Abstract
This study presents a novel integration of bibliometric and content analysis to comprehensively examine the research trends and scientific landscape of paver blocks. The investigation of 379 articles and reviews published across 174 journals reveals a steady growth in research output, with a notable surge in publications and citations from 2016 to 2024, underlining the increasing importance of this field. India, Malaysia, and the United States emerge as major contributors, with India leading in publication count (143) and the United States demonstrating high research impact through total citations (1,312) and citations per paper (48.59). Keyword examination highlights the prominence of sustainable materials, waste utilization, and innovative design strategies, while an in-depth review of highly cited papers unveils the potential for incorporating various waste streams to produce high-quality, eco-friendly paver blocks. Over the years, the research focus has expanded from conventional materials to recycled aggregates, permeable designs, and photocatalytic applications. This study identifies research gaps, such as the need for long-term performance assessment and life cycle analysis, and recommends future directions, including integrating paver blocks into urban planning and design strategies. The findings guide researchers and policymakers in the development of sustainable, resilient, and multifunctional paver block solutions.
1 Introduction
Paver blocks have emerged as a versatile and widely used composite construction material in the built environment, offering durability, aesthetic appeal, and ease of installation [1–3]. These precast concrete units find applications in pedestrian walkways, parking areas, roadways, and landscaping projects [4–6]. The growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly construction practices has further fueled the interest in paver blocks as researchers explore innovative materials and production techniques to enhance their performance and minimize environmental impact [7,8].
Extensive research has been conducted on various aspects of paver blocks, including mix design optimization, mechanical properties, durability, and the incorporation of waste materials [9–12]. Studies have investigated the use of recycled aggregates, such as recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) [13,14], reclaimed asphalt pavement [15–17], and waste foundry sand [18,19], as partial or complete replacements for natural aggregates in paver block production. Furthermore, researchers in this field have also proposed the use of different supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash [20,21], silica fume [22], and metakaolin [23], to enhance the strength and durability of paver blocks. Using waste materials conserves natural resources and promotes the circular economy by diverting waste from landfills [24].
Despite all the research efforts put forward, there are areas to improve in order to have a broader picture of the research landscape in paver blocks. In addition, traditional literature reviews might focus on given topics or simply a few studies, thus ignoring larger patterns and connections inside the field [25]. Bibliometric analysis as a tool can overcome the limitation of simply counting the number of research publications by giving a numerical and statistical assessment of many research publications [26,27]. Along with content analysis that explores the qualitative characteristics of the literature, a profound comprehension of research themes, weaknesses, and future directions can be mastered [28]. This holistic approach enables investigators to identify critical topics, significant authors, as well as collaboration networks which at the end guides the next research efforts and then accelerate innovation in the study of paver block [29,30].
Considering the fact that assessing and analyzing scientific literature in a systematic and data-driven way is necessary, this research intends to conduct a bibliometric and content analysis of the scientific literature in this field. The objectives of this study are twofold: (1) to delineate the research trends, main themes, and research collaborations by means of bibliometric analysis and (2) to give the summary of the status quo results, knowledge gaps, and future directions by means of content analysis. Quantitative and qualitative approaches are combined in this study to obtain a comprehensive knowledge about the paver block research field. This will later contribute to the developing of sustainable construction methods and innovative paver block solutions.
The scope of this study encompasses a wide range of paver block research, including mix design, materials characterization, mechanical properties, durability, environmental impact, and the incorporation of waste materials. The bibliometric analysis will cover research publications indexed in major scientific databases, while the content analysis will focus on a selected set of high-impact and relevant studies. Through this systematic and data-driven approach, this study aims to provide valuable insights and recommendations for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers involved in paver block research and sustainable construction practices.
2 Methodology
This study employed a combination of quantitative and qualitative analysis methods, specifically bibliometric analysis and content analysis, to comprehensively examine the research trends and scientific landscape of paver block literature [31]. The methodology consisted of two main stages: data collection, processing, and cleaning; and data analysis, which included both bibliometric analysis and content analysis.
2.1 Data collection, processing, and cleaning
The bibliometric data for this study were collected from the Scopus database, which is considered a reliable and comprehensive source for such analyses, minimizing potential biases and omissions that may result from using a limited set of journals [32,33]. The search query used to retrieve relevant publications was TITLE-ABS-KEY (“paver block*” OR “interlocking concrete block*” OR “interlocking paver*” OR “permeable paver*” OR “pervious paver*” OR “porous paver*” OR “concrete paving block*” OR “precast concrete paver*”). The search was limited to articles and reviews published in English, with no restrictions on the period, covering all publications from the first relevant paper until 2024.
The raw bibliometric data were exported from Scopus in CSV format and processed using Microsoft Excel for data cleaning and analysis. The data cleaning involved correcting inconsistencies, removing duplicates, and standardizing the format [34,35]. The data refinement process, including the application of inclusion and exclusion criteria, is illustrated in the PRISMA diagram provided in Figure 1.
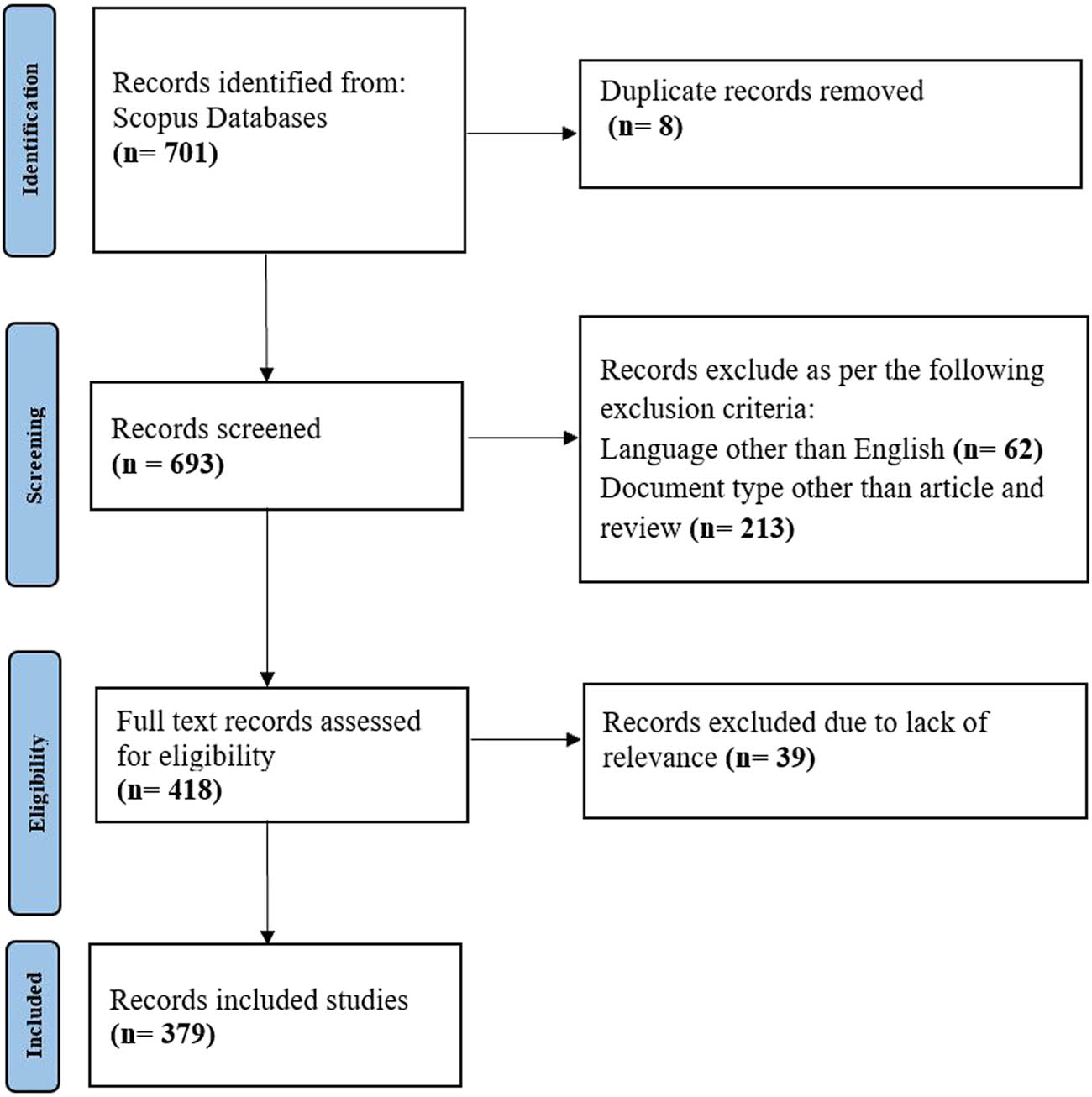
PRISMA diagram illustrating the data collection, processing, and selection process.
2.2 Data analysis
The data analysis stage consisted of two main components: bibliometric and content analysis. These analyses aimed to understand the paver block research landscape comprehensively, identifying prominent themes, trends, and gaps.
2.2.1 Bibliometric analysis
The bibliometric analysis, a quantitative approach, focused on several key indicators, including publication evolution over time, geographical distribution, and collaboration among countries, influential sources of publication, productive authors and their collaboration networks, and keyword occurrence and co-occurrence analyses [36,37]. Tableau was used to create visualizations and graphs, while VOSviewer software (version 1.6.17) was employed to generate and analyze bibliometric networks, such as co-authorship, keyword co-occurrence, and citation linkages [38].
2.2.2 Content analysis
To complement the quantitative bibliometric analysis, a qualitative content analysis was conducted on the top ten most cited articles in the paver block literature [39]. The content analysis examined the research objectives, methodologies, key findings, and implications of these influential studies. Particular attention was given to the incorporation of waste materials in paver block production, innovative design strategies for enhancing paver block performance and sustainability, and the optimization of mix designs and processing techniques. The content analysis aimed to provide a deeper understanding of the most significant contributions and trends in the field and identify potential areas for future research [40]. In summary, this study integrates bibliometric and content analysis to comprehensively and rigorously assess the paver block research landscape. Using Scopus as the data source, along with Excel, Tableau, and VOSviewer for data processing, analysis, and visualization, ensures a transparent and replicable approach to mapping the scientific knowledge in this domain.
