Abstract
3D segmentation has become a widely used technique. However, automatic segmentation does not deliver high accuracy in optically dense images and manual segmentation lowers the throughput drastically. Therefore, we present a workflow for 3D segmentation being able to forecast segments based on a user-given ground truth. We provide the possibility to correct wrong forecasts and to repeatedly insert ground truth in the process. Our aim is to combine automated and manual segmentation and therefore to improve accuracy by a tunable amount of manual input.
1 Introduction
3D microscopic-imaging has numerous fields of application in biology and medicine, e.g. to analyze model organisms like mouse [1], zebrafish [2] or fruit fly [3]. An important aim is to reconstruct 3D surfaces or volumes from a set of 2D images called stack. As the manual annotation is time-consuming, automated image processing is applied to identify and quantify specific structures known as segments. For data sets with homogeneous segments, high-contrast and clear edges, there are plenty of sophisticated methods and tools to automatically annotate and quantify these segments (e.g. [4], [5], [6], [7]).
However, if image quality is low or if connected structures change rapidly across the slices of a stack, an accurate automated segmentation is impossible. Although, there are interactive software packages for segmentation, either they require good image quality [7] or contain only a few automatic segmentation methods [8]. Thus, effort is required to either perform the segmentation manually or to correct inaccurate automatic segmentation results, which limits accurate segmentation possibilities of 3D image stacks in high-throughput.
Figure 1 shows an exemplary electron microscopy (EM) image of a neuromuscular junction in mouse. An automatic segmentation and forecast of the edges is impossible due to the variable contrast, filigree structures of interest and non-smooth edge transitions across the slices. However, a highly accurate segmentation is needed, to visualize and analyze the folded membrane in 3D and to derive new insights about the 3D structure and the signal transmission at the neuromuscular junction.
![Figure 1 Electron microscopic image of the neuromuscular junction in mouse. Colored lines are results of a manual and a semi-automatic LiveWire segmentation. Regions below and above the segmentation lines are the pre- and postsynapse, respectively (adapted from [9]).](/document/doi/10.1515/cdbme-2016-0097/asset/graphic/j_cdbme-2016-0097_fig_001.jpg)
Electron microscopic image of the neuromuscular junction in mouse. Colored lines are results of a manual and a semi-automatic LiveWire segmentation. Regions below and above the segmentation lines are the pre- and postsynapse, respectively (adapted from [9]).
An idea to increase segmentation accuracy is to support automatic algorithms with ground truth given by experts. In [9], we presented such a workflow, introducing a semi-automatic method based on the LiveWire technique [10], [11] (Figure 1): The original grayscale image is filtered using an objectness filter [12] and a subsequent binarization optimizes the edges, such that a semi-automatic segmentation approach can be optimally supported. The user is asked to manually click a few points along the structures of interest in the grayscale image and the LiveWire algorithm automatically connects these points by searching for the shortest path between neighboring points in the filtered binary image.
In the present paper, we use the discussed semi-automatic segmentation and extend it to support and accelerate the 3D segmentation. We add a minimal amount of manual input, to finally extract high-quality 3D surfaces of structures of interest from large EM images. Semi-automatically annotated segments are used to forecast the segmentation to adjacent slices by automatically projecting a subset of the contour pixels to the next slice. Projected pixels are again automatically connected using the LiveWire approach. Wrong propagations can be corrected by using a higher number of click points or by manually moving erroneous segments to the correct positions. Corrected segmentations yield to further ground truth which can then be propagated to adjacent slices. There is no need for parameter modifications, which allows non-experts to operate the tool.
