Abstract
The present study deals with a microwave-assisted oxidation roasting oxide–sulphide zinc ore technology of with addition of manganese dioxide. Effects of roasting parameters such as MnO2 addition level, roasting temperature, and holding time are studied by using the Central Composite Design (CCD). Meanwhile, zinc calcines are characterized by phase compositions analyses(XRD), structure characteristics of minerals (FT-IR), micro-area chemical analyses (SEM-EDAX) and elemental valence bonding analyses (XPS), which prove to be in accordance with the CCD results. The optimum roasting conditions are decided as MnO2 addition level being 85.14 %, roasting temperature 680 °C, and holding time 41 mins, and oxidation degree of zinc can reach 88.22 %. Besides, when MnO2 addition level reaches a certain value, zinc will aggregate in a form of ZnMn2O4, one battery material.
Introduction
With increasing scarce supply of non-ferrous metal resources, research on efficient utilization of non-traditional metal resources, such as oxide–sulphide zinc ore, is urgent [1, 2]. The oxide–sulphide zinc ore has a considerable reserve, intricate composition and complex mineralogy, thus it can’t be ineffectively processed by the existing technology [3].
MnO2 can act as an additive catalyst, which has been demonstrated the value of strengthening oxidation roasting, meanwhile fixing sulfur and suppressing emission of sulfur-containing flue gas [4]. Li et al. [5] separated and recovered antimony from high arsenic-bearing flue dusts through selective oxidation using MnO2, in which the arsenic was removed through a volatilization, and antimony was oxidized to Sb2O4 staying in the roasted products. Zhang et al. [6] investigated the feasibility of oxidative degradation of toxic nitrocellulose acid wastewater using low-grade MnO2 ore as a cheap oxidant and the simultaneous release of Mn2+ for preparation of electrolytic manganese metal, and proved that TOC removal was signifâicantly correlated with the release of Mn. It also can be referred that MnO2 displays a promising application prospect in oxidation roasting.
The response surface methodology (RSM) is a powerful technology, which can eliminate and lower the time consuming and expensive of “one factor at a time optimization approach” [7, 8], via a minimum number of experimental trials by a Central Composite Design (CCD). What’s more, the CCD allows simultaneous optimization of conditions and identifies significant interactions among variables [9, 10, 11].
This work is devoted to optimizing microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore with addition of manganese dioxide. CCD of RSM is employed to investigate the effect of significant operating parameters, including MnO2 addition level, roasting temperature and holding time on oxidation degree of zinc ore to find the most suitable combination of variables to achieve a maximum phase transformation result.
Materials and methods
Materials and regents
The oxide-sulphide zinc is from a domestic lead and zinc smelter. Main chemical composition and mineralogical analysis of oxide–sulphide zinc ore are presented in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. Figure 1 gives the XRD pattern of raw ore. These detections affirm that this oxide–sulphide zinc ore consists of a large amount of ZnS, ZnCO3, SiO2 and CaCO3, small amount of FeS2, PbS and Zn2SiO4, and trace amounts of Fe2O3 and PbCO3. All chemical regents used for this experiment are analytical pure.
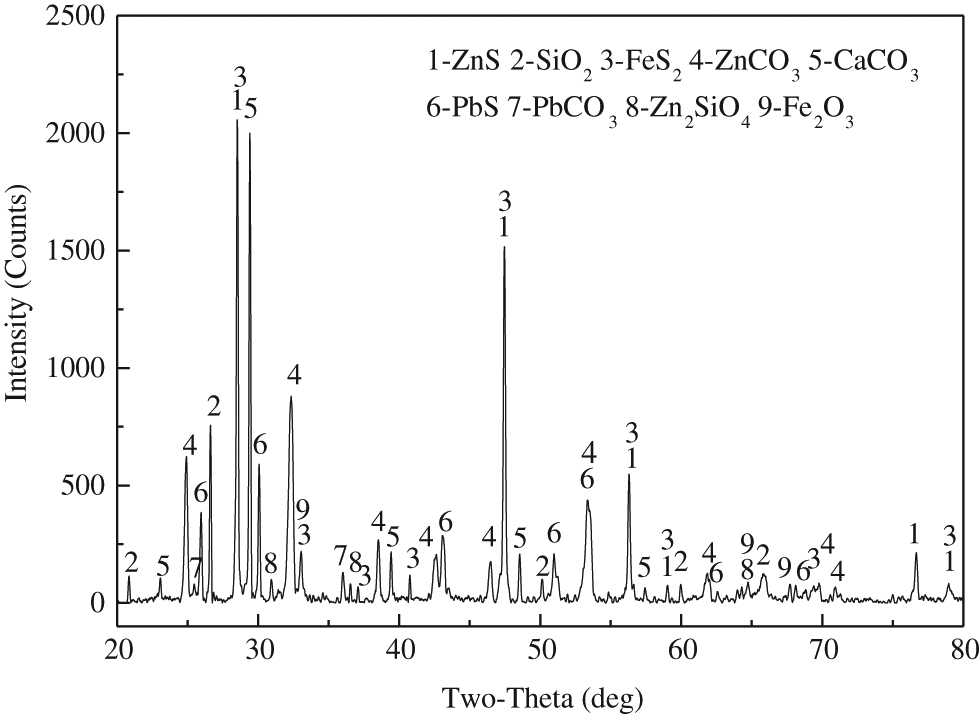
XRD pattern of oxide–sulphide zinc ore.
Main chemical composition of oxide–sulphide zinc ore (mass fraction, wt%).
| Zn | CaO | SiO2 | S | Fe | Pb | Al2O3 | MgO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24.91 | 11.96 | 10.30 | 10.20 | 7.70 | 4.80 | 1.27 | 0.22 |
Mineralogical analysis of oxide–sulphide zinc ore.
| Zinc phase | ZnS | ZnCO3 | Zn2SiO4 | ZnFe2O4 | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass fraction/wt% | 11.06 | 9.68 | 4.00 | 0.052 | 24.91 |
| Distribution/wt% | 44.61 | 39.04 | 16.13 | 0.21 | 100 |
Instrumental analyses
The XRD patterns of samples are recorded in a Rigaku D/MAX-3B X-ray diffractometer with a detecting speed of 4 deg/min. SEM-EDAX analyses obtains in a FEI Quanta 200 scanning electron microscope. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) performs in a LAS-3000 surface analysis system (RIBER, France).
Process variables and design of experiments
Design-Expert is applied to build the matrix and generate the response surface models. A CCD with three levels and three factors is adopted in this study, as it can evaluate quadratic interactions between pairs of factors while minimizing the number of required experiments [12]. The influences and values of three factors examined include MnO2 addition level, holding time and roasting temperature. 20 experiments with different factor values are performed. The response is measured for each experiment and the oxidation degree are evaluated based on an established mathematical model.
The microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore with addition of manganese dioxide conducts as: mix zinc ore and MnO2 at some mass ratio, then roast the mixture in a self-made high temperature microwave equipment according to the CCD design. After a period of constant temperature heating, characterize the zinc calcines.
Results and discussion
Fitting the process models
The 3-factor CCD matrix and experimental results obtained for the microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore with addition of manganese dioxide are presented in Table 3, in which the correlation of oxidation degree (Y) with MnO2 addition level (X1), holding time (X2) and calcination temperature (X3) taken as variables is studied.