3 Results
3.1 Bibliometric analysis
3.1.1 Publication trends
Figure 2 shows the publication evolution in the field of paver block research. The annual scientific production shows a steady growth trend over the years, with some interesting fluctuations. This growth can be attributed to the increasing importance of sustainable construction practices and the need for alternative materials in the construction industry [41,42]. In the early years, from 1983 to 1991, the number of publications remained relatively low, ranging from 1 to 4 per year, with no significant impact on citations. This suggests that the field of paver block research was still in its early stages, with limited interest from the scientific community. However, a noticeable increase in publications started in 1992, with a peak of five publications in 2000. This indicates a growing interest in paver block research during this period, which can be attributed to the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable construction practices. The year 2002 stands out as a remarkable year, with a single publication garnering an impressive 364 citations. This highly influential work, titled “Use of recycled concrete aggregate in concrete paving blocks” by Poon et al. [43], significantly contributed to the field by demonstrating the feasibility of using RCA in paver block production. From 2005 onward, there is a consistent increase in the number of publications, with a substantial rise in citations. The year 2007 marks a significant milestone, with four publications collectively amassing 453 citations, highlighting the impact and relevance of the research conducted during this year. The annual scientific production in paver block research reaches new heights from 2016 to 2024, with a substantial increase in both publications and citations. This upward trend aligns with the global push toward sustainable development goals and the increasing demand for eco-friendly construction materials. The year 2016 saw a surge in publications, with 26 articles published, accompanied by an impressive 782 citations. This growth continues, with the highest number of publications (60) recorded in 2023, demonstrating the growing interest and investment in this field.
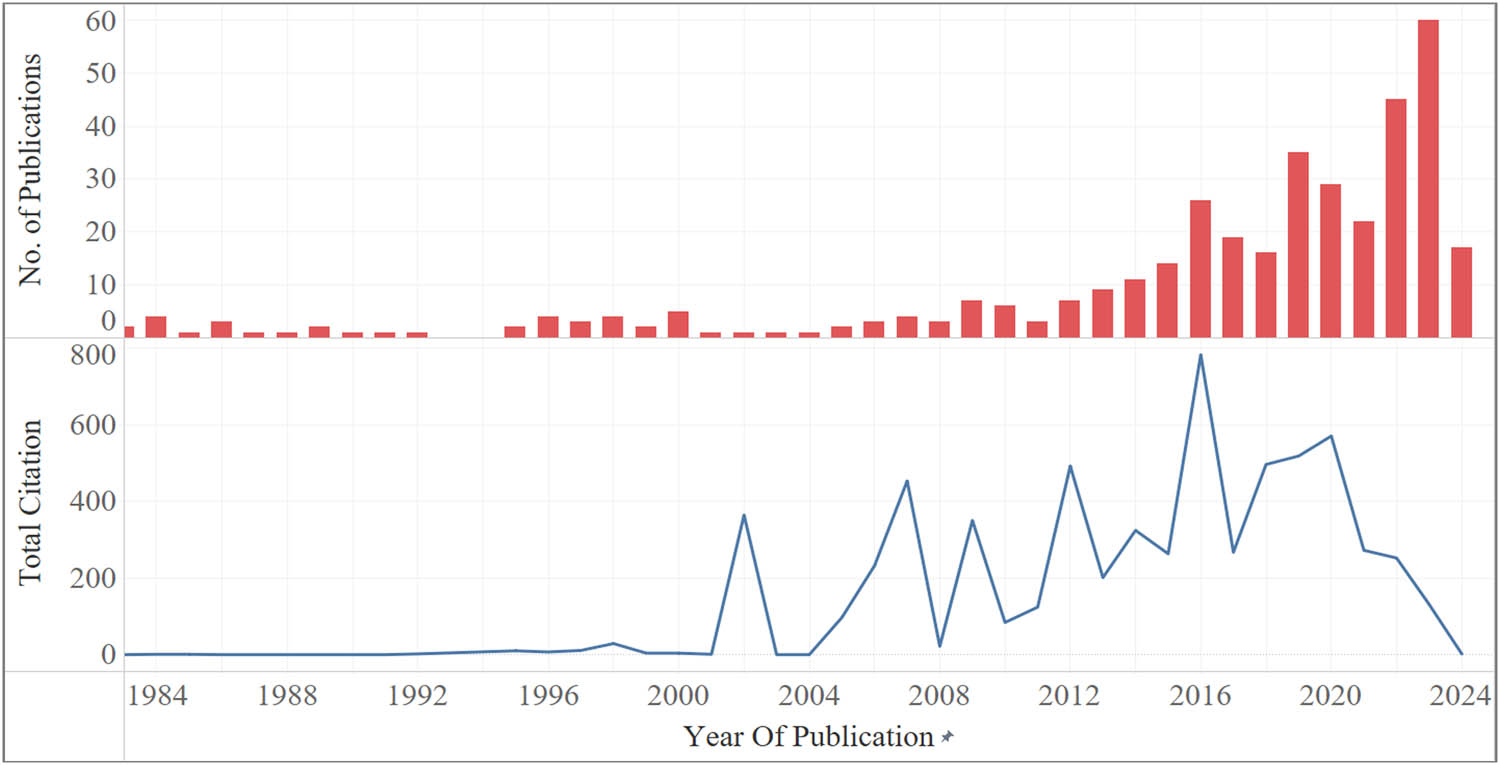
Evolution of publication output and citations for paver block research.
Overall, the analysis of the evolution of publication in the field of paver block research reveals a positive growth trend, with increasing annual scientific production and a corresponding rise in citations. The data highlights the years 2002 and 2007 and the period from 2016 to 2024 as particularly significant in terms of research output and impact, reflecting the ongoing development and importance of this field in sustainable construction practices. The increasing research indicates that the study of paver block is in its “growth stage” and has great potential for further development.
To further investigate the temporal distribution of keywords used in search string, Figure 3 presents a stacked area plot illustrating the frequency of each keyword from 1983 to 2024. This graph reveals the relative prominence and evolution of keywords over time, providing insights into the changing research focus within the paver block domain.
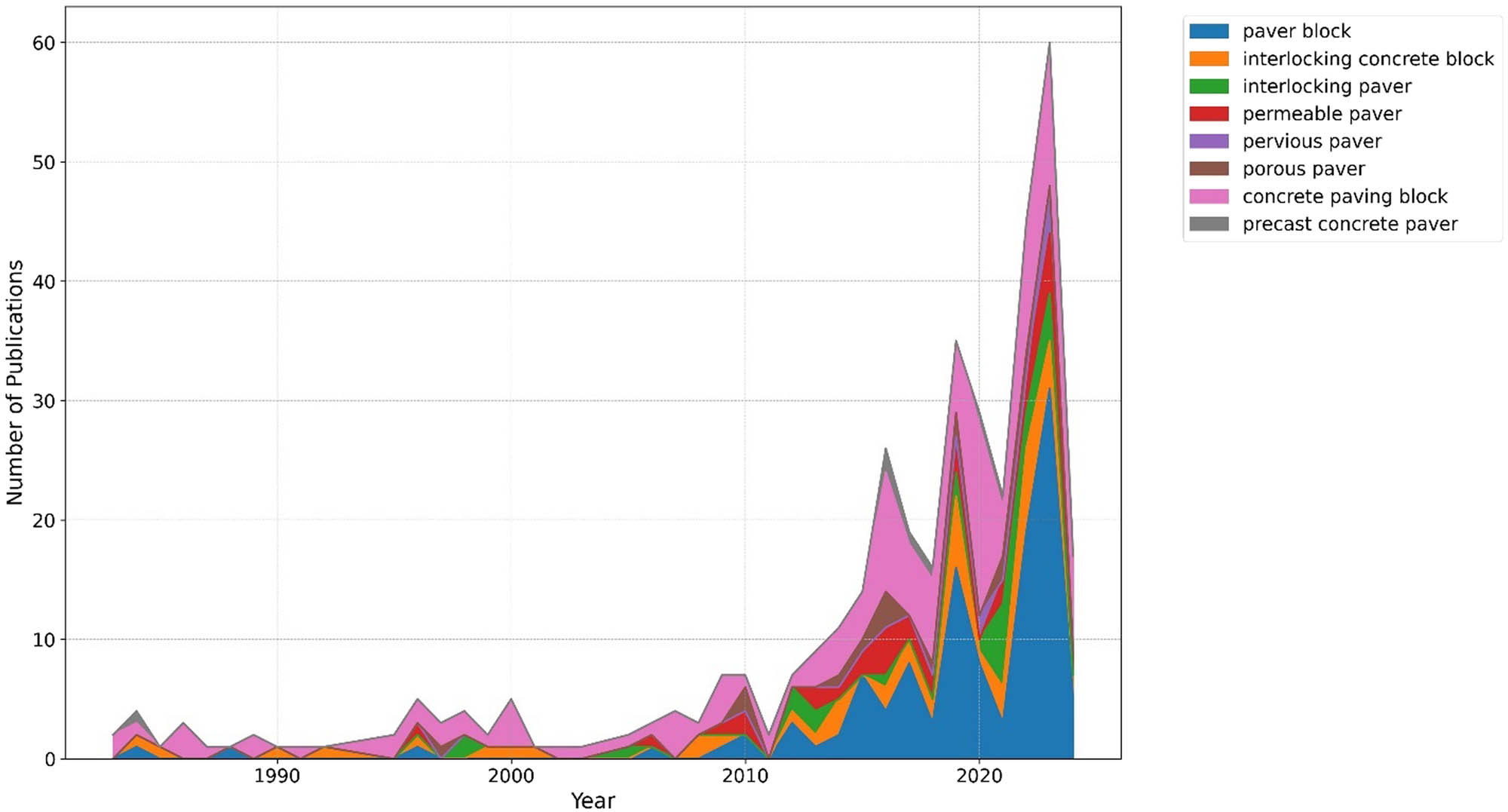
Search string keyword frequency over time.
As shown in Figure 3, the keyword “paver block” has maintained its dominance throughout the years, while other keywords such as “interlocking concrete block,” “permeable paver,” and “concrete paving block” have gained increasing attention, particularly in the last decade. This trend suggests a growing interest in specific paver block types and their functional properties, reflecting the advancements and priorities in paver block research.
