Abstract
Four different configurations of a mass supporting system consisting of a few prototypes of wire rope isolators are considered in the article. These are named “triangle,” “star,” “parallel,” and “serial” configurations. Reasonable models of a fixture assembly that could be utilized as models for cargo transportation are tested statically and dynamically in the laboratory. The main aim of this study is to investigate the impact of the configuration of damper settings on the effectiveness of vibration and shock isolation (in three directions) and to develop a suitable method to determine nonlinear properties and stiffness characteristics of the tested system. The purpose is also to investigate the sensitivity of the tested systems on the eccentricity of vertical loads and its influence on identification results. Experiments are carried out on the specially designed stand for the model parameters identification.
1 Introduction
Wire rope isolators are commonly used to eliminate vibrations of various origins. They are successfully used to reduce the level of vibrations and shocks, for example, in the transport of sensitive devices, in aviation systems, and in vibration isolation of small and large building structures. Wire rope isolators, compared to other types of dampers, are distinguished by their simple construction and low failure rate. Multiple wire rope dampers are often arranged in different configurations and are used to obtain the desired damping effects. The operational requirements for shock absorbers with damping rope elements are similar to those for other types of passive vibro-isolators and are related to their functionality, reliability, and durability in the foreseen operating conditions and the assumed operating time.
In car and rail transport devices, active and semiactive dampers are increasingly used, based, for example, on the use of magneto-rheological fluids in control systems [1,2,3], whose characteristics self-adjust to a type of the driven road surface. However, due to a considerably more complex construction, they are more expensive in production and exploitation than passive shock absorbers. For these reasons, manufacturers develop new design solutions for passive shock absorbers, whose characteristics possess similar properties as in the case of active shock absorbers. One of such designs is the hydraulic damper with an additional flow channel (bypass), controlled by a relative displacement of the piston [4,5]. Another example would be a damper having an additional inner cylinder in which the oil flow is controlled by the displacement of the auxiliary piston [6]. Due to such modifications, the nature of damping force characteristics changes from a hard one to a soft one, depending on the amplitude and frequency of excitation.
One of the main criteria for the selection of a shock absorber – also a linear one – is the criterion based on the natural vibration frequency and the assumed fundamental excitation frequency. Tinker and Cutchins [7] propose a semiempirical model having nonlinear stiffness, nth-power velocity damping, and variable Coulomb friction damping for wire rope isolators. The authors compare the obtained results to experimental data, determining static stiffness curves, hysteresis curves, phase trajectories, and frequency response curves. On the basis of the analysis, Tinker and Cutchins [7] prove that the energy dissipated due to the damping increases with increased excitation amplitude. Balaji et al. [8] investigate the influence of wire rope isolator operation configuration on the damping efficiency. The authors utilize the harmonic signal of excitation with a constant amplitude for different values of the frequency. The influence of dampers load magnitude on the behavior of the system is also analyzed. However, the study [9] by Balaji et al. investigated the vertical static stiffness of circular vibration isolators. Experimental tests are carried out on a testing machine, both in compression and stretching of the vibro-isolator along its vertical axis. The authors determine the influence of geometric parameters of a circular vibration isolator on its stiffness characteristics. The hysteretic behavior of wire rope isolators, due to interwire friction and geometric nonlinearities, is investigated experimentally and numerically by Salvatore et al. [10]. In an earlier study [11], Vaiana et al. propose a novel rate-independent model to predict the hysteretic response of wire rope isolators along their two principal transverse directions, namely roll and shear directions. However, in an another study [12], Vaiana et al. conducted a series of dynamic tests to enable the use of wire rope isolators (WRIs) for seismic protection of lightweight structures.
Despite the large number of studies that present the characteristics of wire rope dampers [13,14,15,16], only limited articles are available describing the influence of the mutual interaction of a set of dampers on the effectiveness of vibration damping with different directional configurations of vibration isolators. In the available research, models that are most often tested consist only of one damper [9,13]. The catalogs provide information on where to place the dampers, but there is no information about the directional influence of their setting. In this article, based on previous experimental studies, it is proved that the manner of setting the wire rope dampers – their directionality – influences on the effectiveness of vibration damping. Therefore, four configurations of a few prototypes of wire rope isolators, “triangle,” “star,” “parallel,” and “serial,” are considered in this study. The stiffness characteristics of the tested system are also determined, and the sensitivity of the system to the eccentricity of vertical loads and its influence on the identification results are investigated.
2 A prototype of the wire rope isolator
Wire rope isolators are often designed as a system of two parallel plates fitted with stainless steel wire rope coils. From the theoretical point of view, it is interesting if existing models of known wire rope isolators are good enough for solving combined engineering problems. The Bouc–Wen model and its various modifications are generally used for the modeling of symmetrical hysteretic behaviors [13,17,18,19]. The shape of hysteresis depends on primary isolator parameters such as the rope material, its diameter, the number of wire rope coils, and a type of rope lay. The real influence on hysteresis has also friction appearing between cables creating main rope lay.
There were designed and made some prototypes of wire rope isolators to carry out some identification tests in the laboratory conditions. All parts of tested wire rope isolators and the assembly were fabricated at the laboratory workshop of Cracow University of Technology. It was decided to utilize standard flexible steel wire rope DIN 3055 ϕ3 mm 6 × 7 + FC. Prototypes are nontypically equipped with supplementary plates to which are perpendicularly welded threaded rods. Supplementary plates are fitted by means of screw joints to the essential system of wire rope isolator. There was assumed that such assembly should enable stabilization and lateral vibro-isolation of high overall dimension cargos when it would be required to apply a special configuration of isolators. A chosen, one of rope isolator prototypes, is shown in Figure 1.

A prototype of wire rope isolator.
There was a special assembly, each consisting of three wire rope isolator prototypes for the determination of nonlinear properties of wire dampers and for the analysis of influences of their configurations on vibration isolation effectiveness. Figure 2 shows two different configurations, namely “triangle” (Figure 2a) and “star” (Figure 2b).

