Abstract
C19H22N2O2, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 19.3063(4) Å, b = 5.83200(10) Å, c = 14.7996(3) Å, β = 92.715(1)°, V = 1664.48(6) Å3, Z = 4, R gt (F) = 0.0423, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1102, T = 100(2) K.
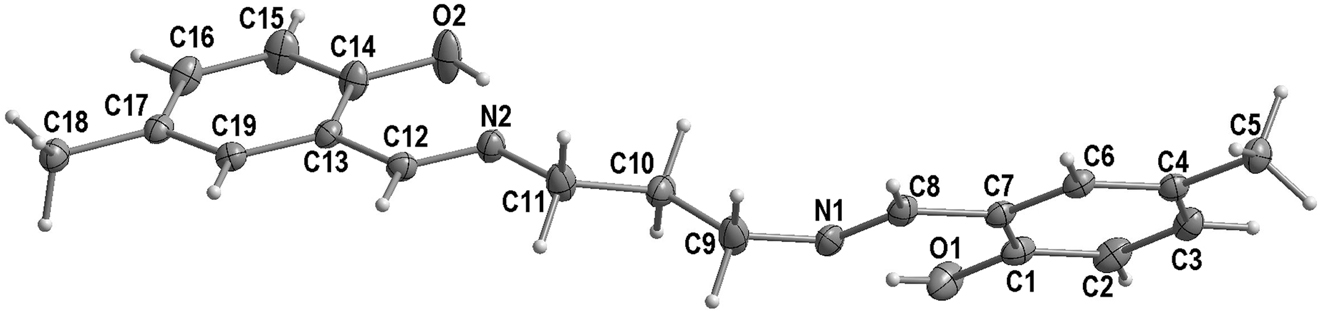
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.44 × 0.39 × 0.33 mm |
| Wavelength: | Cu Kα radiation (1.54178 Å) |
| μ: | 0.64 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker SMART Apex-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 66.8°, 96% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 17,078, 2818, 0.041 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | I obs > 2 σ(I obs), 2575 |
| N(param)refined: | 213 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.81206 (8) | 0.6886 (3) | 0.30440 (10) | 0.0287 (3) |
| C2 | 0.87955 (8) | 0.7683 (2) | 0.29892 (10) | 0.0327 (4) |
| H2A | 0.887618 | 0.914471 | 0.273133 | 0.039* |
| C3 | 0.93485 (8) | 0.6371 (3) | 0.33055 (10) | 0.0296 (4) |
| H3 | 0.980550 | 0.694931 | 0.325968 | 0.036* |
| C4 | 0.92561 (7) | 0.4208 (2) | 0.36927 (9) | 0.0256 (3) |
| C5 | 0.98661 (8) | 0.2776 (3) | 0.40219 (11) | 0.0326 (4) |
| H5A | 0.971548 | 0.118938 | 0.410774 | 0.049* |
| H5B | 1.005590 | 0.339013 | 0.459826 | 0.049* |
| H5C | 1.022393 | 0.281639 | 0.357412 | 0.049* |
| C6 | 0.85811 (7) | 0.3428 (2) | 0.37430 (9) | 0.0248 (3) |
| H6 | 0.850499 | 0.196294 | 0.400062 | 0.030* |
| C7 | 0.80083 (7) | 0.4712 (2) | 0.34299 (9) | 0.0243 (3) |
| C8 | 0.73110 (7) | 0.3780 (3) | 0.34833 (10) | 0.0287 (3) |
| H8 | 0.725134 | 0.231154 | 0.374611 | 0.034* |
| C9 | 0.60952 (8) | 0.3859 (3) | 0.32523 (13) | 0.0438 (5) |
| H9A | 0.613306 | 0.249316 | 0.364905 | 0.053* |
| H9B | 0.592026 | 0.334995 | 0.264545 | 0.053* |
| C10 | 0.55888 (8) | 0.5540 (3) | 0.36317 (11) | 0.0322 (4) |
| H10A | 0.554359 | 0.688536 | 0.322515 | 0.039* |
| H10B | 0.577304 | 0.608376 | 0.422955 | 0.039* |
| C11 | 0.48792 (8) | 0.4486 (3) | 0.37346 (12) | 0.0371 (4) |
| H11A | 0.470656 | 0.384241 | 0.314726 | 0.044* |
| H11B | 0.491539 | 0.321829 | 0.417903 | 0.044* |
| C12 | 0.37444 (7) | 0.5928 (3) | 0.38494 (10) | 0.0267 (3) |
| H12 | 0.359468 | 0.460389 | 0.352108 | 0.032* |
| C13 | 0.32289 (7) | 0.7585 (2) | 0.41226 (9) | 0.0242 (3) |
| C14 | 0.34274 (8) | 0.9615 (3) | 0.45794 (11) | 0.0319 (4) |
| C15 | 0.29194 (9) | 1.1161 (3) | 0.48124 (13) | 0.0381 (4) |
| H15 | 0.304830 | 1.253449 | 0.512165 | 0.046* |
| C16 | 0.22283 (8) | 1.0720 (3) | 0.45988 (11) | 0.0324 (4) |
| H16 | 0.188915 | 1.180246 | 0.476460 | 0.039* |
| C17 | 0.20162 (7) | 0.8730 (2) | 0.41466 (10) | 0.0256 (3) |
| C18 | 0.12648 (8) | 0.8250 (3) | 0.39069 (11) | 0.0316 (4) |
| H18A | 0.117236 | 0.849437 | 0.325719 | 0.047* |
| H18B | 0.097430 | 0.928573 | 0.424766 | 0.047* |
| H18C | 0.115783 | 0.665793 | 0.405955 | 0.047* |
