Abstract
Background
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a zoonotic disease caused by hantavirus infection. Patients with severe HFRS may develop multiple organ failure or even death, which makes HFRS a serious public health problem.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we included a total of 155 consecutive patients who were diagnosed with HFRS, of whom 109 patients served as a training cohort and 46 patients as an independent verification cohort. In the training set, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was used to screen the characteristic variables of the risk model. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to construct a nomogram containing the characteristic variables selected in the LASSO regression model.
Results
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the nomogram indicated that the model had good discrimination. The calibration curve exhibited that the nomogram was in good agreement between the prediction and the actual observation. Decision curve analysis and clinical impact curve suggested that the predictive nomogram had clinical utility.
Conclusion
In this study, we established a simple and feasible model to predict severity in patients with HFRS, with which HFRS would be better identified and patients can be treated early.
1 Introduction
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a rodent-borne zoonotic disease caused by hantavirus infection. HFRS can be caused by Hantaan virus (HTNV), Dobrava virus (DOBV), Seoul virus (SEOV), Amur virus (AMV), Puumala virus (PUUV), etc. The severity of HFRS patients caused by different viral infections is also different [1]. HFRS is characterized by systemic vascular endothelial dysfunction and increased vascular permeability. The clinical manifestations include fever, hemorrhage, renal insufficiency, thrombocytopenia, and shock [2,3]. HFRS is mainly prevalent in Asia and Europe, while China is the most serious epidemic area in the world. A total of 1,118,124 cases were reported during 2008–2018 in China, which accounts for more than 90% of global HFRS cases [4,5,6]. In China, HFRS is mainly infected by HTNV and SEOV, and the mortality rate of HFRS caused by these viruses is between 5 and 15%, making it a serious public health concern [7]. Until now, there is no effective antiviral treatment for HFRS, which leads to a high mortality rate in critically ill cases. Early and accurate assessment of the severity and prognosis of HFRS patients is of great significance for guiding clinical treatment and the reasonable allocation of medical resources.
However, currently, there is no simple and effective model to predict the severity in patients with HFRS. A study shows that the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score is related to the severity of HFRS, but this scoring system is more complex compared with other scoring systems. Besides, it does not include the clinical characteristics of patients and cannot directly reflect the severity of patients, so its clinical application is limited [8]. Nomogram is a statistical prediction model established based on the characteristic phenotype of the disease, which is used to predict the probability of a certain outcome event in a population with certain characteristics in the future. Nomogram transforms the complex regression equation into a visual graph, making the results of the prediction model more readable and convenient to evaluate the patient’s condition [9]. With this clinical prediction model, doctors can simply and accurately predict the patient’s condition, thereby providing a basis for clinical decision-making. Consequently, in this study, we retrospectively analyzed the clinical characteristics and laboratory results of HFRS patients and aimed to develop and verify a simple and applicable nomogram that predicts the severity of the patient’s condition. It will be the first nomogram of HFRS.
2 Methods
2.1 Study population
This study retrospectively analyzed a total of 155 consecutive patients diagnosed with HFRS in Jingzhou Central Hospital from January 1, 2015, to December 31, 2019. One hundred nine patients from January 1, 2015, to December 31, 2018, served as a training cohort, and 46 patients from January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019, served as an independent verification cohort. Patients with confirmed HFRS were included in this study. The diagnostic criteria of the patients were as follows: (1) acute fever, accompanied by abnormal renal function, thrombocytopenia, etc.; and (2) the hantavirus-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) M antibody in the peripheral blood was positive. The exclusion criteria included: (1) age <8 years; (2) pregnant women; and (3) acute or chronic nephropathy and hematological diseases.
2.2 Data collection
Well-trained doctors extracted the patient’s demographic characteristics, basic diseases, clinical manifestations, and laboratory parameters through the electronic medical record system. Laboratory parameters included complete blood count, urine routine, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), liver and kidney function, electrolytes, myocardial enzymes, and hantavirus-specific antibodies.
According to the clinical characteristics of patients, such as body temperature, blood pressure, urine output, edema, and renal injury indicators like urinary protein and urea nitrogen, the severity of HFRS was divided into four clinical types [10]. The four clinical types were as follows: (1) the mild group had renal injury without hypotension and oliguria; (2) the moderate group had obvious uremia, bulbar conjunctival edema, skin and mucosal hemorrhage, and acute renal failure with typical oliguria; (3) the severe group showed severe uremia, bulbar conjunctiva and peritoneal or pleural effusion, skin and mucosal bleeding, hypotension, and acute renal failure with oliguria (patients with daily output of 50–500 mL ≤5 days or urine output <100 mL/day ≤2 days); (4) the critically ill group had one or more of the following manifestations compared with the severe group: refractory shock (≥2 days), heart failure, pulmonary edema, visceral hemorrhage, cerebral edema, severe secondary infection, and severe acute renal failure with oliguria (urine volume 50–500 mL/day >5 days) or anuria (urine <100 mL/day >2 days) or blood urea nitrogen (BUN) >42.84 mmol/L. In this study, patients were divided into two groups. The mild group was composed of mild and moderate patients, while the severe group was composed of severe and critically ill patients.
-
Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was reviewed and approved for publication by the Institutional Review Board of Jinghzou Central Hospital, and the requirement for informed consent from the study participants was waived.
-
Consent for publication: Not applicable.
2.3 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses in this study were carried out using R software (version 4.0.3; http://www.r-project.org). The statistical significance levels of all reports were double tailed, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The R software packages involved in the implementation of R software mainly include compareGroups, glmnet, rms, pROC, rmda, and so on. The demographic characteristics, basic diseases, clinical manifestations, and laboratory parameters were statistically analyzed by compareGroups R software package, in which the Shapiro–Wilks test was performed to determine whether it was normal or nonnormal distribution. Continuous variables with a normal distribution were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), while nonnormally distributed continuous variables were expressed as the median (interquartile range). Categorical variables were presented as percentages (%). LASSO regression is a model in which the L1-norm constraint term is added to the cost function of the linear regression model. It is used to analyze medical data with high dimension, strong correlation, and small samples by controlling the parameter lambda for variable screening and complexity adjustment [11]. In this study, the glmnet package in LASSO regression was used to select the best predictive characteristics of risk factors from HFRS patients. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was applied to construct the nomogram of the predictive model by including the selected variables with non-zero coefficient characteristics in the LASSO regression model [12].
