Abstract
Ensuring optimal climate conditions during cultivation is essential for successful and reproducible cell culture based investigation. Being the gold standard, carbon dioxide incubators fulfill this demand in various geometries and sizes to suit diverse cultivation applications. A door opening results in a climate breakdown followed by a restoration period during which optimal conditions cannot be guaranteed. The following paper investigates the influence of incubator door design to optimize climate retainment during the above mentioned event.
1 Introduction
Cell culture assays have become standardized methods in the toolbox also of medical engineers e.g. to test new materials for cytotoxicity as an alternative for animal testing [1]. Therefore, a broad range of established cell lines are available, which are comfortable to handle. Nevertheless, biological systems like cell cultures are sensitive to temperature and CO2 fluctuation. Thus the employment of a suitable incubator is important [1], because the probe has to reside for a long time in an optimal thermal and gaseous environment e.g. 37°C, 10 Vol-% CO2, >90% rh. Though it is not required to ensure the absolute niveau of the parameters rather than keeping them as constant as possible within the limits [1]. The inspection of atmosphere constancy of an incubator is regulated in the DIN 12880 [2].
During access to the incubator due to door opening the climate is exchanged with the surrounding atmosphere. Based on our experience a duration of more than 30 s the distinct gaseous components have emanated to the external environment. Furthermore the inside of the incubator is cooling down. Improvement of the door opening kinematic may hold potential to reduce said exchange and also induced turbulence i.e. air movement during door opening. This may lead to lowering impact on the samples, saving valuable and costly resources and lower the risk to introduce potential harmful particles as carrier for bacteria [3] into the incubator’s atmosphere. Investigations via experimental light section flow visualization [4], [5] and CFD simulation have been conducted to compare an adjusted door opening concept to the conventional incubator design.
2 Materials and methods
The typical carbon dioxide incubator relies on a two-fold swing door concept consisting of an outer temperature regulated metal door and an inner glass door. In contrast to the standard design a sliding door concept, as shown in Figure 1, is suggested to replace the inner door. It is expected to reduce turbulence and induced suction to the inner gas volume when being operated. The new door concept is compared to the state of the art by CFD-simulation and an experiment of visualization of fluid flow via light section. The simulation is performed with ANSYS Fluent®. The geometry of an incubator prototype is used to define the inner volume with three perforated shelves (modelled as pressure jump boundary conditions) in place. Both door concepts are modelled to comply with the real dimensions. The sliding door model is derived from the working prototype, used for the light section investigation. Its opening area is slightly reduced compared to the swing door. The movement of both doors is realized by using dynamic meshes with user defined functions (UDF) applied to the moving boundaries. The k-ε turbulence model is applied. The setup of the light section experiment is shown in Figure 2. A mock-up of an incubator is used enclosing an inner volume of approx. 180 l which is temperature regulated (37°C) and filled with effect fog for every run of the experiment. The aperture of the mock-up allows mounting of either a swing door or the prototype of the sliding door concept. The inner volume is also equipped with three perforated shelves. During door opening the fog emanates and is visualized by a laser plane projected perpendicular to the aperture plane. Light section images are taken with a camera system from door opening until after 30 s. Characteristic dimensions for simulation and experiment are listed in Table 1.
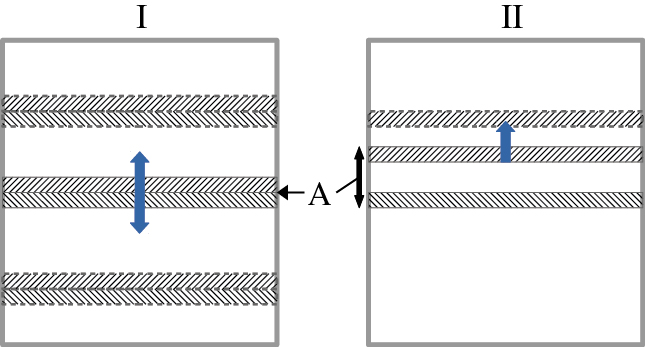
Sliding door concept for a carbon dioxide incubator. The door is horizontally split into an upper and lower section (I) which are initially connected. The linked sections can be moved up and down to the preferred the access access postion (A). If the position of interest has been reached the link between both sections may be severed and the access zone may be extended to a height that is comfortable to retrieve a sample from the inside of the incubator (II).
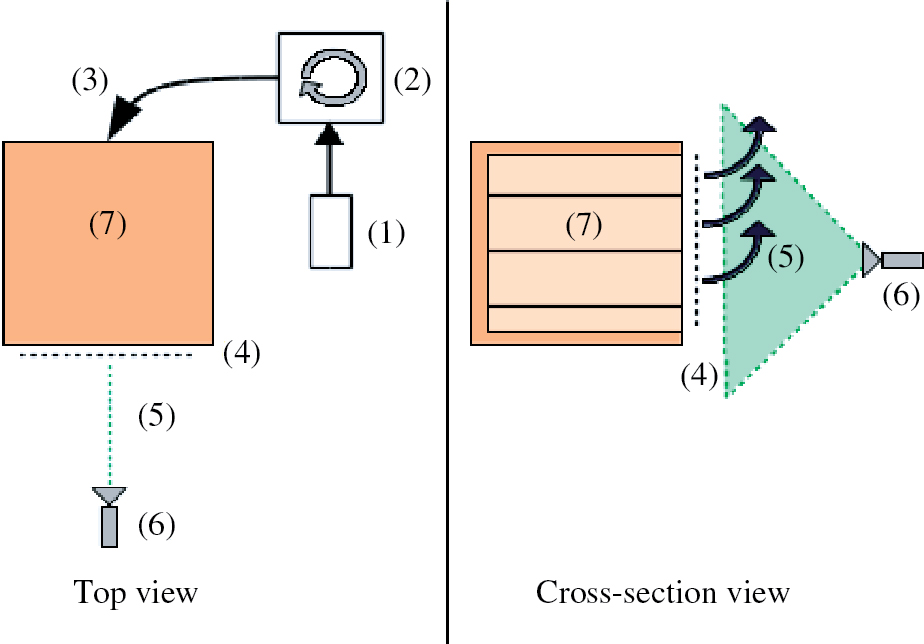
Sketch of the light section experiment in top and cross-section view: (1) fog machine, (2) fog homogenizer, (3) fog injection to the mock-up, (4) aperture with door system, (5) laser plane, (6) laser source with line generator (7) incubator mock-up.
