Abstract
C11H15CdN4O6, monoclinic, P21/n (no. 14), a = 11.1387(15) Å, b = 10.3933(14) Å, c = 12.2891(17) Å, β = 105.319(2)°, Z = 4, V = 1372.1(3) Å3, Rgt(F) = 0.0286, wRref(F2) = 0.0477, T = 296(2) K.
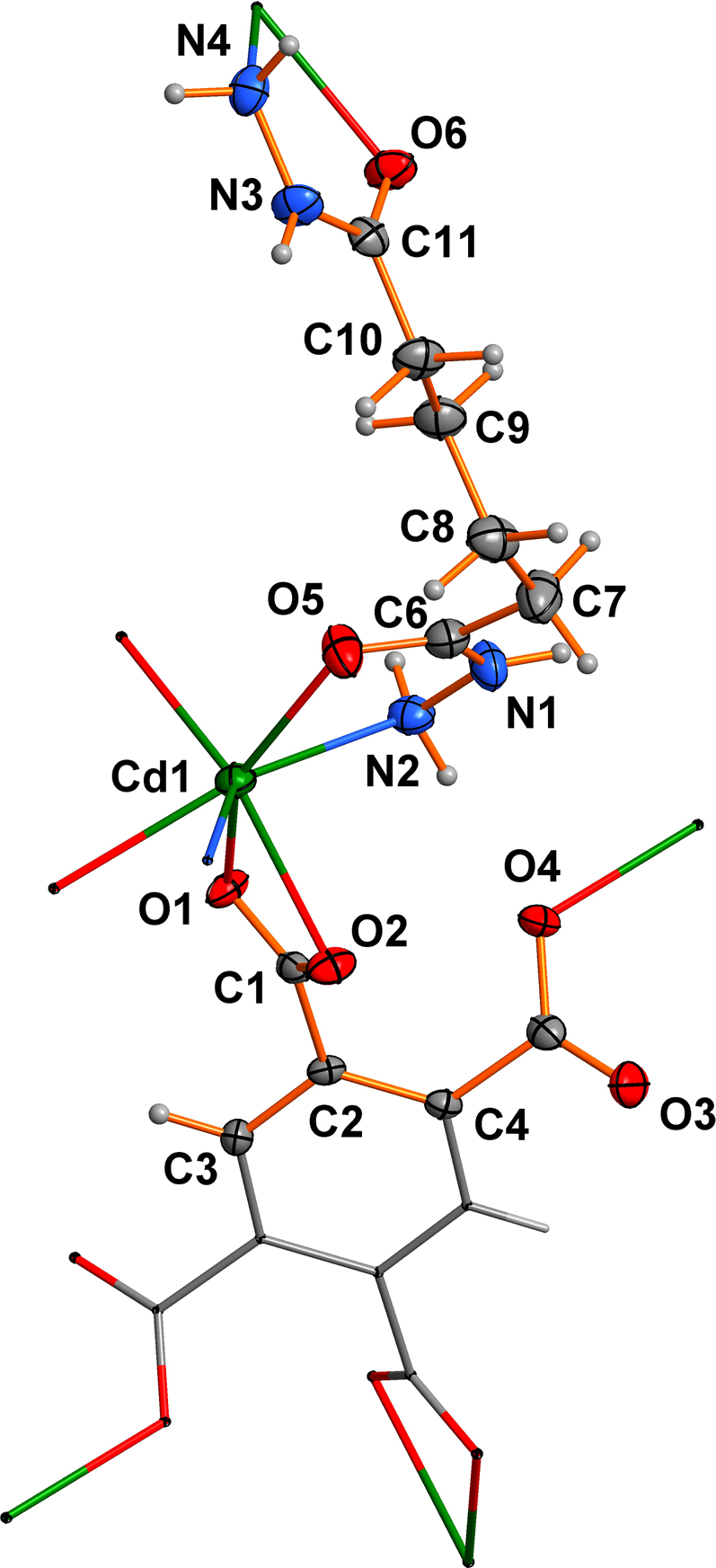
Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colorless prism |
| Size: | 0.32 × 0.31 × 0.28 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.63 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex-III, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.0°, 99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7847, 2966, 0.035 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 2324 |
| N(param)refined: | 200 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Shelx [2, 3], Diamond [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd1 | 0.60643 (2) | 0.19229 (2) | 0.16712 (2) | 0.01766 (8) |
| O1 | 0.82720 (17) | 0.1852 (2) | 0.16547 (16) | 0.0218 (5) |
| O2 | 0.69441 (17) | 0.0556 (2) | 0.04887 (16) | 0.0222 (5) |
| O3 | 0.82900 (19) | −0.2851 (2) | 0.04777 (18) | 0.0282 (5) |
| O4 | 0.85391 (19) | −0.15641 (19) | 0.19838 (17) | 0.0254 (5) |
| O5 | 0.43704 (19) | 0.0986 (2) | 0.22782 (19) | 0.0316 (6) |
| O6 | 0.12613 (19) | 0.1328 (2) | 0.54508 (17) | 0.0288 (5) |
| N1 | 0.5739 (2) | −0.0581 (3) | 0.3011 (2) | 0.0290 (7) |
| H1 | 0.586555 | −0.133593 | 0.330668 | 0.035* |
| N2 | 0.6746 (2) | 0.0170 (2) | 0.2884 (2) | 0.0251 (6) |
| H2A | 0.725321 | −0.031738 | 0.260864 | 0.030* |
| H2B | 0.717310 | 0.045954 | 0.355689 | 0.030* |
| N3 | −0.0373 (2) | 0.2228 (3) | 0.4215 (2) | 0.0279 (7) |
| H3A | −0.081536 | 0.229573 | 0.352884 | 0.033* |
| N4 | −0.0665 (2) | 0.2965 (3) | 0.5080 (2) | 0.0269 (6) |
| H4A | −0.130412 | 0.260780 | 0.527426 | 0.032* |
| H4B | −0.088622 | 0.375532 | 0.482705 | 0.032* |
| C1 | 0.8026 (3) | 0.0981 (3) | 0.0910 (2) | 0.0172 (7) |
