Abstract
C6H6O3S, orthorhombic, Pca21 (no. 29), a = 15.3524(8) Å, b = 5.7180(3) Å, c = 15.3395(9) Å, V = 1346.58(13) Å3, Z = 8, Rgt(F) = 0.0253, wRref (F2) = 0.0663, T = 200(2) K.
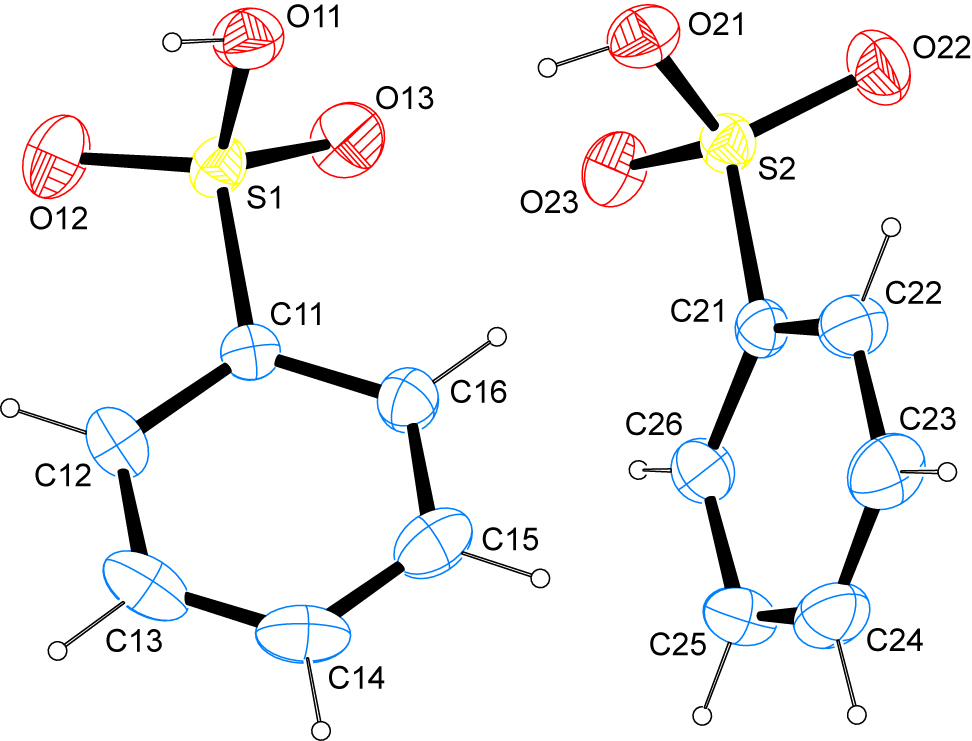
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.59 × 0.39 × 0.31 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.42 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 12225, 3347, 0.018 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3131 |
| N(param)refined: | 183 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], WinGX/ORTEP [3], Mercury [4], PLATON [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.48937 (2) | 0.62083 (7) | 0.34964 (2) | 0.02512 (9) |
| O11 | 0.50174 (8) | 0.4325 (2) | 0.42190 (9) | 0.0332 (3) |
| H11 | 0.5013 | 0.4972 | 0.4711 | 0.050* |
| O12 | 0.54553 (7) | 0.8141 (2) | 0.36461 (10) | 0.0405 (3) |
| O13 | 0.49883 (9) | 0.4937 (3) | 0.26923 (9) | 0.0379 (3) |
| C11 | 0.38057 (9) | 0.7068 (3) | 0.36070 (10) | 0.0230 (3) |
| C12 | 0.36157 (12) | 0.9151 (3) | 0.40372 (11) | 0.0314 (3) |
| H12 | 0.4067 | 1.0141 | 0.4244 | 0.038* |
| C13 | 0.27448 (13) | 0.9737 (3) | 0.41539 (14) | 0.0417 (4) |
| H13 | 0.2597 | 1.1161 | 0.4437 | 0.050* |
| C14 | 0.20903 (12) | 0.8264 (3) | 0.38613 (13) | 0.0414 (4) |
| H14 | 0.1498 | 0.8667 | 0.3958 | 0.050* |
| C15 | 0.22926 (11) | 0.6220 (3) | 0.34316 (14) | 0.0393 (4) |
| H15 | 0.1840 | 0.5234 | 0.3224 | 0.047* |
| C16 | 0.31577 (11) | 0.5597 (3) | 0.33011 (10) | 0.0300 (3) |
| H16 | 0.3302 | 0.4186 | 0.3007 | 0.036* |
| S2 | 0.44735 (2) | 0.12395 (6) | 0.10434 (3) | 0.02456 (9) |
| O21 | 0.47898 (8) | 0.0830 (2) | 0.19929 (8) | 0.0338 (3) |
| H21 | 0.4850 | 0.2124 | 0.2245 | 0.051* |
| O22 | 0.45204 (9) | −0.0971 (2) | 0.06195 (11) | 0.0402 (3) |
| O23 | 0.49545 (7) | 0.3180 (2) | 0.06858 (8) | 0.0321 (3) |
| C21 | 0.33755 (9) | 0.2066 (3) | 0.11598 (9) | 0.0231 (3) |
| C22 | 0.28188 (11) | 0.0537 (3) | 0.15878 (12) | 0.0318 (4) |
| H22 | 0.3033 | −0.0882 | 0.1828 | 0.038* |
| C23 | 0.19454 (11) | 0.1112 (3) | 0.16581 (13) | 0.0390 (4) |
| H23 | 0.1558 | 0.0091 | 0.1955 | 0.047* |
| C24 | 0.16355 (11) | 0.3163 (4) | 0.12983 (12) | 0.0388 (4) |
| H24 | 0.1033 | 0.3531 | 0.1339 | 0.047* |
| C25 | 0.21970 (12) | 0.4685 (3) | 0.08784 (12) | 0.0360 (4) |
| H25 | 0.1980 | 0.6097 | 0.0635 | 0.043* |
| C26 | 0.30836 (11) | 0.4152 (3) | 0.08110 (11) | 0.0297 (4) |
| H26 | 0.3475 | 0.5198 | 0.0532 | 0.036* |
Source of material
The compound was obtained commercially (BDH). Crystals suitable for the diffraction studies were taken straight from the bottle and prepared under a constant stream of dry nitrogen due to the hygroscopic nature of the compound.