Configuration sets: (a) “triangle” and (b) “star.”
The assembly consists of two rigid steel circular plates, each of 10 mm thickness, ϕ198 mm diameter, and mass of 2.30 kg. Circular plates are screw joined with three or two wire rope isolator prototypes at different configurations. This assembly enables the realization of static and dynamic tests at variable, simple, or combined loads. In the case of dynamic investigations, the lower plate is fixed to the core of electrodynamic exciter through six stud-bolts. The upper plate states a kind of truss joint, which rigidly fastens the upper pins of isolator prototypes. The upper plate has to be treated, of course, as a preliminary loading mass for investigated isolator sets. In the center of the upper plate is located a hole of ϕ 8.2 mm diameter drilled for a calibrated stud-bolt, which is to enable rigidly fastening additional loading masses. During the assembly of each configuration sets of wire rope isolator prototypes, there was carrying out carefully leveling process. It ought to assure that surfaces of the upper and the lower plates are in parallel.
3 Experimental studies
3.1 Description of the stands
Two experimental stands were designed to find out whether the directional arrangement of isolator prototypes influences on the effectiveness of vibration damping. These two stands are intended to carry out planned quasi-static tests and dynamical tests as well.
Typical static stiffness characteristics in vertical direction can be obtained at the stand presented in Figure 3, but the instrumentation used at the stand enables broader range of investigations such as lateral deflections. According to the narrow range of planned tests of isolator set deflections, it was decided to apply the precision laser displacement sensor LD 1605-20 for measurements. It holds a linear characteristic through the measurement range (−10 mm to +10 mm) with a resolution of 6 µm.
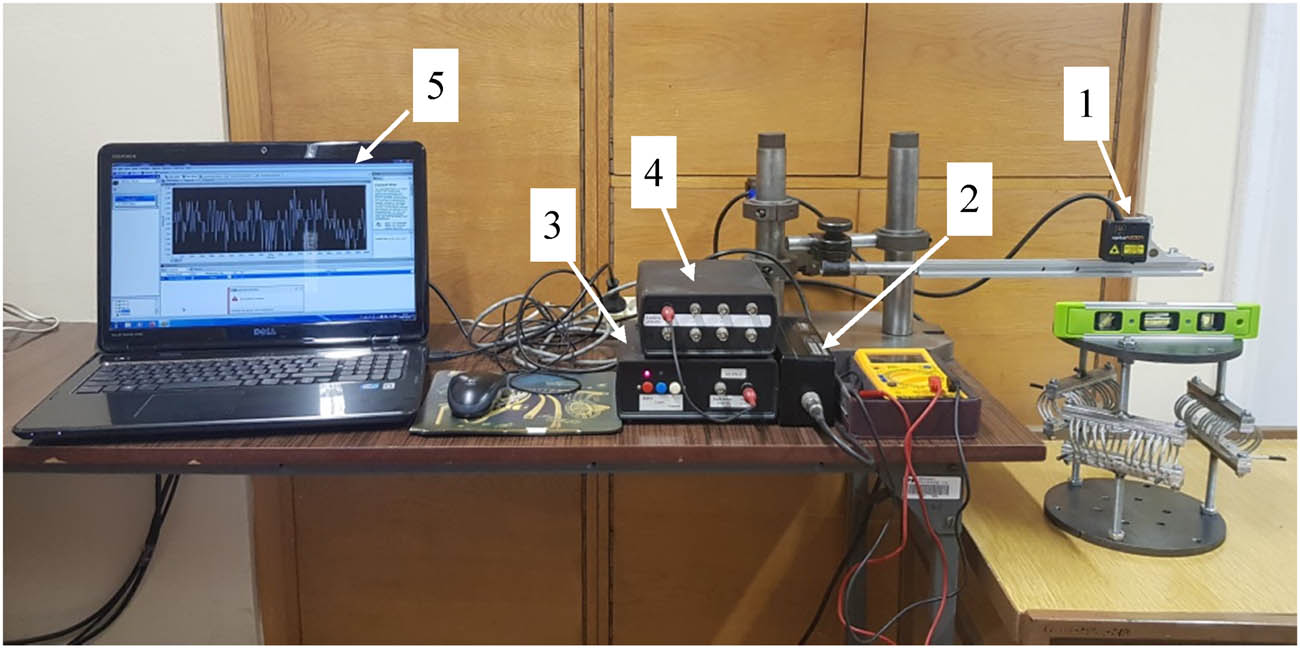

Stand for static characteristic investigations: (1) laser, (2) laser conditioner, (3) laser power supply, (4) converter card, and (5) computer.
For dynamic measurements, the electrodynamic exciter of TIRA vib type that was mounted into the rigid steel frame anchored to the foundation concrete block was utilized (Figure 4). The exciter enables the generation of vertical vibration up to acceleration a pk = 110/ms2 at a displacement amplitude up to x pk = 25.4 mm and frequency to 4.5 kHz. On the input of exciter, the power amplifier was led control signal from arbitrary generator Rigol DG2022. There were used triple-axis MEMS accelerometers of ADXL 325 analog type that outputs signals after antialiasing filtration were led to the inputs of A/D converter card NI-USB 6009. Digitized voltage signals from accelerometers were recorded in the measurement computer using the Signal Express from LabView programs.

