Abstract
CCDC no.: 2016723
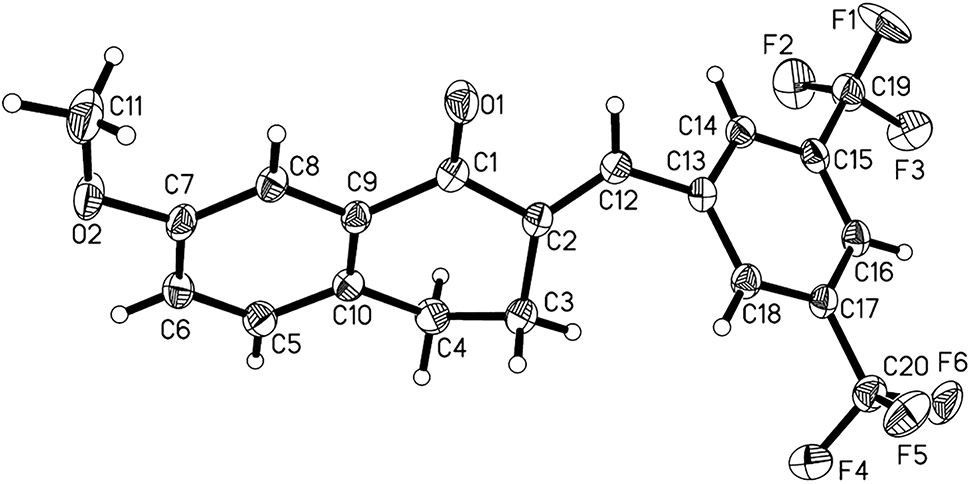
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless block |
| Size: | 0.13 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.14 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | SuperNova, Ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.5°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 8090, 3297, 0.027 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2189 |
| N(param)refined: | 282 |
| Programs: | CrysAlisPRO [1], SHELX [2], [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.47461 (19) | 0.1153 (3) | 0.1241 (2) | 0.0519 (7) |
| C2 | 0.36909 (17) | 0.0798 (3) | 0.10808 (19) | 0.0502 (6) |
| C3 | 0.28942 (19) | 0.1754 (4) | 0.0325 (2) | 0.0656 (8) |
| H3A | 0.291862 | 0.282213 | 0.054855 | 0.079* |
| H3B | 0.224084 | 0.132339 | 0.019421 | 0.079* |
| C4 | 0.30470 (19) | 0.1750 (4) | −0.0585 (2) | 0.0683 (8) |
| H4A | 0.294702 | 0.069663 | −0.084519 | 0.082* |
| H4B | 0.255408 | 0.242855 | −0.105403 | 0.082* |
| C5 | 0.4261 (2) | 0.3093 (4) | −0.1090 (2) | 0.0648 (8) |
| H5 | 0.373400 | 0.328156 | −0.168287 | 0.078* |
| C6 | 0.5207 (2) | 0.3600 (3) | −0.0913 (2) | 0.0632 (8) |
| H6 | 0.531200 | 0.413260 | −0.138502 | 0.076* |
| C7 | 0.60023 (19) | 0.3324 (3) | −0.0040 (2) | 0.0554 (7) |
| C8 | 0.58468 (18) | 0.2523 (3) | 0.06519 (19) | 0.0523 (7) |
| H8 | 0.638189 | 0.231863 | 0.123758 | 0.063* |
| C9 | 0.48839 (17) | 0.2014 (3) | 0.04756 (18) | 0.0467 (6) |
| C10 | 0.40796 (18) | 0.2302 (3) | −0.03959 (19) | 0.0530 (7) |
| C11 | 0.7751 (2) | 0.3566 (5) | 0.0911 (3) | 0.0959 (12) |
| H11A | 0.765592 | 0.399739 | 0.143713 | 0.144* |
| H11B | 0.833515 | 0.402354 | 0.089219 | 0.144* |
| H11C | 0.783664 | 0.245171 | 0.098772 | 0.144* |
| C12 | 0.35570 (18) | −0.0359 (3) | 0.15895 (19) | 0.0520 (7) |
| H12 | 0.413263 | −0.086342 | 0.201750 | 0.062* |
| C13 | 0.25978 (17) | −0.0934 (3) | 0.15514 (18) | 0.0492 (6) |
| C14 | 0.24401 (19) | −0.2546 (3) | 0.15445 (19) | 0.0536 (7) |
| H14 | 0.294294 | −0.323454 | 0.158182 | 0.064* |
| C15 | 0.1539 (2) | −0.3130 (3) | 0.14822 (19) | 0.0552 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0797 (2) | −0.2134 (3) | 0.14618 (19) | 0.0566 (7) |
| H16 | 0.019643 | −0.253201 | 0.142653 | 0.068* |
| C17 | 0.09560 (18) | −0.0542 (3) | 0.14942 (19) | 0.0507 (6) |
| C18 | 0.18432 (18) | 0.0053 (3) | 0.15334 (19) | 0.0533 (7) |
| H18 | 0.193578 | 0.113288 | 0.154787 | 0.064* |
| C19 | 0.1377 (3) | −0.4860 (4) | 0.1444 (3) | 0.0774 (9) |
| C20 | 0.0177 (2) | 0.0556 (4) | 0.1499 (3) | 0.0663 (8) |
| F1a | 0.1920 (7) | −0.5559 (10) | 0.2203 (7) | 0.125 (3) |
| F3a | 0.0422 (5) | −0.5177 (10) | 0.1291 (7) | 0.101 (3) |
| F6a | −0.0607 (8) | −0.0103 (14) | 0.1545 (10) | 0.112 (4) |
| F1′a | 0.2287 (7) | −0.5661 (10) | 0.1883 (8) | 0.134 (3) |