2 Methods
An overview of the workflow for the proposed user-guided semi-automatic segmentation is depicted in Figure 2.
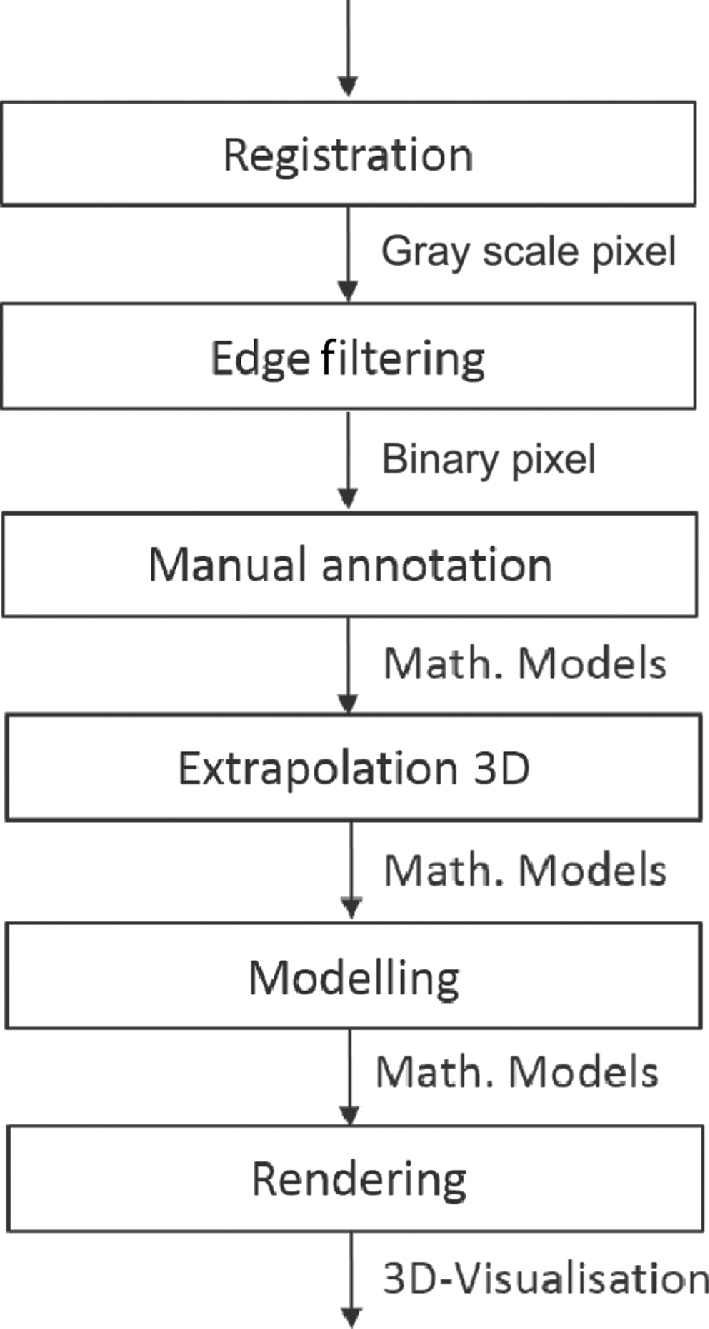
Workflow for automatic segment propagation.
In a first step, a combination of rigid and elastic registration (for initialization and refinement, respectively) is applied using the open-source software Fiji to align all images automatically [13]. This method worked well in practice, but any other registration approach may be used if more appropriate for a given data set.
The registered grayscale image is filtered to obtain emphasized edges. We therefore implemented a filter pipeline in XPIWIT [14] and call it from MATLAB. The filter pipeline consists of an objectness filter that uses the eigenvalues of the Hessian matrix at each pixel location in order to emphasize line-like structures in 2D images [12]. Due to the non-smooth edge transitions between neighboring slices, we apply the edge enhancement on all slices separately, instead of using a plane-enhancement algorithm directly in 3D. A subsequent binarization is used to equalize the intensity of all edges and the enhanced image can then be used as input for the semi-automatic segmentation. The filter steps and the corresponding XPIWIT pipeline are shown in Figure 3. Next, the user is asked to manually annotate edges in the grayscale image by clicking pixels belonging to an edge of a structure of interest. A LiveWire algorithm connects the selected points and delivers a mathematical model for the edge as described in [9].

Preprocessing steps for optimal edge enhancement of a raw input image (left) and the corresponding processing pipeline implemented in XPIWIT (right) are shown.
To propagate the model to the next slice (extrapolation) we seek for pixels being similar to the click points in adjacent slices, optimizing their position and repeating the LiveWire algorithm on these virtual click points as detailed in the next section. As an automatic extrapolation step might be error-prone in some cases, a possibility for manual correction needs to be provided as well. Having annotated segments in all stacks, modeling and rendering allows to derive features from the segmented structures of interest and to generate interactive 3D visualisations.
2.1 Segmentation propagation
To further speed up the semi-automatic segmentation, we developed a prediction strategy that allows to automatically propagate the manually segmented contours to adjacent slices. For each pixel of a manually segmented contour, we calculate the surface normal using finite differences. A few equally distant points along the contour are selected for propagation to the adjacent slices. For all selected propagation points, we perform a line search along the normal direction within a radius of a few pixels that is defined by the maximally expected distance between corresponding structures in neighboring slices. The best match along the normal line is identified using Computer Vision techniques like template matching with normalized cross correlation or the correlation coefficient as similarity measures as well as descriptor matching using FREAK descriptors [15]. Furthermore, we developed a combined distance measure using the FREAK descriptor matching distance, the distance to the ground truth contour as well as the intensity information of the image. Propagated points are then connected via the LiveWire approach yielding a prediction of the ground truth segment in the adjacent slice.
2.2 Interactive graphical user interface
To control the presented segmentation framework, we developed a prototypical GUI (Figure 4). Manually or semi-automatically segmented structures of interest can be completed using the proposed propagation methods. In cases where the automatic propagation failed to reconstruct the correct structures, the user can modify segments by repeating the manual segmentation or by manipulating the propagated segments. All propagated segments can in turn again be used to perform predictions, i.e., the segmentation consists of multiple repetitions of semi-automatic segmentation, prediction and correction.
