Abstract
8[C23H22F7I1N2O4S1], monoclinic, Cc (no. 9), a = 19.762(3) Å, b = 24.690(4) Å, c = 12.106(2) Å, β = 113.696(2)°, V = 5408.8(15) Å3, Z = 1, R gt (F) = 0.0488, wR ref (F 2) = 0.1411, T = 296(2) K.
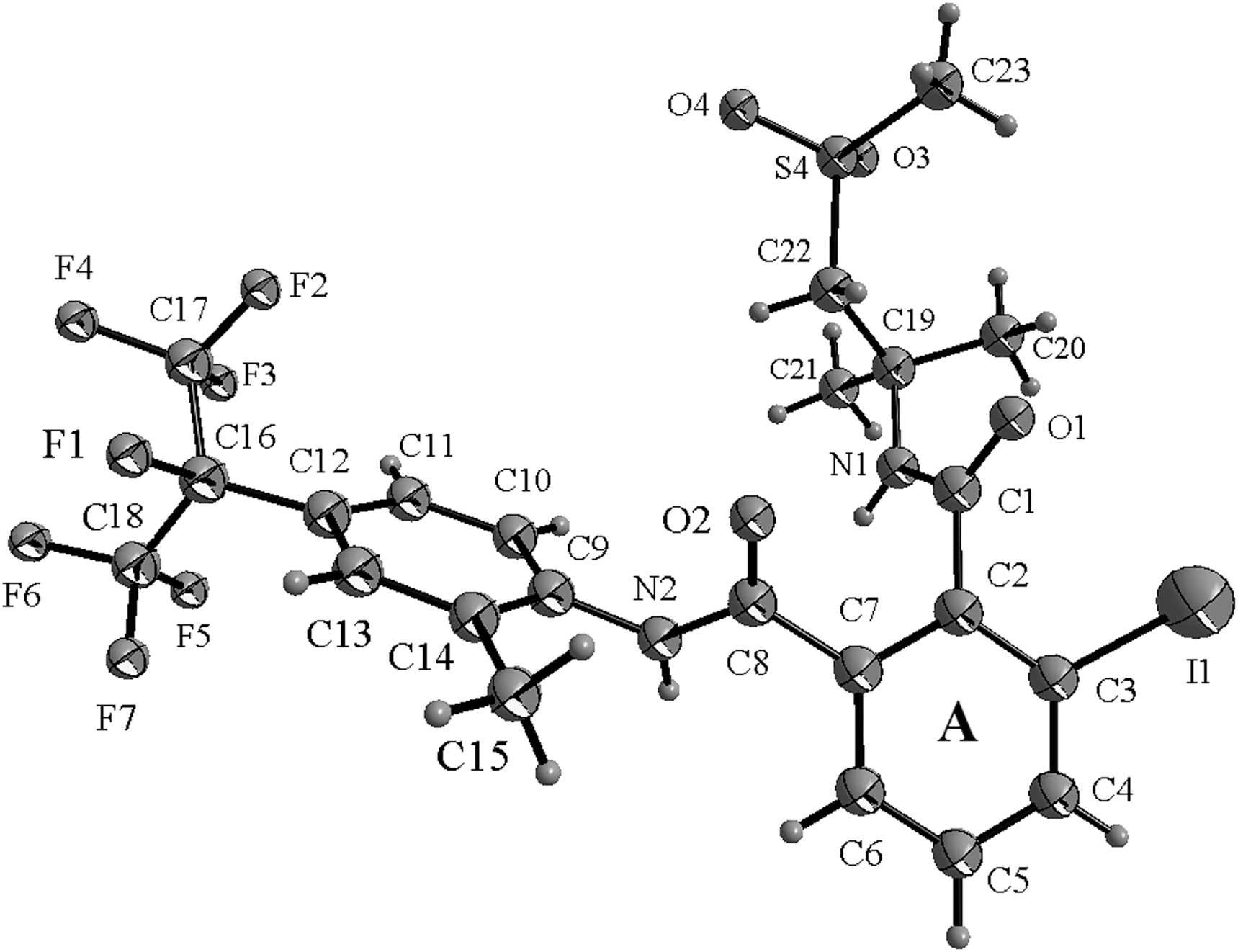
The asymmetric unit of the title crystal structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless block |
| Size: | 0.21 × 0.16 × 0.13 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.34 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θ max, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, R int: | 20,707, 9580, 0.027 |
| Criterion for I obs, N(hkl)gt: | 8203 |
| N(param)refined: | 693 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2, 3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | U iso*/U eq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.3214 (4) | 0.2403 (3) | −0.0290 (6) | 0.0404 (16) |
| C2 | 0.2995 (4) | 0.1950 (3) | 0.0318 (6) | 0.0391 (15) |
| C3 | 0.3091 (5) | 0.1407 (4) | 0.0062 (7) | 0.0491 (18) |
| C4 | 0.2835 (6) | 0.0987 (4) | 0.0526 (10) | 0.067 (2) |
| H4 | 0.289174 | 0.063165 | 0.032527 | 0.080* |
| C5 | 0.2488 (6) | 0.1097 (4) | 0.1296 (10) | 0.065 (2) |
| H5 | 0.233742 | 0.081380 | 0.165102 | 0.078* |
| C6 | 0.2370 (5) | 0.1617 (4) | 0.1531 (8) | 0.059 (2) |
| H6 | 0.210986 | 0.168330 | 0.200951 | 0.071* |
| C7 | 0.2622 (4) | 0.2055 (3) | 0.1085 (7) | 0.0402 (15) |
| C8 | 0.2535 (4) | 0.2620 (3) | 0.1429 (6) | 0.0422 (16) |
| C9 | 0.1665 (4) | 0.3244 (3) | 0.1698 (7) | 0.0466 (17) |
| C10 | 0.1207 (5) | 0.3592 (4) | 0.0817 (8) | 0.055 (2) |
| H10 | 0.105407 | 0.350772 | 0.000383 | 0.066* |
| C11 | 0.0976 (6) | 0.4077 (4) | 0.1173 (12) | 0.074 (3) |
| H11 | 0.067233 | 0.431490 | 0.058865 | 0.089* |
| C12 | 0.1195 (7) | 0.4204 (4) | 0.2380 (12) | 0.073 (3) |
| C13 | 0.1662 (7) | 0.3853 (5) | 0.3230 (10) | 0.073 (3) |
| H13 | 0.183007 | 0.394640 | 0.404142 | 0.087* |
| C14 | 0.1889 (5) | 0.3367 (4) | 0.2922 (8) | 0.058 (2) |
| C15 | 0.2371 (10) | 0.2995 (7) | 0.3871 (10) | 0.103 (5) |
| H15A | 0.242812 | 0.312921 | 0.464859 | 0.155* |
| H15B | 0.284629 | 0.297427 | 0.383374 | 0.155* |
