Abstract
C14H14BaN12O15, monoclinic, C2/c (no. 15), a = 21.787(4) Å, b = 6.7594(11) Å, c = 18.143(3) Å, β = 102.456(2)°, V = 2609.0(8) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0209, wRref(F2) = 0.0567, T = 296(2) K.
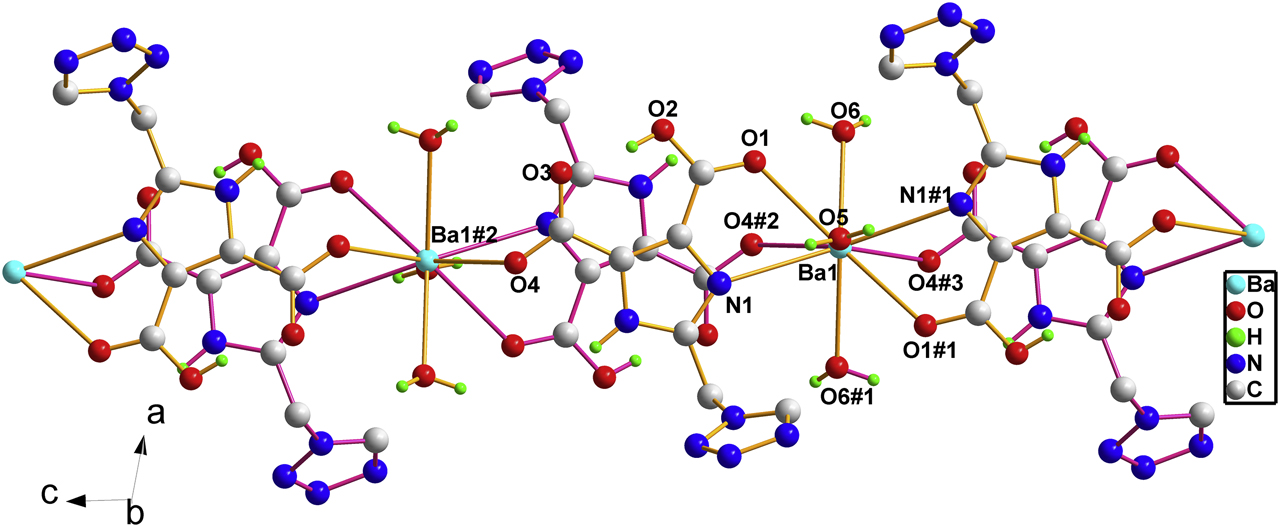
A part of the polymeric title crystal structure is shown in the Figure (#1 = −x, y, 0.5−z; #2 = −x, −y, 1−z, #3 = x, −y, −0.5+z). Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.20 × 0.18 × 0.15 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 1.62 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.4°, >99 % |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 7939, 3174, 0.019 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3033 |
| N(param)refined: | 191 |
| Programs: | SHELX [1], Bruker [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba1 | 0.000000 | −0.03302(2) | 0.250000 | 0.02661(6) |
| O1 | 0.08744(7) | −0.1912(3) | 0.37305(8) | 0.0410(4) |
| O2 | 0.12099(6) | −0.2841(3) | 0.49134(8) | 0.0397(3) |
| H2 | 0.104121 | −0.323273 | 0.524886 | 0.059* |
| O3 | 0.07947(7) | −0.3248(2) | 0.60551(8) | 0.0371(3) |
| O4 | −0.01132(7) | −0.2772(2) | 0.64014(7) | 0.0338(3) |
| O5 | 0.000000 | −0.4287(4) | 0.250000 | 0.142(2) |
| H5 | 0.006590 | −0.508505 | 0.216330 | 0.213* |
| O6 | 0.12169(10) | 0.1028(3) | 0.27319(11) | 0.0639(5) |
| H6C | 0.134012 | 0.198995 | 0.249878 | 0.096* |
| H6D | 0.136022 | 0.102475 | 0.320638 | 0.096* |
| N1 | −0.03704(7) | −0.1765(2) | 0.38795(8) | 0.0226(3) |
| N2 | −0.07360(7) | −0.2189(2) | 0.49158(8) | 0.0223(3) |
| H2A | −0.100054 | −0.225143 | 0.523520 | 0.027* |
| N3 | −0.17954(7) | −0.3304(3) | 0.33880(9) | 0.0324(3) |
| N4 | −0.20982(9) | −0.4553(3) | 0.37632(14) | 0.0466(5) |
| N5 | −0.22477(10) | −0.6081(4) | 0.33334(16) | 0.0595(6) |
| N6 | −0.20451(11) | −0.5848(4) | 0.26813(16) | 0.0638(7) |
| C1 | 0.07690(8) | −0.2324(3) | 0.43464(10) | 0.0261(3) |
| C2 | 0.01188(7) | −0.2230(2) | 0.44692(9) | 0.0199(3) |
| C3 | −0.01022(7) | −0.2490(2) | 0.51200(9) | 0.0203(3) |
| C4 | 0.02102(9) | −0.2872(3) | 0.59196(9) | 0.0252(3) |
| C5 | −0.08748(8) | −0.1770(3) | 0.41696(9) | 0.0225(3) |
| C6 | −0.15296(8) | −0.1453(3) | 0.37311(11) | 0.0306(4) |
| H6A | −0.178765 | −0.095112 | 0.406334 | 0.037* |
| H6B | −0.152818 | −0.047620 | 0.333971 | 0.037* |
| C7 | −0.17625(12) | −0.4118(5) | 0.27337(15) | 0.0506(6) |
| H7 | −0.157137 | −0.356011 | 0.237177 | 0.061* |
| O7 | 0.17338(8) | 0.1956(3) | 0.43363(11) | 0.0605(5) |
| H7A | 0.191034 | 0.305220 | 0.428304 | 0.091* |
| H7B | 0.202284 | 0.110870 | 0.448274 | 0.091* |
| O8 | 0.22961(10) | 0.5705(3) | 0.44047(16) | 0.0749(7) |
| H8A | 0.237056 | 0.653122 | 0.408187 | 0.112* |
| H8B | 0.201696 | 0.618432 | 0.461567 | 0.112* |
Source of material
All chemicals were of AR grade and were used without purification. A mixture of BaCl2⋅2H2O (0.03 mmol), H3tmidc systematic name: 2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid; (0.03 mmol), methanol (2 mL) and distilled water (2 mL) was sealed in a 25 mL Teflon lined stainless steel container and heated at 393 K for 72 h. After the mixture had been allowed to cool to room temperature at a rate of 5 K h−1, light yellow crystals of {[Ba(H2tmidc)2(H2O)3]⋅4H2O}n suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained (yield 46.6%, based on H3tmidc).