Boundary conditions of experimental and simulated setup.
| Simulation | |
|---|---|
| Inner volume of incubator (w × h × d) | 590 mm × 590 mm × 538 mm |
| Inner atmosphere | 37°C, 10 Vol-% CO2, 95 % rh |
| Outer atmosphere | 20°C, room air |
| Aperture of swing door (w × h) | 590 mm × 590 mm |
| Aperture of sliding door (w × h) | 480 mm × 480 mm |
| Light section experiment | |
| Inner volume of incubator (w × h × d) | 590 mm × 590 mm × 538 mm |
| Inner atmosphere | ∼37°C, effect fog |
| room air mixture | |
| Outer atmosphere | 20°C, room air |
| Aperture of swing door (w × h) | 590 mm × 590 mm |
| Aperture of sliding door (w × h) | 480 mm × 480 mm |
3 Results
3.1 Simulation results
As a result of the post-processing of the simulated data Figure 3 shows the magnitude of the induced velocity in the vertical symmetrical plane of the incubator in the relevant area during door opening with the respective opening kinematic. Both opening processes are simulated to be finished after 1 s. Especially at the beginning of the swing door opening the induced velocity in the opening gap between the door and the incubator is very high due to the suction of the opening door. The velocity magnitude remains high throughout the opening process as a result of the fluid displacement, thus there are also eddies disturbing the atmosphere inside the incubator. In contrast, the sliding door concept induces only little air movement during door opening in the area surrounding the moving part of the door, leading to much smaller eddies. Figure 4 visualizes the average and extremal values of carbon dioxide concentration in the incubator over the time span between the closed door and 15 s after the beginning of opening, determined at the coordinates within the incubator defined in DIN 12880 [2]. The rapid decline of the minimum curve of the swinging door during the first second is due to the described high velocities close to the door, resulting in a fast mixing between the inner and surrounding atmosphere, whereas in the sliding concept the suction is much smaller, resulting in much less mixing. Exchange of atmosphere is then achieved only by natural convection and diffusion leading to a much smaller amount of climate loss during door opening. After door opening these mechanisms result in a steady decline of the before established atmosphere. The atmosphere using the sliding approach is declining slower.
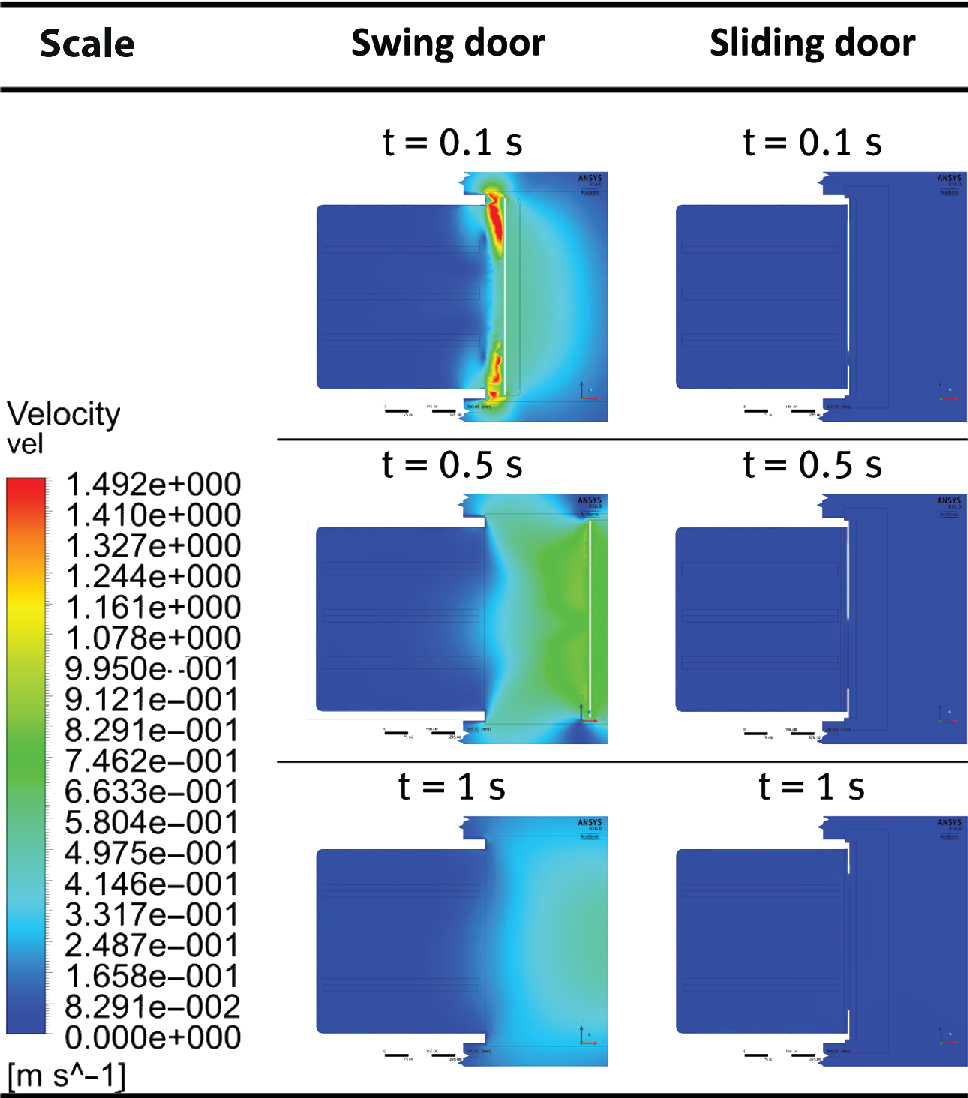
Comparison of resulting air flow induced by door opening in the vertical symmetrical plane of the incubator.