| F3′a | 0.0819 (10) | −0.5374 (12) | 0.1776 (10) | 0.191 (6) |
| F6′a | −0.0677 (6) | −0.0156 (16) | 0.1276 (11) | 0.129 (5) |
| F2 | 0.1286 (2) | −0.5476 (2) | 0.06383 (19) | 0.1223 (9) |
| F4 | −0.00985 (15) | 0.1597 (3) | 0.07954 (16) | 0.1039 (7) |
| F5 | 0.04895 (15) | 0.1423 (3) | 0.22760 (16) | 0.1035 (7) |
| O1 | 0.54603 (13) | 0.0733 (3) | 0.19655 (15) | 0.0733 (6) |
| O2 | 0.69088 (14) | 0.3898 (3) | 0.00556 (15) | 0.0751 (6) |
aOccupancy: 0.5.
Source of material
An amount of 5 mL (25%) of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution was added dropwise to the mixture of 7-methoxy-1-tetralone and 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzaldehyde in 10 mL methanol and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. The in process-control was monitored by silica gel thin layer chromatography (TLC, 254 nm). When the reaction was stopped, the precipitate was filtered from the reaction and dissolved with ethyl acetate. The organic phase was washed successively by water and brine, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After filtration, the ethyl acetate was condensed in vacuo to yield a white solid, which was purified by silica-gel column chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:2, v/v). Suitable crystals of the title compound were obtained by recrystallization in dichloromethane and methanol (1:1, v/v) system and dried under vacuo at 65 °C for 3 h.
Experimental details
The H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with d(C–H) = 0.97 Å (methylene), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C), and d(C–H) = 0.93 Å (aromatic), Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Comment
During inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases in the central nervous system (CNS), microglia are activated and polarized into pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype, which mediate neuroinflammation and play a key role in the progression of brain diseases [4], [5]. The inflammatory process may lead to excessive release of inflammatory mediators or cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-6 and so on [6]. The activation of NF-κB is a result of underlying inflammation and the expression of the inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNF-α can be down-regulated by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB, and play an anti-inflammatory role [7], [8], [9]. Furthermore, inhibiting the activation of NF-κB can produce anti-neuroinflammatory effects on activated microglial cells [10]. Therefore, the study of NF-κB inhibitors with anti-neuroinflammatory properties and low toxicity is of great significance in the treatment of inflammatory neurodegenerative CNS diseases [11].
