Abstract
C22H16FN3O2, triclinic, P
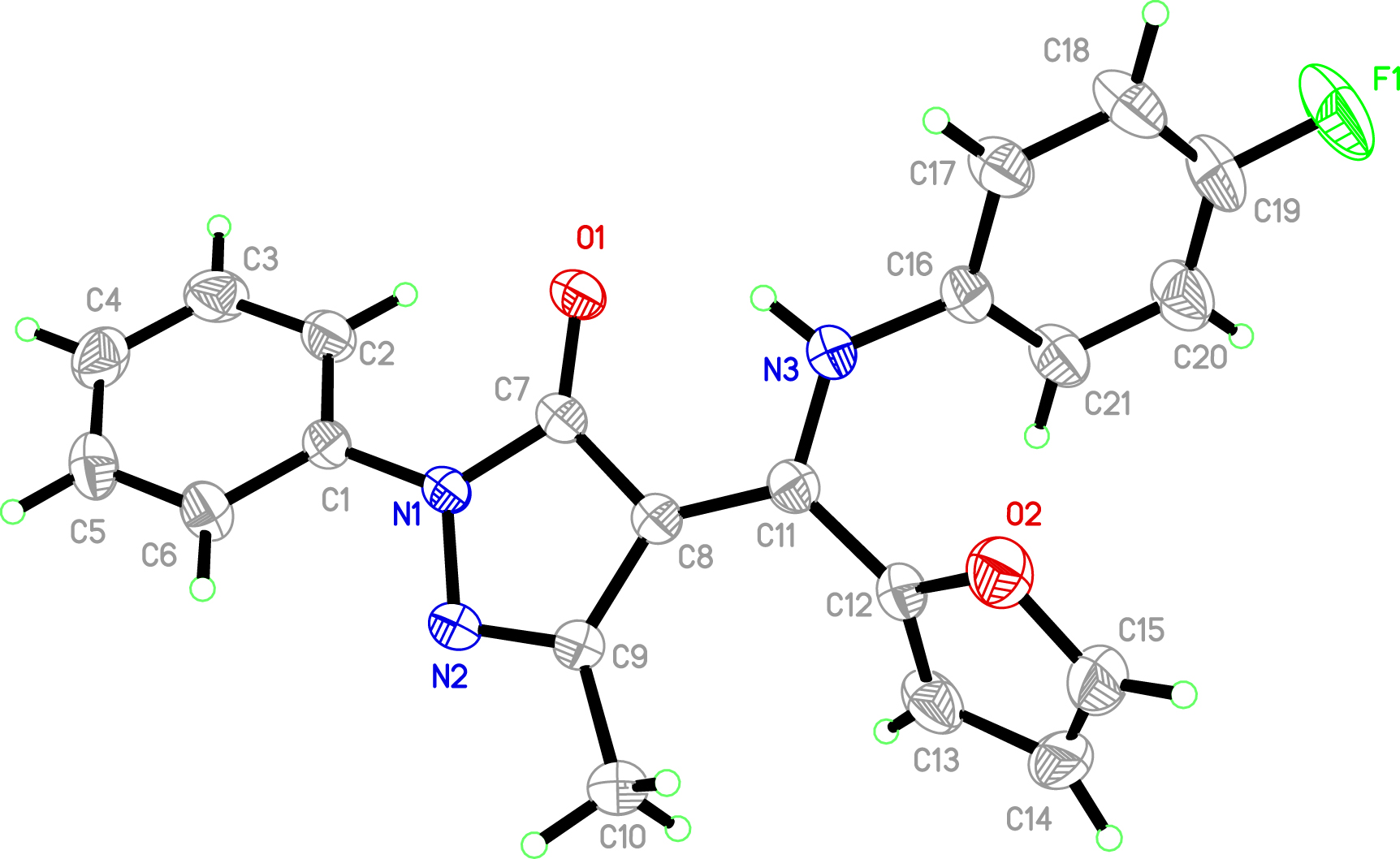
The crystal structure is shown in the figure. Tables 1 and 2 contain details on crystal structure and measurement conditions and a list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Yellow block |
| Size: | 0.32 × 0.26 × 0.20 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.10 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 25.0°, 98% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 4758, 3143, 0.022 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2 σ(Iobs), 2275 |
| N(param)refined: | 250 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], SHELX [2], WinGX/ORTEP [3], PLATON [4] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3A | 0.889 (3) | 0.317 (3) | 0.137 (2) | 0.053 (8)* |
| F1 | 0.5745 (3) | 0.2596 (4) | 0.59296 (16) | 0.1249 (9) |
| O1 | 0.9798 (2) | 0.2247 (2) | 0.01124 (14) | 0.0605 (5) |
| O2 | 0.6355 (3) | 0.7131 (2) | 0.14741 (18) | 0.0716 (6) |
| N1 | 0.9336 (3) | 0.3865 (2) | −0.18788 (16) | 0.0467 (5) |
| N2 | 0.8553 (3) | 0.5467 (2) | −0.25126 (17) | 0.0475 (5) |
| N3 | 0.8118 (3) | 0.3974 (3) | 0.15034 (17) | 0.0505 (5) |
| C1 | 1.0287 (3) | 0.2835 (3) | −0.2487 (2) | 0.0438 (6) |
| C2 | 1.0598 (4) | 0.1262 (3) | −0.2036 (2) | 0.0576 (7) |
| H2 | 1.015731 | 0.087924 | −0.133425 | 0.069* |
| C3 | 1.1558 (4) | 0.0280 (3) | −0.2631 (3) | 0.0697 (8) |
| H3 | 1.178932 | −0.077683 | −0.231571 | 0.084* |
| C4 | 1.2186 (4) | 0.0825 (4) | −0.3685 (3) | 0.0696 (8) |
| H4 | 1.282999 | 0.014638 | −0.408175 | 0.083* |
| C5 | 1.1851 (4) | 0.2384 (4) | −0.4145 (2) | 0.0640 (8) |
| H5 | 1.225724 | 0.276401 | −0.486369 | 0.077* |
| C6 | 1.0916 (3) | 0.3392 (3) | −0.3550 (2) | 0.0546 (7) |
| H6 | 1.070974 | 0.444399 | −0.386264 | 0.065* |
| C7 | 0.9140 (3) | 0.3552 (3) | −0.0680 (2) | 0.0466 (6) |
| C8 | 0.8038 (3) | 0.5050 (3) | −0.0569 (2) | 0.0438 (6) |
| C9 | 0.7793 (3) | 0.6159 (3) | −0.1748 (2) | 0.0443 (6) |
| C10 | 0.6910 (4) | 0.7897 (3) | −0.2175 (3) | 0.0649 (8) |
| H10A | 0.723473 | 0.831082 | −0.295128 | 0.097* |
| H10B | 0.721215 | 0.829515 | −0.163622 | 0.097* |