We evaluated the performance of the nomogram through discrimination and calibration in the training population and the verification population, respectively. Since the consistency index (C-index) is equivalent to the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) in logistic regression, we used the AUC to evaluate the discriminative ability of the nomogram [13]. The Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test is performed to evaluate the calibration of the nomogram, and a calibration curve is drawn to visualize the consistency between the predicted results and the observed results [14]. By quantifying the net benefit under each risk threshold probability, the decision curve analysis (DCA) of the model is drawn to evaluate the clinical validity of the nomogram [15]. We drew a nomogram plot and a calibration plot based on the rms R package. The pROC R package was used to draw the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and calculate the C-index. The rmda R package was used to draw the DCA and the clinical impact curve.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with HFRS
A total of 155 HFRS patients were included in our study, of whom 11 died, with a mortality rate of 7.10%. Table 1 summarizes the demographic characteristics of HFRS in the training cohort and the verification cohort, showing that there is no significant difference in gender, age, basic disease, clinical disease classification, and clinical outcome between the two populations. We analyzed the clinical characteristics of mild and severe groups in the training cohort of 109 patients with HFRS. The median age of the training cohort was 53 years, including 79 men and 30 women (Table 2). The most common clinical manifestations of HFRS patients were fever (90.8%), oliguria (58.7%), nausea (35.8%), chills (35.8%), vomiting (33.0%), diarrhea (28.4%), headache (26.6%), low back pain (25.7%), fatigue (22.0%), abdominal distension (20.2%), and so on. Among the aforementioned symptoms, only oliguria and arthralgia were statistically different between the critically ill group and the mild group. The results of laboratory examination showed that the levels of white blood cells (WBCs), neutrophils, lymphocytes, procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), urine protein, urea nitrogen, creatinine, cystatin C, creatine kinase, creatine kinase muscle-brain isoform (CK-MB), and myoglobin increased more significantly in severe HFRS patients, while the levels of platelets (PLT), hemoglobin (Hb), albumin, and calcium (Ca) decreased more significantly in severe patients.
Baseline characteristics of patients with HFRS in the training and validation cohorts
| Characteristic | All patients | Training cohort | Validation cohort | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 155 | N = 109 | N = 46 | ||
| Sex | 0.790 | |||
| Female | 41 (26.5%) | 30 (27.5%) | 11 (23.9%) | |
| Male | 114 (73.5%) | 79 (72.5%) | 35 (76.1%) | |
| Age, years | 54.0 (47.0–62.0) | 53.0 (47.0–62.0) | 55.0 (50.0–63.8) | 0.323 |
| Basic disease | 0.139 | |||
| No | 109 (70.3%) | 81 (74.3%) | 28 (60.9%) | |
| Yes | 46 (29.7%) | 28 (25.7%) | 18 (39.1%) | |
| Clinical type | 0.474 | |||
| Mild | 69 (44.5%) | 46 (42.2%) | 23 (50.0%) | |
| Severe | 86 (55.5%) | 63 (57.8%) | 23 (50.0%) | |
| Clinical outcomes | 0.508 | |||
| Deceased | 11 (7.10%) | 9 (8.26%) | 2 (4.35%) | |
| Survived | 144 (92.9%) | 100 (91.7%) | 44 (95.7%) | |
Basic diseases include hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, chronic liver disease, chronic lung disease, and other diseases. P values indicate differences between training and validation cohorts. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Demographic and clinical features of patients with HFRS in the training cohorts
| Characteristic | All patients | Mild | Severe | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 109 | N = 46 | N = 63 | ||
| Sex | 0.218 | |||
| Female | 30 (27.5%) | 16 (34.8%) | 14 (22.2%) | |
| Male | 79 (72.5%) | 30 (65.2%) | 49 (77.8%) | |
| Age, years | 53.0 (47.0–62.0) | 50.5 (47.0–62.0) | 57.0 (46.5–62.5) | 0.337 |
| Signs and symptoms | ||||
| Fever | 0.186 | |||
| No | 10 (9.17%) | 2 (4.35%) | 8 (12.7%) | |
| Yes | 99 (90.8%) | 44 (95.7%) | 55 (87.3%) | |
| Chills | 0.428 | |||
| No | 70 (64.2%) | 32 (69.6%) | 38 (60.3%) | |
| Yes | 39 (35.8%) | 14 (30.4%) | 25 (39.7%) | |
| Headache | 1.000 | |||
| No | 80 (73.4%) | 34 (73.9%) | 46 (73.0%) | |
| Yes | 29 (26.6%) | 12 (26.1%) | 17 (27.0%) | |
| Nausea | 1.000 | |||
| No | 70 (64.2%) | 30 (65.2%) | 40 (63.5%) | |
| Yes | 39 (35.8%) | 16 (34.8%) | 23 (36.5%) | |
| Vomiting | 0.053 | |||
| No | 73 (67.0%) | 36 (78.3%) | 37 (58.7%) | |
| Yes | 36 (33.0%) | 10 (21.7%) | 26 (41.3%) | |
| Abdominal bloating | 0.917 | |||
| No | 87 (79.8%) | 36 (78.3%) | 51 (81.0%) | |
| Yes | 22 (20.2%) | 10 (21.7%) | 12 (19.0%) | |
| Poor appetite | 0.356 | |||
| No | 95 (87.2%) | 38 (82.6%) | 57 (90.5%) | |
| Yes | 14 (12.8%) | 8 (17.4%) | 6 (9.52%) | |
| Abdominal pain | 0.731 | |||
| No | 100 (91.7%) | 43 (93.5%) | 57 (90.5%) | |
| Yes | 9 (8.26%) | 3 (6.52%) | 6 (9.52%) | |
| Backache | 0.762 | |||
| No | 81 (74.3%) | 33 (71.7%) | 48 (76.2%) | |
| Yes | 28 (25.7%) | 13 (28.3%) | 15 (23.8%) | |
| Diarrhea | 0.124 | |||
| No | 78 (71.6%) | 37 (80.4%) | 41 (65.1%) | |
| Yes | 31 (28.4%) | 9 (19.6%) | 22 (34.9%) | |
| Dyspnea | 0.072 | |||
| No | 104 (95.4%) | 46 (100%) | 58 (92.1%) | |
| Yes | 5 (4.59%) | 0 (0.00%) | 5 (7.94%) | |
| Oliguria | 0.010 | |||
| No | 45 (41.3%) | 26 (56.5%) | 19 (30.2%) | |
| Yes | 64 (58.7%) | 20 (43.5%) | 44 (69.8%) | |
| Cough | 0.731 | |||
| No | 100 (91.7%) | 43 (93.5%) | 57 (90.5%) | |
| Yes | 9 (8.26%) | 3 (6.52%) | 6 (9.52%) | |
| Expectoration | 1.000 | |||