Existing studies have used 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one (DHN) derivatives with anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activities as novel allergic and inflammatory responses modifiers [12], [13] and as potential retinoic acid (RA)-metabolizing enzymes inhibitors to treat skin diseases and cancer. However, DHN derivatives are rarely developed as anti-neuroinflammatory drugs, so the synthesis of novel benzylidene-substituted DHN derivatives with anti-neuroinflammatory activities are of great significance. Our group also synthesized some of these compounds in the early stage, and studied their anti-neuroinflammatory activity. The results showed that the fluorine-substituted compounds had higher activities [14], [15]. In this study, a new benzylidene-substituted DHN was designed and synthesized through Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction.
The crystal structure analysis revealed that the title compound crystallized in the monoclinic space group P21/c. The ORTEP diagram is presented in the Figure. There is only a drug molecule in the asymmetric unit. The configuration at the C(2)=C(11) olefinic 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl and carbonyl moiety showed an E stereochemistry [7], [16]. Because of the distorting effect of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, the 7-methoxyphenyl and 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl groups are not coplanar with each other, with a dihedral angle of approximately 70°. This twisted configuration may increase likelihood of interactions with bioactive molecules, for the purposes of creating more potent biological activity [17]. Bond lengths and angles are all in the expected ranges [17], [18].
Funding source: National Natural Science Foundation of China
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020XDRH105
Funding source: Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan of Yantai
Award Identifier / Grant number: 2020XDRH105
Author contribution: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
Research funding: This work was supported by Science and Technology Innovation Development Plan of Yantai (No. 2020XDRH105) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473104).
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Rigaku OD. CrysAlisPRO; Rigaku Oxford Diffraction Ltd: Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122 https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8 https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
4. Goldmann, T., Prinz, M. Role of microglia in CNS autoimmunity. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 208093.https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/208093.Search in Google Scholar
5. Gao, C. L., Hou, G. G., Liu, J., Ru, T., Xu, Y. Z., Zhao, S. Y., Ye, H., Zhang, L. Y., Chen, K. X., Guo, Y. W., Pang, T., Li, X. W. Synthesis and target identification of benzoxepane derivatives as potential anti-neuroinflammatory agents for ischemic stroke. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2429–2439; https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201912489.Search in Google Scholar
6. Zhang, J. Q., Zhang, Q., Xu, Y. R., Li, H. X., Zhao, F. L., Wang, C. M., Liu, Z., Liu, P., Liu, Y. N., Meng, Q. G., Zhao, F. Synthesis and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of C20 epimeric ocotillol-type triterpenes and protopanaxadiol. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 292–301; https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0770-0994.Search in Google Scholar
7. Yao, B. R., Sun, Y., Chen, S. L., Suo, H. D., Zhang, Y. L., Wei, H., Wang, C. H., Zhao, F., Cong, W., Xin, W. Y., Hou, G. G. Dissymmetric pyridyl-substituted 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones as anti-hepatoma agents by inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 167, 187–199; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.02.020.Search in Google Scholar
8. Li, N., Xin, W. Y., Yao, B. R., Cong, W., Wang, C. H., Hou, G. G. N-phenylsulfonyl-3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone derivatives as activation NF-κB inhibitors in hepatic carcinoma cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 531–544; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.027.Search in Google Scholar
