Abstract
Global heating, depletions, and high cost of fossil fuels ensued the exploitation of AC sources of energy such as solar stamina. The peculiarities of photovoltaic PV module are a condition for dimensioning and designing a PV system. The causation for developing PV modules beneficial for electrical applications, this manner permits the development of new hefty-performances stand-alone PV system. PV ingredients are permitting the computation of the demeanor of the total system in medley scenarios. In this work, a comparison between calculation solar program and manual mathematical method are made according to Mosul-Iraq site.
1 Introduction
PV is a manner of procreating electrical power by changing solar radiation to DC electricity using semiconductors that induct in PV technology. PV generation uses solar panel compounded of many solar cells. Because of the growing demand of clean energy sources, the fabrication of PV modules has developed considerably in recent years [1]. PV is one of the essential universal trends connected to gaining energy from renewable energy sources (RES) [2]. PV inability has important effect on the safety, accuracy, and energy balance of PV devices [3]. PV systems are growing rapidly, starting from low capacity to high capacity around 40,000 MW at the end of 2010. More than 100 countries use PV system [4]. PV is a technology that credibly converts sun light to DC electricity. Variable kinds of PV modules accredit on the rating scale of the power. Solar cell is a fabric cited by famous semiconductors like silicon [5]. Changeability in the temperature will affect the solar module efficiency, and because of these mutations this technology is facing big defiance in its power finesse rendition. Reintegrated of clean energy is considered a screed route [6]. Efficiency is a very significant signal for PV systems [7]. The requirement to decrease the environmental effect of conventional fossil fuels, as well as the depletion of these resources and the intense increase in fossil fuel prices, is the cause for the rising use of RES [8]. PV technology is very well suited to supply the stand-alone locations. It has good reliability [9].
Are obtained from calculation solar program by software package according to the longitudinal and latitude site in formation for a certain loads are given various premiums about the PV generation [10].
2 Literature review
Angga Romana, Eko Adhi Setiawan, and Kurnianto Joyonegoro (2018) studied the design of solar PV system according to two methods: Australia/New Zealand Standard and manual methods. The two methods take constant values for DC voltage bus (48 V) and oversupply coefficient (2). They concluded that Australian design method is better than the manual method [11].
Preeti Bhatt and Arunima Verma (2014) studied the design of solar PV system. They made a comparison between congenital and nano PV system they take (200 V) for bus voltage but did not include the dirt factor tilt angle, inverter efficiency, and oversupply coefficient in the calculations of solar PV system design for conventional and nano types. They concluded that nano PV system cannot be used for high power load on computation of its low conversion efficiency and the design for three phase load requirement of the whole building [12].
Ayaz A. Khamisani (2019) studied the design of off-grid solar PV system. He included the system losses in the calculations and he depended on the PWM charge controller instead of MPPT charge controller in the design of the charger. Solar PV system (off-grid) type systems more agreeable to areas where the consumer opts not to be supply back the energy that generated at this end and the electrisation is yet to be accomplished [13].
3 The uniqueness of this work
PV models have nonlinear characteristics of voltage–current relationship, and therefore, there is only unique point for stand-alone solar PV system as compared with the other previous design; in this work all practical environmental conditions are included in the design according to calculation solar program, and all main practical environmental conditions are taken from this program and compensated in the mathematical method. These practical conditions gave true sizing of PV modules, batteries, charge controller, and inverter as compared with previous works.
4 Stand-alone/off grid solar PV system
PV systems are considered a simple application for the customers to connect their loads to the grid [14]. Battery storage system is used in off-grid PV systems for providing the electricity during cloudy days and at night. The weather changes and the year round conditions must be considered at designing these systems [15]. When sun does not appear for many continuous days, back-up generators are required such as diesel, gasoline, and petroleum. The advantages of stand-alone PV systems are to give adequate energy to a house hold and powering the place which are distant from the grid [16]. Off-grid systems have further ingredients and these systems are considered expensive and comparatively costlier than grid direct system [17]. Table 1 illustrates the PV system components.
PV system components
| Particular | Company |
|---|---|
| PV modules | ATERSA |
| Batteries | STECA TAROM |
| MPPT controller | KHUN |
| Inverter | VICIRO |
Figure 1 represents the stand-alone PV system.
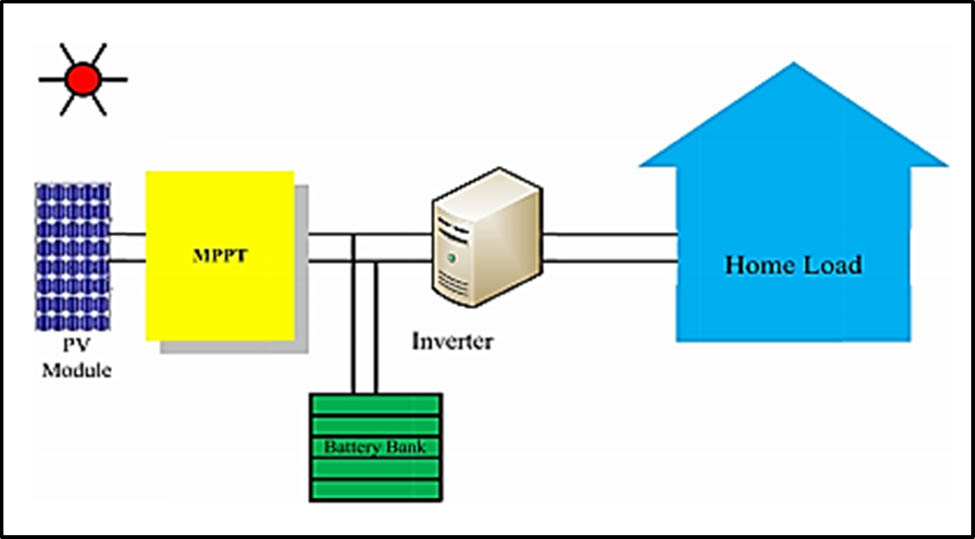
Stand-alone PV system.