Experimental details
The H atoms were visible on Fourier difference maps but were geometrically placed and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2-1.5 Ueq (C,O) using the appropriate SHELXL AFIX commands.
Comment
Benzene is among the most important synthons in chemistry. Via electrophilic substitution reactions a vast variety of functionalized derivatives is readily available. The interplay between activating and deactivating substituents as well as the competition and synergism between inductive and mesomeric effects allows for the seemingly endless functionalization of the respective archaetype hydrocarbon scaffold. The latter gives rise to a large toolbox of new synthons that can be applied for the production of dyes, medications, catalysts and ligands for novel coordination compounds. Several simple and fundamental derivatives of benzene are powerful and versatile reagents themselves and have entered the preparative chemist’s toolbox decades ago. One notable example for the latter statement is benzenesulphonic acid which is readily available upon reacting benzene with concentrated sulphuric acid [6] and serves – just like its close chemical relative para-toluenesulphonic acid – as an acidic reagent of intermediate strength whose solubility in organic solvents is of crucial interest. During the preparation of a number of multidentate organic ligands for transition metals by means of acid-catalyzed condensation reactions, the possibility of accidentially isolating the catalyst in crystalline form existed. Surprisingly, the crystal and molecular structures of benzenesulphonic acid have not been reported as of today. Only a co-crystal of the title compound with tris-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)stibane(V) oxide is apparent in the literature [7].
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains two complete independent molecules. The formal S=O double bonds are found at lengths of 1.4202(13) Å and 1.4391(13) Å in the first and at 1.4235(12) Å and 1.4413(12) Å in the second molecule, numbered S1-C16 and S2-C26, respectively, while the S–O bond lengths involving the hydroxyl group are significantly longer with values of 1.5571(13) Å and 1.5531(13) Å. While the numerical values found for the S=O bonds are in good agreement with data depopsited with the Cambridge Structural Database [8] for compounds that feature free para-toluenesulphonic acid in the crystal structure, the pertaining S–O bond lengths involving the sulphur-bonded OH group are – on average – markedly longer. Sulphur-carbon bond distances are more uniform, with distances of 1.7494(14) Å and 1.7599(15)°, respectively, however, they deviate to smaller values in comparison to the values reported for crystal structures featuring free para-toluenesulphonic acid. Intracyclic C–C–C angles span a range of 117.96(17)–121.99(15)° in the first molecule and 118.36(16)–121.83(15)° in the second, with the largest angle invariably found on the carbon atom bearing the sulphonic acid group. The least-squares planes as defined by the non-hydrogen atoms of each aromatic moiety intersect at an angle of 57.97(9)°.
In the crystal, classical hydrogen bonds of the O–H…O type are observed next to C–H…O contacts whose range falls by more than 0.1 Å below the sum of van-der–Waals radii of the participating atoms. The classical hydrogen bonds alternate between the first molecule present in the asymmetric unit acting as donor with one of the formally double-bonded oxygen atoms in the second molecule acting as acceptor and vice versa. The C–H…O contacts exclusively involve only one of the two molecules present in the asymmetric in terms of donors and acceptors. These contacts are supported by the C–H group in para position to the sulphonic acid group as donor, with the double-bonded oxygen atom that does not already serve as acceptor to classical hydrogen bonds as acceptor. In terms of graph-set analysis [9], [10], the descriptor for the classical hydrogen bonds is DD at the unary and
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs Andiswa Judy Mfakado for helpful discussions.
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: None declared.
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Suche in Google Scholar
4. Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez‐Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J., Wood, P. A. Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807067908.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Spek, A. L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155; https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Becker, H. G. O., Beckert, R., Domschke, G., Fanghänel, E., Habicher, W. D., Metz, P., Pavel, D., Schwetlick, K. Organikum – Organisch-chemisches Grundpraktikum, 21st ed.; Wiley‐VCH Weinheim, 2001.Suche in Google Scholar
7. Huber, F., Westhoff, T., Preut, H. Tris(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)antimony dihydroxide; synthesis and reaction with sulfonic acids RSO3H (R = C6H5, CF3). crystal structure of [2,4,6-(CH3)3C6H2]3SbO.HO3SC6H5. J. Organomet. Chem. 1987, 323, 173–180; https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-328x(87)80366-2.Suche in Google Scholar
8. Allen, F. H. The cambridge structural database: a quarter of a million crystal structures and rising. Acta Crystallogr. 2002, B58, 380–388; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768102003890.Suche in Google Scholar
9. Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L., Chang, N.-L. Patterns in hydrogen bonding: functionality and graph set analysis in crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 1555–1573; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.199515551.Suche in Google Scholar
10. Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C., Bernstein, J. Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. 1990, B46, 256–262; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768189012929.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2020 Pholani Manana et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3