9. Sun, Y., Gao, Z. F., Yan, W. B., Yao, B. R., Xin, W. Y., Wang, C. H., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Discovery of novel NF-κB inhibitor based on scaffold hopping: 1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 198, 112366; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112366.Search in Google Scholar
10. Liu, J., Xu, Y. R., Yang, J. J., Wang, W. Z., Zhang, J. Q., Zhang, R. Z., Meng, Q. G. Discovery, semisynthesis, biological activities, and metabolism of ocotillol-type saponins. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 373–378; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2017.01.001.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zeng, K. W., Wang, S., Dong, X., Jiang, Y., Tu, P. F. Sesquiterpene dimer (DSF-52) from Artemisia argyi inhibits microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of NF-κB, JNK/p38 MAPKs and Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 298–306; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2013.08.016.Search in Google Scholar
12. Barlow, J. W., Zhang, T., Woods, O., Byrne, A. J., Walsh, J. J. Novel mast cell-stabilising amine derivatives of 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one and 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[7]annulen-5-one. Med. Chem. 2011, 7, 213–223 https://doi.org/10.2174/157340611795564222.Search in Google Scholar
13. Kirby, A. J., Le, L. R., Maharlouie, F., Mason, P., Nicholls, P. J., Smith, H. J., Simons, C. Inhibition of retinoic acid metabolising enzymes by 2-(4-aminophenylmethyl)-6-hydroxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)- one and related compounds. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2003, 18, 27–33 https://doi.org/10.1080/1475636021000049221.Search in Google Scholar
14. Sun, Y., Gao, Z. F., Wang, C. H., Hou, G. G. Synthesis, crystal structures and anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted 1,4,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[h]quinazolin-2-amine derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. 2019, C75, 1157–1165 https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229619010118.Search in Google Scholar
15. Sun, Y., Zhou, Y. Q., Liu, Y. K., Zhang, H. Q., Hou, G. G., Meng, Q. G., Hou, Y. Potential anti-neuroinflammatory NF-κB inhibitors based on 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one derivatives. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1631–1640; https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2020.1804899.Search in Google Scholar
16. Li, N., Xin, W. Y., Yao, B. R., Wang, C. H., Cong, W., Zhao, F., Li, H. J., Hou, Y., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Novel dissymmetric 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones as potential antitumor agents with biological evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 147, 21–33; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.01.088.Search in Google Scholar
17. Li, N., Yao, B. Y., Wang, C. H., Meng, Q. G., Hou, G. G. Synthesis, crystal structure and activity evaluation of novel 3,4-dihydro-1-benzoxepin-5(2H)-one derivatives as protein-tyrosine kinase (PTK) inhibitors. Acta Crystallogr. 2017, C73, 1003–1009 https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053229617015145.Search in Google Scholar
18. El-Sayed, N. E., Almaneai, N. M., Ghabbour, H. A., Alafeefy, A. M. Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylidene)-6-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H18O4. Z. Kristallogr. NCS 2017, 232, 203–205.10.1515/ncrs-2016-0195Search in Google Scholar
© 2020 Ming-Zhu Luan et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- The crystal structure of 3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, C30H46O3·1/6H2O
- The crystal structure of (3S,12R,20R,24R)-3,12-diacetyl-20,24-epoxy-dammarane-3,12,25–triol–ethyl acetate (4/1), C34H56O6⋅ 0.25(C4H8O2)
- A new polymorph of tetrakis(dimethylammonium) catena-poly[tetrakis(μ2-sulfato-κ2O:O′)dizinc(II)], Zn2C8H32N4O16S4
- Crystal structure of 10-oxysophoridine, C15H22N2O2
- The crystal structure of (5R,8R,9R,10R,12R,13R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O4
- Synthesis, crystal structure and optical property of 1,6-bis(p-tolylthio)pyrene, C30H22S2
- The crystal structure of hexakis(2-(pyridin-2-ylamino)pyridin-1-ium) decavanadate(V) dihydrate, C60H64N18O30V10
- Preparation and crystal structure of a cationic olefin polymerization precatalyst: (1,7-bis(2,6–dichlorophenyl)-1,7-di-aza-4-oxo-heptan-1,4,7-triyl)dimethyl zirconium(IV), C18H20Cl4N2OZr