5 Materials and methods
Many materials and two calculation methods are suggested in this work.
5.1 Materials
Materials used in this work are given in Table 2.
Materials of suggested PV system
| Name/type | Shapes | Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Solar panel: ATERSA A-100M MONOCRISTALINO |
 |
Product warranty 10 years, P max (100 Wp), V max (18.95 V), I max (5.28 A), V oc (22.21 V), I sc (5.79 A), panel efficiency (15.07%) |
| Regulator: STECA TAROM 245 PWM. |
 |
System voltage 12 V/24 V, input I sc (45 A), maximum output current at load (45 A), maximum self-consumption (14 mA), charge voltage of the boost (14.4 V) and (28.8 V), floating case end of charge voltage (13.7 V) and (27.4 V), equalization charge (14.7 V) (29.4 V). Deep discharge protection (SOC/LVD) < 30% SOC/11.1 V (22.2 V/44.4 V) |
| Battery: KHUN 100 AH TUBULAR-PLATE. |
 |
Model type LPTT 12100H, warranty 5 years, rated capacity 100 A h, inverter support 10KYA-900 VA, nominal voltage 12 V, tall tubular technology, depth of discharge 80% |
| Inverters: VICTRON MULTIPLUS C 24/2000/50-30. |
 |
1,600 W constant output and 4,000 W peak current for 24 V battery voltage. Combination of inverter with transfer switch and 50 A battery charger. Provides pure sine wave at 50 Hz. VE.Bus communication port allows extensive possibilities in terms of connection, configuration, and controlling of victron multiplus devices. Supports three-phase operation (three units of the same model needed). Supports parallel operation – up to six units can be connected parallel to increase system power if needed. Inverter efficiency 94% |
| Appliances: Television, refrigerator, microwave oven, computer, and lighting | ||
5.2 Methods
Calculation solar program is an implementation that determines the energy during 24 h, requested of a house hold and depending on the numerate that represented by batteries required and number of PV modules [18]. The implementations included the presumptive wattage of each appliance. Calculation solar program the appliances are collected to gather into four categories called entertainment, cleaning, air-conditioning, and lighting energy requested for each category is determined separately then displayed [19]. The forerunner version ditto numerates the rating of the inverter and the charge controller that required by the solar system [20]. These are necessary components for a solar system. In addition, the full clone takes within the account the system efficiency, depth of discharge, and offline verses online usage [21]. Solar are rate of the peak sunshine hours, there are three various estimation manners. The estimation manners annexing use of air mass formula, half-sine model and NASA solar insolation data [22]. The mechanism for calculating the area and panel tilt angle was included.
The proposed model is said to perform better at energy prediction than software tools such as PV watts, PV system, or ret screen. The approach was validated on two 5 MW PV plants in the same district of Mosul-Iraq [23]. Method to curriculum the demeanor of a PV apparatus as a prosthesis to the equivalent circuit model. In some implementation a very prompt and cushy approach to a solar panel demeanor is required [24]. Daytime temperature and global horizontal insolation (GHI) are the two core parameters affecting the PV plant output. According to these parameters, Mosul can be classified into 15 climatic zones [25]. From National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Mosul is classified into various climatic zones. Finally, the results show a decisive study to select the best PV technology for various climatic zones of Mosul [26].
6 Location and orientation
From basemap the installation is situated: unnamed road, Mosul, Iraq; the coordinates: 36.541461, 43.19386. PV array is bought according to the following peculiarity: inclination: 73°
Disorientation belonging the south: 6°. AC with a voltage of 230 is used in this system [27].
6.1 Consumption
The energy consumption is determined from appliances and lighting per day. Tables 3 and 4 show the appliances and lighting consumption per day.
Consume appliances per day
| Consumer appliances (day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Appliances | Hours (h) | Power (W) | Energy (W h/day) |
| Computer | 5 | 300 | 1,500 |
| Television | 3 | 70 | 210 |
| Microwave oven | 0.8 | 800 | 640 |
| Refrigerator | 8 | 195 | 1,560 |
| Total | 3,910 | ||
Lighting consumption
| Consumption by lighting (day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | N° | Hours (h) | Power (W) | Energy (W h/day) |
| Fluorescent lamp | 2 | 5 | 11 | 110 |
| Fluorescent tube | 2 | 5 | 30 | 300 |
| Bulb | 2 | 5 | 60 | 600 |
| Total | 1,010 | |||
6.2 Theoretical total daily energy 4,920 W h/day
Theoretical energy per day is 4,920 W h/day; the parameters given in Table 5 are used by the calculation of yield (performance ratio) [28,29,30,31,32,33].
Performance ratios
| Battery depth of discharge | 80% |
| Battery losses coefficient | 5% |
| Wiring loss coefficient | 5% |
| Loss coefficient of DC/AC conversion | 6% |
| Self-discharge coefficient of battery | 0.5% |
| Autonomy system | 3 days |
| Performance ratio | 81.9% |
Table 6 represents the calculation of PV modules number.