Central composite design arrangement and results of microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore with addition of manganese dioxide.
| No. | MnO2 addition level (%) | Holding time (mins) | Roasting temperature (℃) | Oxidation degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 85.14 | 49.87 | 709.46 | 87.72 |
| 2 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 750.00 | 70.03 |
| 3 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 66.01 |
| 4 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 67.12 |
| 5 | 105.52 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 93.81 |
| 6 | 25.38 | 20.13 | 590.54 | 17.48 |
| 7 | 85.14 | 20.13 | 709.46 | 85.42 |
| 8 | 5.00 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 6.87 |
| 9 | 25.38 | 49.87 | 590.54 | 23.24 |
| 10 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 64.94 |
| 11 | 85.14 | 20.13 | 590.54 | 83.41 |
| 12 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 550.00 | 56.58 |
| 13 | 85.14 | 49.87 | 590.54 | 83.46 |
| 14 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 66.72 |
| 15 | 55.26 | 60.00 | 650.00 | 68.58 |
| 16 | 55.26 | 10.00 | 650.00 | 61.44 |
| 17 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 68.18 |
| 18 | 25.38 | 49.87 | 709.46 | 38.22 |
| 19 | 25.38 | 20.13 | 709.46 | 30.42 |
| 20 | 55.26 | 35.00 | 650.00 | 64.85 |
Regression equation
Following a polynomial regression model correlation, the mathematical relationship of oxidation degree with operating variables can be obtained as:
Through a comparison of prediction values using the above equation with experimental values, it is found that, oxidation degree has R2 value of 0.9942, which explains this model possesses a high fitting degree, and 99.42 % of the experimental data can be explained.
Surface and contour plots
In the response surface optimization experiments, it needs to perform an accuracy analysis for the model, which is accomplished by a RSM experimental design. On the basis of regression and variance analysis, two-dimensional and three-dimensional response surfaces of the regression model are established. Response surface plots for MnO2 adding level vs. roasting temperature vs. holding time corresponding to the optimized quadratic model (formula 1) is obtained as in Figure 2.
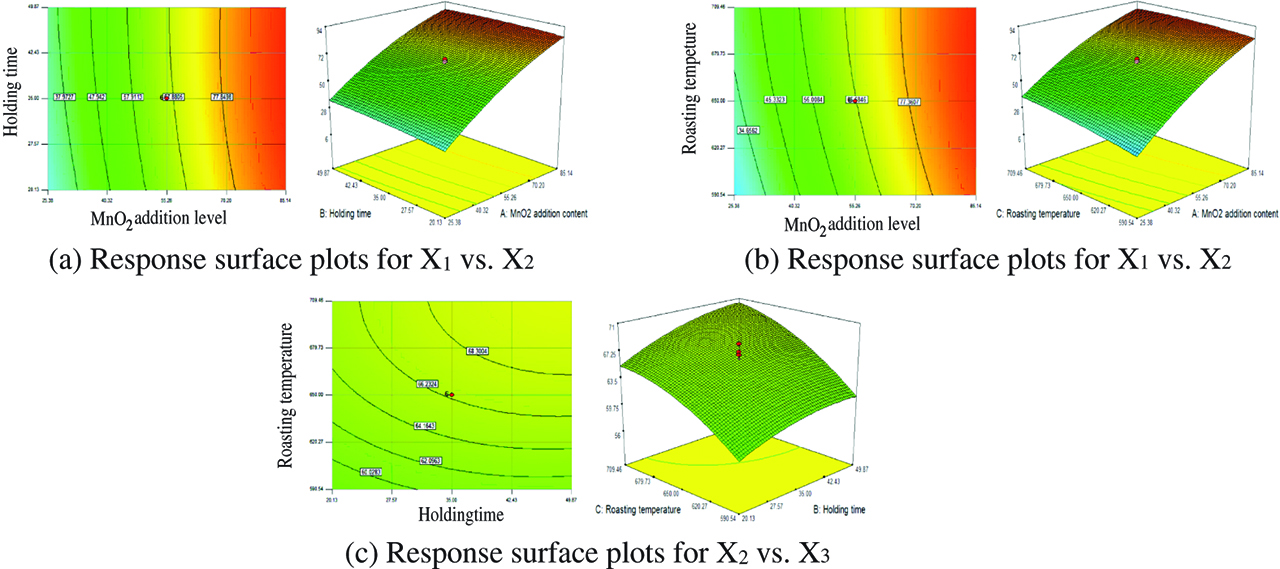
Response surface plots for MnO2 adding level vs. holding time vs. roasting temperature. (a) Response surface plots for X1 vs. X2. (b) Response surface plots for X1 vs. X3. (c) Response surface plots for X2 vs. X3.
Figure 2 (a) illustrates the 3D response curves and contour for MnO2 adding level vs. holding time. It can be seen that the oxidation rate is positively correlated with MnO2 addition level and holding time, that is, with the increasing of MnO2 level or holding time, oxidation rate will improve. Figure 2 (b) and (c) display same behaviors.
Optimization and verification
By the prediction function of response surface software, optimization is carried out to determine MnO2 addition level, roasting temperature and holding time. The experimental results are compared with predicted values. Optimization process parameters of the regression mode are as Table 4.
Optimization process parameters of the regression model.
| MnO2 addition level (%) | Holding time (mins) | Roasting temperature (℃) | Oxidation degree (%) | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85.14 | 41.21 | 679.49 | 88.22018 | 0.42122 |
Under conditions of optimized process parameters, the results (oxidation degree) of two parallel experiments are basically close to 88 %, which verifies the reliability of optimization results.
Zinc calcines analyses
Phase compositions analyses
The XRD patterns of zinc calcines corresponding to Table 3 compare in Figure 3. As can be seen, MnO2 addition level is the critical factor for microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore. When MnO2 addition level is 5 %, main phase of zinc exists as ZnS, and part exist as ZnO and ZnFe2O4. Besides, MnO2 has been reduced to MnO.
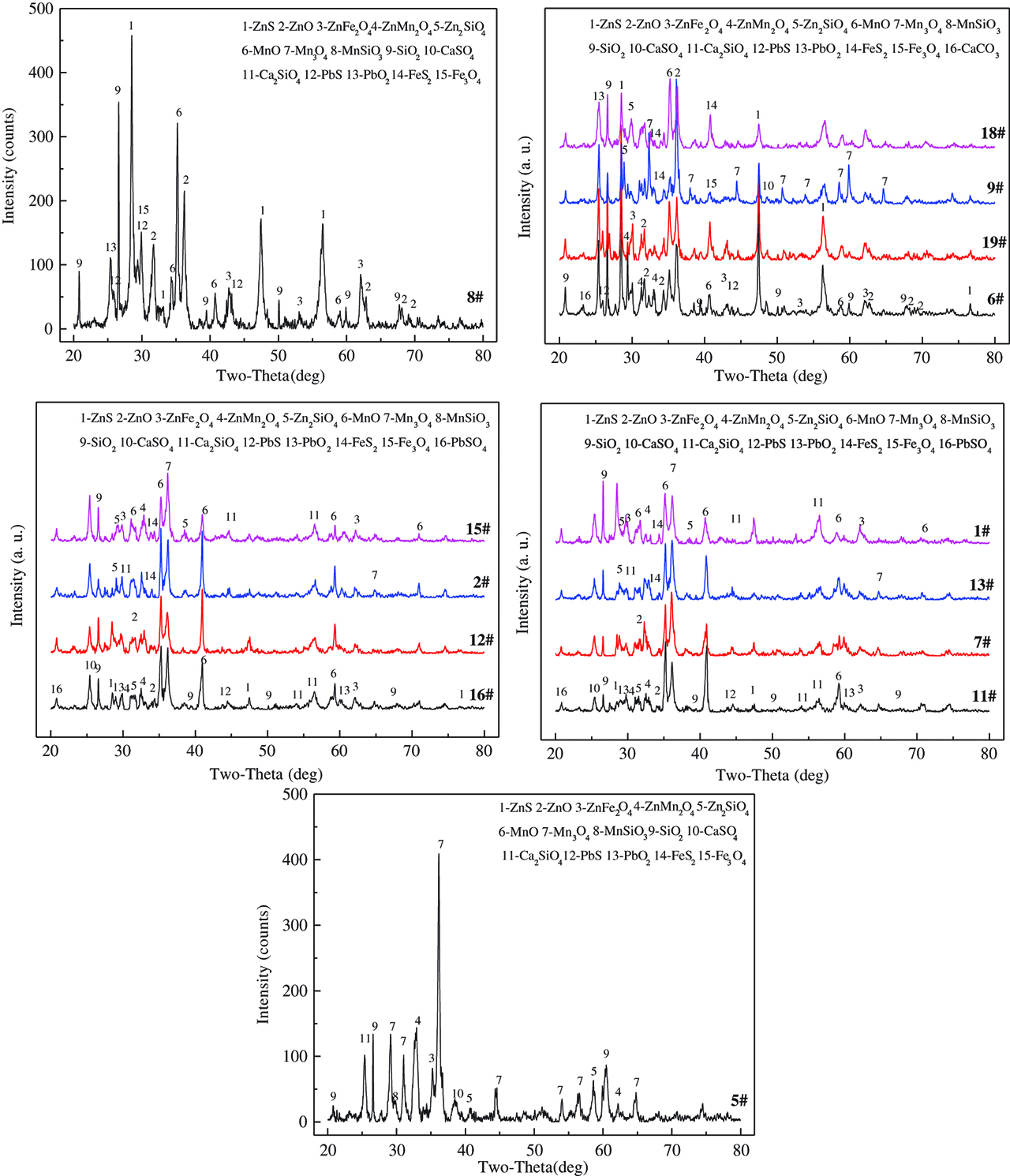
XRD patterns of zinc calcine.