Experimental details
Hydrogen atoms on carbon atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C–H = 0.97 (CH2) or 0.93 Å (aromatic). Hydrogen atoms of the nondeprotonated carboxylic acid groups of H2tmidc− were refined as riding atoms, with O–H = 0.82 Å. Hydrogen atoms on nitrogen atoms and hydrogen atoms of the water molecules were located in a difference Fourier map and the N–H and O–H distances were constrained to 0.9 and 0.85 Å, respectively. Hydrogen atoms were refined with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C, N) or 1.5 Ueq(O).
Comment
It is well known that imidazole, tetrazole and their derivatives have been widely used as excellent building blocks for the preparation of complexes since they coordinate with most of metal ions with diverse coordination modes [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10]. The N-heterocyclic carboxylic acid, 2-(1H-tetrazol-1-methyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid and the deprotonated anions are excellent ligands as there are potential N-donors and O-donors. Researchers have reported two transition metal complexes based on H3tmidc and investigated their crystal structures and biological activities [11], [12]. In order to further enrich the number of complexes based on this ligand, we selected H3tmidc as ligand to react with BaCl2⋅2H2O and obtained a new complex {[Ba(H2tmidc)2(H2O)3]⋅4H2O}n.
There is one half Ba(II) ion, one H2tmidc− anion ligand, one and a half coordinated water molecules and two solvent water molecules in each asymmetric unit. The Ba1 ion is nine-coordinated by two N atoms from two H2tmidc− anions and seven O atoms from four H2tmidc− anions and three water molecules leading to a distorted BaN2O7 environment. The Ba–N bond length is 2.9541(14) Å, while the Ba–O distances span from 2.675(3) to 2.8669(14) Å, all of which are comparable to those observed for the other Ba(II) complexes based on N-heterocyclic carboxylic acids [13], [14]. Ba(II) ions are linked by H2tmidc− anion ligands into one-dimensional chains that run along the c axis. The intrachain Ba1–Ba1#2 distance is 9.0825(15) Å. There are O–H…O intramolecular hydrogen bonds between carboxyl and carboxylate groups, and O–H…O, O–H…N and N–H…O inter molecular hydrogen bonds involving carboxylate groups, imidazole ring, tetrazole ring, coordination water molecules and solvent water molecules. In addition, there are π–π stacking interactions between imidazole rings of adjacent chains with a centroid-centroid distance of 3.5699(7) Å, which is in the range for common π–π interactions [15], [16], [17]. Adjacent chains are linked by the aforementioned hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions, to a three-dimensional architecture in the solid state.
