Abstract
Background
Foreign bodies in the kidney have rarely been reported. However, they can be a clinical problem for urologists. We report on a patient with a residual segment of guidewire coating embedded in the renal parenchyma following computed tomography (CT)-guided percutaneous nephrostomy drainage (PCND), and our successful minimally invasive management with retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS).
Case presentation
A 40-year-old female with urosepsis due to a right upper ureteral stone with hydronephrosis received emergent CT-guided PCND and subsequent ureteroscopic lithotripsy, double J stent insertion, and percutaneous catheter removal. Follow-up radiography showed a coiled object within the upper pole parenchyma of the right kidney, which might be the remnant of a guidewire used during the PCND procedure. Flexible ureteroscopy (fURS) was performed. Under fluoroscopy, the foreign body was localized, the renal parenchyma was incised with laser, and the foreign body was retrieved using a stone basket.
Conclusion
Although guidewire breakage is uncommon, clinicians should keep it in mind during interventional procedures. Several methods can be used to eradicate foreign objects from the urinary tract, and the first choice should always be the least invasive one. RIRS with fURS is considered as a safe, efficient, and minimally invasive option for the extraction of foreign bodies from the kidney. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive case report detailing the removal of a foreign object by RIRS in the English literature.
1 Introduction
Foreign bodies in the kidney have rarely been reported and it has seldom been elaborated in the urological literature [1]. However, foreign bodies in the urinary tract can be a clinical problem for urologists. Foreign bodies can be introduced to the kidney by penetration during a traumatic incident, by oral ingestion, and intestinal perforation, and sometimes even because of the accidental leaving of items in the body during medical procedures [2,3,4,5,6].
We hereby report a patient with a residual guidewire segment left behind in the kidney during computed tomography (CT)-guided percutaneous nephrostomy drainage (PCND), and our successful minimally invasive management with retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive case report detailing the removal of a foreign object by RIRS in the English literature.
2 Case presentation
A 40-year-old female who had a medical history of Sicca syndrome and regularly received follow-up at the rheumatology clinic, presented at our emergency department with right flank pain and a fever of up to 40° Celsius for several days. She had no history of trauma and there was no personal or family history of diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, or malignancies. A physical examination revealed right costovertebral knocking tenderness. Urine examination revealed seven white blood cells per high-power field. Laboratory tests revealed leukopenia with a total white blood cell count of 2,300/μL (normal range: 4,000–10,000/μL) and an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 17.4 mg/dL (normal range: 0.0–0.79 mg/dL). Renal function test results were within normal ranges.
CT revealed a 1 cm right upper ureteral stone causing upper stream hydronephrosis and obstructive uropathy. The patient received emergent CT-guided PCND by radiologists and was admitted for infection control. After her infection was controlled, ureteroscopy with laser lithotripsy with a double J stent insertion was performed. The PCND tube was removed during the surgery and the patient was discharged the following day.
During her postoperative follow-up at our outpatient department, the patient still complained of right flank pain and gross hematuria off and on. She denied muscle strain, skeletal trauma, fever, dysuria, and changes in bowel habits. A physical examination revealed knocking tenderness at the right costovertebral angle. Laboratory tests were within the normal range including white blood cell count, CRP, and renal function test.
A plain radiograph of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (KUB) showed a new radiopaque lesion in the right renal shadow compared with the pre-PCND plain film (Figure 1). This artifact was considered to be a retained ruptured guidewire or fragments of the PCND. Further CT imaging was performed to determine the precise anatomical location and the radiodensity of the object, which was revealed to be a curvilinear hyperdense coil within the upper pole parenchyma of the right kidney (Figure 2a–c). The radiologists judged that the coil could be the remnants of a guidewire used during the PCND procedure.