| No | 104 (95.4%) | 44 (95.7%) | 60 (95.2%) | |
| Yes | 5 (4.59%) | 2 (4.35%) | 3 (4.76%) | |
| Chest tightness | 0.394 | |||
| No | 104 (95.4%) | 45 (97.8%) | 59 (93.7%) | |
| Yes | 5 (4.59%) | 1 (2.17%) | 4 (6.35%) | |
| Black stool | 1.000 | |||
| No | 106 (97.2%) | 45 (97.8%) | 61 (96.8%) | |
| Yes | 3 (2.75%) | 1 (2.17%) | 2 (3.17%) | |
| Fatigue | 0.521 | |||
| No | 85 (78.0%) | 34 (73.9%) | 51 (81.0%) | |
| Yes | 24 (22.0%) | 12 (26.1%) | 12 (19.0%) | |
| Orbita pain | 0.261 | |||
| No | 106 (97.2%) | 46 (100%) | 60 (95.2%) | |
| Yes | 3 (2.75%) | 0 (0.00%) | 3 (4.76%) | |
| Myalgia | 0.163 | |||
| No | 100 (91.7%) | 40 (87.0%) | 60 (95.2%) | |
| Yes | 9 (8.26%) | 6 (13.0%) | 3 (4.76%) | |
| Arthralgia | 0.029 | |||
| No | 105 (96.3%) | 42 (91.3%) | 63 (100%) | |
| Yes | 4 (3.67%) | 4 (8.70%) | 0 (0.00%) | |
| Pulmonary hemorrhage | 0.508 | |||
| No | 107 (98.2%) | 46 (100%) | 61 (96.8%) | |
| Yes | 2 (1.83%) | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (3.17%) | |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 0.072 | |||
| No | 104 (95.4%) | 46 (100%) | 58 (92.1%) | |
| Yes | 5 (4.59%) | 0 (0.00%) | 5 (7.94%) | |
| Cerebral hemorrhage | 0.508 | |||
| No | 107 (98.2%) | 46 (100%) | 61 (96.8%) | |
| Yes | 2 (1.83%) | 0 (0.00%) | 2 (3.17%) | |
| History of rat exposure | 0.507 | |||
| No | 33 (30.3%) | 16 (34.8%) | 17 (27.0%) | |
| Yes | 76 (69.7%) | 30 (65.2%) | 46 (73.0%) | |
| Highest temperature, °C | 39.0 ± 0.63 | 39.1 ± 0.59 | 39.0 ± 0.65 | 0.192 |
| Time from symptom onset to admission | 5.00 (4.00–7.00) | 5.00 (4.00–7.00) | 5.00 (4.00–6.00) | 0.173 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| WBC, ×109/L | 20.5 (12.4–30.6) | 12.6 (9.53–21.5) | 25.2 (17.5–35.8) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, ×109/L | 9.98 (6.41–18.7) | 6.52 (4.58–10.0) | 14.3 (9.30–22.2) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes, ×109/L | 5.54 (3.69–8.13) | 4.78 (3.07–6.75) | 6.30 (4.06–9.25) | 0.021 |
| Hb, g/L | 107 ± 20.1 | 115 ± 16.0 | 100 ± 20.5 | <0.001 |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 32.0 (15.0,59.0) | 54.0 (35.2,93.0) | 22.0 (12.0,35.0) | <0.001 |
| Atypical lymphocyte, % | 7.50 ± 5.67 | 6.67 ± 4.39 | 8.10 ± 6.42 | 0.173 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 3.12 (1.00–7.46) | 1.21 (0.60–2.15) | 6.16 (2.26–10.7) | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/L | 42.9 (23.5–56.0) | 30.9 (19.2–49.9) | 51.0 (32.3–73.6) | 0.001 |
| Urine protein | 0.002 | |||
| 1+ | 12 (11.0%) | 8 (17.4%) | 4 (6.35%) | |
| 2+ | 34 (31.2%) | 18 (39.1%) | 16 (25.4%) | |
| 3+ | 44 (40.4%) | 19 (41.3%) | 25 (39.7%) | |
| 4+ | 19 (17.4%) | 1 (2.17%) | 18 (28.6%) | |
| Albumin, g/L | 26.8 (23.8–29.8) | 27.9 (24.8–31.5) | 25.7 (23.2–28.9) | 0.022 |
| ALT, U/L | 62.9 (41.7–108) | 59.2 (43.0–110) | 72.2 (41.7–106) | 0.556 |
| AST, U/L | 104 (67.7–184) | 82.7 (58.2–158) | 115 (77.9–222) | 0.051 |
| TBIL, μmol/L | 13.9 (10.8–19.0) | 12.9 (10.8–17.0) | 14.7 (11.2–23.9) | 0.114 |
| DBIL, μmol/L | 5.30 (3.80–8.00) | 4.70 (3.70–5.77) | 6.20 (4.20–10.5) | 0.006 |
| Urea nitrogen, mmol/L | 21.8 (14.4–28.5) | 14.2 (10.1–18.7) | 26.7 (21.9–31.6) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, μmol/L | 483 (220–616) | 215 (142–309) | 604 (514–723) | <0.001 |
| Uric acid, μmol/L | 596 (485–713) | 616 (498–699) | 594 (484–744) | 0.927 |
| Cystatin C, mg/L | 3.73 (2.32–4.53) | 2.32 (1.81–3.11) | 4.37 (3.72–6.12) | <0.001 |
| Ca, mmol/L | 1.72 ± 0.21 | 1.85 ± 0.16 | 1.62 ± 0.19 | <0.001 |
| K, mmol/L | 4.65 ± 0.70 | 4.27 ± 0.57 | 4.94 ± 0.65 | <0.001 |
| P, mmol/L | 0.75 (0.46–0.98) | 0.89 (0.74–1.06) | 0.53 (0.38–0.83) | <0.001 |
| Creatine Kinase, U/L | 184 (87.8–376) | 111 (69.4–206) | 211 (124–408) | 0.002 |
| CK-MB, U/L | 40.4 (24.7–54.6) | 33.1 (18.3–50.0) | 45.1 (27.9–71.2) | 0.001 |
| cTnI, μg/L | 0.05 (0.01–0.31) | 0.02 (0.01–0.80) | 0.06 (0.02–0.21) | 0.085 |
| Myoglobin, μg/L | 166 (58.9–289) | 65.3 (47.7–281) | 236 (92.2–377) | <0.001 |
P values indicate differences between mild and severe groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Abbreviations: WBC, white blood cell; Hb, hemoglobin; PCT, procalcitonin; CRP, C-reactive protein; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TBIL, total bilirubin; DBIL, direct bilirubin; Ca, calcium; K, potassium; P, phosphorus; CK-MB, creatine kinase muscle-brain isoform; cTnI, cardiac troponin I.
3.2 Prognostic factors in patients with severe HFRS
After excluding variables with irrelevant characteristics from the training cohort, 54 variables were finally included in the LASSO regression for analysis (Figure 1a). The parameter lambda (λ) was selected by using tenfold cross-validation based on the minimum standard in the LASSO model. The two vertical dashed lines in Figure 1b represent the log(λ) of the minimum mean square error (left dashed line) and the log(λ) of the minimum distance standard error (right dashed line). To provide a simple and accurate clinical model, six variables corresponding to the log(λ) of minimum mean square error, “neutrophils,” “Hb,” “Platelets,” “Creatinine,” “Ca,” and “Dyspnea,” were selected into the model (Figure 2, Table 3).

Predictive factors for patients with severe HFRS were selected by LASSO regression. (a) Fifty-four variables from the training cohort were included in the LASSO regression (y-axis). The average number of predictors was shown at the top x-axis. (b) The parameter lambda (λ) was selected by using tenfold cross-validation based on the minimum standard in the LASSO model. The two vertical dashed lines represent the log(λ) of the minimum mean square error (left dashed line) and the log(λ) of the minimum distance standard error (right dashed line). HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; λ, lambda.

