Abstract
Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 (α2δ1) has been identified as a marker of cancer stem cells in multiple malignant tumor types. However, α2δ1’s role in the prognosis of hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) was not reported. In our study, ten pairs of HSCC and peritumoral normal tissues were used for immunohistochemistry assessment. And α2δ1 expression levels of 34 more HSCC samples were also evaluated, represented by the integral optic density using Image-Pro Plus. Clinicopathological associations and prognostic value of α2δ1 were analyzed. As a result, α2δ1 expression was frequently increased in HSCC tissues. Although the correlation between patients’ clinicopathological characteristics and their α2δ1 expression levels was not significant, α2δ1 expression was significantly correlated with unfavorable overall survival (OS) (P = 0.018) and progression-free survival (PFS) (P = 0.023). Univariate and multivariate cox regression analyses suggested α2δ1’s prognostic role for both OS and PFS (P = 0.013 and 0.011, respectively). This study specifically demonstrated that α2δ1 regularly increased in HSCC compared with peritumoral tissues, and α2δ1 could act as a promising prognostic marker in HSCC patients.
1 Introduction
Hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC), as a subtype of head and neck cancer, is not very common, with an incidence of less than ten cases/million people each year [1,2]. However, it is one of the most life-threatening types of head and neck cancer, with high malignancy, poor prognosis, and high morbidity [3]. The disease stands out by the undermentioned aspects: intricate anatomy of the primary tumor sites and thus difficulty in early diagnosis; tendency of local recurrence, metastasis, and secondary primary tumors. So far clinical and experimental exploration has not enhanced the 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of HSCC to a satisfactory level [4]. Identifying prognostic markers could be helpful in improving prognosis and guiding personalized treatments.
Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1 (α2δ1), encoded by CACNA2D1 gene, is a member of the α2/δ subunit family. α2/δ subunit is reported as auxiliary subunits of calcium channels located at the plasma membrane, whose function is to increase the channels’ biophysical properties [5]. α2δ1 was first confirmed by Zhao et al. in liver cancer as a marker for cancer stem cells (CSCs) [6]. The study found that tumor cells with a positive α2δ1 expression had greater tumorigenic capacity in vitro and a tendency of chemoresistance. The prognostic value of α2δ1 expression was also evaluated. Subsequently, more and more evidence suggested α2δ1’s prognostic role in patients with lung cancer and ovarian cancer [7,8,9,10]. Inspired by these studies, our laboratory is conducting a series of studies focusing on α2δ1 in head and neck cancer. We demonstrated that α2δ1 positive tumor cells exhibited CSC characteristics in laryngeal cancer [11]. In addition, we are working on α2δ1’s involvement in multi-drug resistance. This article, as a clinical histological evidence, is aimed to determine the value of α2δ1 in clinical practice.
This pilot single-center study is aimed to assess α2δ1 protein expression levels via immunohistochemistry (IHC) in the present study, and identify the reliability of α2δ1 being a prognostic marker in HSCC biopsy specimens collected prior to cancer treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Bioethics Committee of Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University (Batch number: 2019-P2-187-01), and registered in Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (http://www.chictr.org.cn/Registration number: ChiCTR1900027706). All patients understood and signed the informed consent before the experiments. The study conformed with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki), printed in the British Medical Journal (18 July 1964).
2.2 Patients and materials
The eligible HSCC patients were selected based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria: HSCC patients with pathological diagnosis; informed consent obtained or waiver of consent; and follow-up information available. Exclusion criteria: Failed to get informed consent; multiple cancers; lack of histological diagnosis; and no follow-up information. Forty-four paraffin-embedded tumor specimens with HSCC were collected from eligible patients who received surgery-oriented comprehensive treatment at Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University between May 2014 and January 2019.
For selected patients, two sessions of induction chemotherapy (cisplatin, 75 mg/m2, d1; 5-fluorouracil, 750 mg/m2), or induction CRT (additional RT dose of 40–50 Gy) were administered as preoperative treatment. The patients would be re-evaluated afterwards, to determine whether to perform open surgery or not. Following the principles of complete tumor removal and functional preservation, surgical procedures were specified based on the workups. Procedures of larynx preservation surgery consisted of partial hypopharyngectomy and partial laryngo-hypopharyngectomy including extended supra-glottic laryngo-hypopharyngectomy, supra-cricoid hemi-laryngo-hypopharyngectomy, and vertical hemi-laryngo-hypopharyngectomy. When larynx could not be preserved, the following procedures could be performed: total laryngectomy with partial hypopharyngectomy and total laryngo-hypopharyngectomy with or without cervical esophagectomy. All patients received adjuvant post-operative radiotherapy delivered by IMRT within 6 weeks: 5 days a week, 2 Gy per day over a 7-week period, reaching a total dose of 70 Gy.