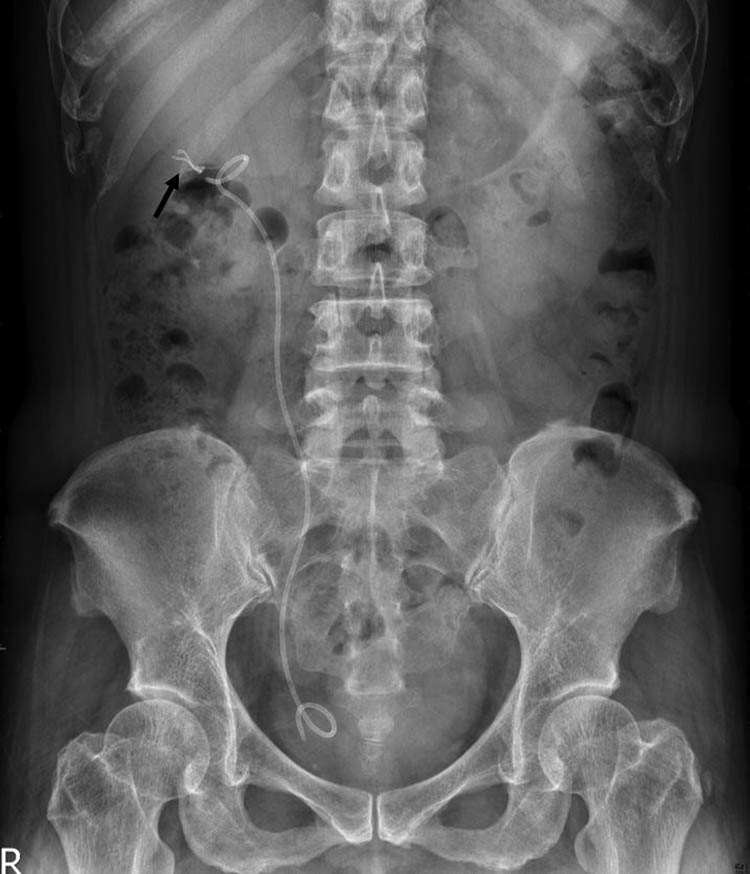
Post-PCND follow-up KUB show a new radiopaque lesion (arrow) in right kidney area.
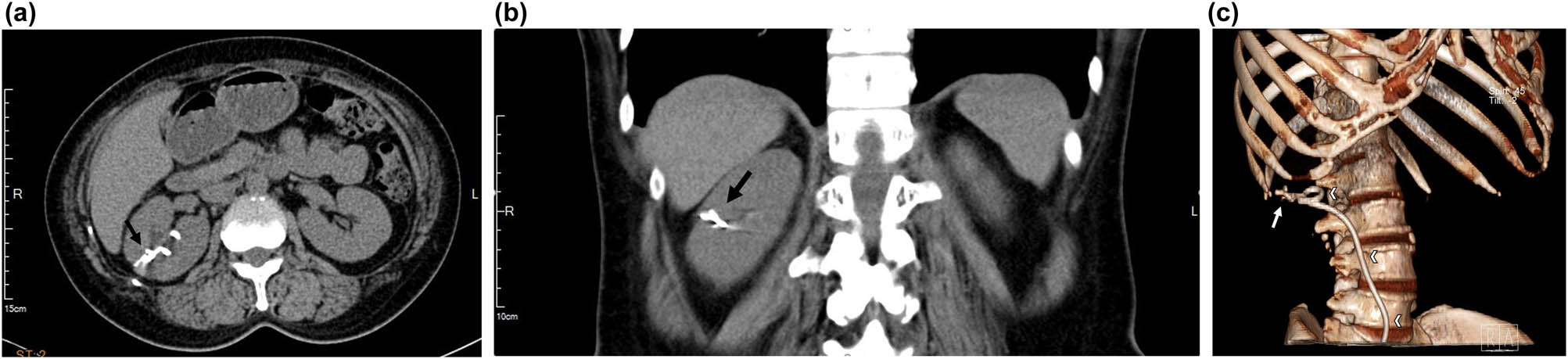
Computed tomography image of the intrarenal foreign body (arrow) and its relationship with right double J ureter stent (arrowheads). (a) Transverse cut, (b) coronal cut, and (c) reconstruction.