| C2 | 0.9070 (2) | 0.0450 (3) | 0.0478 (2) | 0.0137 (6) |
| C3 | 0.9776 (3) | 0.1300 (3) | 0.0027 (2) | 0.0161 (6) |
| H3 | 0.962917 | 0.217875 | 0.005232 | 0.019* |
| C4 | 0.9307 (2) | −0.0869 (3) | 0.0459 (2) | 0.0137 (6) |
| C5 | 0.8648 (2) | −0.1853 (3) | 0.1000 (2) | 0.0185 (6) |
| C6 | 0.4586 (3) | −0.0109 (3) | 0.2668 (3) | 0.0251 (7) |
| C7 | 0.3576 (3) | −0.1045 (3) | 0.2747 (3) | 0.0388 (9) |
| H7A | 0.383275 | −0.147862 | 0.347062 | 0.047* |
| H7B | 0.350671 | −0.169223 | 0.216551 | 0.047* |
| C8 | 0.2300 (3) | −0.0464 (3) | 0.2629 (3) | 0.0322 (9) |
| H8A | 0.209268 | 0.007089 | 0.195782 | 0.039* |
| H8B | 0.169497 | −0.115533 | 0.251406 | 0.039* |
| C9 | 0.2176 (3) | 0.0338 (3) | 0.3620 (3) | 0.0288 (8) |
| H9A | 0.264359 | 0.112985 | 0.364786 | 0.035* |
| H9B | 0.252117 | −0.013060 | 0.431484 | 0.035* |
| C10 | 0.0814 (3) | 0.0653 (3) | 0.3518 (3) | 0.0274 (8) |
| H10A | 0.048202 | 0.112498 | 0.282297 | 0.033* |
| H10B | 0.035221 | −0.014663 | 0.346518 | 0.033* |
| C11 | 0.0599 (3) | 0.1426 (3) | 0.4480 (3) | 0.0205 (7) |
Source of material
The reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used without further purification.
A mixture of benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylic acid (0.25 mmol, 63.5 mg), NaOH (1.0 mmol, 40 mg) and deionized water (5 mL) was placed in a high-pressure resistant glass bottle (10 mL), the bottle was sealed and heated at 353 K for 30 min. After that, cadmium acetate dihydrate (0.5 mmol, 133 mg) and adipohydrazide (0.5 mmol, 87 mg) were added, and the bottle was sealed and heated at 393 K for 24 h and cooled to room temperature. Colorless prism crystals were obtained by filtration, washed with deionized water and dried in air. Yield 46% based on Cd(II).
Experimental details
H atoms were added using riding models. Their Uiso values were set to 1.2Ueq of the parent atoms.