Ten tumor specimens had a pairing peritumoral tissue sample used as the experimental control. All surgeries were performed by the same experienced surgeon. All patients were informed of the purpose of the study and gave informed consent. The age distribution of all patients ranged from 41 to 74 years with a median age of 58.8 ± 7.49 years. Clinicopathological data of the 44 HSCC patients are shown in Table 1. The patients were followed up until September 1st, 2019. The histologic differentiation of HSCC was classified into well, moderately, and poorly differentiated according to the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th Edition. The definition of OS is the time from the diagnosis of HSCC until death from any cause, while the definition of progression-free survival (PFS) is the time from diagnosis until progression of HSCC or death from any cause.
Association of α2δ1 expression in hypopharyngeal carcinoma patients with clinicopathological characteristics (Chi-square test)
| Parameter | α2δ1 score by IHC | P-value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | α2δ1-low | α2δ1-high | ||
| 44 | 22 (50.0%) | 22 (50.0%) | ||
| Age | 0.763 | |||
| <60 | 23 | 11 (47.8%) | 12 (52.2%) | |
| ≥60 | 21 | 11 (52.4%) | 10 (47.6%) | |
| Gender | 0.635 | |||
| Male | 39 | 19 (48.7%) | 20 (51.3%) | |
| Female | 5 | 3 (60.0%) | 2 (40.0%) | |
| Smoking | 1.000 | |||
| Yes | 36 | 18 (50.0%) | 18 (50.0%) | |
| No | 8 | 4 (50.0%) | 4 (50.0%) | |
| Drinking | 0.750 | |||
| Yes | 29 | 14 (48.3%) | 15 (51.7%) | |
| No | 15 | 8 (53.3%) | 7 (46.7%) | |
| Preoperative treatment | 0.635 | |||
| Yes | 5 | 2 (40.0%) | 3 (60.0%) | |
| No | 39 | 20 (51.3%) | 19 (48.7%) | |
| Histological grade | 0.082 | |||
| Well | 11 | 8 (72.7%) | 3 (27.3%) | |
| Poor/moderate | 33 | 14 (42.4%) | 19 (57.6%) | |
| pT stage | 0.517 | |||
| T1–2 | 14 | 8 (57.1%) | 6 (42.9%) | |
| T3–4 | 30 | 14 (46.7%) | 16 (53.3%) | |
| pN stage | 0.365 | |||
| N0–1 | 21 | 9 (42.9%) | 12 (57.1%) | |
| N2–3 | 23 | 13 (56.5%) | 10 (43.5%) | |
2.3 IHC
The paraffin-embedded HSCC tissues were cut into 3 μm sections. Then, the sections were baked at 60°C for 2 h, then dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated in graded ethanol solutions. Antigen retrieval was done in citrate buffer in a microwave at 99°C for 15 min. To block the endogenous peroxidase, all sections were incubated with 3% of hydrogen peroxide for 10 min. Blocking was done with 5% of goat serum (#ZLI-9022, ZSGB-BIO, China) for 1 h at ambient temperature. Primary mouse anti-human antibody (CACNA2D1 Monoclonal Antibody [20A], 1:250, # MA3-921, ThermoFisher, USA) incubation was done overnight at 4°C. After washing three times in PBS, the reaction enhancement solution from #PV-9002 kit (ZSGB-BIO, China) was added dropwise for 20 min. Then, the goat anti-mouse secondary antibody from the kit was incubated for 20 min at room temperature. Afterward, diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (#ZLI-9019, ZSGB-BIO, China) was used to develop color for 3 min. Staining with hematoxylin, 0.1% of hydrochloric acid differentiation, dehydration, transparency, and neutral resin sealing were performed successively. Negative control slides omitting the primary antibodies were generated for all assays.
