Abstract
C36H52F2N8O14, triclinic, P
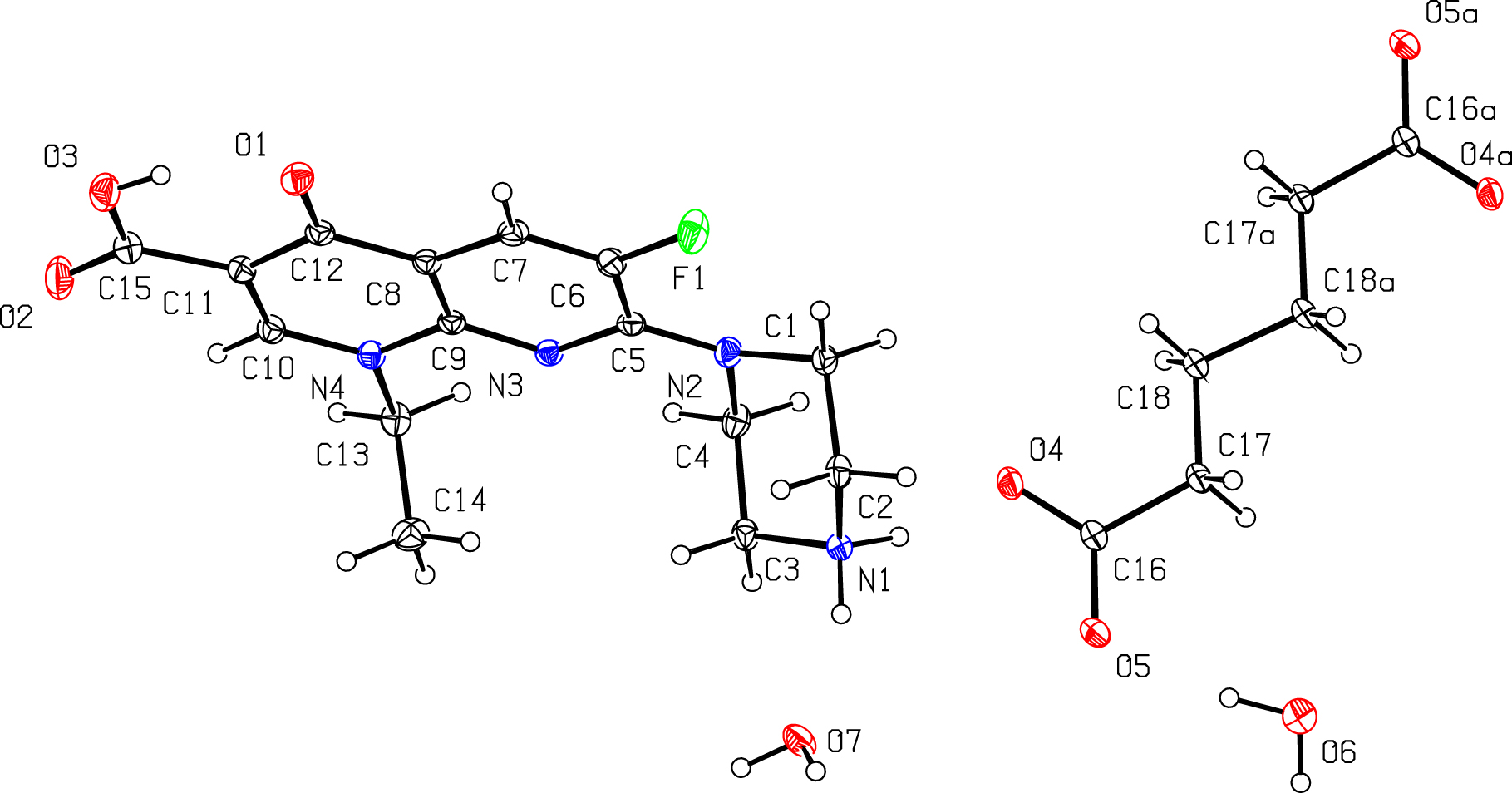
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless needle |
| Size | 0.32 × 0.04 × 0.03 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.12 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker D8 venture, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 27.1°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 16926, 4372, 0.032 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 3462 |
| N(param)refined: | 282 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], SHELX [3, 4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.54391 (18) | 0.08485 (10) | 0.08471 (6) | 0.0433 (3) |
| O1 | 0.78452 (16) | 0.38446 (12) | −0.12696 (6) | 0.0286 (2) |
| O2 | 0.9589 (2) | 0.86045 (14) | −0.11739 (8) | 0.0439 (3) |
| O3 | 0.91400 (18) | 0.61436 (14) | −0.19045 (7) | 0.0349 (3) |
| H3 | 0.869493 | 0.522204 | −0.184385 | 0.052* |
| N1 | 0.76033 (17) | 0.35227 (14) | 0.37883 (7) | 0.0213 (3) |
| H1A | 0.665036 | 0.333659 | 0.413165 | 0.026* |
| H1B | 0.882142 | 0.369992 | 0.407378 | 0.026* |
| N2 | 0.54156 (19) | 0.33030 (14) | 0.22750 (7) | 0.0238 (3) |
| N3 | 0.66426 (17) | 0.51109 (13) | 0.15404 (7) | 0.0199 (2) |
| N4 | 0.77448 (17) | 0.70845 (13) | 0.08743 (7) | 0.0209 (3) |
| C1 | 0.5295 (2) | 0.18633 (17) | 0.25458 (9) | 0.0261 (3) |
| H1C | 0.509316 | 0.094903 | 0.206168 | 0.031* |
| H1D | 0.413130 | 0.163290 | 0.285818 | 0.031* |
| C2 | 0.7214 (2) | 0.20890 (17) | 0.30832 (9) | 0.0244 (3) |
| H2A | 0.709065 | 0.113885 | 0.329137 | 0.029* |
| H2B | 0.835791 | 0.221342 | 0.275473 | 0.029* |
| C3 | 0.7582 (2) | 0.49702 (17) | 0.35203 (9) | 0.0244 (3) |
| H3A | 0.872950 | 0.526568 | 0.320767 | 0.029* |
| H3B | 0.772422 | 0.586740 | 0.400732 | 0.029* |
| C4 | 0.5625 (2) | 0.46521 (18) | 0.29861 (9) | 0.0254 (3) |
| H4A | 0.447922 | 0.440893 | 0.330597 | 0.030* |
| H4B | 0.562315 | 0.560574 | 0.279870 | 0.030* |
| C5 | 0.6047 (2) | 0.35929 (16) | 0.15643 (8) | 0.0202 (3) |
| C6 | 0.6043 (2) | 0.23981 (16) | 0.08407 (9) | 0.0244 (3) |
| C7 | 0.6601 (2) | 0.27632 (17) | 0.01412 (9) | 0.0234 (3) |
| H7 | 0.659342 | 0.194720 | −0.033083 | 0.028* |