3.1.2 Geographical distribution and international collaboration in paver block research
The analysis of the geographical distribution of paver block research, as summarized in Table 1, reveals that India has made the most significant contribution to this field, with 143 publications accounting for 37.73% of the total. This high productivity may be attributed to the rapid urbanization and infrastructure development in India, which has spurred interest in sustainable construction materials like paver blocks. Malaysia follows India with 28 publications (7.39%), while the United States ranks third with 27 publications (7.12%). However, the United States leads in terms of total citations (1,312) and citations per paper (48.59), indicating the high impact and visibility of the research originating from this country. Brazil and China also feature prominently, with 22 (5.80%) and 15 (3.96%) publications, respectively. Notably, publications from China have garnered a high number of citations (688), with an average of 45.87 citations per paper, suggesting the influential nature of the research. The United Kingdom, Italy, Canada, Hong Kong, and Spain each contribute between 2.64 and 3.17% of the total publications. Among these, Hong Kong stands out with an exceptionally high number of citations per paper (129.70), indicating the significant impact of the research from this region.
Global scientific productivity
| Countries | No. of publications (P) | Publication (%) | Total citation (TC) | TC/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| India | 143 | 37.73 | 1,286 | 9.0 |
| Malaysia | 28 | 7.39 | 332 | 11.9 |
| United States | 27 | 7.12 | 1,312 | 48.6 |
| Brazil | 22 | 5.80 | 306 | 13.9 |
| China | 15 | 3.96 | 688 | 45.9 |
| United Kingdom | 12 | 3.17 | 347 | 28.9 |
| Italy | 12 | 3.17 | 123 | 10.3 |
| Canada | 11 | 2.90 | 157 | 14.3 |
| Hong Kong | 10 | 2.64 | 1,297 | 129.7 |
| Spain | 10 | 2.64 | 179 | 17.9 |
The international collaboration network among countries involved in paver block research, as shown in Figure 4, reveals three main clusters of cooperation, showcasing the global nature of this research field. The first cluster, represented in red, includes China, Germany, Spain, Sri Lanka, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States, suggesting a strong collaborative relationship among these countries. The United States and China appear to be the key players in this cluster, likely due to their significant research output and influence in the field. Moreover, both countries have a high number of citations per paper (48.59 for the United States and 45.87 for China), indicating the substantial impact of their collaborative research. The second cluster, depicted in green, comprises Egypt, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Malaysia, Pakistan, Poland, and Saudi Arabia, indicating active collaboration among these countries. Malaysia seems to be a central node in this cluster, possibly as a bridge connecting the other countries. This is consistent with the geographical distribution data, which places Malaysia as the second most productive country. The high average citations per paper (11.86) for Malaysia further highlight the significance of its collaborative efforts within this cluster. The third cluster, shown in blue, consists of Australia, Canada, India, Italy, and South Korea, with India appearing to be the most prominent collaborator within this group. The role of India in this cluster is not surprising, given its top position in the geographical distribution of paver block research. These clusters reveal interesting trends and differences among countries. For example, while India leads in publication count, the United States and China demonstrate higher citation impacts, suggesting a difference in the influence and visibility of their research. Additionally, countries like Malaysia and India play central roles in connecting researchers from different regions, facilitating international collaboration.
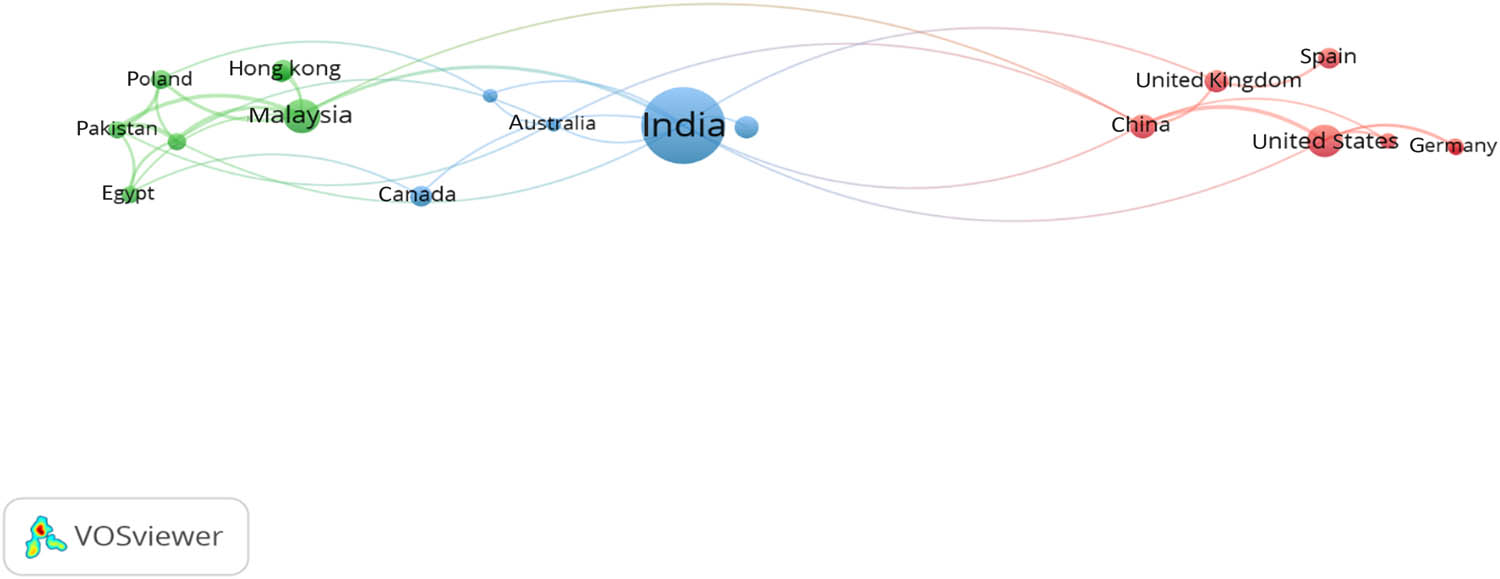
International collaboration network for paver block research.
Interestingly, some countries, such as Hong Kong and Italy, despite having a relatively lower number of publications (10 and 12, respectively) have established strong collaborative ties within their clusters. This suggests that the quality and impact of research, as indicated by the high citations per paper (129.70 for Hong Kong and 10.25 for Italy), may play a crucial role in fostering international collaboration. The key players identified within each cluster, such as the United States, China, Malaysia, and India, have not only contributed significantly to the research output but have also played a vital role in connecting researchers from different countries, facilitating knowledge exchange, and driving innovation in paver block research.
3.1.3 Analysis of the top ten most influential journals in paver block research
The analysis of the top ten most influential journals in paver block research, as listed in Table 2, reveals several interesting findings. Out of the 379 research articles and reviews published across 174 journals, the top ten journals collectively account for 33.86% of the total publications (Figure 5), indicating their significant contribution to the field. Construction and Building Materials emerges as the most prolific journal, with 28 publications (7.39%) and an impressive total citation count of 1,581, resulting in the highest citation per paper ratio (56.46) among the top ten journals. The journal’s h-index of 259 further underscores its substantial impact on the field. Journal of Cleaner Production follows closely, with 12 publications (3.17%) and the second-highest total citation count of 1,100, translating to an average of 91.67 citations per paper and an h-index of 309, which is the highest among the listed journals. This suggests that the journal publishes highly influential and widely cited research in the area of sustainable construction materials, including paver blocks.
Publication metrics of top ten related journals
| Journal name | No. of publications (P) | Publication (%) | Total citation (TC) | TC/P | h-index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction and Building Materials | 28 | 7.39 | 1,581 | 56.46 | 259 |
| Materials Today: Proceedings | 17 | 4.49 | 32 | 1.88 | 88 |
| Concrete Precasting Plant and Technology | 14 | 3.69 | 2 | 0.14 | 11 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 12 | 3.17 | 1,100 | 91.67 | 309 |
| Case Studies in Construction Materials | 12 | 3.17 | 311 | 25.92 | 62 |
| Road Materials and Pavement Design | 11 | 2.90 | 114 | 10.36 | 65 |
| Indian Concrete Journal | 9 | 2.37 | 13 | 1.44 | 28 |
| Erosion Control | 9 | 2.37 | 1 | 0.11 | 3 |
| Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering | 8 | 2.11 | 182 | 22.75 | 138 |
| International Journal of Pavement Engineering | 7 | 1.85 | 33 | 4.71 | 67 |
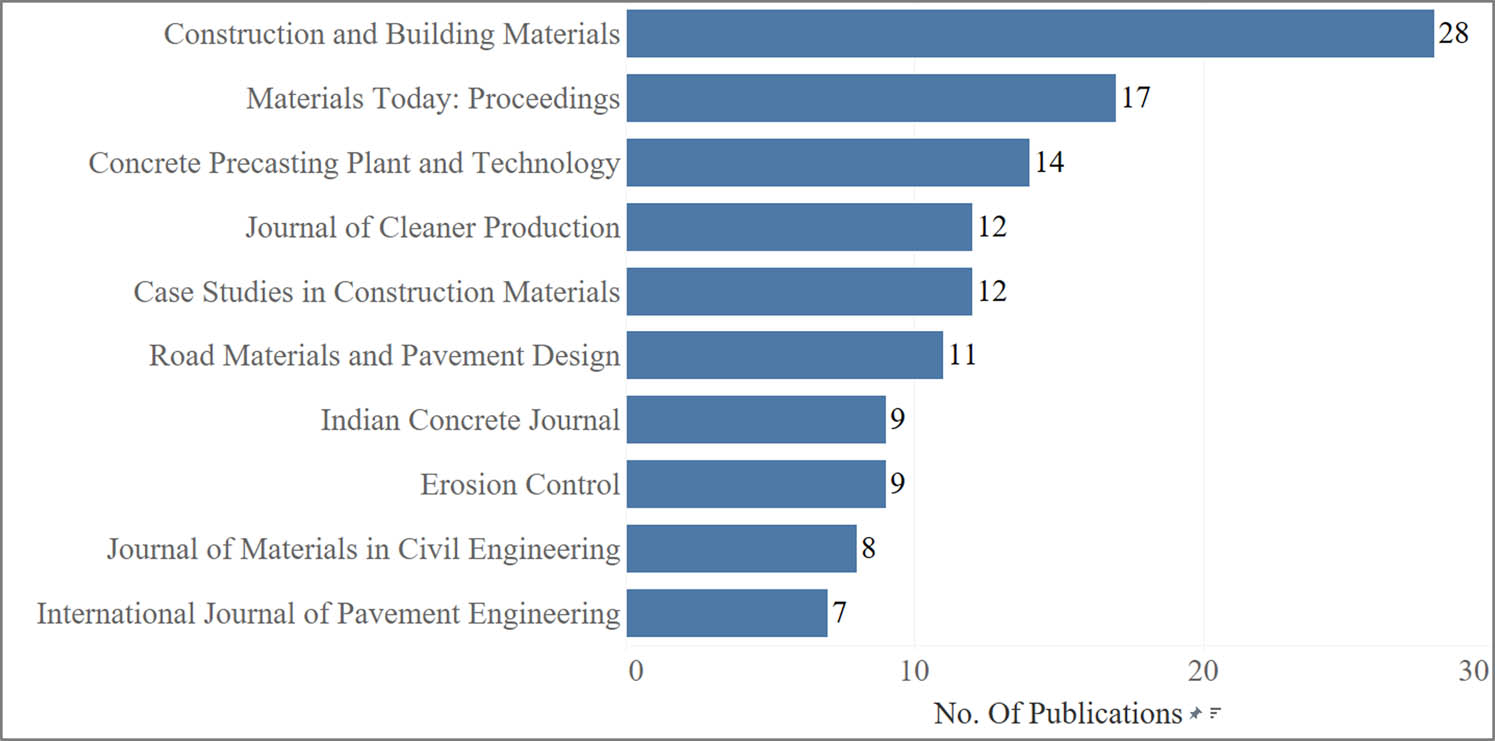
Top ten most prolific journals.