Stand and instrumentation for dynamic measurements: (1) electrodynamic exciter, (2) generator, (3) power amplifier and exciter power supply, (4) accelerometers, (5) converter card, and (6) computer.
3.2 Static tests on different wire rope isolator configurations
There were considered different configurations of protected masssupport in order to investigate the influence of directional arrangement of isolators on effectiveness of vibration damping. First, two configurations, “triangle” and “star,” each consisting of three wire rope isolator prototypes, as it was shown in Figure 2, were gradually uploaded and then unloaded. Many tests were performed in different ranges of loads to derive static characteristics of isolator arrangements. For instance, during the test_12 presented in Figure 5, following masses were added in sequence: 5.88, 1, 0.94, 0.76, 0.74 kg, and then they were removed in the reverse order.
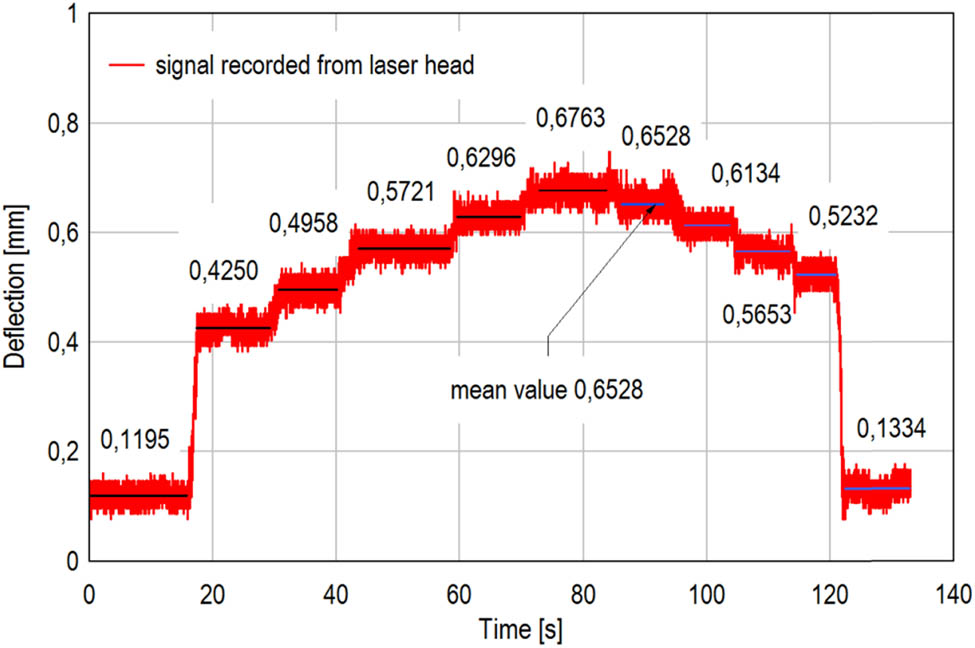
Deflection of upper plate vs time recorded during sequential uploading and unloading of upper plate of stand; “triangle” configuration of three isolators at the test_12.
Figure 5 presents an example of deflection estimation based on signal recorded by displacement sensor laser head for “triangle” configuration of three isolators at the test_12. The mean values corresponding to the each level of load were estimated as averages of laser head indications by using least square method (LSM). It can be observed that during removing successive masses (i.e., decreasing the whole load), the upper plate rarely return to its previous position. This nonlinear phenomenon is typical for wire rope isolators, and the reason is occurrence of friction. In such case, characteristic of the relation between deflection of the tested isolator system and its load has a hysteresis loop shape. The internal area of a such hysteresis loop can be considered as a measure of quantity of friction in quasi-static load conditions but not in dynamical action.
Figure 6 shows a few exemplary hysteresis loops obtained in measurements for two configurations: “triangle” in Figure 6a and “star” in Figure 6b. Further, applying LSQ method was assigned average static stiffness characteristics shown in Figure 7.

Hysteresis loops acquired from gradually uploading and unloading tests for configurations: (a) “triangle” and (b) “star.”

Comparison of static stiffness characteristics for two configurations.
It can be noticed that the average of curves from tests in “star” configuration reaches higher quantities of deflections than the average from tests in “triangle” configuration at the same loadings. Hence, “star” configuration demonstrates lower stiffness in comparison to “triangle” configuration in the whole range of tests. Figures 6 and 7 prove that directional arrangement of wire rope isolator systems has influence on effectiveness of vibration damping.
3.2.1 Tests on configurations consisting of two isolators
The reasonable conclusion from the previous results referring to the effect of directional arrangement of isolator systems was to investigate how on compression stiffness of wire rope isolator systems influences lateral shear accompanying to free compression. Lateral shear and rolling phenomena appearing during free compression of wire rope isolators were further analyzed experimentally. In source literature where wire rope isolator compression tests have been broad described, the shear phenomenon influence is often omitted due to the testing stand construction that features one-directional loading pass as in strength testing machines. Contrary to test conditions described in many studies, in this paper are assumed conditions of free compression, which referred rather to investigate of combined stress states.
The aim of further investigations was to determine static and dynamic characteristics of two configuration, namely “parallel” and “serial”, each consisting of two isolators. It was assumed that Y axis of coordinates is parallel to the isolators of the central axes, and Z axis is perpendicular to the surfaces of the upper and the lower plates as shown in Figure 8.

Configuration sets: (a) “parallel” and (b) “serial.”
Similarly as in case of tests on “star” and “triangle” configurations, also during tests on “parallel” and “serial” configurations were observed displacements in lateral directions X and Y (beside the superior displacements in Z direction).
There were proposed and done a few different supplementary tests in order to precisely investigate the lateral shear effect. In the first it were measured displacements in lateral directions X and Y by laser sensor while the upper plate of the stand was under vertical down and up cyclic load test. A result of one of such a free compression cyclic tests is presented in chart in Figure 9.

Lateral displacement in Y direction at “parallel” configuration.
The different series of tests on “parallel” and “serial” configurations were connected with acquisition of measurement data during vertical gradual loading, whereas the influence of noncoaxiallity of loading was analyzed.
Figure 9 presents changes of the upper plate lateral displacements (along Y axis) perpendicular to the vertical loading direction Z during cyclic down and up 5 kg load tests carried out on “parallel” configuration of two wire rope isolators. Similar characteristics were obtained for the second lateral direction X, but the range of displacement changes was less than those for Y direction. It was additionally noticed that vertical, symmetry axis of the upper plate was subjected to a small angle deviation what can cause instability of the whole system in extreme case. Dangerous of loss of stability is greater for “serial” than for “parallel” configuration.
Figure 10 shows a comparison of displacements in vertical Z direction for two different configurations. The upper plate of the stand was loaded by masses in the following order: 5.88, 2.27, 1.35, 1, 0.94, 0.76, 0.74, and 0.49 kg. It can be noticed that at “serial” configuration, a set of isolators increasing the vertical displacement is higher than those at “parallel” configuration. In addition, in case of “serial” configuration, after adding the mass of 0.94 kg, the loss of stability occurred.

Vertical displacements in Z direction at two configurations.
We also investigated the influence of noncoaxial upper plate sequential loading on static stiffness characteristics. Quantity of measured permissible noncoaxiallity was changed by choosing clearance between load-center pin and diameters of holes inside the loading masses. The clearance was selected between limits 0.25 and 1 mm. It was established that the clearance about 0.3 mm ensures enough repeatability of measurement results.
Only “parallel” configuration of two isolators was further considered. There were determined hysteresis loops to identify average static stiffness characteristics similarly as before for “star” and “triangle” configurations but previously consisting of three isolators. The main reason for authors was looking for an answer for a question if it would be correct to apply additivity theorem to static stiffness measured in vertical direction despite identified lateral deflection influences. An exemplary hysteresis loop obtained in quasi-static successive uploading and unloading process carried out on “parallel” configuration of two isolators is presented in Figure 11. The identified average static stiffness characteristic was evaluated using LSQ method.

An exemplary hysteresis loop and identified static stiffness approximation of two wire rope isolator prototypes working in “parallel” configuration.
In engineering practice, it is required to compare static stiffness characteristics made for different configurations and different numbers of isolators in the same chart, considering the number of supporting isolators under the assumption that additivity property is acceptable. It was done here, and the result shown in Figure 12 is a sort of proof that such assumption was correct in case of using wire rope isolators.