| C8 | 0.7197 (2) | 0.43658 (16) | 0.01162 (8) | 0.0202 (3) |
| C9 | 0.7176 (2) | 0.54752 (16) | 0.08445 (8) | 0.0193 (3) |
| C10 | 0.8334 (2) | 0.75503 (17) | 0.02061 (9) | 0.0233 (3) |
| H10 | 0.874117 | 0.865640 | 0.024276 | 0.028* |
| C11 | 0.8383 (2) | 0.65234 (17) | −0.05282 (9) | 0.0229 (3) |
| C12 | 0.7808 (2) | 0.48434 (17) | −0.06104 (9) | 0.0215 (3) |
| C13 | 0.7742 (2) | 0.82801 (17) | 0.16431 (9) | 0.0250 (3) |
| H13A | 0.653363 | 0.787528 | 0.190421 | 0.030* |
| H13B | 0.766842 | 0.926942 | 0.150991 | 0.030* |
| C14 | 0.9600 (3) | 0.86489 (19) | 0.22403 (10) | 0.0333 (4) |
| H14A | 1.079962 | 0.904474 | 0.198286 | 0.050* |
| H14B | 0.964654 | 0.768135 | 0.239229 | 0.050* |
| H14C | 0.955917 | 0.945997 | 0.273334 | 0.050* |
| H6A | 0.613 (3) | 0.199 (2) | 0.6641 (11) | 0.050* |
| C15 | 0.9083 (2) | 0.71961 (19) | −0.12192 (10) | 0.0293 (3) |
| O4 | 0.43462 (15) | 0.27607 (12) | 0.45897 (6) | 0.0269 (2) |
| O5 | 0.62103 (16) | 0.27011 (13) | 0.56760 (7) | 0.0312 (3) |
| C16 | 0.4586 (2) | 0.22506 (16) | 0.52098 (9) | 0.0209 (3) |
| C17 | 0.2825 (2) | 0.10104 (17) | 0.54002 (9) | 0.0241 (3) |
| H17A | 0.318657 | 0.001184 | 0.533308 | 0.029* |
| H17B | 0.264444 | 0.137634 | 0.598421 | 0.029* |
| C18 | 0.0825 (2) | 0.06374 (17) | 0.48852 (9) | 0.0263 (3) |
| H18A | 0.098142 | 0.027198 | 0.429838 | 0.032* |
| H18B | 0.041942 | 0.161861 | 0.496040 | 0.032* |
| O6 | 0.5790 (2) | 0.15812 (16) | 0.70852 (8) | 0.0443 (3) |
| H6B | 0.664408 | 0.219882 | 0.750489 | 0.066* |
| O7 | 1.15544 (15) | 0.43331 (13) | 0.43775 (7) | 0.0312 (3) |
| H7A | 1.238263 | 0.378885 | 0.442282 | 0.047* |
| H7B | 1.222447 | 0.527083 | 0.433637 | 0.047* |
Source of material
The mixture of enoxacin (160 mg, 0.5 mmol) and adipic acid (36.5 mg, 0.25 mmol) was dissolved in 8 mL of deionized water. The resulting mixture was stirred and dissolved in a constant temperature water bath at 50 °C to obtain a clear solution, which was filtered and placed in a 10 mL glass bottle. The bottle was sealed with a film with a puncture hole. The filtrate was slowly evaporated at room temperature. Crystal of the title compound were obtained after two days.