| H15C | 0.215099 | 0.264180 | 0.374767 | 0.155* |
| C16 | 0.0909 (10) | 0.4696 (6) | 0.277 (2) | 0.113 (6) |
| C17 | 0.1001 (10) | 0.5218 (7) | 0.224 (2) | 0.120 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0252 (13) | 0.4609 (9) | 0.297 (2) | 0.128 (6) |
| C19 | 0.2691 (4) | 0.3053 (3) | −0.2012 (6) | 0.0439 (16) |
| C20 | 0.3163 (6) | 0.2824 (5) | −0.2652 (9) | 0.068 (3) |
| H20A | 0.365207 | 0.274896 | −0.206647 | 0.102* |
| H20B | 0.318756 | 0.308466 | −0.322329 | 0.102* |
| H20C | 0.294229 | 0.249601 | −0.306609 | 0.102* |
| C21 | 0.1916 (6) | 0.3156 (5) | −0.2925 (10) | 0.071 (3) |
| H21A | 0.172299 | 0.283242 | −0.338216 | 0.106* |
| H21B | 0.192322 | 0.344162 | −0.345978 | 0.106* |
| H21C | 0.160951 | 0.326091 | −0.251616 | 0.106* |
| C22 | 0.2998 (5) | 0.3572 (4) | −0.1269 (8) | 0.056 (2) |
| H22A | 0.340168 | 0.346644 | −0.052364 | 0.067* |
| H22B | 0.261246 | 0.372025 | −0.105472 | 0.067* |
| C23 | 0.4266 (7) | 0.4010 (5) | −0.1450 (13) | 0.084 (3) |
| H23A | 0.445594 | 0.426902 | −0.184493 | 0.126* |
| H23B | 0.435927 | 0.365041 | −0.165484 | 0.126* |
| H23C | 0.450587 | 0.405917 | −0.059227 | 0.126* |
| C24 | 0.0051 (4) | 0.2088 (3) | 0.9579 (7) | 0.0419 (16) |
| C25 | −0.0119 (4) | 0.2631 (3) | 0.8960 (7) | 0.0414 (16) |
| C26 | −0.0494 (5) | 0.3024 (4) | 0.9309 (7) | 0.0507 (18) |
| C27 | −0.0677 (5) | 0.3521 (4) | 0.8729 (8) | 0.057 (2) |
| H27 | −0.093314 | 0.377724 | 0.897322 | 0.069* |
| C28 | −0.0475 (5) | 0.3631 (3) | 0.7793 (8) | 0.057 (2) |
| H28 | −0.058964 | 0.396514 | 0.740719 | 0.069* |
| C29 | −0.0098 (5) | 0.3245 (3) | 0.7414 (7) | 0.0514 (19) |
| H29 | 0.002981 | 0.331985 | 0.677020 | 0.062* |
| C30 | 0.0085 (4) | 0.2748 (3) | 0.8000 (6) | 0.0384 (15) |
| C31 | 0.0559 (4) | 0.2360 (3) | 0.7680 (7) | 0.0439 (16) |
| C32 | 0.0698 (4) | 0.1870 (4) | 0.6033 (7) | 0.0514 (19) |
| C33 | 0.1013 (6) | 0.1396 (4) | 0.6603 (9) | 0.063 (2) |
| H33 | 0.099568 | 0.130356 | 0.733587 | 0.075* |
| C34 | 0.1362 (7) | 0.1052 (5) | 0.6069 (11) | 0.076 (3) |
| H34 | 0.156911 | 0.072722 | 0.644300 | 0.091* |