Static stiffness characteristics are reduced in two-thirds, gained on the base of tests at “triangle” configuration and tests at “star” configuration in comparison to the characteristic measured in tests at “parallel” configuration consisting of two absorbers.
3.3 Characteristics determined in dynamic measurements
The primary aim of dynamic experiments was to identify dynamical parameters of chosen sets of wire rope isolator prototypes, taking into consideration modifications of the tests conditions. These applied and fixed conditions include step control of isolator loading, control of amplifier power at input of exciter, and little changes done in quantity of loading coaxiallity.
Figure 13 shows two sets of isolator prototypes mounted into the core of the electrodynamic exciter. Figure 14 (see left side) shows the “triangle” configuration of three isolators where a loading for the assembly states only the mass of the upper plate. The right side shows the “parallel” configuration of two isolators fully loaded.

Configuration sets: (a) “triangle” of three isolators and (b) “parallel” of two isolators.
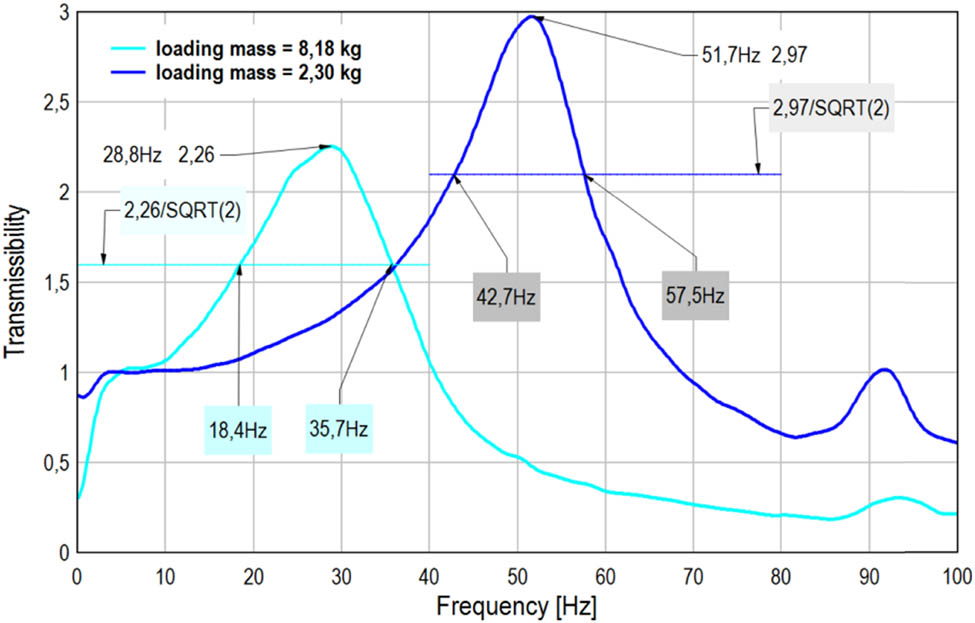
Transmissibility characteristic measured in Z direction; excitation sweep signal 1–300 Hz within 20 s.
An effectiveness of vibro-isolator action can be evaluated based on transmissibility characteristic introduced in frequency range. Tests were carried out on the stand using measurement facility as shown in Figure 4. An exemplary identification procedure of estimation of dynamical parameters of the set of three wire rope isolators working in, “triangle” configuration is shown in Figure 14. Transmissibility in this chart was determined using power spectral density (PSD) for output and input accelerations measured in Z vertical direction.
According to the fact that sweep signal from arbitrary generator was used as an excitation input signal, it was required to check whether frequency of the response acceleration signal would be also linearly variable. It can be proven by applying short time frequency analysis to the response acceleration signal, the result in form of waterfall FFT with spectrogram is shown in Figure 15.

Waterfall FFT and spectrogram obtained from the response acceleration signal measured in Z direction from one of the tests at “parallel” configuration; excitation sweep signal 1–100 Hz within 30 s.
Table 1 shows the values of the parameters determined with the use of the characteristics from Figure 14, where m – loading mass (kg), f res – resonant frequency (Hz), f u, f l – upper and lower frequency (Hz) designated for average time T av, δ – coefficient of internal friction, and C d – dynamical stiffness (N/m). The parameters are defined by the following formulae:
Values of the parameters determined from Figure 14
| No. | m (kg) | f res (Hz) | f u (Hz) | f l (Hz) | Δf (Hz) | δ | C d (N/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark blue chart | 2.30 | 51.7 | 57.5 | 42.7 | 14.8 | 0.286 | 242,700 |
| Light blue chart | 8.18 | 28.8 | 35.7 | 18.4 | 17.3 | 0.600 | 267,860 |
Analysis of the chart in Figure 15 induces the inference that frequency of the response acceleration signal varies linearly just like in input excitation signal; thus transmissibility characteristics are valuable for searching dynamical parameters.
In the next dynamical analyses, the “parallel” isolator configuration by controlling of amplifier power at input of exciter and changing the period and frequency range of excitation sweep signal were investigated. Nine tests were carried out on “parallel” set loaded with 12 kg additive masses that give the whole loading acting on two isolators about 14.4 kg considering the mass of the upper plate and fasteners and centering elements.
Dynamic characteristics were determined by utilizing the excitation function in shape of sweep type, similarly as before. It was chosen sweep signal with 30 s period linear grow of frequency in ranges 1–200 Hz (Figure 16a) and 1–50 Hz (Figure 16b) and at fixed exciter amplifier parameters: voltage RMS amplitude of 4.5 V and current RMS amplitude of 1.4 A hence at power P RMS = 6.3 W.

Transmissibility characteristics (power at input of exciter 6.3 W): (a) excitation sweep signal 1–200 Hz within 30 s and (b) excitation sweep signal 1–50 Hz within 30 s.
Figure 16 shows transmissibility vs frequency relations drawn for three directions: X, Y, and Z where vertical Z is the main direction of kinematic excitation. Transmissibility in this chart was determined as previously using PSD relations for output and input accelerations measured simultaneously in X, Y, and Z directions using 3-D ADXL 325 accelerometers.
Analysis of obtained results indicates that first resonant frequency appears in X direction at a frequency of about 6.8 Hz and in Y direction at a frequency of 9.6 Hz and in Z direction at a frequency of 10.4–11 Hz. It can be deduced that decreasing the upper limit of frequency range at sweep signal from 200 (Figure 16a) to 50 Hz (Figure 16b) implies increasing of action time of the investigated sets in resonances. It has been noticed that this action time did not have essential influence on values of resonant frequencies.
There was an interesting question what kind of influence on dynamic characteristics of “parallel” configuration has the level of power at the input of the exciter. There were carried out a few tests by controlling of the amplifier power at the input of exciter in order to answer of this question. Figure 17 shows transmissibility characteristics drawn at fixed exciter amplifier parameters: voltage RMS amplitude of 7 V and current RMS amplitude of 2 A, hence at power P RMS = 14 W.

