in AIoT domains
- Safety risk sources of autonomous mobile machines
- Special Issue: 49th KKBN - Part I
- Residual magnetic field as a source of information about steel wire rope technical condition
- Monitoring the boundary of an adhesive coating to a steel substrate with an ultrasonic Rayleigh wave
- Detection of early stage of ductile and fatigue damage presented in Inconel 718 alloy using instrumented indentation technique
- Identification and characterization of the grinding burns by eddy current method
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part II
- Selection of MR damper model suitable for SMC applied to semi-active suspension system by using similarity measures


