Abstract
C26H24N2O8, monoclinic, P21/c (no. 14), a = 6.9170(9) Å, b = 26.012(3) Å, c = 12.7449(17) Å, β = 91.896(4)°, V = 2291.9(5) Å3, Z = 4, Rgt(F) = 0.0471, wRref(F2) = 0.1320, T = 90 K.
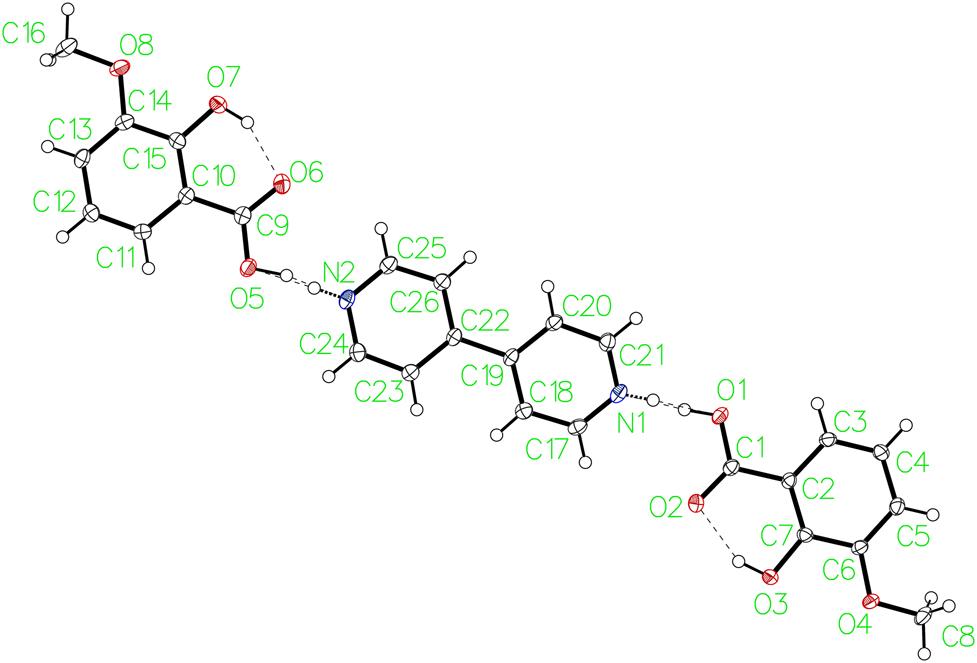
The molecular structure is shown in the figure. Table 1 contains crystallographic data and Table 2 contains the list of the atoms including atomic coordinates and displacement parameters.
Data collection and handling.
| Crystal: | Colourless plate |
| Size: | 0.45 × 0.13 × 0.02 mm |
| Wavelength: | Mo Kα radiation (0.71073 Å) |
| μ: | 0.11 mm−1 |
| Diffractometer, scan mode: | Bruker Apex-II, φ and ω |
| θmax, completeness: | 29.6°, >99% |
| N(hkl)measured, N(hkl)unique, Rint: | 25,125, 6412, 0.071 |
| Criterion for Iobs, N(hkl)gt: | Iobs > 2σ(Iobs), 4674 |
| N(param)refined: | 346 |
| Programs: | Bruker [1], Olex2 [2], Shelx [3] |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2).