Nomogram to predict the risk of severity in patients with HFRS. To use the nomogram in clinical practice, a line can be drawn up to calculate the patient’s total score by the value of each predictor variable, and then, a line can be drawn down based on the total score to find out the possibility of severe HFRS. HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; Hb, hemoglobin; Ca, calcium.
Prognostic factors in patients with severe HFRS
| Intercept and variable | β | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 4.437 | 84.523 (0.001–3.508 × 107) | 0.465 |
| Neutrophils | 0.013 | 1.013 (0.913–1.139) | 0.811 |
| Hb | −0.037 | 0.963 (0.916–1.004) | 0.103 |
| Platelets | −0.009 | 0.991 (0.965–1.0140) | 0.481 |
| Creatinine | 0.011 | 1.011 (1.007–1.017) | 0.001 |
| Ca | −2.632 | 0.072 (0.000–16.208) | 0.361 |
| Dyspnea | 18.937 | 1.676 × 108 (0.000–NA) | 0.994 |
Abbreviations: HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; β, regression coefficient; CI, confidence interval; Hb, hemoglobin; Ca, calcium; NA, not applicable.
3.3 Development and verification of a nomogram
The regression model based on six independent variables for predicting the severity of HFRS determined by LASSO regression analysis was represented by a nomogram (Figure 2). According to the nomogram, we can get the points corresponding to each predictor and then record the total score of these points, so as to accurately predict the risk of serious illness in the corresponding HFRS patients. As shown in Figure 3a and b, the AUC of the nomogram in the training and validation cohorts is 0.969 (95% CI: 0.935–1.000) and 0.934(95% CI: 0.847–1.000), respectively. The AUC values of these two cohorts are more than 0.9, indicating that the model has good discrimination. In the training cohort and the validation cohort, the calibration plot and Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test showed that the P values were 0.745 and 0.398, respectively; both P values were >0.05, demonstrating that the predicted probability of nomogram was in good agreement with the real results (Figure 4a and b).

ROC curve to evaluate the discriminative performance of the nomogram in the training and validation cohorts. (a) Training cohort. (b) Validation cohort. ROC, receiver operating characteristic.

Calibration curves for training and validation of the nomogram. (a) Training cohort. (b) Validation cohort. The x-axis represents the nomogram-predicted probability and the y-axis represents the actual probability of severe HFRS. The black solid line represents the predictive performance of the nomogram, and the diagonal gray line represents the ideal nomogram model. HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
3.4 Clinical utility
DCA shows that using nomogram to predict the risk of severe illness in HFRS patients can benefit patients if the threshold probability of the patient or doctor is between 0 and 1 (Figure 5a). Within this range, according to the nomogram, the net benefit is comparable, but there are multiple overlaps.
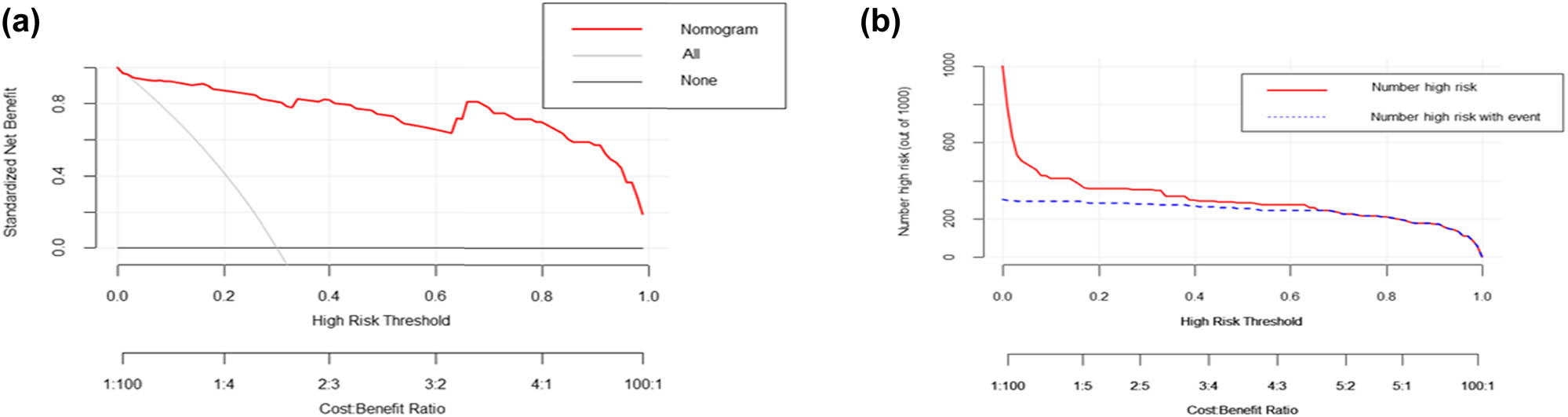
The decision curve and clinical impact curve analysis of the nomogram for predicting severe HFRS. (a) The DCA compares the clinical net benefits of scenarios that predict the probability of severe HFRS: a perfect predictive model (solid grey line), no screening (horizontal solid black line), and screening based on the nomogram (solid red line). The y-axis measures the net benefit. DCA shows that using nomogram to predict the risk of severe HFRS can benefit patients if the threshold probability of the patient or doctor is between 0 and 1. (b) Clinical impact curve of the nomogram plots the number of HFRS patients classified as high risk, and the number of cases classified as high risk with the event at each risk threshold. HFRS, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome; DCA, decision curve analysis.
4 Discussion
HFRS is an infectious disease of global concern caused by hantavirus infection, which is characterized by increased vascular permeability, acute thrombocytopenia, and renal damage. China has recorded the highest number of confirmed HFRS cases in the world [3]. HFRS patients can be clinically manifested as mild, moderate, severe, and critical. Generally, HFRS caused by HTNV and SEOV infection is more serious, with a mortality rate of 5–15% [7]. The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical characteristics and laboratory examination of patients with HFRS and establish a nomogram to predict the severity of the disease. Through this simple and feasible prediction model, we can identify the patient’s condition early and provide patients with better medical measures promptly to reduce patient mortality.
The typical course of HFRS can be divided into five different stages: fever, hypotension, oliguria, polyuria, and recovery. In the hypotension stage, one-third of the deaths of HFRS patients are related to irreversible shock, and thrombocytopenia and leukocytosis are the characteristics of this stage. Thrombocytopenia can cause petechiae of the skin or mucous membranes, conjunctival congestion, hematemesis, hemoptysis, hematuria, and fatal intracranial hemorrhage [16]. In addition, platelet dysfunction may also lead to abnormal blood coagulation [17]. In the training cohort (Table 2), there were 63 seriously ill patients, including 2 patients with pulmonary hemorrhage, 5 patients with gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and 2 patients with intracranial hemorrhage. However, there is no statistical difference between severe and mild patients due to the small sample size.
In this study, the platelet count decreased more significantly in the severe group. At the same time, after the parameter λ was selected by the tenfold cross-validation based on the minimum standard in the LASSO model, the platelet count was also included in the regression model, indicating that platelet count can be used as a predictor of the severity of HFRS patients.
