Abstract
Temperature significantly affects the physical and mechanical properties of granite. To have a comprehensive understanding of the thermal cycle effect on uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) and thermal damage rate, a series of thermal cycle experiments on granite specimens were carried out with five types of designed temperatures and five types of cycle number of thermal treatments. The experimental results indicate that UCS decreases and thermal damage rate increases as temperature and thermal cycle increase. UCS of specimens cooled in water condition after thermal damage treatment are lower than those cooled in air condition. In addition, two new phenomena related to thermal damage rate were observed. Firstly, previous studies have shown that a rapid value reduction of UCS of specimens with one thermal cycle treatment under air cooling condition can be observed at 400∘C. While the temperature threshold for the specimens treated with more than one thermal cycle under water cooling condition increases to 550∘C. Secondly, a thoroughly antipodal evolution law of the thermal damage rate for the specimens with multiple thermal cycle treatments is also observed as compared to those treated by only one thermal cycle. These differences might be induced by the different microcrack initial time and their development speed. The new findings are important to understand the failure mechanism and variation process of physical and mechanical properties of granite specimens subjected to thermal cycles.
1 Introduction
Granite is a type of rock widely used for constructions (i.e., buildings, tunnels, bridges, etc.) owing to its good physical and mechanical properties, such as high uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) and modulus of elasticity [1]. However, during the life cycle, it is inevitable to encounter sudden external environmental factors which will reduce the physical and mechanical properties. Temperature is one of such key factors. Great changes in temperature, especially subjected to high temperature, different thermal expansion of different granite components will lead to a creation of inter-granular compressive and tensile forces. Once these thermal stresses exceed the strength, the original cracks propagate and new cracks initiate [2, 3]. Consequently, rapid degradations of the physical and mechanical properties of the granite occur [4, 5, 6], which results in reducing the service life in constructions or affecting the stability of the constructions. It is therefore important to have a comprehensive understanding of the thermal effect on physical and mechanical properties of the granite.
Extensive laboratory studies have been carried out to investigate the thermal effect on physical and mechanical properties of granite [7, 8, 9]. Jansen et al. [10] studied the thermal induced microcracks of Lac du Bonnet granite using ultrasonic imaging and acoustic emission monitoring. Chaki et al. [11] evaluated the influence of thermal damage on porosity, permeability and ultrasonic wave evolutions. Shao et al. [12] investigated the cool rate effect on physical and mechanical properties of granite. Chen et al. [13] assessed the thermal heating rate effect on physical and mechanical properties of Beishan granite. A series of uniaxial compression tests were carried out by Yang et al. [14] to evaluate the effect of high temperature treatments (200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700 and 800∘C) on the crack damage, strength and deformation failure behavior of a type of granite. Hu et al. [15] studied the variation of compressive strength, elastic modulus, tensile strength, and fracture toughness of granite after high-temperature treatment. Fan et al. [16] presented an investigation of thermal effect on micro-properties of granite through X-ray CT technique. These studies were all based on one time thermal treatment in term of heating the specimens to a designed temperature with a specific heating rate.
Tiskatine et al. [17] performed a series of thermal cycle experiments on two granite specimens. The charge cycle was carried out in an oven for one hour at 650∘C with a heating rate of 25∘C/min, and a discharge cycle was carried out in ambient air for thirty minutes at 20∘C with a cooling rate of 20∘C/min. The grain specimens disintegrated into small pieces after only ten thermal cycles. This study indicates that thermal cycle significantly affects the microcracks and physical and mechanical properties. So far, corresponding studies are rarely reported and comprehensive understanding of the thermal cycle effect on granite physical and mechanical properties are still insufficient. However, it is important for us to have an accuracy stability assessment of the buildings or projects constructed by granite subjected to several time fires or to several cycles of high temperatures in a fire.
In this study, a series of thermal cycle experiments on 93 granite specimens were carried out with five designed temperatures and five thermal cycles as well as related uniaxial compression tests were conducted for aforementioned aim. Based on the experimental results, the relationships among the UCS, the elevated temperature and thermal cycles were analyzed. What’s more, to better evaluate the degree of the degeneration of the UCS induced by the thermal damage, a thermal damage index, Dσc, was defined. The temperature and thermal cycle effects on Dσc and the rate of Dσc changes were also discussed.
2 Specimen preparation and laboratory test
2.1 Specimen preparation
The granite specimens to be tested were cored from a granite block which was collected from Zhangzhou, Fujian Province, China. The mineral composition and physical properties of the granite are presented in Table 1. Triplicate specimens were prepared for each group test in standard size recommended by International Society for Rock Mechanics standards [18]. The diameter was 50 mm and length was 100 mm. The end surfaces were flat with an accuracy of 0.02 mm.

MTS816 servo-controlled rock mechanics experimental system
Mineral composition and physical properties of granite specimens that were tested
| Mineral composition of specimens | Moisture content (%) | density (g/cm3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feldspar (%) | Quartz (%) | Amphibole (%) | Mica (%) | ||
| 35 | 40 | 20 | 5 | 0.31 | 2.97 |
2.2 Thermal cycle treatment
The charge cycle was carried out in a furnace (type CYM-100) to reach a designed temperature with a heating rate of 10∘C/min, and a discharge cycle was carried out in water to have a quick cooling down to the water temperature (20∘C). In order to investigate the temperature and cycle effects, five types of designed temperatures including 250∘C, 350∘C, 450∘C, 550∘C and 650∘C and five types of cycle number of thermal treatments (i.e., 1, 5, 10, 15 and 20 times) were designed. As shown in Table 2, five group tests for each temperature were conducted with different thermal cycles, such as for 250∘C, thermal treatment were carried out by 1, 5, 10, 15 and 20 times. Therefore, a total of 25 group tests for water cooling condition were carried out. Simultaneously, for comparison, 5 group tests under air cooling (AG) condition (cooled in air to room temperature at 25∘C) were also conducted with one time thermal treatment (250∘C, 350∘C, 450∘C, 550∘C and 650∘C). What’s more, 1 group of specimens were set to measure the original UCS (UCS0) of the granite without thermal treatment at room temperature (25∘C). In other words, totally 31 group tests were carried out. Each group test was repeated three times based on the prepared triplicate specimens.