| Atom | x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.1488 (2) | 0.33321 (5) | 0.39798 (10) | 0.0164 (3) |
| C2 | 0.32354 (19) | 0.30060 (5) | 0.39479 (10) | 0.0147 (3) |
| C3 | 0.3691 (2) | 0.27359 (5) | 0.30307 (10) | 0.0171 (3) |
| H3A | 0.287959 | 0.275990 | 0.243602 | 0.021* |
| C4 | 0.5326 (2) | 0.24373 (6) | 0.30102 (11) | 0.0187 (3) |
| H4 | 0.561497 | 0.225917 | 0.240237 | 0.022* |
| C5 | 0.6562 (2) | 0.23995 (6) | 0.39011 (11) | 0.0181 (3) |
| H5A | 0.767171 | 0.219828 | 0.388024 | 0.022* |
| C6 | 0.6139 (2) | 0.26601 (5) | 0.48102 (10) | 0.0160 (3) |
| C7 | 0.4465 (2) | 0.29675 (5) | 0.48407 (10) | 0.0154 (3) |
| C8 | 0.8782 (2) | 0.22887 (6) | 0.57887 (12) | 0.0268 (3) |
| H8A | 0.976734 | 0.238913 | 0.531699 | 0.040* |
| H8B | 0.830637 | 0.195357 | 0.559851 | 0.040* |
| H8C | 0.931471 | 0.228037 | 0.649353 | 0.040* |
| C9 | 0.5586 (2) | 0.07387 (5) | 0.31047 (11) | 0.0170 (3) |
| C10 | 0.74424 (19) | 0.10248 (5) | 0.31791 (10) | 0.0152 (3) |
| C11 | 0.8053 (2) | 0.13242 (5) | 0.23358 (10) | 0.0159 (3) |
| H11 | 0.727475 | 0.135376 | 0.172947 | 0.019* |
| C12 | 0.9801 (2) | 0.15734 (5) | 0.24090 (11) | 0.0177 (3) |
| H12 | 1.021426 | 0.176585 | 0.184377 | 0.021* |
| C13 | 1.0969 (2) | 0.15412 (5) | 0.33233 (11) | 0.0183 (3) |
| H13 | 1.215866 | 0.170805 | 0.335830 | 0.022* |
| C14 | 1.0361 (2) | 0.12618 (5) | 0.41775 (11) | 0.0170 (3) |
| C15 | 0.8597 (2) | 0.09921 (5) | 0.41040 (10) | 0.0161 (3) |
| C16 | 1.3035 (2) | 0.15430 (6) | 0.52587 (13) | 0.0253 (3) |
| H16A | 1.347720 | 0.153616 | 0.598051 | 0.038* |
| H16B | 1.272224 | 0.188975 | 0.505895 | 0.038* |
| H16C | 1.403527 | 0.141496 | 0.482426 | 0.038* |
| C17 | 0.6459 (2) | 0.40244 (5) | 0.40800 (11) | 0.0187 (3) |
| H17 | 0.700538 | 0.393133 | 0.472909 | 0.022* |
| C18 | 0.4767 (2) | 0.43064 (6) | 0.40500 (11) | 0.0177 (3) |
| H18 | 0.418900 | 0.439987 | 0.467034 | 0.021* |
| C19 | 0.39245 (19) | 0.44510 (5) | 0.30780 (11) | 0.0154 (3) |
| C20 | 0.4869 (2) | 0.43039 (5) | 0.21812 (11) | 0.0176 (3) |
| H20 | 0.437275 | 0.439659 | 0.152091 | 0.021* |
| C21 | 0.6554 (2) | 0.40184 (6) | 0.22774 (11) | 0.0192 (3) |
| H21 | 0.716340 | 0.391837 | 0.167081 | 0.023* |
| C22 | 0.20895 (19) | 0.47480 (5) | 0.29949 (11) | 0.0151 (3) |
| C23 | 0.1542 (2) | 0.50732 (5) | 0.38053 (10) | 0.0172 (3) |
| H23 | 0.232326 | 0.510615 | 0.440958 | 0.021* |
| C24 | −0.0170 (2) | 0.53456 (6) | 0.37018 (11) | 0.0183 (3) |
| H24 | −0.052492 | 0.556019 | 0.424652 | 0.022* |
| C25 | −0.0809 (2) | 0.50091 (5) | 0.20513 (11) | 0.0189 (3) |
| H25 | −0.160049 | 0.499230 | 0.144807 | 0.023* |
| C26 | 0.0876 (2) | 0.47206 (5) | 0.20979 (11) | 0.0173 (3) |