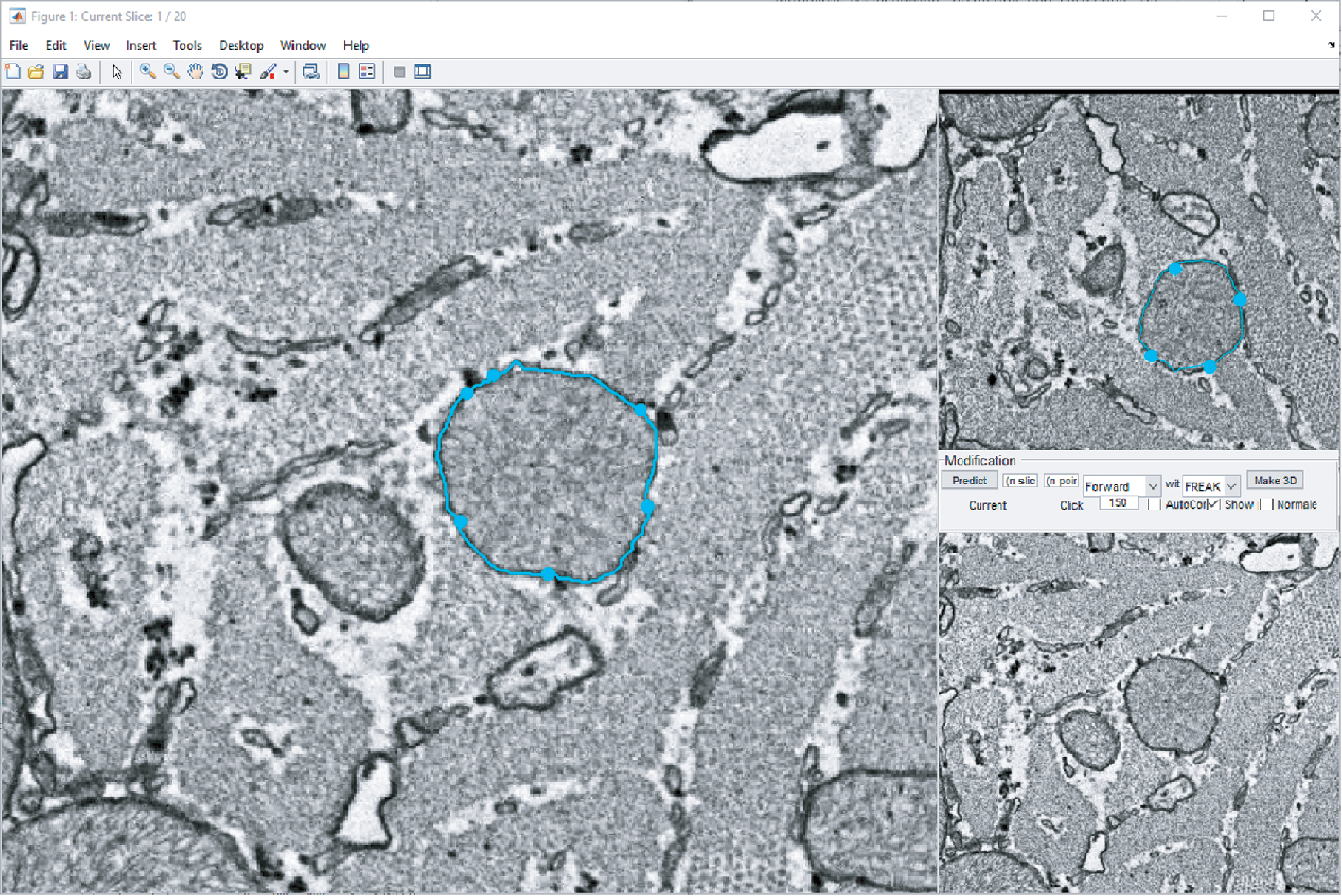
Screenshot of the MATLAB-based GUI prototype that consists of a main segmentation window (left), previews of adjacent slices and controls for the propagation algorithm (right).
3 Results
We evaluated the proposed segment propagation on a small detail that was cropped from a large electron microscopy stack. A randomly selected structure was segmented manually in five adjacent slices and served as a ground truth reference. The same structure was segmented using the semi-automatic LiveWire approach to measure the time reduction required for segmentation. The first slice of the LiveWire segmentation was subsequently propagated to the remaining four slices using template matching with the normalized cross correlation (NCC) or the correlation coefficient (CorrCoeff), FREAK descriptors as well as a combined measure that consisted of the FREAK descriptor matching distance, the distance to the original contour and the intensity of the original image. For all slices and all methods, we calculated the maximum and mean distance to the ground truth contour in pixels as well as the root mean squared deviation (RMSD). Furthermore, the required time for the segmentation was measured in seconds. The quantitative results are summarized in Table 1 and visualized in Figure 5. The best segmentation quality was achieved with the LiveWire approach (semi-automatic) as well as the combined approach (automatic), with an average distance of less than a pixel to the ground truth. Both template matching approaches (NCC and CorrCoeff) failed to predict the first slice and are thus not practically usable in this scenario. The plain FREAK algorithm performed slightly worse than the combined strategy. Compared to a manual segmentation of the five slices that took 214s, the processing times decreased by 78% for the LiveWire approach and by 93% for all propagation-based methods. Thus, the combined strategy turns out to be the best choice with respect to quality and time consumption.
Comparison of different segmentation strategies.
| Method | Max Dist. | Mean Dist. | RMSD | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiveWire | 9.49 | 0.34 | 0.84 | 47.11 |
| NCC | 50.99 | 2.41 | 7.79 | 16.50 |
| CorrCoeff | 43.38 | 2.28 | 7.13 | 16.20 |
| FREAK | 13.60 | 0.44 | 1.23 | 16.04 |
| Combined | 5.83 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 16.31 |

Qualitative comparison of the different segmentation methods including manual (Ground Truth) and semi-automatic (LiveWire) annotations as well as automatic propagation of a LiveWire segmentation on the first slice using normalized cross correlation (NCC), correlation coefficient (CorrCoeff), FREAK descriptors and a combined measure as described in Section 2.1.