Mean values of UCS and thermal damage index of specimens
| Temperature | Uniaxial compressive strength UCST (MPa) | Thermal damage index (Dσc) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (∘C) | Treatment times of thermal cycles | Treatment times of thermal cycles | ||||||||||
| Air cooling | Water cooling | Air cooling | Water cooling | |||||||||
| (AG) | (AG) | |||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | |
| 25 | 125 (UCS0) | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 250 | 110 | 107 | 90 | 66 | 58 | 40 | 0.120 | 0.144 | 0.280 | 0.472 | 0.536 | 0.680 |
| 350 | 107 | 90 | 68 | 53 | 47 | 36 | 0.144 | 0.280 | 0.456 | 0.576 | 0.624 | 0.712 |
| 450 | 77 | 68 | 61 | 50 | 50 | 35 | 0.384 | 0.456 | 0.512 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.720 |
| 550 | 59 | 59 | 50 | 41 | 43 | 37 | 0.528 | 0.528 | 0.600 | 0.672 | 0.658 | 0.704 |
| 650 | 46 | 36 | 29 | 26 | 25 | 15 | 0.632 | 0.712 | 0.768 | 0.792 | 0.800 | 0.880 |
2.3 Uniaxial compression test
Uniaxial compression test was conducted on an MTS816 servo-controlled rock mechanics experimental system (as shown in Figure 1). Prior to the application of a constant axial strain loading rate (1.0×10−5/s), silicon grease was greased to the top and bottom surface of the specimen to mitigate the end friction effect between the specimen and testing machine.
3 Results
The mean UCS of each group test and the thermal damage index, Dσc, which was defined to evaluate the degree of the degeneration of the UCS induced by the thermal damage were shown in Table 2. UCS of each test was directly obtained from the stress-strain curve. Mean UCS were calculated based on the UCS values of each group. Dσc can be calculated using Eq. (1) corresponding to a ratio of mean UCS after thermal treatment (UCST) to the mean original UCS (UCS0) of each group.
Table 2 shows that the mean value of UCS0 is 125MPa. It can be found in Figure 2a that for specimens treated with the same thermal cycles, UCS decreases while Dσc increases as temperature increases. Especially between 550 and 650∘C, there is a significant reduction of UCS of specimens cooled in water, i.e., the USC of specimen with one thermal cycle decreases from 59 to 39 MPa (corresponding Dσc increases from 0.528 to 0.712, see the black line with square). The comparison between the specimens (1 thermal cycle) cooled in air (AG) (marked with gray line with rhombus) and cooled in water (marked with black line with square) indicates that the cooling type does not affect the UCS of the specimens at 250∘C much, while it affects the UCS more significantly as the temperatures increase to 350∘C and 450∘C, the UCS of specimens cooled in water are smaller than those cooled in air. The same phenomenon also can be observed at 650∘C. It might be due to more microcracks were formed by cooling in water at those temperatures. Figure 2b indicates that thermal cycle significantly affects the UCS, UCS decreases as the thermal cycle increases, especially at low temperature. One possible reason is that when the specimens are subjected to low temperatures, very few microcracks are formed inducing a small Dσc (see Figure 2b). The specimens thus have a high originalUCS (one thermal cycle). The increment of the thermal cycles forms more microcracks and reduces the UCS significantly with a greater acceleration of the increment of Dσc. While for the specimens are subjected to high temperature, much more microcracks are formed at the first thermal cycle resulting in small original UCS. It is difficult to quickly form more microcracks in the following thermal cycles. Therefore, the reduction rate of UCS in high temperature is smaller.
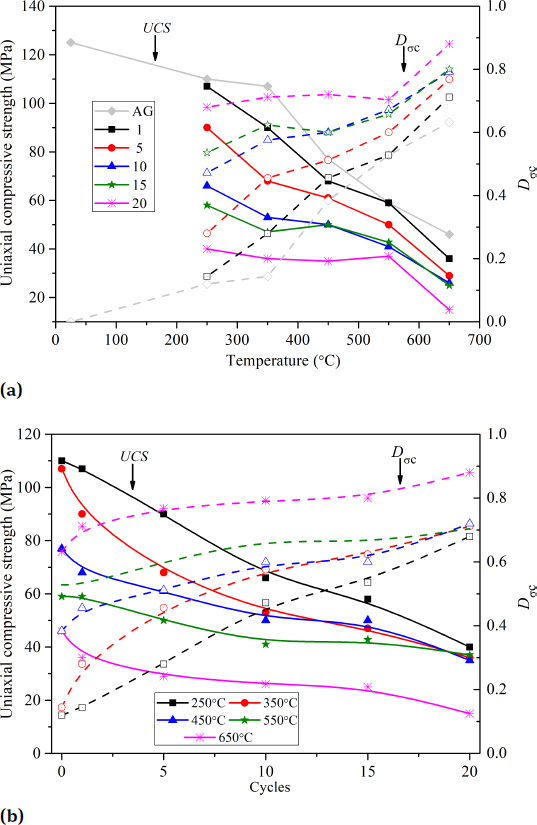
UCS (solid line) and thermal damage index, Dσc, (dotted line) versus (a) elevated temperature, and (b) thermal cycles
4 Discussions
It can be observed from Figure 2a that the temperature thresholds of having a rapid value reduction of UCS of specimens under different cooling conditions are different. In order to improve the reliability of the observed phenomenon, some test results of UCS of specimens subjected to various temperatures and cooled in AG condition from previous studies [2, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23] are shown in Figure 3a with the same type test results obtained from this study. These results indicate that the UCS of granite specimens cooled in AG condition have a rapid reduction at 400∘C which is lower than those cooled in water condition. The acceleration of the value of the Dσc also can be observed at the same temperature in Figure 3b. The studies of Etienne and Poupert [24], Nasseri et al. [25, 26], Chaki et al. [11], Chen et al. [22] and Inserra et al. [27] suggested that the rapid reduction of UCS at 400∘C is primarily due to the microcrack initiates at such a temperature and results in an acceleration of linear expansion α (a ratio of increment in specimen length direction to the specimen length, see the red and brown dotted lines in Figures 3a and 3b). However, in this study, the temperature threshold of significant reduction of UCS of granite specimens cooled in water condition delays to 550∘C, especially in specimens with large thermal cycles (see Figure 2a). This phenomenon might be caused by that microcracks initiated earlier after specimens were treated by larger thermal cycles and cooled in water which results in having a low UCS at low temperature (i.e., the UCS at 250∘C is 36MPa after 20 thermal cycles). As temperature increases to 350∘C and 450∘C, the temperature does not have the ability to generate more microcracks. Since the temperature exceeds 550∘C, more newer microcracks are generated quickly, causing rapid reduction of UCS at 550∘C.