We therefore performed RIRS with flexible ureteroscopy (fURS) (SemiFlex Scope™) via a ureteral access sheath (Well Lead ClearPetra 11/13French–36 cm) under intraoperative C-arm fluoroscopy. There was no visible foreign body or attachment points within the pyelocalyceal system in the fURS field. We then located our fURS at a suspicious site under C-arm fluoroscopy guidance, which could be the location of the embedded coil within the renal parenchyma. To aim our target, we operated C-arm fluoroscopy not only in vertical axial but also in horizontal axial and at an angle of 45°. Unfortunately, the target could not be seen under direct ureteroscopic vision. We only identified a hint of a defect, which could have been the penetration site of the previous PCND procedure. A Holmium-YAG Laser (Lumenis® VersaPulse® PowerSuite™ 200 μm laser system, 1.5 J and 20 Hz) was used to cut through the pit defect and the underlying renal parenchyma to gradually expose the embedded foreign body (Figure 3). To prevent patient from bleeding during laser cutting, we kept in low power setting, which would cause less injury to the surrounding tissue. To avoid unnecessary injury to renal parenchyma, anesthesiologist helped to control the patient’s breath which could minimize the movement of her kidney during laser cutting. A coiled object was finally observed (Figure 4) and it was carefully retrieved using a Boston Scientific Zero Tip™ Nitinol stone basket. The specimen was a 12 cm long tube-like object (Figure 5), which was determined to be with the coating layer of a guidewire, which had broken during the previous CT-guided PCND. The procedure was completed by careful hemostasis and the placement of a 4.7 French–22 cm (Cook Medical) double J ureteral stent.
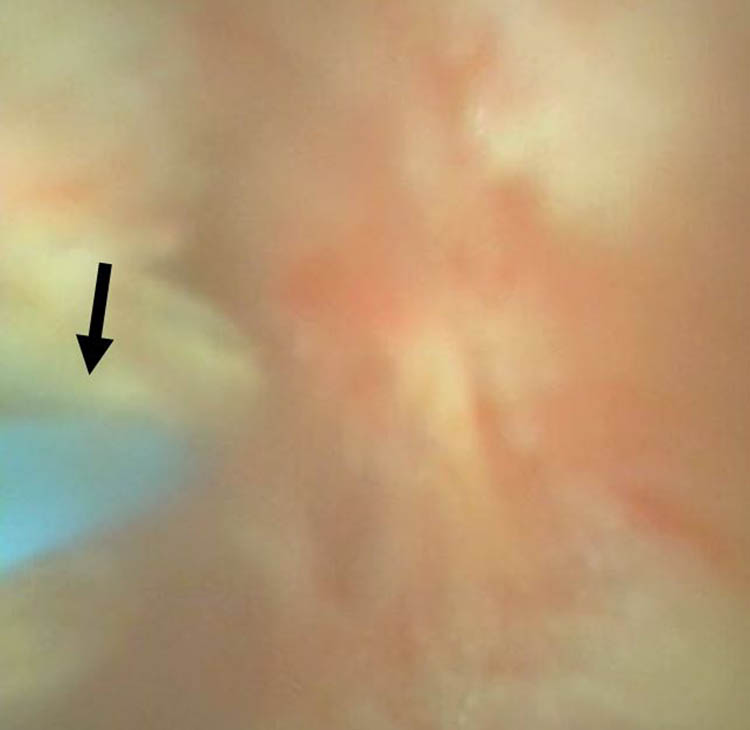
The video image of fURS and the laser probe (arrow) for cutting the underlying renal parenchyma for exposure of the embedded material.
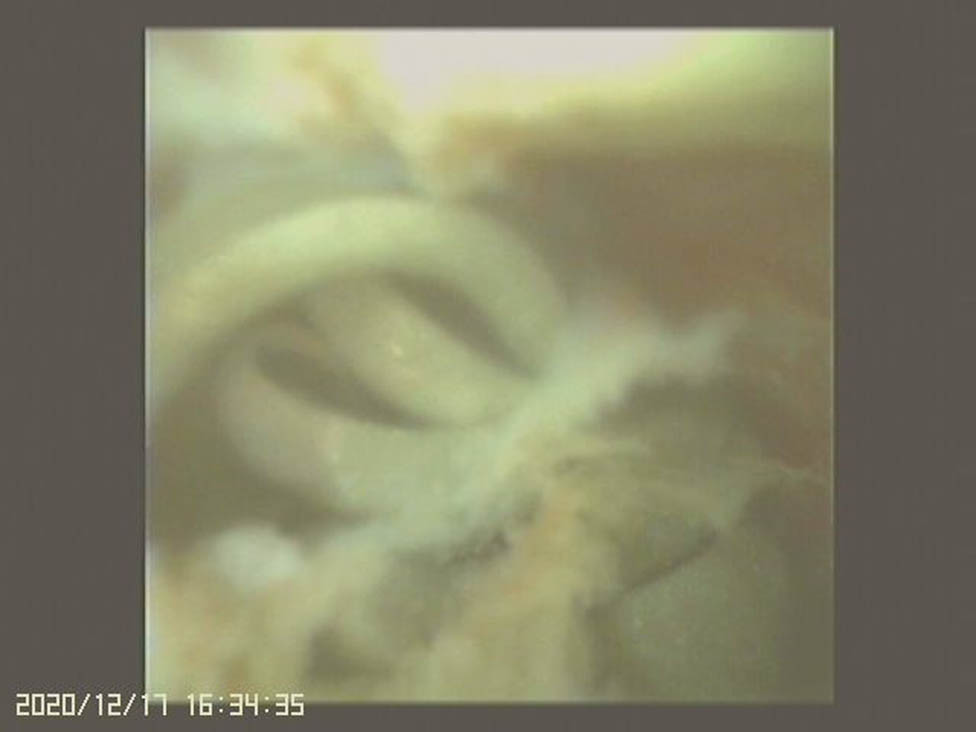
The video image of fURS and the coiled element.
