Abstract
C14H15AsClNOS, monoclinic, P21 (no. 4), a = 5.2852(2) Å, b = 13.3035(6) Å, c = 10.7522(5) Å, β = 90.130(2) Å, V = 756.00(6) Å3, Z = 2, Rgt(F) = 0.0200, wRref(F2) = 0.0503, T = 200(2) K.
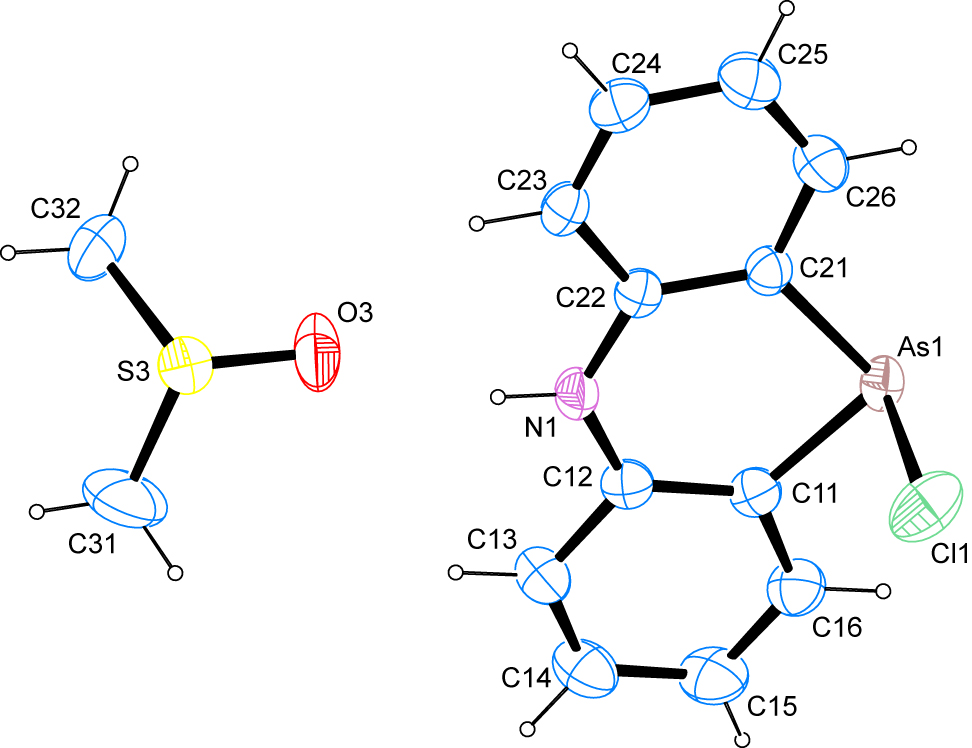
The molecular structure is shown in the Figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.50 × 0.40 × 0.30 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 2.55 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker APEX-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 28.3°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 6536, 3458, 0.015 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3278 |
| N(param)refined: | 212 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], WinGX/ORTEP [3], Mercury [4], PLATON [5] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As1 | −0.09517 (4) | 0.48504 (3) | 0.15347 (2) | 0.03070 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.15457 (17) | 0.37728 (7) | 0.04100 (8) | 0.0564 (2) |
| N1 | 0.2992 (4) | 0.5005 (2) | 0.38523 (19) | 0.0305 (5) |
| C11 | 0.1646 (5) | 0.58025 (19) | 0.1905 (2) | 0.0276 (5) |
| C12 | 0.3254 (4) | 0.57271 (19) | 0.2939 (2) | 0.0263 (5) |
| C13 | 0.5254 (5) | 0.6424 (2) | 0.3066 (3) | 0.0313 (6) |
| H13 | 0.637250 | 0.637527 | 0.375589 | 0.038* |
| C14 | 0.5598 (6) | 0.7166 (2) | 0.2209 (3) | 0.0391 (6) |
| H14 | 0.696935 | 0.762179 | 0.230016 | 0.047* |
| C15 | 0.3948 (6) | 0.7261 (3) | 0.1197 (3) | 0.0448 (7) |
| H15 | 0.416279 | 0.778848 | 0.061109 | 0.054* |
| C16 | 0.2009 (6) | 0.6578 (2) | 0.1063 (3) | 0.0392 (6) |
| H16 | 0.088926 | 0.664068 | 0.037469 | 0.047* |
| C21 | −0.0752 (5) | 0.41224 (19) | 0.3068 (2) | 0.0285 (5) |
| C22 | 0.1151 (5) | 0.4282 (2) | 0.3951 (2) | 0.0294 (5) |
| C23 | 0.1230 (5) | 0.3652 (2) | 0.5008 (3) | 0.0371 (6) |
| H23 | 0.252429 | 0.374264 | 0.561185 | 0.045* |
| C24 | −0.0542 (6) | 0.2912 (2) | 0.5171 (3) | 0.0447 (7) |
| H24 | −0.044685 | 0.249049 | 0.588250 | 0.054* |
| C25 | −0.2487 (6) | 0.2767 (2) | 0.4306 (3) | 0.0453 (8) |
| H25 | −0.372825 | 0.226099 | 0.443029 | 0.054* |
| C26 | −0.2566 (5) | 0.3373 (2) | 0.3272 (3) | 0.0383 (6) |
| H26 | −0.388363 | 0.328178 | 0.268040 | 0.046* |
| H1 | 0.405 (5) | 0.508 (2) | 0.438 (2) | 0.030 (7)* |
| S3a | 0.8146 (3) | 0.55342 (12) | 0.67438 (15) | 0.0454 (5) |
| O3a | 0.598 (5) | 0.5610 (12) | 0.5898 (17) | 0.060 (3) |
| C31a | 0.7704 (17) | 0.6574 (5) | 0.7760 (7) | 0.069 (2) |
| H31Aa | 0.801214 | 0.720047 | 0.730626 | 0.104* |
| H31Ba | 0.889156 | 0.652337 | 0.845900 | 0.104* |
| H31Ca | 0.596627 | 0.657015 | 0.807583 | 0.104* |
| C32a | 0.749 (3) | 0.4560 (6) | 0.7822 (7) | 0.109 (4) |
| H32Aa | 0.731727 | 0.392078 | 0.737781 | 0.164* |
| H32Ba | 0.590680 | 0.471054 | 0.825928 | 0.164* |
| H32Ca | 0.887473 | 0.451193 | 0.842560 | 0.164* |
| S4b | 0.7087 (5) | 0.50598 (18) | 0.7137 (2) | 0.0537 (9) |
| O4b | 0.605 (7) | 0.5364 (18) | 0.596 (2) | 0.060 (3) |
| C41b | 0.9955 (18) | 0.5644 (11) | 0.7441 (10) | 0.089 (4) |