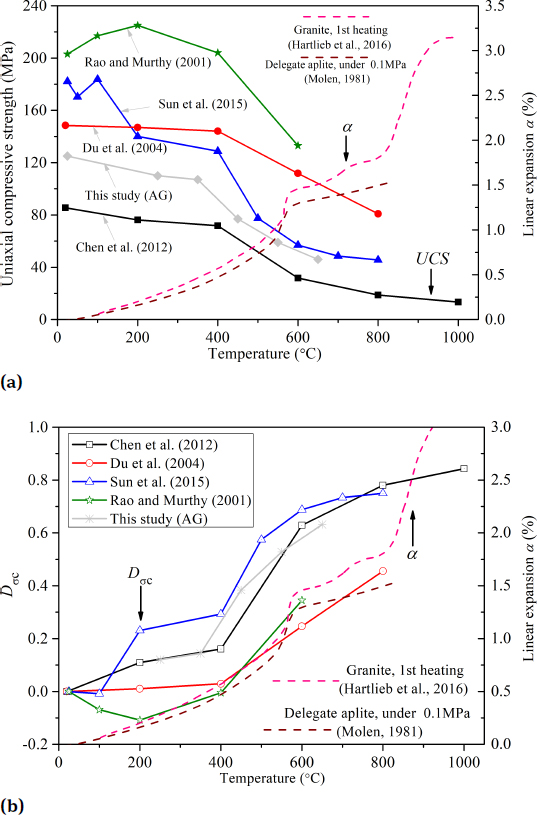
(a) UCS (solid line) and linear expansion, α, (dotted line), and (b) thermal damage index, Dσc, (solid line) and α (dotted line), of granite versus elevated temperature
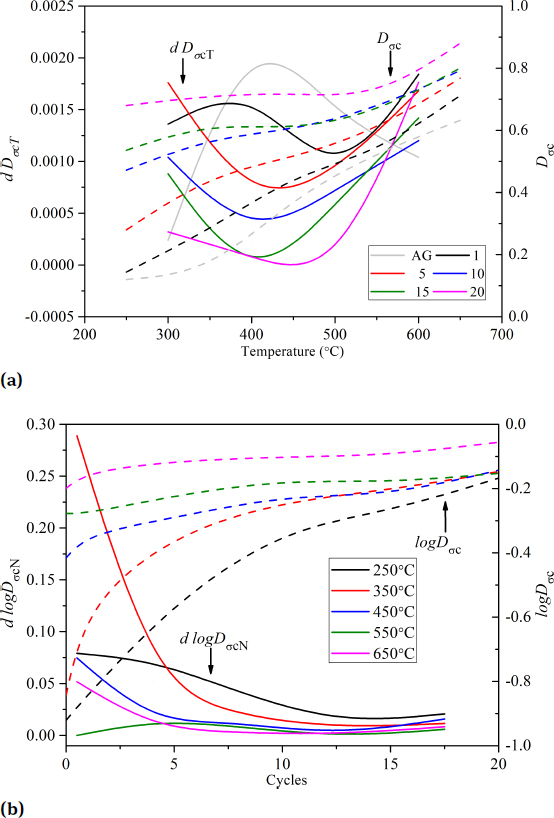
(a) rate of thermal damage index (Dσc) change related to temperature, dDσcT, (solid line) and Dσc (dotted line) versus temperatures, and (b) another type of rate of thermal damage index change related to thermal cycles, dlogDσcN, (solid line) and logDσc (dotted line), versus cycles
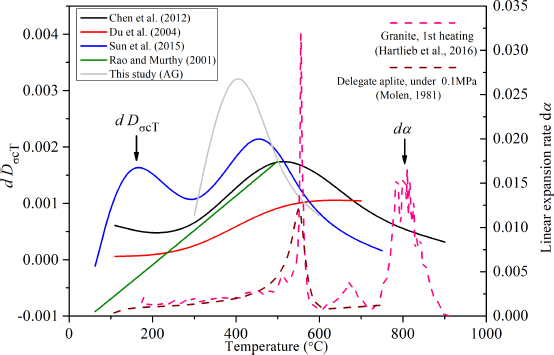
Rate of thermal damage index (Dσc) change related to temperature, dDσcT, (solid line) and rate of linear expansion (α) change, dα/dT, (dotted line), versus elevated temperature
The comparison between Figures 2a and 3b shows that the evolution of the rate of the Dσc change for specimens cooled in air or water conditions are different, especially for the temperature thresholds of the acceleration of the increment of Dσc which are 400∘C and 550∘C, respectively. To better understand the details of the evolution of the rate of Dσc change, two types of the rate of Dσc change including dDσcT and dlogDσcN were defined in Eqs. (2) and (3), respectively.
where DσcT is defined as the Dσc related to the specimen subjected to a T(∘C) temperature; DσcN is defined as the Dσc related to the specimen treated after N thermal cycles.