With further addition of MnO2, ZnMn2O4 forms. Main zinc-containing phases change to ZnS, ZnO and ZnFe2O4, as adds 25.37 % MnO2. Besides, there also generate a little ZnMn2O4 and a new phase-Mn3O4. After that, ZnMn2O4 and ZnFe2O4 domain, meanwhile MnO gradually transforms to Mn3O4. Thus, the reaction with addition of MnO2 can be deduced as, ZnS first oxidizes to ZnO, and then transforms to ZnMn2O4 with MnO. Compared to MnO2 addition level, roasting temperature and holding time can be judged to be unobvious factors.
Structure characteristic of minerals
Figure 4 analyzes the structure characteristic of zinc calcines presented in Table 3.
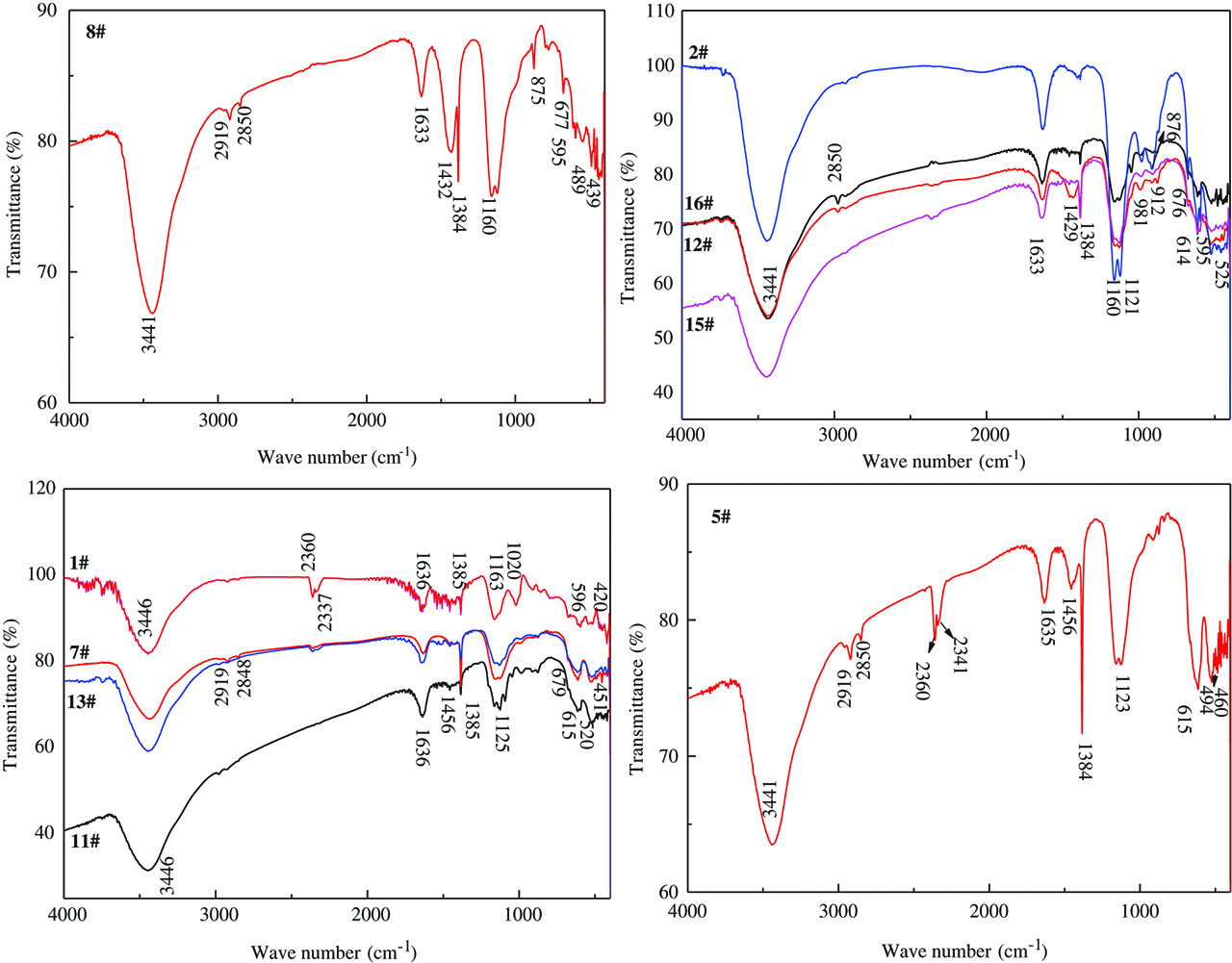
FT-IR spectra of zinc calcines.
It can be seen from the figures that main transmission peaks include 3441, 2919, 2850, 2341, 1635, 1456, 1384, 1123, 615 and 525 cm−1. Wherein, 452 cm−1 is caused by Zn-O stretching vibration [13]. Vibration spectrum at 505, 614 and 677 cm−1 are attributed to Mn-O [14, 15], which also demonstrates the presence of ZnMn2O4. No. 8 is the only one without spectra of ZnMn2O4, and verifies the XRD detection results.
Micro-area chemical analysis
Micro-area chemical analysis is performed on No. 8 zinc calcine in Table 3, and result is shown in Figure 5, for which addition amount of manganese dioxide is 5 %, roasting temperature is 650 °C, and holding time is 35 mins. According to the EDAX analyses and elemental distribution map scanning, there can divide three mineral zones in the observation horizon, zone 1# is the regional aggregation of MnO, ZnS, ZnO and PbS. Zone 2# is the coexistence area of MnO and ZnO, which appear as a fine dispersed state, and their contents are not high. Mineral components of zone 3# are basically similar as 1#, while possess a higher content of sulphur and Si. Judging from the elemental distribution map scanning, Zn, Pb, Mn, Fe and S present in a substantially uniform state, and elemental symbiosis phenomena will not occur, while SiO2 remains aggregate separately.