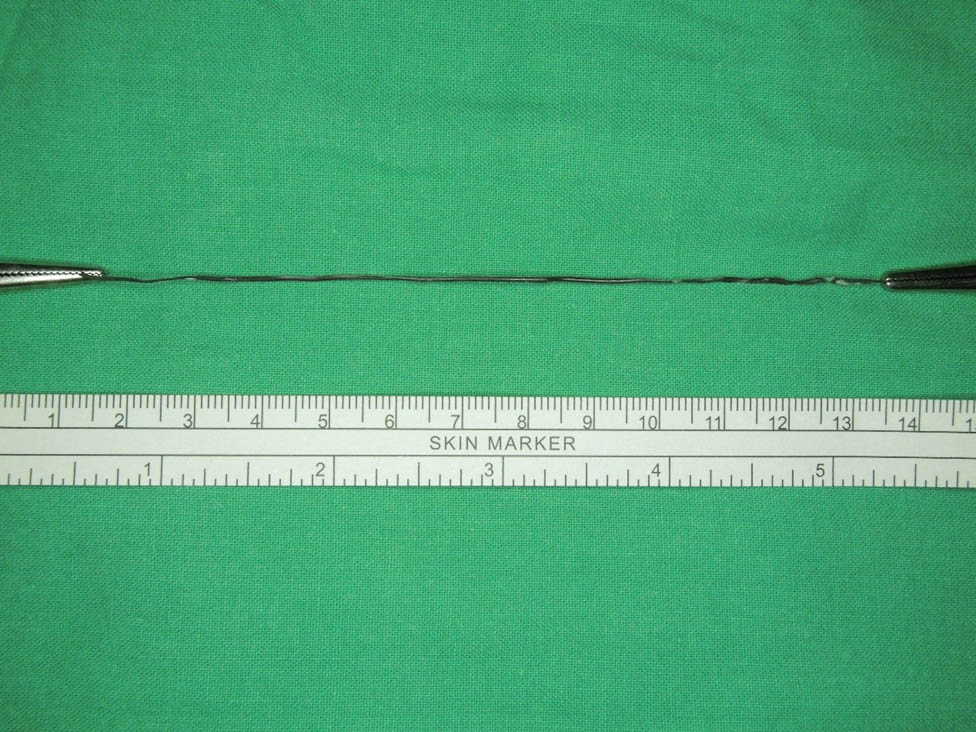

The retrieved specimen from RIRS (12 cm).
Postoperative KUB revealed the disappearance of the radiopaque lesion in the right renal shadow (Figure 6). The patient’s symptoms also improved and neither flank pain nor gross hematuria was noted during follow-up. Three weeks after the procedure, the double J stent was removed without complications.