The comparison between the specimens (1 thermal cycle) cooled in AG condition (marked with gray solid line shown in Figure 4a) and cooled in water (marked with black solid line shown in Figure 4a) shows that the cooling type affects the evolution of the dDσcT. As shown in Figure 4a, dDσcT of AG condition is in an ascending order before 400∘C, then decreases as temperature increases. This result is in consist with previous studies shown in Figure 5 [19–22]. Figure 5 shows that the maximum value of dDσcT in different studies are among 400-550∘C. In the ascending order stage of dDσcT, corresponding rate of linear expansion change (dα/dT) also increases which also can be observed in Figure 5. Figure 6 indicates that the acceleration of the increment of dα/dT results in an increment of linear expansion (α). The increasing of α represents the amount of the formed microcracks increasing.
While for the water cooling condition (black solid line in Figure 4a), there is a high dDσcT at the initial temperature (300∘C) induced by more formed microcracks because of quick cooling process in water. During 350-500∘C, temperature effect on dDσcT is small until the temperature reaches to 550∘C. What’s more, Figure 4a also shows that the specimens treated by more numbers of thermal cycles (i.e., 5, 10, 15 and 20) also have a high dDσcT at the initial temperature (300∘C) but a thoroughly antipodal evolution of dDσcT as that of AG condition. dDσcT decreases when the values of temperature between 300∘C and 450∘C, and changes to increase as temperatures higher than 450∘C. This indicates that thermal cycle influences the evolution process of the dDσcT. More microcracks are produced at 250∘Cwhen more of thermal cycles are carried out. The following temperatures ranging from 300∘C to 450∘C damage the specimens slightly further, causing smaller dDσcT with more times of thermal cycle treatment at 300∘C and dDσcT decreases between 300∘C and 450∘C. When the temperature exceeds 500∘C, thermal cycle treatment damages the specimens more quickly and dDσcT starts to increase.
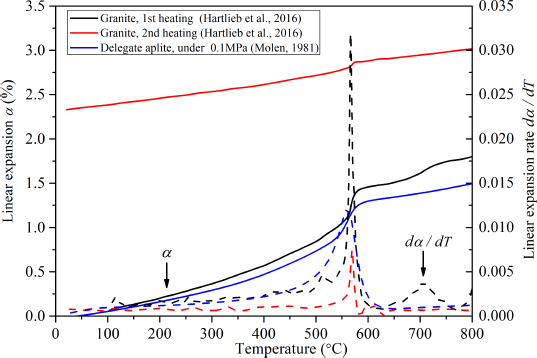
Linear expansion (α) (solid line) and rate of linear expansion (α) change, dα/dT, (dotted line), versus elevated temperature
Figure 4b indicates that dlogDσcN is in descending order as thermal cycle increases, especially under the thermal cycle number among 1-10. What’s more, low temperatures relates to a high and rapid reduction of the dlogDσcN.
5 Conclusion
According to the experimental results obtained from a series of thermal cycle experiments on 93 with five types of designed temperatures and five types of cycle number of thermal treatments, the following conclusions can be drawn:
Uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of granite specimens decreases as temperature and thermal cycle increase.
In general,UCS of granite specimens cooled in water condition after thermal damage treatment are lower than those cooled in air condition.
Previous studies have shown that a rapid reduction of UCS of specimens with one thermal cycle treatment and under air cooling condition can be observed at 400∘C. While for the specimens treated with more times of thermal cycles and under water cooling condition, a new temperature threshold of significant reduction of UCS is observed in this study which is 550∘C.
The same phenomenon can also be observed from the thermal damage index, Dσc, which increases as temperature and thermal cycle increase.
What’s more, a thoroughly antipodal evolution of the rate of Dσc changes for the specimens treated by several times of thermal cycles and under water cooling condition during heating process is also observed in this study as compared to that for the specimens with one time of thermal treatment and under and under air cooling condition.
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41672279, 41807233) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20180662).
References
[1] Y. Shen, Y. Wang, Y. Y. Yang, Q. Sun, T. Luo, and H. Zhang, Construction and Building Materials, 213 (2019) 156-166.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.078Search in Google Scholar
[2] I. V. D. Molen, Tectonophysics, 73 (1981) 323-342.10.1016/0040-1951(81)90221-3Search in Google Scholar
[3] X. L. Xu and M. Karakus, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 103 (2018) 195-204.10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.01.030Search in Google Scholar
[4] F. E. Heuze, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 20(1) (1983) 3-10.10.1016/0148-9062(83)91609-1Search in Google Scholar
[5] Q. Sun, W. Zhang, Y. Zhu, and Z. Huang, Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 52(8) (2019) 2691-2699, DOI:10.1007/s00603-019-1733-0.10.1007/s00603-019-1733-0Search in Google Scholar
[6] P. K. Gautam, A. K. Verma, P. Sharma, and T. N. Singh, Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 51 (2018) 2949-2956, DOI:10.1007/s00603-018-1493-2.10.1007/s00603-018-1493-2Search in Google Scholar
[7] V. Pires, L. G. Rosa, and A. Dionísio, Construction and Building Materials, 64 (2014) 440-450.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.03.035Search in Google Scholar
[8] P. Vazquez, M. Acuña, D. Benavente, S. Gibeaux, I. Navarro, and M. Gomez-Heras, Construction and Building Materials, 104 (2016) 263-275.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.051Search in Google Scholar
[9] H. Guo, W. Guo, Y. Zhai, and Y. Su, Construction and Building Materials, 155 (2017) 427-440.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.090Search in Google Scholar
[10] D. P. Jansen, S. R. Carlson, R. P. Young, and D. A. Hutchins, Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B12) (1993) 22231-22243.10.1029/93JB01816Search in Google Scholar
[11] S. Chaki, M.Takarli, and W.P. Agbodjan, Construction and Building Materials, 22(7) (2008) 1456-1461.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.04.002Search in Google Scholar
[12] S. Shao, P.G. Ranjith, P.L.P. Wasantha, and B.K. Chen, Geothermics, 54 (2015) 96-108.10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.11.005Search in Google Scholar
[13] S. Chen, C. Yang, and G.Wang, Applied Thermal Engineering, 110 (2017) 1533-1542.10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.075Search in Google Scholar