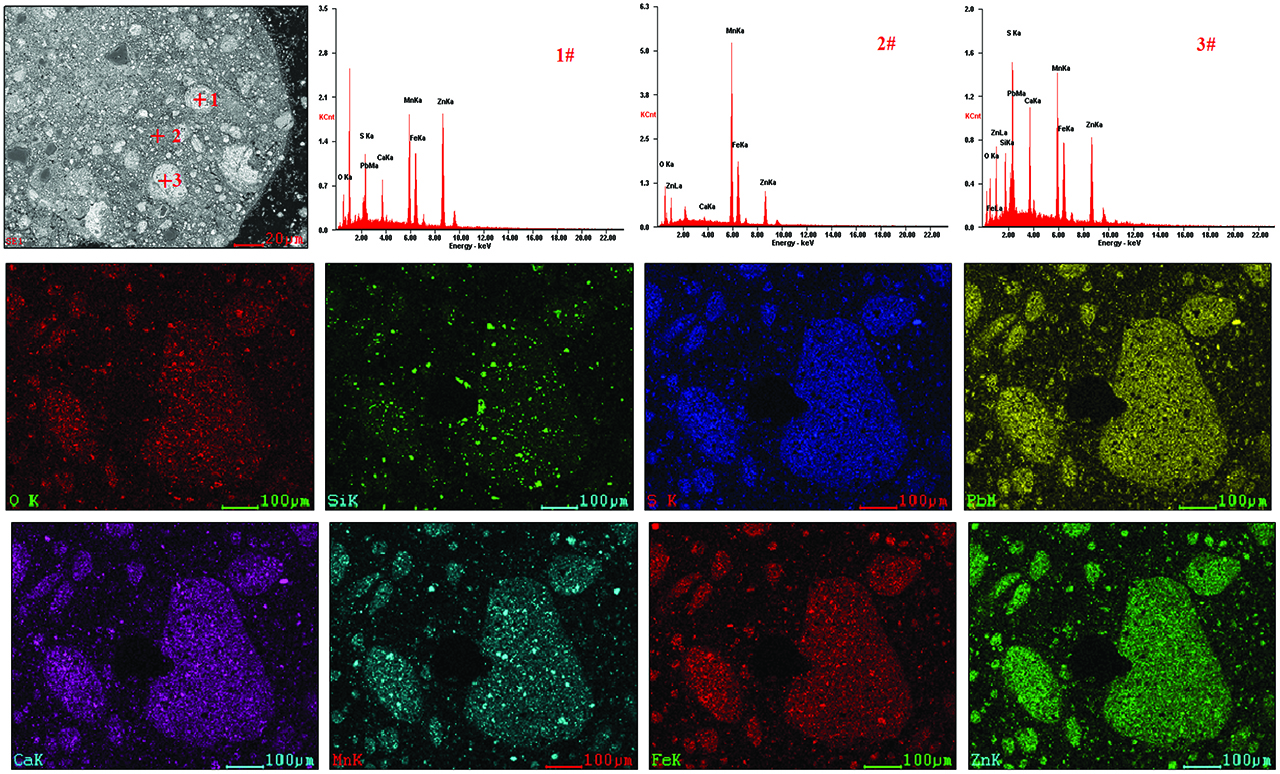
SEM-EDAX analysis of zinc calcine (No. 8).
The zinc calcine (NO. 5) in Figure 6 obtains under conditions of MnO2 addition level being 105.52 %, roasting temperature 650 °C, and holding time 35 mins, in which a phenomenon of melt aggregation emerges. EDAX results prove ZnMn2O4 is the eutectic of ZnO, MnO and MnO2, which is consistent with the results of XRD analysis. Furthermore, Mn, O and Zn will accumulate together, that is, ZnMn2O4, and Ca, S and O form a CaSO4 symbiont. A small amount of PbSO4 also presents.
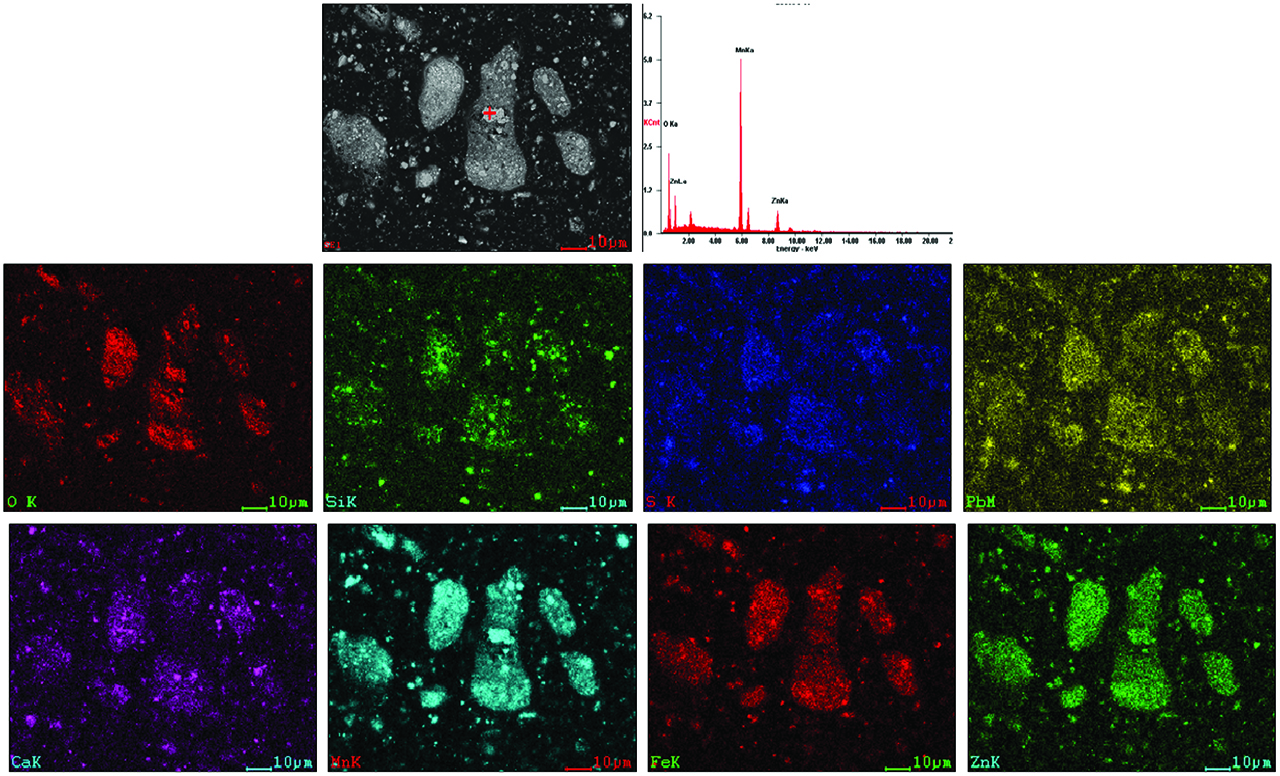
SEM-EDAX analysis of zinc calcine (No. 5).
Elemental valence bonding analysis
The XPS detail spectra of S and Mn are shown in Figure 7. S2p diffraction peaks can be divided into two energy bands, ~ 168 eV attributed to high value sulphates, and ~ 160 eV attributed to low value sulphide [16, 17]. Through comparing, content of high value sulphate increases with gradually doping MnO2. When the doping level reaches 55.26 %, there just exists a low amount of S2-.