| H10C | 0.571362 | 0.820277 | −0.221347 | 0.097* |
| C11 | 0.7452 (3) | 0.5199 (3) | 0.05040 (19) | 0.0431 (6) |
| C12 | 0.6120 (3) | 0.6629 (3) | 0.0608 (2) | 0.0467 (6) |
| C13 | 0.4582 (3) | 0.7500 (4) | 0.0036 (2) | 0.0700 (9) |
| H13 | 0.411302 | 0.738354 | −0.058262 | 0.084* |
| C14 | 0.3817 (4) | 0.8674 (4) | 0.0616 (4) | 0.0921 (13) |
| H14 | 0.274449 | 0.948200 | 0.042782 | 0.111* |
| C15 | 0.4924 (6) | 0.8374 (4) | 0.1451 (3) | 0.0940 (13) |
| H15 | 0.474505 | 0.894596 | 0.196074 | 0.113* |
| C16 | 0.7466 (3) | 0.3692 (3) | 0.2643 (2) | 0.0468 (6) |
| C17 | 0.8574 (4) | 0.2886 (3) | 0.3641 (2) | 0.0621 (7) |
| H17 | 0.972349 | 0.258713 | 0.356710 | 0.075* |
| C18 | 0.7990 (4) | 0.2517 (4) | 0.4755 (2) | 0.0769 (9) |
| H18 | 0.873732 | 0.195886 | 0.543213 | 0.092* |
| C19 | 0.6313 (4) | 0.2982 (4) | 0.4838 (2) | 0.0745 (9) |
| C20 | 0.5191 (4) | 0.3784 (4) | 0.3878 (3) | 0.0782 (9) |
| H20 | 0.404314 | 0.409484 | 0.396599 | 0.094* |
| C21 | 0.5766 (4) | 0.4136 (4) | 0.2765 (2) | 0.0642 (8) |
| H21 | 0.500464 | 0.467533 | 0.209442 | 0.077* |
Source of material
All reagents were obtained from commercial sources and used without further purification. A mixture of a 10 mL HPMFP (2 mmol, 0.5366 g) anhydrous ethanol solution, and a 10 mL 4-fluoroaniline (2 mmol, 0.2221 g) anhydrous ethanol solution was refluxed for ca. 3 h, adding a few drops of glacial acetic acid as a catalyst. Then ethanol was removed by evaporation and the resulting yellow precipitate formed was filtered off, washed with cold anhydrous ethanol and dried in air. Yellow block crystals suitable for analysis were obtained by slowly evaporation of a solution in anhydrous ethanol at room temperature for a few days.
Experimental details
The structure was solved by direct methods with the SHELXS-2018 program [2]. The H atoms bonded to N3 atoms were located in difference maps and refined freely. Other H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C–H = 0.93 for phenyl and furyl, 0.96 for methyl H atoms, and refined as riding, with Uiso(H) values of 1.2Ueq(C) for phenyl and furyl H and 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H.