| H41Ab | 1.118214 | 0.545731 | 0.679965 | 0.133* |
| H41Bb | 1.058349 | 0.543067 | 0.825761 | 0.133* |
| H41Cb | 0.971965 | 0.637488 | 0.743802 | 0.133* |
| C42b | 0.535 (2) | 0.5638 (14) | 0.8342 (8) | 0.094 (5) |
| H42Ab | 0.471946 | 0.629117 | 0.805607 | 0.140* |
| H42Bb | 0.644969 | 0.573529 | 0.906740 | 0.140* |
| H42Cb | 0.391934 | 0.520852 | 0.857113 | 0.140* |
aOccupancy: 0.578(4).
bOccupancy: 0.422(4).
Source of material
The title compound was synthesized upon the recrystallization of phenarsazine chloride from warm dimethyl sulfoxide. Crystals suitable for the diffraction studies were obtained upon cooling of the solution to room temperature.
Experimental details
The position of the H atom attached to N1 was refined subject to a distance restraint. All other H atoms were placed geometrically and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2-1.5 Ueq (C) using the appropriate SHELXL AFIX commands. The dimethylsufoxide molecule was found to be disordered over two positions with refined occupancies of 0.578(4) and 0.422(4), respectively. The Flack parameter [6] refined to 0.023(10) and was determined using full-matrix least squares.
Comment
The effect of size and steric presence of large ions on chemical and spectroscopic properties of compounds have been a focus of research for many decades. Among the many effects that can be attributed to the spatial requirements of counterions are the glass transition temperature in ionomers [7], surfactant modifying properties [8], the charge transfer in radical ions [9] and polymer-modified electrodes [10], as well as the structural and vibrational spectroscopic behavior of DNA building blocks [11]. Furthermore, the benefit of chosing the adequate size of counterions to crystallize ionic compounds has been confirmed and reviewed on many occasions [12]. Gaining crystallographic information about a vast variety of large anions has seen significant growth upon the introduction of bulky cations that have simplified the crystallization of these compounds. A remarkable example in this aspect for instance the group of chlorido coordination compounds of gallium that apply cations derived from the phenarsazine scaffold [13], [14]. At the onset of a research project aimed at the characterization of large anionic compounds, we set out to create a novel set of phenarsazine-inspired cations via phenarsazine chloride as the starting material. To confirm the successful synthesis of the latter, a diffraction study of the recrystallized compound was conducted. The crystal structures of solvent - free phenarsazine chloride [15], [16] and phenarsazine bromide [15] have been reported earlier; however, no hydrogen atoms had been included in the refinement process. Furthermore, the crystal structure of the para-xylene solvate of phenarsazine chloride has been mentioned earlier [16]; however, no structural data has been deposited with the Cambridge Structural Database.