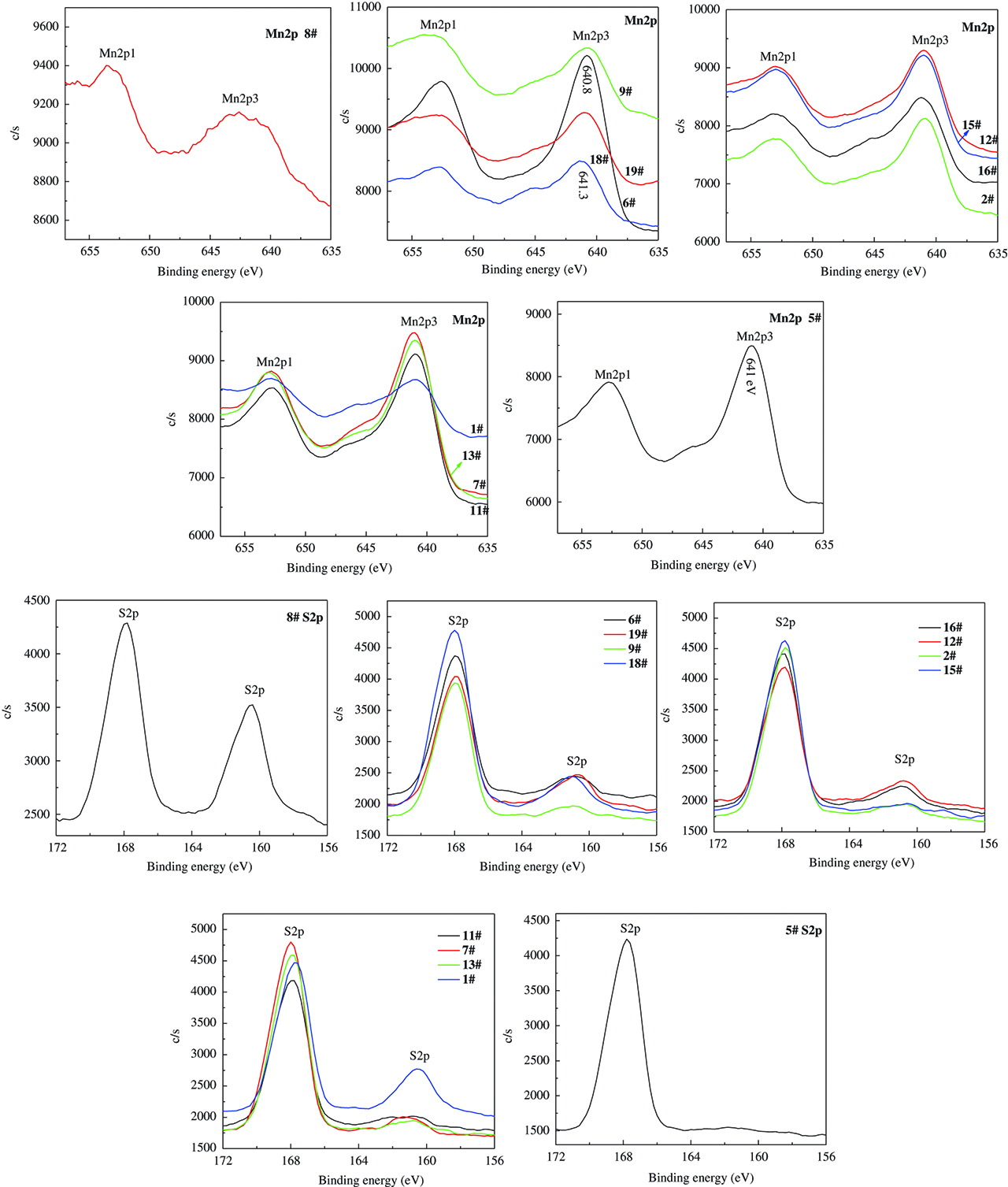
XPS detail spectra of S and Mn in zinc calcine with different MnO2 level.
Umezawa and Reilley [18] reported that the Mn2p3 peak of MnO2 is at 643.4 eV. Mn2p3 valence band energy of MnFe2O4, CuMn2O4 and Mn3O4 is at 641.0 eV [19, 20, 21]. Mn2p3 peak between 640.7 eV and 641 eV belongs to the MnO [22, 23]. According to the reported data, increasing amount of MnO2 will render Mn2p spectrum shift to high value, namely, MnO transforms to ZnMn2O4.
Conclusions
In this paper, reaction mechanism of microwave-assisted oxidation roasting of oxide–sulphide zinc ore with addition of MnO2 is discussed, and optimum roasting conditions are decided by exploiting response surface methodology, and ascertained by microscopic analysis. Results show that,
The optimized conditions for this design are MnO2 addition level being 85.14 %, roasting temperature 680 °C, and holding time 41 mins, and oxidation degree of zinc can reach 88.22 %.
When MnO2 addition level reaches a certain value, aggregation phenomenon of zinc appears, and content of S obviously decreases. According to the EDAX analysis, appearance of ZnMn2O4 is confirmed.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Project supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program, 2014CB643404) and Yunnan Provincial Department of Education Science Research Fund Project (2016zzx291).
References
[1] D. Yang, H. Zhu and J. Chen, Hydrometallurgical Zinc Process and Technology, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing (2006).Suche in Google Scholar
[2] K. Yang, S. Li, L. Zhang, J. Peng, W. Chen, F. Xie and A. Ma, Hydrometallurgy, 166 (2016) 243–251.10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.07.012Suche in Google Scholar
[3] K. Yang, L. Zhang, X. Zhu, J. Peng, S. Li, A. Ma, H. Li and F. Zhu, J. Hazard. Mater., 343 (2018) 315–323.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.049Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Y. Zhu, C. Liu, Q. Yang, P. Li, Y. Sun and D. Xu, Adv. Mat. Res, Trans. Tech. Publ., 773 (2013) 634–638.10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.773.634Suche in Google Scholar
[5] L. Li, F. Wang, D. Zhong, C. Tan and Y. Yu, ISIJ Int., 57 (2017) 581–586.10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-362Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Y. Zhang, J. Cai, Z. Dan, Y. Tian, N. Duan and B. Xin, J. Chem. Technol. Biot. (2017).Suche in Google Scholar
[7] A. Asfaram, M. Ghaedi, A. Goudarzi and M. Rajabi, Dalton T., 44 (2015) 14707–14723.10.1039/C5DT01504ASuche in Google Scholar
[8] S. Chowdhury, S. Chakraborty and P.D. Saha, Environ. Sci. Pollut. R., 20 (2013) 1698–170510.1007/s11356-012-0989-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] P. Das, P. Banerjee and S. Monda, Environ. Sci. Pollut. R., 22 (2015) 1318–1328.10.1007/s11356-014-3419-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] A. Asfaram, M. Ghaedi, S. Agarwal, I. Tyagi and V.K. Gupta, RSC Adv., 5 (2015) 18438–18450.10.1039/C4RA15637DSuche in Google Scholar
[11] F. Priscila, Z.M. Magriotis, M.A. Rossi, R.F. Resende and C.A. Nunes, J. Environ. Manage., 130 (2013) 417–428.10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.08.067Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] M.W. Amer, R.A. Ahmad and A.M. Awwad, Int. J. Ind. Chem., 6 (2015) 67–75.10.1007/s40090-014-0030-8Suche in Google Scholar
[13] L. Zhang, H. Cheng, R. Zong and Y. Zhu, J. Phys. Chem. C, 113 (2009) 2368–2374.10.1021/jp807778rSuche in Google Scholar
[14] P.K. Sharma and M.S. Whittingham, Mater. Lett., 48 (2001) 319–323.10.1016/S0167-577X(00)00320-7Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Z. Bai, N. Fan, C. Sun, Z. Ju, C. Guo, J. Yang and Y. Qian, Nanoscale, 5 (2013) 2442–2447.10.1039/c3nr33211jSuche in Google Scholar
[16] T.N. Khmeleva, W. Skinner and D.A. Beattie, Int. J. Miner. Process., 76 (2005) 43–53.10.1016/j.minpro.2004.10.001Suche in Google Scholar
[17] A. Parker, C. Klauber, A. Kougianos, H.R. Watling and W. Van Bronswijk, Hydrometallurgy, 71 (2003) 265–276.10.1016/S0304-386X(03)00165-8Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Y. Umezawa and C.N. Reilley, Anal. Chem., 50 (1978) 1290–1295.10.1021/ac50031a025Suche in Google Scholar
[19] V.A.M. Brabers, F.M. Van Setten and P.S.A. Knapen, J. Solid State Chem., 49 (1983) 93–98.10.1016/0022-4596(83)90220-7Suche in Google Scholar
[20] M. Oku and K. Hirokawa, J. Electron. Spectrosc., 8 (1976) 475–481.10.1016/0368-2048(76)80034-5Suche in Google Scholar
[21] B.R. Strohmeier and D.M. Hercules, J. Phys. Chem., 88 (1984) 4922–4929.10.1021/j150665a026Suche in Google Scholar
[22] M. Oku, K. Hirokawa and S. Ikeda, J. Electron. Spectrosc., 7 (1975) 465–473.10.1016/0368-2048(75)85010-9Suche in Google Scholar
[23] A. Aoki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 15 (1976) 305.10.1143/JJAP.15.305Suche in Google Scholar
© 2019 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Public License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Review Article
- Research on the Influence of Furnace Structure on Copper Cooling Stave Life
- Influence of High Temperature Oxidation on Hydrogen Absorption and Degradation of Zircaloy-2 and Zr 700 Alloys
- Correlation between Travel Speed, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Wear Characteristics of Ni-Based Hardfaced Deposits over 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Factors Influencing Gas Generation Behaviours of Lump Coal Used in COREX Gasifier
- Experiment Research on Pulverized Coal Combustion in the Tuyere of Oxygen Blast Furnace
- Phosphate Capacities of CaO–FeO–SiO2–Al2O3/Na2O/TiO2 Slags
- Microstructure and Interface Bonding Strength of WC-10Ni/NiCrBSi Composite Coating by Vacuum Brazing
- Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding of Dissimilar 6061/7075 Aluminum Alloy
- Solvothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Monodisperse Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Hollow Nanospheres
- On the Capability of Logarithmic-Power Model for Prediction of Hot Deformation Behavior of Alloy 800H at High Strain Rates
- 3D Heat Conductivity Model of Mold Based on Node Temperature Inheritance
- 3D Microstructure and Micromechanical Properties of Minerals in Vanadium-Titanium Sinter
- Effect of Martensite Structure and Carbide Precipitates on Mechanical Properties of Cr-Mo Alloy Steel with Different Cooling Rate
- The Interaction between Erosion Particle and Gas Stream in High Temperature Gas Burner Rig for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Permittivity Study of a CuCl Residue at 13–450 °C and Elucidation of the Microwave Intensification Mechanism for Its Dechlorination
- Study on Carbothermal Reduction of Titania in Molten Iron
- The Sequence of the Phase Growth during Diffusion in Ti-Based Systems
