Abstract
C6H18ClN3O7S, trigonal, P31c (no. 159), a = 8.3990(14) Å, b = 8.3990(14)∘, c = 9.6208(17) Å, V = 587.76(17) Å3, Z = 2, R gt (F) = 0.0497, wR ref (F2) = 0.1404, T = 300.15 K.
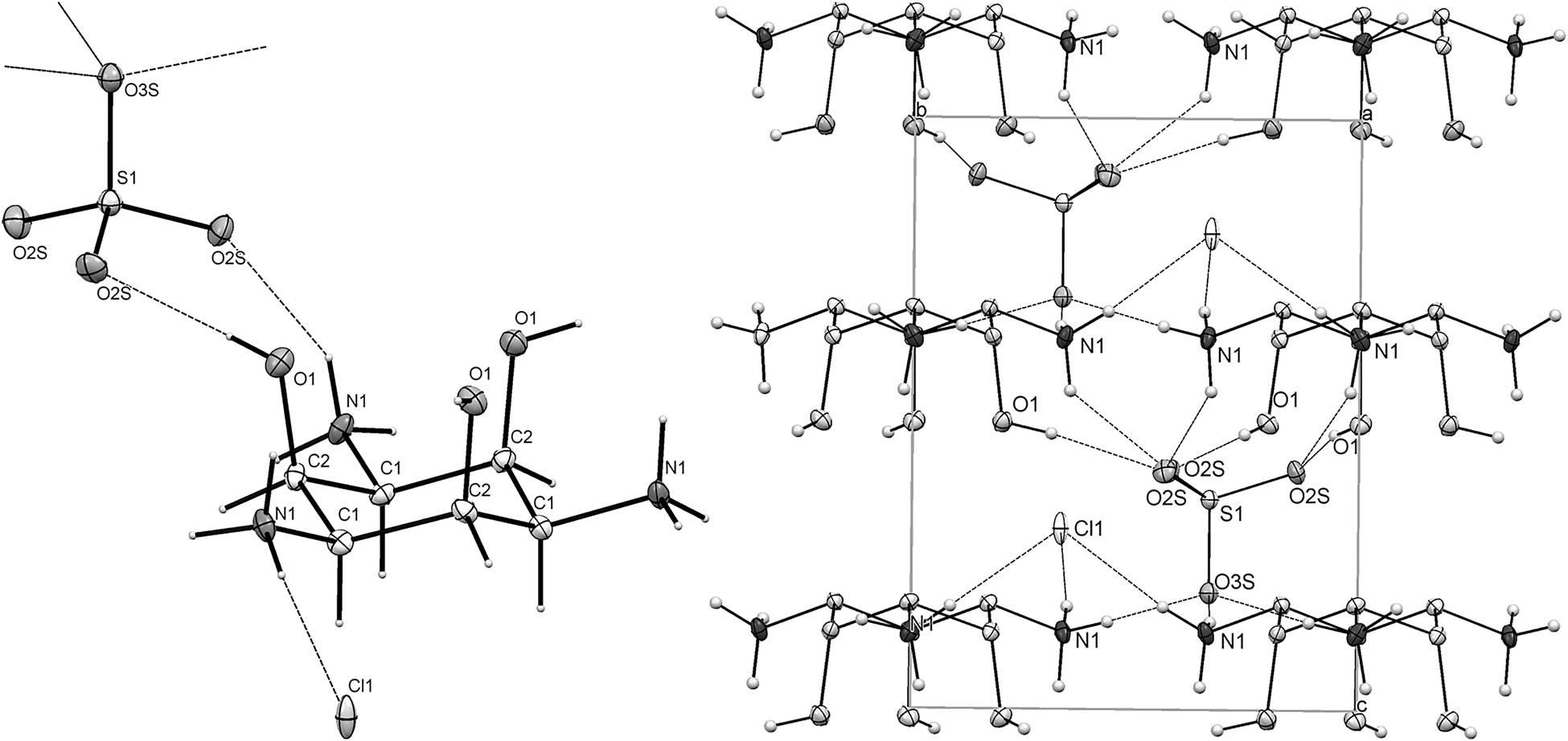
The molecular structure of the title compound and 3D packing along a-axis are presented in the Figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of atoms, including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless prism |
| size: | 0.45 × 0.07 × 0.05 mm |
| Wavelength: | MoKα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.54 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.7°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 1923, 753, 0.046 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 648 |
| N(param)refined: | 57 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1, 2], SHELX [3, 4], Olex2 [5], Mercury [6] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2). The sign (*) distinguishes the isotropic parameters (Uiso*) from equivalent isotropic parameters (Ueq )
| Atom | X | Y | Z | Uiso/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl1 | 0.666667 | 0.333333 | 0.1949 (5) | 0.0319 (11) |
| S1 | 0.666667 | 1.333333 | 0.6444 (3) | 0.0215 (8) |
| O1 | 0.7954 (8) | 0.9966 (7) | 0.5153 (7) | 0.0272 (14) |
| H1 | 0.743824 | 1.054749 | 0.534496 | 0.041* |
| O2S | 0.5753 (8) | 1.1402 (6) | 0.5971 (7) | 0.0306 (13) |
| O3S | 0.666667 | 1.333333 | 0.8028 (10) | 0.026 (2) |
| N1 | 0.6599 (8) | 0.6608 (8) | 0.3708 (7) | 0.0237 (15) |
| H1A | 0.651569 | 0.563658 | 0.326896 | 0.028* |
| H1B | 0.560576 | 0.669403 | 0.352483 | 0.028* |
| H1C | 0.667730 | 0.648046 | 0.461927 | 0.028* |
| C2 | 0.8202 (10) | 0.9990 (11) | 0.3714 (10) | 0.0207 (15) |
| H2 | 0.716462 | 1.000265 | 0.325758 | 0.025* |
| C1 | 0.8266 (11) | 0.8302 (11) | 0.3223 (8) | 0.0206 (16) |
| H1D | 0.825454 | 0.829876 | 0.220471 | 0.025* |
Source of material
Single crystals of the title compound were obtained during the interaction of 2,4,6-triaminocyclohexane-1,3,5-triol·1.5H2SO4 [7] (0.1 g, 0.32 mmol) and K2PtI6 (molar ratio: Pt:taci = 1) at pH 3 in the presence of diluted HCl (0.002 mol/L) and heating at T = 60 °C for 3 h. Colorless crystals were separated from the reaction system a few hours later.