PV calculation
| ATERSA A-100M Monocristalino | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Open circuit voltage (V oc) | 22.21 V | Voltage at max. power | 18.95 V |
| Short circuit current (I sc) | 5.79 A | Current at max. power | 5.28 A |
| Max. power | 100 W | Temperature coefficient of power (C) | 0.44% |
| Real power | 98.2928 W | No. of serial model | 2 |
| Total Pico Power module | 800 Wp | No. of parallel modules | 4 |
| Optimization installation/needs most | 0.7 | Total modules | 8 |
| The degree of optimization election equipment/real n | 70% | ||
7 Regulator specifications
The specifications of the regulator are given in Table 7.
Regulator specifications
| STECA TAROM 245 PWM | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | 48 | Tension (V) | 12–24 |
| Consumption (mA) | 14 | Rated power (W) | 0.3 |
| Utilization ray | 0.7 | Capacity (A) | 45 |
| The degree of optimization election equipment/real n | No. of regulator | 1 | |
8 Batteries calculations
Energy, depth of discharge, bus voltage, and days of autonomy are entered in the batteries calculations.
Nominal voltage of battery: 24 V.
Depth of discharge: 80%.
Days of autonomy: 3 days.
Daily real energy: 6,007 W h/day.
Battery capacity calculated helpful: 751 A h.
Actual capacity batteries calculated: 1,252 A h.
Battery specifications are given in Table 8.
Battery specifications
| KHUN 100 AH TUBULAR-PLATE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10: 200 A h | C20: 200 A h | C40: 200 A h | C100: 200 A h | C120: 200 A h |
| Tension | 12 V | No. of series pcs element | 2 | |
| Nominal capacity accumulate | 200 A h | No. of parallel pcs element | 1 | |
| Nominal voltage of the battery | 24 V | Total element | 2 | |
| The degree of optimization election equipment/real n | 16% | |||
9 Inverter charger
The choice of inverter charger is given in Table 9.
Inverter specifications
| VICTRON MULTIPLUS C 24/2000/50/30 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tension | 24 V | Rated power | 2,000 W |
| Nominal capacity accumulate | 1,600 W | Instant power | 4,000 W |
| Battery nominal voltage | 11 W | Efficiency | 94% |
| Utilization ray | 86% | No. of inverter | 1 |
| The degree of optimization election equipment/real n | 117% | ||
The elements that obtained from the calculation solar program are summarized in Table 10.
Stand-alone PV components (calculation solar program)
| Units | Elements |
|---|---|
| 8 | Module type – ATERSA A-100M MONOCRISTALINO |
| 1 | Regulator type – STECA TAROM 245 PWM |
| 2 | Battery type – KHUN 100 AH TUBULAR-PLATE |
| 1 | Type of inverter – VICTRON MULTIPLUS C 24/2000/50-30 |
10 Mathematical calculations
The mathematical calculations are obtained according to the theoretical total daily energy:
10.1 PV sizing
Total load (W h) = 3,910 + 1,010 = 4,920 W h.
Power of PV module = 100 W.
Then,
10.2 Battery sizing
No. of series batteries is
No. of parallel batteries is
10.3 Inverter sizing
where f o is the oversupply coefficient.
The elements obtained from the mathematical calculations are summarized in Table 11.
Stand-alone PV components (mathematical calculations)
| Units | Elements |
|---|---|
| 8 | Module type – ATERSA A-100M MONOCRISTALINO |
| 2 | Battery type – KHUN 100 AH TUBULAR-PLATE |
| 1 | Type of inverter – VICTRON MULTIPLUS C 24/2000/50-30 (MPPT built-in) |
11 Discrepancy
The discrepancy between calculation solar program and mathematical method are made in this work: The solar PV components (PV sizing, battery sizing, charger sizing, and inverter sizing) are included in this study for two methods. Effective coefficients of the calculation solar program in the equations of the mathematical method in addition to the data of Mosul base map, like performance ratios, days of autonomy, nominal battery voltage, battery efficiency, inverter efficiency, and sun are rate.
The number of PV modules, batteries, chargers, and inverter capacity are appeared approximately equal. As compared with the literature review, all necessary parameters of calculation solar program are included in this work; therefore, the sizing of all solar PV system components obtained from this work is accurate and closed to the truth as compared with the previous works, and also this work can be applied on all types (conventional and nano) solar PV system.
12 Presumptions
The presumption effects of the practical conditions are:
Dust particles are litters in the midair and are readily carried by the wind; these dust particles generated from industrial ambient cause 80% softening in the PV electrical output. Also the effect of dust and sighting will decrease the efficiency.
The poor solar irradiant and inclination angle will lead to the fakir PV systems, also the wrong angles will cause a poor received of radiation.
Day of autonomy can be expressed by the time that the load can be met with the batteries a lone unrested any solar inputs, embarking from full charged battery state, this may perform to sorely low average state of charge premium over broad periods of the year which is fully damaging for batteries bank.
13 Conclusion
The comparison results of two methods appear that the number of PV modules, batteries, and inverter are equally for same provenance and specifications of solar PV system components depending on the real cautions of calculation solar program and the theoretical mathematical calculations. Stand-alone PV system is more reliable than the on-grid PV system because of using battery storage system that gives more stability for this system. Days of autonomy have a large effect on the number of the batteries, which in turn will effect on the total cost of the system.