| H26 | 0.119525 | 0.451094 | 0.153844 | 0.021* |
| H1Aa | 0.844 (12) | 0.373 (3) | 0.314 (5) | 0.040* |
| H1Bb | −0.064 (6) | 0.3530 (15) | 0.318 (2) | 0.040* |
| H2Bb | 0.342 (6) | 0.0588 (12) | 0.227 (2) | 0.031* |
| H2Aa | −0.232 (13) | 0.551 (3) | 0.278 (5) | 0.040* |
| N1 | 0.73415 (18) | 0.38805 (5) | 0.32100 (10) | 0.0186 (3) |
| N2 | −0.13397 (18) | 0.53112 (5) | 0.28421 (10) | 0.0180 (2) |
| O1 | 0.04370 (16) | 0.33450 (4) | 0.31118 (8) | 0.0234 (2) |
| O2 | 0.10698 (15) | 0.35762 (4) | 0.47794 (8) | 0.0223 (2) |
| O3 | 0.41371 (16) | 0.32155 (4) | 0.57534 (8) | 0.0228 (2) |
| H3 | 0.307 (3) | 0.3391 (8) | 0.5615 (14) | 0.034* |
| O4 | 0.72337 (15) | 0.26493 (4) | 0.57248 (8) | 0.0231 (2) |
| O5 | 0.46117 (15) | 0.07778 (4) | 0.22146 (8) | 0.0205 (2) |
| O6 | 0.50174 (15) | 0.04783 (4) | 0.38533 (8) | 0.0228 (2) |
| O7 | 0.80804 (16) | 0.07094 (4) | 0.49432 (8) | 0.0222 (2) |
| H7 | 0.699 (3) | 0.0567 (8) | 0.4768 (15) | 0.033* |
| O8 | 1.13486 (15) | 0.12267 (4) | 0.51279 (8) | 0.0227 (2) |
-
aOccupancy: 0.32 (4), bOccupancy: 0.68 (4).
Source of material
4,4′-Bipyridine (156.2 mg, 1.0 mmol) and o-vanillic acid (168.1 mg, 1.0 mmol) were dissolved using excess methanol in a 200 mL beaker. The beaker was left open to allow for crystal formation upon slow evaporation. Coformers were sourced from Combi-Blocks (o-vanillic acid, 97% and 4,4′-bipyridine, 97%). Methanol was purchased from Fischer Chemical (HPLC grade; 99.9%). No further material refinement was necessary.
Experimental details
X-ray diffraction data was collected using a Bruker Smart Apex-II CCD diffractometer installed at a rotating anode source (MoKα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å) and equipped with an Oxford Cryosystems (Cryostream700) nitrogen gas-flow apparatus. Five sets of data (290 frames each) were collected by the rotation method with 0.5° frame-width (ω scan). The sample was run at 90 K. Using Olex2, the structure was solved with intrinsic phasing via the ShelXT structure solution program and refined with the ShelXL software suite [2, 3]. The atomic coordinates of H atoms attached to heteroatoms were freely refined with thermal parameters constrained to be Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(N) or 1.5Ueq(O). H atoms connected to carbon atoms were placed geometrically (C–H = 0.95 Å) and refined with thermal parameters constrained to be Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The disordered protons were initially refined independently, however given the similar refined occupancies the disorder was ultimately modeled as correlated using a single occupancy parameter (Table 2).