Transmissibility characteristics; excitation sweep signal 1–100 Hz within 30 s; power at input of exciter = 14 W.
By making a comparison between Figures 16 and 17, it can be noticed that over two times change in power rather slightly influences on character of curves – their mutual localization and has only a little influence on values of resonant frequencies and values of their ordinates. The first resonant frequencies measured in X, Y, and Z directions are moved to lower values.
4 Conclusion
The article presents an analysis of isolator systems made of two parallel steel plates connected with three or two wire rope isolator prototypes, set in various configurations. This assembly enables realization of static and dynamic tests at variable, simple, or combined loads. On the basis of a large number of tests and the determined characteristics, it has been proven that the directionality of the damper setting has an impact on the effectiveness of damping vibrations and shocks. The proper orientation of the wire rope dampers enables to reduce their number and obtaining the desired damping effect. It has been shown that the directional arrangement of wire rope isolators has a clear impact on the static stiffness of their configuration and thus on the effectiveness of vibration damping. The study has a practical aspect for engineers.
A properly adopted model of the whole isolator system additionally allows for a detailed study of the lateral shear and rolling phenomena appearing during free compression of wire rope isolators. The problem of shear and roll is rarely discussed in the available literature. Attention is drawn to the fact that the structural model of the isolator system must consider the possibility of loss of stability in the case of the lack of mass guidance in relation to the damper mounting into the basis.
The additivity property for the vertical static stiffness of wire rope isolators is experimentally proven, whereas for dynamic stiffness it can rather be considered as nonadditive quantity.
Some exemplary identification procedures of the estimation of dynamical parameters of the set of three or two wire rope isolator prototypes working in different configurations are also shown in the article.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Demir O, Keskin I, Cetin S. Modeling and control of a nonlinear half-vehicle suspension system: a hybrid fuzzy logic approach. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012;67(3):2139–51.10.1007/s11071-011-0135-ySearch in Google Scholar
[2] Prabakar RS, Sujatha C, Narayanan S. Response of a half-car model with optimal magnetorheological damper parameters. J Vib Control. 2016;22(3):784–98.10.1177/1077546314532300Search in Google Scholar
[3] Ferdek U, Łuczko J. Performance comparison of active and semi-active SMC and LQR regulators in a quarter-car model. J Theor Appl Mech. 2015;53(4):811–22.10.15632/jtam-pl.53.4.811Search in Google Scholar
[4] Ferdek U, Łuczko J. Nonlinear modeling and analysis of a shock absorber with a bypass. J Theor Appl Mech. 2018;56(3):615–29.10.15632/jtam-pl.56.3.615Search in Google Scholar
[5] Lee CT, Moon BY. Simulation and experimental validation of vehicle dynamic characteristics for displacement-sensitive shock absorber using fluid-flow modelling. Mech Syst Sig Process. 2006;20(2):373–88.10.1016/j.ymssp.2004.09.006Search in Google Scholar
[6] Łuczko J, Ferdek U. Nonlinear dynamics of a vehicle with a displacement-sensitive mono-tube shock absorber. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020;100(1):185–202.10.1007/s11071-020-05532-7Search in Google Scholar
[7] Tinker ML, Cutchins MA. Damping phenomena in a wire rope vibration isolation system. J Sound Vib. 1992;157(1):7–18.10.1016/0022-460X(92)90564-ESearch in Google Scholar
[8] Balaji PS, Moussa L, Rahaman ME, Tiong PLY, Ho LH, Adnan A. Performance study of wire rope isolators for vibration isolation equipment and structures. J Eng Applied Sci. 2016;11(18):11036–42.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Balaji PS, Moussa L, Khandoker N, Shyh TY, Rahman ME, Ho LH. Experimental study on vertical static stiffnesses of polycal wire rope isolators. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 217, Issue 1. Bristol, UK: IOP Publishing; 2017. p. 012032.10.1088/1757-899X/217/1/012032Search in Google Scholar
[10] Salvatore A, Carboni B, Chen LQ, Lacarbonara W. Nonlinear dynamic response of a wire rope isolator: Experiment, identification and validation. Eng Struct. 2021;238:112121.10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112121Search in Google Scholar
[11] Vaiana N, Marmo F, Sessa S, Rosati L. Modeling of the hysteretic behavior of wire rope isolators using a novel rate-independent model. Nonlinear dynamics of structures, systems and devices. Vol. 1. Cham: Springer; 2020. p. 309–17.10.1007/978-3-030-34713-0_31Search in Google Scholar
[12] Vaiana N, Spizzuoco M, Serino G. Wire rope isolators for seismically base-isolated lightweight structures: experimental characterization and mathematical modeling. Eng Struct. 2017;140:498–514.10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.02.057Search in Google Scholar
[13] Rashidi S, Ziaei-Rad S. Experimental and numerical vibration analysis of wire rope isolators under quasi-static and dynamic loadings. Eng Struct. 2017;148:328–39.10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.06.061Search in Google Scholar
[14] Leblouba M, Rahman ME, Barakat S. Behavior of polycal wire rope isolators subjected to large lateral deformations. Eng Struct. 2019;191:117–28.10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.04.039Search in Google Scholar
[15] Tu S, Lu X, Zhu X. Effect of structure parameters on polycal wire rope isolator stiffness-damping characteristics. Shock Vib. 2019;2019:1–10.10.1155/2019/4525798Search in Google Scholar
[16] Prost C, Abdelnour B. Influence and enhancement of damping properties of wire rope isolators for naval applications. Sound Vib. 2018;8:1–4.10.32604/sv.2018.03641Search in Google Scholar
[17] Carboni B, Lacarbonara W, Brewick PT, Masri SF. Dynamical response identification of a class of nonlinear hysteretic systems. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2018;29(13):2795–810.10.1177/1045389X18778792Search in Google Scholar
[18] Vaiana N, Sessa S, Marmo F, Rosati L. A class of uniaxial phenomenological models for simulating hysteretic phenomena in rate-independent mechanical systems and materials. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018;93(3):1647–69.10.1007/s11071-018-4282-2Search in Google Scholar
[19] Vaiana N, Sessa S, Rosati L. A generalized class of uniaxial rate-independent models for simulating asymmetric mechanical hysteresis phenomena. Mech Syst Sig Process. 2021;146:106984.10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106984Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Urszula Ferdek and Melania Dukała, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical studies of the synergistic combination effect of thymus mastichina and illicium verum essential oil extracts on the corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in dilute acid solution
- Adoption of Business Intelligence to Support Cost Accounting Based Financial Systems — Case Study of XYZ Company
- Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis of a Hybrid Renewable Energy Supply Options for University Buildings in Saudi Arabia
- Optimized design of a semimetal gasket operating in flange-bolted joints
- Behavior of non-reinforced and reinforced green mortar with fibers
- Field measurement of contact forces on rollers for a large diameter pipe conveyor
- Development of Smartphone-Controlled Hand and Arm Exoskeleton for Persons with Disability
- Investigation of saturation flow rate using video camera at signalized intersections in Jordan