It is noteworthy that Materials Today: Proceedings has published 17 articles (4.49%) on paver block research, indicating a growing interest in this topic among material science researchers. However, the relatively low citation count (32) and average citations per paper (1.88) suggest that these articles may be more recent or focused on niche aspects of paver block research. On the other hand, journals such as Case Studies in Construction Materials and Road Materials and Pavement Design have published fewer articles (12 and 11, respectively) but have garnered higher average citations per paper (25.92 and 10.36, respectively), indicating the publication of impactful research.
The presence of journals from various disciplines, such as construction materials (Construction and Building Materials, Case Studies in Construction Materials), cleaner production (Journal of Cleaner Production), pavement engineering (Road Materials and Pavement Design, International Journal of Pavement Engineering), and civil engineering (Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering), highlights the multidisciplinary nature of paver block research. This diversity in journal scope suggests that paver block research encompasses a wide range of aspects, including material properties, sustainability, pavement design, and civil engineering applications.
In total, the 379 research articles and reviews published in the 174 journals have amassed an impressive 6,366 citations, emphasizing the growing interest and impact of paver block research. The analysis of the top ten most influential journals provides valuable insights into the key players driving the advancement of this field and the multidisciplinary nature of the research being conducted.
3.1.4 Most productive authors and their collaboration
Table 3 presents the productivity and citation impact of the leading authors in paver block research. The analysis of the top ten most productive authors in paver block research reveals intriguing insights into the distribution of research output and impact across countries and individuals. Sunitha V. and Arjun Siva Rathan R.T. from India lead the list with nine publications each, followed by Poon C.S. from Hong Kong with eight publications. However, when considering the total citations and average citations per publication, Poon C.S. stands out with an impressive 1,154 total citations and an average of 144.25 citations per paper, indicating the high impact and influence of their work. Ling T.C. from China also demonstrates a strong research impact, with six publications garnering 401 total citations and an average of 66.83 citations per paper. Interestingly, while Sunitha V. and Arjun Siva Rathan R.T. have the highest number of publications, all nine of Arjun Siva Rathan R.T.’s papers are first-authored, whereas Sunitha V. has no first-author publications (Figure 6), suggesting a potential mentorship or collaboration dynamic between the two researchers. Bahurudeen A., another researcher from India, has five publications with a notable average of 43.40 citations per paper despite no first-author publications. The presence of multiple authors from India, Malaysia, and Pakistan among the top ten most productive researchers highlights the significant contributions of these countries to paver block research.
Productivity and citation impact of leading authors in paver block research
| Author | Country | No. of publications (P) | Total citation (TC) | TC/P | First author publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunitha V. | India | 9 | 30 | 3.33 | 0 |
| Arjun Siva Rathan R.T. | India | 9 | 30 | 3.33 | 9 |
| Poon C.S. | Hong Kong | 8 | 1,154 | 144.25 | 3 |
| Nor H.M. | Malaysia | 7 | 114 | 16.29 | 0 |
| Ling T.C. | China | 6 | 401 | 66.83 | 5 |
| Bahurudeen A. | India | 5 | 217 | 43.40 | 0 |
| Javed M.F. | Pakistan | 5 | 49 | 9.80 | 0 |
| Nandi S. | India | 5 | 28 | 5.60 | 5 |
| Iftikhar B. | Malaysia | 4 | 39 | 9.75 | 4 |
| Vafaei M. | Malaysia | 4 | 39 | 9.75 | 0 |
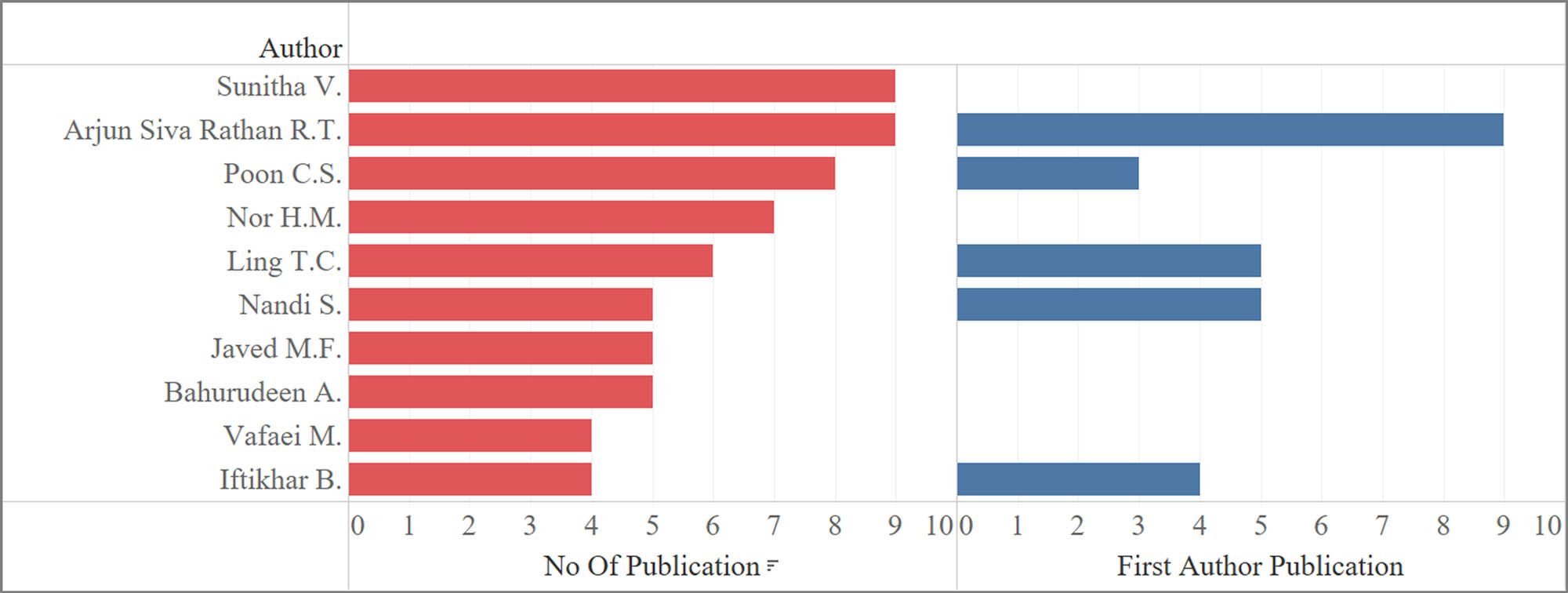
Comparison of total publications and first-author contributions among paver block researchers.
To gain insights into the collaboration patterns among authors in paver block research, a co-authorship network (Figure 7) was generated using VOSviewer, with the condition that a minimum of three co-authored documents per author was required for inclusion. Out of 1,072 authors who have published papers on paver blocks, only 39 met this criterion, suggesting that extensive collaboration among authors is relatively limited. The network diagram reveals the formation of several small clusters, indicating that collaborations tend to occur within specific research groups or institutions rather than spanning a wide network of authors. The largest cluster centers around the partnership between Poon C.S. and Ling T.C., two highly influential authors in the field, as evidenced by their high citation counts and average citations per paper. This strong collaboration likely contributes to their significant impact on paver block research. Other notable clusters include the collaboration between Sunitha V. and Arjun Siva Rathan R.T., who have co-authored all nine of their publications, as well as a group of authors from Malaysia, including Iftikhar B., Vafaei M., and Nor H.M. The relatively isolated nature of these clusters suggests that there may be opportunities for increased cross-institutional and international collaboration in paver block research, which could potentially lead to more diverse perspectives and innovative approaches in the field.