[14] S. Q. Yang, P. Ranjith, H.W. Jing,W. L. Tian, and Y. Ju, Geothermics, 65 (2017) 180–197.10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.09.008Search in Google Scholar
[15] J. Hu, Q. Sun, and X. Pan, Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11(2) (2018) 43.10.1007/s12517-018-3395-8Search in Google Scholar
[16] L. F. Fan, J. W. Gao, Z. J. Wu, S. Q. Yang, and G. W. Ma, Applied Thermal Engineering, 140 (2018) 505-519.10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.074Search in Google Scholar
[17] R. Tiskatine, A. Eddemani, L. Gourdo, B. Abnay, A. Ihlal, A. Aharoune, et al., Applied Energy, 171 (2016) 243-255.10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.061Search in Google Scholar
[18] Z. T. Bieniawski and M. J. Bernede, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining sciences&Geomechanics Abstracts, 16(2) (1979) 137-140.10.1016/0148-9062(79)91450-5Search in Google Scholar
[19] G. M. N. Rao and C. R.Murthy, Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 38(2) (2001) 427-440.10.1139/e00-091Search in Google Scholar
[20] Q. Sun, W. Q. Zhang, L. Xue, Z. Z. Zhang, and T. M. Su, Environmental Earth Sciences, 74 (2015) 2341-2349.10.1007/s12665-015-4234-9Search in Google Scholar
[21] S. J. Du, H. Liu, H. T. Zhi, and H. H. Chen, Chinese Journal Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23(14) (2004) 2359-2364.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Y. L. Chen, J. Ni, W. Shao, and R. Azzam, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 56(15) (2012) 62-66.10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.07.026Search in Google Scholar
[23] P. Hartlieb. M. Toifl, F. Kuchar, R. Meisels, and T. Antretter, Minerals Engineering, 91 (2016) 34-41. 2510.1016/j.mineng.2015.11.008Search in Google Scholar
[24] F. H. Etienne and R. Poupert, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 26(2) (1989) 125-134.10.1016/0148-9062(89)90001-6Search in Google Scholar
[25] M. H. B. Nasseri, A. Schubnel, and R. P. Young, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 44 (2007) 601-616.10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.09.008Search in Google Scholar
[26] M.H.B. Nasseri, B.S.A. Tatone, G. Grasselli, and R.P. Young, Pure and Applied Geophysics, 166 (2009) 801-822.10.1007/s00024-009-0476-3Search in Google Scholar
[27] C. Inserra, S. Biwa, and Y.Q. Chen, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 62(5) (2013) 96-104.10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.05.001Search in Google Scholar
© 2019 C. Xu et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Review Article
- Research on the Influence of Furnace Structure on Copper Cooling Stave Life
- Influence of High Temperature Oxidation on Hydrogen Absorption and Degradation of Zircaloy-2 and Zr 700 Alloys
- Correlation between Travel Speed, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Wear Characteristics of Ni-Based Hardfaced Deposits over 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Factors Influencing Gas Generation Behaviours of Lump Coal Used in COREX Gasifier
- Experiment Research on Pulverized Coal Combustion in the Tuyere of Oxygen Blast Furnace
- Phosphate Capacities of CaO–FeO–SiO2–Al2O3/Na2O/TiO2 Slags
- Microstructure and Interface Bonding Strength of WC-10Ni/NiCrBSi Composite Coating by Vacuum Brazing
- Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding of Dissimilar 6061/7075 Aluminum Alloy
- Solvothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Monodisperse Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Hollow Nanospheres
- On the Capability of Logarithmic-Power Model for Prediction of Hot Deformation Behavior of Alloy 800H at High Strain Rates
- 3D Heat Conductivity Model of Mold Based on Node Temperature Inheritance
- 3D Microstructure and Micromechanical Properties of Minerals in Vanadium-Titanium Sinter
- Effect of Martensite Structure and Carbide Precipitates on Mechanical Properties of Cr-Mo Alloy Steel with Different Cooling Rate
- The Interaction between Erosion Particle and Gas Stream in High Temperature Gas Burner Rig for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Permittivity Study of a CuCl Residue at 13–450 °C and Elucidation of the Microwave Intensification Mechanism for Its Dechlorination
- Study on Carbothermal Reduction of Titania in Molten Iron
- The Sequence of the Phase Growth during Diffusion in Ti-Based Systems
- Growth Kinetics of CoB–Co2B Layers Using the Powder-Pack Boriding Process Assisted by a Direct Current Field
- High-Temperature Flow Behaviour and Constitutive Equations for a TC17 Titanium Alloy
- Research on Three-Roll Screw Rolling Process for Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Bar
- Continuous Cooling Transformation of Undeformed and Deformed High Strength Crack-Arrest Steel Plates for Large Container Ships
- Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors of the Sticker between Solidified Shell and Mold in Continuous Casting of Steel
- Casting Defects in Transition Layer of Cu/Al Composite Castings Prepared Using Pouring Aluminum Method and Their Formation Mechanism
- Effect of Current on Segregation and Inclusions Characteristics of Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting
- Investigation of Growth Kinetics of Fe2B Layers on AISI 1518 Steel by the Integral Method
- Microstructural Evolution and Phase Transformation on the X-Y Surface of Inconel 718 Ni-Based Alloys Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting under Different Heat Treatment
- Characterization of Mn-Doped Co3O4 Thin Films Prepared by Sol Gel-Based Dip-Coating Process
- Deposition Characteristics of Multitrack Overlayby Plasma Transferred Arc Welding on SS316Lwith Co-Cr Based Alloy – Influence ofProcess Parameters
- Elastic Moduli and Elastic Constants of Alloy AuCuSi With FCC Structure Under Pressure
- Effect of Cl on Softening and Melting Behaviors of BF Burden
- Effect of MgO Injection on Smelting in a Blast Furnace
- Structural Characteristics and Hydration Kinetics of Oxidized Steel Slag in a CaO-FeO-SiO2-MgO System
- Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Oxidation Roasting of Oxide–Sulphide Zinc Ore with Addition of Manganese Dioxide Using Response Surface Methodology