2.4 IHC scoring method
Each section was scanned using the Pannoramic 250 Flash Scanner (3DHistech, Budapest, Hungary). All the scanned images were analyzed by Image-Pro Plus software version 6.0 (Media Cybernetics, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA). The magnification was 20× for HE sections and 20×/100× for IHC staining. The positive staining in images was quantified as integral optical density (IOD)/area, that is, mean density = density sum/area sum [12]. In detail, five fields with the strongest expression of α2δ1 were chosen from each section and the average value of mean density was calculated.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The patients were separated into two groups (high vs low expression) by median IOD value, 6.035. Chi-square test was used to compare differences between categorical variables. OS and PFS were determined by Kaplan–Meier survival plots and log-rank test. For survival analysis, univariate analysis was conducted using log-rank tests. All variables with P < 0.10 on univariate analysis were included in cox regression models. All statistical analyses were achieved by SPSS version 26.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY).
3 Results
3.1 α2δ1 expression regularly increased in HSCC tissues
According to immunohistochemical analysis, the staining pattern of α2δ1 was principally detected at the membrane and cytoplasm for both HSCC tissues and peritumoral tissues, with yellow/brown particles representing positive expression. The expression of α2δ1 was variable among the 44 HSCC samples (Figure S1). Representative immunohistochemical staining images showed that α2δ1 protein expression significantly increased in HSCC tissues compared to the corresponding peritumoral tissues (Figure 1a and b). Quantitative analyses evaluated in ten paired HSCC and peritumoral tissues confirmed the result of statistical significance (P = 0.0359) (Figure 1c).
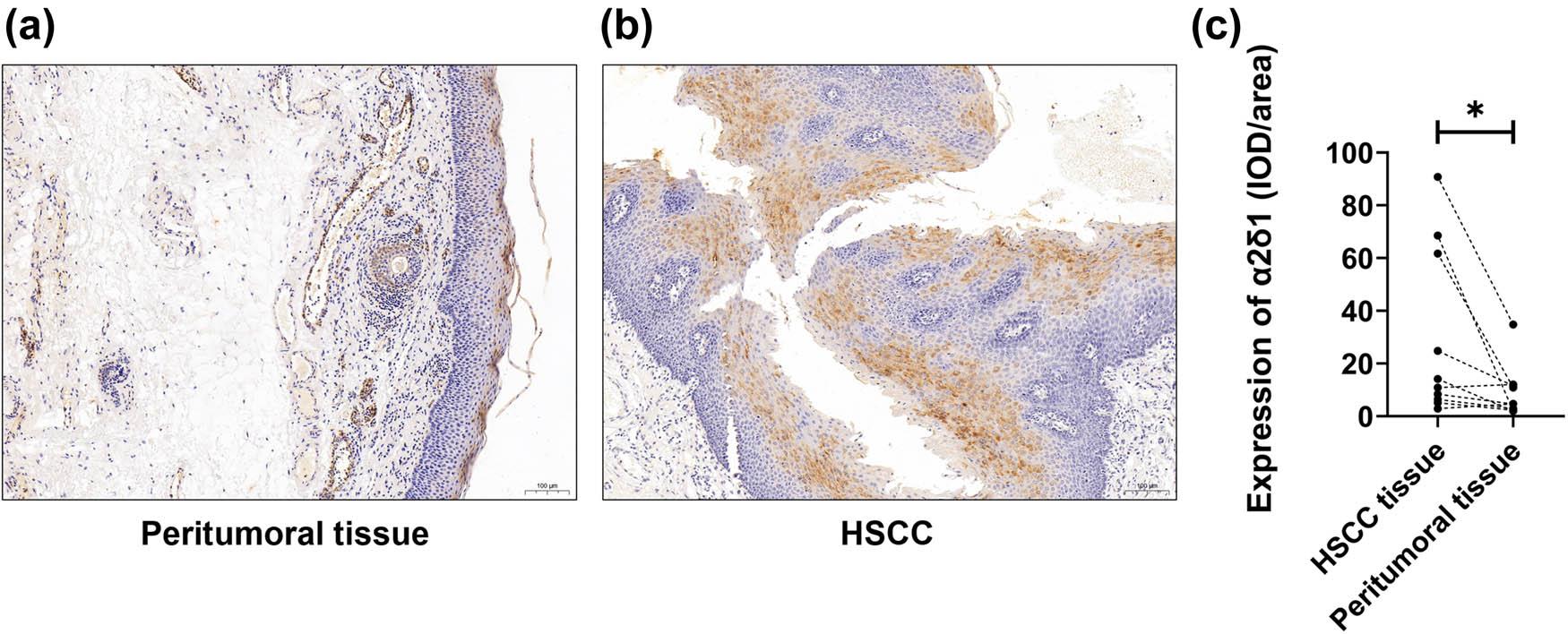
Expression level of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) and paired peritumoral mucosal tissues. Expression of α2δ1 in (a) paired peritumoral tissue (100×) and (b) HSCC tissue (100×). (c) Expression level of α2δ1 was significantly increased in paired peritumoral tissue than those in HSCC tissues (n = 10, P = 0.0359).