4 Conclusion and outlook
In the present contribution, we introduced a new approach for improved semi-automatic segmentation of large-scale 3D image stacks. The method does not require tedious parameter tuning and can help to significantly speed up segmentation tasks in scenarios where entirely automated processing is impossible. By propagating manual annotations to adjacent slices and by using sophisticated correction, a close to error-free segmentation can be achieved.
Further work will be put on the development of a graphical user interface that condenses all involved workflow steps and to extend the quantification of speed and quality improvements of the proposed segmentation approach. To improve the interactivity and usability of the framework we plan to develop an efficient C++-based application with highly interactive visualisation, editing and prediction capabilities as well as parallel execution of segment propagations in the background. The envisioned application will provide a powerful tool to enable detailed analyses of large-scale 3D microscopic image data sets.
Author’s Statement
Research funding: The project is funded by the Helmholtz Association (Program BioInterfaces (NP, RM, MR), the German Research Foundation DFG (JS, RM, Grant No MI 1315/4), the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (IVM, Grant No 13GW0044), University of Heidelberg (RS, JP, IVM), University of Kaiserslautern (HL) and the Heidelberg Karlsruhe Research Partnership - HEiKA (JS, MR, HL). Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest. Informed Consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study. Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
References
[1] Dhenain M, Ruffins SW, Jacobs RE. Three-Dimensional digital mouse atlas using High-Resolution MRI. Dev Biol. 2001;232:458–70.10.1006/dbio.2001.0189Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Mikut R, Dickmeis T, Driever W, Geurts P, Hamprecht F, Kausler BX, et al. Automated processing of zebrafish imaging data - a survey. Zebrafish. 2013;10:401–21.10.1089/zeb.2013.0886Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Peng H, Chung P, Long F, Qu L, Jenett A, Seeds AM, et al. Brainaligner: 3D registration atlases of drosophila brains. Nat Methods. 2011;8:493–8.10.1038/nmeth.1602Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Berning M, Boergens K, Helmstaedter M. SegEM: efficient image analysis for high-resolution connectomics. Neuron. 2015;87:1193—206.10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Genovesio A, Liedl T, Emiliani V, Parak W, Coppey-Moisan M, Olivo-Marin J. Multiple particle tracking in 3D+ t microscopy: method and application to the tracking of endocytosed quantum dots. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2006;15:1062–70.10.1109/TIP.2006.872323Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Kreshuk A, Straehle C, Sommer C, Koethe U, Cantoni M, Knott G, et al. Automated detection and segmentation of synaptic contacts in nearly isotropic serial electron microscopy images.PLoS One. 2011;6:e24899.10.1371/journal.pone.0024899Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Sommer C, Straehle C, Kothe U, Hamprecht F. ilastik: interactive learning and segmentation toolkit. In: Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, IEEE; 2011. p. 230–3.10.1109/ISBI.2011.5872394Search in Google Scholar
[8] Saalfeld S, Cardona A, Hartenstein V, Tomancak P. CATMAID: collaborative annotation toolkit for massive amounts of image data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1984–6.10.1093/bioinformatics/btp266Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Portl J, Stegmaier J, Mang I, Schröder R, Reischl M, Leitte H. Visualization for error-controlled surface reconstruction from large electron microscopy image stacks. In: Proc. IEEE Visualisation Conference; 2015.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Bradski G. The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Journal of Software Tools; 2000.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Mortensen EN, Barrett WA. Intelligent scissors for image composition. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, ACM; 1995. p. 191–8.10.1145/218380.218442Search in Google Scholar
[12] Antiga L. Generalizing vesselness with respect to dimensionality and shape. The Insight Journal. 2007;3:1–14.10.54294/urgadxSearch in Google Scholar
[13] Saalfeld S, Fetter R, Cardona A, Tomancak P. Elastic volume reconstruction from series of ultra-thin microscopy sections. Nat Methods. 2012;9:717–20.10.1038/nmeth.2072Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Bartschat A, Hübner E, Reischl M, Mikut R, Stegmaier J. XPIWIT - an XML pipeline wrapper for the insight toolkit. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:315–7.10.1093/bioinformatics/btv559Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Alahi A, Ortiz R, Vandergheynst P. Freak: fast retina keypoint. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2012. p. 510–7.10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247715Search in Google Scholar
©2016 Markus Reischl et al., licensee De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Synthesis and characterization of PIL/pNIPAAm hybrid hydrogels
- Novel blood protein based scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering
- Cell adhesion and viability of human endothelial cells on electrospun polymer scaffolds
- Effects of heat treatment and welding process on superelastic behaviour and microstructure of micro electron beam welded NiTi
- Long-term stable modifications of silicone elastomer for improved hemocompatibility
- The effect of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of PLLA tubular specimens
- Biocompatible wear-resistant thick ceramic coating
- Protection of active implant electronics with organosilicon open air plasma coating for plastic overmolding
- Examination of dielectric strength of thin Parylene C films under various conditions
- Open air plasma deposited antimicrobial SiOx/TiOx composite films for biomedical applications
- Systemic analysis about residual chloroform in PLLA films
- A macrophage model of osseointegration
- Towards in silico prognosis using big data
- Technical concept and evaluation of a novel shoulder simulator with adaptive muscle force generation and free motion