- The crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl(4,4-dimethyl-2,2-dipyridyl-κ2N,N′)- (pyrazole-κN)rhenium(I) nitrate, C18H16O3N4Re
- Synthesis and crystal structure of hexaaquacopper(II) 2,5-dicarboxyterephthalate, C10H16O14Cu
- The crystal structure of (8R,10R,12R,14R)- 12-hydroxy-16-(5-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)- 4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyltetradecahydro-3H- cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,6(2H)-dione, C30H48O5
- Structure of the mixed crystal (S)-(6-(bromo/chloro)-2-methoxy-2,6-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)(phenyl)methanol, C17H14Br0.5Cl0.5NO2
- The crystal structure of trans-tetraaqua-bis(4-acetylphenoxyacetato-κ1O)manganese(II), C20H26O12Mn
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- Crystal structure of DL-α-(methylaminomethyl)benzyl alcohol, C9H13NO
- The crystal structure of dipentaerthritol hexanitrate, C10H16N6O19
- Crystal structure of N,N-diphenylformamide, C13H11NO
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen- 1(2H)-one, C20H14F6O2
- Crystal structure of ortho-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O2 – a second polymorph and deposition of 3D coordinates
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O:O')-(2-(4-(2,4,4-trimethylpentan-2-yl)phenoxy)propanoato-κ2O,O')yttrium(III)], C51H79O11Y
- Crystal structure of benzylthiouronium chloride, C8H11ClN2S
- Synthesis and crystal structure of tert-butyl (2′R,3R,3′R,4a′R,9a′S)-1-acetyl-5-chloro-3″-methyl-2,5″,9′-trioxo-1″-phenyl-1″,4a′,5″,9a′-tetrahydro-1′H,3′H,9′H-dispiro[indoline-3,4′-xanthene-2′,4″-pyrazole]-3′-carboxylate, C36H32ClN3O7
- Crystal structure of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde, C8H8O3
- Crystal structure of poly[diaqua-(m3-3′,5′-dicarboxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3,4-dicarboxylato-K4O,O′:O″:O‴) cadmium(II)], C16H11O10Cd
- Crystal structure of {tetraaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)}-{triaqua-bis(1-(4-hydroxy-2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)-2-((4aS,6R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-5,8a-dimethyl-2-methylenedecahydronaphthalen-1-yl)ethane-1-sulfonato-k2O,O') calcium(II)} – water – acetone (1/1/8/2)
- Synthesis and crystal structure of bis{2-bromo-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxy-imino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato- κ2N,O}zinc(II)-methanol(1/2), C65H60Br4N8O9Zn2
- Crystal structure of benzenesulphonic acid
- Crystal structure of N-benzyl-N-nicotinoyl-nicotine amide C19H15N3O2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ3-2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonato-κ4N:N′,O:O′)silver(I)], C12H18O8N4S2Ag2
- Crystal structure of 1,4-bis(methylpyridinium benzene) bis(1,2-dicyanoethene-1,2-dithiolato-κ2S:S)nickel(II), C26H18N6NiS4
- Crystal structure of the Cu(II) complex chlorido-(6-oxo-2-phenyl-1,6-dihydropyrimidine-4-carboxylato-k2N,O)-(phenanthroline-k2N,N')copper(II), C23H15ClCuN4O3
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride acetic acid solvate, C14H13AsClNO2
- Crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-3,3′,4,5′-biphenyl tetracarboxylate- κ3O,O′:O′′) -(μ2-4,4′-bis(pyrid-4-yl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)zinc(II)], C27H18NO9Zn
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(μ2-3-amino-benzenedisulfonato-κ2N:O)-bis (3-methyl-isoquinoline-κN)silver(I)], C26H24N3O3SAg
- Crystal structure of 2-((4-Aminophenyl)thio)acetic acid, C8H9NO2S
- Crystal structure of phenarsazine chloride dimethylsulfoxide solvate, C14H15AsClNOS
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide, C8H8N4O
- Crystal structure of chlorido{hydridotris[3-phenyl-5-methylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}copper(II), C30H28BClCuN6
- Crystal structure of benzanthrone – a redetermination for correct molecular geometry and localization of hydrogen atoms
- Crystal structure of 4-bromobenzaldehyde – complete redetermination at 200 K, C7H5BrO
- Crystal structure and spectroscopic properties of chlorido{hydridotris[3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}(3-,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl-κN)copper(II), C20H30BClCuN8
- The crystal structure of 4-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)(pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)benzonitrile, C22H20N2O