3.2 α2δ1 expression and its clinicopathological associations
Based on the regularly increased expression of α2δ1 protein in HSCC tissues, the clinical value of α2δ1 expression levels was investigated. After calculating the density means of α2δ1, patients were separated into two groups (low vs high expression) according to the median protein expression of tumor tissues. The correlation between α2δ1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics, including age of diagnosis, gender, smoking history, history of alcohol drinking, preoperative treatment, histological grade, pathological T (pT) stage, and pathological N (pN) stage was analyzed. However, no significant association was identified between patients’ clinicopathological characteristics and their α2δ1 protein expression levels (P > 0.05; Table 1). The result implied the potential correlation between histological grade (well differentiated vs poorly/moderately differentiated) and α2δ1 protein expression levels (P = 0.082). Therefore, we were inclined to hypothesize that the other clinicopathological parameters may not be correlated with cancer cell stemness.
3.3 α2δ1 expression was associated with poor OS and PFS
The OS and PFS of 44 HSCC patients with a positive or negative α2δ1 expression were estimated by Kaplan–Meier statistical analyses. The results showed that the expression of α2δ1 in HSCC was significantly associated with poor OS (P = 0.0018, Figure 2a) and PFS (P = 0.023, Figure 2b).
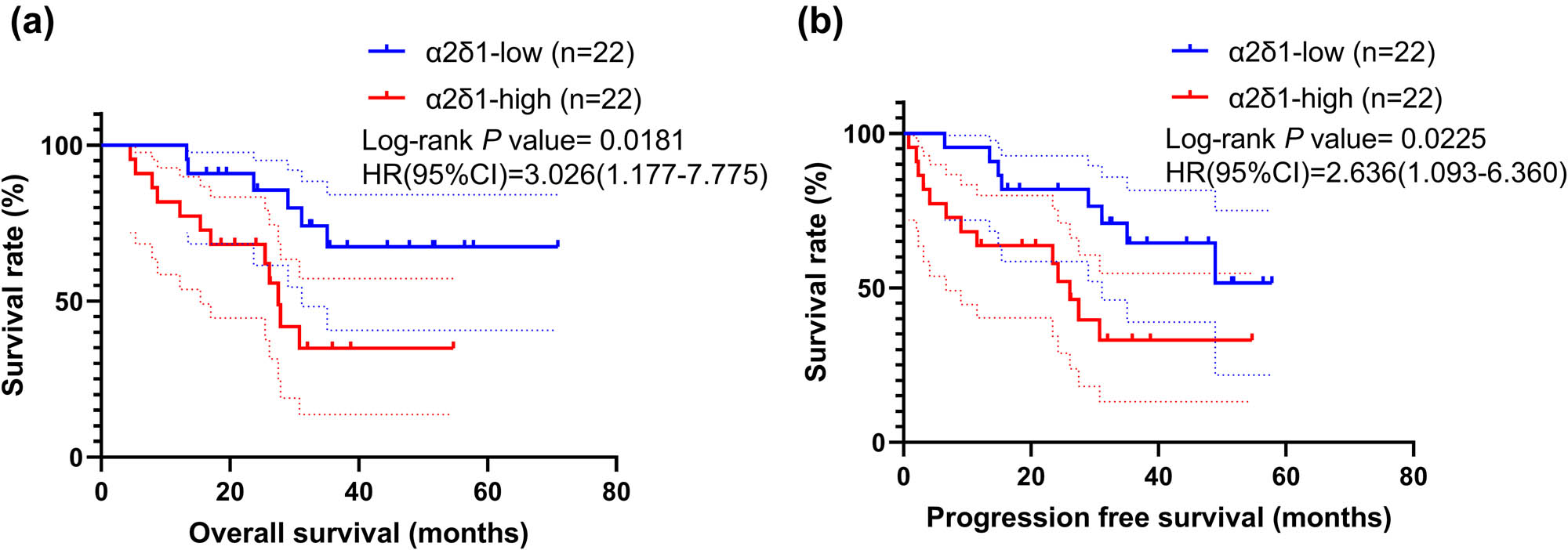
Kaplan–Meier curves for overall survival and progression free survival in HSCC patients (n = 44). (a) High α2δ1 expression groups had significantly lower OS than low α2δ1 expression groups. (b) High α2δ1 expression groups had significantly lower PFS than low α2δ1 expression groups. Hazard ratio (HR) and its 95% confidence interval, and Log-rank P value are shown.