Comment
Researchers have focused on coordination polymers due to their versatile architecture and potential applications for luminescent properties, magnetic interactions, catalytic ability, and so on [5, 6]. As a versatile ligand benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylate has been widely used to construct transition metal or rare earth metal complexes using its multiple coordination function modes.
The asymmetric unit of the complex consists of one Cd ion, one adipohydrazide ligand and one half of a fully deprotonated benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylate (btc4−). The btc4− ligand is located on a center of inversion (see the Figure). The central Cd ion is coordinated by a chelating carboxylate group (O1 and O2) and a monodentate carboxylate group (O4) from two btc4− ligands. In addition, two adipohydrazide ligands provide two oxygen atoms (O5 and O6) and two nitrogen atoms (N2 and N4) to coordinate with the central cadmium ion, forming a distorted single capped octahedron. Each Cd ion is connected by two btc4− ligands to form a two-dimensional network with a rhombic-shaped grid [7]. The adipohydrazide ligands are interspersed in the two-dimensional structure, ensuring the Cd ion to form a seven-coordinated conformation, enhancing the stability of the coordination polymer. The Cd–O bond distances fall in the range of 2.239(2)–2.4646 (19) Å and the Cd–N bond distances are 2.349(2) and 2.356(2) Å. All the bond lengths around the Cd1 center are within the normal range [8, 9]. The N–N bond distances are 1.410(3) and 1.415(3) Å, which are in good agreement with the reported information [10, 11].
Funding source: Hubei Provincial Central Committee Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2019ZYYD074
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This work was supported by Hubei Provincial Central Committee Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Project (No. 2019ZYYD074).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. APEX2, SAINT and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXTL – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053273314026370.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Brandenburg, K. DIAMOND. Visual Crystal Structure Information System. Ver. 4.0; Crystal Impact: Bonn, Germany, 2015.Search in Google Scholar
5. Zhou, Y., Yoon, J. Recent progress in fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of amino acids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 52–67; https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15159b.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
6. Dhakshinamoorthy, A., Garcia, H. Catalysis by metal nanoparticles embedded on metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5262–5284; https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35047e.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Shi, R., Zhu, X., Lin, S. Y., Su, Y. Y., Zhang, S. Y. Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato-bis[μ2-1(1H-imidazol-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-dinickel(II)], NiC17H14N5. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 817–819; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0027.Search in Google Scholar
8. Cai, H., Xu, C., Zhou, Y. P., Tong, X. Q., Guo, Y. Molecular tectonics of mixed-ligand metal-organic frameworks: positional isomeric effect, and structural diversification. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1108, 263–268; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.12.006.Search in Google Scholar
9. Lin, J. D., Cheng, J. W., Du, S. W. Five d10 3D metal-organic frameworks constructed from aromatic polycarboxylate acids and flexible imidazole-based ligands. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 3345–3353; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg8002614.Search in Google Scholar
10. Lo, K. M., Lee, S. M., Tiekink, E. R. T. Crystal structure of heanedihydrazide, C6H14N4O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2020, 235, 1257–1258; https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2020-0301.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zabierowski, P., Oszajca, M., Hodorowicz, M., Matoga, D. Ladder-chain zinc coordination polymers based on adipic acid dihydrazide precursor: synthesis and structural transformations. Polyhedron 2017, 121, 25–36; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2016.09.053.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Yuhong Long et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of 3-bromonitrobenzene at 200 K, C6H4BrNO2 – temperature effects on cell constants
- Crystal structure of (E)-ethyl 2-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methyleneaminooxy)acetate, C14H13NO5