- Crystal structure of 4-ethyl-3-phenylisoquinolin-1(2H)-one, C17H15NO
- Crystal structure of (tricyclohexylphosphane-κP)-[(Z)-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-O-methylthiocarbamato-k1S]gold(I), C26H40AuFNOPS
- Crystal structure of (3S,8R,10R,12R,14R)-12-hydroxy-4,4,8,10,14-pentamethyl-17-((R)-2,6,6-trimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl) hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl acetate, C32H54O4
- The crystal structure of 2-[(S)-1-(naphthalen-1-yl)ethyl]-2,3,7,7a- tetrahydro-3a,6-epoxyisoindol-1(6H)-one, C19H20NO2
- Crystal structure of {hydridotris[3-(t-butyl)-5-isopropylpyrazol-1-yl-κN3]borato}thallium(I), C30H52BN6Tl
- Synthesis and crystal structure of 1-octyl-3-phenylquinoxalin-2(1H)-one, C22H26N2O
- The crystal structure of 2,6-difluorophenol, C6H4F2O
- 4-(9H-Fluoren-9-yl)-4-methylmorpholin-4-ium bromide, C18H20BrNO
- The crystal structure of 2,4-dimethylimidazole monohydrate, C5H10N2O
- The crystal structure of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, C5H8N2
- The crystal structure of 3-ammonio-4-aminobenzoate, C7H8N2O2 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of 4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-3-ium-2-ylthio)-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dienolate chloride monohydrate, C14H15N4O5S2Cl
- The crystal structure of butyrylferrocene, C14H16FeO
- The crystal structure of bi-1,1′-cyclopentane-1,1′-diol, C10H18O2
- The crystal structure of 2-iso-propylimidazole, C6H10N2
- The crystal structure of aqua-tris (1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-dionato-κ2O,O′)-lanthanum(III), C45H35LaO7
- Crystal structure of (3E,5E)-3,5-bis-4-methoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-1-methylpiperidin-4-one, C24H21F6NO3
- The crystal structure of 3,5-dichloro-6-diazo-2,4-dinitrocyclohexa-2,4-dien-1-one, C6Cl2N4O5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-methylquinolin-8-olato-κ2N,O)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C29H23AsNO2Rh
- Crystal structure of (1aS,1a1S,2S)-4a-butoxy-1a,1a1,2,4a,5,6-hexahydro-1H-cyclobuta[de]naphthalen-2-yl-4-nitrobenzoate, C22H25NO5
- Crystal structure of carbonyl(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-olato-k2O,O′)(triphenylarsine-κAs)rhodium(I), C24H19AsNO3Rh
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[triqua-bis(μ2-4-carboxy-2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylato-k3N,O:O′)barium(II)] tetrahydrate, C14H14BaN12O15
- Crystal structure of (E)-3′,6′-bis(ethylamino)-2-((quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene)amino)spiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one, C35H32N6O2
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-5-chloro-salicylato-κ3O,O′:O′)-bis(5-chloro-salicylato-κ2O,O′)-bis(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N′) dilead(II) – water (1/2), C52H36C14N4O14Pb2·2(H2O)
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-ethoxycarbonyl-3,5-dimethyl-2-(pyrrole-2-ylmethyleneamino)-3′,6′-dihydroxylspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one-methanol (1/1), C31H29N3O7
- The crystal structure of 5H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine-6,11-dione, C14H9NO2
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(4-fluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)-7-methoxy-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one, C19H14F4O2
- The crystal structure of N-(2-methoxy-4,5-bis[phenylselanyl]phenyl)picolinamide, C25H20N2O2Se2
- The crystal structure of (E)-2-(5-bromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-N-phenylhydrazine-1- carboxamide monohydrate, C14H14BrN3O3
- Crystal structure of fac-tricarbonyl-(nitrato-k1O)-bis(pyridine-κN)-rhenium, C13H10O6N3Re
- Crystal structure of (E)-2-(((1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methylene)amino)-3′,6′-dihydroxyspiro[isoindoline-1,9′-xanthen]-3-one — methanol (1/2), C27H25N3O6
- The crystal structure of 4-amino-N′-(4-aminobenzoyl)benzohydrazide monohydrate, C14H16N4O3
- Crystal structure of bis(amino(carbamothioylamino)methaniminium) 5-hydroxyisophthalate monohydrate, C12H20N8O6S2
- The crystal structure of 2-(chloromethyl)pyridine, C6H6ClN
- The crystal structure of 1-bromo-4-iodo-benzene, C6H4BrI
- The crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-nitro-phenol, C8H9NO3
- The crystal structure of 3-chloropropionic acid, C3H5ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetic acid, C9H10O3