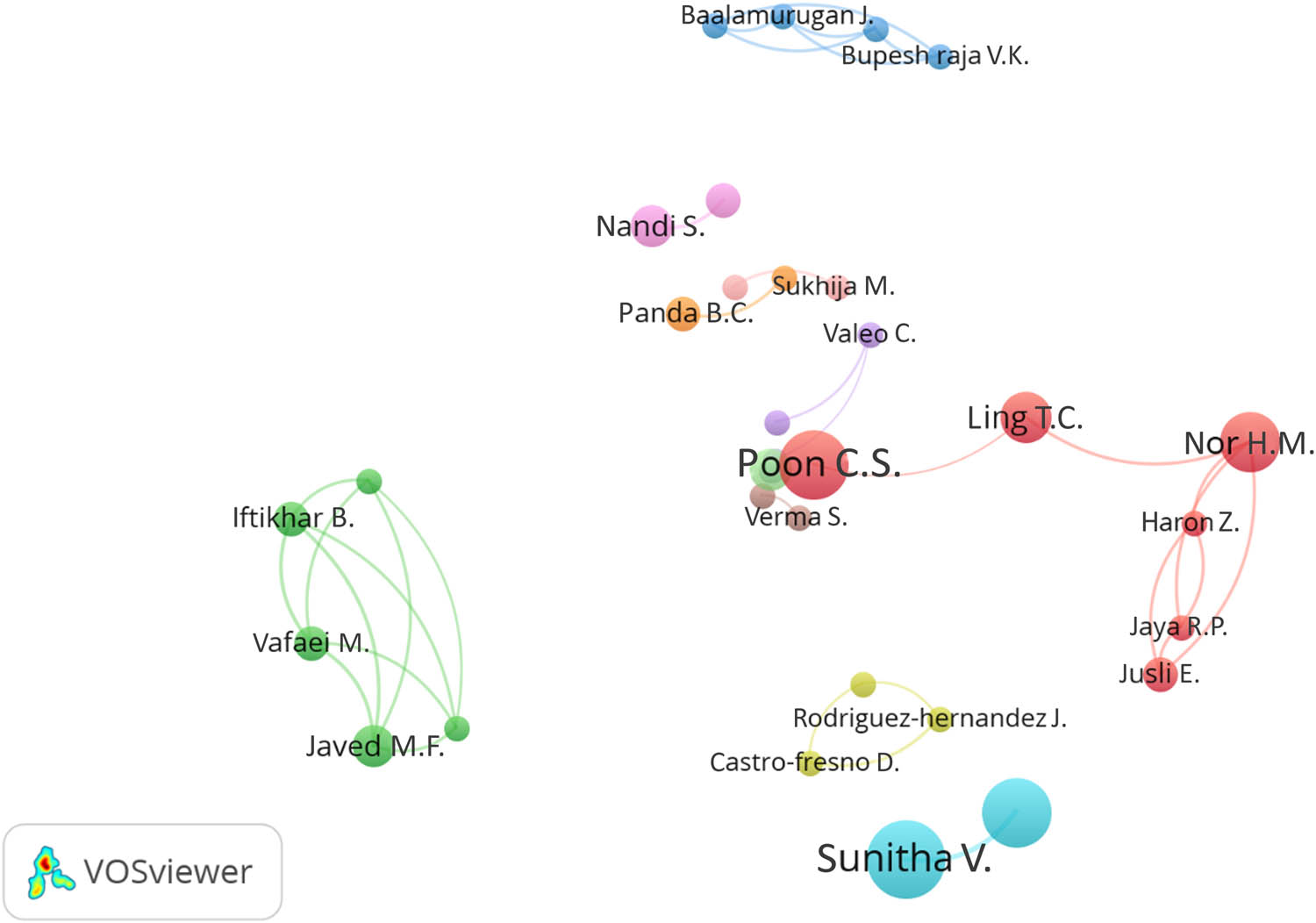
Co-authorship network of paver block researchers.
3.1.5 Keyword occurrence frequency and co-occurrence analysis
The keyword occurrence frequency and co-occurrence network provide valuable insights into the research trends and hotspots within the field of paver block research. The keyword data have been cleaned to ensure clarity and consistency by converting plurals to singulars, expanding abbreviations to full forms, and unifying synonymous terms. The analysis of the refined keyword occurrence frequency reveals that “paver block” is the most prominent keyword, appearing 85 times, followed by “compressive strength” (49 occurrences), “concrete paver block” (44 occurrences), and “concrete” (29 occurrences) (Figure 8). The high frequency of these keywords strongly suggests that the primary focus of research in this field has been on the mechanical properties and performance of paver blocks, with concrete being the most widely studied material.
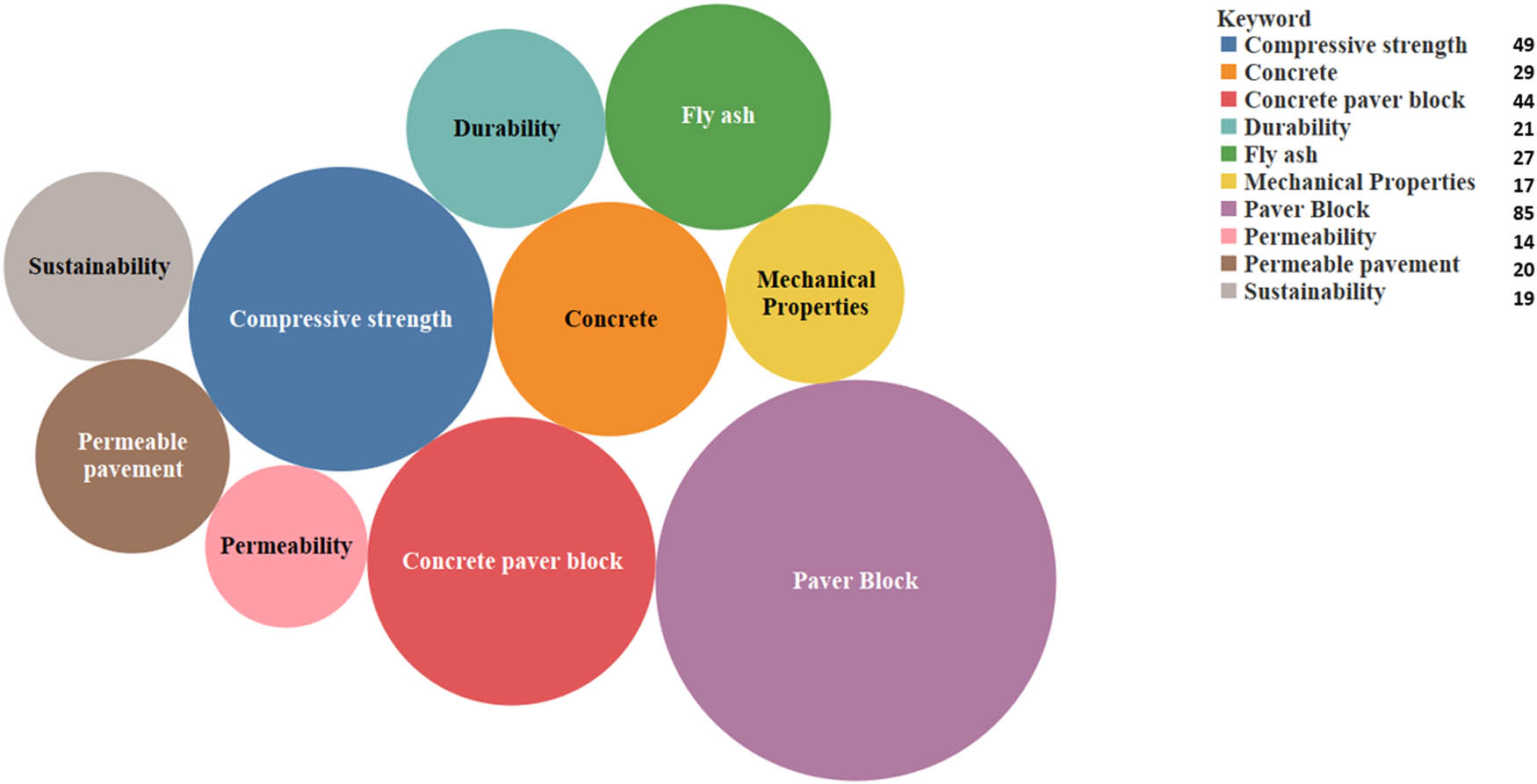
Top ten keywords with highest occurrence frequency.
The keyword data highlight the increasing importance of sustainability and eco-friendly materials in paver block research. “Fly ash,” a waste material from coal-fired power plants, appears 27 times, indicating its growing use as a sustainable alternative to traditional cement in paver block production. The keyword “sustainability” itself occurs 19 times, underscoring the rising emphasis on developing environmentally friendly paver block solutions. Furthermore, the presence of keywords such as “permeable pavement” (20 occurrences) and “permeability” (14 occurrences) reflects the growing interest in the design and development of paver blocks that can facilitate stormwater management and reduce urban runoff.
The refined keyword data also emphasize the significance of long-term performance and durability in paver block research. “Durability” appears 21 times, while “mechanical properties” occur 17 times, highlighting the need to investigate the longevity and structural integrity of paver blocks under various environmental conditions. This focus on durability and mechanical properties is crucial for ensuring the successful application of paver blocks in real-world scenarios and promoting their widespread adoption in the construction industry.
The network visualization of the keyword co-occurrence (Figure 9) further elucidates the main research areas within the paver block domain. The largest cluster (red) focuses on permeable pavements, with prominent keywords such as “permeability, “permeable pavement,” “stormwater,” and “pervious concrete,” emphasizing the significant research attention given to the development and analysis of paver blocks with enhanced water permeability and stormwater management capabilities. The second cluster (green) revolves around the materials and sustainability aspects of paver blocks, with keywords like “fly ash,” “geopolymer,” and “cement,” indicating the exploration of alternative and eco-friendly materials in paver block production. The third cluster (blue) delves into the engineering properties and recycling, as evident from keywords such as “reclaimed asphalt pavement,” “recycled aggregate,” and “durability.”

Keyword network visualization for paver block research.
The smaller clusters in the network visualization provide further insights into specific research areas. The fourth cluster (yellow) focuses on specific mechanical properties and materials, such as “compressive strength,” “density,” and “crumb rubber,” while the fifth cluster (violet) is centered around the interlocking nature and optimization of paver blocks. The sixth cluster (cyan) represents the basic constituents of paver blocks, such as “coarse aggregate.”
The interconnectedness of the clusters in the keyword co-occurrence network suggests that researchers are exploring the synergies between different aspects of paver blocks, such as materials, mechanical properties, and environmental performance, to develop holistic and sustainable solutions. The presence of clusters related to recycled materials and waste utilization underscores the growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles in paver block research, aligning with the findings from the keyword occurrence frequency analysis.
3.2 Content analysis of top ten highly cited papers
3.2.1 Review of the most prominent paver block studies
Figure 10 shows the top ten most influential publications on concrete paving blocks, which are all research articles. Most of these studies focused on the incorporation of various waste materials, such as recycled aggregates, waste marble, cathode ray tube (CRT) glass, and marble sludge, in the production of concrete paving blocks. The findings demonstrate the feasibility of utilizing these waste materials as partial replacements for natural aggregates or cement while maintaining or even enhancing the properties of the resulting paving blocks.

Ten most cited academic papers.
Several studies investigated the use of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste in paving blocks [43,44]. These studies found that replacing natural aggregates with recycled aggregates at levels up to 50% had minimal impact on the compressive strength of the blocks while increasing the transverse strength. The incorporation of common construction and demolition waste contaminants, such as crushed clay brick, tiles, glass, and wood chips, at a level of 10% in RCAs was found to be acceptable without significantly compromising the quality of the paving blocks [44].
The application of photocatalytic materials, particularly titanium dioxide (TiO2), in concrete paving blocks for air purification purposes, was explored in several studies [45,46]. These studies investigated the influence of mixed design parameters, such as TiO2 type, content, and application method, on the pollutant degradation efficiency of the paving blocks. The findings indicated that optimal mix designs, incorporating finer TiO2 powder, higher TiO2 dosages, and the use of recycled materials like glass aggregates, could enhance the photocatalytic performance of the blocks.