14 Future prospects and drawback
Stand-alone PV system is expected to grow very quickly from now to 2030. The drawbacks of these systems are very high initial cost, especially the storage back and the dust in the weather.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our special thanks to our affiliation (NTU).
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Ahsan S, Javed K, Rana AS, Shan MZ. Design and cost analysis of 1 kw photovoltaic system based on actual performance in Indian scenario. Department of Electrical Engineering, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India; 2016 July 5. p. 642–4.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Małek A, Caban J, Wojciechowski L. Charging electric cars as a way to increase the use of energy produced from RES. De Gruyter | Published online; 2020 March 8.10.1515/eng-2020-0009Search in Google Scholar
[3] Kilikevičienė K, Matijošius J, Kilikevičius A, Jurevičius M, Makarskas V, Caban J, et al. Research of the energy losses of photovoltaic (PV) modules after hail simulation using a newly-created testbed. Des. 2019;23:453–9.10.3390/en12234537Search in Google Scholar
[4] Ayop R, Isa NM, Tan CW. Components sizing of photovoltaic stand-alone system based on loss of power supply probability. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;221:2731–43.10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.079Search in Google Scholar
[5] Mahmood AL. “Design and simulation of stand-alone pv system for electronic and communications engineering department laboratories in Al-Nahrain University”. Al-Nahrain University, College of Engineering, Electronic and Communications Engineering Department, Baghdad, Iraq. EAI Endorsed Trans Energy. Belgium: European Alliance for Innovation; 2019 Jun 6;6:2233–9.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Petrakopoulou F. On the economics of stand-alone renewable hybrid power plants in remote regions. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;118:63–74.10.1016/j.enconman.2016.03.070Search in Google Scholar
[7] Kilikevičienė K, Matijošius J, Fursenko A, Kilikevičius A. Tests of hail simulation and research of the resulting impact on the structural reliability of solar cells. Eksploatacja Niezawodnosc – Maint Reliab. 2019 Feb 3;21:275–81.10.17531/ein.2019.2.12Search in Google Scholar
[8] Derkacz AJ, Dudziak A. Savings and investment decisions in the polish energy sector. Sustainability. 2021 Feb 13;13:553–8.10.3390/su13020553Search in Google Scholar
[9] El Shenawy ET, Hegazy AH, Abdellatef M. Design and optimization of stand-alone PV system for Egyptian rural communities. Int J Appl Eng Res. 2017;12(20):10433–46.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Shukla AK, Sudhakar K, Baredar P. Design, simulation and economic analysis of stand-alone roof top solar PV system in India. Sol Energy. 2016;136:437–49.10.1016/j.solener.2016.07.009Search in Google Scholar
[11] Romana A, Setiawan EA, Joyonegoro K. Comparison of two calculation methods for designing the solar electric power system for small islands. Published by EDP Sciences. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. E3S Web of Conferences. Berline: DE Gruyter; 2018.10.1051/e3sconf/20186702052Search in Google Scholar
[12] Bhatt P, Verma A. Design and cost analysis of PV system using nano solar cell. Kanpur, India: Int J Sci Res Publ. Department of Electrical Engineering, HBTI; 2014 March 7. ISSN 2250-3153.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Khamisani AA. Design methodology of off-grid PV solar powered system (A case study of solar powered bus shelter). Goolincoln Avenue Charleston, IL: Eastern Illinois University; 2019.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Dufo López R, Lujano Rojas JM, Bernal Agustín JL. Comparison of different lead–acid battery life time prediction models for use in simulation of stand-alone photovoltaic systems. App Energy. 2014 Feb 15;115:242-53.10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.11.021Search in Google Scholar
[15] Bouabdallah A, Olivier JC, Bourguet S, Machmoum M, Schaeffer E. Safe sizing methodology applied to a stand-alone photovoltaic system. Renew Energy. 2015;80:266–74.10.1016/j.renene.2015.02.007Search in Google Scholar
[16] Monaaf DA, Al-falahi SDG, Jaya Singhe HE. A review on recent size optimization methodologies for stand-alone solar and wind hybrid renewable energy system. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;143:252–74.10.1016/j.enconman.2017.04.019Search in Google Scholar
[17] Askari IB, Ameri M. Techno-economic feasibility analysis of stand-alone renewable energy systems (PV/bat, Wind/bat and Hybrid PV/wind/bat) in Kerman, Iran. Energ Source Part B. 2012;7:45–60.10.1080/15567240903330384Search in Google Scholar
[18] Sreeraj E, Chatterjee K, Bandy Pathway S. Design of isolated renewable hybrid power systems. Sol Energy. 2010;84:1124–36.10.1016/j.solener.2010.03.017Search in Google Scholar
[19] Ghafoor A, Munir A. Design and economics analysis of an off-grid PV system for household electrification renewable and sustainable. Energy Rev. 2015;42:496–502.10.1016/j.rser.2014.10.012Search in Google Scholar
[20] Wu YC, Chen MJ, Huang SH, Tsai MT, Li CH. Maximum power point tracking on stand-alone solar power system. Three-Point-Weighting Method Incorporating Mid-point Tracking. Electrical Power Energy System. Berline: DE Gruyter; 2013. p. 14–24.10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.03.008Search in Google Scholar
[21] Irwan YM, Amelia AR, Irwanto M, Fareq M, Leow WZ, Gomesh N, et al. Stand-alone photovoltaic (SAPV) system assessment using PVSYST software. International Conference on Alternative Energy in Developing Countries and Emerging Economies. Vol. 79, Berline: DE Gruyter; 2015. p. 596–603.10.1016/j.egypro.2015.11.539Search in Google Scholar
[22] Patra S, Kishor N, Mohanty SR, Ray PK. Power quality assessment in 3-U grid connected PV system with single and dual stage circuits. Electr Power Energy Syst. 2015;75:275–88.10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.09.014Search in Google Scholar
[23] Metwally HMB, Farahat MA. Performance analysis of 3.6 kW rooftop grid connected photovoltaic system Egypt. International Conference on Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST). Cairo, Egypt: Cyberleninka; 2011 March. p. 11–4.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Al-Waeli AH, Kazem HA, Chaichan T. Review and design of a stand-alone PV system performance. Int J Comput Appl Sci IJOCAAS. 2016 Aug 4;1(1):1–6.10.24842/1611/0001Search in Google Scholar