Experimental details
All hydrogen atoms are placed on their calculated positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms. The absolute structure was established by anomalous dispersion [8], Flack parameter is -0.08(11).
Comment
The title compound is the triprotonated form of the ligand all-cis-2,4,6-triaminocyclohexane-1,3,5-triol, which is known by a trivial name taci. The remarkable coordination ability of taci to various metal cations and the structure of most of its complexes, some of which with a proven bioactivity profile, have been studied in detail [9]. The determination of the crystal structure of the neutral compound as taci· 2H2O [10] and of those compounds in which taci participates as protonated cations [11], [12], [13] has been previously reported. In this study, the crystal structure of the triprotonated taci balanced with sulfate and chloride counter anions is presented.
The asymmetric unit of the structure contains 1/3 of [H3taci]3+ and 1/3 of each counter ion. The [H3taci]3+ cations adopt a chair conformation with three hydroxy groups (O–C - 1.398 Å) in axial and three azaniumyl groups (N–C - 1.486 Å) in equatorial position (left part of the figure). The sulfate ions possess typical tetrahedral geometry as the S and O3S atoms occupy a special position on a 3-fold axis while O2S-atom resides in a general position, forming three crystallographically equivalent bonds of all four sulfur oxygen bonds in the anion. The 3D packing of the title compound is constructed of alternating planes parallel to the ab-plane of the crystal cell where the [H3taci]3+ cations are disposed. The distance between adjacent planes is 4.810 Å. The sulfate and chloride anions are located between the planes. In detail, the sulfate anions are located almost in the middle of a channel, forming nine hydrogen bonds with surrounding [H3taci]3+ cations (right part of the figure): 3 with hydroxy groups (O⃛O2S - 2.779(9) Å) and 3 with azaniumyl groups (N⃛O2S−$1 - 2.780(9) Å, $1 = −x + y, −x + 1, z) from the upper plane; and 3 H-bonds with azaniumyl groups from the bottom plane (N⃛O3S−$2 - 2.844(6) Å; $2 = +y − 1, x, z − 0.5). The Cl− anions are located closer to the plane here noted as bottom, forming hydrogen bonds only with azaniumyl groups (N⃛Cl1 = 3.254(7) Å). To our point of view, the higher symmetry of the structure is shaped by the H-bonding network.
Funding source: Bulgarian National Science Fund, Ministry of Education and Science of Bulgaria
Award Identifier / Grant number: DN09/16
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Dr. Angel Ugrinov, North Dakota State University.
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: National Science Fund, Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science, Grant No DN09/16.
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2 and SAINT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2013.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2014.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
5. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J., Wood, P. A. Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807067908.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Hegetschweiler, K., Erni, I., Schneider, W., Schmalle, H. 9. Preparation, characterisation, and structure of N-methylated derivatives of 1,3,5–triamino-l,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol: polyalcohols with unusual acidity. Helv. Chim. Acta 1990, 73, 97–105; https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19900730110.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Parsons, S., Flack, H. D., Wagner, T. Use of intensity quontients and differences in absolute structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr 2013, B69, 249–259; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2052519213010014.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Hegetschweiler, K. Polyalcohols and polyaminopolyalcohols as selective receptors for metal ions. Bol. Soc. Chil. Quim. 1997, 42, 257–279.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Hegetschweiler, K., Robert, J., Hancock, D., Chisletta, M., Kradolfer, T., Gramlich, V., Schmalle, H. W. 5. 1,3,5-triamino- 1,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol, a ligand with remarkable versatility for matal ions. complex formation with magnesium(II), calcium(II), stroncium(II), barium (II) and cadmium(II). Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 5273–5284; https://doi.org/10.1021/ic00075a054.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Neis, C., Hegetschweiler, K. Hydrogen bonding in polyaminopolyalcohols: a monohydrate cocrystal of 1,3- diamino-5-azaniumyl-1,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol iodide and 1,3,5-triamino-1,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol. Acta Crystallogr. 2014, C70, 369–399; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614005038.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
12. Gencheva, G., Bontchev, P. R., Sandler, J., Hegetschweiler, K. Crystal structure of tetrakis (1,3,5-triamino-1,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol) decachloride hexachloroplatinate hexahydrate, (H3taci)4[PtCl6]Cl10·6H2O, two different forms of (H3taci)3+ in one crystal. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2000, 215, 183–185; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2000-0191.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Ghisletta, M., Jalett, H., Gerfin, T., Gramlich, V., Hegetschweiler, K. 1,3,5-triamino-1,3,5-trideoxy-cis-inositol, a new ligand with a remarkable versatility for metal ions. safe and efficient ligand preparation and structure of the free ligand and the CoIII complex. Helv. Chim. Acta 1992, 75, 2233–2242; https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19920750709.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2021 Vyara Velcheva et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5