The utilization of waste marble and marble sludge as replacements for natural aggregates and cement, respectively, in paving blocks was also investigated [47,48]. These studies found that the incorporation of waste marble decreased the compressive strength but improved the freeze–thaw durability and abrasion resistance of the paving blocks. Marble sludge, when used as a partial cement replacement at an optimal level of 20%, enhanced the compressive strength, flexural strength, and water absorption of the concrete mixes.
The potential for paving blocks to mitigate stormwater runoff and urban heat island effects was explored by developing permeable and water-retaining paver designs [49,50]. Permeable pavers, such as those made with crushed stone, were found to significantly reduce runoff volume and pollutant discharge compared to conventional asphalt pavement. The novel water-retaining paver blocks demonstrated the ability to temporarily store rainwater for evaporative cooling, thereby reducing surface temperatures and mitigating urban heat island effects.
The use of waste glass, particularly CRT funnel glass, as a fine aggregate in paving blocks was investigated, with a focus on the potential for alkali-silica reaction (ASR) and the effectiveness of mineral admixtures in suppressing ASR expansion [51,52]. These studies found that limiting the CRT glass content to 25% or incorporating an appropriate level of fly ash (10%) could effectively control ASR expansion while maintaining acceptable block properties.
In summary, the content analysis of these influential papers highlights the potential for producing high-quality sustainable concrete paving blocks by incorporating various waste materials and adopting innovative design strategies. The findings support the revision of specifications to allow for higher levels of recycled materials and contaminants in paving block production, thereby promoting the recycling of waste streams. However, careful optimization of mixed designs and processing techniques is necessary to ensure satisfactory performance and durability of the paving blocks.
3.2.2 Gaps and future directions
Based on the content analysis of the ten most influential papers on concrete paving blocks, several potential research gaps and future research directions can be identified:
Long-term performance and durability: While the reviewed studies investigated various properties of paving blocks incorporating waste materials, there is a need for more research on the long-term performance and durability of these products under real-world conditions. Future studies should focus on assessing the resistance of these paving blocks to weathering, traffic loading, and other environmental factors over extended periods.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) and environmental impact: Although the incorporation of waste materials in paving blocks contributes to sustainability by diverting these materials from landfills, a comprehensive LCA of the environmental impact of these products is necessary. Future research should quantify the net environmental benefits of using waste materials in paving blocks, considering factors such as energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion throughout the product life cycle.
Optimization of mix designs and processing techniques: While the reviewed studies explored various mix designs and processing techniques for incorporating waste materials in paving blocks, there is potential for further optimization to maximize waste utilization and enhance product performance. Future research should investigate advanced mix design strategies, such as using nanomaterials or chemical admixtures, and innovative processing techniques, like 3D printing or extrusion, to improve the properties and sustainability of paving blocks.
Combination of multiple waste streams: Most reviewed studies focused on incorporating a single type of waste material in paving blocks. Future research could explore the feasibility and synergistic effects of combining multiple waste streams, such as recycled aggregates, waste glass, and marble sludge, in a single paving block product. This approach could further enhance the sustainability and performance of the blocks.
Photocatalytic efficiency and air purification performance: While some studies investigated the photocatalytic properties of paving blocks containing TiO2, more research is needed to optimize the pollutant degradation efficiency and assess the real-world air purification performance of these products. Future studies should evaluate the long-term stability and effectiveness of photocatalytic paving blocks under various environmental conditions and explore novel photocatalytic materials and activation methods.
Stormwater management and urban heat island mitigation: The reviewed studies highlighted the potential of permeable and water-retaining paving blocks for mitigating stormwater runoff and urban heat island effects. However, further research is needed to quantify the hydrological and thermal performance of these products at a larger scale and under different climatic conditions. Future studies should also investigate the integration of these paving blocks with other sustainable urban drainage systems and green infrastructure elements.
Economic and social implications: While the technical feasibility of incorporating waste materials in paving blocks has been demonstrated, research is needed on the economic and social implications of adopting these sustainable products. Future studies should assess the cost-effectiveness, market acceptance, and societal benefits of using sustainable paving blocks, considering factors such as raw material availability, production costs, and public perception.
Policy and standardization: To facilitate the widespread adoption of sustainable paving blocks, research is needed to inform policy development and standardization efforts. Future studies should engage with policymakers, industry stakeholders, and standardization bodies to develop guidelines, specifications, and incentives that promote the use of waste materials in paving block production and ensure the quality and consistency of these products.
4 Discussion
The bibliometric and content analysis of trends in paver block research has revealed a wealth of insights into the evolution and current state of this field. The steady growth in research output, punctuated by influential papers, underscores the increasing importance and impact of paver block research. The global nature of this field is evident from the geographical distribution of publications, with countries like India, Malaysia, and the United States leading in terms of quantity, while the United States, China, and Hong Kong demonstrate high citation rates, indicating the quality and impact of their research.
Analyzing the most influential journals and authors paints a picture of a multidisciplinary field shaped by key players from various domains, including construction materials, cleaner production, pavement engineering, and civil engineering. However, the co-authorship network reveals a relatively limited degree of collaboration among researchers, suggesting untapped potential for cross-institutional and international partnerships to drive innovation and address complex challenges in paver block technology.
The keyword analysis and content analysis of the top ten highly cited papers bring to the fore the central themes and research focus areas within paver block technology. The emphasis on sustainable materials, waste utilization, and innovative design strategies emerges as a common thread, with studies exploring the incorporation of various waste streams, such as recycled aggregates, waste glass, and marble sludge, into paver block production. The content analysis also highlights the potential of paver blocks to address pressing environmental challenges, such as stormwater management and urban heat island mitigation, by developing permeable and water-retaining paver designs.
These findings have significant implications for both research and practice in the field of paver block technology. The growing body of evidence supporting the feasibility and benefits of incorporating waste materials into paver block production calls for a paradigm shift toward a circular economy approach in the construction industry. This shift requires close collaboration between researchers and practitioners to translate research findings into industry guidelines, best practices, and standards that promote the widespread adoption of sustainable paver block solutions.
Moreover, the potential of paver blocks to contribute to sustainable urban development through their multifunctional benefits in stormwater management and urban heat island mitigation opens up new avenues for integrating paver blocks into urban planning and design strategies. Planners, designers, and policymakers should leverage these findings to create enabling frameworks and incentives that encourage the implementation of innovative paver block solutions in urban environments.
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of this study, such as its reliance on a single database (Scopus) and the focus on a specific set of bibliometric indicators and content analysis criteria. One potential limitation is the language bias, as publications from countries like Brazil, China, and European nations in their native languages might not be fully represented in the Scopus database. This bias could lead to an underestimation of the research contributions from these countries. Moreover, there may be a significant number of implemented paver block constructions, particularly in China, that are not associated with published research. Consequently, the research output analyzed in this study may not fully capture the actual extent of paver block implementation in some countries. Future studies could explore ways to include non-English publications and gather data on unpublished constructions to provide a more comprehensive picture of the global paver block landscape. Further studies could also expand the data sources to include other databases like Web of Science, explore additional indicators such as patent analysis and research funding patterns, and investigate the broader social, economic, and policy dimensions of paver block technology.
5 Conclusion
This study set out to achieve two primary objectives. The first objective was to delineate the research trends, main themes, and research collaborations in paver block research through bibliometric analysis. The second objective was to summarize the status quo results, knowledge gaps, and future directions through content analysis. The bibliometric analysis revealed a steady growth in research output, punctuated by influential papers, underscoring the increasing importance and impact of paver block research. The analysis of the geographical distribution of publications highlighted the global nature of this field, with countries like India, Malaysia, and the United States leading in terms of quantity, while the United States, China, and Hong Kong demonstrated high citation rates, indicating the quality and impact of their research. The co-authorship network analysis revealed a relatively limited degree of collaboration among researchers, suggesting untapped potential for cross-institutional and international partnerships to drive innovation and address complex challenges in paver block technology.
The content analysis of the top ten highly cited papers brought to the fore the central themes and research focus areas within paver block technology. The emphasis on sustainable materials, waste utilization, and innovative design strategies emerged as a common thread, with studies exploring the incorporation of various waste streams, such as recycled aggregates, waste glass, and marble sludge, into paver block production. The content analysis also highlighted the potential of paver blocks to address pressing environmental challenges, such as stormwater management and urban heat island mitigation, by developing permeable and water-retaining paver designs.
By integrating bibliometric and content analysis, this study provided a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the research trends, main themes, research collaborations, status quo results, knowledge gaps, and future directions in paver block research. The insights gained from this approach can inform and guide researchers, practitioners, and policymakers in advancing sustainable and high-performance paver block solutions. As the construction industry increasingly embraces the principles of a circular economy and sustainable development, the future of paver block research is filled with opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and transformative impact.
Continued research efforts, cross-disciplinary partnerships, and the effective translation of research findings into industry practices and policies will be crucial for realizing the full potential of paver blocks in creating a more sustainable, resilient, and livable built environment. By building upon the findings of this study and addressing the identified challenges and opportunities, researchers and stakeholders can drive meaningful progress toward a future where paver blocks play a central role in shaping sustainable cities and communities worldwide.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the peer reviewers for their insightful and helpful comments.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and consented to its submission to the journal, reviewed all the results and approved the final version of the manuscript. HC has acquired or interpreted the data, wrote the manuscript, and drew the figures and table. SPSR has reviewed and revised the manuscript. AM has drawn the figures, reviewed and revised the manuscript, and helped in data curation.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Data generated or analyzed during this study are provided within the article.