- The features of Ni2MnIn polycrystalline Heusler alloy thin films formation by pulsed laser deposition
- Selection of a workpiece clamping system for computer-aided subtractive manufacturing of geometrically complex medical models
- Development of Solar-Powered Water Pump with 3D Printed Impeller
- Identifying Innovative Reliable Criteria Governing the Selection of Infrastructures Construction Project Delivery Systems
- Kinetics of Carbothermal Reduction Process of Different Size Phosphate Rocks
- Plastic forming processes of transverse non-homogeneous composite metallic sheets
- Accelerated aging of WPCs Based on Polypropylene and Birch plywood Sanding Dust
- Effect of water flow and depth on fatigue crack growth rate of underwater wet welded low carbon steel SS400
- Non-invasive attempts to extinguish flames with the use of high-power acoustic extinguisher
- Filament wound composite fatigue mechanisms investigated with full field DIC strain monitoring
- Structural Timber In Compartment Fires – The Timber Charring and Heat Storage Model
- Technical and economic aspects of starting a selected power unit at low ambient temperatures
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Adaptation to driver-assistance systems depending on experience
- A SIMULINK implementation of a vector shift relay with distributed synchronous generator for engineering classes
- Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in a static tensile test
- Errors in documenting the subsoil and their impact on the investment implementation: Case study
- Comparison between two calculation methods for designing a stand-alone PV system according to Mosul city basemap
- Reduction of transport-related air pollution. A case study based on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the level of NOx emissions in the city of Krakow
- Driver intervention performance assessment as a key aspect of L3–L4 automated vehicles deployment
- A new method for solving quadratic fractional programming problem in neutrosophic environment
- Effect of fish scales on fabrication of polyester composite material reinforcements
- Impact of the operation of LNG trucks on the environment
- The effectiveness of the AEB system in the context of the safety of vulnerable road users
- Errors in controlling cars cause tragic accidents involving motorcyclists
- Deformation of designed steel plates: An optimisation of the side hull structure using the finite element approach
- Thermal-strength analysis of a cross-flow heat exchanger and its design improvement
- Effect of thermal collector configuration on the photovoltaic heat transfer performance with 3D CFD modeling
- Experimental identification of the subjective reception of external stimuli during wheelchair driving
- Failure analysis of motorcycle shock breakers
- Experimental analysis of nonlinear characteristics of absorbers with wire rope isolators
- Experimental tests of the antiresonance vibratory mill of a sectional movement trajectory
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of CVT rubber belt vibrations
- Is the cubic parabola really the best railway transition curve?
- Transport properties of the new vibratory conveyor at operations in the resonance zone
- Assessment of resistance to permanent deformations of asphalt mixes of low air void content
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Review Articles
- FMEA method in operational reliability of forest harvesters
- Examination of preferences in the field of mobility of the city of Pila in terms of services provided by the Municipal Transport Company in Pila
- Enhancement stability and color fastness of natural dye: A review
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019 - Part II
- Lane Departure Warning Estimation Using Yaw Acceleration
- Analysis of EMG Signals during Stance and Swing Phases for Controlling Magnetorheological Brake applications
- Sensor Number Optimization Using Neural Network for Ankle Foot Orthosis Equipped with Magnetorheological Brake
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering - Part II
- Comparison of STM’s reliability system on the example of selected element
- Technical analysis of the renovation works of the wooden palace floors
- Special Issue: TRANSPORT 2020
- Simulation assessment of the half-power bandwidth method in testing shock absorbers
- Predictive analysis of the impact of the time of day on road accidents in Poland
- User’s determination of a proper method for quantifying fuel consumption of a passenger car with compression ignition engine in specific operation conditions
- Analysis and assessment of defectiveness of regulations for the yellow signal at the intersection
- Streamlining possibility of transport-supply logistics when using chosen Operations Research techniques
- Permissible distance – safety system of vehicles in use
- Study of the population in terms of knowledge about the distance between vehicles in motion
- UAVs in rail damage image diagnostics supported by deep-learning networks
- Exhaust emissions of buses LNG and Diesel in RDE tests
- Measurements of urban traffic parameters before and after road reconstruction
- The use of deep recurrent neural networks to predict performance of photovoltaic system for charging electric vehicles
- Analysis of dangers in the operation of city buses at the intersections
- Psychological factors of the transfer of control in an automated vehicle
- Testing and evaluation of cold-start emissions from a gasoline engine in RDE test at two different ambient temperatures
- Age and experience in driving a vehicle and psychomotor skills in the context of automation
- Consumption of gasoline in vehicles equipped with an LPG retrofit system in real driving conditions
- Laboratory studies of the influence of the working position of the passenger vehicle air suspension on the vibration comfort of children transported in the child restraint system
- Route optimization for city cleaning vehicle
- Efficiency of electric vehicle interior heating systems at low ambient temperatures
- Model-based imputation of sound level data at thoroughfare using computational intelligence
- Research on the combustion process in the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine fueled with rapeseed methyl esters
- Overview of the method and state of hydrogenization of road transport in the world and the resulting development prospects in Poland
- Tribological characteristics of polymer materials used for slide bearings
- Car reliability analysis based on periodic technical tests
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019 - Part II
- DOE Application for Analysis of Tribological Properties of the Al2O3/IF-WS2 Surface Layers
- The effect of the impurities spaces on the quality of structural steel working at variable loads
- Prediction of the parameters and the hot open die elongation forging process on an 80 MN hydraulic press
- Special Issue: AEVEC 2020
- Vocational Student's Attitude and Response Towards Experiential Learning in Mechanical Engineering
- Virtual Laboratory to Support a Practical Learning of Micro Power Generation in Indonesian Vocational High Schools
- The impacts of mediating the work environment on the mode choice in work trips
- Utilization of K-nearest neighbor algorithm for classification of white blood cells in AML M4, M5, and M7
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Case study: Vocational student’s knowledge and awareness level toward renewable energy in Indonesia
- Contribution of collaborative skill toward construction drawing skill for developing vocational course
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part II
- Vocational teachers’ perspective toward Technological Pedagogical Vocational Knowledge
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part I