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R, Z)-2-((3–Fluoropyridin-4-yl) methylene)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6, 6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a] phenanthren-3-one, C36H52FNO3
- Crystal structure of [6,6′-((1E,1′E)-(propane-1,3- diylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methaneylylidene)) bis(3-chlorophenol)-κ4N,N′,O,O′] copper(II), C17H14Cl2CuN2O2
- The crystal structure of 6-amino-2-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of bis[N,N′-ethylenebis(acetylacetoniminato)nickel(II)] sodium perchlorate, C24H36ClN4NaNi2O8
- The crystal structure of 3-methyl-2,6-dinitrophenol, C7H6N2O5
- The crystal structure of 5-chloro-2-(quinolin-8-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione, C17H9ClN2O2
- Crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis{2-carboxy-4-((5-carboxypyridin-3-yl)oxy)benzoato-κ1 N}cobalt(II) dihydrate C28H28O20N2Co
- Crystal structure of 3-allyl-4-(2-bromoethyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-(p-tolyl)furan, C23H23BrO2
- The crystal structure of 6,6′-(((2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)azanediyl)bis(methylene))bis(benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-ol ato-κ4N,N′,O,O′)-(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylato-N,O,O′)-titanium(IV)-dichloromethane(1/1), C27H25N3O10Ti
- Crystal structure of (((1E,1′E)-1,2-phenylenebis(methaneylylidene))bis(hydrazin-1-yl-2-ylidene))bis(aminomethaniminium) dinitrate C10H16N10O6
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triaqua-(μ 2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ 2 N:N′)-(4,4′-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diyl)dibenzoato-κ 1 O)nickel(II)]N,N′-dimethylformamide (1/1), C28H35N8O8Ni
- The crystal structure of 3,3′-[1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)]bis(1-ethenyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) dichloride – dichloromethane – water (1/1/1), C19H24Cl4N4O1
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(methane-1,1-diyl)bis(3-propyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium) bis(hexafluoridophosphate), C13H22F12N4P2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C12H8Cl4Sn
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 4-acetylpyrene, C18H12O
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(butane-1,4-diylbis(azanylylidene))bis(methanylylidene))bis(4-methoxyphenol), C20H24N2O4
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(((5-((triphenylstannyl)thio)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)imino)methyl)phenol, C27H21N3OS2Sn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ3N,O:O)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)lead(II) – N,N-dimethylformamide – water (1/2/4), C54H58N6O16Pb2
- Crystal structure of methyl 4-acetoxy-3-methoxybenzoate, C11H12O5
- Crystal structure of 2,2′-(propane-1,3-dilylbis(azaneylylidene))bis(methanylylidene)bis(4-methylphenol), C19H22N2O2
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-methylphenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Cl2Sn
- Crystal structure of methyl (E)-3-(4-acetoxyphenyl)acrylate, C12H12O4
- The crystal structure of bis(benzoato-κ2 O,O′)-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2 N,N′)-copper(II), C28H22CuN2O4
- Crystal structure of (8R,10R,14R,Z)-12-hydroxy-2-((6-methoxypyridin-2-yl)methylene)-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)hexadecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one–water (2/1), C37H56NO4.5
- Crystal structure of dimethyl-bis(4-bromophenyl-κC1)tin(IV), C14H14Br2Sn
- The crystal structure of the cocrystal di-μ2-chlorido-octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O,O′)tetratin(IV) ─ octamethyl-di-μ3-oxido-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O′)-bis(μ2-2,3,4,5-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2 O:O;O′)tetratin(IV) C58H54Cl2F24O16Sn8
- Crystal structure of 3-iodo-N 2-(2-methyl-1-(methylsulfonyl)propan-2-yl)-N 1-(2-methyl-4-(perfluoropropan-2-yl)phenyl)phthalamide, C23H22F7I1N2O4S1
- Crystal structure of 1-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e]indol-1-yl)-naphthalen-2-ol – dichloromethane – dimethyl sulfoxide (1/1/1), C28H18BrNO·CH2Cl2·C2H6SO
- Crystal structure of [meso-5,7,7,12,14,14,-hexamethyl-1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane]nickel(II) diperchlorate – dimethylsulphoxide (1/2), C20H48Cl2N4NiO10S2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,3-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S:S) palladium(II), C26H18N6PdS4
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C24H16N2O4Cu
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC)-bis(triphenylarsine oxide-κO)tin(IV), C48H38As2Cl4O2Sn
- Crystal structure of (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane-κ 8 N 2, O 6) potassium cyclopentadienide, [K([2.2.2]crypt)]Cp, C23H41KN2O6