3.4 α2δ1 expression in HSCC was an independent risk factor for OS and PFS
Univariate and multivariate analyses were tested to estimate the association of α2δ1 protein expression and the above clinicopathological parameters in terms of OS and PFS in HSCC by using cox regression method. Confounding factors were categorized as binary variables: age (<60 vs ≥60), histological grade (well vs poor/moderate), pT stage (T1–2 vs T3–4), and pN stage (N0–1 vs N2–3). The analyses revealed that pT stage and α2δ1 expression were independent risk factors for OS and PFS (P < 0.05) when evaluated by multivariate analysis. Patients with α2δ1-high expression had poorer OS and PFS than those with α2δ1-low expression (HR = 4.135 for OS and 4.138 for PFS) (Tables 2 and 3).
Univariate and multivariate analysis of OS in HSCC (Cox regression)
| Covariate | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Age | 0.643 | 0.244–1.697 | 0.373 | |||
| Gender | 0.042 | 0.000–42.970 | 0.370 | |||
| Smoking | 1.284 | 0.292–5.639 | 0.741 | |||
| Drinking | 1.644 | 0.535–5.046 | 0.385 | |||
| Pre-treat | 1.005 | 0.229–4.406 | 0.995 | |||
| HG | 2.675 | 0.608–11.766 | 0.193 | |||
| pT | 3.566 | 1.009–12.598 | 0.048 | 4.231 | 1.142–15.682 | 0.031 |
| pN | 0.531 | 0.196–1.443 | 0.215 | |||
| α2δ1 | 3.530 | 1.222–10.196 | 0.020 | 4.135 | 1.352–12.643 | 0.013 |
HG: histological grade; Pre-treat: preoperative treatment.
Univariate and multivariate analysis of PFS in HSCC (Cox regression)
| Covariate | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Age | 0.680 | 0.258–1.790 | 0.435 | |||
| Gender | 0.041 | 0.000–28.893 | 0.340 | |||
| Smoking | 1.510 | 0.343–6.640 | 0.586 | |||
| Drinking | 1.799 | 0.586–5.528 | 0.305 | |||
| Pre-treat | 0.897 | 0.205–3.925 | 0.885 | |||
| HG | 2.953 | 0.673–12.966 | 0.151 | |||
| pT | 3.388 | 0.963–11.920 | 0.057 | 3.991 | 1.092–14.580 | 0.036 |
| pN | 0.543 | 0.200–1.472 | 0.230 | |||
| α2δ1 | 3.592 | 1.250–10.324 | 0.018 | 4.138 | 1.382–12.389 | 0.011 |
HG: histological grade; Pre-treat: preoperative treatment.
4 Discussion
α2δ1 dysregulation has been found in multiple cancer types. As far as we know, this study is the first to explore the protein expression level and prognostic significance in HSCC. We wish that our findings will make contributions to the diagnosis and treatment of the disease and improve the prognostic expectations for HSCC patients.
In our study, we first analyzed the expression status of α2δ1 in paired HSCC and normal hypopharyngeal mucosa tissues by IHC. α2δ1 expression yielded the highest staining at the tumor center. Our results proved that α2δ1 protein expression was elevated in HSCC tissues compared with the matched peritumoral hypopharyngeal tissues. Then, the prognostic significance of α2δ1 in HSCC tissue was studied. From the Kaplan–Meier survival curves of our cohort, patients’ α2δ1 protein expression was observed to be correlated with their clinical outcomes. Also, the patients with higher expression level of α2δ1 were inclined to have both shorter OS and PFS statistically. The multivariate cox regression analysis revealed α2δ1 and pT acted as independent predictors for OS in HSCC patients.