- Hydraulic Study of Bubble Migration in Liquid Titanium Alloy Melt during Vertical Centrifugal Casting Process
- Investigation on Double Wire Metal Inert Gas Welding of A7N01-T4 Aluminum Alloy in High-Speed Welding
- Oxidation Behaviour of Welded ASTM-SA210 GrA1 Boiler Tube Steels under Cyclic Conditions at 900°C in Air
- Study on the Evolution of Damage Degradation at Different Temperatures and Strain Rates for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Pack-Boriding of Pure Iron with Powder Mixtures Containing ZrB2
- Evolution of Interfacial Features of MnO-SiO2 Type Inclusions/Steel Matrix during Isothermal Heating at Low Temperatures
- Effect of MgO/Al2O3 Ratio on Viscosity of Blast Furnace Primary Slag
- The Microstructure and Property of the Heat Affected zone in C-Mn Steel Treated by Rare Earth
- Microwave-Assisted Molten-Salt Facile Synthesis of Chromium Carbide (Cr3C2) Coatings on the Diamond Particles
- Effects of B on the Hot Ductility of Fe-36Ni Invar Alloy
- Impurity Distribution after Solidification of Hypereutectic Al-Si Melts and Eutectic Al-Si Melt
- Induced Electro-Deposition of High Melting-Point Phases on MgO–C Refractory in CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 – (MgO) Slag at 1773 K
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 14Cr-ODS Steels with Zr Addition
- A Review of Boron-Rich Silicon Borides Basedon Thermodynamic Stability and Transport Properties of High-Temperature Thermoelectric Materials
- Siliceous Manganese Ore from Eastern India:A Potential Resource for Ferrosilicon-Manganese Production
- A Strain-Compensated Constitutive Model for Describing the Hot Compressive Deformation Behaviors of an Aged Inconel 718 Superalloy
- Surface Alloys of 0.45 C Carbon Steel Produced by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam
- Deformation Behavior and Processing Map during Isothermal Hot Compression of 49MnVS3 Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel
- A Constitutive Equation for Predicting Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of BFe10-1-2 Cupronickel Alloy through Double Multiple Nonlinear Regression
- Oxidation Behavior of Ferritic Steel T22 Exposed to Supercritical Water
- A Multi Scale Strategy for Simulation of Microstructural Evolutions in Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Titanium Alloy
- Partition Behavior of Alloying Elements in Nickel-Based Alloys and Their Activity Interaction Parameters and Infinite Dilution Activity Coefficients
- Influence of Heating on Tensile Physical-Mechanical Properties of Granite
- Comparison of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy P-MIG Welded Joints Filled with Different Wires
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thick Plate Friction Stir Welds for 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy
- Research Article
- Kinetics of oxide scale growth on a (Ti, Mo)5Si3 based oxidation resistant Mo-Ti-Si alloy at 900-1300∘C
- Calorimetric study on Bi-Cu-Sn alloys
- Mineralogical Phase of Slag and Its Effect on Dephosphorization during Converter Steelmaking Using Slag-Remaining Technology
- Controllability of joint integrity and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 6061-T6 aluminum and AZ31B magnesium alloys based on stationary shoulder
- Cellular Automaton Modeling of Phase Transformation of U-Nb Alloys during Solidification and Consequent Cooling Process
- The effect of MgTiO3Adding on Inclusion Characteristics
- Cutting performance of a functionally graded cemented carbide tool prepared by microwave heating and nitriding sintering
- Creep behaviour and life assessment of a cast nickel – base superalloy MAR – M247
- Failure mechanism and acoustic emission signal characteristics of coatings under the condition of impact indentation
- Reducing Surface Cracks and Improving Cleanliness of H-Beam Blanks in Continuous Casting — Improving continuous casting of H-beam blanks
- Rhodium influence on the microstructure and oxidation behaviour of aluminide coatings deposited on pure nickel and nickel based superalloy
- The effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of grain oriented silicon steel
- Effect of Arc Power on the Wear and High-temperature Oxidation Resistances of Plasma-Sprayed Fe-based Amorphous Coatings
- Short Communication
- Novel Combined Feeding Approach to Produce Quality Al6061 Composites for Heat Sinks
- Research Article
- Micromorphology change and microstructure of Cu-P based amorphous filler during heating process
- Controlling residual stress and distortion of friction stir welding joint by external stationary shoulder
- Research on the ingot shrinkage in the electroslag remelting withdrawal process for 9Cr3Mo roller
- Production of Mo2NiB2 Based Hard Alloys by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis
- The Morphology Analysis of Plasma-Sprayed Cast Iron Splats at Different Substrate Temperatures via Fractal Dimension and Circularity Methods
- A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook, Modified Johnson–Cook, Modified Zerilli–Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict Hot Deformation Behavior of TA2
- Dynamic absorption efficiency of paracetamol powder in microwave drying
- Preparation and Properties of Blast Furnace Slag Glass Ceramics Containing Cr2O3
- Influence of unburned pulverized coal on gasification reaction of coke in blast furnace
- Effect of PWHT Conditions on Toughness and Creep Rupture Strength in Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Welds
- Role of B2O3 on structure and shear-thinning property in CaO–SiO2–Na2O-based mold fluxes
- Effect of Acid Slag Treatment on the Inclusions in GCr15 Bearing Steel
- Recovery of Iron and Zinc from Blast Furnace Dust Using Iron-Bath Reduction
- Phase Analysis and Microstructural Investigations of Ce2Zr2O7 for High-Temperature Coatings on Ni-Base Superalloy Substrates
- Combustion Characteristics and Kinetics Study of Pulverized Coal and Semi-Coke
- Mechanical and Electrochemical Characterization of Supersolidus Sintered Austenitic Stainless Steel (316 L)
- Synthesis and characterization of Cu doped chromium oxide (Cr2O3) thin films
- Ladle Nozzle Clogging during casting of Silicon-Steel