- Usability evaluation of a locomotor therapy device considering different strategies
- Hypoxia-on-a-chip
- Integration of a semi-automatic in-vitro RFA procedure into an experimental setup
- Fabrication of MEMS-based 3D-μECoG-MEAs
- High speed digital interfacing for a neural data acquisition system
- Bionic forceps for the handling of sensitive tissue
- Experimental studies on 3D printing of barium titanate ceramics for medical applications
- Patient specific root-analogue dental implants – additive manufacturing and finite element analysis
- 3D printing – a key technology for tailored biomedical cell culture lab ware
- 3D printing of hydrogels in a temperature controlled environment with high spatial resolution
- Biocompatibility of photopolymers for additive manufacturing
- Biochemical piezoresistive sensors based on pH- and glucose-sensitive hydrogels for medical applications
- Novel wireless measurement system of pressure dedicated to in vivo studies
- Portable auricular device for real-time swallow and chew detection
- Detection of miRNA using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor and antibody amplification
- Simulation and evaluation of stimulation scenarios for targeted vestibular nerve excitation
- Deep brain stimulation: increasing efficiency by alternative waveforms
- Prediction of immediately occurring microsleep events from brain electric signals
- Determining cardiac vagal threshold from short term heart rate complexity
- Classification of cardiac excitation patterns during atrial fibrillation
- An algorithm to automatically determine the cycle length coverage to identify rotational activity during atrial fibrillation – a simulation study
- Deriving respiration from high resolution 12-channel-ECG during cycling exercise
- Reducing of gradient induced artifacts on the ECG signal during MRI examinations using Wilcoxon filter
- Automatic detection and mapping of double potentials in intracardiac electrograms
- Modeling the pelvic region for non-invasive pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring
- Postprocessing algorithm for automated analysis of pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring signals
- Best practice: surgeon driven application in pelvic operations
- Vasomotor assessment by camera-based photoplethysmography
- Classification of morphologic changes in photoplethysmographic waveforms
- Novel computation of pulse transit time from multi-channel PPG signals by wavelet transform
- Efficient design of FIR filter based low-pass differentiators for biomedical signal processing
- Nonlinear causal influences assessed by mutual compression entropy
- Comparative study of methods for solving the correspondence problem in EMD applications
- fNIRS for future use in auditory diagnostics
- Semi-automated detection of fractional shortening in zebrafish embryo heart videos
- Blood pressure measurement on the cheek
- Derivation of the respiratory rate from directly and indirectly measured respiratory signals using autocorrelation
- Left cardiac atrioventricular delay and inter-ventricular delay in cardiac resynchronization therapy responder and non-responder
- An automatic systolic peak detector of blood pressure waveforms using 4th order cumulants
- Real-time QRS detection using integrated variance for ECG gated cardiac MRI
- Preprocessing of unipolar signals acquired by a novel intracardiac mapping system
- In-vitro experiments to characterize ventricular electromechanics
- Continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure in the operating room: a cuffless optical technology at the fingertip
- Application of microwave sensor technology in cardiovascular disease for plaque detection
- Artificial blood circulatory and special Ultrasound Doppler probes for detecting and sizing gaseous embolism
- Detection of microsleep events in a car driving simulation study using electrocardiographic features
- A method to determine the kink resistance of stents and stent delivery systems according to international standards
- Comparison of stented bifurcation and straight vessel 3D-simulation with a prior simulated velocity profile inlet
- Transient Euler-Lagrange/DEM simulation of stent thrombosis
- Automated control of the laser welding process of heart valve scaffolds
- Automation of a test bench for accessing the bendability of electrospun vascular grafts
- Influence of storage conditions on the release of growth factors in platelet-rich blood derivatives
- Cryopreservation of cells using defined serum-free cryoprotective agents
- New bioreactor vessel for tissue engineering of human nasal septal chondrocytes
- Determination of the membrane hydraulic permeability of MSCs
- Climate retainment in carbon dioxide incubators
- Multiple factors influencing OR ventilation system effectiveness
- Evaluation of an app-based stress protocol
- Medication process in Styrian hospitals
- Control tower to surgical theater
- Development of a skull phantom for the assessment of implant X-ray visibility
- Surgical navigation with QR codes
- Investigation of the pressure gradient of embolic protection devices
- Computer assistance in femoral derotation osteotomy: a bottom-up approach
- Automatic depth scanning system for 3D infrared thermography
- A service for monitoring the quality of intraoperative cone beam CT images
- Resectoscope with an easy to use twist mechanism for improved handling
- In vitro simulation of distribution processes following intramuscular injection
- Adjusting inkjet printhead parameters to deposit drugs into micro-sized reservoirs
- A flexible standalone system with integrated sensor feedback for multi-pad electrode FES of the hand
- Smart control for functional electrical stimulation with optimal pulse intensity
- Tactile display on the remaining hand for unilateral hand amputees
- Effects of sustained electrical stimulation on spasticity assessed by the pendulum test
- An improved tracking framework for ultrasound probe localization in image-guided radiosurgery
- Improvement of a subviral particle tracker by the use of a LAP-Kalman-algorithm
- Learning discriminative classification models for grading anal intraepithelial neoplasia
- Regularization of EIT reconstruction based on multi-scales wavelet transforms