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: We are very grateful for the financial assistance provided by Qinglan Project of Jiangsu Province (2020).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Bruker. SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2000.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Bruker. APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Guo, X.-Y., Chen, J.-H., Meng, X. R. Crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua[(μ2-4,5-dicarboxylato-2-(2-carboxylatophenyl)imidazol-1-ido-κ4N,O,, O′: N′)] (μ2-4,4′-bipyridine κ2N:N′)-N:) dicopper(II)], C22H14Cu2N4O7. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2020, 235, 771–773. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2019-0887.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Li, X.-F., Yang, Y.-Q., Li, Y.-X., Yang, H.-X., Zhao, W.-F., Meng, X. R. Synthesis, crystal structure, and BSA binding studies of new Co(II) and Ni(II) complexes of 2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylate. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2020, 505, 119469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.119469.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Cheng, D., Liu, Y.-J., Cheng, F.-R., Yang, H.-X., Meng, X. R. Synthesis, structure and fluorescence properties of a Zn(II) coordination polymer based on 2-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylate. J. Chem. Res. 2018, 42, 490–493. https://doi.org/10.3184/174751918x15366068518341.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Vukadinovic, Y., Burkhardt, L., Papcke, A., Miletic, A., Fritsch, L., Altenburger, B., Schoch, R., Neuba, A., Lochbrunner, S., Bauer, M. When Donors turn into acceptors: ground and excited state properties of FeII complexes with amine-substituted tridentate bisimidazole-2-ylidene pyridine ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8762–8774. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00393.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Li, S.-S., Zhao, X.-Y., Huang, Q.-Y., Meng, X. R. Crystal structure of bis(acetato-O∖k)bis{2-((1H-tetrazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-∖k{N}zinc(II), C22H22N12O4Zn. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2018, 233, 693–695. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2018-0022.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Liu, B., Zhao, D., Li, T., Meng, X.-R. Syntheses, structures, and fluorescent properties of two new Zn(II) coordination polymers containing 2-((benzoimidazolyl)methyl)-1H-tetrazole. J. Coord. Chem. 2013, 66, 139–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2012.749351.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Wurzenberger, M. H. H., Lommel, M., Gruhne, M. S., Szimhardt, N., Stierstorfer, J. Refinement of copper(II) azide with 1-alkyl-5H-tetrazoles: adaptable energetic complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202002823.Suche in Google Scholar
11. Guo, X.-Y., Zhang, J.-D., Li, Y.-Y., Li, X.-J., Meng, X.-R. Synthesis, structure, and BSA binding studies of a new Co(II) complex based on 2-(1H-tetrazol-1-methyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 119, 108055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108055.Suche in Google Scholar
12. Yan, H.-Y., Li, Y.-X., Yang, H.-X., Li, X.-J. Synthesis, molecular structure and BSA-binding properties of a new binuclear Cd(II) complex based on 2-(1H-tetrazol-1-methyl)-1H-imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylic acid. Z. Naturforsch. 2020, 75b, 537–544. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-2020-0017.Suche in Google Scholar
13. Cai, S.-L., Zheng, S.-R., Wen, Z.-Z., Fan, J., Zhang, W.-G. Construction of Ba(II) coordination polymers based on imidazole-based dicarboxylate ligands: structural diversity tuned by alcohol solvents. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 3575–3582. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg3004068.Suche in Google Scholar
14. Chen, G., Lan, H. H., Li, Z. X., Li, D. J., Peng, G. J., Cai, S. L., Zheng, S. R., Zhang, W. G. Syntheses, structures, and luminescent properties of two alkaline earth metal coordination polymers from hydroxymethyl imidazole dicarboxylate. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 44, 792–799. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1070328418120023.Suche in Google Scholar
15. Yang, Y.-Q., Su, C.-F., Zhang, J.-D., Yang, H.-X., Zhang, G.-Y., Meng, X.-R. Construction of Cd(II) complexes based on 2-(1H-imidazol-1-methyl)-1H-benzimidazole and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 3762–3775. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2016.1237634.Suche in Google Scholar
16. Li, X. F., Cheng, D., Meng, X. R., Yang, H. X. Effects of two benzenedicarboxylic acids on the CdII construction of coordination polymers incorporating a flexible N-donor ligand. Acta Crystallogr. 2019, C75, 643–649. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229619005758.Suche in Google Scholar
17. Wei, X., Li, J. H., Huang, Q. Y., Meng, X. R. Two new isostructural mercury(II) complexes involving the N-heterocyclic 1-[(benzotriazol-1-yl)methyl]-1H-1,3-imidazole ligand: syntheses, structures and properties. Acta Crystallogr. 2017, C73, 314–318. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229617003199.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2020 Wei Xie et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3