The structure solution from the experimental data collected in this study shows the presence of the desired phenarsazine chloride product as well as one molecule of dimethyl sulfoxide in the asymmetric unit. The solvent molecule is disordered over two positions, as described in the experimental section. The As–Cl bond length of 2.2950(8) Å is slightly longer than the most commonly-reported arsenic–chlorine bond lengths deposited with the Cambridge Structural Database [17]. The angles around the arsenic atom were measured at 96.32(8)° and 96.76(11)° towards the chlorine atom as well as 96.14(8)° for the intracyclic angle thus ruling out classical hybridization of the heavier pnicogen atom. The least-squares planes as defined by the respective atoms of the two aromatic moieties on the one hand as well as the central six-membered heterocyclic ring on the other hand enclose angles of 2.93(11)° and 3.82(12)° while the two planes of the outer aromatic moieties intersect at an angle of 3.99(13)°. A puckering analysis [18] of the central six-membered ring shows the latter to adopt a 4C1 conformation on atoms N1 and As1 [19]. In the crystal structure, classical hydrogen bonds of the N–H···O type as well as C–H···O and C–H···Cl contacts are observed. The classical hydrogen bonds employ the oxygen atom of the disordered solvent molecule as an acceptor. The latter atom also serves as an acceptor for the C–H···O contacts that are supported by a) one of the hydrogen atoms in ortho-position to the N–H group and b) one of the hydrogen atoms in para-position to the N–H group in the other phenyl ring. The C–H···Cl contacts stem from one of the hydrogen atoms on one of the methyl groups of the solvent molecule as well as the remaining hydrogen atom in para-position to the N–H group. In total, these contacts connect the entities in the crystal structure to a three-dimensional network. In terms of graph-set analysis [20], [21], the classical hydrogen bonds requires a D descriptor on the unary level while the C–H···O are to be described by means of a DD descriptor on the same level. The graph-set descriptor for C–H···Cl contacts is
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms Andiswa Mfakadolo for helpful discussions.
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: None declared.
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8 https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and ORTEP for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854 https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
4. Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J., Wood, P. A. Mercury CSD 2.0 – new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470 https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889807067908.Search in Google Scholar
5. Spek, A. L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155 https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
6. Flack, H. D. On enantiomorph-polarity estimation. Acta Crystallogr. 1983, A39, 876–881 https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
7. Enokida, J. S., Hu, W., Fang, H., Morgan, B. F., Beyer, F. L., Winter, H. H., Coughlin, E. B. Modifying the structure and dynamics of ionomers through counterion sterics. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1767–1776 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02116.Search in Google Scholar
8. Oh, S. G., Shah, D. O. Effect of counterions on the interfacial tension and emulsion droplet size in the oil/water/dodecyl sulfate system. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 284–286 https://doi.org/10.1021/j100104a003.Search in Google Scholar
9. Piotrowiak, P., Miller, J. R. Counterion effects in intramolecular charge transfer in radical anions. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 13052–13060 https://doi.org/10.1021/j100152a004.Search in Google Scholar
10. Mathias, M. F., Haas, O. Effect of counterion type on charge transport at redox polymer-modified electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 9217–9225 https://doi.org/10.1021/j100138a025.Search in Google Scholar
11. Minguirbara, A., Vamhindi, B. S. D. R., Koyambo-Konzapa, S. J. b, Nsangou, M. Effects of counterions and solvents on the geometrical and vibrational features of dinucleoside-monophosphate (dNMP): case of 3′,5′-dideoxycytidine-monophosphate (dDCMP). J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, Article 99 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-020-04369-6.Search in Google Scholar
12. Roof, L. C., Kolis, J. W. New developments in the coordination chemistry of inorganic selenide and telluride ligands. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1037–1080 https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00019a010.Search in Google Scholar
13. Burford, N., Ragogna, P. J., Sharp, K., McDonald, R., Ferguson, M. J. Arsinophosphonium cations from arsenium-phosphine and -bisphosphine coordination chemistry. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 9453–9460 https://doi.org/10.1021/ic050989w.Search in Google Scholar
14. Conrad, E., Burford, N., Werner-Zwanziger, U., McDonald, R., Ferguson, M. J. Phosphinopnictinophosphonium frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2465–2467 https://doi.org/10.1039/b924918d.Search in Google Scholar
15. Fukuyo, M., Nakatsu, K., Shimada, A. The crystal and molecular structure of 10-halo-5, 10-dihydrophenarsazine. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 39, 1614–1615 https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.39.1614.Search in Google Scholar
16. Camerman, A., Trotter, J. 115. Stereochemistry of arsenic. part XIII. 10-chloro-5,10-dihydrophenarsazine. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 730–738. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9650000730.Search in Google Scholar
17. Allen, F. H. The Cambridge Structural Database: a quarter of a million crystal structures and rising. Acta Crystallogr. 2002, B58, 380–388 https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768102003890.Search in Google Scholar
18. Cremer, D., Pople, J. A. General definition of ring puckering coordinates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 1354–1358 https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00839a011.Search in Google Scholar
19. Boeyens, J. C. A. The conformation of six-membered rings. J. Cryst. Mol. Struct. 1978, 8, 317–320 https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01200485.Search in Google Scholar
20. Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L., Chang, N.-L. Patterns in hydrogen bonding: functionality and graph set analysis in crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1995, 34, 1555–1573 https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.199515551.Search in Google Scholar
21. Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C., Bernstein, J. Graph-set analysis of hydrogen-bond patterns in organic crystals. Acta Crystallogr. 1990, B46, 256–262 https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108768189012929.Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Arthur Averdunk et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3