[25] Ajao KR, Oladosu OA, Pocola OT. Using HOMER power optimization software for cost benefit analysis of hybrid-solar power generation relative to utility cost in Nigeria. IJRRAS. 2011;7:96–102.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Chaichan MT, Mohammed BA, Kazem HA. Effect of pollution and cleaning on photovoltaic performance based on experimental study. Int J Sci Eng Res. 2015 Apr;6(4):594–601.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Abed FM, Al-Douri Y, Al-Shahery GMY. Review on the energy and renewable energy status in Iraq: the outlooks. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;39:816–27.10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.026Search in Google Scholar
[28] Alamsyah T, Sopian K, Shahrir A. Techno economics analysis of a photovoltaic system to provide electricity for a household in Malaysia. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Renewable Energy: Environment Protection Energy Solution for Sustainable Development, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Belgium: European Alliance for Innovation; 2003. p. 387–96.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Hamoodi SA, Hameed FI, Hamoodi AN. Pitch angle control of wind turbine using adaptive Fuzzy-PID controller. Mosul, Iraq: Northern Technical University (NTU), Engineering Technical College, EAI endorsed transactions on energy web; 2020 Jul. 7. p. 1–8.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Hamoodi SA, Hamoodi AN, Haydar GM. Automated Irrig Syst based soil moisture using arduino board. Bulletin of electrical engineering and informatics. Iraq: Northeren Technical University (NTU), Engineering Technical College; 2020 June 3. p. 870–6.10.11591/eei.v9i3.1736Search in Google Scholar
[31] Hamoodi AN, Hamoodi SA, Mohammed RA. Photovoltaic modeling and effecting of temperature and irradiation on I–V and P–V characteristics. Northeren Technical University (NTU), Engineering Technical College, Iraq. Int J Appl Eng Res Res India Publ. 2018;13(5):3123–7. http://www.ripublication.comSearch in Google Scholar
[32] Hamoodi AN, Hamoodi SA, Ibrahim MA. “Power factor correction of AC to DC converter using boost chopper”. Northeren Technical University (NTU), Engineering Technical College, Iraq. J Eng Appl Sci. 2018;13(Special Issue 8):6440–5.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Hamoodi AN, Hamoodi SA, Abdulla AG. “Photovoltaic-battery system tested under sun irradiance”. Northeren Technical University (NTU), Engineering Technical College, Iraq. Lond J Eng Res. 2018;18(2):65–75.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Rasha A. Mohammed et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical studies of the synergistic combination effect of thymus mastichina and illicium verum essential oil extracts on the corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in dilute acid solution
- Adoption of Business Intelligence to Support Cost Accounting Based Financial Systems — Case Study of XYZ Company
- Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis of a Hybrid Renewable Energy Supply Options for University Buildings in Saudi Arabia
- Optimized design of a semimetal gasket operating in flange-bolted joints
- Behavior of non-reinforced and reinforced green mortar with fibers
- Field measurement of contact forces on rollers for a large diameter pipe conveyor
- Development of Smartphone-Controlled Hand and Arm Exoskeleton for Persons with Disability
- Investigation of saturation flow rate using video camera at signalized intersections in Jordan
- The features of Ni2MnIn polycrystalline Heusler alloy thin films formation by pulsed laser deposition
- Selection of a workpiece clamping system for computer-aided subtractive manufacturing of geometrically complex medical models
- Development of Solar-Powered Water Pump with 3D Printed Impeller
- Identifying Innovative Reliable Criteria Governing the Selection of Infrastructures Construction Project Delivery Systems
- Kinetics of Carbothermal Reduction Process of Different Size Phosphate Rocks
- Plastic forming processes of transverse non-homogeneous composite metallic sheets
- Accelerated aging of WPCs Based on Polypropylene and Birch plywood Sanding Dust
- Effect of water flow and depth on fatigue crack growth rate of underwater wet welded low carbon steel SS400
- Non-invasive attempts to extinguish flames with the use of high-power acoustic extinguisher
- Filament wound composite fatigue mechanisms investigated with full field DIC strain monitoring
- Structural Timber In Compartment Fires – The Timber Charring and Heat Storage Model
- Technical and economic aspects of starting a selected power unit at low ambient temperatures
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Adaptation to driver-assistance systems depending on experience
- A SIMULINK implementation of a vector shift relay with distributed synchronous generator for engineering classes
- Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in a static tensile test
- Errors in documenting the subsoil and their impact on the investment implementation: Case study
- Comparison between two calculation methods for designing a stand-alone PV system according to Mosul city basemap
- Reduction of transport-related air pollution. A case study based on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the level of NOx emissions in the city of Krakow
- Driver intervention performance assessment as a key aspect of L3–L4 automated vehicles deployment
- A new method for solving quadratic fractional programming problem in neutrosophic environment
- Effect of fish scales on fabrication of polyester composite material reinforcements
- Impact of the operation of LNG trucks on the environment
- The effectiveness of the AEB system in the context of the safety of vulnerable road users
- Errors in controlling cars cause tragic accidents involving motorcyclists
- Deformation of designed steel plates: An optimisation of the side hull structure using the finite element approach
- Thermal-strength analysis of a cross-flow heat exchanger and its design improvement
- Effect of thermal collector configuration on the photovoltaic heat transfer performance with 3D CFD modeling
- Experimental identification of the subjective reception of external stimuli during wheelchair driving
- Failure analysis of motorcycle shock breakers
- Experimental analysis of nonlinear characteristics of absorbers with wire rope isolators
- Experimental tests of the antiresonance vibratory mill of a sectional movement trajectory
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of CVT rubber belt vibrations
- Is the cubic parabola really the best railway transition curve?