| C35 | 0.1398 (6) | 0.1191 (5) | 0.5008 (11) | 0.072 (3) |
| C36 | 0.1081 (6) | 0.1673 (5) | 0.4445 (9) | 0.069 (3) |
| H36 | 0.110865 | 0.176621 | 0.372031 | 0.083* |
| C37 | 0.0733 (5) | 0.2012 (4) | 0.4927 (8) | 0.057 (2) |
| C38 | 0.0397 (6) | 0.2524 (5) | 0.4290 (9) | 0.076 (3) |
| H38A | 0.062589 | 0.262305 | 0.375394 | 0.114* |
| H38B | 0.047265 | 0.280719 | 0.487136 | 0.114* |
| H38C | −0.012304 | 0.247171 | 0.383565 | 0.114* |
| C39 | 0.1807 (7) | 0.0840 (6) | 0.4446 (14) | 0.095 (4) |
| C42 | −0.0434 (5) | 0.1146 (3) | 0.9414 (8) | 0.0490 (18) |
| C43 | −0.0555 (7) | 0.1167 (5) | 1.0589 (10) | 0.074 (3) |
| H43A | −0.024012 | 0.143797 | 1.111258 | 0.111* |
| H43B | −0.043995 | 0.082015 | 1.098040 | 0.111* |
| H43C | −0.106206 | 0.125457 | 1.040756 | 0.111* |
| C44 | 0.0283 (6) | 0.0855 (4) | 0.9605 (10) | 0.068 (3) |
| H44A | 0.036337 | 0.086870 | 0.887414 | 0.102* |
| H44B | 0.025116 | 0.048464 | 0.981798 | 0.102* |
| H44C | 0.068662 | 0.102932 | 1.024212 | 0.102* |
| C45 | −0.1111 (5) | 0.0864 (3) | 0.8475 (8) | 0.0506 (18) |
| H45A | −0.153290 | 0.110144 | 0.830186 | 0.061* |
| H45B | −0.120412 | 0.053934 | 0.884307 | 0.061* |
| C46 | −0.2017 (6) | 0.0531 (5) | 0.6206 (10) | 0.070 (3) |
| H46A | −0.207546 | 0.041174 | 0.541826 | 0.105* |
| H46B | −0.230727 | 0.085097 | 0.613474 | 0.105* |
| H46C | −0.218001 | 0.025029 | 0.659227 | 0.105* |
| F1 | 0.1488 (9) | 0.4850 (6) | 0.4041 (12) | 0.180 (5) |
| F2 | 0.1548 (8) | 0.5255 (5) | 0.1951 (15) | 0.162 (4) |
| F3 | 0.0377 (9) | 0.5198 (6) | 0.1150 (16) | 0.183 (5) |
| F4 | 0.0930 (7) | 0.5658 (4) | 0.2815 (14) | 0.152 (4) |
| F5 | −0.0260 (8) | 0.4434 (7) | 0.1993 (18) | 0.189 (6) |
| F6 | −0.0056 (8) | 0.5021 (5) | 0.3272 (15) | 0.165 (5) |
| F7 | 0.0309 (11) | 0.4240 (8) | 0.3690 (19) | 0.203 (6) |
| I1 | 0.36428 (5) | 0.12208 (4) | −0.10412 (7) | 0.0916 (3) |
| I2 | −0.07813 (4) | 0.28808 (3) | 1.07728 (6) | 0.0813 (3) |
| N1 | 0.2632 (3) | 0.2637 (3) | −0.1176 (5) | 0.0417 (14) |
| H1 | 0.219654 | 0.253770 | −0.126091 | 0.050* |
| N2 | 0.1853 (3) | 0.2745 (3) | 0.1336 (6) | 0.0462 (15) |