Comment
2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid, known commonly as o-vanillic acid, has been under investigation for its medicinal benefits such as its anti-allergenic inflammatory response [4]. Despite the rise in interest and utility of this molecule, only a handful of crystal structures containing o-vanillic acid have been reported [5], [6], [7]. As such additional co-crystals and/or salts of o-vanillic acid may aid in further understanding its solid-state interactions. In this report the coformer 4,4′-bipyridine (4,4′-BIPY) was selected due to its ability to form a variety of crystalline systems including metal-organic frameworks, co-crystals, and salts [8], [9], [10].
o-Vanillic acid co-crystallizes with 4,4′-BIPY in a 2:1 ratio in the monoclinic spacegroup (P21/c). Subsequent refinements revealed the presence of disorder involving the acidic protons of the carboxylic acid groups of the vanillic acid and the pyridyl groups of the 4,4′-BIPY. For each of the two crystallographically unique acid groups, the proton was disordered over two positions. In one case, the proton was located near the oxygen, and in the second case the proton was located near the nitrogen of the pyridyl group. The ratio of the occupancies (HO:HN) of the disordered protons when refined independently were determined to be 0.68225:0.31775 and 0.68721:0.31279. Given the similar values, the occupancies were treated with a single parameter in the final model and determined to be 0.68(4):0.32(4).
These values may be interpreted as a partial charge transfer with the proton being transferred to the nitrogen resulting in a salt 32(4)% of the time. The other 68(4)% of the time, the protons reside on the acid oxygen resulting in charge neutral carboxylic acid and pyridyl groups. The two acids and the 4,4′-BIPY together form discrete hydrogen bonded trimolecular assemblies. These assemblies form slipped stacks through π–π interactions approximately along [100]. Lateral Van der Waals interatactions approximately along [001] give rise to 2-D sheets. These sheets form alternating layers along [010] in which each layer is rotated by 180°.
Funding source: National Science Foundation
Award Identifier / Grant number: DMR-2003932
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by: National Science Foundation, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (award No. DMR-2003932).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and approved submission.
-
Research funding: National Science Foundation, Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (award No. DMR-2003932).
-
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this article.
References
1. BRUKER. SAINT, APEX2 and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2009.Search in Google Scholar
2. Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K., Puschmann, H. Olex2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726.Search in Google Scholar
3. Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122; https://doi.org/10.1107/s0108767307043930.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Kim, M. C., Kim, S. J., Kim, D. S., Jeon, Y. D., Park, S. J., Lee, H. S., Um, J. Y., Hong, S. H. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 525–532; https://doi.org/10.3109/08923973.2010.547500.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
5. Fang, Z.-Q., Zeng, R.-H., Yang, M., Liu, H., Chen, X.-L. 2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid monohydrate. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, E64, o691; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536808006065.Search in Google Scholar
6. Liu, Z.-H., Qiu, Y.-C., Li, Y.-H., Zeng, R.-H., Deng, H. 2-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid. Acta Crystallogr. 2007, E63, o2616–o2617; https://doi.org/10.1107/s1600536807018739.Search in Google Scholar
7. Fronczek, F. R. CCDC 1525788: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination; Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre: Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2017.Search in Google Scholar