- Transport properties of the new vibratory conveyor at operations in the resonance zone
- Assessment of resistance to permanent deformations of asphalt mixes of low air void content
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Review Articles
- FMEA method in operational reliability of forest harvesters
- Examination of preferences in the field of mobility of the city of Pila in terms of services provided by the Municipal Transport Company in Pila
- Enhancement stability and color fastness of natural dye: A review
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019 - Part II
- Lane Departure Warning Estimation Using Yaw Acceleration
- Analysis of EMG Signals during Stance and Swing Phases for Controlling Magnetorheological Brake applications
- Sensor Number Optimization Using Neural Network for Ankle Foot Orthosis Equipped with Magnetorheological Brake
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering - Part II
- Comparison of STM’s reliability system on the example of selected element
- Technical analysis of the renovation works of the wooden palace floors
- Special Issue: TRANSPORT 2020
- Simulation assessment of the half-power bandwidth method in testing shock absorbers
- Predictive analysis of the impact of the time of day on road accidents in Poland
- User’s determination of a proper method for quantifying fuel consumption of a passenger car with compression ignition engine in specific operation conditions
- Analysis and assessment of defectiveness of regulations for the yellow signal at the intersection
- Streamlining possibility of transport-supply logistics when using chosen Operations Research techniques
- Permissible distance – safety system of vehicles in use
- Study of the population in terms of knowledge about the distance between vehicles in motion
- UAVs in rail damage image diagnostics supported by deep-learning networks
- Exhaust emissions of buses LNG and Diesel in RDE tests
- Measurements of urban traffic parameters before and after road reconstruction
- The use of deep recurrent neural networks to predict performance of photovoltaic system for charging electric vehicles
- Analysis of dangers in the operation of city buses at the intersections
- Psychological factors of the transfer of control in an automated vehicle
- Testing and evaluation of cold-start emissions from a gasoline engine in RDE test at two different ambient temperatures
- Age and experience in driving a vehicle and psychomotor skills in the context of automation
- Consumption of gasoline in vehicles equipped with an LPG retrofit system in real driving conditions
- Laboratory studies of the influence of the working position of the passenger vehicle air suspension on the vibration comfort of children transported in the child restraint system
- Route optimization for city cleaning vehicle
- Efficiency of electric vehicle interior heating systems at low ambient temperatures
- Model-based imputation of sound level data at thoroughfare using computational intelligence
- Research on the combustion process in the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine fueled with rapeseed methyl esters
- Overview of the method and state of hydrogenization of road transport in the world and the resulting development prospects in Poland
- Tribological characteristics of polymer materials used for slide bearings
- Car reliability analysis based on periodic technical tests
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019 - Part II
- DOE Application for Analysis of Tribological Properties of the Al2O3/IF-WS2 Surface Layers
- The effect of the impurities spaces on the quality of structural steel working at variable loads
- Prediction of the parameters and the hot open die elongation forging process on an 80 MN hydraulic press
- Special Issue: AEVEC 2020
- Vocational Student's Attitude and Response Towards Experiential Learning in Mechanical Engineering
- Virtual Laboratory to Support a Practical Learning of Micro Power Generation in Indonesian Vocational High Schools
- The impacts of mediating the work environment on the mode choice in work trips
- Utilization of K-nearest neighbor algorithm for classification of white blood cells in AML M4, M5, and M7
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Case study: Vocational student’s knowledge and awareness level toward renewable energy in Indonesia
- Contribution of collaborative skill toward construction drawing skill for developing vocational course
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part II
- Vocational teachers’ perspective toward Technological Pedagogical Vocational Knowledge
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part I
- Profile of system and product certification as quality infrastructure in Indonesia
- Prediction Model of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluid Damper Hysteresis Loop using Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
- A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters
- Facile rheological route method for LiFePO4/C cathode material production
- Mosque design strategy for energy and water saving
- Epoxy resins thermosetting for mechanical engineering
- Estimating the potential of wind energy resources using Weibull parameters: A case study of the coastline region of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
- Special Issue: CIRMARE 2020
- New trends in visual inspection of buildings and structures: Study for the use of drones
- Special Issue: ISERT 2021
- Alleviate the contending issues in network operating system courses: Psychomotor and troubleshooting skill development with Raspberry Pi
- Special Issue: Actual Trends in Logistics and Industrial Engineering - Part II
- The Physical Internet: A means towards achieving global logistics sustainability
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part I
- Construction work cost and duration analysis with the use of agent-based modelling and simulation
- Corrosion rate measurement for steel sheets of a fuel tank shell being in service
- The influence of external environment on workers on scaffolding illustrated by UTCI
- Allocation of risk factors for geodetic tasks in construction schedules
- Pedestrian fatality risk as a function of tram impact speed
- Technological and organizational problems in the construction of the radiation shielding concrete and suggestions to solve: A case study
- Finite element analysis of train speed effect on dynamic response of steel bridge
- New approach to analysis of railway track dynamics – Rail head vibrations
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part I
- Design of production lines and logistic flows in production
- The planning process of transport tasks for autonomous vans
- Modeling of the two shuttle box system within the internal logistics system using simulation software
- Implementation of the logistics train in the intralogistics system: A case study
- Assessment of investment in electric buses: A case study of a public transport company
- Assessment of a robot base production using CAM programming for the FANUC control system
- Proposal for the flow of material and adjustments to the storage system of an external service provider
- The use of numerical analysis of the injection process to select the material for the injection molding
- Economic aspect of combined transport
- Solution of a production process with the application of simulation: A case study
- Speedometer reliability in regard to road traffic sustainability
- Design and construction of a scanning stand for the PU mini-acoustic sensor
- Utilization of intelligent vehicle units for train set dispatching
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part I
- LVRT enhancement of DFIG-driven wind system using feed-forward neuro-sliding mode control
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part I
- Prediction of future paths of mobile objects using path library
- Model predictive control for a multiple injection combustion model
- Model-based on-board post-injection control development for marine diesel engine
- Intelligent temporal analysis of coronavirus statistical data
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical studies of the synergistic combination effect of thymus mastichina and illicium verum essential oil extracts on the corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in dilute acid solution
- Adoption of Business Intelligence to Support Cost Accounting Based Financial Systems — Case Study of XYZ Company
- Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis of a Hybrid Renewable Energy Supply Options for University Buildings in Saudi Arabia
- Optimized design of a semimetal gasket operating in flange-bolted joints
- Behavior of non-reinforced and reinforced green mortar with fibers
- Field measurement of contact forces on rollers for a large diameter pipe conveyor
- Development of Smartphone-Controlled Hand and Arm Exoskeleton for Persons with Disability
- Investigation of saturation flow rate using video camera at signalized intersections in Jordan
- The features of Ni2MnIn polycrystalline Heusler alloy thin films formation by pulsed laser deposition
- Selection of a workpiece clamping system for computer-aided subtractive manufacturing of geometrically complex medical models
- Development of Solar-Powered Water Pump with 3D Printed Impeller
- Identifying Innovative Reliable Criteria Governing the Selection of Infrastructures Construction Project Delivery Systems
- Kinetics of Carbothermal Reduction Process of Different Size Phosphate Rocks
- Plastic forming processes of transverse non-homogeneous composite metallic sheets
- Accelerated aging of WPCs Based on Polypropylene and Birch plywood Sanding Dust
- Effect of water flow and depth on fatigue crack growth rate of underwater wet welded low carbon steel SS400
- Non-invasive attempts to extinguish flames with the use of high-power acoustic extinguisher
- Filament wound composite fatigue mechanisms investigated with full field DIC strain monitoring
- Structural Timber In Compartment Fires – The Timber Charring and Heat Storage Model
- Technical and economic aspects of starting a selected power unit at low ambient temperatures
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Adaptation to driver-assistance systems depending on experience
- A SIMULINK implementation of a vector shift relay with distributed synchronous generator for engineering classes
- Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in a static tensile test
- Errors in documenting the subsoil and their impact on the investment implementation: Case study
- Comparison between two calculation methods for designing a stand-alone PV system according to Mosul city basemap
- Reduction of transport-related air pollution. A case study based on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the level of NOx emissions in the city of Krakow
- Driver intervention performance assessment as a key aspect of L3–L4 automated vehicles deployment
- A new method for solving quadratic fractional programming problem in neutrosophic environment
- Effect of fish scales on fabrication of polyester composite material reinforcements
- Impact of the operation of LNG trucks on the environment
- The effectiveness of the AEB system in the context of the safety of vulnerable road users
- Errors in controlling cars cause tragic accidents involving motorcyclists
- Deformation of designed steel plates: An optimisation of the side hull structure using the finite element approach
- Thermal-strength analysis of a cross-flow heat exchanger and its design improvement
- Effect of thermal collector configuration on the photovoltaic heat transfer performance with 3D CFD modeling
- Experimental identification of the subjective reception of external stimuli during wheelchair driving
- Failure analysis of motorcycle shock breakers
- Experimental analysis of nonlinear characteristics of absorbers with wire rope isolators
- Experimental tests of the antiresonance vibratory mill of a sectional movement trajectory
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of CVT rubber belt vibrations
- Is the cubic parabola really the best railway transition curve?