- Thermodynamics and Industrial Trial on Increasing the Carbon Content at the BOF Endpoint to Produce Ultra-Low Carbon IF Steel by BOF-RH-CSP Process
- Research Article
- Effect of Boundary Conditions on Residual Stresses and Distortion in 316 Stainless Steel Butt Welded Plate
- Numerical Analysis on Effect of Additional Gas Injection on Characteristics around Raceway in Melter Gasifier
- Variation on thermal damage rate of granite specimen with thermal cycle treatment
- Effects of Fluoride and Sulphate Mineralizers on the Properties of Reconstructed Steel Slag
- Effect of Basicity on Precipitation of Spinel Crystals in a CaO-SiO2-MgO-Cr2O3-FeO System
- Review Article
- Exploitation of Mold Flux for the Ti-bearing Welding Wire Steel ER80-G
- Research Article
- Furnace heat prediction and control model and its application to large blast furnace
- Effects of Different Solid Solution Temperatures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the AA7075 Alloy After T6 Heat Treatment
- Study of the Viscosity of a La2O3-SiO2-FeO Slag System
- Tensile Deformation and Work Hardening Behaviour of AISI 431 Martensitic Stainless Steel at Elevated Temperatures
- The Effectiveness of Reinforcement and Processing on Mechanical Properties, Wear Behavior and Damping Response of Aluminum Matrix Composites
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- Review Article
- Research on the Influence of Furnace Structure on Copper Cooling Stave Life
- Influence of High Temperature Oxidation on Hydrogen Absorption and Degradation of Zircaloy-2 and Zr 700 Alloys
- Correlation between Travel Speed, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Wear Characteristics of Ni-Based Hardfaced Deposits over 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Factors Influencing Gas Generation Behaviours of Lump Coal Used in COREX Gasifier
- Experiment Research on Pulverized Coal Combustion in the Tuyere of Oxygen Blast Furnace
- Phosphate Capacities of CaO–FeO–SiO2–Al2O3/Na2O/TiO2 Slags
- Microstructure and Interface Bonding Strength of WC-10Ni/NiCrBSi Composite Coating by Vacuum Brazing
- Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding of Dissimilar 6061/7075 Aluminum Alloy
- Solvothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Monodisperse Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Hollow Nanospheres
- On the Capability of Logarithmic-Power Model for Prediction of Hot Deformation Behavior of Alloy 800H at High Strain Rates
- 3D Heat Conductivity Model of Mold Based on Node Temperature Inheritance
- 3D Microstructure and Micromechanical Properties of Minerals in Vanadium-Titanium Sinter
- Effect of Martensite Structure and Carbide Precipitates on Mechanical Properties of Cr-Mo Alloy Steel with Different Cooling Rate
- The Interaction between Erosion Particle and Gas Stream in High Temperature Gas Burner Rig for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Permittivity Study of a CuCl Residue at 13–450 °C and Elucidation of the Microwave Intensification Mechanism for Its Dechlorination
- Study on Carbothermal Reduction of Titania in Molten Iron
- The Sequence of the Phase Growth during Diffusion in Ti-Based Systems
- Growth Kinetics of CoB–Co2B Layers Using the Powder-Pack Boriding Process Assisted by a Direct Current Field
- High-Temperature Flow Behaviour and Constitutive Equations for a TC17 Titanium Alloy
- Research on Three-Roll Screw Rolling Process for Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Bar
- Continuous Cooling Transformation of Undeformed and Deformed High Strength Crack-Arrest Steel Plates for Large Container Ships
- Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors of the Sticker between Solidified Shell and Mold in Continuous Casting of Steel
- Casting Defects in Transition Layer of Cu/Al Composite Castings Prepared Using Pouring Aluminum Method and Their Formation Mechanism
- Effect of Current on Segregation and Inclusions Characteristics of Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting
- Investigation of Growth Kinetics of Fe2B Layers on AISI 1518 Steel by the Integral Method
- Microstructural Evolution and Phase Transformation on the X-Y Surface of Inconel 718 Ni-Based Alloys Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting under Different Heat Treatment
- Characterization of Mn-Doped Co3O4 Thin Films Prepared by Sol Gel-Based Dip-Coating Process
- Deposition Characteristics of Multitrack Overlayby Plasma Transferred Arc Welding on SS316Lwith Co-Cr Based Alloy – Influence ofProcess Parameters
- Elastic Moduli and Elastic Constants of Alloy AuCuSi With FCC Structure Under Pressure
- Effect of Cl on Softening and Melting Behaviors of BF Burden
- Effect of MgO Injection on Smelting in a Blast Furnace
- Structural Characteristics and Hydration Kinetics of Oxidized Steel Slag in a CaO-FeO-SiO2-MgO System
- Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Oxidation Roasting of Oxide–Sulphide Zinc Ore with Addition of Manganese Dioxide Using Response Surface Methodology
- Hydraulic Study of Bubble Migration in Liquid Titanium Alloy Melt during Vertical Centrifugal Casting Process
- Investigation on Double Wire Metal Inert Gas Welding of A7N01-T4 Aluminum Alloy in High-Speed Welding
- Oxidation Behaviour of Welded ASTM-SA210 GrA1 Boiler Tube Steels under Cyclic Conditions at 900°C in Air
- Study on the Evolution of Damage Degradation at Different Temperatures and Strain Rates for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Pack-Boriding of Pure Iron with Powder Mixtures Containing ZrB2
- Evolution of Interfacial Features of MnO-SiO2 Type Inclusions/Steel Matrix during Isothermal Heating at Low Temperatures
- Effect of MgO/Al2O3 Ratio on Viscosity of Blast Furnace Primary Slag
- The Microstructure and Property of the Heat Affected zone in C-Mn Steel Treated by Rare Earth
- Microwave-Assisted Molten-Salt Facile Synthesis of Chromium Carbide (Cr3C2) Coatings on the Diamond Particles
- Effects of B on the Hot Ductility of Fe-36Ni Invar Alloy
- Impurity Distribution after Solidification of Hypereutectic Al-Si Melts and Eutectic Al-Si Melt
- Induced Electro-Deposition of High Melting-Point Phases on MgO–C Refractory in CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 – (MgO) Slag at 1773 K