8. Walton, I. M., Cox, J. M., Myers, S. D., Benson, C. A., Mitchell, T. B., Bateman, G. S., Sylvester, E. D., Chen, Y.-S., Benedict, J. B. Determination of the dehydration pathway in a flexible metal-organic framework by dynamic in situ x-ray diffraction. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 7, 034305; https://doi.org/10.1063/4.0000015.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
9. Mudsainiyan, R. K., Jassal, A. K., Pandey, S. K. Structural diversity from co-crystal to 1D coordination polymers of 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid with 4,4′-bipyridine as coligand: structural and computational approach. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 3363–3381; https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2020.1853108.Search in Google Scholar
10. Sylvester, E., McGovern, M., Young Lee, A., Nguyen, P., Park, J., Benedict, J. B. Partial charge transfer in the salt co-crystal of l-ascorbic acid and 4,4′-bi-pyridine. Acta Crystallogr. 2019, E75, 728–731; https://doi.org/10.1107/s2056989019005334.Search in Google Scholar
© 2022 Devin J. Angevine and Jason B. Benedict, published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co
Articles in the same Issue
- Frontmatter
- New Crystal Structures
- Crystal structure of N-((3s,5s,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-2-(3-benzoylphenyl)propanamide, C26H29NO2
- The crystal structure of bis(μ2-5-chloro-2-oxido-N-(1-oxidopropylidene)benzohydrazonato-κ5 N,O,O′:N′,O′′)-octakis(pyridine-κ1 N)trinickel(II) C60H56Cl2N12Ni3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,5-di-p-tolylpentane-1,5-dione, C25H23ClO2
- The crystal structure of 2,4,4-triphenyl-4H-benzo[b][1,4]oxaphosphinin-4-ium bromide – dichloromethane (1/1), C27H22BrCl2OP
- The crystal structure of 2-(3,6-di-tert-butyl-1,8-diiodo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)acetonitrile, C22H24I2N2
- Crystal structure of 3-phenylpropyl 2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoate, C23H24O3
- The crystal structure of (4-fluorophenyl)(5-(hydroxymethyl)furan-2-yl)methanol, C12H11FO3
- Crystal structure of the dihydrate of tetraethylammonium 1,3,5-thiadiazole-5-amido-2-carbamate, C11H27N5O4S
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-[(p-tolylamino)(furan-2-yl)methylene]-3-phenyl-1-1-p-tolyl-1H-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-5(4H)-one, C28H23N3O2
- The crystal structure of (E)-3-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-ferrocenylprop-2-en-1-one, C19H15ClFeO
- The pseudosymmetric crystal structure of 3-((1R,2S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-1-ium-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium hexachloridostannate(IV), C10H16N2SnCl6
- Crystal structure of (2-(1-hydroxyheptyl)octahydro-8aH-chromene-5,8,8a-triol), C16H30O5
- The crystal structure of N-cyclohexyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C14H19NO3
- Crystal structure of 1-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-4-methoxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene-2,7-diol from Arundina graminifolia, C22H20O4
- The crystal structure of N-cyclopentyl-3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzamide, C13H17NO3
- The crystal structure of 2,5,5-triphenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one, C21H16N2O
- Crystal structure of 1H-1,2,3-Triazolo[4,5-b]-pyridin-4-ium nitrate, C5H5N5O3
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-bromophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-2,5-diphenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one, C26H18BrN3O2
- Crystal structure of 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-1,8-naphthyridine, C16H14N2O
- The crystal structure of 3-([1,1′-biphenyl]-2-yl)-1,2-diphenylbenzo[b]phosphole-1-oxide, C32H23OP
- The crystal structure of ammonium (E)-4-((4-carboxyphenyl)diazenyl)benzoate, C14H13N3O4
- Crystal structure of bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane sulfate, C5H10N8O4S
- The crystal structure of phenantroline-κ2 N,N′-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2 N,O)copper(II), C36H24N4O4Cu