In patients with viral hemorrhagic fever, platelets can cause abnormal homeostasis and inflammatory activation, thereby inhibiting the body’s antiviral immune response and thus making patients have a high level of viremia. This mechanism leads to the aggravation of the patient’s condition [18]. Other studies have shown that WBC, PLT, platelet distribution width (PDW), and PCT can be used as valuable parameters for the severity of HFRS patients, especially the change of PDW on the first day of hospitalization is related to the survival rate of severe HFRS patients and can be used as a potential predictor [19]. In this study, the increase of WBC in patients with severe HFRS was significantly higher than that in mild patients, whereas a study showed that compared with leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia may better predict the prognosis of severe acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with acute HTNV infection [20]. Neutrophil activation is usually common in bacterial infections. It is interesting to note that markers of neutrophil activation, such as myeloperoxidase (MPO), human neutrophil elastase (HNE), histone, and interleukin-8 (IL-8), are significantly increased in the blood and tissue of patients with severe HFRS. These results suggest that neutrophils can be activated by endothelial cells infected by hantavirus and may help to determine the degree of renal pathological damage in patients with severe HFRS [21]. In our study, neutrophil in patients with severe HFRS was also higher than that in mild patients, which may further support this view from a clinical perspective.
Acute renal failure can occur in patients with severe HFRS, usually caused by tubulointerstitial and glomerular damage [22]. In addition, the increase of platelet production and platelet activation may cause intravascular coagulation, the accumulation of inflammatory cells, and the release of proinflammatory cytokines in the kidney tissue, which can also lead to kidney damage [23,24]. In this study, renal function impairment indicators such as urine protein, urea nitrogen, creatinine, and cystatin C were significantly increased in severe HFRS patients. Previous studies have also confirmed that plasma cystatin C and alpha-1-microglobulin (A1M) can be used as early and sensitive markers of renal injury in patients with HFRS and can predict AKI [25,26]. The complexity adjustment of LASSO regression model is controlled by the parameter λ to avoid overfitting. The larger the λ, the greater the penalty for a linear model with more variables, and a model with fewer variables is finally obtained [11]. So, in the end, only creatinine is included in the prediction model. Patients present with acute renal failure are often accompanied by hypocalcemia. Wang et al. [27] studied the prognostic ability of serum calcium in patients with severe AKI, and the results showed that low Ca concentration was an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with severe AKI. Similarly, in our study, the average serum calcium concentration in HFRS patients was lower than the normal level, especially in severely ill patients.
In addition, patients with HFRS can also experience acute cardiovascular events such as acute myocardial infarction and stroke, indicating that the increased levels of myocardial injury indicators such as creatine kinase, CK-MB, and myoglobin can predict the risk of disease progression in patients [28]. Another study showed that hypoproteinemia in patients with acute HFRS was associated with the severity of the patient’s disease, which is consistent with our findings [29]. The clinical manifestations of HFRS patients are diverse, including fever, headache, fatigue, myalgia, back pain, and so on [30]. In addition to the aforementioned symptoms in this study, gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distension, and respiratory symptoms such as cough and dyspnea were also manifested. Severe HFRS patients may initially present with dry cough, followed by tachycardia, dyspnea, and then may rapidly progress to noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, hypotension, and circulatory failure, with a case-fatality rate of about 45% [31].
On the basis of LOSSA regression, we finally included six predictive indicators: “neutrophils,” “Hb,” “platelets,” “creatinine,” “Ca,” and “dyspnea” to establish a nomogram. The AUC value of the nomogram is greater than 0.9 in both the training cohort and the verification cohort, indicating that the predictive model has a high value. Both the calibration plot and the Hosmer–Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test show that the prediction probability of the nomogram is in good agreement with the real results. In addition, to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of nomogram, we applied DCA to provide observations of clinical results based on threshold probability, from which net benefits can be derived (net benefit is defined as the proportion of true positives minus the proportion of false positives, weighted by the relative harm of false-positive and false-negative results) [15,32]. In this study, if the threshold probability of the patient or doctor is between 0 and 1, the use of the nomogram to assess the risk of severe illness in HFRS patients can benefit patients. The clinical impact curve also intuitively shows that the nomogram has a better overall net benefit within a wide range of threshold probability and affecting the prognosis of patients.
However, our research also has some limitations. First, it is designed to be retrospective, and the inherent limitations of this type of research inevitably affect the choice of patients. Second, although we collected patient data from different periods to validate the model, it came from a single center. If possible, we still need cohorts from other research centers to validate the model. Finally, the number of cases in our study is relatively small, which may weaken the predictive ability of the current model.
5 Conclusion
This study developed and verified a novel nomogram for predicting the condition of patients with HFRS, which is the first nomogram used to predict HFRS. On the basis of these six laboratory and clinical parameters, clinicians can easily and accurately assess the individual risk of HFRS patients, make correct clinical decisions, and provide the best treatment for patients.
Acknowledgements
We thank all patients and medical staff at Jingzhou Central Hospital who were involved in this study.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by Hubei Province Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project (WJ2018H178 to Yi Sun) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2019CFB567 to Yi Sun).