- Growth Kinetics of CoB–Co2B Layers Using the Powder-Pack Boriding Process Assisted by a Direct Current Field
- High-Temperature Flow Behaviour and Constitutive Equations for a TC17 Titanium Alloy
- Research on Three-Roll Screw Rolling Process for Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Bar
- Continuous Cooling Transformation of Undeformed and Deformed High Strength Crack-Arrest Steel Plates for Large Container Ships
- Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors of the Sticker between Solidified Shell and Mold in Continuous Casting of Steel
- Casting Defects in Transition Layer of Cu/Al Composite Castings Prepared Using Pouring Aluminum Method and Their Formation Mechanism
- Effect of Current on Segregation and Inclusions Characteristics of Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting
- Investigation of Growth Kinetics of Fe2B Layers on AISI 1518 Steel by the Integral Method
- Microstructural Evolution and Phase Transformation on the X-Y Surface of Inconel 718 Ni-Based Alloys Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting under Different Heat Treatment
- Characterization of Mn-Doped Co3O4 Thin Films Prepared by Sol Gel-Based Dip-Coating Process
- Deposition Characteristics of Multitrack Overlayby Plasma Transferred Arc Welding on SS316Lwith Co-Cr Based Alloy – Influence ofProcess Parameters
- Elastic Moduli and Elastic Constants of Alloy AuCuSi With FCC Structure Under Pressure
- Effect of Cl on Softening and Melting Behaviors of BF Burden
- Effect of MgO Injection on Smelting in a Blast Furnace
- Structural Characteristics and Hydration Kinetics of Oxidized Steel Slag in a CaO-FeO-SiO2-MgO System
- Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Oxidation Roasting of Oxide–Sulphide Zinc Ore with Addition of Manganese Dioxide Using Response Surface Methodology
- Hydraulic Study of Bubble Migration in Liquid Titanium Alloy Melt during Vertical Centrifugal Casting Process
- Investigation on Double Wire Metal Inert Gas Welding of A7N01-T4 Aluminum Alloy in High-Speed Welding
- Oxidation Behaviour of Welded ASTM-SA210 GrA1 Boiler Tube Steels under Cyclic Conditions at 900°C in Air
- Study on the Evolution of Damage Degradation at Different Temperatures and Strain Rates for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Pack-Boriding of Pure Iron with Powder Mixtures Containing ZrB2
- Evolution of Interfacial Features of MnO-SiO2 Type Inclusions/Steel Matrix during Isothermal Heating at Low Temperatures
- Effect of MgO/Al2O3 Ratio on Viscosity of Blast Furnace Primary Slag
- The Microstructure and Property of the Heat Affected zone in C-Mn Steel Treated by Rare Earth
- Microwave-Assisted Molten-Salt Facile Synthesis of Chromium Carbide (Cr3C2) Coatings on the Diamond Particles
- Effects of B on the Hot Ductility of Fe-36Ni Invar Alloy
- Impurity Distribution after Solidification of Hypereutectic Al-Si Melts and Eutectic Al-Si Melt
- Induced Electro-Deposition of High Melting-Point Phases on MgO–C Refractory in CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 – (MgO) Slag at 1773 K
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 14Cr-ODS Steels with Zr Addition
- A Review of Boron-Rich Silicon Borides Basedon Thermodynamic Stability and Transport Properties of High-Temperature Thermoelectric Materials
- Siliceous Manganese Ore from Eastern India:A Potential Resource for Ferrosilicon-Manganese Production
- A Strain-Compensated Constitutive Model for Describing the Hot Compressive Deformation Behaviors of an Aged Inconel 718 Superalloy
- Surface Alloys of 0.45 C Carbon Steel Produced by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam
- Deformation Behavior and Processing Map during Isothermal Hot Compression of 49MnVS3 Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel
- A Constitutive Equation for Predicting Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of BFe10-1-2 Cupronickel Alloy through Double Multiple Nonlinear Regression
- Oxidation Behavior of Ferritic Steel T22 Exposed to Supercritical Water
- A Multi Scale Strategy for Simulation of Microstructural Evolutions in Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Titanium Alloy
- Partition Behavior of Alloying Elements in Nickel-Based Alloys and Their Activity Interaction Parameters and Infinite Dilution Activity Coefficients
- Influence of Heating on Tensile Physical-Mechanical Properties of Granite
- Comparison of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy P-MIG Welded Joints Filled with Different Wires
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thick Plate Friction Stir Welds for 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy
- Research Article
- Kinetics of oxide scale growth on a (Ti, Mo)5Si3 based oxidation resistant Mo-Ti-Si alloy at 900-1300∘C
- Calorimetric study on Bi-Cu-Sn alloys
- Mineralogical Phase of Slag and Its Effect on Dephosphorization during Converter Steelmaking Using Slag-Remaining Technology
- Controllability of joint integrity and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 6061-T6 aluminum and AZ31B magnesium alloys based on stationary shoulder
- Cellular Automaton Modeling of Phase Transformation of U-Nb Alloys during Solidification and Consequent Cooling Process
- The effect of MgTiO3Adding on Inclusion Characteristics
- Cutting performance of a functionally graded cemented carbide tool prepared by microwave heating and nitriding sintering
- Creep behaviour and life assessment of a cast nickel – base superalloy MAR – M247
- Failure mechanism and acoustic emission signal characteristics of coatings under the condition of impact indentation
- Reducing Surface Cracks and Improving Cleanliness of H-Beam Blanks in Continuous Casting — Improving continuous casting of H-beam blanks
- Rhodium influence on the microstructure and oxidation behaviour of aluminide coatings deposited on pure nickel and nickel based superalloy
- The effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of grain oriented silicon steel
- Effect of Arc Power on the Wear and High-temperature Oxidation Resistances of Plasma-Sprayed Fe-based Amorphous Coatings
- Short Communication
- Novel Combined Feeding Approach to Produce Quality Al6061 Composites for Heat Sinks
- Research Article
- Micromorphology change and microstructure of Cu-P based amorphous filler during heating process
- Controlling residual stress and distortion of friction stir welding joint by external stationary shoulder
- Research on the ingot shrinkage in the electroslag remelting withdrawal process for 9Cr3Mo roller
- Production of Mo2NiB2 Based Hard Alloys by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis
- The Morphology Analysis of Plasma-Sprayed Cast Iron Splats at Different Substrate Temperatures via Fractal Dimension and Circularity Methods