| C19 | 0.25266 (7) | 0.7184 (2) | 0.39178 (9) | 0.0248 (3) |
| H19 | 0.239309 | 0.581013 | 0.361196 | 0.030* |
| N1 | 0.67781 (7) | 0.4894 (2) | 0.31845 (9) | 0.0340 (3) |
| N2 | 0.43897 (6) | 0.6204 (2) | 0.40381 (9) | 0.0291 (3) |
| O1 | 0.75882 (6) | 0.8209 (2) | 0.27355 (8) | 0.0400 (3) |
| H1 | 0.721521 | 0.747671 | 0.276516 | 0.060* |
| O2 | 0.41009 (6) | 1.0089 (2) | 0.47933 (10) | 0.0473 (4) |
| H2 | 0.435110 | 0.903102 | 0.460415 | 0.071* |
Source of material
The salicylaldimine compound was synthesized and obtained in good yields from a 2:1 reaction ratio of substituted salicylaldehyde 2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzaldehyde with 1,3-diaminopropane in dry methanol under reflux. The compound was obtained as a yellow solid with yields of 96%.
Experimental details
Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies for the compound were obtained after four weeks by slow diffusion and evaporation of hexane into a concentrated solution of the compound in dichloromethane (DCM). Crystal evaluation and data collection were done on a Bruker Smart APEX2 diffractometer [1] Crystal evaluation and data collection were done on a Bruker SMART 1000 CCD diffractometer with Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) equipped with an Oxford Cryostream low temperature apparatus operating at 100(1) K. The structure was solved by direct method using the SHELXS [2] program and refined with SHELXL [3].
All hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined in riding models with U iso assigned the values of 1.2 times or 1.5 times those of their parent atoms and the distances of C–H were constrained to 0.95 Å for all the aromatic H atoms, 0.98 Å for the CH3 protons and 0.9 for CH2 protons or 0.84 Å for the hydroxy group H atoms, respectively. The idealized tetrahedral OH refined as rotating group. The visual crystal structure information was performed using Diamond [4].
Comment
N,O-salicylaldimines are Schiff base ligands with the ability to coordinate transition metal ions via the hard nitrogen and oxygen donor atoms. This leads to a stabilization of the metal complexes against reduction and eventually give good thermal stability [5]. It is also easy to manipulate their steric and electronic properties. The early transition metal complexes have been shown to exhibit high oxophilic nature [6, 7]. Despite this shortcoming, a lot of research has been conducted on salicylaldimine complexes and their application as catalysts in polymerization reactions. For instance, group four metal-complexes of titanium and zirconium have been synthesized and tested, which showed significant (co)polymerization of ethylene [8], [9], [10]. Their salicylaldimine complexes have also been shown to exhibit stability, catalytic activity and greater tolerance for polar monomers in olefin polymerization [11].