Experimental details
Absorption corrections were applied by using multi-scan program [1]. Using Olex2 [2], the structure was solved with the ShelXT [3] structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL [4] refinement package. The H atoms were fixed, fixed Uiso were set to 1.2 times of all C(H) groups, C(H,H) groups and N(H,H) groups; 1.5 times of C(H,H,H,H) groups, O(H) groups and O(H,H) groups.
Comment
As a third-generation quinolone antibiotic, enoxacin has antibacterial effects on Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus, Helicobacter, etc., which has no cross with other antibiotics [5]. Although enoxacin has good permeability as a BCS class II drug, its solubility is extremely poor, which made it difficult to achieve optimal antibacterial activity. Recently, many studies on quinolone antibiotics with enoxacin-like structures have reported that solubility, permeability and efficacy was improved through the formation of drug salts/co-crystals [6]. For example, the solubility of enrofloxacin with the pharmaceutical salts/co-crystals of maleic, succinic, and oxalic acids was significantly higher, the solubility and stability of the drug [7]. Thus, we believe that the medicinal salt/co-crystal of enoxacin can also be prepared by drug co-crystal technology, which will improve the solubility and permeability of enoxacin and improve the clinical efficacy.
The title crystal was formed by connecting the raw materials enoxacin, adipic acid and water molecules through a protonation/deprotonation reaction of the starting materials followed by crystallisation. The asymmetric unit consists of one monoprotonated enoxacine cation, one half of an adipate and two water molecules. N1H1A in the piperazinium group participates in a classical N1–H1A⃛O4 hydrogen bond to the oxygen atom of the adipate (see the figure). Furthermore the N1H1B in the piperazine group is involved in a N1–H1B⃛O7 hydrogen bond with water molecule (d(N1⃛O7) = 2.7180(16) Å; N1–H1B⃛O7 = 161.5°). Two oxygen atoms in a molecule of the adipate dianion form three hydrogen bonds with two water molecules: O6–H6A⃛O5 (d(O6⃛O5) = 2.7989(17) Å; angle: O6–H6A⃛O5 = 167(2)°); O7–H7A⃛O41(1 = 1 + x, +y, +z; d(O7⃛O4) = 2.7726(15) Å; angle: O7–H7A⃛O4 = 174.9°); O7–H7B⃛O52 (2 = 2−x, 1−y, 1−z; d(O7⃛O5) = 2.7340(15) Å; angle: O7–H7A⃛O5 = 175.5°). Bond lengths and angles derived from the title crystal structure are in the expected ranges.
Funding source: Zhejiang Province Basic Public Welfare Research Project
Award Identifier / Grant number: LGJ20B060001
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: This research was supported by the Zhejiang Province Basic Public Welfare Research Project (LGJ20B060001).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. Bruker. Apex3 v. 2016.9-0 and SAINT v. 8.37A; Bruker Axs Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Suche in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT – integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053273314026370.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
4. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Suche in Google Scholar
5. Jaber, L. A., Bailey, E. M., Rybak, M. J. Enoxacin: a new fluoroquinolone. Clin. Pharm. 1989, 8, 97–107.Suche in Google Scholar
6. Rajendran, M. A., Allada, R., Sajid, S. S. Co-crystals for generic pharmaceuticals: an outlook on solid oral dosage formulations. Recent. Adv. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2021, 15, 15–36; https://doi.org/10.2174/2667387815666210203151209.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Karanam, M., Choudhury, A. R. Structural landscape of pure enrofloxacin and its novel salts: enhanced solubility for better pharmaceutical applicability. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 1626–1637; https://doi.org/10.1021/cg301831s.Suche in Google Scholar
Supplementary Material
The online version of this article offers supplementary material (https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2022-0162).
© 2022 Cheng-Jun Jiang and Ying-Fan Xia, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co