- The crystal structure of tris(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)phosphine oxide, C18H18N3OP
- The crystal structure of N-(2′-hydroxymethyl-5′-phenyl-3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′:3′,1″-terphenyl]- 1′(2′H)-yl)-P,P-diphenylphosphinic amide, C37H34NO2P
- Crystal structure of (E)-4-(6-(4-(2-(pyridin-4-yl)vinyl)phenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine, C21H20N4O2
- Crystal structure of 5-(adamantan-1-yl)-3-[(4-trifluoromethylanilino)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2-thione, C20H22F3N3OS
- Crystal structure of 2,2-dichloro-1-(4-chloro-1H-indol-1-yl)ethan-1-one, C10H6Cl3NO
- The crystal structure of 4-(((3-bromo-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C28H16Br2F6N4O2
- The crystal structure of 1H-benzimidazole-2-carboxamide, C8H7N3O
- The crystal structure of Histidinium hydrogensquarate, C10H11N3O6
- The crystal structure of 3-amino-5-carboxypyridin-1-ium iodide, C6H7IN2O2
- Crystal structure of (E)-amino(2-(3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzylidene)hydrazineyl)methaniminium nitrate hemihydrate C10H16N5O5.5
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(4,5-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane, C8H6N8O8
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II), C14H12N6O6Mn
- The crystal structure of catena-poly[aqua-2,2′bipyridine-κ2N,N′-(μ2-5-ethoxyisophthalato-κ 4O,O′:Oʺ,O′ʺ)cadmium(II)] monohydrate, C20H20CdN2O7
- The crystal structure of (1S,3R)-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-3-(methoxycarbonyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-2-iumchloride monohydrate, C22H27ClN2O3
- Crystal structure of 1-isopropyl-3-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, C11H15N5
- The crystal structure of (2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)- bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylate-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C34H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of the cocrystal 1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazoctane ─ 2,3-dihydroindole (1/1), C12H17N9O8
- Crystal structure of 3-acetyl-6-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one monohydrate, C11H10O5
- Crystal structure of 6,9-diamino-2-ethoxyacridinium 3,5-dinitrobenozate — dimethylsulfoxide — water (1/1/1), C24H27N5O9S
- The crystal structure of 4,4′-bipyridinium bis-(2-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoate), 2(C8H7.68O4)·C10H8.64N2
- Crystal structure of (Z)-4-(((4-fluorophenyl)amino)(furan-2-yl)methylene)-5-methyl-2-phenyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-pyrazol-3-one
- The crystal structure of bis(4-chloro-2-(((2-chloroethyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O)-oxidovanadium(IV), C18H16Cl4N2O3V
- The crystal structure of 17-(bromoethynyl)-17-hydroxy-10, 13-dimethyl- 1,2,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one, C21H27BrO2
- The crystal structure of 4-((6-fluoropyridin-2-yloxy)methyl)benzonitrile, C13H9FN2O
- Crystal structure of (Z)-2-(1-bromo-2-phenylvinyl)-5-ethyl-2-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C15H17Br1O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[tribenzyl-κ1C-(μ2-6-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboxylato-κ2O:O’)tin(IV)-dichloromethane-methanol (1/1/1), C29H31Cl2NO4Sn
- Crystal structure of bis{2-(tert-butyl)-6-((E)-((4-((E)-1-(methoxyimino)ethyl)phenyl)imino)methyl)phenolato-κ2N,O}zinc(II), C40H46N4O4Zn
- Crystal structure of diaqua-bis(μ2-2-carboxy-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorobenzoato-κ2O:O′)-bis(phenanthroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(μ2-3,4,5,6-tetrafluorophthalato-κ3O:O,O′)dieuropium(III) – phenanthroline (1/2), C40H19EuF8N4O9
- The crystal structure of diaqua-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O) manganese(II) — water — dimethylformamide (1/2/1), C27H31N3O9Mn
- The crystal structure of bis(pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylato-κ2N,O)-copper(ii), C14H8N6O4Cu