- Profile of system and product certification as quality infrastructure in Indonesia
- Prediction Model of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluid Damper Hysteresis Loop using Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
- A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters
- Facile rheological route method for LiFePO4/C cathode material production
- Mosque design strategy for energy and water saving
- Epoxy resins thermosetting for mechanical engineering
- Estimating the potential of wind energy resources using Weibull parameters: A case study of the coastline region of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
- Special Issue: CIRMARE 2020
- New trends in visual inspection of buildings and structures: Study for the use of drones
- Special Issue: ISERT 2021
- Alleviate the contending issues in network operating system courses: Psychomotor and troubleshooting skill development with Raspberry Pi
- Special Issue: Actual Trends in Logistics and Industrial Engineering - Part II
- The Physical Internet: A means towards achieving global logistics sustainability
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part I
- Construction work cost and duration analysis with the use of agent-based modelling and simulation
- Corrosion rate measurement for steel sheets of a fuel tank shell being in service
- The influence of external environment on workers on scaffolding illustrated by UTCI
- Allocation of risk factors for geodetic tasks in construction schedules
- Pedestrian fatality risk as a function of tram impact speed
- Technological and organizational problems in the construction of the radiation shielding concrete and suggestions to solve: A case study
- Finite element analysis of train speed effect on dynamic response of steel bridge
- New approach to analysis of railway track dynamics – Rail head vibrations
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part I
- Design of production lines and logistic flows in production
- The planning process of transport tasks for autonomous vans
- Modeling of the two shuttle box system within the internal logistics system using simulation software
- Implementation of the logistics train in the intralogistics system: A case study
- Assessment of investment in electric buses: A case study of a public transport company
- Assessment of a robot base production using CAM programming for the FANUC control system
- Proposal for the flow of material and adjustments to the storage system of an external service provider
- The use of numerical analysis of the injection process to select the material for the injection molding
- Economic aspect of combined transport
- Solution of a production process with the application of simulation: A case study
- Speedometer reliability in regard to road traffic sustainability
- Design and construction of a scanning stand for the PU mini-acoustic sensor
- Utilization of intelligent vehicle units for train set dispatching
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part I
- LVRT enhancement of DFIG-driven wind system using feed-forward neuro-sliding mode control
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part I
- Prediction of future paths of mobile objects using path library
- Model predictive control for a multiple injection combustion model
- Model-based on-board post-injection control development for marine diesel engine
- Intelligent temporal analysis of coronavirus statistical data
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Electrochemical studies of the synergistic combination effect of thymus mastichina and illicium verum essential oil extracts on the corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in dilute acid solution
- Adoption of Business Intelligence to Support Cost Accounting Based Financial Systems — Case Study of XYZ Company
- Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis of a Hybrid Renewable Energy Supply Options for University Buildings in Saudi Arabia
- Optimized design of a semimetal gasket operating in flange-bolted joints
- Behavior of non-reinforced and reinforced green mortar with fibers
- Field measurement of contact forces on rollers for a large diameter pipe conveyor
- Development of Smartphone-Controlled Hand and Arm Exoskeleton for Persons with Disability
- Investigation of saturation flow rate using video camera at signalized intersections in Jordan
- The features of Ni2MnIn polycrystalline Heusler alloy thin films formation by pulsed laser deposition
- Selection of a workpiece clamping system for computer-aided subtractive manufacturing of geometrically complex medical models
- Development of Solar-Powered Water Pump with 3D Printed Impeller
- Identifying Innovative Reliable Criteria Governing the Selection of Infrastructures Construction Project Delivery Systems
- Kinetics of Carbothermal Reduction Process of Different Size Phosphate Rocks
- Plastic forming processes of transverse non-homogeneous composite metallic sheets
- Accelerated aging of WPCs Based on Polypropylene and Birch plywood Sanding Dust
- Effect of water flow and depth on fatigue crack growth rate of underwater wet welded low carbon steel SS400
- Non-invasive attempts to extinguish flames with the use of high-power acoustic extinguisher
- Filament wound composite fatigue mechanisms investigated with full field DIC strain monitoring
- Structural Timber In Compartment Fires – The Timber Charring and Heat Storage Model
- Technical and economic aspects of starting a selected power unit at low ambient temperatures
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Adaptation to driver-assistance systems depending on experience
- A SIMULINK implementation of a vector shift relay with distributed synchronous generator for engineering classes
- Evaluation of measurement uncertainty in a static tensile test
- Errors in documenting the subsoil and their impact on the investment implementation: Case study
- Comparison between two calculation methods for designing a stand-alone PV system according to Mosul city basemap
- Reduction of transport-related air pollution. A case study based on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the level of NOx emissions in the city of Krakow
- Driver intervention performance assessment as a key aspect of L3–L4 automated vehicles deployment
- A new method for solving quadratic fractional programming problem in neutrosophic environment
- Effect of fish scales on fabrication of polyester composite material reinforcements
- Impact of the operation of LNG trucks on the environment
- The effectiveness of the AEB system in the context of the safety of vulnerable road users
- Errors in controlling cars cause tragic accidents involving motorcyclists
- Deformation of designed steel plates: An optimisation of the side hull structure using the finite element approach
- Thermal-strength analysis of a cross-flow heat exchanger and its design improvement
- Effect of thermal collector configuration on the photovoltaic heat transfer performance with 3D CFD modeling
- Experimental identification of the subjective reception of external stimuli during wheelchair driving
- Failure analysis of motorcycle shock breakers
- Experimental analysis of nonlinear characteristics of absorbers with wire rope isolators
- Experimental tests of the antiresonance vibratory mill of a sectional movement trajectory
- Experimental and theoretical investigation of CVT rubber belt vibrations
- Is the cubic parabola really the best railway transition curve?
- Transport properties of the new vibratory conveyor at operations in the resonance zone
- Assessment of resistance to permanent deformations of asphalt mixes of low air void content
- COVID-19 lockdown impact on CERN seismic station ambient noise levels
- Review Articles
- FMEA method in operational reliability of forest harvesters