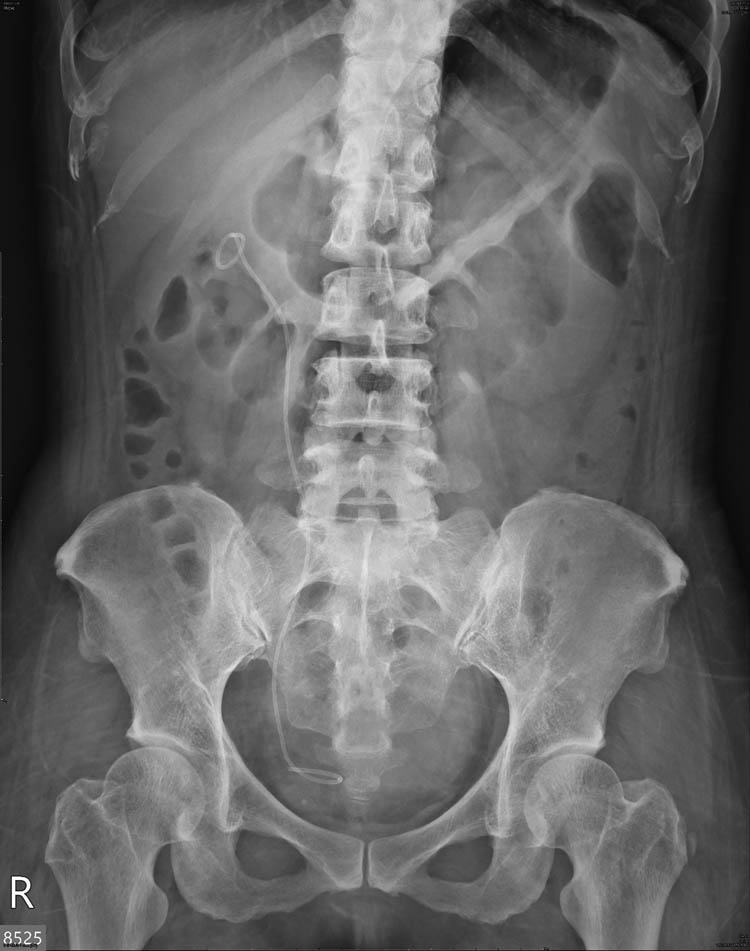
Postoperative KUB showed disappearance of the radiopaque lesion at right kidney area. Right double J ureteral stent were in situ.
-
Consent for publication: Informed consent was obtained in both written and verbal format from the patient to publish this case report and any accompanying images.
-
Consent for the treatment (Informed consent): Informed consent has obtained from all individuals included in this study.
3 Discussion and conclusion
Foreign bodies in the kidney and renal pelvis are rarely reported; however, urologists should be reminded of their clinical symptoms and roentgen signs [7]. Symptoms related to foreign bodies vary between individuals; some may be troublesome due to irritative symptoms and some may be totally asymptomatic. Hematuria and flank pain are the most common symptoms, especially for upper urinary tract foreign bodies [6]. It is important to carefully remove all foreign body fragments whether they are symptomatic or not. It has been reported that foreign bodies can become a nidus for stone formation, and they can cause intractable bacterial infections [3,6,8,9]. A correct diagnosis and clear preoperative identification of the anatomical location of the foreign body can guide the clinical decision and can help urologists to minimize the potential harm to the patient.
Management can be challenging depending on the size, shape, mobility and location of the foreign bodies [6,9]. Furthermore, thorough history taking and optimal imaging are the most important factors during the preoperative evaluation. [9]. There have been some previously published case reports describing intrarenal foreign bodies. Manassero et al. demonstrated an open nephrectomy using an anterolateral extraperitoneal approach for the retrieval of an intrarenal device [4]. Sener et al. dissected the right ureter and excised a guidewire introducer foreign body, through a right iliac incision with a ureteroneocystostomy and Lich-Gregoire anastomosis [10]. Upadhyay et al. removed three encrusted metallic foreign bodies from the right kidney by nephroscopy through a 32 French nephrostomy tract [2]. Singh et al. performed a transperitoneal laparoscopic exploration and removed a 4.5 cm long malleable copper wire from the left renal parenchyma [1]. Tüdös et al. used a rigid ureterorenoscopy with a 8.5/11.5 French and grasping forceps to extract a wooden toothpick from the right renal pelvis [11].
In the present case, the guidewire fragments were tightly embedded in the renal tissue without extension into the pyelocalyceal system or to the outside of the renal parenchyma. Partial nephrectomy, percutaneous nephroscopy, semi-rigid ureteroscopy, RIRS with fURS, and observation were all potential choices for our patient. The intrarenal foreign body from our patient was similar to the device which was retrieved by Manassero et al. through an open nephrectomy [4]. However, the risks, including bleeding, infection, and injury to the renal tissue, associated with those more invasive procedures pose a threat to the patient and can potentially cause morbidity if not handled well. Since several methods can be used to eradicate foreign objects from the urinary tract, the first choice should always be the least invasive one. RIRS was the least invasive and therefore most appropriate choice for our case.
Iatrogenic-retained foreign body is an important issue for all urologists and radiologists, not only because of the physical problems it can cause the patient but also because it may result in legal action. Hennessey et al. summarized that the placement of a percutaneous nephrostomy and associated percutaneous procedures accounted for 35% of all upper tract retained foreign objects [12]. More attention must be paid to avoid these unnecessary consequences. Careful examination of the instruments before and after procedures is essential and could decrease the incidence of such unwanted complications [13].