| H2 | 0.151071 | 0.250602 | 0.103721 | 0.055* |
| N3 | 0.0315 (4) | 0.2220 (3) | 0.6520 (6) | 0.0480 (15) |
| H3 | −0.010131 | 0.235105 | 0.603317 | 0.058* |
| N4 | −0.0431 (4) | 0.1700 (3) | 0.8969 (6) | 0.0441 (14) |
| H4A | −0.076099 | 0.178089 | 0.826944 | 0.053* |
| O1 | 0.3856 (3) | 0.2531 (3) | −0.0024 (5) | 0.0543 (14) |
| O2 | 0.3051 (3) | 0.2934 (2) | 0.1810 (6) | 0.0546 (14) |
| O3 | 0.2969 (5) | 0.4088 (3) | −0.3209 (6) | 0.080 (2) |
| O4 | 0.3236 (5) | 0.4594 (3) | −0.1341 (8) | 0.079 (2) |
| O5 | 0.0578 (3) | 0.2023 (2) | 1.0562 (5) | 0.0555 (14) |
| O6 | 0.1154 (3) | 0.2203 (3) | 0.8463 (5) | 0.0574 (15) |
| O7 | −0.0862 (4) | 0.1134 (3) | 0.6563 (6) | 0.0622 (15) |
| O8 | −0.0678 (4) | 0.0185 (3) | 0.7230 (7) | 0.0705 (17) |
| S3 | −0.10845 (12) | 0.06747 (8) | 0.70715 (19) | 0.0500 (4) |
| S4 | 0.33232 (13) | 0.41046 (9) | −0.1915 (2) | 0.0571 (5) |
| F13 | 0.1693 (6) | 0.0073 (4) | 0.3237 (10) | 0.127 (3) |
| F9 | 0.2957 (5) | 0.0537 (5) | 0.4547 (11) | 0.141 (4) |
| F12 | 0.0712 (6) | 0.0408 (6) | 0.3216 (12) | 0.152 (4) |
| F10 | 0.2978 (6) | 0.1098 (6) | 0.5918 (13) | 0.155 (4) |
| F8 | 0.1672 (10) | 0.1079 (7) | 0.3186 (15) | 0.194 (6) |
| C41 | 0.1393 (8) | 0.0392 (7) | 0.3720 (17) | 0.108 (5) |
| C40 | 0.2584 (9) | 0.0800 (8) | 0.5047 (18) | 0.108 (5) |
| F11 | 0.2628 (10) | 0.0404 (7) | 0.6038 (15) | 0.191 (6) |
| F14 | 0.1408 (11) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.4750 (17) | 0.197 (6) |
Source of material
Twenty percent flubendiamide water dispersible granules (10 g) were dissolved in 30 mL acetone, and the filtrate was concentrated and crystallized after suction filtration to obtain an off-white solid product (1.58 g) with a yield of 79%. The off-white solid was recrystallized from methanol, and colorless crystals were obtained at room temperature after a few days.
Experimental details
All H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined as riding atoms, with C–H = 0.90–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5 U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2 U eq(C) for all other H atoms.
Comment