References
[1] Yeo JS, Koting S, Onn CC, Mo KH. An overview on the properties of eco-friendly concrete paving blocks incorporating selected waste materials as aggregate. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2021;28(23):29009–36.10.1007/s11356-021-13836-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Iftikhar B, Alih SC, Vafaei M, Ali M, Javed MF, Asif U, et al. Experimental study on the eco-friendly plastic-sand paver blocks by utilising plastic waste and basalt fibers. Heliyon. 2023;9(6):1–12.10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17107Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Nandi S, Ransinchung GDRN. Laboratory investigation of Portland cement concrete paver blocks made with reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. Road Mater Pavement Des. 2022;23(3):546–64.10.1080/14680629.2020.1830153Search in Google Scholar
[4] Ahmad S, Dawood O, Lashin MMA, Khattak SU, Javed MF, Aslam F, et al. Effect of coconut fiber on low-density polyethylene plastic-sand paver blocks. Ain Shams Eng J. 2023;14(8):101982.10.1016/j.asej.2022.101982Search in Google Scholar
[5] Velumani P, Senthilkumar S. Production of sludge-incorporated paver blocks for efficient waste management. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2018;68(6):626–36.10.1080/10962247.2017.1395373Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Fwa TF. Concrete slabs and blocks for car park paving. Transp Res Rec. 1987;1127:63.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Angelin Lincy G, Velkennedy R. Experimental optimization of metakaolin and nanosilica composite for geopolymer concrete paver blocks. Struct Concr. 2021;22(S1):E442–451.10.1002/suco.201900555Search in Google Scholar
[8] Iftikhar B, Alih SC, Vafaei M, Javed MF, Rehman MF, Abdullaev SS, et al. Predicting compressive strength of eco-friendly plastic sand paver blocks using gene expression and artificial intelligence programming. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):12149.10.1038/s41598-023-39349-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Singh S, Ransinchung GDRN, Kumar P. Feasibility study of RAP aggregates in cement concrete pavements. Road Mater Pavement Des. 2019;20(1):151–70.10.1080/14680629.2017.1380071Search in Google Scholar
[10] Brand AS, Roesler JR. Ternary concrete with fractionated reclaimed asphalt pavement. ACI Mater J. 2015;112(1):155–64.10.14359/51687176Search in Google Scholar
[11] Poon CS, Chan D. Paving blocks made with recycled concrete aggregate and crushed clay brick. Constr Build Mater. 2006;20(8):569–77.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.01.044Search in Google Scholar
[12] Ghafoori N, Sukandar BM. Abrasion resistance of concrete block pavers. ACI Mater J. 1995;92(1):25–36.10.14359/1174Search in Google Scholar
[13] Saraswat P, Singh B. Utilization of recycled concrete aggregates in LDPE-bonded cementless paver blocks. Constr Build Mater. 2024;419:135467.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135467Search in Google Scholar
[14] Wang X, Chin CS, Xia J. Material characterization for sustainable concrete paving blocks. Appl Sci (Switz). 2019;9(6):1197.10.3390/app9061197Search in Google Scholar
[15] Settari C, Debieb F, Kadri EH, Boukendakdji O. Assessing the effects of recycled asphalt pavement materials on the performance of roller compacted concrete. Constr Build Mater. 2015;101:617–21.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.039Search in Google Scholar
[16] Shi X, Mukhopadhyay A, Liu KW. Mix design formulation and evaluation of portland cement concrete paving mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Constr Build Mater. 2017;152:756–68.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.06.174Search in Google Scholar
[17] Nandi S, Naga GRR, Sahdeo SK. Utilization of wollastonite, jarosite, and their blends for the sustainable development of concrete paver block mixes containing reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2024;31(13):20048–72.10.1007/s11356-024-32338-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Iqbal MF, Javed MF, Rauf M, Azim I, Ashraf M, Yang J, et al. Sustainable utilization of foundry waste: forecasting mechanical properties of foundry sand based concrete using multi-expression programming. Sci Total Environ. 2021;780:146524.10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146524Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Parashar A, Aggarwal P, Saini B, Aggarwal Y, Bishnoi S. Study on performance enhancement of self-compacting concrete incorporating waste foundry sand. Constr Build Mater. 2020;251:118875.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118875Search in Google Scholar
[20] Ahirrao SP, Borse KN, Bagrecha S. Eco-friendly pavement blocks of waste glass fly ash and dust. Int J Civ Struct Environ Infrastruct Eng Res Dev. 2013;3(5):75–8.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Hamza M, Shahzada K, Iqbal M, Khan EA. Evaluation of mechanical properties of paver blocks by replacing cement with fly ash and marble waste. Discov Appl Sci. 2024 May;6(5):221.10.1007/s42452-024-05843-zSearch in Google Scholar
[22] Chindaprasirt P, Sinsiri T, Napia C, Jaturapitakkul C. Solidification of heavy metal sludge using cement, fly ash and silica fume. Indian J Eng Mater Sci. 2013;20(5):405–14.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Sarath Chandra Kumar B, Ramesh K. Experimental study on strength properties of metakaolin and GGBS based geopolymer concrete. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci. 2016;11(21):12414–22.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Sandanayake M, Bouras Y, Haigh R, Vrcelj Z. Current sustainable trends of using waste materials in concrete—a decade review. Sustainability (Switz). 2020;12:9622.10.3390/su12229622Search in Google Scholar
[25] Iftikhar B, Alih SC, Vafaei M, Alrowais R, Bashir MT, Khalil A, et al. A scientometric analysis approach on the plastic sand. Heliyon. 2023;9:e14457.10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14457Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Farooq R. A review of knowledge management research in the past three decades: a bibliometric analysis. VINE J Inf Knowl Manag Syst. 2024;54(2):339–78.10.1108/VJIKMS-08-2021-0169Search in Google Scholar
[27] Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2021;133:285–96.10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070Search in Google Scholar
[28] Ospina-Mateus H, Quintana Jiménez LA, Lopez-Valdes FJ, Salas-Navarro K. Bibliometric analysis in motorcycle accident research: a global overview. Scientometrics. 2019;121(2):793–815.10.1007/s11192-019-03234-5Search in Google Scholar
[29] Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F. Science mapping software tools: review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2011;62(7):1382–402.10.1002/asi.21525Search in Google Scholar
[30] van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523–38.10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Paul J, Criado AR. The art of writing literature review: what do we know and what do we need to know? Int Bus Rev. 2020;29(4):101717.10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717Search in Google Scholar
[32] Pizzi S, Caputo A, Corvino A, Venturelli A. Management research and the UN sustainable development goals (SDGs): a bibliometric investigation and systematic review. J Clean Prod. 2020;276:124033.10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124033Search in Google Scholar
[33] Ranjbari M, Saidani M, Shams Esfandabadi Z, Peng W, Lam SS, Aghbashlo M, et al. Two decades of research on waste management in the circular economy: Insights from bibliometric, text mining, and content analyses. J Clean Prod. 2021;314:128009.10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128009Search in Google Scholar
[34] Bhatt Y, Ghuman K, Dhir A. Sustainable manufacturing. Bibliometrics and content analysis. J Clean Prod. 2020;260:120988.10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120988Search in Google Scholar
[35] Cuellar-Pompa L, Rodríguez-Gómez JÁ, Novo-Muñoz MM, Rodríguez-Novo N, Rodríguez-Novo YM, Martínez-Alberto CE. Description and analysis of research on death and dying during the COVID-19 pandemic, Published in Nursing Journals Indexed in SCOPUS. Nurs Rep. 2024 Mar;14(2):655–74.10.3390/nursrep14020050Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Piwowar-Sulej K, Krzywonos M, Kwil I. Environmental entrepreneurship – bibliometric and content analysis of the subject literature based on H-Core. J Clean Prod. 2021;295:126277.10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126277Search in Google Scholar
[37] Wali SB, Hannan MA, Ker PJ, Rahman MA, Mansor M, Muttaqi KM, et al. Grid-connected lithium-ion battery energy storage system: a bibliometric analysis for emerging future directions. J Clean Prod. 2022;334:130272.10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130272Search in Google Scholar
[38] Wahyuningrum IFS, Humaira NG, Budihardjo MA, Arumdani IS, Puspita AS, Annisa AN, et al. Environmental sustainability disclosure in Asian countries: bibliometric and content analysis. J Clean Prod. 2023;411:137195.10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137195Search in Google Scholar
[39] Prashar A, Sunder MV. A bibliometric and content analysis of sustainable development in small and medium-sized enterprises. J Clean Prod. 2020;245:118665.10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118665Search in Google Scholar
[40] Goyal R, Sharma H, Sharma A. A thorough examination of organizations from an ethical viewpoint: a bibliometric and content analysis of organizational virtuousness studies. Bus Ethics Environ Responsib. 2024 Jan;33(1):129–44.10.1111/beer.12597Search in Google Scholar
[41] Vashistha P, Oinam Y, Shi J, Pyo S. Application of lime mud as a sustainable alternative construction material: a comprehensive review of approaches. J Build Eng. 2024;87:109114.10.1016/j.jobe.2024.109114Search in Google Scholar
[42] Panghal H, Kumar A. Enhancing concrete performance: surface modification of recycled coarse aggregates for sustainable construction. Constr Build Mater. 2024;411:134432.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134432Search in Google Scholar
[43] Poon CS, Kou SC, Lam L. Use of recycled aggregates in molded concrete bricks and blocks. Constr Build Mater. 2002;16(5):281–9.10.1016/S0950-0618(02)00019-3Search in Google Scholar
[44] Poon CS, Chan D. Effects of contaminants on the properties of concrete paving blocks prepared with recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater. 2007;21(1):164–75.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.06.031Search in Google Scholar
[45] Hüsken G, Hunger M, Brouwers HJH. Experimental study of photocatalytic concrete products for air purification. Build Environ. 2009;44(12):2463–74.10.1016/j.buildenv.2009.04.010Search in Google Scholar
[46] Poon CS, Cheung E. NO removal efficiency of photocatalytic paving blocks prepared with recycled materials. Constr Build Mater. 2007;21(8):1746–53.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2006.05.018Search in Google Scholar
[47] Gencel O, Ozel C, Koksal F, Erdogmus E, Martínez-Barrera G, Brostow W. Properties of concrete paving blocks made with waste marble. J Clean Prod. 2012;21(1):62–70.10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.08.023Search in Google Scholar
[48] Mashaly AO, El-Kaliouby BA, Shalaby BN, El-Gohary AM, Rashwan MA. Effects of marble sludge incorporation on the properties of cement composites and concrete paving blocks. J Clean Prod. 2016;112:731–41.10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.023Search in Google Scholar
[49] Gilbert JK, Clausen JC. Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from asphalt, paver, and crushed stone driveways in Connecticut. Water Res. 2006;40(4):826–32.10.1016/j.watres.2005.12.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Qin Y, He Y, Hiller JE, Mei G. A new water-retaining paver block for reducing runoff and cooling pavement. J Clean Prod. 2018;199:948–56.10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.250Search in Google Scholar
[51] Ling TC, Poon CS. Use of recycled CRT funnel glass as fine aggregate in dry-mixed concrete paving blocks. J Clean Prod. 2014;68:209–15.10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.084Search in Google Scholar
[52] Lam CS, Poon CS, Chan D. Enhancing the performance of pre-cast concrete blocks by incorporating waste glass – ASR consideration. Cem Concr Compos. 2007;29(8):616–25.10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2007.03.008Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Research on damage evolution mechanisms under compressive and tensile tests of plain weave SiCf/SiC composites using in situ X-ray CT