- Assessing MRI susceptibility artefact through an indicator of image distortion
- EyeGuidance – a computer controlled system to guide eye movements
- A framework for feedback-based segmentation of 3D image stacks
- Doppler optical coherence tomography as a promising tool for detecting fluid in the human middle ear
- 3D Local in vivo Environment (LivE) imaging for single cell protein analysis of bone tissue
- Inside-Out access strategy using new trans-vascular catheter approach
- US/MRI fusion with new optical tracking and marker approach for interventional procedures inside the MRI suite
- Impact of different registration methods in MEG source analysis
- 3D segmentation of thyroid ultrasound images using active contours
- Designing a compact MRI motion phantom
- Cerebral cortex classification by conditional random fields applied to intraoperative thermal imaging
- Classification of indirect immunofluorescence images using thresholded local binary count features
- Analysis of muscle fatigue conditions using time-frequency images and GLCM features
- Numerical evaluation of image parameters of ETR-1
- Fabrication of a compliant phantom of the human aortic arch for use in Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experimentation
- Effect of the number of electrodes on the reconstructed lung shape in electrical impedance tomography
- Hardware dependencies of GPU-accelerated beamformer performances for microwave breast cancer detection
- Computer assisted assessment of progressing osteoradionecrosis of the jaw for clinical diagnosis and treatment
- Evaluation of reconstruction parameters of electrical impedance tomography on aorta detection during saline bolus injection
- Evaluation of open-source software for the lung segmentation
- Automatic determination of lung features of CF patients in CT scans
- Image analysis of self-organized multicellular patterns
- Effect of key parameters on synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPIONs)
- Radiopacity assessment of neurovascular implants
- Development of a desiccant based dielectric for monitoring humidity conditions in miniaturized hermetic implantable packages
- Development of an artifact-free aneurysm clip
- Enhancing the regeneration of bone defects by alkalizing the peri-implant zone – an in vitro approach
- Rapid prototyping of replica knee implants for in vitro testing
- Protecting ultra- and hyperhydrophilic implant surfaces in dry state from loss of wettability
- Advanced wettability analysis of implant surfaces
- Patient-specific hip prostheses designed by surgeons
- Plasma treatment on novel carbon fiber reinforced PEEK cages to enhance bioactivity
- Wear of a total intervertebral disc prosthesis
- Digital health and digital biomarkers – enabling value chains on health data
- Usability in the lifecycle of medical software development
- Influence of different test gases in a non-destructive 100% quality control system for medical devices
- Device development guided by user satisfaction survey on auricular vagus nerve stimulation
- Empirical assessment of the time course of innovation in biomedical engineering: first results of a comparative approach
- Effect of left atrial hypertrophy on P-wave morphology in a computational model
- Simulation of intracardiac electrograms around acute ablation lesions
- Parametrization of activation based cardiac electrophysiology models using bidomain model simulations
- Assessment of nasal resistance using computational fluid dynamics
- Resistance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Inspiratory and expiratory elastance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Determination of regional lung function in cystic fibrosis using electrical impedance tomography
- Development of parietal bone surrogates for parietal graft lift training
- Numerical simulation of mechanically stimulated bone remodelling
- Conversion of engineering stresses to Cauchy stresses in tensile and compression tests of thermoplastic polymers
- Numerical examinations of simplified spondylodesis models concerning energy absorption in magnetic resonance imaging
- Principle study on the signal connection at transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
- Influence of Siluron® insertion on model drug distribution in the simulated vitreous body
- Evaluating different approaches to identify a three parameter gas exchange model
- Effects of fibrosis on the extracellular potential based on 3D reconstructions from histological sections of heart tissue
- From imaging to hemodynamics – how reconstruction kernels influence the blood flow predictions in intracranial aneurysms
- Flow optimised design of a novel point-of-care diagnostic device for the detection of disease specific biomarkers
- Improved FPGA controlled artificial vascular system for plethysmographic measurements
- Minimally spaced electrode positions for multi-functional chest sensors: ECG and respiratory signal estimation
- Automated detection of alveolar arches for nasoalveolar molding in cleft lip and palate treatment
- Control scheme selection in human-machine- interfaces by analysis of activity signals
- Event-based sampling for reducing communication load in realtime human motion analysis by wireless inertial sensor networks
- Automatic pairing of inertial sensors to lower limb segments – a plug-and-play approach
- Contactless respiratory monitoring system for magnetic resonance imaging applications using a laser range sensor
- Interactive monitoring system for visual respiratory biofeedback
- Development of a low-cost senor based aid for visually impaired people
- Patient assistive system for the shoulder joint
- A passive beating heart setup for interventional cardiology training
Articles in the same Issue
- Synthesis and characterization of PIL/pNIPAAm hybrid hydrogels
- Novel blood protein based scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering
- Cell adhesion and viability of human endothelial cells on electrospun polymer scaffolds
- Effects of heat treatment and welding process on superelastic behaviour and microstructure of micro electron beam welded NiTi
- Long-term stable modifications of silicone elastomer for improved hemocompatibility
- The effect of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of PLLA tubular specimens