- A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook, Modified Johnson–Cook, Modified Zerilli–Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict Hot Deformation Behavior of TA2
- Dynamic absorption efficiency of paracetamol powder in microwave drying
- Preparation and Properties of Blast Furnace Slag Glass Ceramics Containing Cr2O3
- Influence of unburned pulverized coal on gasification reaction of coke in blast furnace
- Effect of PWHT Conditions on Toughness and Creep Rupture Strength in Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Welds
- Role of B2O3 on structure and shear-thinning property in CaO–SiO2–Na2O-based mold fluxes
- Effect of Acid Slag Treatment on the Inclusions in GCr15 Bearing Steel
- Recovery of Iron and Zinc from Blast Furnace Dust Using Iron-Bath Reduction
- Phase Analysis and Microstructural Investigations of Ce2Zr2O7 for High-Temperature Coatings on Ni-Base Superalloy Substrates
- Combustion Characteristics and Kinetics Study of Pulverized Coal and Semi-Coke
- Mechanical and Electrochemical Characterization of Supersolidus Sintered Austenitic Stainless Steel (316 L)
- Synthesis and characterization of Cu doped chromium oxide (Cr2O3) thin films
- Ladle Nozzle Clogging during casting of Silicon-Steel
- Thermodynamics and Industrial Trial on Increasing the Carbon Content at the BOF Endpoint to Produce Ultra-Low Carbon IF Steel by BOF-RH-CSP Process
- Research Article
- Effect of Boundary Conditions on Residual Stresses and Distortion in 316 Stainless Steel Butt Welded Plate
- Numerical Analysis on Effect of Additional Gas Injection on Characteristics around Raceway in Melter Gasifier
- Variation on thermal damage rate of granite specimen with thermal cycle treatment
- Effects of Fluoride and Sulphate Mineralizers on the Properties of Reconstructed Steel Slag
- Effect of Basicity on Precipitation of Spinel Crystals in a CaO-SiO2-MgO-Cr2O3-FeO System
- Review Article
- Exploitation of Mold Flux for the Ti-bearing Welding Wire Steel ER80-G
- Research Article
- Furnace heat prediction and control model and its application to large blast furnace
- Effects of Different Solid Solution Temperatures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the AA7075 Alloy After T6 Heat Treatment
- Study of the Viscosity of a La2O3-SiO2-FeO Slag System
- Tensile Deformation and Work Hardening Behaviour of AISI 431 Martensitic Stainless Steel at Elevated Temperatures
- The Effectiveness of Reinforcement and Processing on Mechanical Properties, Wear Behavior and Damping Response of Aluminum Matrix Composites
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- Review Article
- Research on the Influence of Furnace Structure on Copper Cooling Stave Life
- Influence of High Temperature Oxidation on Hydrogen Absorption and Degradation of Zircaloy-2 and Zr 700 Alloys
- Correlation between Travel Speed, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Wear Characteristics of Ni-Based Hardfaced Deposits over 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Factors Influencing Gas Generation Behaviours of Lump Coal Used in COREX Gasifier
- Experiment Research on Pulverized Coal Combustion in the Tuyere of Oxygen Blast Furnace
- Phosphate Capacities of CaO–FeO–SiO2–Al2O3/Na2O/TiO2 Slags
- Microstructure and Interface Bonding Strength of WC-10Ni/NiCrBSi Composite Coating by Vacuum Brazing
- Refill Friction Stir Spot Welding of Dissimilar 6061/7075 Aluminum Alloy
- Solvothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Monodisperse Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 Hollow Nanospheres
- On the Capability of Logarithmic-Power Model for Prediction of Hot Deformation Behavior of Alloy 800H at High Strain Rates
- 3D Heat Conductivity Model of Mold Based on Node Temperature Inheritance
- 3D Microstructure and Micromechanical Properties of Minerals in Vanadium-Titanium Sinter
- Effect of Martensite Structure and Carbide Precipitates on Mechanical Properties of Cr-Mo Alloy Steel with Different Cooling Rate
- The Interaction between Erosion Particle and Gas Stream in High Temperature Gas Burner Rig for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Permittivity Study of a CuCl Residue at 13–450 °C and Elucidation of the Microwave Intensification Mechanism for Its Dechlorination
- Study on Carbothermal Reduction of Titania in Molten Iron
- The Sequence of the Phase Growth during Diffusion in Ti-Based Systems
- Growth Kinetics of CoB–Co2B Layers Using the Powder-Pack Boriding Process Assisted by a Direct Current Field
- High-Temperature Flow Behaviour and Constitutive Equations for a TC17 Titanium Alloy
- Research on Three-Roll Screw Rolling Process for Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Bar
- Continuous Cooling Transformation of Undeformed and Deformed High Strength Crack-Arrest Steel Plates for Large Container Ships
- Formation Mechanism and Influence Factors of the Sticker between Solidified Shell and Mold in Continuous Casting of Steel
- Casting Defects in Transition Layer of Cu/Al Composite Castings Prepared Using Pouring Aluminum Method and Their Formation Mechanism
- Effect of Current on Segregation and Inclusions Characteristics of Dual Alloy Ingot Processed by Electroslag Remelting
- Investigation of Growth Kinetics of Fe2B Layers on AISI 1518 Steel by the Integral Method
- Microstructural Evolution and Phase Transformation on the X-Y Surface of Inconel 718 Ni-Based Alloys Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting under Different Heat Treatment
- Characterization of Mn-Doped Co3O4 Thin Films Prepared by Sol Gel-Based Dip-Coating Process
- Deposition Characteristics of Multitrack Overlayby Plasma Transferred Arc Welding on SS316Lwith Co-Cr Based Alloy – Influence ofProcess Parameters
- Elastic Moduli and Elastic Constants of Alloy AuCuSi With FCC Structure Under Pressure
- Effect of Cl on Softening and Melting Behaviors of BF Burden
- Effect of MgO Injection on Smelting in a Blast Furnace
- Structural Characteristics and Hydration Kinetics of Oxidized Steel Slag in a CaO-FeO-SiO2-MgO System
- Optimization of Microwave-Assisted Oxidation Roasting of Oxide–Sulphide Zinc Ore with Addition of Manganese Dioxide Using Response Surface Methodology
- Hydraulic Study of Bubble Migration in Liquid Titanium Alloy Melt during Vertical Centrifugal Casting Process
- Investigation on Double Wire Metal Inert Gas Welding of A7N01-T4 Aluminum Alloy in High-Speed Welding
- Oxidation Behaviour of Welded ASTM-SA210 GrA1 Boiler Tube Steels under Cyclic Conditions at 900°C in Air
- Study on the Evolution of Damage Degradation at Different Temperatures and Strain Rates for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
- Pack-Boriding of Pure Iron with Powder Mixtures Containing ZrB2
- Evolution of Interfacial Features of MnO-SiO2 Type Inclusions/Steel Matrix during Isothermal Heating at Low Temperatures