It is widely acknowledged for oncologists that higher pT staging indicates worse OS and PFS in HSCC, so the result of pT being an independent risk factor for survival is not surprising. However, the clinical significance of α2δ1 expression in HSCC has not been reported. The result that the expression of α2δ1 has the parallel hazard ratio with pT as independent predictors for OS and PFS is inspiring. It suggests that patients with high α2δ1 are supposed to be treated with more aggressive strategies and close follow-ups. Considering the fact that α2δ1 was reported as a functional marker for CSCs [8,10,11], it might serve as a potential candidate for therapeutic target of HSCC in the future.
The clinical histological analysis of α2δ1 has been conducted in liver cancer and epithelial ovarian cancers [6,9]. Both the studies confirmed higher α2δ1 protein expression indicating worse clinical outcome, which was similar to our study. In addition, the former study also found higher α2δ1 protein expression in tumor tissues than in peritumoral tissues. And the latter study found that α2δ1 protein expression of tumor was correlated with its histological grade, though we did not reach this conclusion.
The mechanism underlying the prognostic value of α2δ1 was mainly because of its role as a marker for CSCs. α2δ1 subunit participated in the formulation of T-type and L-type voltage gated calcium channel (VGCC). It was reported that T-type VGCC was involved in the biological procedure of cell cycle progression and stemness maintenance [13], while L-type VGCC was associated with stem cell differentiation [14,15]. Intracellular calcium played an essential role in stem cells’ self-renewing, proliferation, and differentiation [14,16]. Further experiments confirmed α2δ1-positive tumor cells possessed the capacity of tumorigenic in vitro and in vivo, chemoresistance, and radioresistance [6,7,8], providing more evidence to its role as a CSC marker and a prognostic marker of cancer. However, no significant correlation was found between the α2δ1-positive staining and any other clinicopathologic factor other than histological grades, OS, and PFS in our study. Hence, we would like to deduce that the other clinicopathological characteristics may not associate with cancer cell stemness or chemo-radioresistance.
We tried to mine the mRNA transcriptional and survival data of CACNA2D1 from online databases such as the cancer genome atlas and GEO datasets, in order to provide more evidence for the prognostic value of α2δ1 according to the bioinformatic methods we used before [17]. But the mRNA level of CACNA2D1 was not significantly altered between tumor and normal tissues, and did not correlate with the patients’ survival time as well (data not shown). The discrepancy might come from the two techniques, RNA-seq and IHC, based separately on RNA and protein level. We deemed that IHC straightforwardly reflecting the protein expression level, and as the most widely used method in clinical practices, was convincing.
IHC has gained significance in diagnosis of diseases and has already taken a crucial position in predicting patients’ prognosis [18]. The result of IHC is usually interpreted by visual assessment. However, the subjectivity and interpretation reproducibility of IHC could be inevitable pitfalls [19]. New demands on the accuracy, reproducibility, and quality of IHC are required for medicine in the new era [20]. To meet these criteria, Image-Pro Plus software was employed to quantify IHC staining levels automatically, and the results were satisfactory.
HSCC being a relatively uncommon disease, only 44 patients were enrolled in our study. Although the study design was elaborated, the limited number of patients and the nature of retrospective study made potential selection bias and confounding bias inevitable. To further guarantee α2δ1’s predictive role in the prognosis of HSCC patients, a multicenter, prospective study with more participants was needed.
5 Conclusion
This study distinguishes itself from the others by first exploring the expression levels of α2δ1 in HSCC tumor and adjacent normal tissues and by showing the prognostic significance of α2δ1 in HSCC tissues. The present study suggested that α2δ1 could serve as a new prognostic biomarker for HSCC based on regular IHC analysis.
Abbreviations
- α2δ1
-
voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
- CSCs
-
cancer stem cells
- HSCC
-
hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- IHC
-
immunohistochemistry
- IOD
-
integral optical density
- OS
-
overall survival
- PFS
-
progression-free survival
- VGCC
-
voltage gated calcium channel
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
-
Funding information: This study was supported by Science and Technology Bureau of Enshi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture (jcy2019000040), Research and Development Project of Scientific Research Instruments and Equipment of Chinese Academy of Sciences – major instruments project (YJKYYQ20180039) and the Digestive Medical Coordinated Development Center of Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals (No. XXZ0604).