- Structural optimization of trays in bolt support systems
- Continuum percolation of the realistic nonuniform ITZs in 3D polyphase concrete systems involving the aggregate shape and size differentiation
- Multiscale water diffusivity prediction of plain woven composites considering void defects
- The application of epoxy resin polymers by laser induction technologies
- Analysis of water absorption on the efficiency of bonded composite repair of aluminum alloy panels
- Experimental research on bonding mechanical performance of the interface between cementitious layers
- A study on the effect of microspheres on the freeze–thaw resistance of EPS concrete
- Influence of Ti2SnC content on arc erosion resistance in Ag–Ti2SnC composites
- Cement-based composites with ZIF-8@TiO2-coated activated carbon fiber for efficient removal of formaldehyde
- Microstructure and chloride transport of aeolian sand concrete under long-term natural immersion
- Simulation study on basic road performance and modification mechanism of red mud modified asphalt mixture
- Extraction and characterization of nano-silica particles to enhance mechanical properties of general-purpose unsaturated polyester resin
- Roles of corn starch and gellan gum in changing of unconfined compressive strength of Shanghai alluvial clay
- A review on innovative approaches to expansive soil stabilization: Focussing on EPS beads, sand, and jute
- Experimental investigation of the performances of thick CFRP, GFRP, and KFRP composite plates under ballistic impact
- Preparation and characterization of titanium gypsum artificial aggregate
- Characteristics of bulletproof plate made from silkworm cocoon waste: Hybrid silkworm cocoon waste-reinforced epoxy/UHMWPE composite
- Experimental research on influence of curing environment on mechanical properties of coal gangue cementation
- Multi-objective optimization of machining variables for wire-EDM of LM6/fly ash composite materials using grey relational analysis
- Synthesis and characterization of Ag@Ni co-axial nanocables and their fluorescent and catalytic properties
- Beneficial effect of 4% Ta addition on the corrosion mitigation of Ti–12% Zr alloy after different immersion times in 3.5% NaCl solutions
- Study on electrical conductive mechanism of mayenite derivative C12A7:C
- Fast prediction of concrete equivalent modulus based on the random aggregate model and image quadtree SBFEM
- Research on uniaxial compression performance and constitutive relationship of RBP-UHPC after high temperature
- Experimental analysis of frost resistance and failure models in engineered cementitious composites with the integration of Yellow River sand
- Influence of tin additions on the corrosion passivation of TiZrTa alloy in sodium chloride solutions
- Microstructure and finite element analysis of Mo2C-diamond/Cu composites by spark plasma sintering
- Low-velocity impact response optimization of the foam-cored sandwich panels with CFRP skins for electric aircraft fuselage skin application
- Research on the carbonation resistance and improvement technology of fully recycled aggregate concrete
- Study on the basic properties of iron tailings powder-desulfurization ash mine filling cementitious material
- Preparation and mechanical properties of the 2.5D carbon glass hybrid woven composite materials
- Improvement on interfacial properties of CuW and CuCr bimetallic materials with high-entropy alloy interlayers via infiltration method
- Investigation properties of ultra-high performance concrete incorporating pond ash
- Effects of binder paste-to-aggregate ratio and polypropylene fiber content on the performance of high-flowability steel fiber-reinforced concrete for slab/deck overlays
- Interfacial bonding characteristics of multi-walled carbon nanotube/ultralight foamed concrete
- Classification of damping properties of fabric-reinforced flat beam-like specimens by a degree of ondulation implying a mesomechanic kinematic
- Influence of mica paper surface modification on the water resistance of mica paper/organic silicone resin composites
- Impact of cooling methods on the corrosion behavior of AA6063 aluminum alloy in a chloride solution
- Wear mechanism analysis of internal chip removal drill for CFRP drilling
- Investigation on acoustic properties of metal hollow sphere A356 aluminum matrix composites
- Uniaxial compression stress–strain relationship of fully aeolian sand concrete at low temperatures
- Experimental study on the influence of aggregate morphology on concrete interfacial properties
- Intelligent sportswear design: Innovative applications based on conjugated nanomaterials
- Research on the equivalent stretching mechanical properties of Nomex honeycomb core considering the effect of resin coating
- Numerical analysis and experimental research on the vibration performance of concrete vibration table in PC components
- Assessment of mechanical and biological properties of Ti–31Nb–7.7Zr alloy for spinal surgery implant
- Theoretical research on load distribution of composite pre-tightened teeth connections embedded with soft layers
- Coupling design features of material surface treatment for ceramic products based on ResNet
- Optimizing superelastic shape-memory alloy fibers for enhancing the pullout performance in engineered cementitious composites
- Multi-scale finite element simulation of needle-punched quartz fiber reinforced composites
- Thermo-mechanical coupling behavior of needle-punched carbon/carbon composites
- Influence of composite material laying parameters on the load-carrying capacity of type IV hydrogen storage vessel
- Review Articles
- Effect of carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of aluminum matrix composites: A review
- On in-house developed feedstock filament of polymer and polymeric composites and their recycling process – A comprehensive review
- Research progress on freeze–thaw constitutive model of concrete based on damage mechanics
- A bibliometric and content analysis of research trends in paver blocks: Mapping the scientific landscape
- Bibliometric analysis of stone column research trends: A Web of Science perspective
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Research on damage evolution mechanisms under compressive and tensile tests of plain weave SiCf/SiC composites using in situ X-ray CT
- Structural optimization of trays in bolt support systems
- Continuum percolation of the realistic nonuniform ITZs in 3D polyphase concrete systems involving the aggregate shape and size differentiation
- Multiscale water diffusivity prediction of plain woven composites considering void defects
- The application of epoxy resin polymers by laser induction technologies
- Analysis of water absorption on the efficiency of bonded composite repair of aluminum alloy panels
- Experimental research on bonding mechanical performance of the interface between cementitious layers
- A study on the effect of microspheres on the freeze–thaw resistance of EPS concrete
- Influence of Ti2SnC content on arc erosion resistance in Ag–Ti2SnC composites
- Cement-based composites with ZIF-8@TiO2-coated activated carbon fiber for efficient removal of formaldehyde
- Microstructure and chloride transport of aeolian sand concrete under long-term natural immersion
- Simulation study on basic road performance and modification mechanism of red mud modified asphalt mixture
- Extraction and characterization of nano-silica particles to enhance mechanical properties of general-purpose unsaturated polyester resin
- Roles of corn starch and gellan gum in changing of unconfined compressive strength of Shanghai alluvial clay
- A review on innovative approaches to expansive soil stabilization: Focussing on EPS beads, sand, and jute
- Experimental investigation of the performances of thick CFRP, GFRP, and KFRP composite plates under ballistic impact
- Preparation and characterization of titanium gypsum artificial aggregate
- Characteristics of bulletproof plate made from silkworm cocoon waste: Hybrid silkworm cocoon waste-reinforced epoxy/UHMWPE composite
- Experimental research on influence of curing environment on mechanical properties of coal gangue cementation
- Multi-objective optimization of machining variables for wire-EDM of LM6/fly ash composite materials using grey relational analysis
- Synthesis and characterization of Ag@Ni co-axial nanocables and their fluorescent and catalytic properties
- Beneficial effect of 4% Ta addition on the corrosion mitigation of Ti–12% Zr alloy after different immersion times in 3.5% NaCl solutions
- Study on electrical conductive mechanism of mayenite derivative C12A7:C
- Fast prediction of concrete equivalent modulus based on the random aggregate model and image quadtree SBFEM
- Research on uniaxial compression performance and constitutive relationship of RBP-UHPC after high temperature
- Experimental analysis of frost resistance and failure models in engineered cementitious composites with the integration of Yellow River sand
- Influence of tin additions on the corrosion passivation of TiZrTa alloy in sodium chloride solutions
- Microstructure and finite element analysis of Mo2C-diamond/Cu composites by spark plasma sintering
- Low-velocity impact response optimization of the foam-cored sandwich panels with CFRP skins for electric aircraft fuselage skin application
- Research on the carbonation resistance and improvement technology of fully recycled aggregate concrete
- Study on the basic properties of iron tailings powder-desulfurization ash mine filling cementitious material
- Preparation and mechanical properties of the 2.5D carbon glass hybrid woven composite materials
- Improvement on interfacial properties of CuW and CuCr bimetallic materials with high-entropy alloy interlayers via infiltration method
- Investigation properties of ultra-high performance concrete incorporating pond ash
- Effects of binder paste-to-aggregate ratio and polypropylene fiber content on the performance of high-flowability steel fiber-reinforced concrete for slab/deck overlays
- Interfacial bonding characteristics of multi-walled carbon nanotube/ultralight foamed concrete
- Classification of damping properties of fabric-reinforced flat beam-like specimens by a degree of ondulation implying a mesomechanic kinematic
- Influence of mica paper surface modification on the water resistance of mica paper/organic silicone resin composites
- Impact of cooling methods on the corrosion behavior of AA6063 aluminum alloy in a chloride solution
- Wear mechanism analysis of internal chip removal drill for CFRP drilling
- Investigation on acoustic properties of metal hollow sphere A356 aluminum matrix composites
- Uniaxial compression stress–strain relationship of fully aeolian sand concrete at low temperatures
- Experimental study on the influence of aggregate morphology on concrete interfacial properties
- Intelligent sportswear design: Innovative applications based on conjugated nanomaterials
- Research on the equivalent stretching mechanical properties of Nomex honeycomb core considering the effect of resin coating
- Numerical analysis and experimental research on the vibration performance of concrete vibration table in PC components
- Assessment of mechanical and biological properties of Ti–31Nb–7.7Zr alloy for spinal surgery implant
- Theoretical research on load distribution of composite pre-tightened teeth connections embedded with soft layers
- Coupling design features of material surface treatment for ceramic products based on ResNet
- Optimizing superelastic shape-memory alloy fibers for enhancing the pullout performance in engineered cementitious composites
- Multi-scale finite element simulation of needle-punched quartz fiber reinforced composites
- Thermo-mechanical coupling behavior of needle-punched carbon/carbon composites
- Influence of composite material laying parameters on the load-carrying capacity of type IV hydrogen storage vessel
- Review Articles
- Effect of carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of aluminum matrix composites: A review
- On in-house developed feedstock filament of polymer and polymeric composites and their recycling process – A comprehensive review
- Research progress on freeze–thaw constitutive model of concrete based on damage mechanics
- A bibliometric and content analysis of research trends in paver blocks: Mapping the scientific landscape
- Bibliometric analysis of stone column research trends: A Web of Science perspective