-
Author contributions: Y.Z., H.Q.M. and S.Y.: conceived the study idea and performed interpretation, manuscript writing, and final approval. F.Z.P.: performed data analysis and collection. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Due to the finalization of the clinical study report, the data analyzed during the current study are not publicly available, but can be obtained from the correspondent author under reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HFRS
-
hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome
- LASSO
-
least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- Hb
-
hemoglobin
- Ca
-
calcium
- AUC
-
area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
- CI
-
confidence interval
- HTNV
-
Hantaan virus
- DOBV
-
Dobrava virus
- SEOV
-
Seoul virus
- AMV
-
Amur virus
- PUUV
-
Puumala virus
- SOFA
-
sequential organ failure assessment
- Ig
-
immunoglobulin
- PCT
-
procalcitonin
- CRP
-
C-reactive protein
- BUN
-
blood urea nitrogen
- SD
-
standard deviation
- C-index
-
consistency index
- DCA
-
decision curve analysis
- ROC
-
receiver operating characteristic
- WBC
-
white blood cell
- CK-MB
-
creatine kinase muscle-brain isoform
- PLT
-
platelet
- λ
-
lambda
- PDW
-
platelet distribution width
- AKI
-
acute kidney injury
- MPO
-
myeloperoxidase
- HNE
-
human neutrophil elastase
- IL-8
-
interleukin-8
- A1M
-
alpha-1-microglobulin
References
[1] Bi Z, Formenty PB, Roth CE. Hantavirus infection: a review and global update. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2008;2:3–23.10.3855/jidc.317Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Ma Y, Liu B, Yuan B, Wang J, Yu H, Zhang Y, et al. Sustained high level of serum VEGF at convalescent stage contributes to the renal recovery after HTNV infection in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:812386.10.1155/2012/812386Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Vaheri A, Strandin T, Hepojoki J, Sironen T, Henttonen H, Makela S, et al. Uncovering the mysteries of hantavirus infections. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:539–50.10.1038/nrmicro3066Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Zhang S, Wang S, Yin W, Liang M, Li J, Zhang Q, et al. Epidemic characteristics of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China, 2006-2012. BMC Infect Dis. 2014;14:384.10.1186/1471-2334-14-384Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Zheng Y, Zhou BY, Wei J, Xu Y, Dong JH, Guan LY, et al. Persistence of immune responses to vaccine against haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in healthy adults aged 16–60 years: results from an open-label 2-year follow-up study. Infect Dis (Lond). 2018;50:21–6.10.1080/23744235.2017.1353704Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Wang X, Shen W, Qin Y, Ying L, Li H, Lu J, et al. A case-control study on the risk factors for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20:103.10.1186/s12879-020-4830-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Jonsson CB, Figueiredo LT, Vapalahti O. A global perspective on hantavirus ecology, epidemiology, and disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23:412–41.10.1128/CMR.00062-09Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Yu Z, Zhou N, Li A, Chen J, Chen H, He Z, et al. Performance assessment of the SAPS II and SOFA scoring systems in hanta virus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Int J Infect Dis. 2017;63:88–94.10.1016/j.ijid.2017.08.003Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Park SY. Nomogram: an analogue tool to deliver digital knowledge. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;155:1793.10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.12.107Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Bai X, Xu Z. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House; 2013.Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw. 2010;33:1–22.10.18637/jss.v033.i01Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Kidd AC, McGettrick M, Tsim S, Halligan DL, Bylesjo M, Blyth KG. Survival prediction in mesothelioma using a scalable Lasso regression model: instructions for use and initial performance using clinical predictors. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2018;5:e240.10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000240Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Heyard R, Timsit JF, Held L. Validation of discrete time-to-event prediction models in the presence of competing risks. Biom J. 2020;62:643–57.10.1002/bimj.201800293Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Kramer AA, Zimmerman JE. Assessing the calibration of mortality benchmarks in critical care: The Hosmer-Lemeshow test revisited. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2052–6.10.1097/01.CCM.0000275267.64078.B0Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Vickers AJ, Elkin EB. Decision curve analysis: a novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med Decis Making. 2006;26:565–74.10.1177/0272989X06295361Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Avsic-Zupanc T, Saksida A, Korva M. Hantavirus infections. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;21S:e6–e16.10.1111/1469-0691.12291Suche in Google Scholar
[17] Cosgriff TM, Lee HW, See AF, Parrish DB, Moon JS, Kim DJ, et al. Platelet dysfunction contributes to the haemostatic defect in haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85:660–3.10.1016/0035-9203(91)90386-DSuche in Google Scholar
[18] Zapata JC, Cox D, Salvato MS. The role of platelets in the pathogenesis of viral hemorrhagic fevers. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2858.10.1371/journal.pntd.0002858Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Fan X, Liu Z, Fu S, Sang J, Deng H, Li F, et al. Platelet distribution width at first day of hospital admission in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome caused by hantaan virus may predict disease severity and critical patients’ survival. Dis Markers. 2018;2018:9701619.10.1155/2018/9701619Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Wang M, Wang J, Wang T, Li J, Hui L, Ha X. Thrombocytopenia as a predictor of severe acute kidney injury in patients with Hantaan virus infections. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53236.10.1371/journal.pone.0053236Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Strandin T, Makela S, Mustonen J, Vaheri A. Neutrophil activation in acute hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is mediated by hantavirus-infected microvascular endothelial cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2098.10.3389/fimmu.2018.02098Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Muranyi W, Bahr U, Zeier M, van der Woude FJ. Hantavirus infection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3669–79.10.1681/ASN.2005050561Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Hepojoki J, Vaheri A, Strandin T. The fundamental role of endothelial cells in hantavirus pathogenesis. Front Microbiol. 2014;5:727.10.3389/fmicb.2014.00727Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Connolly-Andersen AM, Sundberg E, Ahlm C, Hultdin J, Baudin M, Larsson J, et al. Increased thrombopoiesis and platelet activation in hantavirus-infected patients. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:1061–9.10.1093/infdis/jiv161Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Hansson M, Gustafsson R, Jacquet C, Chebaane N, Satchell S, Thunberg T, et al. Cystatin C and alpha-1-microglobulin predict severe acute kidney injury in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Pathogens. 2020;9:666.10.3390/pathogens9080666Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Ma Y, Li Q, Wang J, Xu Z, Song C, Zhuang R, et al. Cystatin C, a novel urinary biomarker for sensitive detection of acute kidney injury during haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Biomarkers. 2010;15:410–7.10.3109/1354750X.2010.482214Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Wang B, Li D, Gong Y, Ying B, Cheng B. Association of serum total and ionized calcium with all-cause mortality incritically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;494:94–9.10.1016/j.cca.2019.03.1616Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Connolly-Andersen AM, Hammargren E, Whitaker H, Eliasson M, Holmgren L, Klingstrom J, et al. Increased risk of acute myocardial infarction and stroke during hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: a self-controlled case series study. Circulation. 2014;129:1295–302.10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001870Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Kim YO, Yoon SA, Ku YM, Yang CW, Kim YS, Kim SY, et al. Serum albumin level correlates with disease severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2003;18:696–700.10.3346/jkms.2003.18.5.696Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Munir N, Jahangeer M, Hussain S, Mahmood Z, Ashiq M, Ehsan F, et al. Hantavirus diseases pathophysiology, their diagnostic strategies and therapeutic approaches: a review. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2021;48:20–34.10.1111/1440-1681.13403Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] de Oliveira SV, Faccini-Martínez Á. Hantavirus infection and the renal syndrome[M]//tropical nephrology. Cham: Springer; 2020. p. 175–9210.1007/978-3-030-44500-3_14Suche in Google Scholar
[32] Collins GS, Reitsma JB, Altman DG, Moons KG. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): the TRIPOD statement. BMJ. 2015;350:g7594.10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014508Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2021 Zheng Yang et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Identification of ZG16B as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer
- Behçet’s disease with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Suffering from Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with and without Metabolic Syndrome”
- Research Articles
- GPR37 promotes the malignancy of lung adenocarcinoma via TGF-β/Smad pathway
- Expression and role of ABIN1 in sepsis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Additional baricitinib loading dose improves clinical outcome in COVID-19
- The co-treatment of rosuvastatin with dapagliflozin synergistically inhibited apoptosis via activating the PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury rats
- SLC12A8 plays a key role in bladder cancer progression and EMT
- LncRNA ATXN8OS enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- Case Report
- Serratia marcescens as a cause of unfavorable outcome in the twin pregnancy
- Spleno-adrenal fusion mimicking an adrenal metastasis of a renal cell carcinoma: A case report and embryological background
- Research Articles
- TRIM25 contributes to the malignancy of acute myeloid leukemia and is negatively regulated by microRNA-137
- CircRNA circ_0004370 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibits cell apoptosis of esophageal cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 axis
- LncRNA XIST regulates atherosclerosis progression in ox-LDL-induced HUVECs
- Potential role of IFN-γ and IL-5 in sepsis prediction of preterm neonates
- Rapid Communication
- COVID-19 vaccine: Call for employees in international transportation industries and international travelers as the first priority in global distribution
- Case Report
- Rare squamous cell carcinoma of the kidney with concurrent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: A case report and review of the literature
- An infertile female delivered a baby after removal of primary renal carcinoid tumor
- Research Articles
- Hypertension, BMI, and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- Case Report
- Coexistence of bilateral macular edema and pale optic disc in the patient with Cohen syndrome
- Research Articles
- Correlation between kinematic sagittal parameters of the cervical lordosis or head posture and disc degeneration in patients with posterior neck pain
- Review Articles
- Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the lung: An analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Research Articles
- Thermography in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
- Pemetrexed-based first-line chemotherapy had particularly prominent objective response rate for advanced NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Comparison of single and double autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma patients
- The influence of smoking in minimally invasive spinal fusion surgery
- Impact of body mass index on left atrial dimension in HOCM patients
- Expression and clinical significance of CMTM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- miR-142-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting LMX1A through Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5–8-year-old children
- Early MRI imaging and follow-up study in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as a biomarker for the diagnosis of strangulated intestinal obstruction: A meta-analysis
- miR-128-3p inhibits apoptosis and inflammation in LPS-induced sepsis by targeting TGFBR2
- Dynamic perfusion CT – A promising tool to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Biomechanical evaluation of self-cinching stitch techniques in rotator cuff repair: The single-loop and double-loop knot stitches
- Review Articles
- The ambiguous role of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) in human immunity
- Case Report
- Membranous nephropathy with pulmonary cryptococcosis with improved 1-year follow-up results: A case report
- Fertility problems in males carrying an inversion of chromosome 10
- Acute myeloid leukemia with leukemic pleural effusion and high levels of pleural adenosine deaminase: A case report and review of literature
- Metastatic renal Ewing’s sarcoma in adult woman: Case report and review of the literature
- Burkitt-like lymphoma with 11q aberration in a patient with AIDS and a patient without AIDS: Two cases reports and literature review
- Skull hemophilia pseudotumor: A case report
- Judicious use of low-dosage corticosteroids for non-severe COVID-19: A case report
- Adult-onset citrullinaemia type II with liver cirrhosis: A rare cause of hyperammonaemia
- Clinicopathologic features of Good’s syndrome: Two cases and literature review
- Fatal immune-related hepatitis with intrahepatic cholestasis and pneumonia associated with camrelizumab: A case report and literature review
- Research Articles
- Effects of hydroxyethyl starch and gelatin on the risk of acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: A multicenter retrospective comparative clinical study
- Significance of nucleic acid positive anal swab in COVID-19 patients
- circAPLP2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by upregulating HELLS by targeting miR-335-5p
- Ratios between circulating myeloid cells and lymphocytes are associated with mortality in severe COVID-19 patients
- Risk factors of left atrial appendage thrombus in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation
- Clinical features of hypertensive patients with COVID-19 compared with a normotensive group: Single-center experience in China
- Surgical myocardial revascularization outcomes in Kawasaki disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Decreased chromobox homologue 7 expression is associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in cervical cancer
- FGF16 regulated by miR-520b enhances the cell proliferation of lung cancer
- Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications
- Accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer using logistic regression
- miR-377 inhibition enhances the survival of trophoblast cells via upregulation of FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Prognostic significance of TRIM28 expression in patients with breast carcinoma
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis of KPNA2 in six major human cancers
- Exosomal-mediated transfer of OIP5-AS1 enhanced cell chemoresistance to trastuzumab in breast cancer via up-regulating HMGB3 by sponging miR-381-3p
- A four-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis of recurrence patients with gastric cancer
- Knockdown of circ_0003204 alleviates oxidative low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury: Circulating RNAs could explain atherosclerosis disease progression
- Propofol postpones colorectal cancer development through circ_0026344/miR-645/Akt/mTOR signal pathway
- Knockdown of lncRNA TapSAKI alleviates LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells through the miR-205/IRF3 pathway
- COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
- Clinical analysis of 11 cases of nocardiosis
- Cis-regulatory elements in conserved non-coding sequences of nuclear receptor genes indicate for crosstalk between endocrine systems
- Four long noncoding RNAs act as biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma
- Real-world evidence of cytomegalovirus reactivation in non-Hodgkin lymphomas treated with bendamustine-containing regimens
- Relation between IL-8 level and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level
- Nomogram prediction model for renal anaemia in IgA nephropathy patients
- Effect of antibiotic use on the efficacy of nivolumab in the treatment of advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- A nomogram for predicting metabolic steatohepatitis: The combination of NAMPT, RALGDS, GADD45B, FOSL2, RTP3, and RASD1
- Clinical and prognostic features of MMP-2 and VEGF in AEG patients
- The value of miR-510 in the prognosis and development of colon cancer
- Functional implications of PABPC1 in the development of ovarian cancer
- Prognostic value of preoperative inflammation-based predictors in patients with bladder carcinoma after radical cystectomy
- Sublingual immunotherapy increases Treg/Th17 ratio in allergic rhinitis
- Prediction of improvement after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- Effluent Osteopontin levels reflect the peritoneal solute transport rate
- circ_0038467 promotes PM2.5-induced bronchial epithelial cell dysfunction
- Significance of miR-141 and miR-340 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between hair cortisol concentration and metabolic syndrome
- Microvessel density as a prognostic indicator of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of BCR–ABL gene variants in patients of chronic myeloid leukemia
- Knee alterations in rheumatoid arthritis: Comparison of US and MRI
- Long non-coding RNA TUG1 aggravates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury by sponging miR-493-3p/miR-410-3p
- lncRNA MALAT1 regulated ATAD2 to facilitate retinoblastoma progression via miR-655-3p
- Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting severity in patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome: A retrospective study
- Analysis of COVID-19 outbreak origin in China in 2019 using differentiation method for unusual epidemiological events
- Laparoscopic versus open major liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-matched analysis of short- and long-term outcomes
- Travelers’ vaccines and their adverse events in Nara, Japan
- Association between Tfh and PGA in children with Henoch–Schönlein purpura
- Can exchange transfusion be replaced by double-LED phototherapy?