- Biocompatible wear-resistant thick ceramic coating
- Protection of active implant electronics with organosilicon open air plasma coating for plastic overmolding
- Examination of dielectric strength of thin Parylene C films under various conditions
- Open air plasma deposited antimicrobial SiOx/TiOx composite films for biomedical applications
- Systemic analysis about residual chloroform in PLLA films
- A macrophage model of osseointegration
- Towards in silico prognosis using big data
- Technical concept and evaluation of a novel shoulder simulator with adaptive muscle force generation and free motion
- Usability evaluation of a locomotor therapy device considering different strategies
- Hypoxia-on-a-chip
- Integration of a semi-automatic in-vitro RFA procedure into an experimental setup
- Fabrication of MEMS-based 3D-μECoG-MEAs
- High speed digital interfacing for a neural data acquisition system
- Bionic forceps for the handling of sensitive tissue
- Experimental studies on 3D printing of barium titanate ceramics for medical applications
- Patient specific root-analogue dental implants – additive manufacturing and finite element analysis
- 3D printing – a key technology for tailored biomedical cell culture lab ware
- 3D printing of hydrogels in a temperature controlled environment with high spatial resolution
- Biocompatibility of photopolymers for additive manufacturing
- Biochemical piezoresistive sensors based on pH- and glucose-sensitive hydrogels for medical applications
- Novel wireless measurement system of pressure dedicated to in vivo studies
- Portable auricular device for real-time swallow and chew detection
- Detection of miRNA using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor and antibody amplification
- Simulation and evaluation of stimulation scenarios for targeted vestibular nerve excitation
- Deep brain stimulation: increasing efficiency by alternative waveforms
- Prediction of immediately occurring microsleep events from brain electric signals
- Determining cardiac vagal threshold from short term heart rate complexity
- Classification of cardiac excitation patterns during atrial fibrillation
- An algorithm to automatically determine the cycle length coverage to identify rotational activity during atrial fibrillation – a simulation study
- Deriving respiration from high resolution 12-channel-ECG during cycling exercise
- Reducing of gradient induced artifacts on the ECG signal during MRI examinations using Wilcoxon filter
- Automatic detection and mapping of double potentials in intracardiac electrograms
- Modeling the pelvic region for non-invasive pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring
- Postprocessing algorithm for automated analysis of pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring signals
- Best practice: surgeon driven application in pelvic operations
- Vasomotor assessment by camera-based photoplethysmography
- Classification of morphologic changes in photoplethysmographic waveforms
- Novel computation of pulse transit time from multi-channel PPG signals by wavelet transform
- Efficient design of FIR filter based low-pass differentiators for biomedical signal processing
- Nonlinear causal influences assessed by mutual compression entropy
- Comparative study of methods for solving the correspondence problem in EMD applications
- fNIRS for future use in auditory diagnostics
- Semi-automated detection of fractional shortening in zebrafish embryo heart videos
- Blood pressure measurement on the cheek
- Derivation of the respiratory rate from directly and indirectly measured respiratory signals using autocorrelation
- Left cardiac atrioventricular delay and inter-ventricular delay in cardiac resynchronization therapy responder and non-responder
- An automatic systolic peak detector of blood pressure waveforms using 4th order cumulants
- Real-time QRS detection using integrated variance for ECG gated cardiac MRI
- Preprocessing of unipolar signals acquired by a novel intracardiac mapping system
- In-vitro experiments to characterize ventricular electromechanics
- Continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure in the operating room: a cuffless optical technology at the fingertip
- Application of microwave sensor technology in cardiovascular disease for plaque detection
- Artificial blood circulatory and special Ultrasound Doppler probes for detecting and sizing gaseous embolism
- Detection of microsleep events in a car driving simulation study using electrocardiographic features
- A method to determine the kink resistance of stents and stent delivery systems according to international standards
- Comparison of stented bifurcation and straight vessel 3D-simulation with a prior simulated velocity profile inlet
- Transient Euler-Lagrange/DEM simulation of stent thrombosis
- Automated control of the laser welding process of heart valve scaffolds
- Automation of a test bench for accessing the bendability of electrospun vascular grafts
- Influence of storage conditions on the release of growth factors in platelet-rich blood derivatives
- Cryopreservation of cells using defined serum-free cryoprotective agents
- New bioreactor vessel for tissue engineering of human nasal septal chondrocytes
- Determination of the membrane hydraulic permeability of MSCs
- Climate retainment in carbon dioxide incubators
- Multiple factors influencing OR ventilation system effectiveness
- Evaluation of an app-based stress protocol
- Medication process in Styrian hospitals
- Control tower to surgical theater
- Development of a skull phantom for the assessment of implant X-ray visibility
- Surgical navigation with QR codes
- Investigation of the pressure gradient of embolic protection devices
- Computer assistance in femoral derotation osteotomy: a bottom-up approach
- Automatic depth scanning system for 3D infrared thermography
- A service for monitoring the quality of intraoperative cone beam CT images
- Resectoscope with an easy to use twist mechanism for improved handling
- In vitro simulation of distribution processes following intramuscular injection
- Adjusting inkjet printhead parameters to deposit drugs into micro-sized reservoirs
- A flexible standalone system with integrated sensor feedback for multi-pad electrode FES of the hand