-
Author contribution: The authors, Y.D. and Q.L., contributed equally to the study. Y.D., Q.L., Q.Z., and L.L. conceived and designed the research. Q.L., S.L., M.Y., and X.W. conducted the main experiments. Q.L., Y.D., and S.L. interpreted and analyzed the data. Q.L., Y.D., and Q.Z. were responsible for revision for important intellectual content. Y.D., S.L., and X.W. prepared figures and tables. Y.D., Q.Z., and L.L. drafted, edited, and revised manuscript. Q.Z. and L.L. were responsible for supervision. All authors read and approved the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the research in ensuring that the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
-
Conflict of interest: None.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Appendix
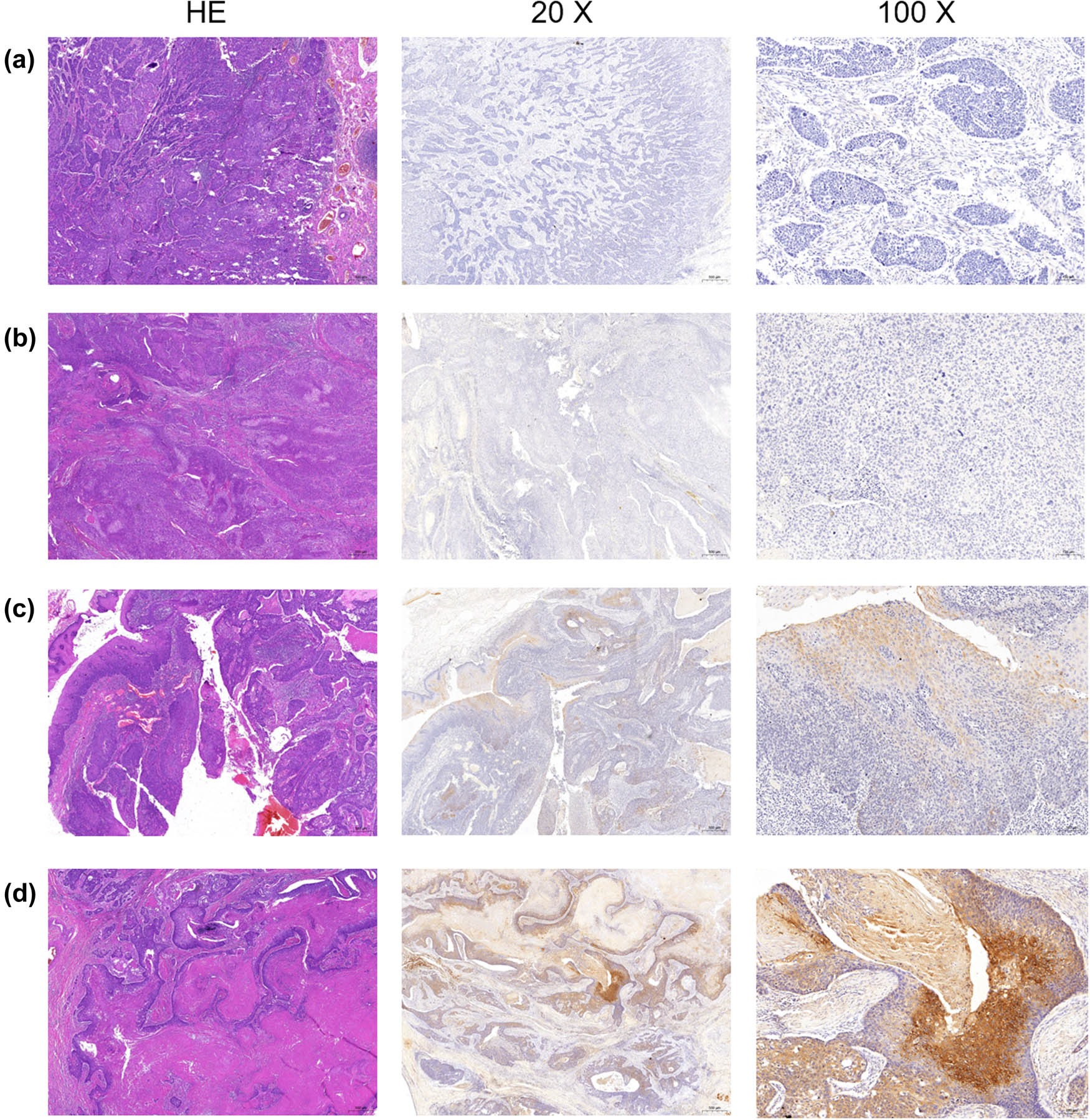
The expression of α2δ1 was variable among HSCC samples. The histological images of 4 representative cases (a–d) were presented. For each case, the HE staining section and immunohistochemistry staining of α2δ1 with different magnifications (20× and 100×) were shown. The expression of α2δ1 varied greatly among these 4 HSCC samples.