- Crystal structure of poly[(μ2-1-(1-imidazolyl)-4-(imidazol-1-ylmethyl)benzene-κ2N:N′)-(μ3-pyridazine-4,5-dicarboxylate-κ3O:O′:N)]copper(II) hydrate, C19H16CuN6O5
- Crystal structure of acrinidinium tetrafluorohydrogenphthalate, C21H11F4NO4
- Crystal structure of 2-(1H-pyrazol-3-yl-κN)pyridine-κN-bis(2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)pyridinato-κ2C,N)iridium(III) sesquihydrate, C30H18F4IrN5·1.5[H2O]
- Crystal structure of 2-(2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-5-methyl-1,3-dioxane-5-carboxylic acid, C12H13N1O7
- The crystal structure of 1,2-bis(pyridinium-4-yl)ethane diperchlorate, C12H14N2·2ClO4 – a second polymorph
- The crystal structure of [(1,10-phenantroline-κ2N,N′)-bis(6-phenylpyridine-2-carboxylato-κ2N,O)manganese(II)] monohydrate, C36H26N4O5Mn
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,2,3,3,5,5,5-heptamethyl-1,1,4,4- tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)pentasilan-1-yl)ditellane, C38H114Si18Te2
- Crystal structure of 1,2-bis(2,4-dinitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethane – dimethylformamide (1/1), C11H13N9O9
- Crystal structure of (Z)-3-((tert-butylamino) methylene)-2-(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl) chroman-4-one, C24H23NO3
- Synthesis and crystal structure of (E)-1-(4-(((E)-3-(tert-butyl)-2-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)phenyl)ethan-1-one O-ethyl oxime, C21H26N2O2
- Crystal structure of the double salt bis(5-amino-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)methane hydrogen oxalate hemioxalate, C8H11N8O6
- Hydrothermal synthesis and crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-4-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]benzoato-κ2N:O)cobalt(II)]–1,2bi(4-pyridyl)ethene–water (1/1/1), C50H50N8O8Co
- Crystal structure of 3-(3-bromophenyl)-1′,3′-dimethyl-2′H,3H,4H-spiro[furo[3, 2-c]chromene-2,5′-pyrimidine]-2′,4,4′,6′(1′H,3′H) tetraone, C22H15BrN2O6
- The crystal structure of poly[aqua-(μ2-4,4′- bis(imidazolyl)biphenyl-κ2N:N′)-(μ2-3-nitrobenzene-1,2-dicarboxylato-κ2O:O′)]copper (II) hydrate, C26H21N5O8Cu
- The crystal structure of bis(4-(6-carboxy-8-ethyl-3-fluoro-5-oxo-5,8-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridin-2- yl)piperazin-1-ium) adipate tetrahydrate, C36H52F2N8O14
- Synthesis and crystal structure of poly[aqua(μ4-(1R,2S,4R)-4-hydroxy-1-((7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-sulfonatophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromen-8-yl)methyl)pyrrolidin-1-ium-2-carboxylate-κ4O:O′:O″:O‴)sodium(I)] monohydrate, C21H22NNaO12S
- Crystal structure of chlorido-(η6-toluene)(2,2′-bipyridine-κ2N,N′)ruthenium(II) hexafluorophosphate, C17H16ClN2RuPF6
- The crystal structure of (R)-6-hydroxy-8-methoxy-3-methylisochroman-1-one, C11H12O4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[(5,5,7,12,12,14-hexamethyl -1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane- κ4N,N′,Nʺ,N‴)nickel(II)-(μ2-perchlorato-κ2O:O′)] 3,5-dicarboxybenzoate – methanol (1/2), C27H49ClN4NiO12
- The crystal structure of 4-(chloromethyl)benzonitrile, C8H6ClN
- The crystal structure of dimethylammonium 8-[(7,9-dioxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]decan-8-ylidene)methyl]-9-oxo-6,10-dioxaspiro[4.5]dec-7-en-7-olate, C19H25NO8
- Crystal structure of (2R,3S,4S,5R,6S)-2-(acetoxymethyl)-6-((1-acetyl-5-bromo-4-chloro-1H-indol-3-yl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate hemihydrate C24H25BrClNO11
- The crystal structure of the co-crystal tetrakis[2-(tris(4-methoxyphenyl)stannyl)ethyl]silane – tetrahydrofuran – toluene – tetrahydrofurane (1/1/1), C103H116O13SiSn4
- Crystal structure of methyl 3-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)propanoate, C16H13NO4
- Crystal structure of ethyl (Z)-3-amino-2-cyano-3-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)acrylate, C15H12N2O4
- Crystal structure of methyl 2-(1,3-dioxo-1H-benzo[de]isoquinolin-2(3H)-yl)acetate, C15H11NO4
- Crystal structure of catena-poly[diaqua-bis(μ2-1,3-di(1H-imidazol-1-yl)propane-κ2N:N′)cobalt(II)] tetrafluoroterephthalate, C26H28N8O6F4Co