- Smart control for functional electrical stimulation with optimal pulse intensity
- Tactile display on the remaining hand for unilateral hand amputees
- Effects of sustained electrical stimulation on spasticity assessed by the pendulum test
- An improved tracking framework for ultrasound probe localization in image-guided radiosurgery
- Improvement of a subviral particle tracker by the use of a LAP-Kalman-algorithm
- Learning discriminative classification models for grading anal intraepithelial neoplasia
- Regularization of EIT reconstruction based on multi-scales wavelet transforms
- Assessing MRI susceptibility artefact through an indicator of image distortion
- EyeGuidance – a computer controlled system to guide eye movements
- A framework for feedback-based segmentation of 3D image stacks
- Doppler optical coherence tomography as a promising tool for detecting fluid in the human middle ear
- 3D Local in vivo Environment (LivE) imaging for single cell protein analysis of bone tissue
- Inside-Out access strategy using new trans-vascular catheter approach
- US/MRI fusion with new optical tracking and marker approach for interventional procedures inside the MRI suite
- Impact of different registration methods in MEG source analysis
- 3D segmentation of thyroid ultrasound images using active contours
- Designing a compact MRI motion phantom
- Cerebral cortex classification by conditional random fields applied to intraoperative thermal imaging
- Classification of indirect immunofluorescence images using thresholded local binary count features
- Analysis of muscle fatigue conditions using time-frequency images and GLCM features
- Numerical evaluation of image parameters of ETR-1
- Fabrication of a compliant phantom of the human aortic arch for use in Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experimentation
- Effect of the number of electrodes on the reconstructed lung shape in electrical impedance tomography
- Hardware dependencies of GPU-accelerated beamformer performances for microwave breast cancer detection
- Computer assisted assessment of progressing osteoradionecrosis of the jaw for clinical diagnosis and treatment
- Evaluation of reconstruction parameters of electrical impedance tomography on aorta detection during saline bolus injection
- Evaluation of open-source software for the lung segmentation
- Automatic determination of lung features of CF patients in CT scans
- Image analysis of self-organized multicellular patterns
- Effect of key parameters on synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPIONs)
- Radiopacity assessment of neurovascular implants
- Development of a desiccant based dielectric for monitoring humidity conditions in miniaturized hermetic implantable packages
- Development of an artifact-free aneurysm clip
- Enhancing the regeneration of bone defects by alkalizing the peri-implant zone – an in vitro approach
- Rapid prototyping of replica knee implants for in vitro testing
- Protecting ultra- and hyperhydrophilic implant surfaces in dry state from loss of wettability
- Advanced wettability analysis of implant surfaces
- Patient-specific hip prostheses designed by surgeons
- Plasma treatment on novel carbon fiber reinforced PEEK cages to enhance bioactivity
- Wear of a total intervertebral disc prosthesis
- Digital health and digital biomarkers – enabling value chains on health data
- Usability in the lifecycle of medical software development
- Influence of different test gases in a non-destructive 100% quality control system for medical devices
- Device development guided by user satisfaction survey on auricular vagus nerve stimulation
- Empirical assessment of the time course of innovation in biomedical engineering: first results of a comparative approach
- Effect of left atrial hypertrophy on P-wave morphology in a computational model
- Simulation of intracardiac electrograms around acute ablation lesions
- Parametrization of activation based cardiac electrophysiology models using bidomain model simulations
- Assessment of nasal resistance using computational fluid dynamics
- Resistance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Inspiratory and expiratory elastance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Determination of regional lung function in cystic fibrosis using electrical impedance tomography
- Development of parietal bone surrogates for parietal graft lift training
- Numerical simulation of mechanically stimulated bone remodelling
- Conversion of engineering stresses to Cauchy stresses in tensile and compression tests of thermoplastic polymers
- Numerical examinations of simplified spondylodesis models concerning energy absorption in magnetic resonance imaging
- Principle study on the signal connection at transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
- Influence of Siluron® insertion on model drug distribution in the simulated vitreous body
- Evaluating different approaches to identify a three parameter gas exchange model
- Effects of fibrosis on the extracellular potential based on 3D reconstructions from histological sections of heart tissue
- From imaging to hemodynamics – how reconstruction kernels influence the blood flow predictions in intracranial aneurysms
- Flow optimised design of a novel point-of-care diagnostic device for the detection of disease specific biomarkers
- Improved FPGA controlled artificial vascular system for plethysmographic measurements
- Minimally spaced electrode positions for multi-functional chest sensors: ECG and respiratory signal estimation
- Automated detection of alveolar arches for nasoalveolar molding in cleft lip and palate treatment
- Control scheme selection in human-machine- interfaces by analysis of activity signals
- Event-based sampling for reducing communication load in realtime human motion analysis by wireless inertial sensor networks
- Automatic pairing of inertial sensors to lower limb segments – a plug-and-play approach
- Contactless respiratory monitoring system for magnetic resonance imaging applications using a laser range sensor
- Interactive monitoring system for visual respiratory biofeedback
- Development of a low-cost senor based aid for visually impaired people
- Patient assistive system for the shoulder joint
- A passive beating heart setup for interventional cardiology training