- The crystal structure of bis(2-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O,O′)-(phenantroline-κ2N,N′)manganese(II) - methanol (1/3), C27H28N4O9Mn
- Crystal structure of 4-(dimethylamino)pyridinium dibromido-tris(4-chlorophenyl-κC)stannate(IV), C25H23Br2Cl3N2Sn
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-1-(4-cyanobenzenesulfonyl)-3,5-bis(3-fluorobenzylidene)piperidin-4-one-dichloromethane (1/1), C27H20Cl2F2N2O3S
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis(4-fluorobenzylidene)-1-((4-trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonyl)piperidin-4-one, C26H18F5NO3S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(4-methyl-2-((phenylimino)methyl)phenolato-κ2 N,O)-(pyridine-κ1 N)platinum(II), C19H17ClN2OPt
- Crystal structure of (4-methylbenzyl)(triphenyl)phosphonium chloride dihydrate, C26H28ClO2P
- The crystal structure of poly[μ2-chlorido-(μ2-1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane-κ2N:N′silver(I)], C12H12AgClN2
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ4-benzene-1,2,4,5-tetracarboxylato)-bis(μ2-adipohydrazide)dicadmium], C11H15N4O6Cd
- The crystal structure of (E)-N′-(butan-2-ylidene)isonicotinohydrazide 0.5 hydrate C10H13N3O·0.5H2O
- The crystal structure of bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)-(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2 N,N′)zinc(II) monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Zn
- The crystal structure of (1R *,2S *)-1,2-bis(2-fluorophenyl)-3,8-dimethoxyacenaphthene-1,2-diol, C26H20F2O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-1-((2-ethyl-4-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzotriazole-κ2N:N′)-(nitrato-κ2O,O′)silver (I)], C13H15Ag1N6O3
- The crystal structure of [(phenantroline-κ2 N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2 N,O)cobalt(II)]monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Co
- Crystal structure of (1E)-N′-[(1E)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]-2-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylidene]hydrazine-1-carbohydrazonamide, C 17 H 17 Cl 2 N 5
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-((tert-butylimino)methyl)-4-chlorophenol, C11H14ClNO
- Crystal structure of all-cis-2,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexane- 1,3,5-triaminium chloride sulfate, C6H18ClN3O7S
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(dimethyl sulfoxide-κO)bis(4-methylphenyl-κC 1)tin(IV), C18H26Cl2O2S2Sn
- Crystal structure of dichlorido-bis(4-chlorophenyl-κC 1)(2,2′-bipyridyl-κ 2 N,N′)tin(IV), C22H16Cl4N2Sn
- Redetermination of the crystal structure of (E)-5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde oxime, C 7 H 6 BrNO 2
- The crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(4-methylbenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium 4-methylbenzoate, C9H13N4 + C8H7O2 −
- Crystal structure of 2-chloro-3-(isopentylamino)naphthalene-1,4-dione, C 15 H 16 ClNO 2
- The crystal structure of bis(2-acetyl-5-methoxyphenyl)carbonate 1.5 hydrate, C19H18O7
- The crystal structure of poly[(μ 4-4,4′-(azanediylbis(methylene))dibenzoato-κ 4 O:N:O′:Oʺ)zinc(II)], C16H13NO4Zn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[(1,10-phenanthroline-k2N,N′)-(μ3-tetraoxidomoybdato(VI)-k3O:O′:O″)manganese(II)] C12H8N2O4MoMn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(4-hydroxyl-5-(methoylcarbonyl)thiophene-2-carboxylato-κ1 O)-(μ2-piperazine-1,4-diylbis(pyridin-4-ylmethanone)-κ2 N:N′)silver(I)] monohydrate, C23H23AgN4O8S
- Crystal structure of bis(4-bromo-2-(((3-bromopropyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxido-vanadium(IV), C20H20Br4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of (2a′S,2a1′S,3R,5a′S,7′R)-5-(furan-3-yl)-2a′,2a1′-dihydroxy-7′-methyldecahydro-2H-spiro[furan-3,6′-naphtho[1,8-bc]furan]-2,2′(2a′H)-dione, C19H22O7
- The crystal structure of 3-bromopicolinic acid, C6H4BrNO2
- Crystal structure of 1,1′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methylene))bis(pyridin-1-ium) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2 S,S) platinum(II), C26H18N6PtS4
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 5-(8-((3-carboxyazetidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonate monohydrate, C20H19NO10S
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium bromide, C6H7BrN2O2
- The crystal structure of (2-hydroxy-5-methyl-phenyl)-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-methanone hemihydrate, C11H10.5N2O2.5
- Crystal structure of tetraaqua-(2-(4-formylphenoxy)acetato-k1O)cadmium(II), C18H22O12Cd
- Crystal structure of diethyl 6,12-dimethyl-3,9-di-p-tolyl-3,9-diazapentacyclo[6.4.0.02,7.04,11.05,10]dodecane-1,5-dicarboxylate, C32H38N2O4
- Crystal structure of (E)-N′-(1-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)-4-hydroxy – tetrahydrofuran (2/1), C17H16ClFN2O2.5