Flubendiamide, 3-iodo-N-(2-methanesulfonyl-1,1-dmethylethyl)-N′-(2-methyl-4-(1,2,2,2-tetrafluoro-1-trifluoromethylethyl)phenyl)phthalamide, is a new modern insecticide of phthalic acid diamides commercialized by Japan's Shinko Co., Ltd. and Bayer Crop Science Company of Germany [5], [6], [7]. In 1993, Nihon Nohyaku discovered the parent compound of flubendiamide during the research and development of the herbicide of pyrazine dicarboxamide. Through the discovery of effective substituents, he synthesized flubendiamide in 1998. Flubendiamide is a systemic foliar insecticide with extremely high activity against a broad spectrum of lepidopteran insects [8], [9], [10]. And it works fast and lasts for a long time. However, the toxicity to mammals is extremely low, and non-target organisms have almost no impact. It is less harmful to the biological enrichment and biomagnification that may cause animals in the body, reflecting excellent environmental performance [11]. Currently, there are more than 200 crops registered for flubendiamide [12]. The mechanism of action of bisamide insecticides is relatively novel compared to traditional nerve agents. They are a type of muscle toxins, mainly contact and stomach poisons, and insecticides with antifeedant activity [13, 14]. The mechanism of action of flubendiamide is to activate the calcium ion release channel in the ryanodine receptor cells, leading to the uncontrolled release of stored calcium ions, and ultimately causing insects to stop eating, lethargy, contractile paralysis and until death [15].
There are two crystallographic independent molecules in the asymmetric unit (molecule A and B in the figure). In the molecule of the title compound bond lengths and angles are very similar to those given in the literature [16, 17]. The torsion angles of C3–C2–C1–N1, C2–C1–N1–C19, C1–N1–C19–C22, N1–C19–C22–S4 and C19–C22–S4–C23 of the molecule A are 103.3(8)°, 173.0(7)°, 68.7(9)°, 166.7(6)° and 93.9(9)°, respectively. Those torsion angles of the molecule B are 98.6(9)°, 174.5(7)°, 175.4(7)°, 73.1(8)° and 166.4(7)°, respectively.