- circ_0005962 functions as an oncogene to aggravate NSCLC progression
- Circular RNA VANGL1 knockdown suppressed viability, promoted apoptosis, and increased doxorubicin sensitivity through targeting miR-145-5p to regulate SOX4 in bladder cancer cells
- Serum intact fibroblast growth factor 23 in healthy paediatric population
- Algorithm of rational approach to reconstruction in Fournier’s disease
- A meta-analysis of exosome in the treatment of spinal cord injury
- Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Dexmedetomidine may decrease the bupivacaine toxicity to heart
- Hypoxia stimulates the migration and invasion of osteosarcoma via up-regulating the NUSAP1 expression
- Long noncoding RNA XIST knockdown relieves the injury of microglia cells after spinal cord injury by sponging miR-219-5p
- External fixation via the anterior inferior iliac spine for proximal femoral fractures in young patients
- miR-128-3p reduced acute lung injury induced by sepsis via targeting PEL12
- HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis
- Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 is elevated in serum of patients with heart failure and correlates with the disease severity and patient’s prognosis
- Cell population data in identifying active tuberculosis and community-acquired pneumonia
- Prognostic value of microRNA-4521 in non-small cell lung cancer and its regulatory effect on tumor progression
- Mean platelet volume and red blood cell distribution width is associated with prognosis in premature neonates with sepsis
- 3D-printed porous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of hADMSCs
- Association of gene polymorphisms with women urinary incontinence
- Influence of COVID-19 pandemic on stress levels of urologic patients
- miR-496 inhibits proliferation via LYN and AKT pathway in gastric cancer
- miR-519d downregulates LEP expression to inhibit preeclampsia development
- Comparison of single- and triple-port VATS for lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Fluorescent light energy modulates healing in skin grafted mouse model
- Silencing CDK6-AS1 inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory damage in HK-2 cells
- Predictive effect of DCE-MRI and DWI in brain metastases from NSCLC
- Severe postoperative hyperbilirubinemia in congenital heart disease
- Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- Clinical factors predicting ureteral stent failure in patients with external ureteral compression
- Novel H2S donor proglumide-ADT-OH protects HUVECs from ox-LDL-induced injury through NF-κB and JAK/SATA pathway
- Triple-Endobutton and clavicular hook: A propensity score matching analysis
- Long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the progression of diabetic nephropathy and the activation of NF-κB pathway in high glucose-treated renal tubular epithelial cells by the miR-182-5p/GPRC5A axis
- Serum exosomal miR-122-5p, GAS, and PGR in the non-invasive diagnosis of CAG
- miR-513b-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells by targeting TRIB1
- Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p
- The diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-92a in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Prognostic value of α2δ1 in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study
- No significant benefit of moderate-dose vitamin C on severe COVID-19 cases
- circ_0000467 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cells through regulating KLF12 expression by sponging miR-4766-5p
- Downregulation of RAB7 and Caveolin-1 increases MMP-2 activity in renal tubular epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions
- Educational program for orthopedic surgeons’ influences for osteoporosis
- Expression and function analysis of CRABP2 and FABP5, and their ratio in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- GJA1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating TGF-β-induced activation and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatic stellate cells
- lncRNA-ZFAS1 promotes the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting miR-34b to regulate VEGFA expression
- Anticoagulation is the answer in treating noncritical COVID-19 patients
- Effect of late-onset hemorrhagic cystitis on PFS after haplo-PBSCT
- Comparison of Dako HercepTest and Ventana PATHWAY anti-HER2 (4B5) tests and their correlation with silver in situ hybridization in lung adenocarcinoma
- VSTM1 regulates monocyte/macrophage function via the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Comparison of vaginal birth outcomes in midwifery-led versus physician-led setting: A propensity score-matched analysis
- Treatment of osteoporosis with teriparatide: The Slovenian experience
- New targets of morphine postconditioning protection of the myocardium in ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of HSP90/Akt and C5a/NF-κB
- Superenhancer–transcription factor regulatory network in malignant tumors
- β-Cell function is associated with osteosarcopenia in middle-aged and older nonobese patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Clinical features of atypical tuberculosis mimicking bacterial pneumonia
- Proteoglycan-depleted regions of annular injury promote nerve ingrowth in a rabbit disc degeneration model
- Effect of electromagnetic field on abortion: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- MALAT1 promotes malignant pleural mesothelioma by sponging miR-141-3p
- Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia–reperfusion model
- miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway
- Identification of LIG1 and LIG3 as prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer
- MitoQ inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by enhancing PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy
- Dissecting role of founder mutation p.V727M in GNE in Indian HIBM cohort
- circATP2A2 promotes osteosarcoma progression by upregulating MYH9
- Prognostic role of oxytocin receptor in colon adenocarcinoma
- Review Articles
- The function of non-coding RNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome
- Role of cesarean section in the development of neonatal gut microbiota: A systematic review
- Small cell lung cancer transformation during antitumor therapies: A systematic review
- Research progress of gut microbiota and frailty syndrome
- Recommendations for outpatient activity in COVID-19 pandemic
- Rapid Communication
- Disparity in clinical characteristics between 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia and leptospirosis
- Use of microspheres in embolization for unruptured renal angiomyolipomas
- COVID-19 cases with delayed absorption of lung lesion
- A triple combination of treatments on moderate COVID-19
- Social networks and eating disorders during the Covid-19 pandemic
- Letter
- COVID-19, WHO guidelines, pedagogy, and respite
- Inflammatory factors in alveolar lavage fluid from severe COVID-19 pneumonia: PCT and IL-6 in epithelial lining fluid
- COVID-19: Lessons from Norway tragedy must be considered in vaccine rollout planning in least developed/developing countries
- What is the role of plasma cell in the lamina propria of terminal ileum in Good’s syndrome patient?
- Case Report
- Rivaroxaban triggered multifocal intratumoral hemorrhage of the cabozantinib-treated diffuse brain metastases: A case report and review of literature
- CTU findings of duplex kidney in kidney: A rare duplicated renal malformation
- Synchronous primary malignancy of colon cancer and mantle cell lymphoma: A case report
- Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography and pathologic characters of CD68 positive cell in primary hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumors: A case report and literature review
- Persistent SARS-CoV-2-positive over 4 months in a COVID-19 patient with CHB
- Pulmonary parenchymal involvement caused by Tropheryma whipplei
- Mediastinal mixed germ cell tumor: A case report and literature review
- Ovarian female adnexal tumor of probable Wolffian origin – Case report
- Rare paratesticular aggressive angiomyxoma mimicking an epididymal tumor in an 82-year-old man: Case report
- Perimenopausal giant hydatidiform mole complicated with preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism: A case report and literature review
- Primary orbital ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report
- Primary aortic intimal sarcoma masquerading as intramural hematoma
- Sustained false-positive results for hepatitis A virus immunoglobulin M: A case report and literature review
- Peritoneal loose body presenting as a hepatic mass: A case report and review of the literature
- Chondroblastoma of mandibular condyle: Case report and literature review
- Trauma-induced complete pacemaker lead fracture 8 months prior to hospitalization: A case report
- Primary intradural extramedullary extraosseous Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PIEES/PNET) of the thoracolumbar spine: A case report and literature review
- Computer-assisted preoperative planning of reduction of and osteosynthesis of scapular fracture: A case report
- High quality of 58-month life in lung cancer patient with brain metastases sequentially treated with gefitinib and osimertinib
- Rapid response of locally advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma to apatinib: A case report
- Retrieval of intrarenal coiled and ruptured guidewire by retrograde intrarenal surgery: A case report and literature review
- Usage of intermingled skin allografts and autografts in a senior patient with major burn injury
- Retraction
- Retraction on “Dihydromyricetin attenuates inflammation through TLR4/NF-kappa B pathway”
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part I
- An artificial immune system with bootstrap sampling for the diagnosis of recurrent endometrial cancers
- Breast cancer recurrence prediction with ensemble methods and cost-sensitive learning