- Transport properties of the new vibratory conveyor at operations in the resonance zone
- Assessment of resistance to permanent deformations of asphalt mixes of low air void content
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Review Articles
- FMEA method in operational reliability of forest harvesters
- Examination of preferences in the field of mobility of the city of Pila in terms of services provided by the Municipal Transport Company in Pila
- Enhancement stability and color fastness of natural dye: A review
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019 - Part II
- Lane Departure Warning Estimation Using Yaw Acceleration
- Analysis of EMG Signals during Stance and Swing Phases for Controlling Magnetorheological Brake applications
- Sensor Number Optimization Using Neural Network for Ankle Foot Orthosis Equipped with Magnetorheological Brake
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering - Part II
- Comparison of STM’s reliability system on the example of selected element
- Technical analysis of the renovation works of the wooden palace floors
- Special Issue: TRANSPORT 2020
- Simulation assessment of the half-power bandwidth method in testing shock absorbers
- Predictive analysis of the impact of the time of day on road accidents in Poland
- User’s determination of a proper method for quantifying fuel consumption of a passenger car with compression ignition engine in specific operation conditions
- Analysis and assessment of defectiveness of regulations for the yellow signal at the intersection
- Streamlining possibility of transport-supply logistics when using chosen Operations Research techniques
- Permissible distance – safety system of vehicles in use
- Study of the population in terms of knowledge about the distance between vehicles in motion
- UAVs in rail damage image diagnostics supported by deep-learning networks
- Exhaust emissions of buses LNG and Diesel in RDE tests
- Measurements of urban traffic parameters before and after road reconstruction
- The use of deep recurrent neural networks to predict performance of photovoltaic system for charging electric vehicles
- Analysis of dangers in the operation of city buses at the intersections
- Psychological factors of the transfer of control in an automated vehicle
- Testing and evaluation of cold-start emissions from a gasoline engine in RDE test at two different ambient temperatures
- Age and experience in driving a vehicle and psychomotor skills in the context of automation
- Consumption of gasoline in vehicles equipped with an LPG retrofit system in real driving conditions
- Laboratory studies of the influence of the working position of the passenger vehicle air suspension on the vibration comfort of children transported in the child restraint system
- Route optimization for city cleaning vehicle
- Efficiency of electric vehicle interior heating systems at low ambient temperatures
- Model-based imputation of sound level data at thoroughfare using computational intelligence
- Research on the combustion process in the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine fueled with rapeseed methyl esters
- Overview of the method and state of hydrogenization of road transport in the world and the resulting development prospects in Poland
- Tribological characteristics of polymer materials used for slide bearings
- Car reliability analysis based on periodic technical tests
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019 - Part II
- DOE Application for Analysis of Tribological Properties of the Al2O3/IF-WS2 Surface Layers
- The effect of the impurities spaces on the quality of structural steel working at variable loads
- Prediction of the parameters and the hot open die elongation forging process on an 80 MN hydraulic press
- Special Issue: AEVEC 2020
- Vocational Student's Attitude and Response Towards Experiential Learning in Mechanical Engineering
- Virtual Laboratory to Support a Practical Learning of Micro Power Generation in Indonesian Vocational High Schools
- The impacts of mediating the work environment on the mode choice in work trips
- Utilization of K-nearest neighbor algorithm for classification of white blood cells in AML M4, M5, and M7
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Case study: Vocational student’s knowledge and awareness level toward renewable energy in Indonesia
- Contribution of collaborative skill toward construction drawing skill for developing vocational course
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part II
- Vocational teachers’ perspective toward Technological Pedagogical Vocational Knowledge
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part I
- Profile of system and product certification as quality infrastructure in Indonesia
- Prediction Model of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluid Damper Hysteresis Loop using Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
- A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters
- Facile rheological route method for LiFePO4/C cathode material production
- Mosque design strategy for energy and water saving
- Epoxy resins thermosetting for mechanical engineering
- Estimating the potential of wind energy resources using Weibull parameters: A case study of the coastline region of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
- Special Issue: CIRMARE 2020
- New trends in visual inspection of buildings and structures: Study for the use of drones
- Special Issue: ISERT 2021
- Alleviate the contending issues in network operating system courses: Psychomotor and troubleshooting skill development with Raspberry Pi
- Special Issue: Actual Trends in Logistics and Industrial Engineering - Part II
- The Physical Internet: A means towards achieving global logistics sustainability
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part I
- Construction work cost and duration analysis with the use of agent-based modelling and simulation
- Corrosion rate measurement for steel sheets of a fuel tank shell being in service
- The influence of external environment on workers on scaffolding illustrated by UTCI
- Allocation of risk factors for geodetic tasks in construction schedules
- Pedestrian fatality risk as a function of tram impact speed
- Technological and organizational problems in the construction of the radiation shielding concrete and suggestions to solve: A case study
- Finite element analysis of train speed effect on dynamic response of steel bridge
- New approach to analysis of railway track dynamics – Rail head vibrations
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part I
- Design of production lines and logistic flows in production
- The planning process of transport tasks for autonomous vans
- Modeling of the two shuttle box system within the internal logistics system using simulation software
- Implementation of the logistics train in the intralogistics system: A case study
- Assessment of investment in electric buses: A case study of a public transport company
- Assessment of a robot base production using CAM programming for the FANUC control system
- Proposal for the flow of material and adjustments to the storage system of an external service provider
- The use of numerical analysis of the injection process to select the material for the injection molding
- Economic aspect of combined transport
- Solution of a production process with the application of simulation: A case study
- Speedometer reliability in regard to road traffic sustainability
- Design and construction of a scanning stand for the PU mini-acoustic sensor
- Utilization of intelligent vehicle units for train set dispatching
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part I
- LVRT enhancement of DFIG-driven wind system using feed-forward neuro-sliding mode control
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part I
- Prediction of future paths of mobile objects using path library
- Model predictive control for a multiple injection combustion model
- Model-based on-board post-injection control development for marine diesel engine
- Intelligent temporal analysis of coronavirus statistical data