Funding source: The “13th Five-Year” National Key Research Program of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2017YFD0301604
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 21562022
Funding source: The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: 20161BAB204189
Award Identifier / Grant number: 20181BAB203015
Funding source: Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Jiangxi Province
Award Identifier / Grant number: GJJ180204
Acknowledgments
X-ray data were collected at Instrumental Analysis Center Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang, 330063, People's Republic of China
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by The “13th Five-Year” National Key Research Program of China (2017YFD0301604), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21562022), The Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20161BAB204189, 20181BAB203015), Natural Science Foundation of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ180204).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System (Ver. 4.0); Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Hartunga, S., Iwasakib, M., Ogawab, N., Kreuziga, R. Laboratory tests on sorption and transformation of the insecticide flubendiamide in Japanese tea field soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 904–909; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.027.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Yan, H. H., Xue, C. B., Li, G. Y., Zhao, X. L., Che, X. Z., Wang, L. L. Flubendiamide resistance and Bi-PASA detection of ryanodine receptor G4946E mutation in the diamond-back moth (Plutella xylostella L.). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 115, 73–77; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.09.003.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Singh, B. R., Singh, B., Kooner, R., Singh, B. Simple and efficient method for the estimation of residues of flubendiamide and its metabolite desiodo flubendiamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2299–2302; https://doi.org/10.1021/jf073081s.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
8. Mandil, R., Rahal, A., Prakash, A., Garg, S. K., Gangwar, N. K., Swain, D. K. Ameliorative potential of α-tocopherol against flubendiamide and copper-induced testicular-insult in Wistar rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 260, 91–101; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.11.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Tohnishi, M., Nishimatsu, T., Motoba, K., Hirooka, T., Seo, A. Development of a novel insecticide, flubendiamide. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 508–515; https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.35.508.Search in Google Scholar
10. Bernal, J., Nozal, M. J., Martín, M., Bernal, J. L., Ares, A. M. Trace analysis of flubendiamide in bee pollen using enhanced matrix removal-lipid sorbent clean-up and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 541–547; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.05.037.Search in Google Scholar
11. Cordova, D., Benner, E. A., Sacher, M. D., Rauh, J. J., Sopa, J. S., Lahm, G. P., Selby, T. P., Stevenson, T. M., Flexner, L., Gutteridge, S. Anthranilic diamides: a new class of insecticides with a novel mode of action, ryanodine receptor activation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2006, 84, 196–214; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2005.07.005.Search in Google Scholar
12. Ares, A. M., Valverde, S., Bernal, J. L., Toribio, L., Nozal, M. J., Bernal, J. Determination of flubendiamide in honey at trace levels by using solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 169–176; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.03.162.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
13. Al-Wabel, M. I., Al-Omran, A., El-Naggar, A. H., Nadeem, M., Usman, A. Pyrolysis temperature induced changes in characteristics and chemical composition of biochar produced from conocarpus wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 374–379; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.12.165.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
14. Albarran, A., Celis, R., Hermosin, M. C., Lopez-Pineiro, A., Cornejo, J. Behaviour of simazine in soil amended with the final residue of the olive-oil extraction process. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 717–724; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.09.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
15. Teixeira, L. A., Andaloro, J. T. Diamide insecticides: global efforts to address insect resistance stewardship challenges. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 106, 76–78; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.01.010.Search in Google Scholar
16. Chen, Y. W., Li, Y. X., Pan, L., Liu, J. B., Wan, Y. Y., Chen, W., Xiong, L. X., Yang, N., Song, H. B., Li, Z. M. Synthesis, insecticidal activities and SAR of novel phthalamides targeting calcium channel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 6366–6379; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2014.09.052.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
17. Kehl, A., Gieshoff, T., Schollmeyer, D., Waldvogel, S. R. Electrochemical conversion of phthaldianilides to phthalazin-1,4-diones by dehydrogenative N–N bond formation. Chem. Eur J. 2018, 24, 590–593; https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201705578.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Juan Luo et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5