In conclusion, retained foreign bodies in the urinary tract are uncommon; however, clinicians must still keep them in mind during percutaneous procedures. Although there are several methods for eradicating foreign objects from the urinary tract, the least invasive method that does the least harm to the patient should be the first choice. RIRS with fURS is considered a safe, efficient, and minimally invasive option for the extraction of foreign bodies from the kidney.
Abbreviations
- CRP
-
C-reactive protein
- CT
-
computed tomography
- fURS
-
flexible ureteroscopy.
- KUB
-
kidneys, ureters, and bladder
- PCND
-
percutaneous nephrostomy drainage
- RIRS
-
retrograde intrarenal surgery
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
-
Funding information: No funding was obtained for this study.
-
Author contributions: Assistant for the RIRS procedure: BHC and THC. Data collection and analysis, literature search, and writing of the manuscript: BHC, THC, and YHC. Treatment design, chief surgeon for the RIRS procedure, drafting, and revision of the manuscript: YHC. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content and supervision: MC. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Records and data pertaining to this study are in the patient’s secure medical records in Mackay Memorial Hospital and are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Singh DV , Swami YK , Rana YP , Wani SM . Foreign body in the kidney: An unusual case and its management. Cent Eur J Urol. 2014;66(4):497–500.10.5173/ceju.2013.04.art30Search in Google Scholar
[2] Upadhyay SP , Zahir M , Al Muttari H , Mallick PN . A rare case of unusual migrated foreign bodies in kidney and their successful extraction using retrograde percutaneous nephrostomy. Qatar Med J. 2015;2015(1):7.10.5339/qmj.2015.7Search in Google Scholar
[3] Ahn J , Trost DW , Topham SL , Sos TA . Retained nephrostomy thread providing a nidus for atypical renal calcification. Br J Radiol. 1997;70:309–10.10.1259/bjr.70.831.9166059Search in Google Scholar
[4] Manassero F , Ortori S , Gabellieri C , Gabelloni M , Selli C . An unusual case of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015;87(1):90–2.10.4081/aiua.2015.1.90Search in Google Scholar
[5] Chen WJ , Wang SC , Chen SL , Kao YL . Foreign body in the ureter: A particle of glue after transarterial embolization of a renal pseudoaneurysm during percutaneous nephrostomy. J Chin Med Assoc. 2012;75(4):183–6.10.1016/j.jcma.2012.02.011Search in Google Scholar
[6] Alkan E , Basar MM . Endourological treatment of foreign bodies in the urinary system. JSLS: J Soc Laparoend Surg. 2014;18(3):e2014.00271.10.4293/JSLS.2014.00271Search in Google Scholar
[7] Osmond JD, Jr . Foreign bodies in the kidney; a review of the literature and reports of four additional cases. Radiology. 1953;60(3):375–82.10.1148/60.3.375Search in Google Scholar
[8] Marx R , Venable D . Foreign body migration to the genitourinary tract. J Urol. 1987;137(4):751–2.10.1016/S0022-5347(17)44203-0Search in Google Scholar
[9] Eisenberg ML , Lee KL , Stoller ML . Endoscopic management of retained renal foreign bodies. Urology. 2009;73(6):1189–94.10.1016/j.urology.2008.09.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Sener TE , Cloutier J , Audouin M , Villa L , Traxer O . A guidewire introducer as a ureteral foreign body: A case report. Can Urol Assoc J = J de l’Assoc des Urol du Can. 2015;9(5–6):E384–86.10.5489/cuaj.2626Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Tüdös Z , Čtvrtlík F , Kratochvíl P , Král M . Wooden foreign body in the renal pelvis. Urology. 2016;94:e7–8.10.1016/j.urology.2016.05.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Hennessey DB , Thomas AZ , Lynch TH , Casey RG . Retained upper genitourinary gossypiboma can mimic renal neoplasms: a review of the literature. Internet J Urol. 2012;9(2).Search in Google Scholar
[13] Kumar S , Ganesamoni R , Nanjappa B , Sharma V . Fragmented pigtail percutaneous nephrostomy tubes: Etiology and management. Korean J Urol. 2012;53(7):492–6.10.4111/kju.2012.53.7.492Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2021 Bo-Han Chen et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning