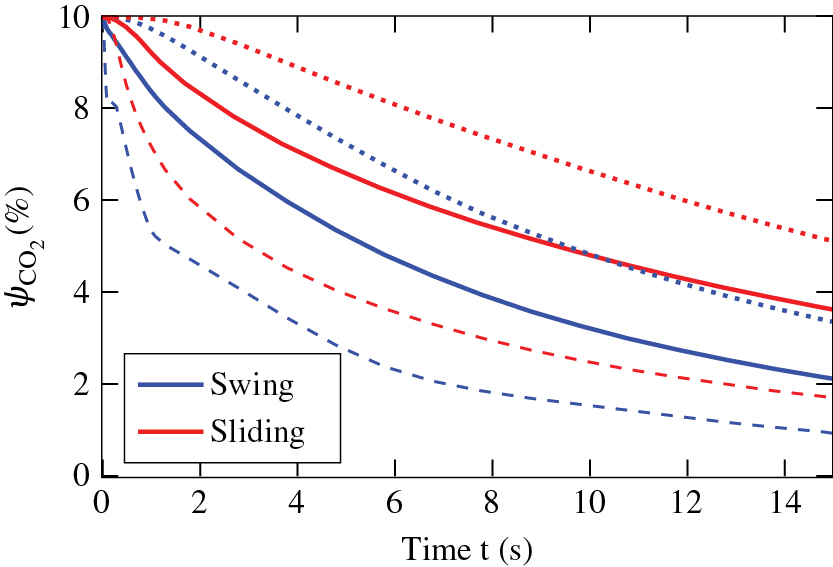
Plot of CO2 volume fraction over a period of 15 s for the swing and the sliding door system: dotted: maximum inside the volume drawn through: mean inside the volume dashed: minimum inside the volume
3.2 Light section results
The resulting movement of fluid from the start (t = 0 s) until finish (t = 1 s) of the door opening process is compared for the swing and the sliding door in Figure 5 . The inner atmosphere (visualized by fog) seems to adhere to the moving swing door (t = 0.5 s, opening angle approx. 45°). Furthermore two major eddies can be recognized on the upper and the lower edge. After door movement has completed (t = 1 s, opening angle 90°) two air drafts on the upper and the lower level can be seen that reach out by the length of the swing door.
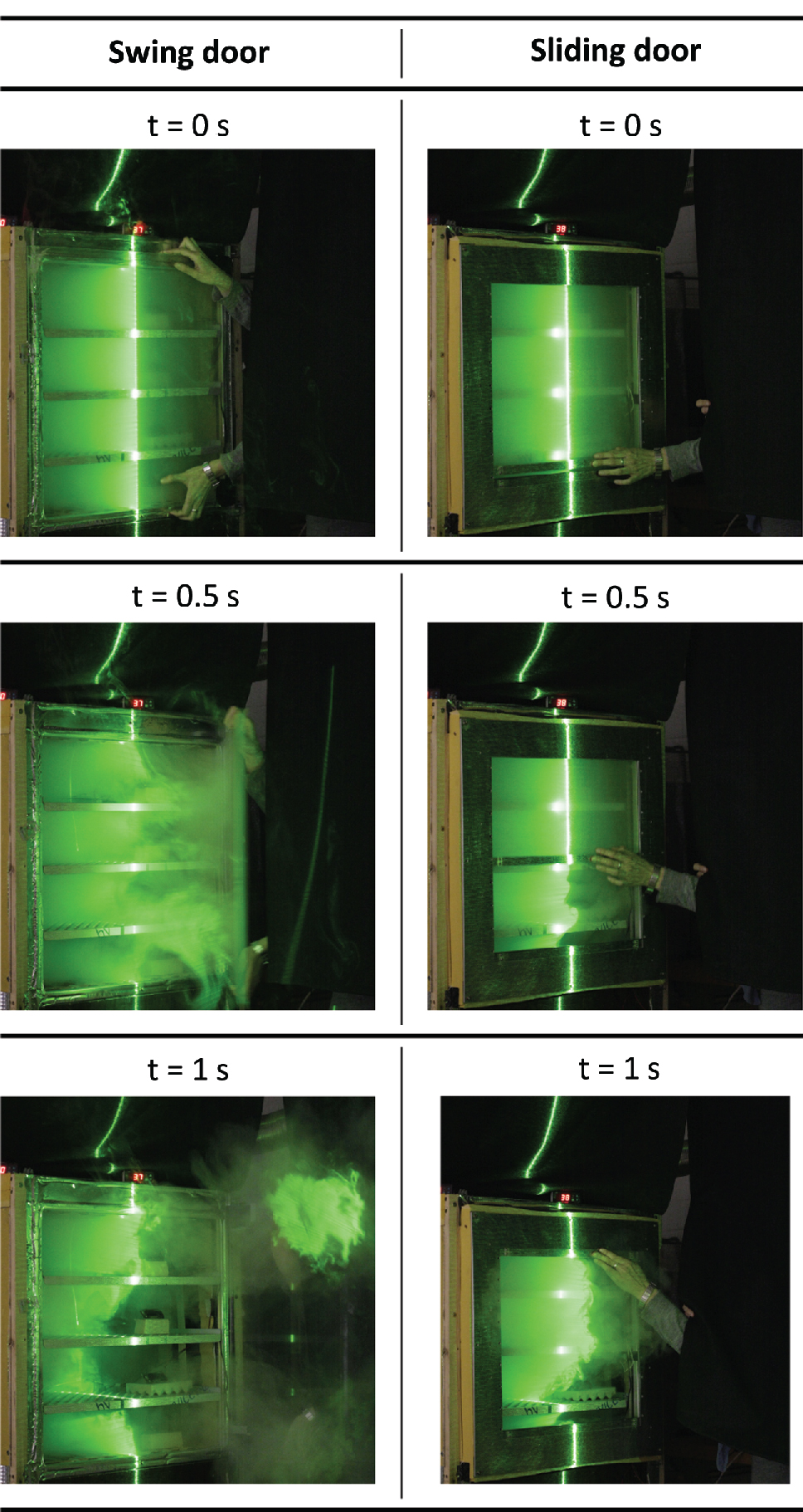
Comparison of swing and sliding concept over the duration (1s) of active door movement by light section photography.
The upward movement of the sliding door generates small delicate eddies. After completion of opening procedure the primary movement direction of the atmosphere is upwards due to natural convection which remains the dominating effect as shown in Figure 6. After 10 s the atmosphere of the swing door has emanated to a higher extent than for the sliding door setup. At t = 20 s the inner atmosphere is nearly depleted whereas emanating atmosphere from the mock-up with the sliding door is still clearly visible. Just before closing the door after 30 s the atmosphere has been exchanged completely with the environment for both concepts.
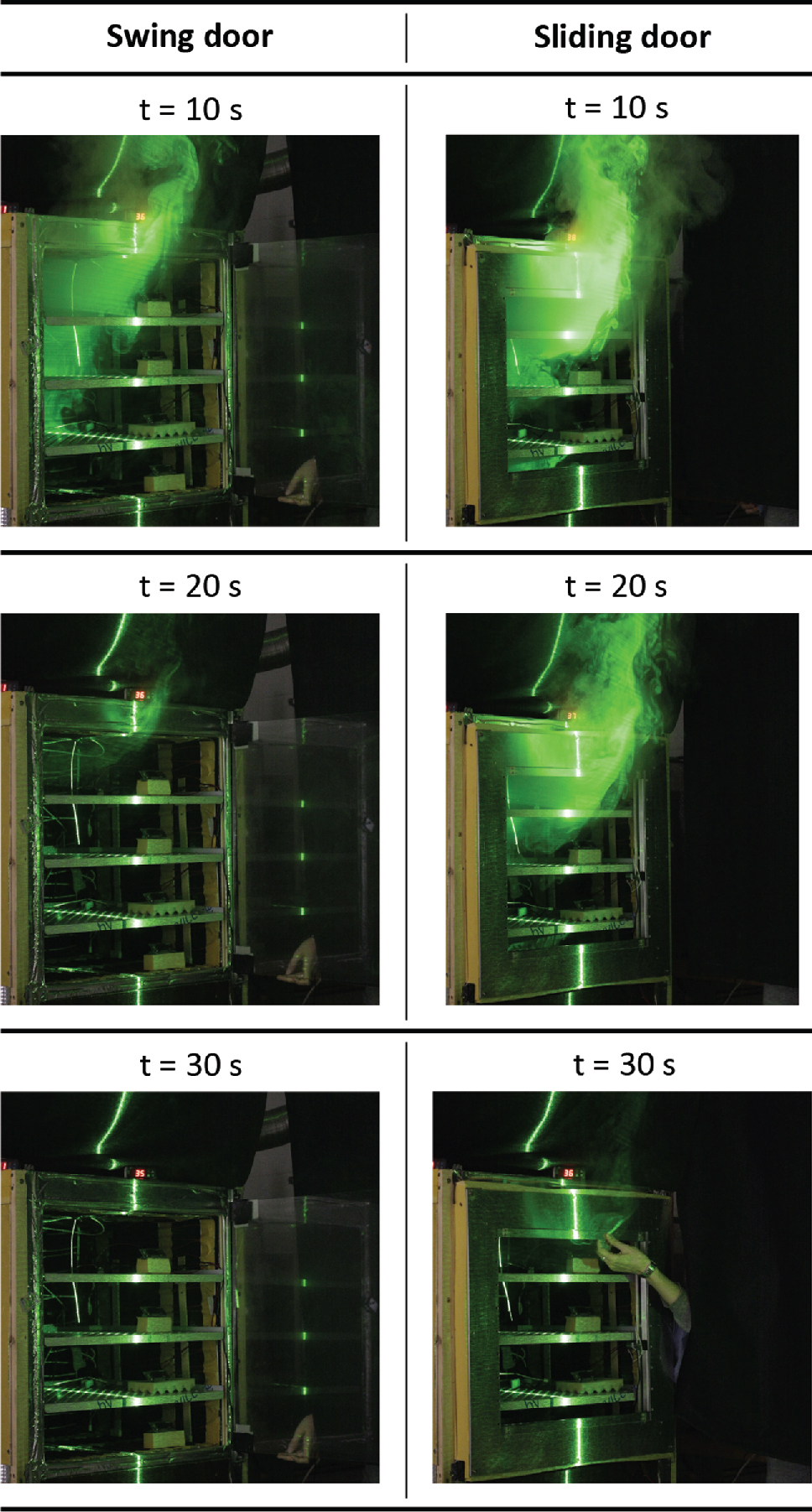
Comparison of resulting atmosphere exchange after active door movement is completed.
4 Discussion and conclusion
The comparison of the suggested sliding with a standard swing door concept shows that there is a high influence during the opening process on fluid movement of door kinematic which is obvious in the simulation as well as in the experiment. The suction of the swing movement induces higher fluid velocity and bigger eddies, which may favor the introduction of particles from the outside and thus increase the risk for contamination. Furthermore the atmosphere exchange or depletion occurs faster for the swing than for the sliding door though this outcome might be biased due to the reduced aperture area. Regarding the performance of both concepts over the standardised duration of 30 s according to DIN 12880 [2] one can state that the atmosphere depletes completely for both concepts. An improvement of retainment might be possible by using the option to individually define the aperture position and area by adjusting the sliding door to the position and aperture size required for access to the inside (cf. Figure 1). A clear advantage is the reduced turbulence of air induced by the sliding mechanism, since this is favorable for clean working conditions as well as clean room environments.
Author’s Statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest. Material and methods: Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study. Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
References
[1] Gstaunthaler G, Lindl T. Zell- und Gewebekultur. 7th ed. Springer Spektrum; 2013.10.1007/978-3-642-35997-2Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Deutsches Institut für Normung eV. Elektrische Laborgeräte und Brutschränke DIN 12880. Beuth Verlag Berlin; 2007.Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Keller M. Biokontaminationskontrolle. In: Gail L, Gommel U, Hortig HP, editors. Reinraumtechnik. Springer; 2011. p. 461–82.10.1007/978-3-642-19435-1_11Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Donges A, Noll R. Springer Series in Optical Sciences: Laser Measurement Technology. Vol. 188. Springe; 2015.10.1007/978-3-662-43634-9Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Eckelmann H. Einführung in die Strömungsmeßtechnik. Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH; 1997.10.1007/978-3-663-09882-9Suche in Google Scholar
©2016 Matthias B. Schuh et al., licensee De Gruyter.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Synthesis and characterization of PIL/pNIPAAm hybrid hydrogels
- Novel blood protein based scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering
- Cell adhesion and viability of human endothelial cells on electrospun polymer scaffolds
- Effects of heat treatment and welding process on superelastic behaviour and microstructure of micro electron beam welded NiTi
- Long-term stable modifications of silicone elastomer for improved hemocompatibility
- The effect of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of PLLA tubular specimens
- Biocompatible wear-resistant thick ceramic coating
- Protection of active implant electronics with organosilicon open air plasma coating for plastic overmolding
- Examination of dielectric strength of thin Parylene C films under various conditions
- Open air plasma deposited antimicrobial SiOx/TiOx composite films for biomedical applications
- Systemic analysis about residual chloroform in PLLA films
- A macrophage model of osseointegration
- Towards in silico prognosis using big data
- Technical concept and evaluation of a novel shoulder simulator with adaptive muscle force generation and free motion
- Usability evaluation of a locomotor therapy device considering different strategies
- Hypoxia-on-a-chip
- Integration of a semi-automatic in-vitro RFA procedure into an experimental setup
- Fabrication of MEMS-based 3D-μECoG-MEAs
- High speed digital interfacing for a neural data acquisition system
- Bionic forceps for the handling of sensitive tissue
- Experimental studies on 3D printing of barium titanate ceramics for medical applications
- Patient specific root-analogue dental implants – additive manufacturing and finite element analysis
- 3D printing – a key technology for tailored biomedical cell culture lab ware
- 3D printing of hydrogels in a temperature controlled environment with high spatial resolution
- Biocompatibility of photopolymers for additive manufacturing
- Biochemical piezoresistive sensors based on pH- and glucose-sensitive hydrogels for medical applications
- Novel wireless measurement system of pressure dedicated to in vivo studies
- Portable auricular device for real-time swallow and chew detection
- Detection of miRNA using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor and antibody amplification
- Simulation and evaluation of stimulation scenarios for targeted vestibular nerve excitation
- Deep brain stimulation: increasing efficiency by alternative waveforms
- Prediction of immediately occurring microsleep events from brain electric signals
- Determining cardiac vagal threshold from short term heart rate complexity
- Classification of cardiac excitation patterns during atrial fibrillation
- An algorithm to automatically determine the cycle length coverage to identify rotational activity during atrial fibrillation – a simulation study
- Deriving respiration from high resolution 12-channel-ECG during cycling exercise
- Reducing of gradient induced artifacts on the ECG signal during MRI examinations using Wilcoxon filter
- Automatic detection and mapping of double potentials in intracardiac electrograms
- Modeling the pelvic region for non-invasive pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring
- Postprocessing algorithm for automated analysis of pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring signals
- Best practice: surgeon driven application in pelvic operations
- Vasomotor assessment by camera-based photoplethysmography
- Classification of morphologic changes in photoplethysmographic waveforms
- Novel computation of pulse transit time from multi-channel PPG signals by wavelet transform
- Efficient design of FIR filter based low-pass differentiators for biomedical signal processing
- Nonlinear causal influences assessed by mutual compression entropy
- Comparative study of methods for solving the correspondence problem in EMD applications
- fNIRS for future use in auditory diagnostics
- Semi-automated detection of fractional shortening in zebrafish embryo heart videos
- Blood pressure measurement on the cheek
- Derivation of the respiratory rate from directly and indirectly measured respiratory signals using autocorrelation
- Left cardiac atrioventricular delay and inter-ventricular delay in cardiac resynchronization therapy responder and non-responder
- An automatic systolic peak detector of blood pressure waveforms using 4th order cumulants
- Real-time QRS detection using integrated variance for ECG gated cardiac MRI
- Preprocessing of unipolar signals acquired by a novel intracardiac mapping system
- In-vitro experiments to characterize ventricular electromechanics
- Continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure in the operating room: a cuffless optical technology at the fingertip
- Application of microwave sensor technology in cardiovascular disease for plaque detection
- Artificial blood circulatory and special Ultrasound Doppler probes for detecting and sizing gaseous embolism
- Detection of microsleep events in a car driving simulation study using electrocardiographic features
- A method to determine the kink resistance of stents and stent delivery systems according to international standards
- Comparison of stented bifurcation and straight vessel 3D-simulation with a prior simulated velocity profile inlet
- Transient Euler-Lagrange/DEM simulation of stent thrombosis
- Automated control of the laser welding process of heart valve scaffolds
- Automation of a test bench for accessing the bendability of electrospun vascular grafts
- Influence of storage conditions on the release of growth factors in platelet-rich blood derivatives
- Cryopreservation of cells using defined serum-free cryoprotective agents
- New bioreactor vessel for tissue engineering of human nasal septal chondrocytes
- Determination of the membrane hydraulic permeability of MSCs
- Climate retainment in carbon dioxide incubators
- Multiple factors influencing OR ventilation system effectiveness
- Evaluation of an app-based stress protocol
- Medication process in Styrian hospitals
- Control tower to surgical theater
- Development of a skull phantom for the assessment of implant X-ray visibility
- Surgical navigation with QR codes
- Investigation of the pressure gradient of embolic protection devices
- Computer assistance in femoral derotation osteotomy: a bottom-up approach
- Automatic depth scanning system for 3D infrared thermography
- A service for monitoring the quality of intraoperative cone beam CT images
- Resectoscope with an easy to use twist mechanism for improved handling
- In vitro simulation of distribution processes following intramuscular injection
- Adjusting inkjet printhead parameters to deposit drugs into micro-sized reservoirs
- A flexible standalone system with integrated sensor feedback for multi-pad electrode FES of the hand
- Smart control for functional electrical stimulation with optimal pulse intensity
- Tactile display on the remaining hand for unilateral hand amputees
- Effects of sustained electrical stimulation on spasticity assessed by the pendulum test
- An improved tracking framework for ultrasound probe localization in image-guided radiosurgery
- Improvement of a subviral particle tracker by the use of a LAP-Kalman-algorithm
- Learning discriminative classification models for grading anal intraepithelial neoplasia
- Regularization of EIT reconstruction based on multi-scales wavelet transforms
- Assessing MRI susceptibility artefact through an indicator of image distortion
- EyeGuidance – a computer controlled system to guide eye movements
- A framework for feedback-based segmentation of 3D image stacks
- Doppler optical coherence tomography as a promising tool for detecting fluid in the human middle ear
- 3D Local in vivo Environment (LivE) imaging for single cell protein analysis of bone tissue
- Inside-Out access strategy using new trans-vascular catheter approach
- US/MRI fusion with new optical tracking and marker approach for interventional procedures inside the MRI suite
- Impact of different registration methods in MEG source analysis
- 3D segmentation of thyroid ultrasound images using active contours
- Designing a compact MRI motion phantom
- Cerebral cortex classification by conditional random fields applied to intraoperative thermal imaging
- Classification of indirect immunofluorescence images using thresholded local binary count features
- Analysis of muscle fatigue conditions using time-frequency images and GLCM features
- Numerical evaluation of image parameters of ETR-1
- Fabrication of a compliant phantom of the human aortic arch for use in Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experimentation
- Effect of the number of electrodes on the reconstructed lung shape in electrical impedance tomography
- Hardware dependencies of GPU-accelerated beamformer performances for microwave breast cancer detection
- Computer assisted assessment of progressing osteoradionecrosis of the jaw for clinical diagnosis and treatment
- Evaluation of reconstruction parameters of electrical impedance tomography on aorta detection during saline bolus injection
- Evaluation of open-source software for the lung segmentation
- Automatic determination of lung features of CF patients in CT scans
- Image analysis of self-organized multicellular patterns
- Effect of key parameters on synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPIONs)
- Radiopacity assessment of neurovascular implants
- Development of a desiccant based dielectric for monitoring humidity conditions in miniaturized hermetic implantable packages
- Development of an artifact-free aneurysm clip
- Enhancing the regeneration of bone defects by alkalizing the peri-implant zone – an in vitro approach
- Rapid prototyping of replica knee implants for in vitro testing
- Protecting ultra- and hyperhydrophilic implant surfaces in dry state from loss of wettability
- Advanced wettability analysis of implant surfaces
- Patient-specific hip prostheses designed by surgeons
- Plasma treatment on novel carbon fiber reinforced PEEK cages to enhance bioactivity
- Wear of a total intervertebral disc prosthesis
- Digital health and digital biomarkers – enabling value chains on health data
- Usability in the lifecycle of medical software development
- Influence of different test gases in a non-destructive 100% quality control system for medical devices
- Device development guided by user satisfaction survey on auricular vagus nerve stimulation
- Empirical assessment of the time course of innovation in biomedical engineering: first results of a comparative approach
- Effect of left atrial hypertrophy on P-wave morphology in a computational model
- Simulation of intracardiac electrograms around acute ablation lesions
- Parametrization of activation based cardiac electrophysiology models using bidomain model simulations
- Assessment of nasal resistance using computational fluid dynamics
- Resistance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Inspiratory and expiratory elastance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Determination of regional lung function in cystic fibrosis using electrical impedance tomography
- Development of parietal bone surrogates for parietal graft lift training
- Numerical simulation of mechanically stimulated bone remodelling
- Conversion of engineering stresses to Cauchy stresses in tensile and compression tests of thermoplastic polymers
- Numerical examinations of simplified spondylodesis models concerning energy absorption in magnetic resonance imaging
- Principle study on the signal connection at transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
- Influence of Siluron® insertion on model drug distribution in the simulated vitreous body
- Evaluating different approaches to identify a three parameter gas exchange model
- Effects of fibrosis on the extracellular potential based on 3D reconstructions from histological sections of heart tissue
- From imaging to hemodynamics – how reconstruction kernels influence the blood flow predictions in intracranial aneurysms
- Flow optimised design of a novel point-of-care diagnostic device for the detection of disease specific biomarkers
- Improved FPGA controlled artificial vascular system for plethysmographic measurements
- Minimally spaced electrode positions for multi-functional chest sensors: ECG and respiratory signal estimation
- Automated detection of alveolar arches for nasoalveolar molding in cleft lip and palate treatment
- Control scheme selection in human-machine- interfaces by analysis of activity signals
- Event-based sampling for reducing communication load in realtime human motion analysis by wireless inertial sensor networks
- Automatic pairing of inertial sensors to lower limb segments – a plug-and-play approach
- Contactless respiratory monitoring system for magnetic resonance imaging applications using a laser range sensor
- Interactive monitoring system for visual respiratory biofeedback
- Development of a low-cost senor based aid for visually impaired people
- Patient assistive system for the shoulder joint
- A passive beating heart setup for interventional cardiology training
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Synthesis and characterization of PIL/pNIPAAm hybrid hydrogels
- Novel blood protein based scaffolds for cardiovascular tissue engineering
- Cell adhesion and viability of human endothelial cells on electrospun polymer scaffolds
- Effects of heat treatment and welding process on superelastic behaviour and microstructure of micro electron beam welded NiTi
- Long-term stable modifications of silicone elastomer for improved hemocompatibility
- The effect of thermal treatment on the mechanical properties of PLLA tubular specimens
- Biocompatible wear-resistant thick ceramic coating
- Protection of active implant electronics with organosilicon open air plasma coating for plastic overmolding
- Examination of dielectric strength of thin Parylene C films under various conditions
- Open air plasma deposited antimicrobial SiOx/TiOx composite films for biomedical applications
- Systemic analysis about residual chloroform in PLLA films
- A macrophage model of osseointegration
- Towards in silico prognosis using big data
- Technical concept and evaluation of a novel shoulder simulator with adaptive muscle force generation and free motion
- Usability evaluation of a locomotor therapy device considering different strategies
- Hypoxia-on-a-chip
- Integration of a semi-automatic in-vitro RFA procedure into an experimental setup
- Fabrication of MEMS-based 3D-μECoG-MEAs
- High speed digital interfacing for a neural data acquisition system
- Bionic forceps for the handling of sensitive tissue
- Experimental studies on 3D printing of barium titanate ceramics for medical applications
- Patient specific root-analogue dental implants – additive manufacturing and finite element analysis
- 3D printing – a key technology for tailored biomedical cell culture lab ware
- 3D printing of hydrogels in a temperature controlled environment with high spatial resolution
- Biocompatibility of photopolymers for additive manufacturing
- Biochemical piezoresistive sensors based on pH- and glucose-sensitive hydrogels for medical applications
- Novel wireless measurement system of pressure dedicated to in vivo studies
- Portable auricular device for real-time swallow and chew detection
- Detection of miRNA using a surface plasmon resonance biosensor and antibody amplification
- Simulation and evaluation of stimulation scenarios for targeted vestibular nerve excitation
- Deep brain stimulation: increasing efficiency by alternative waveforms
- Prediction of immediately occurring microsleep events from brain electric signals
- Determining cardiac vagal threshold from short term heart rate complexity
- Classification of cardiac excitation patterns during atrial fibrillation
- An algorithm to automatically determine the cycle length coverage to identify rotational activity during atrial fibrillation – a simulation study
- Deriving respiration from high resolution 12-channel-ECG during cycling exercise
- Reducing of gradient induced artifacts on the ECG signal during MRI examinations using Wilcoxon filter
- Automatic detection and mapping of double potentials in intracardiac electrograms
- Modeling the pelvic region for non-invasive pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring
- Postprocessing algorithm for automated analysis of pelvic intraoperative neuromonitoring signals
- Best practice: surgeon driven application in pelvic operations
- Vasomotor assessment by camera-based photoplethysmography
- Classification of morphologic changes in photoplethysmographic waveforms
- Novel computation of pulse transit time from multi-channel PPG signals by wavelet transform
- Efficient design of FIR filter based low-pass differentiators for biomedical signal processing
- Nonlinear causal influences assessed by mutual compression entropy
- Comparative study of methods for solving the correspondence problem in EMD applications
- fNIRS for future use in auditory diagnostics
- Semi-automated detection of fractional shortening in zebrafish embryo heart videos
- Blood pressure measurement on the cheek
- Derivation of the respiratory rate from directly and indirectly measured respiratory signals using autocorrelation
- Left cardiac atrioventricular delay and inter-ventricular delay in cardiac resynchronization therapy responder and non-responder
- An automatic systolic peak detector of blood pressure waveforms using 4th order cumulants
- Real-time QRS detection using integrated variance for ECG gated cardiac MRI
- Preprocessing of unipolar signals acquired by a novel intracardiac mapping system
- In-vitro experiments to characterize ventricular electromechanics
- Continuous non-invasive monitoring of blood pressure in the operating room: a cuffless optical technology at the fingertip
- Application of microwave sensor technology in cardiovascular disease for plaque detection
- Artificial blood circulatory and special Ultrasound Doppler probes for detecting and sizing gaseous embolism
- Detection of microsleep events in a car driving simulation study using electrocardiographic features
- A method to determine the kink resistance of stents and stent delivery systems according to international standards
- Comparison of stented bifurcation and straight vessel 3D-simulation with a prior simulated velocity profile inlet
- Transient Euler-Lagrange/DEM simulation of stent thrombosis
- Automated control of the laser welding process of heart valve scaffolds
- Automation of a test bench for accessing the bendability of electrospun vascular grafts
- Influence of storage conditions on the release of growth factors in platelet-rich blood derivatives
- Cryopreservation of cells using defined serum-free cryoprotective agents
- New bioreactor vessel for tissue engineering of human nasal septal chondrocytes
- Determination of the membrane hydraulic permeability of MSCs
- Climate retainment in carbon dioxide incubators
- Multiple factors influencing OR ventilation system effectiveness
- Evaluation of an app-based stress protocol
- Medication process in Styrian hospitals
- Control tower to surgical theater
- Development of a skull phantom for the assessment of implant X-ray visibility
- Surgical navigation with QR codes
- Investigation of the pressure gradient of embolic protection devices
- Computer assistance in femoral derotation osteotomy: a bottom-up approach
- Automatic depth scanning system for 3D infrared thermography
- A service for monitoring the quality of intraoperative cone beam CT images
- Resectoscope with an easy to use twist mechanism for improved handling
- In vitro simulation of distribution processes following intramuscular injection
- Adjusting inkjet printhead parameters to deposit drugs into micro-sized reservoirs
- A flexible standalone system with integrated sensor feedback for multi-pad electrode FES of the hand
- Smart control for functional electrical stimulation with optimal pulse intensity
- Tactile display on the remaining hand for unilateral hand amputees
- Effects of sustained electrical stimulation on spasticity assessed by the pendulum test
- An improved tracking framework for ultrasound probe localization in image-guided radiosurgery
- Improvement of a subviral particle tracker by the use of a LAP-Kalman-algorithm
- Learning discriminative classification models for grading anal intraepithelial neoplasia
- Regularization of EIT reconstruction based on multi-scales wavelet transforms
- Assessing MRI susceptibility artefact through an indicator of image distortion
- EyeGuidance – a computer controlled system to guide eye movements
- A framework for feedback-based segmentation of 3D image stacks
- Doppler optical coherence tomography as a promising tool for detecting fluid in the human middle ear
- 3D Local in vivo Environment (LivE) imaging for single cell protein analysis of bone tissue
- Inside-Out access strategy using new trans-vascular catheter approach
- US/MRI fusion with new optical tracking and marker approach for interventional procedures inside the MRI suite
- Impact of different registration methods in MEG source analysis
- 3D segmentation of thyroid ultrasound images using active contours
- Designing a compact MRI motion phantom
- Cerebral cortex classification by conditional random fields applied to intraoperative thermal imaging
- Classification of indirect immunofluorescence images using thresholded local binary count features
- Analysis of muscle fatigue conditions using time-frequency images and GLCM features
- Numerical evaluation of image parameters of ETR-1
- Fabrication of a compliant phantom of the human aortic arch for use in Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) experimentation
- Effect of the number of electrodes on the reconstructed lung shape in electrical impedance tomography
- Hardware dependencies of GPU-accelerated beamformer performances for microwave breast cancer detection
- Computer assisted assessment of progressing osteoradionecrosis of the jaw for clinical diagnosis and treatment
- Evaluation of reconstruction parameters of electrical impedance tomography on aorta detection during saline bolus injection
- Evaluation of open-source software for the lung segmentation
- Automatic determination of lung features of CF patients in CT scans
- Image analysis of self-organized multicellular patterns
- Effect of key parameters on synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPIONs)
- Radiopacity assessment of neurovascular implants
- Development of a desiccant based dielectric for monitoring humidity conditions in miniaturized hermetic implantable packages
- Development of an artifact-free aneurysm clip
- Enhancing the regeneration of bone defects by alkalizing the peri-implant zone – an in vitro approach
- Rapid prototyping of replica knee implants for in vitro testing
- Protecting ultra- and hyperhydrophilic implant surfaces in dry state from loss of wettability
- Advanced wettability analysis of implant surfaces
- Patient-specific hip prostheses designed by surgeons
- Plasma treatment on novel carbon fiber reinforced PEEK cages to enhance bioactivity
- Wear of a total intervertebral disc prosthesis
- Digital health and digital biomarkers – enabling value chains on health data
- Usability in the lifecycle of medical software development
- Influence of different test gases in a non-destructive 100% quality control system for medical devices
- Device development guided by user satisfaction survey on auricular vagus nerve stimulation
- Empirical assessment of the time course of innovation in biomedical engineering: first results of a comparative approach
- Effect of left atrial hypertrophy on P-wave morphology in a computational model
- Simulation of intracardiac electrograms around acute ablation lesions
- Parametrization of activation based cardiac electrophysiology models using bidomain model simulations
- Assessment of nasal resistance using computational fluid dynamics
- Resistance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Inspiratory and expiratory elastance in a non-linear autoregressive model of pulmonary mechanics
- Determination of regional lung function in cystic fibrosis using electrical impedance tomography
- Development of parietal bone surrogates for parietal graft lift training
- Numerical simulation of mechanically stimulated bone remodelling
- Conversion of engineering stresses to Cauchy stresses in tensile and compression tests of thermoplastic polymers
- Numerical examinations of simplified spondylodesis models concerning energy absorption in magnetic resonance imaging
- Principle study on the signal connection at transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
- Influence of Siluron® insertion on model drug distribution in the simulated vitreous body
- Evaluating different approaches to identify a three parameter gas exchange model
- Effects of fibrosis on the extracellular potential based on 3D reconstructions from histological sections of heart tissue
- From imaging to hemodynamics – how reconstruction kernels influence the blood flow predictions in intracranial aneurysms
- Flow optimised design of a novel point-of-care diagnostic device for the detection of disease specific biomarkers
- Improved FPGA controlled artificial vascular system for plethysmographic measurements
- Minimally spaced electrode positions for multi-functional chest sensors: ECG and respiratory signal estimation
- Automated detection of alveolar arches for nasoalveolar molding in cleft lip and palate treatment
- Control scheme selection in human-machine- interfaces by analysis of activity signals
- Event-based sampling for reducing communication load in realtime human motion analysis by wireless inertial sensor networks
- Automatic pairing of inertial sensors to lower limb segments – a plug-and-play approach
- Contactless respiratory monitoring system for magnetic resonance imaging applications using a laser range sensor
- Interactive monitoring system for visual respiratory biofeedback
- Development of a low-cost senor based aid for visually impaired people
- Patient assistive system for the shoulder joint
- A passive beating heart setup for interventional cardiology training