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains one salicylaldimine molecule. In the structure, the 2-(iminomethyl)-4-methylphenol moieties are on either sides of the propyl linker and enclose a dihedral angle of 52.40(3) comparable to that of in the structure of 4,4′-Dichloro-2,2′- [(1E,1′E)-propane-1,3-diylbis(nitrilomethylidyne)]diphenol [12].
In the crystal, this compound displays two intramolecular hydrogen bonds O–H⃛N with an N⃛O distance of 2.593(2) Å. The bond distances and angles are comparable to those of related compounds [13], [14], [15], [16].
Funding source: University of Eldoret Research grant of 2016
Funding source: University of the Western Cape
Funding source: National Research Foundation of South Africa
Award Identifier / Grant number: 105894
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: We sincerely appreciate the funding from the University of Eldoret Research grant of 2016 and the University of the Western Cape as well as the National Research Foundation of South Africa (Grant number 105894).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEXII; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System (Ver. 4.0); Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Li, C. Q., Wang, F. F., Gao, R., Sun, P., Zhang, N., Wang, J. Bidentate iron complexes based on hyperbranched salicylaldimine ligands and their catalytic behavior toward ethylene oligomerization. Transition Met. Chem. 2017, 42, 339–346; https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-017-0137-9.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Britovsek, G. J. P., Bruce, M., Gibson, V. C., Kimberley, B. S., Maddox, P. J., Mastroianni, S., McTavish, S. J., Redshaw, C., Solan, G. A., Stromberg, S., White, A. J. P., Williams, D. J. Iron and cobalt ethylene polymerization catalysts bearing 2,6-bis(imino)pyridyl ligands: synthesis, structures, and polymerization studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 8728–8740; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja990449w.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Gibson, V. C., Spitzmesser, S. K. Advances in non-metallocene olefin polymerization catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 283–315; https://doi.org/10.1021/cr980461r.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Salata, M. R., Marks, T. J. Synthesis, characterization, and marked polymerization selectivity characteristics of binuclear phenoxyiminato organozirconium catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12–13; https://doi.org/10.1021/ja076857e.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Salata, M. R., Marks, T. J. Catalyst nuclearity effects in olefin polymerization. enhanced activity and comonomer enchainment in ethylene + olefin copolymerizations mediated by bimetallic group 4 phenoxyiminato catalysts. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1920–1933; https://doi.org/10.1021/ma8020745.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Han, S., Yao, E., Qin, W., Zhang, S., Ma, Y. Binuclear heteroligated titanium catalyst based on phenoxyimine ligands: synthesis, characterization, and ethylene (co)polymerization. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4054–4059; https://doi.org/10.1021/ma300384w.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Suo, H., Solan, G. A., Ma, Y., Sun, W. H. Developments in compartmentalized bimetallic transition metal ethylene polymerization catalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 372, 101–116; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.06.006.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Lei, S., Zhu-Ping, X., Zhong, Z., Zhao-Zhao, Z., Hai-Liang, Z. Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2007, E63, o4726.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Nazir, H., Arici, C., Emregül, K. C., Atakol, O. A crystallographic and spectroscopic study on the imine-amine tautomerism of 2-hydroxyaldimine compounds. Z. für Kristallogr. - Cryst. Mater. 2006, 221, 699–704; https://doi.org/10.1524/zkri.2006.221.10.699.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Xue, L. W., Li, X. W., Zhao, G. Q., Yang, W. C. Synthesis, crystal structure, and thermal analysis of a dioxomolybdenum(VI) complex derived from N,N′-bis(5-methylsalicylidene)-1,3-diaminopropane. Synth. React. Inorg. Metal-Org. Nano-Metal Chem. 2013, 43, 1514–1517; https://doi.org/10.1080/15533174.2012.762793.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Steiner, T. The hydrogen bond in the solid state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 48–76; https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<48::aid-anie48>3.0.co;2-u.10.1002/1521-3773(20020104)41:1<48::AID-ANIE48>3.0.CO;2-USuche in Google Scholar
16. Bilge, S., Kiliç, Z., Hayvali, Z., Hökelek, T., Safran, S. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding and tautomerism in Schiff bases: part VI. syntheses and structural investigation of salicylaldimine and naphthaldimine derivatives. J. Chem. Sci. 2009, 121, 989–1001; https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-009-0128-2.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Daniel M. Orang’o et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5