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 14Cr-ODS Steels with Zr Addition
- A Review of Boron-Rich Silicon Borides Basedon Thermodynamic Stability and Transport Properties of High-Temperature Thermoelectric Materials
- Siliceous Manganese Ore from Eastern India:A Potential Resource for Ferrosilicon-Manganese Production
- A Strain-Compensated Constitutive Model for Describing the Hot Compressive Deformation Behaviors of an Aged Inconel 718 Superalloy
- Surface Alloys of 0.45 C Carbon Steel Produced by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam
- Deformation Behavior and Processing Map during Isothermal Hot Compression of 49MnVS3 Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel
- A Constitutive Equation for Predicting Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of BFe10-1-2 Cupronickel Alloy through Double Multiple Nonlinear Regression
- Oxidation Behavior of Ferritic Steel T22 Exposed to Supercritical Water
- A Multi Scale Strategy for Simulation of Microstructural Evolutions in Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Titanium Alloy
- Partition Behavior of Alloying Elements in Nickel-Based Alloys and Their Activity Interaction Parameters and Infinite Dilution Activity Coefficients
- Influence of Heating on Tensile Physical-Mechanical Properties of Granite
- Comparison of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy P-MIG Welded Joints Filled with Different Wires
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thick Plate Friction Stir Welds for 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy
- Research Article
- Kinetics of oxide scale growth on a (Ti, Mo)5Si3 based oxidation resistant Mo-Ti-Si alloy at 900-1300∘C
- Calorimetric study on Bi-Cu-Sn alloys
- Mineralogical Phase of Slag and Its Effect on Dephosphorization during Converter Steelmaking Using Slag-Remaining Technology
- Controllability of joint integrity and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 6061-T6 aluminum and AZ31B magnesium alloys based on stationary shoulder
- Cellular Automaton Modeling of Phase Transformation of U-Nb Alloys during Solidification and Consequent Cooling Process
- The effect of MgTiO3Adding on Inclusion Characteristics
- Cutting performance of a functionally graded cemented carbide tool prepared by microwave heating and nitriding sintering
- Creep behaviour and life assessment of a cast nickel – base superalloy MAR – M247
- Failure mechanism and acoustic emission signal characteristics of coatings under the condition of impact indentation
- Reducing Surface Cracks and Improving Cleanliness of H-Beam Blanks in Continuous Casting — Improving continuous casting of H-beam blanks
- Rhodium influence on the microstructure and oxidation behaviour of aluminide coatings deposited on pure nickel and nickel based superalloy
- The effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of grain oriented silicon steel
- Effect of Arc Power on the Wear and High-temperature Oxidation Resistances of Plasma-Sprayed Fe-based Amorphous Coatings
- Short Communication
- Novel Combined Feeding Approach to Produce Quality Al6061 Composites for Heat Sinks
- Research Article
- Micromorphology change and microstructure of Cu-P based amorphous filler during heating process
- Controlling residual stress and distortion of friction stir welding joint by external stationary shoulder
- Research on the ingot shrinkage in the electroslag remelting withdrawal process for 9Cr3Mo roller
- Production of Mo2NiB2 Based Hard Alloys by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis
- The Morphology Analysis of Plasma-Sprayed Cast Iron Splats at Different Substrate Temperatures via Fractal Dimension and Circularity Methods
- A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook, Modified Johnson–Cook, Modified Zerilli–Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict Hot Deformation Behavior of TA2
- Dynamic absorption efficiency of paracetamol powder in microwave drying
- Preparation and Properties of Blast Furnace Slag Glass Ceramics Containing Cr2O3
- Influence of unburned pulverized coal on gasification reaction of coke in blast furnace
- Effect of PWHT Conditions on Toughness and Creep Rupture Strength in Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Welds
- Role of B2O3 on structure and shear-thinning property in CaO–SiO2–Na2O-based mold fluxes
- Effect of Acid Slag Treatment on the Inclusions in GCr15 Bearing Steel
- Recovery of Iron and Zinc from Blast Furnace Dust Using Iron-Bath Reduction
- Phase Analysis and Microstructural Investigations of Ce2Zr2O7 for High-Temperature Coatings on Ni-Base Superalloy Substrates
- Combustion Characteristics and Kinetics Study of Pulverized Coal and Semi-Coke
- Mechanical and Electrochemical Characterization of Supersolidus Sintered Austenitic Stainless Steel (316 L)
- Synthesis and characterization of Cu doped chromium oxide (Cr2O3) thin films
- Ladle Nozzle Clogging during casting of Silicon-Steel
- Thermodynamics and Industrial Trial on Increasing the Carbon Content at the BOF Endpoint to Produce Ultra-Low Carbon IF Steel by BOF-RH-CSP Process
- Research Article
- Effect of Boundary Conditions on Residual Stresses and Distortion in 316 Stainless Steel Butt Welded Plate
- Numerical Analysis on Effect of Additional Gas Injection on Characteristics around Raceway in Melter Gasifier
- Variation on thermal damage rate of granite specimen with thermal cycle treatment
- Effects of Fluoride and Sulphate Mineralizers on the Properties of Reconstructed Steel Slag
- Effect of Basicity on Precipitation of Spinel Crystals in a CaO-SiO2-MgO-Cr2O3-FeO System
- Review Article
- Exploitation of Mold Flux for the Ti-bearing Welding Wire Steel ER80-G
- Research Article
- Furnace heat prediction and control model and its application to large blast furnace
- Effects of Different Solid Solution Temperatures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the AA7075 Alloy After T6 Heat Treatment
- Study of the Viscosity of a La2O3-SiO2-FeO Slag System
- Tensile Deformation and Work Hardening Behaviour of AISI 431 Martensitic Stainless Steel at Elevated Temperatures
- The Effectiveness of Reinforcement and Processing on Mechanical Properties, Wear Behavior and Damping Response of Aluminum Matrix Composites