- Effect of MgO/Al2O3 Ratio on Viscosity of Blast Furnace Primary Slag
- The Microstructure and Property of the Heat Affected zone in C-Mn Steel Treated by Rare Earth
- Microwave-Assisted Molten-Salt Facile Synthesis of Chromium Carbide (Cr3C2) Coatings on the Diamond Particles
- Effects of B on the Hot Ductility of Fe-36Ni Invar Alloy
- Impurity Distribution after Solidification of Hypereutectic Al-Si Melts and Eutectic Al-Si Melt
- Induced Electro-Deposition of High Melting-Point Phases on MgO–C Refractory in CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 – (MgO) Slag at 1773 K
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 14Cr-ODS Steels with Zr Addition
- A Review of Boron-Rich Silicon Borides Basedon Thermodynamic Stability and Transport Properties of High-Temperature Thermoelectric Materials
- Siliceous Manganese Ore from Eastern India:A Potential Resource for Ferrosilicon-Manganese Production
- A Strain-Compensated Constitutive Model for Describing the Hot Compressive Deformation Behaviors of an Aged Inconel 718 Superalloy
- Surface Alloys of 0.45 C Carbon Steel Produced by High Current Pulsed Electron Beam
- Deformation Behavior and Processing Map during Isothermal Hot Compression of 49MnVS3 Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel
- A Constitutive Equation for Predicting Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of BFe10-1-2 Cupronickel Alloy through Double Multiple Nonlinear Regression
- Oxidation Behavior of Ferritic Steel T22 Exposed to Supercritical Water
- A Multi Scale Strategy for Simulation of Microstructural Evolutions in Friction Stir Welding of Duplex Titanium Alloy
- Partition Behavior of Alloying Elements in Nickel-Based Alloys and Their Activity Interaction Parameters and Infinite Dilution Activity Coefficients
- Influence of Heating on Tensile Physical-Mechanical Properties of Granite
- Comparison of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy P-MIG Welded Joints Filled with Different Wires
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thick Plate Friction Stir Welds for 6082-T6 Aluminum Alloy
- Research Article
- Kinetics of oxide scale growth on a (Ti, Mo)5Si3 based oxidation resistant Mo-Ti-Si alloy at 900-1300∘C
- Calorimetric study on Bi-Cu-Sn alloys
- Mineralogical Phase of Slag and Its Effect on Dephosphorization during Converter Steelmaking Using Slag-Remaining Technology
- Controllability of joint integrity and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 6061-T6 aluminum and AZ31B magnesium alloys based on stationary shoulder
- Cellular Automaton Modeling of Phase Transformation of U-Nb Alloys during Solidification and Consequent Cooling Process
- The effect of MgTiO3Adding on Inclusion Characteristics
- Cutting performance of a functionally graded cemented carbide tool prepared by microwave heating and nitriding sintering
- Creep behaviour and life assessment of a cast nickel – base superalloy MAR – M247
- Failure mechanism and acoustic emission signal characteristics of coatings under the condition of impact indentation
- Reducing Surface Cracks and Improving Cleanliness of H-Beam Blanks in Continuous Casting — Improving continuous casting of H-beam blanks
- Rhodium influence on the microstructure and oxidation behaviour of aluminide coatings deposited on pure nickel and nickel based superalloy
- The effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of grain oriented silicon steel
- Effect of Arc Power on the Wear and High-temperature Oxidation Resistances of Plasma-Sprayed Fe-based Amorphous Coatings
- Short Communication
- Novel Combined Feeding Approach to Produce Quality Al6061 Composites for Heat Sinks
- Research Article
- Micromorphology change and microstructure of Cu-P based amorphous filler during heating process
- Controlling residual stress and distortion of friction stir welding joint by external stationary shoulder
- Research on the ingot shrinkage in the electroslag remelting withdrawal process for 9Cr3Mo roller
- Production of Mo2NiB2 Based Hard Alloys by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis
- The Morphology Analysis of Plasma-Sprayed Cast Iron Splats at Different Substrate Temperatures via Fractal Dimension and Circularity Methods
- A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook, Modified Johnson–Cook, Modified Zerilli–Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict Hot Deformation Behavior of TA2
- Dynamic absorption efficiency of paracetamol powder in microwave drying
- Preparation and Properties of Blast Furnace Slag Glass Ceramics Containing Cr2O3
- Influence of unburned pulverized coal on gasification reaction of coke in blast furnace
- Effect of PWHT Conditions on Toughness and Creep Rupture Strength in Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel Welds
- Role of B2O3 on structure and shear-thinning property in CaO–SiO2–Na2O-based mold fluxes
- Effect of Acid Slag Treatment on the Inclusions in GCr15 Bearing Steel
- Recovery of Iron and Zinc from Blast Furnace Dust Using Iron-Bath Reduction
- Phase Analysis and Microstructural Investigations of Ce2Zr2O7 for High-Temperature Coatings on Ni-Base Superalloy Substrates
- Combustion Characteristics and Kinetics Study of Pulverized Coal and Semi-Coke
- Mechanical and Electrochemical Characterization of Supersolidus Sintered Austenitic Stainless Steel (316 L)
- Synthesis and characterization of Cu doped chromium oxide (Cr2O3) thin films
- Ladle Nozzle Clogging during casting of Silicon-Steel
- Thermodynamics and Industrial Trial on Increasing the Carbon Content at the BOF Endpoint to Produce Ultra-Low Carbon IF Steel by BOF-RH-CSP Process
- Research Article
- Effect of Boundary Conditions on Residual Stresses and Distortion in 316 Stainless Steel Butt Welded Plate
- Numerical Analysis on Effect of Additional Gas Injection on Characteristics around Raceway in Melter Gasifier
- Variation on thermal damage rate of granite specimen with thermal cycle treatment
- Effects of Fluoride and Sulphate Mineralizers on the Properties of Reconstructed Steel Slag
- Effect of Basicity on Precipitation of Spinel Crystals in a CaO-SiO2-MgO-Cr2O3-FeO System
- Review Article
- Exploitation of Mold Flux for the Ti-bearing Welding Wire Steel ER80-G
- Research Article
- Furnace heat prediction and control model and its application to large blast furnace
- Effects of Different Solid Solution Temperatures on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the AA7075 Alloy After T6 Heat Treatment
- Study of the Viscosity of a La2O3-SiO2-FeO Slag System
- Tensile Deformation and Work Hardening Behaviour of AISI 431 Martensitic Stainless Steel at Elevated Temperatures
- The Effectiveness of Reinforcement and Processing on Mechanical Properties, Wear Behavior and Damping Response of Aluminum Matrix Composites