Comment
4-Acylpyrazolones are an interesting class of β-diketones, containing a pyrazole-bearing moiety. Thus, related metal complexes are used for the separation of elements with similar properties [5]. Some β-diketonate based compounds also have recently provoked a growing interest for various reasons [6], [7], [8]. Only a few studies have involved heterocyclic substituents at the 4-position. In recent years, we have reported the Schiff bases derived from 4-heterocyclic acylpyrazolones and their complexes, which possess high antibacterial activation [9, 10]. Knowledge of the crystal structure of such acylpyrazolones derivatives gives us not only sufficient information about nuclearity of the complex, but is important for the understanding of the compounds in the vapour phase, and the mechanisms of sublimation and decomposition.
In the title crystal structure, the compound crystallized with a structural configuration in which the phenyl ring(C(1)–C(6)) is twisted with a dihedral angle of 23.73(15)° with respect to a plane defined by the pyrazole ring. The O1 atom of pyrazole ring and the O(1)/C(7)/C(8)/C(11)/N(3) plane are nearly coplanar with the largest deviation of 0.028 Å. The bond length of C(8)–C(11) (1.383(3) Å) between the usual C–C and C=C bonds indicates the delocalization of the electrons because of the addition of a proton to N(3) is more favourable than to O(1) in the Fourier map (keto-form). The atom O(1) of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-4-(furoyl)-pyrazolone-5 moiety and the N(3) atom of the 4-Fluoroaniline group are on the same side of C(8)–C(11) bond, which are available for coordination with metal cations. A strong intramolecular N(3)–H(3A)⃛O(1) hydrogen bond is observed, as part of the enamine-keto tautomerism. Two other weak intramolecular bonds C(6)–H(6)⃛O(2) and C(2)–H(2)⃛O(1) are also found, stabilizing the structure. All bond lengths and angles are normal and comparable with those found for related compounds [11], [12], [13].
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: Foundation of Hebei Education Department (No. ZD2020412) and the Foundation of Health Commission of Hebei Province (No. 20201320).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 SADABS; Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, WI, 2008.Search in Google Scholar
2. Sheldrick, G. M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C71, 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229614024218.Search in Google Scholar
3. Farrugia, L. J. WinGX and Ortep for Windows: an update. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 849–854. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889812029111.Search in Google Scholar
4. Spek, A. L. Structure validation in chemical crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 2009, D65, 148–155. https://doi.org/10.1107/s090744490804362x.Search in Google Scholar
5. Nishihama, S., Hirai, T., Komasawa, I. Review of advanced liquid-liquid extraction systems for the separation of metal ions by a combination of conversion of the metal species with chemical reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3085–3091. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie010022+.10.1021/ie010022+Search in Google Scholar
6. Rahman, M., Siddiqui, A. Pyrazoline derivatives: a worthy insight into the recent advances and potential pharmacological activities. Int. J. Pharmaceut. Sci. Drug Res. 2010, 2, 165–175.10.4172/2150-3494.1000021Search in Google Scholar
7. Marchetti, F., Pettinari, C., Pettinari, R. Acylpyrazolone ligands: synthesis, structures, metal coordination chemistry and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 2909–2945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.013.Search in Google Scholar
8. Mukherjee, R. Coordination chemistry with pyrazole-based chelating ligands: molecular structural aspects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 203, 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0010-8545(99)00144-7.Search in Google Scholar
9. Zhang, H.-Q., Li, J.-Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, D. Synthesis, crystal structure and thermal stability of a one-dimensional chain acylpyrazolone complex Zn(C26H15N3O2Cl)2. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 24, 990–993.Search in Google Scholar
10. Li, J.-Z., Li, Y. G., Yu, W.-J. Synthesis, characterization and bioactivity of complexes of rare earth with bis-Schiff base from furoylpyrazolone. J. Rare Earths 2000, 18, 233–236.Search in Google Scholar
11. Zhang, H.-Q., Yang, X., Wu, Q., Chen, H.-L. Crystal structure of (4Z)- 4-{[(2-chlorophenyl)amino](furan-2-yl)methylidene}-3-methyl-1-phenyl -4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-5-one. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, E71, o177–o178. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989015002698.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
12. Zhang, H.-Q., Wu, Q., Jin, T.-Y., Li, Y.-Y., Chen, H.-L. Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(furan-2-yl(phenylamino)methylene)-5-methyl -2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C21H16ClN3O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2018, 233, 883–884. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2018-0075.Search in Google Scholar
13. Zhang, B.-Q., Zhang, L., Zhang, H.-Q., Zhao, C.-L., Chen, B. Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(furan-2-yl(p-tolylamino)methylene)-3-methyl-1-p- tolyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C23H21N3O2. Z. Kristallogr. N. Cryst. Struct. 2016, 231, 281–283. https://doi.org/10.1515/ncrs-2015-0120.Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Qiong Wu et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co