- Examination of preferences in the field of mobility of the city of Pila in terms of services provided by the Municipal Transport Company in Pila
- Enhancement stability and color fastness of natural dye: A review
- Special Issue: ICE-SEAM 2019 - Part II
- Lane Departure Warning Estimation Using Yaw Acceleration
- Analysis of EMG Signals during Stance and Swing Phases for Controlling Magnetorheological Brake applications
- Sensor Number Optimization Using Neural Network for Ankle Foot Orthosis Equipped with Magnetorheological Brake
- Special Issue: Recent Advances in Civil Engineering - Part II
- Comparison of STM’s reliability system on the example of selected element
- Technical analysis of the renovation works of the wooden palace floors
- Special Issue: TRANSPORT 2020
- Simulation assessment of the half-power bandwidth method in testing shock absorbers
- Predictive analysis of the impact of the time of day on road accidents in Poland
- User’s determination of a proper method for quantifying fuel consumption of a passenger car with compression ignition engine in specific operation conditions
- Analysis and assessment of defectiveness of regulations for the yellow signal at the intersection
- Streamlining possibility of transport-supply logistics when using chosen Operations Research techniques
- Permissible distance – safety system of vehicles in use
- Study of the population in terms of knowledge about the distance between vehicles in motion
- UAVs in rail damage image diagnostics supported by deep-learning networks
- Exhaust emissions of buses LNG and Diesel in RDE tests
- Measurements of urban traffic parameters before and after road reconstruction
- The use of deep recurrent neural networks to predict performance of photovoltaic system for charging electric vehicles
- Analysis of dangers in the operation of city buses at the intersections
- Psychological factors of the transfer of control in an automated vehicle
- Testing and evaluation of cold-start emissions from a gasoline engine in RDE test at two different ambient temperatures
- Age and experience in driving a vehicle and psychomotor skills in the context of automation
- Consumption of gasoline in vehicles equipped with an LPG retrofit system in real driving conditions
- Laboratory studies of the influence of the working position of the passenger vehicle air suspension on the vibration comfort of children transported in the child restraint system
- Route optimization for city cleaning vehicle
- Efficiency of electric vehicle interior heating systems at low ambient temperatures
- Model-based imputation of sound level data at thoroughfare using computational intelligence
- Research on the combustion process in the Fiat 1.3 Multijet engine fueled with rapeseed methyl esters
- Overview of the method and state of hydrogenization of road transport in the world and the resulting development prospects in Poland
- Tribological characteristics of polymer materials used for slide bearings
- Car reliability analysis based on periodic technical tests
- Special Issue: Terotechnology 2019 - Part II
- DOE Application for Analysis of Tribological Properties of the Al2O3/IF-WS2 Surface Layers
- The effect of the impurities spaces on the quality of structural steel working at variable loads
- Prediction of the parameters and the hot open die elongation forging process on an 80 MN hydraulic press
- Special Issue: AEVEC 2020
- Vocational Student's Attitude and Response Towards Experiential Learning in Mechanical Engineering
- Virtual Laboratory to Support a Practical Learning of Micro Power Generation in Indonesian Vocational High Schools
- The impacts of mediating the work environment on the mode choice in work trips
- Utilization of K-nearest neighbor algorithm for classification of white blood cells in AML M4, M5, and M7
- Car braking effectiveness after adaptation for drivers with motor dysfunctions
- Case study: Vocational student’s knowledge and awareness level toward renewable energy in Indonesia
- Contribution of collaborative skill toward construction drawing skill for developing vocational course
- Special Issue: Annual Engineering and Vocational Education Conference - Part II
- Vocational teachers’ perspective toward Technological Pedagogical Vocational Knowledge
- Special Issue: ICIMECE 2020 - Part I
- Profile of system and product certification as quality infrastructure in Indonesia
- Prediction Model of Magnetorheological (MR) Fluid Damper Hysteresis Loop using Extreme Learning Machine Algorithm
- A review on the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing: Filament processing, materials, and printing parameters
- Facile rheological route method for LiFePO4/C cathode material production
- Mosque design strategy for energy and water saving
- Epoxy resins thermosetting for mechanical engineering
- Estimating the potential of wind energy resources using Weibull parameters: A case study of the coastline region of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
- Special Issue: CIRMARE 2020
- New trends in visual inspection of buildings and structures: Study for the use of drones
- Special Issue: ISERT 2021
- Alleviate the contending issues in network operating system courses: Psychomotor and troubleshooting skill development with Raspberry Pi
- Special Issue: Actual Trends in Logistics and Industrial Engineering - Part II
- The Physical Internet: A means towards achieving global logistics sustainability
- Special Issue: Modern Scientific Problems in Civil Engineering - Part I
- Construction work cost and duration analysis with the use of agent-based modelling and simulation
- Corrosion rate measurement for steel sheets of a fuel tank shell being in service
- The influence of external environment on workers on scaffolding illustrated by UTCI
- Allocation of risk factors for geodetic tasks in construction schedules
- Pedestrian fatality risk as a function of tram impact speed
- Technological and organizational problems in the construction of the radiation shielding concrete and suggestions to solve: A case study
- Finite element analysis of train speed effect on dynamic response of steel bridge
- New approach to analysis of railway track dynamics – Rail head vibrations
- Special Issue: Trends in Logistics and Production for the 21st Century - Part I
- Design of production lines and logistic flows in production
- The planning process of transport tasks for autonomous vans
- Modeling of the two shuttle box system within the internal logistics system using simulation software
- Implementation of the logistics train in the intralogistics system: A case study
- Assessment of investment in electric buses: A case study of a public transport company
- Assessment of a robot base production using CAM programming for the FANUC control system
- Proposal for the flow of material and adjustments to the storage system of an external service provider
- The use of numerical analysis of the injection process to select the material for the injection molding
- Economic aspect of combined transport
- Solution of a production process with the application of simulation: A case study
- Speedometer reliability in regard to road traffic sustainability
- Design and construction of a scanning stand for the PU mini-acoustic sensor
- Utilization of intelligent vehicle units for train set dispatching
- Special Issue: ICRTEEC - 2021 - Part I
- LVRT enhancement of DFIG-driven wind system using feed-forward neuro-sliding mode control
- Special Issue: Automation in Finland 2021 - Part I
- Prediction of future paths of mobile objects using path library
- Model predictive control for a multiple injection combustion model
- Model-based on-board post-injection control development for marine diesel engine
- Intelligent temporal analysis of coronavirus statistical data