References
[1] Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.10.3322/caac.21262Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Davies L, Welch HG. Epidemiology of head and neck cancer in the United States. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135(3):451–7.10.1016/j.otohns.2006.01.029Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Spector JG, Sessions DG, Haughey BH, Chao KS, Simpson J, El Mofty S, et al. Delayed regional metastases, distant metastases, and second primary malignancies in squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx and hypopharynx. Laryngoscope. 2001;111(6):1079–87.10.1097/00005537-200106000-00028Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Newman JR, Connolly TM, Illing EA, Kilgore ML, Locher JL, Carroll WR. Survival trends in hypopharyngeal cancer: a population-based review. Laryngoscope. 2015;125(3):624–9.10.1002/lary.24915Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Dolphin AC. Calcium channel auxiliary alpha2delta and beta subunits: trafficking and one step beyond. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(8):542–55.10.1038/nrn3311Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Zhao W, Wang L, Han H, Jin K, Lin N, Guo T, et al. 1B50-1, a mAb raised against recurrent tumor cells, targets liver tumor-initiating cells by binding to the calcium channel alpha2delta1 subunit. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(4):541–56.10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.025Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Sui X, Geng JH, Li YH, Zhu GY, Wang WH. Calcium channel alpha2delta1 subunit (CACNA2D1) enhances radioresistance in cancer stem-like cells in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:5009–18.10.2147/CMAR.S176084Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Yu J, Wang S, Zhao W, Duan J, Wang Z, Chen H, et al. Mechanistic exploration of cancer stem cell marker voltage-dependent calcium channel alpha2delta1 subunit-mediated chemotherapy resistance in small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(9):2148–58.10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1932Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Yu D, Holm R, Goscinski MA, Trope CG, Nesland JM, Suo Z. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of Cacna2d1 expression in epithelial ovarian cancers: a retrospective study. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6(9):2088–97.Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Ma Y, Yang X, Zhao W, Yang Y, Zhang Z. Calcium channel α2δ1 subunit is a functional marker and therapeutic target for tumor-initiating cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(3):257.10.1038/s41419-021-03522-0Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Huang C, Li Y, Zhao W, Zhang A, Lu C, Wang Z, et al. Alpha2delta1 may be a potential marker for cancer stem cell in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2019;24(1):97–107.10.3233/CBM-181947Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Holmqvist A, Zhang H, Li Y, Adell G, et al. Survivin expression quantified by image pro-plus compared with visual assessment. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2009;17(6):530–5.10.1097/PAI.0b013e3181a13bf2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Rodríguez-Gómez JA, Levitsky KL, López-Barneo J. T-type Ca2+ channels in mouse embryonic stem cells: modulation during cell cycle and contribution to self-renewal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;302(3):C494–504.10.1152/ajpcell.00267.2011Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Forostyak O, Forostyak S, Kortus S, Sykova E, Verkhratsky A, Dayanithi G. Physiology of Ca(2+) signalling in stem cells of different origins and differentiation stages. Cell Calc. 2016;59(2-3):57–66.10.1016/j.ceca.2016.02.001Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] D’Ascenzo M, Piacentini R, Casalbore P, Budoni M, Pallini R, Azzena GB, et al. Role of L-type Ca2+ channels in neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23(4):935–44.10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04628.xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Li GR, Deng XL. Functional ion channels in stem cells. World J stem Cell. 2011;3(3):19–24.10.4252/wjsc.v3.i3.19Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Dong Y, Lu S, Wang Z, Liu L. CCTs as new biomarkers for the prognosis of head and neck squamous cancer. Open Med. 2020;15(1):672–88.10.1515/med-2020-0114Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Gil J, Wu HS. Applications of image analysis to anatomic pathology: realities and promises. Cancer Invest. 2003;21(6):950–9.10.1081/CNV-120025097Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Hammes LS, Korte JE, Tekmal RR, Naud P, Edelweiss MI, Valente PT, et al. Computer-assisted immunohistochemical analysis of cervical cancer biomarkers using low-cost and simple software. Appl Immunohistochem Mol morphol. 2007;15(4):456–62.10.1097/01.pai.0000213151.64310.70Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Cregger M, Berger AJ, Rimm DL. Immunohistochemistry and quantitative analysis of protein expression. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130(7):1026–30.10.5858/2006-130-1026-IAQAOPSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Qiang Liu et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning

